Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Calcium silicate-based sealers remnants in isthmuses of mesial roots of mandibular molars: an in vitro evaluation
- David Saldanha de Brito Alencar, Ana Cristina Padilha Janini, Lauter Eston Pelepenko, Brenda Fornazaro Moraes, Francisco Haiter Neto, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Marina Angélica Marciano
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(3):e25. Published online July 15, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e25
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
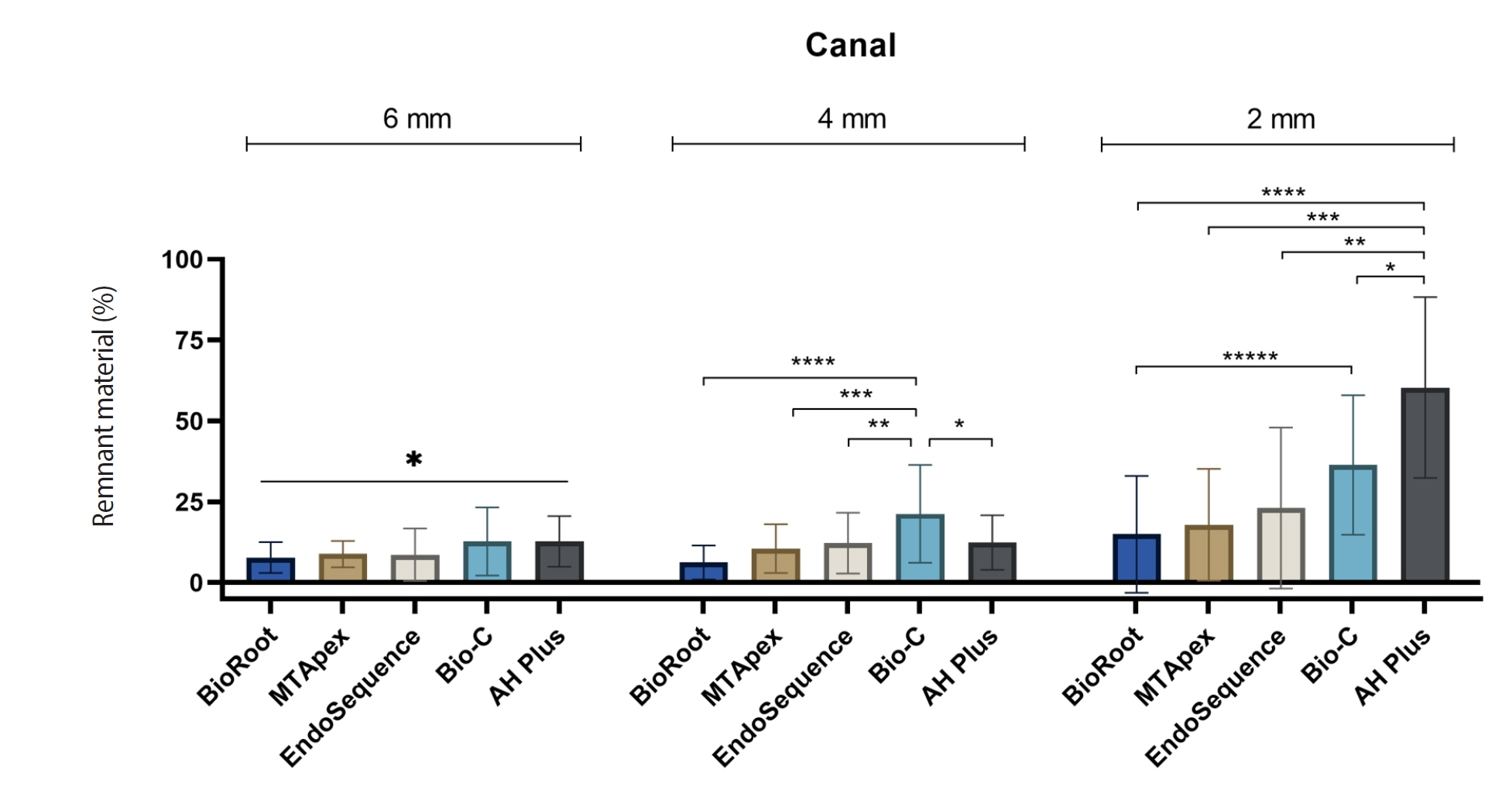
Endodontic retreatment aims to address treatment failure through the removal of root canal filling materials. This in vitro study evaluated the presence of filling material remnants in the mesial root canals, specifically focusing on the isthmuses, of mandibular molars after retreatment.
Methods
One hundred extracted mandibular molar mesial roots with isthmuses were prepared with an R25 file, obturated with one of five calcium silicate-based sealers (BioRoot RCS [Septodont], MTApex [Ultradent Products Inc.], EndoSequence BC Sealer HiFlow [Brasseler USA], Bio-C Sealer [Angelus]) or an epoxy resin-based sealer (AH Plus Jet [Dentsply Maillefer]), all stained with rhodamine B, and stored at 37ºC for 30 days to allow for setting. Retreatment was subsequently performed using R40 and XP-endo Finisher R instruments (FKG Dentaire) with 2.5% sodium hypochlorite irrigation. The presence of remaining filling material was then assessed using confocal microscopy, and setting times were tested per ISO 6876:2012.
Results
AH Plus Jet showed the most remnants at 2 mm and the longest retreatment time. Calcium silicate-based sealers exhibited prolonged setting times under dry conditions, with EndoSequence BC Sealer HiFlow showing a particularly extended setting period.
Conclusions
Despite retreatment, residues remained in all canals and isthmus regions, particularly Bio-C Sealer and AH Plus Jet in apical areas, emphasizing the difficulty of complete removal and the persistence of filling material. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bonding effects of mechanical removal of bioceramic sealer residues using glycine or glass microparticles abrasion
Jesus Aranda, Julia de Freitas Ceccato, Eduardo Fernández Godoy, João Felipe Besegato, Joissi Ferrari Zaniboni, Regina Guenka Palma-Dibb, Milton Carlos Kuga
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2026; 148: 104289. CrossRef
- Bonding effects of mechanical removal of bioceramic sealer residues using glycine or glass microparticles abrasion
- 2,038 View
- 113 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Influence of access cavity design on calcium hydroxide removal using different cleaning protocols: a confocal laser scanning microscopy study
- Seda Falakaloğlu, Merve Yeniçeri Özata, Betül Güneş, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Mustafa Gündoğar, Burcu Güçyetmez Topal
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(3):e25. Published online July 24, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e25
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to evaluate the influence of endodontic access cavities design on the removal of calcium hydroxide medication of the apical third of mandibular incisor root canal walls and dentinal tubules with different cleaning protocols: EDDY sonic activation, Er,Cr:YSGG laser-activated irrigation, or conventional irrigation with IrriFlex.
Materials and Methods Seventy-eight extracted human mandibular incisors were assigned to 6 experimental groups (
n = 13) according to the endodontic access cavity and cleaning protocol for calcium hydroxide removal: traditional access cavity (TradAC)/EDDY; ultraconservative access cavity performed in the incisal edge (UltraAC.Inc)/EDDY; TradAC/Er,Cr:YSGG; UltraAC.Inc/Er,Cr:YSGG; TradAC/IrriFlex; or UltraAC.Inc/IrriFlex. Confocal laser scanning microscopy images were used to measure the non-penetration percentage, maximum residual calcium hydroxide penetration depth, and penetration area at 2 and 4 mm from the apex. Data were statistically analyzed using Shapiro-Wilk and WRS2 package for 2-way comparison of non-normally distributed parameters (depth of penetration, area of penetration, and percentage of non-penetration) according to cavity and cleaning protocol with the significance level set at 5%.Results The effect of cavity and cleaning protocol interactions on penetration depth, penetration area and non-penetration percentage was not found statistically significant at 2 and 4 mm levels (
p > 0.05).Conclusions The present study demonstrated that TradAC or UltraAC.Inc preparations with different cleaning protocols in extracted mandibular incisors did not influence the remaining calcium hydroxide at 2 and 4 mm from the apex.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Apical Preparation Size and Preparation Taper on Smear Layer Removal Using Two Different Irrigation Needles: A Scanning Electron Microscopy Study
Rania Lebbos, Naji Kharouf, Deepak Mehta, Jamal Jabr, Cynthia Kamel, Roula El Hachem, Youssef Haikel, Marc Krikor Kaloustian
European Journal of Dentistry.2025; 19(03): 678. CrossRef - Combination of Chitosan Nanoparticles, EDTA, and Irrigation Activation Enhances TGF-β1 Release from Dentin: A Laboratory Study
Sıla Nur Usta, Emre Avcı, Ayşe Nur Oktay, Cangül Keskin
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(8): 1081. CrossRef
- Effect of Apical Preparation Size and Preparation Taper on Smear Layer Removal Using Two Different Irrigation Needles: A Scanning Electron Microscopy Study
- 3,057 View
- 73 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Bonding effects of cleaning protocols and time-point of acid etching on dentin impregnated with endodontic sealer
- Tatiane Miranda Manzoli, Joissi Ferrari Zaniboni, João Felipe Besegato, Flávia Angélica Guiotti, Andréa Abi Rached Dantas, Milton Carlos Kuga
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(2):e21. Published online April 6, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e21
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to investigate the bonding effects of cleaning protocols on dentin impregnated with endodontic sealer residues using ethanol (E) or xylol (X). The effects of dentin acid etching immediately (I) or 7 days (P) after cleaning were also evaluated. For bonding to dentin, universal adhesive (Scotchbond Universal; 3M ESPE) was used. The persistence of sealer residues, hybrid layer formation and microshear bond strength were the performed analysis.
Materials and Methods One hundred and twenty bovine dentin specimens were allocated into 4 groups (
n = 10): G1 (E+I); G2 (X+I); G3 (E+P); and G4 (X+P). The persistence of sealer residues was evaluated by SEM. Confocal laser scanning microscopy images were taken to measure the formed hybrid layer using the Image J program. For microshear bond strength, 4 resin composite cylinders were placed over the dentin after the cleaning protocols. ANOVA followed by Tukey test and Kruskal-Wallis followed by Dunn test were used for parametric and non-parametric data, respectively (α = 5%).Results G2 and G4 groups showed a lower persistence of residues (
p < 0.05) and thicker hybrid layer than the other groups (p < 0.05). No bond strength differences among all groups were observed (p > 0.05).Conclusions Dentin cleaning using xylol, regardless of the time-point of acid etching, provided lower persistence of residues over the surface and thicker hybrid layer. However, the bond strength of the universal adhesive system in etch-and-rinse strategy was not influenced by the cleaning protocols or time-point of acid etching.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficacy of Post-Endodontic Access Cavity Cleaning Techniques: A Randomized Clinical Study
Ayse Karadayi, Elif Irem Altintas, Ezgi Tüter Bayraktar, Bora Korkut
Journal of Endodontics.2026; 52(2): 166. CrossRef - Does cleaning of post space before cementation of fiber reinforced post affect the push-out bond strength to resin cement?
Maher S. Hajjaj, Khalid A. Alghamdi, Abdulrahman A. Alshehri, Hassan A. Almusallam, Nabeel M. Munshi, Osamah A. Alsulimani, Naseeba H. Khouja, Yousef A. Alnowailaty, Saeed J. Alzahrani
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of the Use of a Mixed Solution of Equal Amounts of Amyl Acetate, Acetone, and Ethanol on the Cleaning of Endodontic Sealer Residues on the Bond Strength of the Fiber Post Cementation System: A Laboratory Investigation
Antonia Patricia Oliveira Barros, Ana Paula Aparecida Raimundo Alves Freitas, Frederico Guilherme Otto Kokol, Elizangela Maria Pereira de Souza, Adirson Jorge Junior, Cristiane de Melo Alencar, Marcelo Ferrarezi de Andrade, Milton Carlos Kuga
The Open Dentistry Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of the application protocol and bonding strategy of the universal adhesive on dentin previously impregnated with bioceramic sealer
Antonia Patricia Oliveira Barros, Joatan Lucas de Sousa Gomes Costa, Jardel Camilo do Carmo Monteiro, Lucas David Galvani, Marcelo Ferrarezi de Andrade, José Roberto Cury Saad, Milton Carlos Kuga
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2024; 134: 103765. CrossRef - Influência do protocolo de remoção de resíduos de cimentos à base de resina epóxi sobre a interface de adesão com o adesivo universal, utilizado na estratégia condiciona-e-lava
Paulo Firmino Da Costa Neto, Mariana Bena Gelio, Elisângela Maria Pereira De Souza, Jardel Camilo do Carmo Monteiro, Adirson Jorge Júnior, Thais Piragine Leandrin, José Roberto Cury Saad, Milton Carlos Kuga
Cuadernos de Educación y Desarrollo.2023; 15(5): 4802. CrossRef
- Efficacy of Post-Endodontic Access Cavity Cleaning Techniques: A Randomized Clinical Study
- 2,327 View
- 40 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- The effect of using nanoparticles in bioactive glass on its antimicrobial properties
- Maram Farouk Obeid, Kareim Moustafa El-Batouty, Mohammed Aslam
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(4):e58. Published online October 29, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e58
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study addresses the effect of using nanoparticles (np) on the antimicrobial properties of bioactive glass (BAG) when used in intracanal medicaments against
Enterococcus faecalis (E. faecalis ) biofilms.Materials and Methods E. faecalis biofilms, grown inside 90 root canals for 21 days, were randomly divided into 4 groups according to the antimicrobial regimen followed (n = 20; BAG-np, BAG, calcium hydroxide [CaOH], and saline). After 1 week, residual live bacteria were quantified in terms of colony-forming units (CFU), while dead bacteria were assessed with a confocal laser scanning microscope.Results Although there was a statistically significant decrease in the mean CFU value among all groups, the nano-group performed the best. The highest percentage of dead bacteria was detected in the BAG-np group, with a significant difference from the BAG group.
Conclusions The reduction of particle size and use of a nano-form of BAG improved the antimicrobial properties of the intracanal treatment of
E. faecalis biofilms-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Size matters: Radiation shielding superiority of borate glasses with nano vs. micro ZnO
Aljawhara H. Almuqrin, M.I. Sayyed, M. Elsafi
Nuclear Engineering and Technology.2025; 57(9): 103614. CrossRef - Effect of Chitosan and bioactive glass nanomaterials as intracanal medicaments on TGF-β1 release from intraradicular dentin
Sarah Salah Hashem, Mohammed M. Khalefa, Mahmoud Hassan Mohamed, Hemat M. ELSheikh, Fatma Abd El-Rahman Taher
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Er: YAG laser, phthalocyanine activated photodynamic therapy, and bioactive glass nanoparticles on smear layer removal and push out bond strength of quartz fiber posts to canal dentin: a SEM assessment
Okba Mahmoud, Erum Zain
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Advancements in Root Canal Therapy: Translational Innovations and the Role of Nanoparticles in Endodontic Treatment
Noha M. Badawi, Mohamed M. Kataia, Hadeel A. Mousa, Mozhgan Afshari
Journal of Nanotechnology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Propolis in Endodontics—Unveiling Its Therapeutic Potential: A Narrative Review
Poorani Durai, Santha Devy A, Mithila Mohan, Harish Ramalingam, Shasidharan P, Rahul Chaurasia M
World Journal of Dentistry.2025; 16(10): 959. CrossRef - Application of Nanomaterials in Endodontics
Farzaneh Afkhami, Yuan Chen, Laurence J. Walsh, Ove A. Peters, Chun Xu
BME Frontiers.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Antimicrobial efficacy of newly prepared nano-tricalcium silicate-58s bioactive glass-based endodontic sealer
Nawal Atiya Al-Sabawi, Sawsan Hameed Al-Jubori
Endodontology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Antimicrobial Effects of Formulations of Various Nanoparticles and Calcium Hydroxide as Intra-canal Medications Against Enterococcus faecalis: A Systematic Review
Seema H Bukhari, Dax Abraham, Shakila Mahesh
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of nanoparticles on antibacterial efficacy of intracanal medicament: A scoping review
Alpa Gupta, Arundeep Singh, Vivek Aggarwal
Endodontology.2023; 35(4): 283. CrossRef - Physical properties, marginal adaptation and bioactivity of an experimental mineral trioxide aggregate-like cement modified with bioactive materials
Abigailt Flores-Ledesma, Adriana Tejeda-Cruz, María A. Moyaho-Bernal, Ana Wintergerst, Yoshamin A. Moreno-Vargas, Jacqueline A. Rodríguez-Chávez, Carlos E. Cuevas-Suárez, Kenya Gutiérrez-Estrada, Jesús A. Arenas-Alatorre
Journal of Oral Science.2023; 65(2): 141. CrossRef - Nanopartículas antimicrobianas en endodoncia: Revisión narrativa
Gustavo Adolfo Tovar Rangel , Fanny Mildred González Sáenz , Ingrid Ximena Zamora Córdoba , Lina María García Zapata
Revista Estomatología.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Size matters: Radiation shielding superiority of borate glasses with nano vs. micro ZnO
- 1,680 View
- 26 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref

- Improved dentin disinfection by combining different-geometry rotary nickel-titanium files in preparing root canals
- Marwa M. Bedier, Ahmed Abdel Rahman Hashem, Yosra M. Hassan
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(4):e46. Published online November 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e46

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study was to evaluate the antibacterial effect of different instrumentation and irrigation techniques using confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) after root canal inoculation with
Enterococcus faecalis (E. faecalis ).Materials and Methods Mesiobuccal and mesiolingual canals of extracted mandibular molars were apically enlarged up to a size 25 hand K-file, then autoclaved and inoculated with
E. faecalis . The samples were randomly divided into 4 main groups according to the system of instrumentation and irrigation: an XP-endo Shaper (XPS) combined with conventional irrigation (XPS/C) or an XP-endo Finisher (XPF) (XPS/XPF), and iRaCe combined with conventional irrigation (iRaCe/C) or combined with an XPF (iRaCe/XPF). A middle-third samplewas taken from each group, and then the bacterial reduction was evaluated using CLSM at a depth of 50 µm inside the dentinal tubules. The ratio of red fluorescence (dead cells) to green-and-red fluorescence (live and dead cells) represented the percentage of bacterial reduction. The data were then statistically analyzed using the Kruskal-Wallis test for comparisons across the groups and the Dunn test was used for pairwise comparisons.Results The instrumentation and irrigation techniques had a significant effect on bacterial reduction (
p < 0.05). The iRaCe/XPF group showed the strongest effect, followed by the XPS/XPF and XPS/C group, while the iRaCe/C group had the weakest effect.Conclusions Combining iRaCe with XPF improved its bacterial reduction effect, while combining XPS with XPF did not yield a significant improvement in its ability to reduce bacteria at a depth of 50 µm in the dentinal tubules.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Biofilm-forming activity of Enterococcus faecalis on basic materials of removable dental prosthetic bases
Oksana A. Shuliatnikova, Mikhail V. Yakovlev, Anatoliy P. Godovalov
HERALD of North-Western State Medical University named after I.I. Mechnikov.2025; 17(2): 89. CrossRef - A Short Report on the Effectiveness of Edge Taper Platinum and XP-3D Shaper for the Reduction of Enterococcus faecalis Count in the Root Canal System: An Ex Vivo Study
Hanie Moaveni, Parastou Ghahari, Samira Behrad, Majid Mirmohammadkhani, Sobhan Rashmee, Somayeh Teimoori
Avicenna Journal of Dental Research.2024; 16(2): 77. CrossRef - Shaping ability of non‐adaptive and adaptive core nickel–titanium single‐file systems with supplementary file in ribbon‐shaped canals analysed by micro‐computed tomography
Parichat Chinchiyanont, Kallaya Yanpiset, Danuchit Banomyong, Nathamon Thongbai‐On
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(1): 38. CrossRef - Impact XP-endo finisher on the 1-year follow-up success of posterior root canal treatments: a randomized clinical trial
Ludmila Smith de Jesus Oliveira, Fabricio Eneas Diniz de Figueiredo, Janaina Araújo Dantas, Maria Amália Gonzaga Ribeiro, Carlos Estrela, Manoel Damião Sousa-Neto, André Luis Faria-e-Silva
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(12): 7595. CrossRef - In vitro reduction in Enterococcus faecalis count following root canal preparation with Neolix and XP shaper rotary files
Mina Mehrjouei, Somayeh Teimoori, Majid Mirmohammadkhani, Seyed Majed Mortazavi, Maryam Khorasanchi
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2023; 13(3): 236. CrossRef - Antibacterial efficacy of sodium hypochlorite versus apple cider vinegar against Enterococcus faecalis in contracted endodontic cavity
Kaur Supreet, Karkala Venkappa Kishan, Nimisha Chinmay Shah
Endodontology.2022; 34(4): 254. CrossRef - Ex vivo evaluation of the effectiveness of XP-endo Finisher on the removal of smear layer from the root canal
Sângela Maria PEREIRA, Ceci Nunes CARVALHO, Rudys Rodolfo TAVAREZ, Paulo NELSON-FILHO, Léa Assed Bezerra DA SILVA, Etevaldo Matos MAIA FILHO
RGO - Revista Gaúcha de Odontologia.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Biofilm elimination from infected root canals using four different single files
Sarah A. Hamed, Sarah Shabayek, Hayam Y. Hassan
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The effectiveness of the supplementary use of the XP-endo Finisher on bacteria content reduction: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Ludmila Smith de Jesus Oliveira, Rafaella Mariana Fontes de Bragança, Rafael Sarkis-Onofre, André Luis Faria-e-Silva
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Combination of a new ultrasonic tip with rotary systems for the preparation of flattened root canals
Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Jáder Camilo Pinto, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Adaptive, Rotary, and Manual Root Canal Instrumentation in Primary Molars: A Triple-Armed, Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial
Bhaggyashri A. Pawar, Ajinkya M. Pawar, Anuj Bhardwaj, Dian Agustin Wahjuningrum, Amelia Kristanti Rahardjo, Alexander Maniangat Luke, Zvi Metzger, Anda Kfir
Biology.2021; 10(1): 42. CrossRef - Complete Obturation—Cold Lateral Condensation vs. Thermoplastic Techniques: A Systematic Review of Micro-CT Studies
Shilpa Bhandi, Mohammed Mashyakhy, Abdulaziz S. Abumelha, Mazen F. Alkahtany, Mohamed Jamal, Hitesh Chohan, A. Thirumal Raj, Luca Testarelli, Rodolfo Reda, Shankargouda Patil
Materials.2021; 14(14): 4013. CrossRef - The Effects of Different Endodontic Access Cavity Design and Using XP-endo Finisher on the Reduction of Enterococcus faecalis in the Root Canal System
Pelin Tüfenkçi, Koray Yılmaz
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(3): 419. CrossRef - Irrigation in Endodontics: a Review
Sarah Bukhari, Alaa Babaeer
Current Oral Health Reports.2019; 6(4): 367. CrossRef
- Biofilm-forming activity of Enterococcus faecalis on basic materials of removable dental prosthetic bases
- 1,652 View
- 14 Download
- 14 Crossref

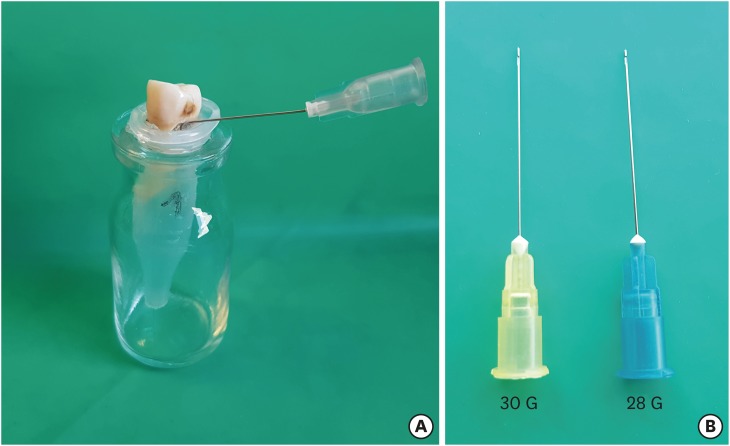
- Influence of size and insertion depth of irrigation needle on debris extrusion and sealer penetration
- Emel Uzunoglu-Özyürek, Hakan Karaaslan, Sevinç Aktemur Türker, Bahar Özçelik
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(1):e2. Published online December 22, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e2
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives To determine the effect of size and insertion depth of irrigation needle on the amount of apical extruded debris and the amount of penetration depth of sealer using a confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM).
Materials and Methods Twenty maxillary premolars were assigned to 2 groups (
n = 10), according to the size of needle tip, 28 G or 30 G. Buccal roots of samples were irrigated with respective needle type inserted 1 mm short of the working length (WL), while palatal roots were irrigated with respective needle type inserted 3 mm short of the WL. Prepared teeth were removed from the pre-weighed Eppendorf tubes. Canals were filled with F3 gutta-percha cone and rhodamine B dye-labeled AH 26 sealer. Teeth were transversally sectioned at 1 and 3 mm levels from the apex and observed under a CLSM. Eppendorf tubes were incubated to evaporate the irrigant and were weighed again. The difference between pre- and post-weights was calculated, and statistical evaluation was performed.Results Inserting needles closer to the apex and using needles with wider diameters were associated with significantly more debris extrusion (
p < 0.05). The position of needles and level of sections had statistically significant effects on sealer penetration depth (p < 0.05 for both).Conclusions Following preparation, inserting narrower needles compatible with the final apical diameter of the prepared root canal at 3 mm short of WL during final irrigation might prevent debris extrusion and improve sealer penetration in the apical third.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of laser-induced pulpal anesthesia of single-rooted teeth with irreversible pulpitis treated by single-visit root canal therapy - A randomized clinical trial
Geeta Asthana, Dhwani Morakhia, Ravina Parmar, Rajashree Tamuli
Endodontology.2025; 37(3): 244. CrossRef - Efficacy of different irrigation needles used in endodontics: an in silico and an in vitro investigation
Maulee Sheth, Ankit Arora, Sonali Kapoor, Balraj Shukla
Biomaterial Investigations in Dentistry.2025; 12: 264. CrossRef - Preliminary insights: exploring irrigation practices during endodontic treatment among general dental practitioners in Malaysia
Kai Qi Chiew, Xin Ni Lim, Shekhar Bhatia, Naveen Chhabra
British Dental Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficiency of diode laser in control of post-endodontic pain: a randomized controlled trial
Hend H. Ismail, Maram Obeid, Ehab Hassanien
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(6): 2797. CrossRef - Endodontic management of an aberrant germinated composite odontome: A case report
Ankit Arora, Kavina Desai, Sonali Kapoor, Seema Gajera
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(3): 684. CrossRef - Potentials of 3D-Modeling in the Preclinical Stage of Root Needle Research
Aleksandr V. Kuligin, Larisa N. Kazakova, Oksana S. Tereshchuk, Vadim V. Bokov
I.P. Pavlov Russian Medical Biological Herald.2022; 30(1): 95. CrossRef - Effect of root canal geometry and needle type on apical extrusion of irrigant: an ex vivo study
Büşra SERÇE FİKİRLİ, Bülent ALTUNKAYNAK, Güven KAYAOĞLU
Acta Odontologica Turcica.2022; 39(3): 58. CrossRef - An in vitro radiological evaluation of irrigant penetration in the root canals using three different irrigation systems: Waterpik WP-100 device, passive irrigation, and manual dynamic irrigation systems
Suragani Hemalatha, Archana Srinivasan, A Srirekha, Lekha Santhosh, C Champa, Ashwija Shetty
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2022; 25(4): 403. CrossRef - Preparation Ability of ProTaper Next and XP-endo Shaper Instruments in Isthmus-containing Root Canal System
Mustafa Sarıkahya, Tayfun Alaçam
Conservative Dentistry and Endodontic Journal.2021; 5(2): 28. CrossRef - Penetration depth of irrigants into root dentine after sonic, ultrasonic and photoacoustic activation
K. M. Galler, V. Grubmüller, R. Schlichting, M. Widbiller, A. Eidt, C. Schuller, M. Wölflick, K.‐A. Hiller, W. Buchalla
International Endodontic Journal.2019; 52(8): 1210. CrossRef
- Effect of laser-induced pulpal anesthesia of single-rooted teeth with irreversible pulpitis treated by single-visit root canal therapy - A randomized clinical trial
- 1,816 View
- 19 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Antifungal effects of synthetic human β-defensin 3-C15 peptide
- Sang-Min Lim, Ki-Bum Ahn, Christine Kim, Jong-Won Kum, Hiran Perinpanayagam, Yu Gu, Yeon-Jee Yoo, Seok Woo Chang, Seung Hyun Han, Won-Jun Shon, Woocheol Lee, Seung-Ho Baek, Qiang Zhu, Kee-Yeon Kum
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(2):91-97. Published online March 17, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.2.91
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this
ex vivo study was to compare the antifungal activity of a synthetic peptide consisting of 15 amino acids at the C-terminus of human β-defensin 3 (HBD3-C15) with calcium hydroxide (CH) and Nystatin (Nys) againstCandida albicans (C. albicans ) biofilm.Materials and Methods C. albicans were grown on cover glass bottom dishes or human dentin disks for 48 hr, and then treated with HBD3-C15 (0, 12.5, 25, 50, 100, 150, 200, and 300 µg/mL), CH (100 µg/mL), and Nys (20 µg/mL) for 7 days at 37℃. On cover glass, live and dead cells in the biomass were measured by the FilmTracer Biofilm viability assay, and observed by confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM). On dentin, normal, diminished and ruptured cells were observed by field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM). The results were subjected to a two-tailedt -test, a one way analysis variance and apost hoc test at a significance level ofp = 0.05.Results C. albicans survival on dentin was inhibited by HBD3-C15 in a dose-dependent manner. There were fewer aggregations ofC. albicans in the groups of Nys and HBD3-C15 (≥ 100 µg/mL). CLSM showedC. albicans survival was reduced by HBD3-C15 in a dose dependent manner. Nys and HBD3-C15 (≥ 100 µg/mL) showed significant fungicidal activity compared to CH group (p < 0.05).Conclusions Synthetic HBD3-C15 peptide (≥ 100 µg/mL) and Nys exhibited significantly higher antifungal activity than CH against
C. albicans by inhibiting cell survival and biofilm.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Anti-fungal peptides: an emerging category with enthralling therapeutic prospects in the treatment of candidiasis
Jyoti Sankar Prusty, Ashwini Kumar, Awanish Kumar
Critical Reviews in Microbiology.2025; 51(5): 755. CrossRef - Current status of antimicrobial peptides databases and computational tools for optimization
Madhulika Jha, Akash Nautiyal, Kumud Pant, Navin Kumar
Environment Conservation Journal.2025; 26(1): 281. CrossRef - Harnessing antimicrobial peptides in endodontics
Xinzi Kong, Vijetha Vishwanath, Prasanna Neelakantan, Zhou Ye
International Endodontic Journal.2024; 57(7): 815. CrossRef - Human β-defensins and their synthetic analogs: Natural defenders and prospective new drugs of oral health
Mumian Chen, Zihe Hu, Jue Shi, Zhijian Xie
Life Sciences.2024; 346: 122591. CrossRef - Candida albicans Virulence Factors and Pathogenicity for Endodontic Infections
Yeon-Jee Yoo, A Reum Kim, Hiran Perinpanayagam, Seung Hyun Han, Kee-Yeon Kum
Microorganisms.2020; 8(9): 1300. CrossRef - Innate Inspiration: Antifungal Peptides and Other Immunotherapeutics From the Host Immune Response
Derry K. Mercer, Deborah A. O'Neil
Frontiers in Immunology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Human salivary proteins and their peptidomimetics: Values of function, early diagnosis, and therapeutic potential in combating dental caries
Kun Wang, Xuedong Zhou, Wei Li, Linglin Zhang
Archives of Oral Biology.2019; 99: 31. CrossRef - Endodontic biofilms: contemporary and future treatment options
Yeon-Jee Yoo, Hiran Perinpanayagam, Soram Oh, A-Reum Kim, Seung-Hyun Han, Kee-Yeon Kum
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Bioactive Peptides Against Fungal Biofilms
Karen G. N. Oshiro, Gisele Rodrigues, Bruna Estéfani D. Monges, Marlon Henrique Cardoso, Octávio Luiz Franco
Frontiers in Microbiology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Anticandidal Potential of Stem Bark Extract from Schima superba and the Identification of Its Major Anticandidal Compound
Chun Wu, Hong-Tan Wu, Qing Wang, Guey-Horng Wang, Xue Yi, Yu-Pei Chen, Guang-Xiong Zhou
Molecules.2019; 24(8): 1587. CrossRef - Synthetic Human β Defensin-3-C15 Peptide in Endodontics: Potential Therapeutic Agent in Streptococcus gordonii Lipoprotein-Stimulated Human Dental Pulp-Derived Cells
Yeon-Jee Yoo, Hiran Perinpanayagam, Jue-Yeon Lee, Soram Oh, Yu Gu, A-Reum Kim, Seok-Woo Chang, Seung-Ho Baek, Kee-Yeon Kum
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2019; 21(1): 71. CrossRef - Candida Infections and Therapeutic Strategies: Mechanisms of Action for Traditional and Alternative Agents
Giselle C. de Oliveira Santos, Cleydlenne C. Vasconcelos, Alberto J. O. Lopes, Maria do S. de Sousa Cartágenes, Allan K. D. B. Filho, Flávia R. F. do Nascimento, Ricardo M. Ramos, Emygdia R. R. B. Pires, Marcelo S. de Andrade, Flaviane M. G. Rocha, Cristi
Frontiers in Microbiology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Perspectives for clinical use of engineered human host defense antimicrobial peptides
María Eugenia Pachón-Ibáñez, Younes Smani, Jerónimo Pachón, Javier Sánchez-Céspedes
FEMS Microbiology Reviews.2017; 41(3): 323. CrossRef - The synthetic human beta-defensin-3 C15 peptide exhibits antimicrobial activity against Streptococcus mutans, both alone and in combination with dental disinfectants
Ki Bum Ahn, A. Reum Kim, Kee-Yeon Kum, Cheol-Heui Yun, Seung Hyun Han
Journal of Microbiology.2017; 55(10): 830. CrossRef - Antibiofilm peptides against oral biofilms
Zhejun Wang, Ya Shen, Markus Haapasalo
Journal of Oral Microbiology.2017; 9(1): 1327308. CrossRef - Humanβ-Defensin 3 Reduces TNF-α-Induced Inflammation and Monocyte Adhesion in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells
Tianying Bian, Houxuan Li, Qian Zhou, Can Ni, Yangheng Zhang, Fuhua Yan
Mediators of Inflammation.2017; 2017: 1. CrossRef - Antifungal Effects of Synthetic Human Beta-defensin-3-C15 Peptide on Candida albicans –infected Root Dentin
Yeon-Jee Yoo, Ikyung Kwon, So-Ram Oh, Hiran Perinpanayagam, Sang-Min Lim, Ki-Bum Ahn, Yoon Lee, Seung-Hyun Han, Seok-Woo Chang, Seung-Ho Baek, Qiang Zhu, Kee-Yeon Kum
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(11): 1857. CrossRef - A 15-amino acid C-terminal peptide of beta-defensin-3 inhibits bone resorption by inhibiting the osteoclast differentiation and disrupting podosome belt formation
Ok-Jin Park, Jiseon Kim, Ki Bum Ahn, Jue Yeon Lee, Yoon-Jeong Park, Kee-Yeon Kum, Cheol-Heui Yun, Seung Hyun Han
Journal of Molecular Medicine.2017; 95(12): 1315. CrossRef
- Anti-fungal peptides: an emerging category with enthralling therapeutic prospects in the treatment of candidiasis
- 1,800 View
- 5 Download
- 18 Crossref

- Effect of three different irrigation solutions applied by passive ultrasonic irrigation
- Carmen Llena, Leopoldo Forner, Raquel Cambralla, Adrian Lozano
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(2):143-148. Published online February 11, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.2.143
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the maximum depth and percentage of irrigant penetration into dentinal tubules by passive ultrasonic irrigation (PUI).
Materials and Methods Thirty extracted human teeth were instrumented and divided into three groups. According to final irrigation regimen, 5.25% sodium hypochlorite (Group A, NaOCl), 2% chlorhexidine (Group B, CHX) and saline solution (Group C, control group) were applied with Irrisafe 20 tips (Acteon) and PUI. Irrigant was mixed with 0.1% rhodamine B. Sections at 2 mm, 5 mm, and 8 mm from the apex were examined with confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM). The percentage and maximum depth of irrigant penetration were measured. Kruskal-Wallis test and Mann-Whitney test were performed for overall comparison between groups at each level and for pairwise comparison, respectively. Within a group, Wilcoxon test was performed among different levels.
p values less than 0.05 were considered significant.Results In all groups, highest penetration depth and percentage of penetration were observed at the 8 mm level. At 2 mm level, Groups A and B had significantly greater depths and percentages in penetration than Group C (
p < 0.05), but there were no significant differences between Groups A and B. At 5 mm level, penetration depths and percentage of penetration was not significantly different among the groups.Conclusions NaOCl and CHX applied by PUI showed similar depth and percentage of penetration at all evaluated levels.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative evaluation of side-vented needle, air sonic, and ultrasonic irrigation techniques on sodium hypochlorite penetration into tubules of dentin in root canal: An in vitro study
Anjali Meena, Nidhi Sharma, Dakshita Joy Sinha, Sarita Singh, Anu Dhawan, Neha Verma
Endodontology.2025; 37(1): 80. CrossRef - The influence of irrigant activation, concentration and contact time on sodium hypochlorite penetration into root dentine: an ex vivo experiment
S. S. Virdee, D. J. J. Farnell, M. A. Silva, J. Camilleri, P. R. Cooper, P. L. Tomson
International Endodontic Journal.2020; 53(7): 986. CrossRef - Sodium hypochlorite penetration into dentinal tubules after manual dynamic agitation and ultrasonic activation: a histochemical evaluation
Luigi Generali, Erica Campolongo, Ugo Consolo, Carlo Bertoldi, Luciano Giardino, Francesco Cavani
Odontology.2018; 106(4): 454. CrossRef - Sonic versus ultrasonic activation for the cleaning of the root canal after post space preparation: an in vitro study.
René Carrasco, Ricardo Román, Makarena Ojeda, Carolina Vergara
Journal Oral Of Research.2015; 4(4): 255. CrossRef
- Comparative evaluation of side-vented needle, air sonic, and ultrasonic irrigation techniques on sodium hypochlorite penetration into tubules of dentin in root canal: An in vitro study
- 1,652 View
- 7 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Bonding efficacy of cured or uncured dentin adhesives in indirect resin
- Ji-Hyun Jang, Bin-Na Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang, Yun-Chan Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, In-Nam Hwang
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(6):490-497. Published online November 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.6.490
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study examined the effect of the uncured dentin adhesives on the bond interface between the resin inlay and dentin.
Materials and Methods Dentin surface was exposed in 24 extracted human molars and the teeth were assigned to indirect and direct resin restoration group. For indirect resin groups, exposed dentin surfaces were temporized with provisional resin. The provisional restoration was removed after 1 wk and the teeth were divided further into 4 groups which used dentin adhesives (OptiBond FL, Kerr; One-Step, Bisco) with or without light-curing, respectively (Group OB-C, OB-NC, OS-C and OS-NC). Pre-fabricated resin blocks were cemented on the entire surfaces with resin cement. For the direct resin restoration groups, the dentin surfaces were treated with dentin adhesives (Group OB-D and OS-D), followed by restoring composite resin. After 24 hr, the teeth were assigned to microtensile bond strength (µTBS) and confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM), respectively.
Results The indirect resin restoration groups showed a lower µTBS than the direct resin restoration groups. The µTBS values of the light cured dentin adhesive groups were higher than those of the uncured dentin adhesive groups (
p < 0.05). CLSM analysis of the light cured dentin adhesive groups revealed definite and homogenous hybrid layers. However, the uncured dentin adhesive groups showed uncertain or even no hybrid layer.Conclusions Light-curing of the dentin adhesive prior to the application of the cementing material in luting a resin inlay to dentin resulted in definite, homogenous hybrid layer formation, which may improve the bond strength.
- 1,637 View
- 10 Download

- Surface roughness of experimental composite resins using confocal laser scanning microscope
- JH Bae, MA Lee, BH Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(1):1-8. Published online January 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.1.001
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of a new resin monomer, filler size and polishing technique on the surface roughness of composite resin restorations using confocal laser scanning microscopy. By adding new methoxylated Bis-GMA (Bis-M-GMA, 2,2-bis[4-(2-methoxy-3-methacryloyloxy propoxy) phenyl] propane) having low viscosity, the content of TEGDMA might be decreased. Three experimental composite resins were made: EX1 (Bis-M-GMA/TEGDMA = 95/5 wt%, 40 mm nanofillers); EX2 (Bis-M-GMA/TEGDMA = 95/5 wt%, 20 mm nanofillers); EX3 (Bis-GMA/TEGDMA = 70/30 wt%, 40 mm nanofillers). Filtek Z250 was used as a reference.
Nine specimens (6 mm in diameter and 2 mm in thickness) for each experimental composite resin and Filtek Z250 were fabricated in a teflon mold and assigned to three groups. In Mylar strip group, specimens were left undisturbed. In Sof-lex group, specimens were ground with #1000 SiC paper and polished with Sof-lex discs. In DiaPolisher group, specimens were ground with #1000 SiC paper and polished with DiaPolisher polishing points. The Ra (Average roughness), Rq (Root mean square roughness), Rv (Valley roughness), Rp (Peak roughness), Rc (2D roughness) and Sc (3D roughness) values were determined using confocal laser scanning microscopy. The data were statistically analyzed by Two-way ANOVA and Tukey multiple comparisons test (p = 0.05).
The type of composite resin and polishing technique significantly affected the surface roughness of the composite resin restorations (p < 0.001). EX3 showed the smoothest surface compared to the other composite resins (p < 0.05). Mylar strip resulted in smoother surface than other polishing techniques (p < 0.05).
Bis-M-GMA, a new resin monomer having low viscosity, might reduce the amount of diluent, but showed adverse effect on the surface roughness of composite resin restorations.
- 1,175 View
- 3 Download

- THE EFFECT OF MULTIPLE APPLICATION ON MICROTENSILE BOND STRENGTH OF ALL-IN-ONE DENTIN ADHESIVE SYSTEMS
- Sung-Ae Son, Bock Hur
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(5):423-429. Published online January 14, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.5.423
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub ABSTRACT The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of multiple application of all-in-one dentin adhesive system on microtensile bond strength using confocal laser scanning microscope and microtensile bond strength test. Flat occlusal dentin surfaces were prepared using low-speed diamond saw. In group I, Scotchbond Multipurpose (SM) was applied by manufacturer’s recommendation. In group II, after Adper Prompt L-Pop was applied for 15s and light cured for 10s, the second coat was re-applied and light-cured. In group III, after light-curing the second layer, the third coat was re-applied and light-cured. Specimens bonded with a resin-composite were sectioned into resin-dentin stick for measuring the adhesive layer thickness by confocal laser scanning microscope and evaluating micro-tensile bond strength. The adhesive layers of three-step dentin adhesive system, 3 coats of Adper Prompt L-Pop had significantly thicker than SM, 2 coats of Adper Prompt L-Pop (p < 0.05). However, there was no significant differences in bond strengths between SM and 3 coats of Adper Prompt L-Pop (p > 0.05). And SM, 3 coats of Adper Prompt L-Pop had significantly higher than 2 coats of Adper Prompt L-Pop in bond strengths (p < 0.05).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of application methods of one-step self-etching adhesives on microtensile bond strength
Chul-Kyu Choi, Sung-Ae Son, Jin-Hee Ha, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Yong-Hun Kwon, Jeong-Kil Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(3): 203. CrossRef
- Influence of application methods of one-step self-etching adhesives on microtensile bond strength
- 1,112 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The effect of hybrid layer thickness on microtensile bond strength of three-step and self-etching dentin adhesive systems
- Hye-Jung Lee, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2003;28(6):491-497. Published online November 30, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.6.491
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the correlation between hybrid layer thickness and bond strength using confocal laser scanning microscope and microtensile bond strength test of two adhesive systems.
The dentin surface of human molars, sectioned to remove the enamel from the occlusal surface. Either Scotchbond Multi-Purpose(3M Dental Product, St. Paul, MN, U.S.A) or Clearfil SE Bond(Kuraray, Osaka, Japan) was bonded to the surface, and covered with resin-composite. The resin-bonded teeth were serially sliced perpendicular to the adhesive interface to measure the hybrid layer thickness by confocal laser scanning microscope. The specimen were trimmed to give a bonded cross-sectional surface area of 1mm2, then the micro-tensile bone test was performed at a crosshead speed of 1.0 mm/min. All fractured surfaces were also observed by stereomicroscope.
There was no significant differences in bond strengths the materials(p>0.05). However, the hybrid layers of three-step dentin adhesive system, SM, had significantly thicker than self-etching adhesive system, CS(p<0.05). Pearson's correlation coefficient showed no correlation between hybrid layer thickness and bond strengths(p>0.05). Bond strengths of dentin adhesive systems were not dependent on the thickness of hybrid layer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Techniques for the restorative management of localized and generalized tooth wear
Alex Milosevic
Dental Update.2023; 50(10): 842. CrossRef
- Techniques for the restorative management of localized and generalized tooth wear
- 1,371 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Effect of dentinal tubules orientation on penetration pattern of dentin adhesives using confocal laser scanning microscopy
- Dong-Jun Kim, Yun-Chan Hwang, Sun-Ho Kim, Won-Mann Oh, In-Nam Hwang
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2003;28(5):392-401. Published online September 30, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.5.392
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the penetration pattern of dentin adhesives according to the orientation of dentinal tubules with confocal laser scanning microscopy. Specimens having perpendicular, parallel and oblique surface to dentinal tubules were fabricated. The primer of dentin adhesives (ALL BOND® 2, CLEARFIL™ SE BOND and PQ1) was mixed with fluorescent material, rhodamine B isothiocyanate (Aldrich Chem. CO., Milw., USA). It was applied to the specimens according to the instructions of manufactures. The specimens were covered with composite resin (Estelite, shade A2) and then cut to a thickness of 500 µm with low speed saw (Isomet™, Buehler, USA). The adhesive pattern of dentin adhesives were observed by fluorescence image using confocal laser scanning microscopy.
The results were as follows.
For the groups with tubules perpendicular to bonded surface, funnel shape of resin tag was observed in all specimen. However, resin tags were more prominent in phosphoric acid etching system (ALL BOND® 2 and PQ1) than self etching system (CLEARFIL™ SE BOND).
For the groups with tubules parallel to bonded surface, rhodamine-labeled primer penetrated into peritubular dentin parallel to the orientation of dentinal tubules. But rhodamine-labeled primer of PQ1 diffused more radially into surrounding intertubular dentin than other dentin adhesive systems.
For the groups with tubules oblique to bonded surface, resin tags appeared irregular and discontinuous. But they penetrated deeper into dentinal tubules than other groups.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bonding efficacy of cured or uncured dentin adhesives in indirect resin
Ji-Hyun Jang, Bin-Na Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang, Yun-Chan Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, In-Nam Hwang
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(6): 490. CrossRef
- Bonding efficacy of cured or uncured dentin adhesives in indirect resin
- 1,289 View
- 9 Download
- 1 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


