Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Effects of different curing methods on the color stability of composite resins
- Massimo Pisano, Alfredo Iandolo, Dina Abdellatif, Andrea Chiacchio, Marzio Galdi, Stefano Martina
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(4):e33. Published online September 5, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e33
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
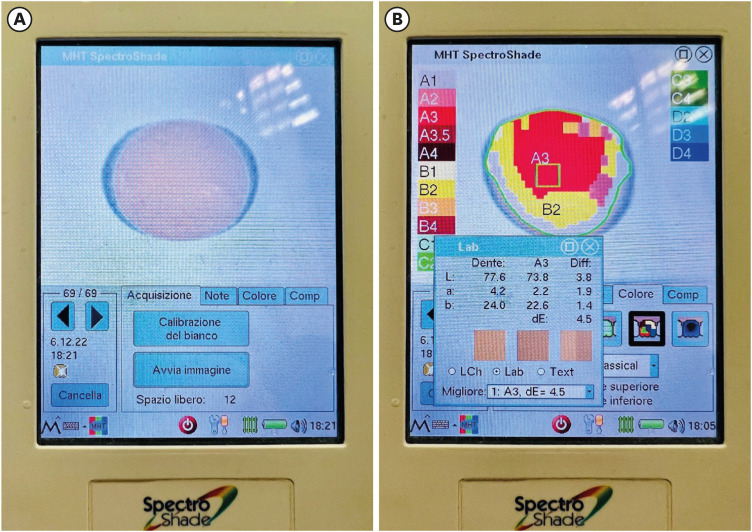
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to compare the effects of different polymerization strategies and the effectiveness of finishing and polishing procedures of composite resins on color stability.
Materials and Methods The samples were divided into 4 main groups according to the polymerization strategy, and all groups except the control group received surface treatment. Each group was subsequently divided into 3 subgroups respectively: Kuraray Clearfil Majesty ES-2 Classic, Premium and Universal. Approximately 24 hours after preparation of the samples, they were immersed for 7 days in a coffee solution. A first color measurement was performed after the preparation of the samples, the second measurement was performed after 7 days in the coffee solution. All measurements were carried out using a dental spectrophotometer to assess the CIE
L *a *b * color parameters.Results There was a statistically significant difference between ΔE values for different procedures (
p = 0.003); in particular, the differences were found only between the groups that received surface treatment and the control group. In addition, a statistically significant difference was observed between the values of ΔE for different composites in the different procedure groups.Conclusions Spectrophotometric analysis showed that the additional photopolymerization and oxygen inhibition procedures did not yield better results in relation to color stability. In addition, finishing and polishing provided better color stability compared to not performing these procedures.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Color Stability Under Challenge: Effects of Thermo-Aging and Mouthrinse Exposure on Anterior Teeth and Esthetic Composites
Gökçe Keçeci, Zehra Güner, Süleyman Ziya Şenyurt, Kamile Erciyas
European Journal of Therapeutics.2026; 32(1): 94. CrossRef - Abrasiveness and Bleaching Level of Toothpastes on Composite Resins: A Quantitative Analysis Using a Novel Brushing Simulator
Simge Meseli, Elif Alkan, Bora Korkut, Ozlem Kanar, Dilek Tagtekin
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(5): 2314. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Direct and Indirect Composite Restorations in Class II Tooth Preparations - An In vivo Study
Akshun Gupta, Garima Arora, Aprajita Mehta, Satish Sane, Siddhi Nevrekar, Apurva Nagrale
Advances in Human Biology.2025; 15(4): 550. CrossRef - Micro- and Nanoplastics and the Oral Cavity: Implications for Oral and Systemic Health, Dental Practice, and the Environment—A Narrative Review
Federica Di Spirito, Veronica Folliero, Maria Pia Di Palo, Giuseppina De Benedetto, Leonardo Aulisio, Stefano Martina, Luca Rinaldi, Gianluigi Franci
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2025; 16(9): 332. CrossRef
- Color Stability Under Challenge: Effects of Thermo-Aging and Mouthrinse Exposure on Anterior Teeth and Esthetic Composites
- 6,349 View
- 345 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Effect of surface sealant on the color stability and whiteness index of single-shade resin composites after staining and bleaching
- Muhammet Fidan, Özhan Yağcı
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(3):e30. Published online July 11, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e30
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
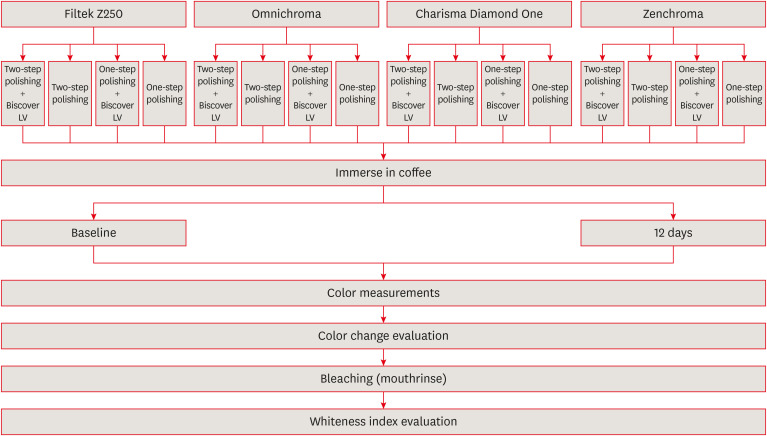
ePub Objectives The aim of the current study was to evaluate the effect of polishing systems and surface sealant on the color stability and whiteness index of single-shade resin composites after staining and bleaching.
Materials and Methods Three single-shade (Omnichroma, Charisma Diamond One, Zenchroma) and one multi-shade (Filtek Z250) materials were tested. From each resin composite, 40 specimens were prepared. The specimens were divided into 4 subgroups (
n = 10) according to the surface treatments: 1-step polishing, 1-step + Biscover LV, 2-step polishing, and 2-step polishing + Biscover LV. Color differences (ΔE00) were calculated after being immersed in the coffee solution for 12 days. After the staining, the specimens were immersed in a whitening mouthrinse (Crest-3D White) for 12 hours. Whiteness index differences (∆WID = WID after staining − WID after bleaching) values were recorded. The generalized linear model was used for analysis (p < 0.05).Results The lowest and highest ΔE00 values were found for Zenchroma and Charisma Diamond One respectively. Sealed groups indicated higher ΔE00 values than nonsealed groups with significant differences (
p = 0.008). The lowest and highest ΔWID values were found for Zenchroma and Charisma Diamond One respectively. Sealed groups indicated lower ΔWID values than nonsealed groups with significant differences (p = 0.022).Conclusions The use of surface sealant increased the discoloration and showed less whiteness change in resin materials. When the 1-step was compared with the 2-step polishing, the effects on the color stability and whiteness index values of the resin materials were similar.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Color and surface properties of conventional, injectable, and 3D-printed resin composites for anterior restorations: influence of a surface sealant
Soner Sismanoglu
Odontology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluating the effects of bleaching on color stability and surface roughness in single-shade and multi-shade resin composites
Hatice Tepe, Özge Çeliksöz, Zeynep Biçer, Batucan Yaman
Anatolian Current Medical Journal.2024; 6(6): 372. CrossRef
- Color and surface properties of conventional, injectable, and 3D-printed resin composites for anterior restorations: influence of a surface sealant
- 3,006 View
- 89 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- A global overview of enamel microabrasion for white spot lesions: a bibliometric review
- Aurélio de Oliveira Rocha, Karina Cardoso, Michely Cristina Goebel, Pablo Silveira Santos, Lucas Menezes dos Anjos, Juliana Silva Ribeiro, Carla Miranda Santana, Mariane Cardoso
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(3):e29. Published online July 11, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e29
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
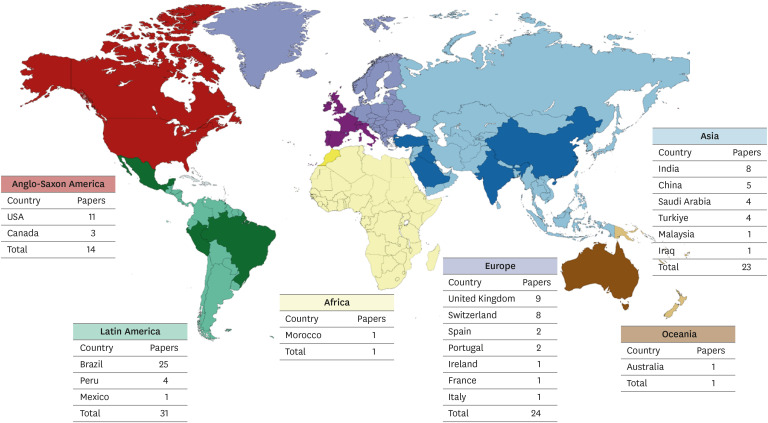
ePub This study aimed to identify and analyze articles on enamel microabrasion for the treatment of white spot lesions. A search was conducted on the Web of Science. The following parameters were recorded and analyzed: number of citations, year, journal, impact factor, study design, theme, country and continent, institution, authors, and keywords. Data was analyzed using VOSviewer software. The initial search resulted in 1,126 documents, of which 94 articles were included. The highest number of citations an article received was 65. The oldest article was published in 1975, and the most recent in 2023. The most frequent study design was case report (
n = 42). Regarding the themes, it was observed that the main objective of the studies was to evaluate the clinical performance of enamel microabrasion (n = 75), primarily using Opalustre (Ultradent Products Inc., South Jordan, UT, USA) (n = 37) for treating white stains caused by dental fluorosis (n = 41). Most articles originated from Latin America (n = 31), mainly from Brazil (n = 26). The most frequent author was Sundfeld RH (n = 10). This study reveals research trends in the field of enamel microabrasion. The publications were mainly case reports/series using Opalustre for the removal of fluorosis stains.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of microabrasion and a remineralizing agent before in-office bleaching on hydrogen peroxide permeability, color alteration, and enamel morphology
Michael Willian Favoreto, Leticia Condolo, Camila Mendes Camargo, Rafael Rodrigues Lima, Karol Carrillo, Abraham Lincoln Calixto, Alessandra Reis, Alessandro D. Loguercio
Journal of Dentistry.2025; 156: 105655. CrossRef - Micro- and Macroabrasion in the Esthetic Zone: A Narrative Review and Case Study
Jose Villalobos-Tinoco, Carlos A. Jurado, Silvia Rojas-Rueda, Nechama S. Citrin, Staley Colvert, Jose Luis Gutierrez-Quintero, Salwa Mekled
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(5): 183. CrossRef - Evaluation of demineralization changes in molar tissues in vitro using electrical impedance spectroscopy
V. D. Goncharov, M. A. Gorelikova, K. V. Shadrina, L. Yu. Orekhova, V. D. Berezkin, E. S. Nemovskaya, A. A. Petrov
Parodontologiya.2025; 30(3): 254. CrossRef
- Impact of microabrasion and a remineralizing agent before in-office bleaching on hydrogen peroxide permeability, color alteration, and enamel morphology
- 5,549 View
- 149 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Errors in light-emitting diodes positioning when curing bulk fill and incremental composites: impact on properties after aging
- Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad, Isadora M. Garcia, Haifa Maktabi, Maria Salem Ibrahim, Qoot Alkhubaizi, Howard Strassler, Fabrício M. Collares, Mary Anne S. Melo
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(4):e51. Published online September 24, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e51

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the effect of improper positioning single-peak and multi-peak lights on color change, microhardness of bottom and top, and surface topography of bulk fill and incremental composites after artificial aging for 1 year.
Materials and Methods Bulk fill and incremental composites were cured using multi-peak and single-peak light-emitting diode (LED) following 4 clinical conditions: (1) optimal condition (no angulation or tip displacement), (2) tip-displacement (2 mm), (3) slight tip angulation (α = 20°) and (4) moderate tip angulation (α = 35°). After 1-year of water aging, the specimens were analyzed for color changes (ΔE), Vickers hardness, surface topography (Ra, Rt, and Rv), and scanning electron microscopy.
Results For samples cured by single-peak LED, the improper positioning significantly increases the color change compared to the optimal position regardless of the type of composite (
p < 0.001). For multi-peak LED, the type of resin composite and the curing condition displayed a significant effect on ΔE (p < 0.001). For both LEDs, the Vickers hardness and bottom/top ratio of Vickers hardness were affected by the type of composite and the curing condition (p < 0.01).Conclusions The bulk fill composite presented greater resistance to wear, higher color stability, and better microhardness than the incremental composite when subjected to improper curing. The multi-peak LED improves curing under improper conditions compared to single-peak LED. Prevention of errors when curing composites requires the attention of all personnel involved in the patient's care once the clinical relevance of the appropriate polymerization reflects on reliable long-term outcomes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A clinical survey of the output intensity of 50 light-curing units in dental clinics across Davangere and Mangalore region using a spectrometer system
Elizbeth Christy Jose, Sakshi Jha, Prema Shantagouda Biradar, J Arun, TN Nandini, Thushara Mohanan
International Journal of Oral Health Sciences.2025; 15(1): 41. CrossRef - The demineralization resistance and mechanical assessments of different bioactive restorative materials for primary and permanent teeth: an in vitro study
Maria Salem Ibrahim, Fahad Rakad Aldhafeeri, Abdullah Sami Banaemah, Mana S. Alhaider, Yousif A. Al-Dulaijan, Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad
BDJ Open.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Inorganic Compounds as Remineralizing Fillers in Dental Restorative Materials: Narrative Review
Leena Ibraheem Bin-Jardan, Dalal Ibrahim Almadani, Leen Saleh Almutairi, Hadi A. Almoabid, Mohammed A. Alessa, Khalid S. Almulhim, Rasha N. AlSheikh, Yousif A. Al-Dulaijan, Maria S. Ibrahim, Afnan O. Al-Zain, Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(9): 8295. CrossRef
- A clinical survey of the output intensity of 50 light-curing units in dental clinics across Davangere and Mangalore region using a spectrometer system
- 1,741 View
- 18 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Effect of the restorative technique on load-bearing capacity, cusp deflection, and stress distribution of endodontically-treated premolars with MOD restoration
- Daniel Maranha da Rocha, João Paulo Mendes Tribst, Pietro Ausiello, Amanda Maria de Oliveira Dal Piva, Milena Cerqueira da Rocha, Rebeca Di Nicoló, Alexandre Luiz Souto Borges
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(3):e33. Published online August 7, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e33
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
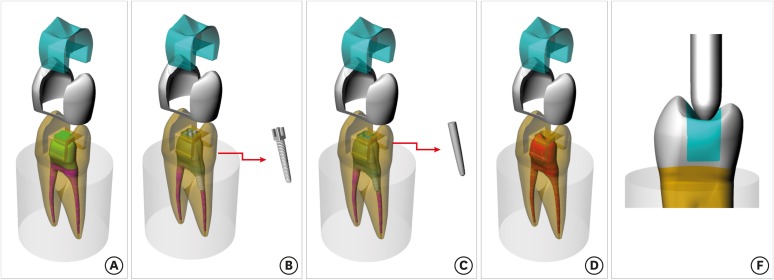
ePub Objectives To evaluate the influence of the restorative technique on the mechanical response of endodontically-treated upper premolars with mesio-occluso-distal (MOD) cavity.
Materials and Methods Forty-eight premolars received MOD preparation (4 groups,
n = 12) with different restorative techniques: glass ionomer cement + composite resin (the GIC group), a metallic post + composite resin (the MP group), a fiberglass post + composite resin (the FGP group), or no endodontic treatment + restoration with composite resin (the CR group). Cusp strain and load-bearing capacity were evaluated. One-way analysis of variance and the Tukey test were used with α = 5%. Finite element analysis (FEA) was used to calculate displacement and tensile stress for the teeth and restorations.Results MP showed the highest cusp (
p = 0.027) deflection (24.28 ± 5.09 µm/µm), followed by FGP (20.61 ± 5.05 µm/µm), CR (17.72 ± 6.32 µm/µm), and GIC (17.62 ± 7.00 µm/µm). For load-bearing, CR (38.89 ± 3.24 N) showed the highest, followed by GIC (37.51 ± 6.69 N), FGP (29.80 ± 10.03 N), and MP (18.41 ± 4.15 N) (p = 0.001) value. FEA showed similar behavior in the restorations in all groups, while MP showed the highest stress concentration in the tooth and post.Conclusions There is no mechanical advantage in using intraradicular posts for endodontically-treated premolars requiring MOD restoration. Filling the pulp chamber with GIC and restoring the tooth with only CR showed the most promising results for cusp deflection, failure load, and stress distribution.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- How to adaptively balance ‘classic’ or ‘conservative’ approaches in tooth defect management: a 3D-finite element analysis study
Jiani Xu, Xu Liang, Lili Hu, Chen Sun, Zhipeng Zhang, Jiawei Yang, Jie Wang
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Inkjet-printed strain gauge sensors: Materials, manufacturing, and emerging applications
Lara Abdel Salam, Samir Mustapha, Alexandra Mikhael, Nisrine Bakri, Sahera Saleh, Massoud L. Khraiche
Sensors and Actuators A: Physical.2025; 394: 116934. CrossRef - Influence of endodontic access cavity design on mechanical properties of a first mandibular premolar tooth: a finite element analysis study
Taha Özyürek, Gülşah Uslu, Burçin Arıcan, Mustafa Gündoğar, Mohammad Hossein Nekoofar, Paul Michael Howell Dummer
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of the Effect of Different Cavity Designs and Temporary Restoration Materials on the Fracture Resistance of Upper Premolars, Undergone Re-treatment: An In-Vitro Study
Parnian Alavinejad, Mohammad Yazdizadeh, Ali Mombeinipour, Ebrahim Karimzadeh
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, India Section B: Biological Sciences.2024; 94(3): 677. CrossRef - Fracture resistance and failure mode of endodontically treated premolars reconstructed by different preparation approaches: Cervical margin relocation and crown lengthening with complete and partial ferrule with three different post and core systems
Mehran Falahchai, Naghmeh Musapoor, Soroosh Mokhtari, Yasamin Babaee Hemmati, Hamid Neshandar Asli
Journal of Prosthodontics.2024; 33(8): 774. CrossRef - Comparison of the stress distribution in base materials and thicknesses in composite resin restorations
Min-Kwan Jung, Mi-Jeong Jeon, Jae-Hoon Kim, Sung-Ae Son, Jeong-Kil Park, Deog-Gyu Seo
Heliyon.2024; 10(3): e25040. CrossRef -
Fracture resistance and failure pattern of endodontically treated maxillary premolars restored with transfixed glass fiber post: an
in vitro
and finite element analysis
Saleem Abdulrab, Greta Geerts, Ganesh Thiagarajan
Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering.2024; 27(4): 419. CrossRef - Influence of size-anatomy of the maxillary central incisor on the biomechanical performance of post-and-core restoration with different ferrule heights
Domingo Santos Pantaleón, João Paulo Mendes Tribst, Franklin García-Godoy
The Journal of Advanced Prosthodontics.2024; 16(2): 77. CrossRef - Influence of internal angle and shape of the lining on residual stress of Class II molar restorations
Qianqian Zuo, Annan Li, Haidong Teng, Zhan Liu
Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering.2024; 27(5): 680. CrossRef - Evaluation of stress distribution in coronal base and restorative materials: A narrative review of finite element analysis studies
Yelda Polat, İzzet Yavuz
Conservative Dentistry Journal.2024; 14(2): 47. CrossRef - The influence of horizontal glass fiber posts on fracture strength and fracture pattern of endodontically treated teeth: A systematic review and meta‐analysis of in vitro studies
Saleem Abdulrab, Greta Geerts, Sadeq Ali Al‐Maweri, Mohammed Nasser Alhajj, Hatem Alhadainy, Raidan Ba‐Hattab
Journal of Prosthodontics.2023; 32(6): 469. CrossRef - Stress distribution of a novel bundle fiber post with curved roots and oval canals
Deniz Yanık, Nurullah Turker
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2022; 34(3): 550. CrossRef - The Effect of Endodontic Treatment and Thermocycling on Cuspal Deflection of Teeth Restored with Different Direct Resin Composites
Cansu Atalay, Ayse Ruya Yazici, Aynur Sidika Horuztepe, Emre Nagas
Conservative Dentistry and Endodontic Journal.2022; 6(2): 38. CrossRef - The use of different adhesive filling material and mass combinations to restore class II cavities under loading and shrinkage effects: a 3D-FEA
P. Ausiello, S. Ciaramella, A. De Benedictis, A. Lanzotti, J. P. M. Tribst, D. C. Watts
Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering.2021; 24(5): 485. CrossRef - Biomechanical Analysis of a Custom-Made Mouthguard Reinforced With Different Elastic Modulus Laminates During a Simulated Maxillofacial Trauma
João Paulo Mendes Tribst, Amanda Maria de Oliveira Dal Piva, Pietro Ausiello, Arianna De Benedictis, Marco Antonio Bottino, Alexandre Luiz Souto Borges
Craniomaxillofacial Trauma & Reconstruction.2021; 14(3): 254. CrossRef - Mechanical Assessment of Glass Ionomer Cements Incorporated with Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for Dental Applications
Manuela Spinola, Amanda Maria Oliveira Dal Piva, Patrícia Uchôas Barbosa, Carlos Rocha Gomes Torres, Eduardo Bresciani
Oral.2021; 1(3): 190. CrossRef - Stress Concentration of Endodontically Treated Molars Restored with Transfixed Glass Fiber Post: 3D-Finite Element Analysis
Alexandre Luiz Souto Borges, Manassés Tercio Vieira Grangeiro, Guilherme Schmitt de Andrade, Renata Marques de Melo, Kusai Baroudi, Laís Regiane Silva-Concilio, João Paulo Mendes Tribst
Materials.2021; 14(15): 4249. CrossRef - Computer Aided Design Modelling and Finite Element Analysis of Premolar Proximal Cavities Restored with Resin Composites
Amanda Guedes Nogueira Matuda, Marcos Paulo Motta Silveira, Guilherme Schmitt de Andrade, Amanda Maria de Oliveira Dal Piva, João Paulo Mendes Tribst, Alexandre Luiz Souto Borges, Luca Testarelli, Gabriella Mosca, Pietro Ausiello
Materials.2021; 14(9): 2366. CrossRef - Effect of Shrinking and No Shrinking Dentine and Enamel Replacing Materials in Posterior Restoration: A 3D-FEA Study
Pietro Ausiello, Amanda Maria de Oliveira Dal Piva, Alexandre Luiz Souto Borges, Antonio Lanzotti, Fausto Zamparini, Ettore Epifania, João Paulo Mendes Tribst
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(5): 2215. CrossRef - Effect of Fiber-Reinforced Composite and Elastic Post on the Fracture Resistance of Premolars with Root Canal Treatment—An In Vitro Pilot Study
Jesús Mena-Álvarez, Rubén Agustín-Panadero, Alvaro Zubizarreta-Macho
Applied Sciences.2020; 10(21): 7616. CrossRef
- How to adaptively balance ‘classic’ or ‘conservative’ approaches in tooth defect management: a 3D-finite element analysis study
- 2,279 View
- 26 Download
- 20 Crossref

- Management of dental erosion induced by gastro-esophageal reflux disorder with direct composite veneering aided by a flexible splint matrix
- Sherin Jose Chockattu, Byathnal Suryakant Deepak, Anubhav Sood, Nandini T. Niranjan, Arun Jayasheel, Mallikarjun K. Goud
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(1):e13. Published online February 6, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e13
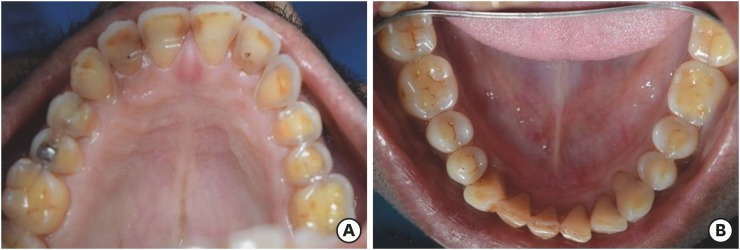
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Dental erosion is frequently overlooked in clinical practice. The management of erosion-induced damage to the dentition is often delayed, such that extensive occlusal rehabilitation is required. These cases can be diagnosed by a careful clinical examination and a thorough review of the patient's medical history and/or lifestyle habits. This case report presents the diagnosis, categorization, and management of a case of gastro-esophageal reflux disease-induced palatal erosion of the maxillary teeth. The early management of such cases is of utmost importance to delay or prevent the progression of damage both to the dentition and to occlusal stability. Non-invasive adhesively bonded restorations aid in achieving this goal.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Acidic Media on Surface Topography and Color Stability of Two Different Glass Ceramics
Fatma Makkeyah, Nesrine A. Elsahn, Mahmoud M. Bakr, Mahmoud Al Ankily
European Journal of Dentistry.2025; 19(01): 173. CrossRef - Mechanical Performance and Surface Roughness of Lithium Disilicate and Zirconia-Reinforced Lithium Silicate Ceramics Before and After Exposure to Acidic Challenge
Ahmed Elsherbini, Salma M. Fathy, Walid Al-Zordk, Mutlu Özcan, Amal A. Sakrana
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(3): 117. CrossRef - Biomechanical reinforcement by CAD-CAM materials affects stress distributions of posterior composite bridges: 3D finite element analysis.
Alaaeldin Elraggal, Islam M. Abdelraheem, David C. Watts, Sandipan Roy, Vamsi Krishna Dommeti, Abdulrahman Alshabib, Khaled Abid Althaqafi, Rania R. Afifi
Dental Materials.2024; 40(5): 869. CrossRef - Surface Properties and Wear Resistance of Injectable and Computer-Aided Design/Computer Aided Manufacturing–Milled Resin Composite Thin Occlusal Veneers
Nesrine A. Elsahn, Hatem M. El-Damanhoury, Zainab Shirazi, Abdul Rahman M. Saleh
European Journal of Dentistry.2023; 17(03): 663. CrossRef - Effect of acidic media on flexural strength and fatigue of CAD-CAM dental materials
Alaaeldin Elraggal, Rania. R Afifi, Rasha A. Alamoush, Islam Abdel Raheem, David C. Watts
Dental Materials.2023; 39(1): 57. CrossRef - Three-year Follow-up of Conservative Direct Composite Veneers on Eroded Teeth
RQ Ramos, NF Coelho, GC Lopes
Operative Dentistry.2022; 47(2): 131. CrossRef - The effects of intrinsic and extrinsic acids on nanofilled and bulk fill resin composites: Roughness, surface hardness, and scanning electron microscopy analysis
Milena F. Alencar, Mirella T. Pereira, Maria D. R. De‐Moraes, Sérgio L. Santiago, Vanara F. Passos
Microscopy Research and Technique.2020; 83(2): 202. CrossRef
- Effect of Acidic Media on Surface Topography and Color Stability of Two Different Glass Ceramics
- 2,328 View
- 21 Download
- 7 Crossref

- A survey on the use of composite resin in Class II restoration in Korea
- Dong-Ho Shin, Se-Eun Park, In-Seok Yang, Juhea Chang, In-Bog Lee, Byeong-Hoon Cho, Ho-Hyun Son
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(2):87-94. Published online March 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.2.087
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to assess the current materials, methods and difficulties according to the year of licence and educational background of Korean dentists in Class II direct composite resin restorations.
Total 17 questions were included in the questionnaire. Questions were broadly divided into two parts; first, operator's information, and second, the materials and methods used in Class II posterior composite restoration. The questionnaire was sent to dentists enrolled in Korean Dental Association via e-mail. Total 12,193 e-mails were distributed to dentists, 2,612 e-mails were opened, and 840 mails (32.2%) were received from respondents. The data was statically analyzed by chi-square test using SPSS(v. 12.0.1, SPSS Inc, Chicago, IL, USA).
Male dentists among respondents was 79%. 60.3% of the respondents acquired their licences recently (1998-2007), and 77% practiced in private offices. 83.4% have acquired their knowledge through school lectures, conferences and seminars.
For the Class II restorations, gold inlays were preferred by 65.7% of respondents, while direct composite resin restorations were used by 12.1% amalgam users were only 4.4% of respondents.
For the restorative technique, 74.4% of respondents didn't use rubber dam as needed. For the matrix, mylar strip (53.4%), metal matrix (33.8%) and Palodent system (6.5%) were used. 99.6% of respondents restored the Class II cavity by incremental layering.
Obtaining of the tight interproximal contact was considered as the most difficult procedure (57.2%) followed by field isolation (21%).
Among various bonding systems, 22.6% of respondents preferred SE Bond and 20.2% used Single Bond. Z-250 was used most frequently among a variety of composite resins.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A review of dental antibacterial agents and antibacterial modification of composite resins and dentin adhesives
Hojin Moon
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2024; 51(4): 189. CrossRef - Comparison of operative techniques between female and male dentists in class 2 and class 5 resin composite restorations
Juhea Chang, Hae-Young Kim, Ho-Hyun Son
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(2): 116. CrossRef
- A review of dental antibacterial agents and antibacterial modification of composite resins and dentin adhesives
- 1,421 View
- 5 Download
- 2 Crossref

- ANALYSIS OF PAPERS PUBLISHED IN THE JOURNAL OF KOREAN ACADEMY OF CONSERVATIVE DENTISTRY DURING THE LAST TEN YEARS
- Ki-Ok Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2002;27(6):622-631. Published online January 14, 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2002.27.6.622
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub ABSTRACT To understand the recent characteristics of the papers published in the Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry(JKACD), All the papers in the JKACD of 1992 to 2001 were analyzed. A total of 513 papers were classified according to its type, field and subject of the study, school and the number of authors, references, and written language.
The results were as follows;
According to the type of the paper, 506(98.6%) were original articles, 3(0.6%) were review articles, and 4(0.8%) were case reports.
Anual proportion of papers in the field of operative dentistry was similar to that of endodontics.
In the field of operative dentistry, esthetic restorative materials and bonding to tooth constituted major subjects of the studies. In the field of endodotics, pulp biology was prominent and canal shaping, endodontic microbiology and canal obturation were steadily reported.
According to author's school, similar number of papers were published in the field of operative dentistry and endodontics in general. However, some schools showed preponderances.
Most studies were done by two or more authors. Studies published by two authors were most.
Fifty(9.7%) papers were done in collaboration with workers of the other field.
Average number of references cited in the papers was 41.2, including domestic references of 1.8. 40.7% of the papers was shown to cite no domestic papers at all.
Twenty-eight(5.5%) papers were written in English, with increasing ratio.
- 730 View
- 1 Download


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


