Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Effect of phytic acid as an endodontic chelator on resin adhesion to sodium hypochlorite-treated dentin
- Mohannad Nassar, Noriko Hiraishi, Md. Sofiqul Islam, Maria JRH. Romero, Masayuki Otsuki, Junji Tagami
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(4):e44. Published online August 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e44
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
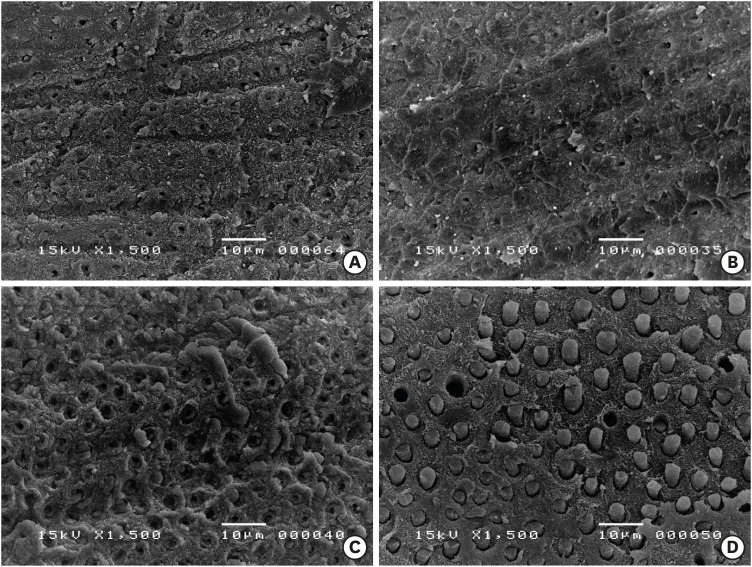
ePub Objectives Phytic acid (IP6), a naturally occurring agent, has been previously reported as a potential alternative to ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA). However, its effect on adhesion to sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl)-treated dentin and its interactions with NaOCl have not been previously reported. Thus, in this study, the effects of IP6 on resin adhesion to NaOCl-treated dentin and the failure mode were investigated and the interactions between the used agents were analyzed.
Materials and Methods Micro-tensile bond strength (µTBS) testing was performed until failure on dentin treated with either distilled water (control), 5% NaOCl, or 5% NaOCl followed with chelators: 17% EDTA for 1 minute or 1% IP6 for 30 seconds or 1 minute. The failed specimens were assessed under a scanning electron microscope. The reaction of NaOCl with EDTA or IP6 was analyzed in terms of temperature, pH, effervescence, and chlorine odor, and the effects of the resulting mixtures on the color of a stained paper were recorded.
Results The µTBS values of the control and NaOCl with chelator groups were not significantly different, but were all significantly higher than that of the group treated with NaOCl only. In the failure analysis, a distinctive feature was the presence of resin tags in samples conditioned with IP6 after treatment with NaOCl. The reaction of 1% IP6 with 5% NaOCl was less aggressive than the reaction of the latter with 17% EDTA.
Conclusions IP6 reversed the adverse effects of NaOCl on resin-dentin adhesion without the chlorine-depleting effect of EDTA.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of Chemical Surface Modification on the Repair Bond Strength of Resin Composite: An In Vitro Study
Md Sofiqul Islam, Shadi El Bahra, Smriti Aryal A C, Vivek Padmanabhan, Abdulaziz Al Tawil, Ihab Saleh, Muhammed Mustahsen Rahman, Upoma Guha
Polymers.2025; 17(4): 513. CrossRef - Advancing Adhesive Strategies for Endodontically Treated Teeth—Part I: Impact of Endodontic Irrigation Protocols on the Chemical Composition and Structural Integrity of Coronal Dentin
Joana A. Marques, Rui I. Falacho, Sara Fateixa, Francisco Caramelo, João Miguel Santos, João Rocha, Markus B. Blatz, João Carlos Ramos, Paulo J. Palma
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2025; 37(7): 1848. CrossRef - Effect of collagen crosslinkers on sodium hypochlorite treated dentin bond strength: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Weiqing Zhou, Shuting Feng, Xiaojun Chu, Shuaimei Xu, Xiongqun Zeng
Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Advancing Adhesive Strategies for Endodontically Treated Teeth—Part II: Dentin Sealing Before Irrigation Increases Long‐Term Microtensile Bond Strength to Coronal Dentin
Joana A. Marques, Rui I. Falacho, Gabriela Almeida, Francisco Caramelo, João Miguel Santos, João Rocha, Markus B. Blatz, João Carlos Ramos, Paulo J. Palma
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2025; 37(7): 1865. CrossRef - Effects of phytic acid and etidronic acid using continuous and sequential chelation on the removal of smear layer, dentin microhardness, and push-out bond strength of calcium silicate-based cement
Ecehan Hazar, Ahmet Hazar
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of free available chlorine in sodium hypochlorite solutions admixed with novel chelating agents
Somya Tyagi, Sonali Taneja, Kandasamy Nagarajan, Divya Chowdhary
Endodontology.2025; 37(2): 188. CrossRef - Effect of different chelating agents, with and without activation, including XP-endo Finisher, on root dentin microhardness: An in vitro study
Mahmoud Mohamed A. Sherif, Mai Hamdy Ragab, Marwa ElSayed Sharaan
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2025; 15(3): 282. CrossRef - Oracle of phytic acid in dental panacea – Insight into properties, therapeutic effect, regeneration, materials interaction and oral physiology
Ummey Salma, C. Pushpalatha, SV. Sowmya, Dominic Augustine, Ahmed Alamoudi, Bassam Zidane, Nassreen Hassan Mohammad Albar, Shilpa Bhandi
The Saudi Dental Journal.2024; 36(8): 1093. CrossRef - In Vitro Bond Strength of Dentin Treated with Sodium Hypochlorite: Effects of Antioxidant Solutions
Guillermo Grazioli, Elisa de León Cáceres, Romina Tessore, Rafael Lund, Ana Monjarás-Ávila, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska, Louis Hardan, Rim Bourgi, Carlos Cuevas-Suárez
Antioxidants.2024; 13(9): 1116. CrossRef - Is a mix – A fix? “A microscopic analysis of depth of penetration of three combinations of irrigants”
Yantrapragada Lakshmi Sunanda, Krishna Prasad Parvathaneni, T. B. V. G. Raju, Abitha Seshadri, Nadimpalli Mahendra Varma, Gowtam Dev Dondapati
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(2): 186. CrossRef - Effect of phytic acid on dentinal collagen solubilization and its binding and debinding potentials to dentin
Diletta Forgione, Mohannad Nassar, Roda Seseogullari-Dirihan, Ahmed Jamleh, Arzu Tezvergil-Mutluay
Journal of Dentistry.2023; 128: 104361. CrossRef - Application of Inositol Hexaphosphate and Inositol in Dental Medicine: An Overview
Ana Druzijanic, Mare Kovic, Marija Roguljic, Livia Cigic, Martina Majstorovic, Ivana Vucenik
Biomolecules.2023; 13(6): 913. CrossRef - Ex-vivo study about antimicrobial effectiveness of phytic acid against Enterococcus faecalis into root canals
Giulia BOSCHI, Giorgio PICCINELLI, Carlo BONFANTI, Stefano A. SALGARELLO
Minerva Dental and Oral Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of phytic acid on bond strength and interfacial integrity of universal adhesive to deep dentin
Ahmed Mostafa Attia, Ahmed Fawzy Abo-Elezz, Rehab Khalil Safy
Brazilian Dental Journal.2022; 33(5): 116. CrossRef - Resin-Based Cement Applied to Enamel and Dentin Pre-Treated with Phytic Acid: An In Vitro Study
Mohannad Nassar, Md. Sofiqul Islam, Smriti Aryal A C, Hatem Mostafa El-Damanhoury, Salvatore Sauro, Noriko Hiraishi
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(24): 11976. CrossRef - Postspace pretreatment with 17% ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid, 7% maleic acid, and 1% phytic acid on bond strength of fiber posts luted with a self-adhesive resin cement
PriyaC Yadav, Ramya Raghu, Ashish Shetty, Subhashini Rajasekhara
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2021; 24(6): 558. CrossRef - Phytic Acid: Properties and Potential Applications in Dentistry
Mohannad Nassar, Rania Nassar, Husain Maki, Abdullah Al-Yagoob, Mahmood Hachim, Abiola Senok, David Williams, Noriko Hiraishi
Frontiers in Materials.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- The Effect of Chemical Surface Modification on the Repair Bond Strength of Resin Composite: An In Vitro Study
- 2,368 View
- 19 Download
- 17 Crossref

- Effect of acidic solutions on the microhardness of dentin and set OrthoMTA and their cytotoxicity on murine macrophage
- Soram Oh, Hiran Perinpanayagam, Yoon Lee, Jae-Won Kum, Yeon-Jee Yoo, Sang-Min Lim, Seok Woo Chang, Won-Jun Shon, Woocheol Lee, Seung-Ho Baek, Kee-Yeon Kum
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(1):12-21. Published online December 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.1.12

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives To evaluate the effects of three acids on the microhardness of set mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) and root dentin, and cytotoxicity on murine macrophage.
Materials and Methods OrthoMTA (BioMTA) was mixed and packed into the human root dentin blocks of 1.5 mm diameter and 5 mm height. Four groups, each of ten roots, were exposed to 10% citric acid (CA), 5% glycolic acid (GA), 17% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), and saline for five minutes after setting of the OrthoMTA. Vickers surface microhardness of set MTA and dentin was measured before and after exposure to solutions, and compared between groups using one-way ANOVA with Tukey test. The microhardness value of each group was analyzed using student
t test. Acid-treated OrthoMTA and dentin was examined by scanning electron microscope (SEM). Cell viability of tested solutions was assessed using WST-8 assay and murine macrophage.Results Three test solutions reduced microhardness of dentin. 17% EDTA demonstrated severe dentinal erosion, significantly reduced the dentinal microhardness compared to 10% CA (
p = 0.034) or 5% GA (p = 0.006). 10% CA or 5% GA significantly reduced the surface microhardness of set MTA compared to 17% EDTA and saline (p < 0.001). Acid-treated OrthoMTA demonstrated microporous structure with destruction of globular crystal. EDTA exhibited significantly more cellular toxicity than the other acidic solutions at diluted concentrations (0.2, 0.5, 1.0%).Conclusions Tested acidic solutions reduced microhardness of root dentin. Five minute's application of 10% CA and 5% GA significantly reduced the microhardness of set OrthoMTA with lower cellular cytotoxicity compared to 17% EDTA.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Removal Efficiency of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate: A narrative Review of Retrieval Techniques
Mohammed A. Hussein, Rasha H. Jehad
Journal of Medical and Oral Biosciences.2025; : 36. CrossRef - Impact of calcium hydroxide and 2-hydroxyisocaproic acid on the microhardness of root dentine: an in vitro study
Nandini T. Niranjan, Protim Ghosh Dastidar, Raghavendra Penukonda, Galvin Sim Siang Lin, Roopa Babannavar, Arun Jaysheel, Harshada Pattar
Odontology.2024; 112(3): 711. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Effect of Chitosan-Based Irrigation Solutions on the Bond Strength of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate to Bulk-Fill Composite
Arzu Şahin Mantı, Bağdagül Helvacıoğlu Kıvanç
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2024; 15(12): 370. CrossRef - Effect of Various Acid Solutions as an Aid in Removing the OrthoMTA-Based Root Canal Filling
Naveen Chhabra, Abhishek Parolia
Materials.2023; 16(13): 4535. CrossRef - Effect of Glycolic Acid, Maleic Acid, and EDTA in the Removal of Smear Layer from Root Canal Dentin
Tarini Mullick, Nidambur Vasudev Ballal
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A comparative evaluation of the effect of various chelating agents on the microhardness of root canal dentin: An in vitro study
Mineet Kaul, Zinnie Nanda, Kranthikumar Reddy, Rahul Deore, Divya Mandlecha, Esha Jaiswal
Endodontology.2023; 35(3): 234. CrossRef - Calcium hydroxide and niobium pentoxide treatment effects before MTA placement
Kolli Sankeerthana, Kittappa Karthikeyan, Sekar Mahalaxmi
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(1): 48. CrossRef - Calcium silicate and calcium aluminate cements for dentistry reviewed
Carolyn Primus, James L. Gutmann, Franklin R. Tay, Anna B. Fuks
Journal of the American Ceramic Society.2022; 105(3): 1841. CrossRef - Influence of Acidic Environmental Conditions on Push‐Out Bonding Strength of Four Calcium Silicate‐Based Materials to Root Dentin
Beliz Özel, Raif Erişen, Boonlert Kukiattrakoon
International Journal of Dentistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The effects of sodium hypochlorite and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid on the microhardness of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate and TotalFill Bioceramic Putty
Jacklyn H.R. Chu, Kalie Y. Chia, Alexander L. Qui, Alex Moule, William N. Ha
Australian Endodontic Journal.2020; 46(1): 33. CrossRef - Pre-application of dentin bonding agent prevents discoloration caused by mineral trioxide aggregate
Yoo-Lim Choi, Young-Eun Jang, Bom Sahn Kim, Jin-Woo Kim, Yemi Kim
BMC Oral Health.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Glycolic acid as the final irrigant in endodontics: Mechanical and cytotoxic effects
Yuri Dal Bello, Hisadora Fracaro Porsch, Ana Paula Farina, Matheus Albino Souza, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Ana Karina Bedran-Russo, Doglas Cecchin
Materials Science and Engineering: C.2019; 100: 323. CrossRef - Carbohydrate-electrolyte drinks exhibit risks for human enamel surface loss
Mary Anne Sampaio de Melo, Vanara Florêncio Passos, Juliana Paiva Marques Lima, Sérgio Lima Santiago, Lidiany Karla Azevedo Rodrigues
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(4): 246. CrossRef
- Removal Efficiency of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate: A narrative Review of Retrieval Techniques
- 2,686 View
- 17 Download
- 13 Crossref

- Effect of intracanal medicaments used in endodontic regeneration procedures on microhardness and chemical structure of dentin
- Ghaeth Hamdon Yassen, George Joseph Eckert, Jeffrey Allen Platt
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(2):104-112. Published online December 24, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.2.104
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study was performed to investigate the effects of different intracanal medicaments on chemical structure and microhardness of dentin.
Materials and Methods Fifty human dentin discs were obtained from intact third molars and randomly assigned into two control groups and three treatment groups. The first control group received no treatment. The second control group (no medicament group) was irrigated with sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl), stored in humid environment for four weeks and then irrigated with ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA). The three treatment groups were irrigated with NaOCl, treated for four weeks with either 1 g/mL triple antibiotic paste (TAP), 1 mg/mL methylcellulose-based triple antibiotic paste (DTAP), or calcium hydroxide [Ca(OH)2] and finally irrigated with EDTA. After treatment, one half of each dentin disc was subjected to Vickers microhardness (
n = 10 per group) and the other half was used to evaluate the chemical structure (phosphate/amide I ratio) of treated dentin utilizing attenuated total reflection Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (n = 5 per group). One-way ANOVA followed by Fisher's least significant difference were used for statistical analyses.Results Dentin discs treated with different intracanal medicaments and those treated with NaOCl + EDTA showed significant reduction in microhardness (
p < 0.0001) and phosphate/amide I ratio (p < 0.05) compared to no treatment control dentin. Furthermore, dentin discs treated with TAP had significantly lower microhardness (p < 0.0001) and phosphate/amide I ratio (p < 0.0001) compared to all other groups.Conclusions The use of DTAP or Ca(OH)2 medicaments during endodontic regeneration may cause significantly less microhardness reduction and superficial demineralization of dentin compared to the use of TAP.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effects of Sodium Dichloroisocyanurate and Calcium Hydroxide as Intracanal Medicaments on Microhardness and Fracture Resistance of Dentin: An In Vitro Study
Fereshte Sobhnamayan, Alireza Adl, Negin Firouzi, Saeed Moravej, Samina Gavahianjahromi
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of allicin-incorporated graphene oxide hydrogel on dentin microhardness
Rathna Piriyanga, Manish Ranjan, Anand Sherwood, Mohammad Fareed, Mohmed Isaqali Karobari
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Recent Advances in Injectable Hydrogel Biotherapeutics for Regenerative Dental Medicine
Renan Dal‐Fabbro, Arwa Daghrery, Caroline Anselmi, Igor Paulino M. Soares, Alexandre Henrique dos Reis‐Prado, Pedro Henrique Chaves de Oliveira, Marco C. Bottino
Macromolecular Bioscience.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Ex vivo analysis of clindamycin’s impact on dentin microhardness and surface chemistry
Mandana Naseri, Farshid Gholami, Kamyar Khosravi, Mohammadreza Vatankhah, Mohammad Atai, Omid Dianat
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(10): 982. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of effect of modified triple antibiotic paste and calcium hydroxide as intracanal medicament on microhardness of root dentin: An in vitro study
Aparna Palekar, Piyush Mantri, Minal Awinashe, Basawaraj Biradar, Mukund Singh
Endodontology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Use of Nanofibers in Regenerative Endodontic Therapy—A Systematic Review
Sebastian Candrea, Alexandrina Muntean, Anida-Maria Băbțan, Antonia Boca, Claudia Nicoleta Feurdean, Ioana Roxana Bordea, Adina Bianca Boșca, Aranka Ilea
Fibers.2024; 12(5): 42. CrossRef - Effect of sodium hypochlorite and ethylenediaminotetraacetic acid activated by laser and ultrasonic energy on surface morphology and chemical composition of intracanal dentin
Adriana Katunarić, Sandra Flinčec Grgac, Dragana Gabrić, Božidar Pavelić, Ivona Bago
Microscopy Research and Technique.2024; 87(4): 818. CrossRef - Development of a Thermoresponsive Core–Shell Hydrogel for Sequential Delivery of Antibiotics and Growth Factors in Regenerative Endodontics
Sayna Shamszadeh, Saeed Asgary, Mohammad Akrami, Fatemeh Mashhadiabbas, Alireza Akbarzadeh Baghban, Forough Shams
Frontiers in Bioscience-Elite.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Intracanal medicaments and coronal sealing materials influence on root fracture resistance and coronal discoloration: An in vitro study
Rasoul Sahebalam, Marzie Boskabady, Maryam Naghavi, Samira Dehghanitafti
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2024; 14(2): 199. CrossRef - Final irrigation with bioglass solution in regenerative endodontic procedure induces tissue formation inside the root canals, collagen maturation, proliferation cell and presence of osteocalcin
Kiani dos Santos de Paula, Alexandre Henrique dos Reis‐Prado, Witalo Pereira de Jesus, Juliana Goto, Lara Cancella de Arantes, Marina Verçosa, Luciano Tavares Angelo Cintra, Edilson Ervolino, Raphael Escorsim Szawka, Murilo Camuri Crovace, Ricardo Alves d
International Endodontic Journal.2024; 57(5): 586. CrossRef - In vitro analysis of compressive strength of root dentin on application of intracanal medicaments for different time periods
Kushal Kumar Ghosh, Sayantan Mukherjee, Paromita Mazumdar, Sahil Ali, Lovely Das
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(12): 1289. CrossRef - Effects of endodontic root canal irrigants on tooth dentin revealed by infrared spectroscopy: a systematic literature review
Hamza Elfarraj, Franco Lizzi, Kerstin Bitter, Paul Zaslansky
Dental Materials.2024; 40(8): 1138. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of antimicrobial efficacy of triple antibiotic paste and propolis extract using three different vehicles as intracanal medicament: An in vitro study
Gunde Veronica, B. V Thimma Reddy, Uday K. Chowdary Birapu, Raghavendra K. Jadadoddi, R Hemanth Kumar, Kanamarlapudi V. Saikiran
Journal of Dr. NTR University of Health Sciences.2024; 13(4): 323. CrossRef - Outcome of Regenerative Endodontic Procedures in Nonvital Immature Permanent Teeth Using 2 Intracanal Medications: A Prospective Randomized Clinical Study
Aladdin Al-Qudah, Mohammad Almomani, Layla Hassoneh, Lama Awawdeh
Journal of Endodontics.2023; 49(7): 776. CrossRef - The Effect of Calcium Hydroxide, Triple Antibiotic Paste and Chlorhexidine on Pain in Teeth with Symptomatic Apical Periodontitis: A Randomised Controlled Trial
Asma Munir Khan, Irfana Khursheed Ahmed Gangoo, Naila Amir Ali, Mansoor Khan, Muhammad Qasim Javed, Mustafa Hussein AlAttas, Ayman M. Abulhamael, Hammam Ahmed Bahammam, Loai Alsofi, Rayan Suliman Al Yahya
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(4): 3091. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of the depth of penetration and postoperative pain associated with the use of continuous chelation using HEBP and standard irrigation protocol in the endodontic treatment of adult permanent nonvital teeth: A randomized controlled tr
Janhvi Samir Parekh, Mrunalini J. Vaidya, Vibha R. Hegde
Endodontology.2023; 35(4): 344. CrossRef - Regenerative Endodontics and Minimally Invasive Dentistry: Intertwining Paths Crossing Over Into Clinical Translation
Hisham Elnawam, Menatallah Abdelmougod, Ahmed Mobarak, Mai Hussein, Hamdy Aboualmakarem, Michael Girgis, Rania El Backly
Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of calcium hydroxide on fracture resistance and microhardness of dentin in human teeth
Simar Sethi, Alpa Gupta, Ansy Hanna Kurian, Dax Abraham, Parul Chauhan, Kritika Aneja, Sucheta Jala, Arundeep Singh
Endodontology.2022; 34(4): 223. CrossRef - Evaluation of Effects of Various Irrigating Solutions on Chemical Structure of Root Canal Dentin Using FTIR, SEM, and EDS: An In Vitro Study
Indu Padmakumar, Dharam Hinduja, Abdul Mujeeb, Raghu Kachenahalli Narasimhaiah, Ashwini Kumar Saraswathi, Mubashir Baig Mirza, Ali Robaian, Syed Nahid Basheer, Mohmed Isaqali Karobari, Giuseppe Alessandro Scardina
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2022; 13(4): 197. CrossRef - The Effects of Double Antibiotic Paste and Amoxicillin-clavulanate Paste Used in Endodontic Regeneration on Microhardness of Radicular Dentine: An In vitro Study
Meenu Madhukumar, Praveena Geetha, K. Radhakrishnan Nair, Manu Unnikrishnan
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2021; 13(Suppl 1): S510. CrossRef - The effect of intracanal medication variations on microhardness of simulated immature root dentin
Pınar Serdar Eymirli, Ayhan Eymirli, Emel Uzunoğlu Özyürek
Australian Endodontic Journal.2021; 47(3): 616. CrossRef - Antibacterial Effect and Bioactivity of Innovative and Currently Used Intracanal Medicaments in Regenerative Endodontics
Sarah Alfadda, Theeb Alquria, Eda Karaismailoglu, Hacer Aksel, Adham A. Azim
Journal of Endodontics.2021; 47(8): 1294. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Effect of Nitrofurantoin Paste as an Intracanal Medicament on the Chemical Structure of Radicular Dentine
Mewan Abdulrahman, Bestoon Faraj, Kawa Dizaye
Sulaimani Dental Journal.2021; 8(2): 8. CrossRef - Effect of hydrogel-based antibiotic intracanal medicaments on crown discoloration
Rayan B. Yaghmoor, Jeffrey A. Platt, Kenneth J. Spolnik, Tien Min Gabriel Chu, Ghaeth H. Yassen
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Microhardness and Fracture Resistance of Radicular Dentin Treated with Different Concentrations of Calcium Hydroxide in Endodontic Regeneration Procedures
Sara N. Hashem, Maha Adel Elhousiny
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.2021; 9(D): 324. CrossRef - Effect of medicaments used in endodontic regeneration on the morphological characteristics of bovine radicular dentin: Experimental immature tooth model
Maira C. Conte, Cleonice da Silveira Teixeira, Eduardo A. Bortoluzzi, Wilson T. Felippe, Luciane G. P. dos Santos, Mariana T. Pandolfo, Patrícia da Agostim Cancelier, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
Microscopy Research and Technique.2020; 83(4): 354. CrossRef - Effect of intracanal medicaments on radicular dentine: An attenuated total reflection-Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy analysis
Promila Verma, Afsana Ansari, Aseem Prakash Tikku, Anil Chandra, Rakesh Kumar Yadav, Ramesh Bharti, Rhythm Bains
Asian Journal of Oral Health and Allied Sciences.2020; 10: 3. CrossRef - Effect of Hydrogel-Based Antibiotic Intracanal Medicaments on Push-Out Bond Strength
Rayan B. Yaghmoor, Jeffrey A. Platt, Kenneth J. Spolnik, Tien Min Gabriel Chu, Ghaeth H. Yassen
European Journal of Dentistry.2020; 14(04): 575. CrossRef - Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Enterococcus faecalis Isolated From Root Canal: An In Vitro Study
Nazanin Zargar, Mohammad J Nasiri, Hengameh Ashraf, Bahareh Hajikhani, Shirin Etminani Esfahani, Maryam Etminani Esfahani
Avicenna Journal of Pharmaceutical Research.2020; 1(2): 60. CrossRef - The Effect of Calcium Hydroxide and Nano–calcium Hydroxide on Microhardness and Superficial Chemical Structure of Root Canal Dentin: An Ex Vivo Study
Mandana Naseri, Leila Eftekhar, Farshid Gholami, Mohammad Atai, Omid Dianat
Journal of Endodontics.2019; 45(9): 1148. CrossRef - Antimicrobial efficacy of clindamycin and triple antibiotic paste as root canal medicaments on tubular infection: An in vitro study
Nazanin Zargar, Motahare Rayat Hosein Abadi, Mohammad Sabeti, Zahra Yadegari, Alireza Akbarzadeh Baghban, Omid Dianat
Australian Endodontic Journal.2019; 45(1): 86. CrossRef - Influence of silver nanoparticle solution on the mechanical properties of resin cements and intrarradicular dentin
Thaís Yumi Umeda Suzuki, Juno Gallego, Wirley Gonçalves Assunção, André Luiz Fraga Briso, Paulo Henrique dos Santos, Chun-Pin Lin
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(6): e0217750. CrossRef - Triple antibiotic paste: momentous roles and applications in endodontics: a review
Ardavan Parhizkar, Hanieh Nojehdehian, Saeed Asgary
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Retention of BioAggregate and MTA as coronal plugs after intracanal medication for regenerative endodontic procedures: an ex vivo study
Suzan Abdul Wanees Amin, Shaimaa Ismail Gawdat
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) application chemical characterization of enamel, dentin and bone
Camila de Carvalho Almança Lopes, Pedro Henrique Justino Oliveira Limirio, Veridiana Resende Novais, Paula Dechichi
Applied Spectroscopy Reviews.2018; 53(9): 747. CrossRef - Chlorhexidine Prevents Root Dentine Mineral Loss and Fracture Caused by Calcium Hydroxide over Time
Michael Ranniery Garcia Ribeiro, Érika Bárbara Abreu Fonseca Thomaz, Darlon Martins Lima, Tarcísio Jorge Leitão, José Bauer, Soraia De Fátima Carvalho Souza
International Journal of Dentistry.2017; 2017: 1. CrossRef - Attachment and proliferation of dental pulp stem cells on dentine treated with different regenerative endodontic protocols
M. A. Alghilan, L. J. Windsor, J. Palasuk, G. H. Yassen
International Endodontic Journal.2017; 50(7): 667. CrossRef - Second-generation Platelet Concentrate (Platelet-rich Fibrin) as a Scaffold in Regenerative Endodontics: A Case Series
Hengameh Bakhtiar, Shahram Esmaeili, Setareh Fakhr Tabatabayi, Mohammad Reza Ellini, Mohammad Hossein Nekoofar, Paul M.H. Dummer
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(3): 401. CrossRef - Antibacterial Effects of Antimicrobials Used in Regenerative Endodontics against Biofilm Bacteria Obtained from Mature and Immature Teeth with Necrotic Pulps
Jordon C. Jacobs, Alex Troxel, Ygal Ehrlich, Kenneth Spolnik, Josef S. Bringas, Richard L. Gregory, Ghaeth H. Yassen
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(4): 575. CrossRef - Triple Antibiotic Polymer Nanofibers for Intracanal Drug Delivery: Effects on Dual Species Biofilm and Cell Function
Divya Pankajakshan, Maria T.P. Albuquerque, Joshua D. Evans, Malgorzata M. Kamocka, Richard L. Gregory, Marco C. Bottino
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(10): 1490. CrossRef - Inhibitory effect of gels loaded with a low concentration of antibiotics against biofilm formation by Enterococcus faecalis and Porphyromonas gingivalis
Amnah A. Algarni, Ghaeth H. Yassen, Richard L. Gregory
Journal of Oral Science.2015; 57(3): 213. CrossRef
- The Effects of Sodium Dichloroisocyanurate and Calcium Hydroxide as Intracanal Medicaments on Microhardness and Fracture Resistance of Dentin: An In Vitro Study
- 2,493 View
- 26 Download
- 41 Crossref

- Calcium hydroxide dressing residues after different removal techniques affect the accuracy of Root-ZX apex locator
- Emel Uzunoglu, Ayhan Eymirli, Mehmet Özgür Uyanik, Semra Çalt, Emre Nagas
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(1):44-49. Published online November 5, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.1.44
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study compared the ability of several techniques to remove calcium hydroxide (CH) from the root canal and determined the influence of CH residues on the accuracy of the electronic apex locator.
Materials and Methods Root canals of 90 human maxillary lateral incisors with confirmed true working length (TWL) were prepared and filled with CH. The teeth were randomly assigned to one of the experimental groups according to the CH removal technique (
n = 14): 0.9% saline; 0.9% saline + master apical file (MAF); 17% ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA); 17% EDTA + MAF; 5.25% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl); 5.25% NaOCl + MAF. Six teeth were used as negative control. After CH removal, the electronic working length was measured using Root-ZX (Morita Corp.) and compared with TWL to evaluate Root-ZX accuracy. All specimens were sectioned longitudinally, and the area of remaining CH (CH) and total canal area were measured using imaging software.Results The EDTA + MAF and NaOCl + MAF groups showed better CH removal than other groups (
p < 0.05). Root-ZX reliability to prevent overestimated working length to be > 85% within a tolerance of ± 1.0 mm (p < 0.05). There was strong negative correlation between amount of CH residues and EAL accuracy (r = -0.800 for ± 0.5 mm;r = -0.940 for ± 1.0 mm).Conclusions The mechanical instrumentation improves the CH removal of irrigation solutions although none of the techniques removed the dressing completely. Residues of CH medication in root canals affected the accuracy of Root-ZX adversely.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of the Effect of Calcium Hydroxide Residues Including Different Vehicles on the Accuracy of Electronic Apex Locators
Simay Koç, Damla Erkal, Dide Tekinarslan, Kürs¸at Er
Journal of Advanced Oral Research.2025; 16(1): 54. CrossRef - Evaluation of heated sodium hypochlorite’s effect on the accuracy of contemporary electronic apex locators: an in vitro study
İkbal Sena Çelebi Keskin, Turgut Yağmur Yalçın
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors influencing the accuracy of electronic apex locators: A scoping review
Shayan Golkar, Abbasali Khademi, Amin Saatchi, Amir Ghorani, Pedram Iranmanesh
Dental Research Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of a new irrigation solution -RISA- on removing calcium hydroxide from artificial standardized grooves in root canals - an in vitro study
İpek Eraslan Akyüz, Salih Düzgün, Hüseyin Sinan Topçuoğlu
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of the accuracy of electronic apex locators and cone-beam computed tomography in detection of root canal perforation and working length during endodontic retreatment
Simay Koç, Hatice Harorlı, Alper Kuştarcı
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Intracanal Medicaments on the Measurement Accuracy of Four Apex Locators: An In Vitro Study
Hamza Cudal, Tuğrul Aslan, Bertan Kesim
Meandros Medical and Dental Journal.2023; 24(3): 215. CrossRef - Electronic Apex Locators and their Implications in Contemporary Clinical Practice: A Review
Zainab Shirazi, Anas Al-Jadaa, Abdul Rahman Saleh
The Open Dentistry Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Apical Patency, Coronal Preflaring and Calcium Hydroxide on the Accuracy of Root ZX Apex Locator for Working Length Determination: An In Vitro Study
Mostafa Godiny, Reza Hatam, Roya Safari-Faramani, Atefeh Khavid, Mohammad Reza Rezaei
Journal of Advanced Oral Research.2022; 13(1): 38. CrossRef - Endodontic cement penetration after removal of calcium hydroxide dressing using XP-endo finisher
Alyssa Sales dos Santos, Maria Aparecida Barbosa de Sá, Marco Antônio Húngaro Duarte, Martinho Campolina Rebello Horta, Frank Ferreira Silveira, Eduardo Nunes
Brazilian Oral Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of glycolic acid for the removal of calcium hydroxide from simulated internal Resorption cavities
Cangül Keskin, Ali Keleş, Öznur Sarıyılmaz
Clinical Oral Investigations.2021; 25(7): 4407. CrossRef - Accuracy of electronic apex locator in the presence of different irrigating solutions
Padmanabh Jha, Vineeta Nikhil, Shalya Raj, Rohit Ravinder, Preeti Mishra
Endodontology.2021; 33(4): 232. CrossRef - Farklı Kanal İçi Ortamların Apeks Bulucuların Doğruluğu Üzerine Etkisi
Asena OKUR, Tuğrul ASLAN, Burak SAĞSEN
Selcuk Dental Journal.2021; 8(3): 859. CrossRef - Evaluation of the accuracy of different apex locators in determiningthe working length during root canal retreatment
Pelin Tufenkci, Aylin Kalaycı
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2020; 14(2): 125. CrossRef - Influence of calcium hydroxide residues after using different irrigants on the accuracy of two electronic apex locators: An in vitro study
NooshinSadat Shojaee, Zahra Zaeri, MohammadMehdi Shokouhi, Fereshteh Sobhnamayan, Alireza Adl
Dental Research Journal.2020; 17(1): 48. CrossRef - The Effect of Calcium Hydroxide and File Sızes on the Accuracy of the Electronic Apex Locator in Simulated Immature Teeth
Leyla AYRANCİ, Ahmet ÇETİNKAYA, Serkan ÖZKAN
Middle Black Sea Journal of Health Science.2019; 5(3): 273. CrossRef - The Effect of File Size and Type and Irrigation Solutions on the Accuracy of Electronic Apex Locators: AnIn VitroStudy on Canine Teeth
Maciej Janeczek, Piotr Kosior, Dagmara Piesiak-Pańczyszyn, Krzysztof Dudek, Aleksander Chrószcz, Agnieszka Czajczyńska-Waszkiewicz, Małgorzata Kowalczyk-Zając, Aleksandra Gabren-Syller, Karol Kirstein, Aleksandra Skalec, Ewelina Bryła, Maciej Dobrzyński
BioMed Research International.2016; 2016: 1. CrossRef
- Evaluation of the Effect of Calcium Hydroxide Residues Including Different Vehicles on the Accuracy of Electronic Apex Locators
- 1,702 View
- 9 Download
- 16 Crossref

- Effect of soft chelating irrigation on the sealing ability of GP/AH Plus root fillings
- Yi-Suk Yu, Tae-Gun Kim, Kwang-Won Lee, Mi-Kyung Yu
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(6):484-490. Published online November 30, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.6.484
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of soft chelating irrigant on the sealing ability of root fillings by using a glucose leakage test.
A total of 45 single-rooted teeth were selected for the study. The teeth were decoronated leaving a total length of 13mm. The root canals prepared using K3 NiTi rotary instruments to an apical dimension of size 45(0.06 taper). The specimens were then randomly divided into 3 experimental groups of 13 roots each and 2 control groups of 3 roots each. Specimen in each group were prepared with different irrigation protocols : group 1, 2.5% NaOCl; group 2, 2.5% NaOCl and 17% EDTA; group 3, 2.5% NaOCl and 15% HEBP. The root canals were filled with gutta-percha and AH Plus sealer using lateral condensation. After 7 days in 37℃, 100% humidity, the coronal-to-apical microleakage was evaluated quantitatively using a glucose leakage model. The leaked glucose concentration was measured with spectrophotometry at 1, 4, 7, 14, 21 and 28 days.
There was a tendency of increase in leakage in all experimental groups during experimental period. HEBP-treated dentin showed no significant difference with EDTA-treated dentin during experimental period. From the 21th day onward, HEBP-treated dentin showed significantly lower leakage than smear-covered dentin. HEBP-treated dentin displayed a similar sealing pattern to EDTA-treated dentin and a better sealing ability than smear-covered dentin. Consequently, a soft chelator(HEBP) could be considered as the possible alternative to EDTA.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of moisture on sealing ability of root canal filling with different types of sealer through the glucose penetration model
Jin-Ah Jang, Hee-Lyang Kim, Mi-Ja Her, Kwang-Won Lee, Mi-Kyung Yu
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(5): 335. CrossRef
- Effect of moisture on sealing ability of root canal filling with different types of sealer through the glucose penetration model
- 1,182 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Time-dependent effects of EDTA application on removal of smear layer in the root canal system
- Ja-Kyong Lee, Sang-Hyuk Park, Gi-Woon Choi
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(3):169-178. Published online May 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.3.169
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study was to verify that the combined application of NaOCl and EDTA was more effective in removal of smear layer than the application of NaOCl alone. Furthermore it was aimed to find out the optimal time for the application of EDTA.
Thirty five single rooted teeth were cleaned and shaped. NaOCl solution was used as an irrigant during instrumentation. After instrumentation, root canals of the control group were irrigated with 5 ml of NaOCl for 2 minutes. 30 sec, 1 min, and 2 min group were irrigated with 5 ml of 17% EDTA for 30 sec, 1 min, and 2 min respectively. Then the roots were examined with scanning electron microscopy for evaluating removal of smear layer and erosion of dentinal tubule.
The results were as follows;
The control group:
The smear layer was not removed at all.
The other groups:
1) Middle⅓: All groups showed almost no smear layer. And the erosion occurred more frequently as increasing irrigation time.
2) Apical⅓: The cleaning effect of 2 min group was better than the others.
The results suggest that 2 min application of 17% EDTA should be adequate to remove smear layer on both apical⅓ and middle⅓.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enhancing the Antibacterial Effect of Erythrosine-Mediated Photodynamic Therapy with Ethylenediamine Tetraacetic Acid
MinKi Choi, Haeni Kim, Siyoung Lee, Juhyun Lee
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2024; 51(1): 32. CrossRef - Apical foramen morphology according to the length of merged canal at the apex
Hee-Ho Kim, Jeong-Bum Min, Ho-Keel Hwang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(1): 26. CrossRef - Effect of moisture on sealing ability of root canal filling with different types of sealer through the glucose penetration model
Jin-Ah Jang, Hee-Lyang Kim, Mi-Ja Her, Kwang-Won Lee, Mi-Kyung Yu
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(5): 335. CrossRef
- Enhancing the Antibacterial Effect of Erythrosine-Mediated Photodynamic Therapy with Ethylenediamine Tetraacetic Acid
- 1,756 View
- 7 Download
- 3 Crossref

- THE EFFECT OF SMEAR LAYER TREATMENT ON THE MICROLEAKAGE
- Jung-Min Lee, Sang-Hyuk Park, Gi-Woon Choi
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(5):378-389. Published online January 14, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.5.378
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Abstract The purpose of this study was to compare the sealing ability of root canal obturation with or without the treatment of smear layer. Eighty extracted human teeth with one canal were selected. Instrumentation was performed with crown-down technique. After instrumentation, root canals of the NaOCl group and NaOCl-6 group were irrigated with 3% NaOCl. EDTA group and EDTA-6 group were irrigated with 17% EDTA. Then all teeth were obturated using continuous wave obturation technique.
NaOCl group and EDTA group were immersed in methylene blue solution for 84hours. NaOCl-6 group and EDTA-6 group were immersed in methylene blue solution for 6months. The teeth were sectioned at 1.5 mm (Level 1), 3.0 mm (Level 2) and 4.5 mm (Level 3) from the root apex. The length of dye-penetrated interface and the circumferential length of canal at each level were measured using Sigma-Scan Pro 5.0.
The mean leakage ratio was decreased cervically.
NaOCl group showed higher mean leakage ratio than EDTA group at each level. But there was significant difference at level 1 only (p < 0.05).
NaOCl-6 group showed higher mean leakage ratio than EDTA-6 group at each level. But there was significant difference at level 1 only (p < 0.05).
NaOCl-6 group showed higher mean leakage ratio than NaOCl group at each level. But there was significant difference at level 1 only (p < 0.05).
EDTA-6 group showed higher mean leakage ratio than EDTA group at each level. But there was no significant difference.
In NaOCl group and NaOCl-6 group, scanning electron micrographs of tooth sections generally covered with smear layer. In EDTA group and EDTA-6 group, tooth sections showing the penetration of sealers to opened dentinal tubules. The results suggest that removal of smear layer was effective to reduce the apical microleakage of the root canal.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of soft chelating irrigation on the sealing ability of GP/AH Plus root fillings
Yi-Suk Yu, Tae-Gun Kim, Kwang-Won Lee, Mi-Kyung Yu
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(6): 484. CrossRef - The effect of MTAD as a final root canal irrigants on the coronal bacterial leakage of obturated root canals
Tae Woo Kim, Seok Woo Chang, Dong Sung Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2008; 33(4): 397. CrossRef
- Effect of soft chelating irrigation on the sealing ability of GP/AH Plus root fillings
- 1,133 View
- 6 Download
- 2 Crossref

- The effects of EDTA and pulsed Nd:YAG laser on apical leakage of canal obturation
- Jin-Soo Kwon, Hee-Joo Lee, Bock Hur
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2003;28(1):50-56. Published online January 31, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.1.050
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effects of EDTA and pulsed Nd:YAG laser on apical leakage of canal obturation. Forty-eight single-rooted teeth were used in this study. The teeth were instrumented up to a size 40 K-file and irrigated with 2.5% NaOCl between each file size. And the teeth were divided into 4 groups. In group A, the root canals were irrigated with a final flush of 5ml 2.5% NaOCl as a control group. The teeth in group B were irrigated with a final flush of 5ml 17% EDTA. The teeth in group C and D were irradiated by pulsed Nd:YAG laser(laser parameters were set at 1W, 100mJ, 10Hz, and 2W, 100mJ, 20Hz respectively).
The results were as follows:
1. Apical leakage was observed in 50% of samples in group A, 30% of samples in group B, 20% of samples in group C, and 10% of samples in group D.
2. The teeth in group B had less leakage than group A, but there was no statistically significant differences(p>0.05).
3. The teeth in group C, D had less leakage than group A, and there was statistically significant differences(p<0.05).
4. The teeth in group C, D had less leakage than group B, but there was no statistically significant differences(p>0.05).
5. There was no significant differences in apical leakage between group C and group D(p>0.05).
- 815 View
- 1 Download


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


