Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
-
Influence of reciprocating and rotary instrumentation on microbial reduction: a systematic review and meta-analysis of
in vitro studies - Selen Küçükkaya Eren, Emel Uzunoğlu-Özyürek, Sevilay Karahan
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(2):e19. Published online March 10, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e19
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to conduct a systematic review and meta-analysis of
in vitro studies regarding the effectiveness of reciprocating and rotary instrumentation on microbial reduction in root canals.Materials and Methods PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, the Cochrane Library, and the gray literature were searched through December 2019. Studies comparing the influence of reciprocating and rotary instrumentation on the removal of microorganisms from root canals that quantified the antimicrobial effect were included. Data extraction was completed using a systematic form for data collection. The risk of bias of the studies was evaluated. Standardized mean differences (SMDs) and confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated using a random effects meta-analysis.
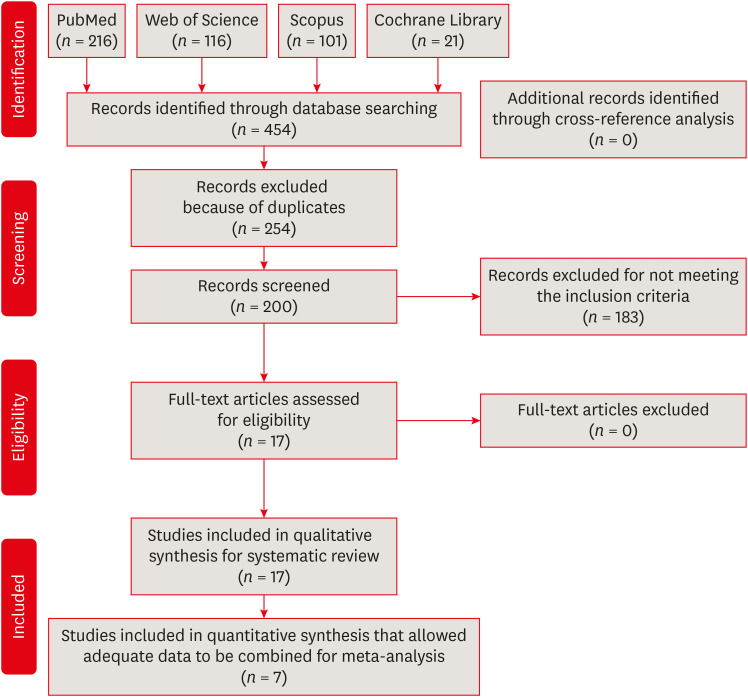
Results Seventeen
in vitro studies were included in this systematic review, of which 7 provided adequate data for inclusion in the meta-analysis. Both reciprocating and rotary systems were similarly effective in reducing the microbial load in infected root canals (SMD [95% CI], 0.0481 [−0.271, 0.367]). Three studies showed a low risk of bias, whereas most of the studies (82%) presented a medium risk.Conclusions Although both techniques decrease the microbial content (with reductions of 23.32%–88.47% and 23.33%–89.86% for reciprocating and rotary instrumentation, respectively)
, they are not able to provide complete disinfection of root canals.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mapping risk of bias criteria in systematic reviews of in vitro endodontic studies: an umbrella review
Rafaella Rodrigues da Gama, Lucas Peixoto de Araújo, Evandro Piva, Leandro Perello Duro, Adriana Fernandes da Silva, Wellington Luiz de Oliveira da Rosa
Evidence-Based Dentistry.2025; 26(4): 179. CrossRef - Fifteen years of engine‐driven nickel–titanium reciprocating instruments, what do we know so far? An umbrella review
Felipe Immich, Lucas Peixoto de Araújo, Rafaella Rodrigues da Gama, Wellington Luiz de Oliveira da Rosa, Evandro Piva, Giampiero Rossi‐Fedele
Australian Endodontic Journal.2024; 50(2): 409. CrossRef - Does minimally invasive canal preparation provide higher fracture resistance of endodontically treated teeth? A systematic review ofin vitrostudies
Sıla Nur Usta, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Seda Falakaloğlu, Mustafa Gündoğar
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of Combined Ultrasonic Tip and Mechanized Instrumentation on the Reduction of the Percentage of Non-Instrumented Surfaces in Oval/Flat Root Canals: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Marcella Dewes Cassal, Pedro Cardoso Soares, Marcelo dos Santos
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of Different Access Cavity Designs and Ni–Ti Files on the Elimination of Enterococcus faecalis from the Root Canal System: An In Vitro Study
Gizem Andac, Atakan Kalender, Buket Baddal, Fatma Basmaci
Applied Sciences.2022; 12(4): 2049. CrossRef - Shaping Properties and Outcomes of Nickel-Titanium Reciprocation Systems in Primary Teeth: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of In Vitro Studies
SelvaKumar Haridoss, Bhavyaa R, Kavitha Swaminathan, Aruna P
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Root Canal Sealers and Obturation Techniques on Vertical Root Fracture Resistance. An In Vitro Experiment
Mazen F. Alkahtany, Khalid H. Almadi, Fahad A. Alahmad, Abdullah M. Alshehri, Abdulrahman A. AlSwayyed, Omar M. AlZahran, Ali AlHadan, Abdulaziz S. Almustafa, Fahim Vohra, Tariq Abduljabbar
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(17): 8022. CrossRef
- Mapping risk of bias criteria in systematic reviews of in vitro endodontic studies: an umbrella review
- 2,454 View
- 35 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref

- Critical evaluation of fracture strength testing for endodontically treated teeth: a finite element analysis study
- Emel Uzunoglu-Özyürek, Selen Küçükkaya Eren, Oğuz Eraslan, Sema Belli
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(2):e15. Published online April 18, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e15
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
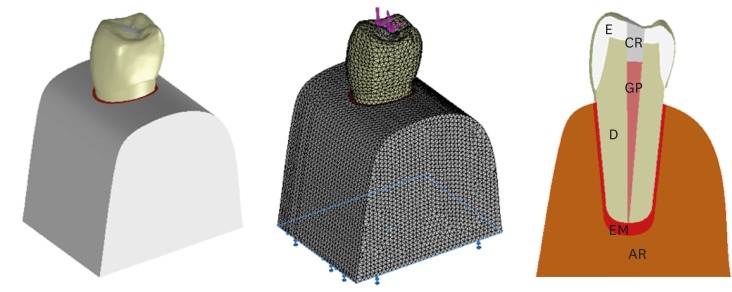
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to investigate whether the diameter and direction of the plunger and simulation of the periodontal ligament (PDL) affected the stress distribution in endodontically treated premolars.
Methods A fracture strength test was simulated via finite element analysis. A base model was set up, and the following parameters were modified: plunger diameter (3 mm vs. 6 mm), plunger direction (vertical vs. 135° angular to the central fossa), and PDL simulation. The analysis was conducted using the CosmosWorks structural analysis program, and the results are presented in terms of von Mises stresses.
Results The smaller plunger increased the stresses at the contact area of the crown, but the plunger diameter had no effect on the stress distribution within the root. An angular plunger direction increased stresses within the root, as well as at the buccal cusp of the crown, compared with the vertical direction. Simulation of the PDL caused higher stress accumulation, especially in the cervical region of the root.
Conclusions The plunger diameter had no effect on the stress distribution in the roots, whereas the plunger direction and PDL simulation did affect the stress distribution. More stringent standards can be established by taking such parameters into account when performing fracture testing in future studies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Access cavity in endodontics: Balancing precision, preservation, and clinical needs
Dina Abdellatif, Ismail Davut Capar, De Fontaine Sarah, Alfredo Iandolo, Christophe Meyer, Davide Mancino
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(6): 573. CrossRef - Assessment of Stress Distribution with 3 Taper Design Preparation of Root Canal Using Finite Element Analysis
Tejasree Rathod, G. Durgabhavani, Pudu Tirupathi, Nusrath Parveen, Yelloji Paramesh, Prabhakar Dharavattu
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2024; 16(Suppl 1): S112. CrossRef - The impact of the filling technique with two sealers in bulk or associated with gutta-percha on the fatigue behavior and failure patterns of endodontically treated teeth
Isabella Marian Lena, Luiza Colpo Chiaratti, Rafaela Oliveira Pilecco, Renan Vaz Machry, João Paulo Mendes Tribst, Cornelis Johannes Kleverlaan, Gabriel Kalil Rocha Pereira, Renata Dornelles Morgental
PeerJ.2024; 12: e18221. CrossRef - Stronger than Ever: Multifilament Fiberglass Posts Boost Maxillary Premolar Fracture Resistance
Naji Kharouf, Eugenio Pedullà, Gianluca Plotino, Hamdi Jmal, Mohammed-El-Habib Alloui, Philippine Simonis, Patrice Laquerriere, Valentina Macaluso, Dina Abdellatif, Raphaël Richert, Youssef Haikel, Davide Mancino
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(8): 2975. CrossRef - Neural network approach to evaluate the physical properties of dentin
Mohammad Ali Saghiri, Ali Mohammad Saghiri, Elham Samadi, Devyani Nath, Julia Vakhnovetsky, Steven M. Morgano
Odontology.2023; 111(1): 68. CrossRef - Modelling and evaluating periodontal ligament mechanical behaviour and properties: A scoping review of current approaches and limitations
Enaiyat Ghani Ovy, Dan L. Romanyk, Carlos Flores Mir, Lindsey Westover
Orthodontics & Craniofacial Research.2022; 25(2): 199. CrossRef - FEAr no more! Finite element analysis in orthodontics
Shilpa Chawla, Shailesh Deshmukh
Journal of the International Clinical Dental Research Organization.2022; 14(1): 6. CrossRef - Influence of Methodological Variables on Fracture Strength Tests Results of Premolars with Different Number of Residual Walls. A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis
Carlo Gaeta, Crystal Marruganti, Emanuele Mignosa, Giovanni Franciosi, Edoardo Ferrari, Simone Grandini
Dentistry Journal.2021; 9(12): 146. CrossRef
- Access cavity in endodontics: Balancing precision, preservation, and clinical needs
- 2,520 View
- 45 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Mineral content analysis of root canal dentin using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy
- Selen Küçükkaya Eren, Emel Uzunoğlu, Banu Sezer, Zeliha Yılmaz, İsmail Hakkı Boyacı
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(1):e11. Published online February 4, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e11
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
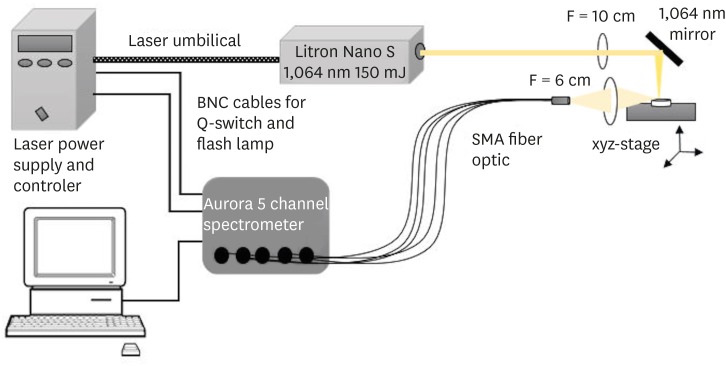
ePub Objectives This study aimed to introduce the use of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) for evaluation of the mineral content of root canal dentin, and to assess whether a correlation exists between LIBS and scanning electron microscopy/energy dispersive spectroscopy (SEM/EDS) methods by comparing the effects of irrigation solutions on the mineral content change of root canal dentin.
Materials and Methods Forty teeth with a single root canal were decoronated and longitudinally sectioned to expose the canals. The root halves were divided into 4 groups (
n = 10) according to the solution applied: group NaOCl, 5.25% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) for 1 hour; group EDTA, 17% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) for 2 minutes; group NaOCl+EDTA, 5.25% NaOCl for 1 hour and 17% EDTA for 2 minutes; a control group. Each root half belonging to the same root was evaluated for mineral content with either LIBS or SEM/EDS methods. The data were analyzed statistically.Results In groups NaOCl and NaOCl+EDTA, the calcium (Ca)/phosphorus (P) ratio decreased while the sodium (Na) level increased compared with the other groups (
p < 0.05). The magnesium (Mg) level changes were not significant among the groups. A significant positive correlation was found between the results of LIBS and SEM/EDS analyses (r = 0.84,p < 0.001).Conclusions Treatment with NaOCl for 1 hour altered the mineral content of dentin, while EDTA application for 2 minutes had no effect on the elemental composition. The LIBS method proved to be reliable while providing data for the elemental composition of root canal dentin.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- In vitro evaluation of antimicrobial photodynamic therapy with photosensitizers and calcium hydroxide on bond strength, chemical composition, and sealing of glass-fiber posts to root dentin
Thalya Fernanda Horsth Maltarollo, Paulo Henrique dos Santos, Henrique Augusto Banci, Mariana de Oliveira Bachega, Beatriz Melare de Oliveira, Marco Hungaro Antonio Duarte, Índia Olinta de Azevedo Queiroz, Rodrigo Rodrigues Amaral, Luciano Angelo Tavares
Lasers in Medical Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Using 5% Apple Vinegar Irrigation Solution Adjunct to Diode Laser on Smear Layer Removal and Calcium/Phosphorus Ion Ratio during Root Canal Treatment
Tarek AA Salam, Haythem SA Kader, Elsayed E Abdallah
CODS - Journal of Dentistry.2024; 15(1): 3. CrossRef - Evaluation of chemical composition of root canal dentin between two age groups using different irrigating solutions: An in vitro sem-eds study
Naresh Kumar K, Abhijith Kallu, Surender L.R, Sravani Nirmala, Narender Reddy
International Dental Journal of Student's Research.2024; 12(1): 18. CrossRef - Minimally invasive management of vital teeth requiring root canal therapy
E. Karatas, M. Hadis, W. M. Palin, M. R. Milward, S. A. Kuehne, J. Camilleri
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effects of a Novel Nanohydroxyapatite Gel and Er: YAG Laser Treatment on Dentin Hypersensitivity
Demet Sahin, Ceren Deger, Burcu Oglakci, Metehan Demirkol, Bedri Onur Kucukyildirim, Mehtikar Gursel, Evrim Eliguzeloglu Dalkilic
Materials.2023; 16(19): 6522. CrossRef - Chitosan Homogenizing Coffee Ring Effect for Soil Available Potassium Determination Using Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy
Xiaolong Li, Rongqin Chen, Zhengkai You, Tiantian Pan, Rui Yang, Jing Huang, Hui Fang, Wenwen Kong, Jiyu Peng, Fei Liu
Chemosensors.2022; 10(9): 374. CrossRef - Quantitative analysis of cadmium in rice roots based on LIBS and chemometrics methods
Wei Wang, Wenwen Kong, Tingting Shen, Zun Man, Wenjing Zhu, Yong He, Fei Liu
Environmental Sciences Europe.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- In vitro evaluation of antimicrobial photodynamic therapy with photosensitizers and calcium hydroxide on bond strength, chemical composition, and sealing of glass-fiber posts to root dentin
- 1,858 View
- 11 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Influence of size and insertion depth of irrigation needle on debris extrusion and sealer penetration
- Emel Uzunoglu-Özyürek, Hakan Karaaslan, Sevinç Aktemur Türker, Bahar Özçelik
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(1):e2. Published online December 22, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e2
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
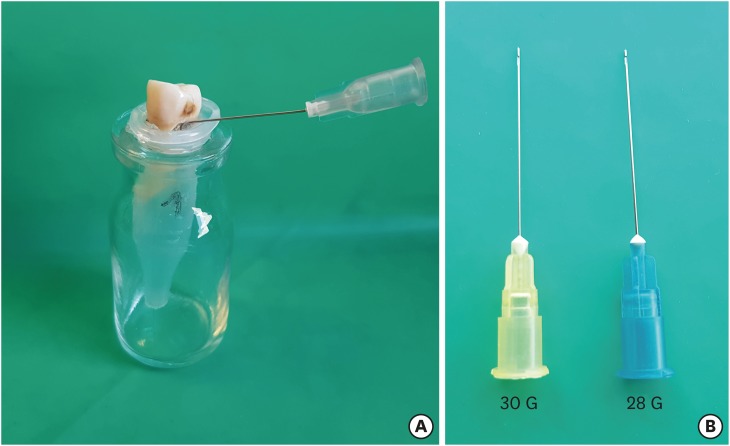
ePub Objectives To determine the effect of size and insertion depth of irrigation needle on the amount of apical extruded debris and the amount of penetration depth of sealer using a confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM).
Materials and Methods Twenty maxillary premolars were assigned to 2 groups (
n = 10), according to the size of needle tip, 28 G or 30 G. Buccal roots of samples were irrigated with respective needle type inserted 1 mm short of the working length (WL), while palatal roots were irrigated with respective needle type inserted 3 mm short of the WL. Prepared teeth were removed from the pre-weighed Eppendorf tubes. Canals were filled with F3 gutta-percha cone and rhodamine B dye-labeled AH 26 sealer. Teeth were transversally sectioned at 1 and 3 mm levels from the apex and observed under a CLSM. Eppendorf tubes were incubated to evaporate the irrigant and were weighed again. The difference between pre- and post-weights was calculated, and statistical evaluation was performed.Results Inserting needles closer to the apex and using needles with wider diameters were associated with significantly more debris extrusion (
p < 0.05). The position of needles and level of sections had statistically significant effects on sealer penetration depth (p < 0.05 for both).Conclusions Following preparation, inserting narrower needles compatible with the final apical diameter of the prepared root canal at 3 mm short of WL during final irrigation might prevent debris extrusion and improve sealer penetration in the apical third.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of laser-induced pulpal anesthesia of single-rooted teeth with irreversible pulpitis treated by single-visit root canal therapy - A randomized clinical trial
Geeta Asthana, Dhwani Morakhia, Ravina Parmar, Rajashree Tamuli
Endodontology.2025; 37(3): 244. CrossRef - Efficacy of different irrigation needles used in endodontics: an in silico and an in vitro investigation
Maulee Sheth, Ankit Arora, Sonali Kapoor, Balraj Shukla
Biomaterial Investigations in Dentistry.2025; 12: 264. CrossRef - Preliminary insights: exploring irrigation practices during endodontic treatment among general dental practitioners in Malaysia
Kai Qi Chiew, Xin Ni Lim, Shekhar Bhatia, Naveen Chhabra
British Dental Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficiency of diode laser in control of post-endodontic pain: a randomized controlled trial
Hend H. Ismail, Maram Obeid, Ehab Hassanien
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(6): 2797. CrossRef - Endodontic management of an aberrant germinated composite odontome: A case report
Ankit Arora, Kavina Desai, Sonali Kapoor, Seema Gajera
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(3): 684. CrossRef - Potentials of 3D-Modeling in the Preclinical Stage of Root Needle Research
Aleksandr V. Kuligin, Larisa N. Kazakova, Oksana S. Tereshchuk, Vadim V. Bokov
I.P. Pavlov Russian Medical Biological Herald.2022; 30(1): 95. CrossRef - Effect of root canal geometry and needle type on apical extrusion of irrigant: an ex vivo study
Büşra SERÇE FİKİRLİ, Bülent ALTUNKAYNAK, Güven KAYAOĞLU
Acta Odontologica Turcica.2022; 39(3): 58. CrossRef - An in vitro radiological evaluation of irrigant penetration in the root canals using three different irrigation systems: Waterpik WP-100 device, passive irrigation, and manual dynamic irrigation systems
Suragani Hemalatha, Archana Srinivasan, A Srirekha, Lekha Santhosh, C Champa, Ashwija Shetty
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2022; 25(4): 403. CrossRef - Preparation Ability of ProTaper Next and XP-endo Shaper Instruments in Isthmus-containing Root Canal System
Mustafa Sarıkahya, Tayfun Alaçam
Conservative Dentistry and Endodontic Journal.2021; 5(2): 28. CrossRef - Penetration depth of irrigants into root dentine after sonic, ultrasonic and photoacoustic activation
K. M. Galler, V. Grubmüller, R. Schlichting, M. Widbiller, A. Eidt, C. Schuller, M. Wölflick, K.‐A. Hiller, W. Buchalla
International Endodontic Journal.2019; 52(8): 1210. CrossRef
- Effect of laser-induced pulpal anesthesia of single-rooted teeth with irreversible pulpitis treated by single-visit root canal therapy - A randomized clinical trial
- 1,816 View
- 19 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Influence of a glide path on the dentinal crack formation of ProTaper Next system
- Sevinç Aktemur Türker, Emel Uzunoğlu
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(4):286-289. Published online September 2, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.4.286
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim was to evaluate dentinal crack formation after root canal preparation with ProTaper Next system (PTN) with and without a glide path.
Materials and Methods Forty-five mesial roots of mandibular first molars were selected. Fifteen teeth were left unprepared and served as controls. The experimental groups consist of mesiobuccal and mesiolingual root canals of remaining 30 teeth, which were divided into 2 groups (
n = 15): Group PG/PTN, glide path was created with ProGlider (PG) and then canals were shaped with PTN system; Group PTN, glide path was not prepared and canals were shaped with PTN system only. All roots were sectioned perpendicular to the long axis at 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 8 mm from the apex, and the sections were observed under a stereomicroscope. The presence/absence of cracks was recorded. Data were analyzed with chi-square tests with Yates correction.Results There were no significant differences in crack formation between the PTN with and without glide path preparation. The incidence of cracks observed in PG/PTN and PTN groups was 17.8% and 28.9%, respectively.
Conclusions The creation of a glide path with ProGlider before ProTaper Next rotary system did not influence dentinal crack formation in root canals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative Evaluation of the Shaping Ability of the Recent, Fifth-generation ProTaper Next and Revo-S NiTi Rotary Endodontic Files Using Three-dimensional Imaging: An Imaging-based Study
Prajna Pattanaik, Akilan Balasubramanian, P. Veeralakshmi, Gautam Singh, Vandana Sadananda, Hina Ahmed, J. Suresh Babu, C. Swarnalatha, Abhishek Singh Nayyar
Journal of Microscopy and Ultrastructure.2025; 13(4): 177. CrossRef - Glide Path in Endodontics: A Literature Review of Current Knowledge
Vlad Mircea Lup, Giulia Malvicini, Carlo Gaeta, Simone Grandini, Gabriela Ciavoi
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(8): 257. CrossRef - Microscopic Assessment of Dentinal Defects Induced by ProTaper Universal, ProTaper Gold, and Hyflex Electric Discharge Machining Rotary File Systems – An in vitro Study
Takhellambam Premlata Devi, Amandeep Kaur, Shamurailatpam Priyadarshini, B. S. Deepak, Sumita Banerjee, Ng Sanjeeta
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2021; 12(3): 230. CrossRef - Influence of Negotiation, Glide Path, and Preflaring Procedures on Root Canal Shaping—Terminology, Basic Concepts, and a Systematic Review
Gianluca Plotino, Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Frederic Bukiet, Nicola M. Grande, Sajesh K. Veettil, Gustavo De-Deus, Hany Mohamed Aly Ahmed
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(6): 707. CrossRef
- Comparative Evaluation of the Shaping Ability of the Recent, Fifth-generation ProTaper Next and Revo-S NiTi Rotary Endodontic Files Using Three-dimensional Imaging: An Imaging-based Study
- 1,590 View
- 5 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Calcium hydroxide dressing residues after different removal techniques affect the accuracy of Root-ZX apex locator
- Emel Uzunoglu, Ayhan Eymirli, Mehmet Özgür Uyanik, Semra Çalt, Emre Nagas
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(1):44-49. Published online November 5, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.1.44
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study compared the ability of several techniques to remove calcium hydroxide (CH) from the root canal and determined the influence of CH residues on the accuracy of the electronic apex locator.
Materials and Methods Root canals of 90 human maxillary lateral incisors with confirmed true working length (TWL) were prepared and filled with CH. The teeth were randomly assigned to one of the experimental groups according to the CH removal technique (
n = 14): 0.9% saline; 0.9% saline + master apical file (MAF); 17% ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA); 17% EDTA + MAF; 5.25% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl); 5.25% NaOCl + MAF. Six teeth were used as negative control. After CH removal, the electronic working length was measured using Root-ZX (Morita Corp.) and compared with TWL to evaluate Root-ZX accuracy. All specimens were sectioned longitudinally, and the area of remaining CH (CH) and total canal area were measured using imaging software.Results The EDTA + MAF and NaOCl + MAF groups showed better CH removal than other groups (
p < 0.05). Root-ZX reliability to prevent overestimated working length to be > 85% within a tolerance of ± 1.0 mm (p < 0.05). There was strong negative correlation between amount of CH residues and EAL accuracy (r = -0.800 for ± 0.5 mm;r = -0.940 for ± 1.0 mm).Conclusions The mechanical instrumentation improves the CH removal of irrigation solutions although none of the techniques removed the dressing completely. Residues of CH medication in root canals affected the accuracy of Root-ZX adversely.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of the Effect of Calcium Hydroxide Residues Including Different Vehicles on the Accuracy of Electronic Apex Locators
Simay Koç, Damla Erkal, Dide Tekinarslan, Kürs¸at Er
Journal of Advanced Oral Research.2025; 16(1): 54. CrossRef - Evaluation of heated sodium hypochlorite’s effect on the accuracy of contemporary electronic apex locators: an in vitro study
İkbal Sena Çelebi Keskin, Turgut Yağmur Yalçın
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors influencing the accuracy of electronic apex locators: A scoping review
Shayan Golkar, Abbasali Khademi, Amin Saatchi, Amir Ghorani, Pedram Iranmanesh
Dental Research Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of a new irrigation solution -RISA- on removing calcium hydroxide from artificial standardized grooves in root canals - an in vitro study
İpek Eraslan Akyüz, Salih Düzgün, Hüseyin Sinan Topçuoğlu
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of the accuracy of electronic apex locators and cone-beam computed tomography in detection of root canal perforation and working length during endodontic retreatment
Simay Koç, Hatice Harorlı, Alper Kuştarcı
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Intracanal Medicaments on the Measurement Accuracy of Four Apex Locators: An In Vitro Study
Hamza Cudal, Tuğrul Aslan, Bertan Kesim
Meandros Medical and Dental Journal.2023; 24(3): 215. CrossRef - Electronic Apex Locators and their Implications in Contemporary Clinical Practice: A Review
Zainab Shirazi, Anas Al-Jadaa, Abdul Rahman Saleh
The Open Dentistry Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Apical Patency, Coronal Preflaring and Calcium Hydroxide on the Accuracy of Root ZX Apex Locator for Working Length Determination: An In Vitro Study
Mostafa Godiny, Reza Hatam, Roya Safari-Faramani, Atefeh Khavid, Mohammad Reza Rezaei
Journal of Advanced Oral Research.2022; 13(1): 38. CrossRef - Endodontic cement penetration after removal of calcium hydroxide dressing using XP-endo finisher
Alyssa Sales dos Santos, Maria Aparecida Barbosa de Sá, Marco Antônio Húngaro Duarte, Martinho Campolina Rebello Horta, Frank Ferreira Silveira, Eduardo Nunes
Brazilian Oral Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of glycolic acid for the removal of calcium hydroxide from simulated internal Resorption cavities
Cangül Keskin, Ali Keleş, Öznur Sarıyılmaz
Clinical Oral Investigations.2021; 25(7): 4407. CrossRef - Accuracy of electronic apex locator in the presence of different irrigating solutions
Padmanabh Jha, Vineeta Nikhil, Shalya Raj, Rohit Ravinder, Preeti Mishra
Endodontology.2021; 33(4): 232. CrossRef - Farklı Kanal İçi Ortamların Apeks Bulucuların Doğruluğu Üzerine Etkisi
Asena OKUR, Tuğrul ASLAN, Burak SAĞSEN
Selcuk Dental Journal.2021; 8(3): 859. CrossRef - Evaluation of the accuracy of different apex locators in determiningthe working length during root canal retreatment
Pelin Tufenkci, Aylin Kalaycı
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2020; 14(2): 125. CrossRef - Influence of calcium hydroxide residues after using different irrigants on the accuracy of two electronic apex locators: An in vitro study
NooshinSadat Shojaee, Zahra Zaeri, MohammadMehdi Shokouhi, Fereshteh Sobhnamayan, Alireza Adl
Dental Research Journal.2020; 17(1): 48. CrossRef - The Effect of Calcium Hydroxide and File Sızes on the Accuracy of the Electronic Apex Locator in Simulated Immature Teeth
Leyla AYRANCİ, Ahmet ÇETİNKAYA, Serkan ÖZKAN
Middle Black Sea Journal of Health Science.2019; 5(3): 273. CrossRef - The Effect of File Size and Type and Irrigation Solutions on the Accuracy of Electronic Apex Locators: AnIn VitroStudy on Canine Teeth
Maciej Janeczek, Piotr Kosior, Dagmara Piesiak-Pańczyszyn, Krzysztof Dudek, Aleksander Chrószcz, Agnieszka Czajczyńska-Waszkiewicz, Małgorzata Kowalczyk-Zając, Aleksandra Gabren-Syller, Karol Kirstein, Aleksandra Skalec, Ewelina Bryła, Maciej Dobrzyński
BioMed Research International.2016; 2016: 1. CrossRef
- Evaluation of the Effect of Calcium Hydroxide Residues Including Different Vehicles on the Accuracy of Electronic Apex Locators
- 1,703 View
- 9 Download
- 16 Crossref

- Effects of dentin moisture on the push-out bond strength of a fiber post luted with different self-adhesive resin cements
- Sevinç Aktemur Türker, Emel Uzunoğlu, Zeliha Yılmaz
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(4):234-240. Published online November 12, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.4.234
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the effects of intraradicular moisture on the pushout bond strength of a fibre post luted with several self-adhesive resin cements.
Materials and Methods Endodontically treated root canals were treated with one of three luting cements: (1) RelyX U100, (2) Clearfil SA, and (3) G-Cem. Roots were then divided into four subgroups according to the moisture condition tested: (I) dry: excess water removed with paper points followed by dehydration with 95% ethanol, (II) normal moisture: canals blot-dried with paper points until appearing dry, (III) moist: canals dried by low vacuum using a Luer adapter, and (IV) wet: canals remained totally flooded. Two 1-mm-thick slices were obtained from each root sample and bond strength was measured using a push-out test setup. The data were analysed using a two-way analysis of variance and the Bonferroni
post hoc test withp = 0.05.Results Statistical analysis demonstrated that moisture levels had a significant effect on the bond strength of luting cements (
p < 0.05), with the exception of G-Cem. RelyX U100 displayed the highest bond strength under moist conditions (III). Clearfil SA had the highest bond strength under normal moisture conditions (II). Statistical ranking of bond strength values was as follows: RelyX U100 > Clearfil SA > G-Cem.Conclusions The degree of residual moisture significantly affected the adhesion of luting cements to radicular dentine.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Push-Out Bond Strength of Different Luting Cements Following Post Space Irrigation with 2% Chitosan: An In Vitro Study
Shimaa Rifaat, Ahmed Rahoma, Hind Muneer Alharbi, Sawsan Jamal Kazim, Shrouq Ali Aljuaid, Basmah Omar Alakloby, Faraz A. Farooqi, Noha Taymour
Prosthesis.2025; 7(1): 18. CrossRef - Dentin bond strength of resin luting agents under a simulated intra-oral environment
Takashi Washino, Hanemi Tsuruta, Masaomi Ikeda, Michael F. Burrow, Toru Nikaido
Asian Pacific Journal of Dentistry.2024; 24(2): 13. CrossRef - Effects of a relined fiberglass post with conventional and self-adhesive resin cement
Wilton Lima dos Santos Junior, Marina Rodrigues Santi, Rodrigo Barros Esteves Lins, Luís Roberto Marcondes Martins
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of dentin moisture on the adhesive properties of luting fiber posts using adhesive strategies
Renata Terumi JITUMORI, Rafaela Caroline RODRIGUES, Alessandra REIS, João Carlos GOMES, Giovana Mongruel GOMES
Brazilian Oral Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of different intraradicular chemical pretreatments on the bond strength of adhesive interface between dentine and fiber post cements: A systematic review and network meta‐analysis
Ana Luiza Barbosa Jurema, Ayla Macyelle de Oliveira Correia, Manuela da Silva Spinola, Eduardo Bresciani, Taciana Marco Ferraz Caneppele
European Journal of Oral Sciences.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - SELF ADEZİV REZİN SİMANLAR / SELF ADHESIVE RESIN CEMENTS
Kübra AMAÇ, Engin ESENTÜRK, Bilge TURHAN BAL
Atatürk Üniversitesi Diş Hekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi.2022; : 1. CrossRef - Postspace pretreatment with 17% ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid, 7% maleic acid, and 1% phytic acid on bond strength of fiber posts luted with a self-adhesive resin cement
PriyaC Yadav, Ramya Raghu, Ashish Shetty, Subhashini Rajasekhara
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2021; 24(6): 558. CrossRef - Development and characterization of biological bovine dentin posts
Alice Gonçalves Penelas, Eduardo Moreira da Silva, Laiza Tatiana Poskus, Amanda Cypriano Alves, Isis Ingrid Nogueira Simões, Viviane Hass, José Guilherme Antunes Guimarães
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2019; 92: 197. CrossRef - Evaluation of the influence of time and concentration of sodium hypochlorite on the bond strength of glass fibre post
Beau Knight, Robert M. Love, Roy George
Australian Endodontic Journal.2018; 44(3): 267. CrossRef - Test methods for bond strength of glass fiber posts to dentin: A review
F. C. Dos Santos, M. D. Banea, H. L. Carlo, S. De Barros
The Journal of Adhesion.2017; 93(1-2): 159. CrossRef - Is the bonding of self-adhesive cement sensitive to root region and curing mode?
Thaynara Faelly BOING, Giovana Mongruel GOMES, João Carlos GOMES, Alessandra REIS, Osnara Maria Mongruel GOMES
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2017; 25(1): 2. CrossRef - A Twofold Comparison between Dual Cure Resin Modified Cement and Glass Ionomer Cement for Orthodontic Band Cementation
Hanaa El Attar, Omnia Elhiny, Ghada Salem, Ahmed Abdelrahman, Mazen Attia
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.2016; 4(4): 695. CrossRef - Shear bond strengths of various self-adhesive resin cements between bovine dentin and 4 types of adherends
Ah-Jin Kim, Da-Ryeong Park, Seunghan Oh, Ji-Myung Bae
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2015; 42(4): 365. CrossRef
- Push-Out Bond Strength of Different Luting Cements Following Post Space Irrigation with 2% Chitosan: An In Vitro Study
- 1,805 View
- 4 Download
- 13 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


