Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Enhancing antimicrobial properties of a resin-based material via incorporation of a powdered phytotherapeutic extract: an in vitro experimental study
- Rodolfo Xavier de Sousa-Lima, Maria Eduarda Lima do Nascimento Marinho, Janielly Cristina Costa da Silva, Moan Jéfter Fernandes Costa, Pedro Henrique Sette-de-Souza, Giana da Silveira Lima, Boniek Castillo Dutra Borges
- Received March 25, 2025 Accepted September 11, 2025 Published online January 20, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2026.51.e2 [Epub ahead of print]
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study aimed to evaluate the degree of conversion (DC), immediate enamel bond strength (IEBS), antimicrobial activity, and release of the active principle of a resin-based material (RBM) enriched with the powdered Schinopsis brasiliensis (Braúna) stem antibacterial extract.
Methods
The RBM was enriched with 0, 1.25, 2.5, 5, 10, and 20 wt% powdered Braúna extract. The DC (n = 7) was assessed using micro-Raman spectroscopy. The IEBS (n = 7) was determined through the microshear test until failure, and failure modes were examined under a stereomicroscope. The antimicrobial activity (n = 15) was assessed by quantifying colony-forming units, and the release of the active principle was determined using ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography. One-way analysis of variance/Tukey and Kruskal-Wallis/Dunn tests were utilized to analyze the data (p < 0.05).
Results
Materials with 10 wt% and 20 wt% extract showed the lowest DC statistically. However, for IEBS, there were no statistically significant differences among the different groups. All materials released the active principle, but only those with 20 wt% and 10 wt% extract could inhibit biofilm formation similarly to 0.12% chlorhexidine.
Conclusions
Adding powdered Braúna extract between 10 wt% and 20 wt% is a promising alternative to provide an antimicrobial function to RBMs.
- 81 View
- 4 Download

- Prevalence of salivary microbial load and lactic acid presence in diabetic and non-diabetic individuals with different dental caries stages
- Monika Mohanty, Shashirekha Govind, Shakti Rath
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(1):e4. Published online January 12, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e4
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
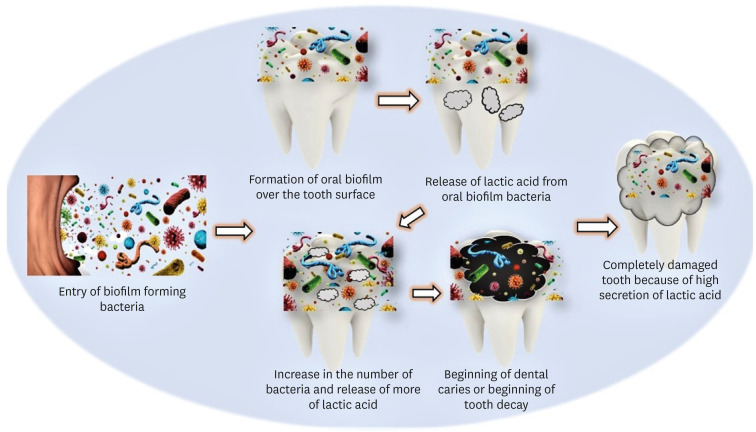
ePub Objectives This study aims to correlate caries-causing microorganism load, lactic acid estimation, and blood groups to high caries risk in diabetic and non-diabetic individuals and low caries risk in healthy individuals.
Materials and Methods This study includes 30 participants divided into 3 groups: Group A, High-risk caries diabetic individuals; Group B, High-risk caries non-diabetic individuals; and Group C, Low-risk caries individuals. The medical condition, oral hygiene, and caries risk assessment (American Dental Association classification and International Caries Detection and Assessment System scoring) were documented. Each individual’s 3 mL of saliva was analyzed for microbial load and lactic acid as follows: Part I: 2 mL for microbial quantity estimation using nutrient agar and blood agar medium, biochemical investigation, and carbohydrate fermentation tests; Part II: 0.5 mL for lactic acid estimation using spectrophotometric analysis. Among the selected individuals, blood group correlation was assessed. The χ2 test, Kruskal-Wallis test, and
post hoc analysis were done using Dunn’s test (p < 0.05).Results Group A had the highest microbial load and lactic acid concentration, followed by Groups B and C. The predominant bacteria were
Lactobacilli (63.00 ± 15.49) andStreptococcus mutans (76.00 ± 13.90) in saliva. Blood Group B is prevalent in diabetic and non-diabetic high-risk caries patients but statistically insignificant.Conclusions Diabetic individuals are more susceptible to dental caries due to high microbial loads and increased lactic acid production. These factors also lower the executing tendency of neutrophils, which accelerates microbial accumulation and increases the risk of caries in diabetic individuals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Oral Health Disparities in Type 2 Diabetes: Examining the Elevated Risk for Dental Caries—A Comparative Study
José Frias-Bulhosa, Maria Conceição Manso, Carla Lopes Mota, Paulo Melo
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(6): 258. CrossRef - Exploring the photosensitizing potential of Nanoliposome Loaded Improved Toluidine Blue O (NLITBO) Against Streptococcus mutans: An in-vitro feasibility study
Swagatika Panda, Lipsa Rout, Neeta Mohanty, Anurag Satpathy, Bhabani Sankar Satapathy, Shakti Rath, Divya Gopinath, Geelsu Hwang
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(10): e0312521. CrossRef - Altered salivary microbiota associated with high-sugar beverage consumption
Xiaozhou Fan, Kelsey R. Monson, Brandilyn A. Peters, Jennifer M. Whittington, Caroline Y. Um, Paul E. Oberstein, Marjorie L. McCullough, Neal D. Freedman, Wen-Yi Huang, Jiyoung Ahn, Richard B. Hayes
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Oral Health Disparities in Type 2 Diabetes: Examining the Elevated Risk for Dental Caries—A Comparative Study
- 2,880 View
- 77 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Can silver diamine fluoride or silver nanoparticle-based anticaries agents to affect enamel bond strength?
- Jaqueline Costa Favaro, Yana Cosendey Toledo de Mello Peixoto, Omar Geha, Flaviana Alves Dias, Ricardo Danil Guiraldo, Murilo Baena Lopes, Sandrine Bittencourt Berger
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(1):e7. Published online January 12, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e7
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
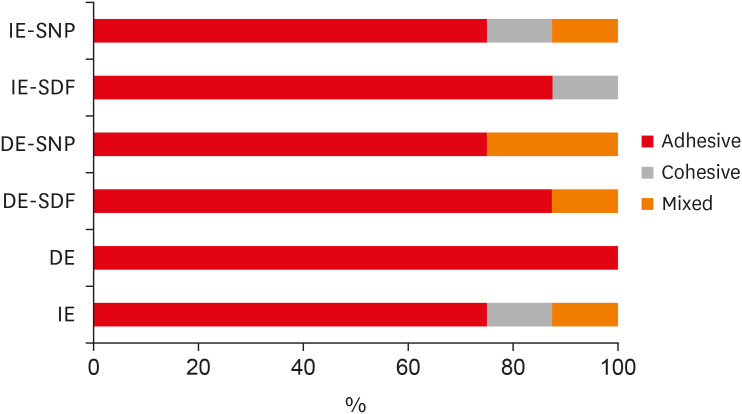
ePub Objectives The aim of the current study is to investigate the effect of different anticaries agents, such as experimental agents based on silver nanoparticles (SNPs) and silver diamine fluoride (SDF), on the micro-shear bond strength (μ-SBS) of composite resin applied to intact enamel (IE) or demineralized enamel (DE).
Materials and Methods Sixty dental enamel fragments were collected from human third molars and categorized into 6 groups (
n = 10): positive control (IE), negative control (DE), IE + SDF, DE + SDF, IE + SNP and DE + SNP. Samples from DE, DE + SDF and DE + SNP groups were subjected to pH cycling; superficial microhardness test was performed to confirm demineralization. Resin composite build-ups were applied to the samples (0.75-mm diameter and 1-mm height) after the treatments (except for IE and DE groups); μ-SBS was also evaluated. Samples were analyzed under a stereomicroscope at 40× magnification to identify failure patterns. Data were subjected to one-way analysis of variance, followed by Tukey's and Dunnett's tests (p < 0.05).Results There was no significant difference among the IE, IE + SNP, DE + SDF, and DE + SNP groups. The IE + SDF and DE groups recorded the highest and the lowest μ-SBS values, respectively. Adhesive-type failures were the most frequent for all treatments.
Conclusions Anticaries agents did not have a negative effect on the μ-SBS of composite resin when it was used on IE or DE.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of Incorporating Nanoparticles to Adhesive Resin on the Demineralization of Enamel: A Systematic Review
Naif Almosa
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(3): 89. CrossRef - Preventing white spot lesions around orthodontic brackets: efficacy of pre-reacted glass-ionomer barrier coat versus silver diamine fluoride: an in vitro study
Enas A. Elshenawy, Safa B. Alawy, Wafaa Yahia Alghonemy, Ahmed Ibrahime El dosoky
BDJ Open.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Research Status of Silver Nanoparticles for Dental Applications
Yanyan Guo, Xiaomei Hou, Sanjun Fan, Chanyuan Jin
Inorganics.2025; 13(5): 168. CrossRef - The use of silver diamine fluoride to prevent/treat enamel carious lesions: a narrative review
Rasha N. AlSheikh
PeerJ.2024; 12: e17897. CrossRef - Phosphoric Acid Etch Partially Restores the Initial Bond Strength of Composite to Silver Diamine Fluoride–Treated Enamel Using Universal Adhesives
Zaher Jabbour, Mijoo Kim, Marc Hayashi, Reuben Kim
Dentistry Journal.2023; 11(7): 161. CrossRef - Efficacy of Nano Silver Fluoride and/or Diode Laser In Enhancing Enamel Anticariogenicity around orthodontic brackets
Aya Anwar Alsherif, Mohamed Ali Farag, Mai Badreldin Helal
BDJ Open.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Amelioration Strategies for Silver Diamine Fluoride: Moving from Black to White
Amjad Almuqrin, Inder Preet Kaur, Laurence J. Walsh, Chaminda Jayampath Seneviratne, Sobia Zafar
Antibiotics.2023; 12(2): 298. CrossRef - The Effect of Loading Time on Color Stability of Various Restorative Materials Bonded to Silver Diamine Fluoride-Treated Demineralized Dentin
Mohammed M Aldosari, Fares S Al-Sehaibany
Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dentistry.2022; Volume 14: 123. CrossRef - In vitro study of the effect of nanosilver fluoride on shear bond strength of orthodontic brackets and demineralization of enamel
Mariam H. El-Toukhy, Eman M. El-Shourbagy, Neveen M. Fakhry
Tanta Dental Journal.2022; 19(4): 281. CrossRef
- Impact of Incorporating Nanoparticles to Adhesive Resin on the Demineralization of Enamel: A Systematic Review
- 1,692 View
- 22 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref

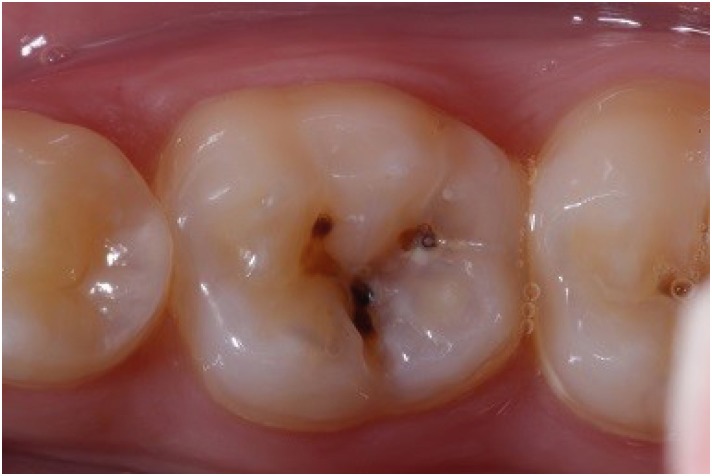
- Functional and aesthetic rehabilitation in posterior tooth with bulk-fill resin composite and occlusal matrix
- Luciana Fávaro Francisconi-dos-Rios, Johnny Alexandre Oliveira Tavares, Luanderson Oliveira, Jefferson Chaves Moreira, Flavia Pardo Salata Nahsan
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(1):e9. Published online January 3, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e9
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The restorative procedure in posterior teeth involves clinical steps related to professional skill, especially when using the incremental technique, which may fail in the long term. A recent alternative is bulk-fill resins, which can reduce polymerization shrinkage, decreasing clinical problems such as marginal leakage, secondary caries, and fracture. This scientific study aims to report a clinical case using bulk-fill resin with an occlusal matrix. As determined in the treatment plan, an acrylic resin matrix was produced to establish an improved oral and aesthetic rehabilitation of the right mandibular first molar, which presented a carious lesion with dentin involvement. The occlusal matrix is a simple technique that maintains the original dental anatomy, showing satisfactory results regarding function and aesthetic rehabilitation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mastery of Aesthetic and Functional Restoration of Maxillary Molars Using the Technique of Direct Restoration (Clinical Case)
Yu. Kolenko
SUCHASNA STOMATOLOHIYA.2025; (2): 67. CrossRef - Color stability of bulk‐fill compared to conventional resin‐based composites: A scoping review
Gaetano Paolone, Mauro Mandurino, Nicola Scotti, Giuseppe Cantatore, Markus B. Blatz
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2023; 35(4): 657. CrossRef - Evaluation of Abfraction Lesions Restored with Three Dental Materials: A Comparative Study
Bogdan Constantin Costăchel, Anamaria Bechir, Alexandru Burcea, Laurența Lelia Mihai, Tudor Ionescu, Olivia Andreea Marcu, Edwin Sever Bechir
Clinics and Practice.2023; 13(5): 1043. CrossRef - Aesthetic restoration of posterior teeth using different occlusal matrix techniques
Elsa Reis Carneiro, Anabela Paula, José Saraiva, Ana Coelho, Inês Amaro, Carlos Miguel Marto, Manuel Marques Ferreira, Eunice Carrilho
British Dental Journal.2021; 231(2): 88. CrossRef
- Mastery of Aesthetic and Functional Restoration of Maxillary Molars Using the Technique of Direct Restoration (Clinical Case)
- 1,432 View
- 20 Download
- 4 Crossref

- The effect of different fluoride application methods on the remineralization of initial carious lesions
- Seon Mi Byeon, Min Ho Lee, Tae Sung Bae
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(2):121-129. Published online May 10, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.2.121
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to assess the effect of single and combined applications of fluoride on the amount of fluoride release, and the remineralization and physical properties of enamel.
Materials and Methods Each of four fluoride varnish and gel products (Fluor Protector, FP, Ivoclar Vivadent; Tooth Mousse Plus, TM, GC; 60 Second Gel, A, Germiphene; CavityShield, CS, 3M ESPE) and two fluoride solutions (2% sodium fluoride, N; 8% tin(ii) fluoride, S) were applied on bovine teeth using single and combined methods (10 per group), and then the amount of fluoride release was measured for 4 wk. The electron probe microanalysis and the Vickers microhardness measurements were conducted to assess the effect of fluoride application on the surface properties of bovine teeth.
Results The amount of fluoride release was higher in combined applications than in single application (
p < 0.05). Microhardness values were higher after combined applications of N with FP, TM, and CS than single application of them, and these values were also higher after combined applications of S than single application of A (p < 0.05). Ca and P values were higher in combined applications of N with TM and CS than single application of them (p < 0.05). They were also increased after combined applications of the S with A than after single application (p < 0.05).Conclusions Combined applications of fluoride could be used as a basis to design more effective methods of fluoride application to provide enhanced remineralization.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Different Topical Fluorides on the Microhardness of Bleached Enamel: In Vitro Study
Soumyashri Das, Mansi Jain, HP Suma Sogi, Sonali Sukesh K, Apurva Gambhir, FNU Gagandeep
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2025; 18(11): 1365. CrossRef - Therapeutic effect of ozone gel on the initial carious lesions
Maha A. Alsharqawy, Wedad M Etman, Mirvat M Salama, Reda G. Saleh
Tanta Dental Journal.2023; 20(3): 203. CrossRef - Evaluation of Remineralization Potential of Natural Substances on Artificially Induced Carious Lesions in Primary Teeth: An In Vitro Study
Kavitha Ramar, Pooja V Ravi, Rajakumar Sekar
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2023; 16(2): 244. CrossRef - Upaya Preventif Kesehatan Gigi dan Mulut dengan Aplikasi Fluor pada Gigi Siswa SMPN 77 Jakarta
Agus Ardinansyah, Mochammad Atmaji Windrianto, Nur Hidayati Nosi Prastiyani
Info Abdi Cendekia.2023; 6(2): 74. CrossRef - Evaluation of the antibacterial activity of Enamelast® and Fluor defender® fluoride varnishes against Streptococcus mutans biofilm: an in vitro study in primary teeth
M. A. Matar, S. S. Darwish, R. S. Salma, W. A. Lotfy
European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry.2023; 24(5): 549. CrossRef - In-vitro evaluation of the anti-cariogenic effect of a hybrid coating associated with encapsulated sodium fluoride and stannous chloride in nanoclays on enamel
Sávio José Cardoso BEZERRA, Ítallo Emídio Lira VIANA, Idalina Vieira AOKI, Simone DUARTE, Anderson Takeo HARA, Taís SCARAMUCCI
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Salivary Fluoride Concentration after Topical Application of Silver Diamine Fluoride and Sodium Fluoride: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Nidhi Agarwal, V Vishnu Priya, Zohra Jabin, Iffat Nasim
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2022; 15(3): 371. CrossRef - Release and Recharge of Fluoride Ions from Acrylic Resin Modified with Bioactive Glass
Zbigniew Raszewski, Danuta Nowakowska, Wlodzimierz Wieckiewicz, Agnieszka Nowakowska-Toporowska
Polymers.2021; 13(7): 1054. CrossRef - Enamel remineralisation-inducing materials for caries prevention
Sri Kunarti, Widya Saraswati, Dur Muhammad Lashari, Nadhifa Salma, Tasya Nafatila
Dental Journal.2021; 54(3): 165. CrossRef - Fluoride Concentration in Saliva following Professional Topical Application of 2% Sodium Fluoride Solution
Manjit Talwar, Amrit Tewari, H. S. Chawla, Vinod Sachdev, Suresh Sharma
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2019; 10(3): 423. CrossRef - Clinical and laboratory evaluation of the Elgydium Protection caries toothpaste effectiveness in patients with high intensity of dental caries
O. A. Zorina, N. B. Petruhina, A. Z. M, O. A. Boriskina, A. A. Tupicin, V. A. Prohodnaja
Stomatologiya.2019; 98(3): 21. CrossRef - Bleaching of simulated stained-remineralized caries lesions in vitro
Sarah S. Al-Angari, Frank Lippert, Jeffrey A. Platt, George J. Eckert, Carlos González-Cabezas, Yiming Li, Anderson T. Hara
Clinical Oral Investigations.2019; 23(4): 1785. CrossRef - Short-Time Antibacterial Effects of Dimethylaminododecyl Methacrylate on Oral Multispecies Biofilm In Vitro
Yujie Zhou, Suping Wang, Xuedong Zhou, Yiran Zou, Mingyun Li, Xian Peng, Biao Ren, Hockin H. K. Xu, Michael D. Weir, Lei Cheng, Yu Chen, Qi Han
BioMed Research International.2019; 2019: 1. CrossRef - Comparison of the Application of Different Fluoride Supplements on Enamel Demineralization Adjacent to Orthodontic Brackets: An In Vitro Study
Arman Mohammadi Shayan, Monireh Rassouli, Soodabeh Kimyai, Hadi Valizadeh, Mohammad Hossein Ahangar Atashi, Sahand Rikhtegaran
Iranian Journal of Orthodontics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of nicomethanol hydrofluoride on dental enamel and synthetic apatites: a role for anti-caries protection
N. Sharkov
European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry.2017; 18(6): 411. CrossRef - Intérêt prophylactique et thérapeutique des chewing-gums sans sucre en orthodontie. Une étude menée auprès de professionnels de santé et de patients
Pauline Ferney, François Clauss, Damien Offner, Delphine Wagner
L'Orthodontie Française.2017; 88(3): 275. CrossRef - Silver Diamine Fluoride Has Efficacy in Controlling Caries Progression in Primary Teeth: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Ana Cláudia Chibinski, Letícia Maíra Wambier, Juliana Feltrin, Alessandro Dourado Loguercio, Denise Stadler Wambier, Alessandra Reis
Caries Research.2017; 51(5): 527. CrossRef - Dental Caries Management of a Patient with a High Caries Risk Based on the Caries Risk Assessment: a Case Peport
Dong-Hyun Lee, Sung-Ok Hong, Seok-Ryun Lee
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2016; 43(3): 231. CrossRef
- Effect of Different Topical Fluorides on the Microhardness of Bleached Enamel: In Vitro Study
- 1,994 View
- 13 Download
- 18 Crossref

- Early caries detection using optical coherence tomography: a review of the literature
- Young-Seok Park, Byeong-Hoon Cho, Seung-Pyo Lee, Won-Jun Shon
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(5):367-376. Published online September 14, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.5.367
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Abstract Early detection of carious lesions increases the possibility of treatment without the need for surgical intervention. Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is an emerging three-dimensional imaging technique that has been successfully used in other medical fields, such as ophthalmology for optical biopsy, and is a prospective candidate for early caries detection. The technique is based on low coherence interferometry and is advantageous in that it is non-invasive, does not use ionizing radiation, and can render three-dimensional images. A brief history of the development of this technique and its principles are discussed in this paper. There have been numerous studies on caries detection, which were mostly
in vitro orex vivo experiments. Through these studies, the feasibility of OCT for caries detection was confirmed. However, further research should be performed, includingin vivo studies of OCT applications, in order to prove the clinical usefulness of this technique. In addition, some technological problems must be resolved in the near future to allow for the use of OCT in everyday practice.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Differential diagnosis of periapical cyst using collagen birefringence pattern of the cyst wall
Hyo Jin Ji, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho, Suk Keun Lee, Jin Woo Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2017; 42(2): 111. CrossRef - How to designin situstudies: an evaluation of experimental protocols
Young-Hye Sung, Hae-Young Kim, Ho-Hyun Son, Juhea Chang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(3): 164. CrossRef
- Differential diagnosis of periapical cyst using collagen birefringence pattern of the cyst wall
- 2,186 View
- 14 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Theory of X-ray microcomputed tomography in dental research: application for the caries research
- Young-Seok Park, Kwang-Hak Bae, Juhea Chang, Won-Jun Shon
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(2):98-107. Published online March 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.2.98
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Caries remains prevalent throughout modern society and is the main disease in the field of dentistry. Although studies of this disease have used diverse methodology, recently, X-ray microtomography has gained popularity as a non-destructive, 3-dimensional (3D) analytical technique, and has several advantages over the conventional methods. According to X-ray source, it is classified as monochromatic or polychromatic with the latter being more widely used due to the high cost of the monochromatic source despite some advantages. The determination of mineral density profiles based on changes in X-ray attenuation is the principle of this method and calibration and image processing procedures are needed for the better image and reproducible measurements. Using this tool, 3D reconstruction is also possible and it enables to visualize the internal structures of dental caries. With the advances in the computer technology, more diverse applications are being studied, such automated caries assessment algorithms.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Synchrotron X-ray Studies of the Structural and Functional Hierarchies in Mineralised Human Dental Enamel: A State-of-the-Art Review
Cyril Besnard, Ali Marie, Sisini Sasidharan, Robert A. Harper, Richard M. Shelton, Gabriel Landini, Alexander M. Korsunsky
Dentistry Journal.2023; 11(4): 98. CrossRef - Revelation of microcracks as tooth structural element by X-ray tomography and machine learning
Irma Dumbryte, Donatas Narbutis, Arturas Vailionis, Saulius Juodkazis, Mangirdas Malinauskas
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Three-dimensional non-destructive visualization of teeth enamel microcracks using X-ray micro-computed tomography
Irma Dumbryte, Arturas Vailionis, Edvinas Skliutas, Saulius Juodkazis, Mangirdas Malinauskas
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Radiological Appraisal of Biodentine and Pulpotec Individually or in Combination with Photo-activated Disinfection as Pulp-capping Cements in Mature Teeth
Pratik Agrawal, Gaurav Patri, Surabhi Soumya, Prasanti K Pradhan, Vijeta Patri
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2021; 22(9): 1014. CrossRef - Ex vivoevaluation of new 2D and 3D dental radiographic technology for detecting caries
Laurence Gaalaas, Donald Tyndall, André Mol, Eric T Everett, Ananta Bangdiwala
Dentomaxillofacial Radiology.2016; 45(3): 20150281. CrossRef - Stationary intraoral digital tomosynthesis using a carbon nanotube X-ray source array
J Shan, A W Tucker, L R Gaalaas, G Wu, E Platin, A Mol, J Lu, O Zhou
Dentomaxillofacial Radiology.2015; 44(9): 20150098. CrossRef - Comparative efficacy of photo-activated disinfection and calcium hydroxide for disinfection of remaining carious dentin in deep cavities: a clinical study
Sidhartha Sharma, Ajay Logani, Naseem Shah
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(3): 195. CrossRef - Current status of dental caries diagnosis using cone beam computed tomography
Young-Seok Park, Jin-Soo Ahn, Ho-Beom Kwon, Seung-Pyo Lee
Imaging Science in Dentistry.2011; 41(2): 43. CrossRef
- Synchrotron X-ray Studies of the Structural and Functional Hierarchies in Mineralised Human Dental Enamel: A State-of-the-Art Review
- 2,357 View
- 10 Download
- 8 Crossref

- The effect of lactic acid concentration and ph of lactic acid buffer solutions on enamel remineralization
- Jung-Won Kwon, Duk-Gyu Suh, Yun-Jung Song, Yun Lee, Chan-Young Lee
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(6):507-517. Published online November 30, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.6.507
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub There are considerable in vitro and in vivo evidences for remineralization and demineralization occurring simultaneously in incipient enamel caries. In order to "heal"the incipient dental caries, many experiments have been carried out to determine the optimal conditions for remineralization. It was shown that remineralization is affected by different pH, lactic acid concentrations, chemical composition of the enamel, fluoride concentrations, etc.
Eighty specimens from sound permanent teeth without demineralization or cracks, 0.15 mm in thickness, were immersed in lactic acid buffered demineralization solutions for 3 days. Dental caries with a surface zone and subsurface lesion were artificially produced. Groups of 10 specimens were immersed for 10 or 12 days in lactic acid buffered remineralization solutions consisting of pH 4.3 or pH 6.0, and 100, 50, 25, or 10 mM lactic acid. After demineralization and remineralization, images were taken by polarizing microscopy (x100) and micro-computed tomography. The results were obtained by observing images of the specimens and the density of the caries lesions was determined.
As the lactic acid concentration of the remineralization solutions with pH 4.3 was higher, the surface zone of the carious enamel increased and an isotropic zone of the subsurface lesion was found. However, the total decalcification depth increased at the same time.
In the remineralization solutions with pH 6.0, only the surface zone increased slightly but there was no significant change in the total decalcification depth and subsurface zone.
In the lactic acid buffer solutions with the lower pH and higher lactic acid concentration, there were dynamic changes at the deep area of the dental carious lesion.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of fluoride concentration in pH 4.3 and pH 7.0 supersaturated solutions on the crystal growth of hydroxyapatite
Haneol Shin, Sung-Ho Park, Jeong-Won Park, Chan-Young Lee
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(1): 16. CrossRef
- Effect of fluoride concentration in pH 4.3 and pH 7.0 supersaturated solutions on the crystal growth of hydroxyapatite
- 1,358 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


