Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Enhancing antimicrobial properties of a resin-based material via incorporation of a powdered phytotherapeutic extract: an in vitro experimental study
- Rodolfo Xavier de Sousa-Lima, Maria Eduarda Lima do Nascimento Marinho, Janielly Cristina Costa da Silva, Moan Jéfter Fernandes Costa, Pedro Henrique Sette-de-Souza, Giana da Silveira Lima, Boniek Castillo Dutra Borges
- Received March 25, 2025 Accepted September 11, 2025 Published online January 20, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2026.51.e2 [Epub ahead of print]
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study aimed to evaluate the degree of conversion (DC), immediate enamel bond strength (IEBS), antimicrobial activity, and release of the active principle of a resin-based material (RBM) enriched with the powdered Schinopsis brasiliensis (Braúna) stem antibacterial extract.
Methods
The RBM was enriched with 0, 1.25, 2.5, 5, 10, and 20 wt% powdered Braúna extract. The DC (n = 7) was assessed using micro-Raman spectroscopy. The IEBS (n = 7) was determined through the microshear test until failure, and failure modes were examined under a stereomicroscope. The antimicrobial activity (n = 15) was assessed by quantifying colony-forming units, and the release of the active principle was determined using ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography. One-way analysis of variance/Tukey and Kruskal-Wallis/Dunn tests were utilized to analyze the data (p < 0.05).
Results
Materials with 10 wt% and 20 wt% extract showed the lowest DC statistically. However, for IEBS, there were no statistically significant differences among the different groups. All materials released the active principle, but only those with 20 wt% and 10 wt% extract could inhibit biofilm formation similarly to 0.12% chlorhexidine.
Conclusions
Adding powdered Braúna extract between 10 wt% and 20 wt% is a promising alternative to provide an antimicrobial function to RBMs.
- 154 View
- 6 Download

- Comparison of remineralization in caries-affected dentin using calcium silicate, glass ionomer cement, and resin-modified glass ionomer cement: an in vitro study
- Kwanchanok Youcharoen, Onwara Akkaratham, Papichaya Intajak, Pipop Saikaew, Sirichan Chiaraputt
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(4):e37. Published online November 14, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e37
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study evaluated the ability of calcium silicate cement (CSC) as a remineralizing agent compared with conventional glass ionomer cement (GIC) and resin-modified GIC (RMGIC) to remineralize artificial caries-affected dentin.
Methods
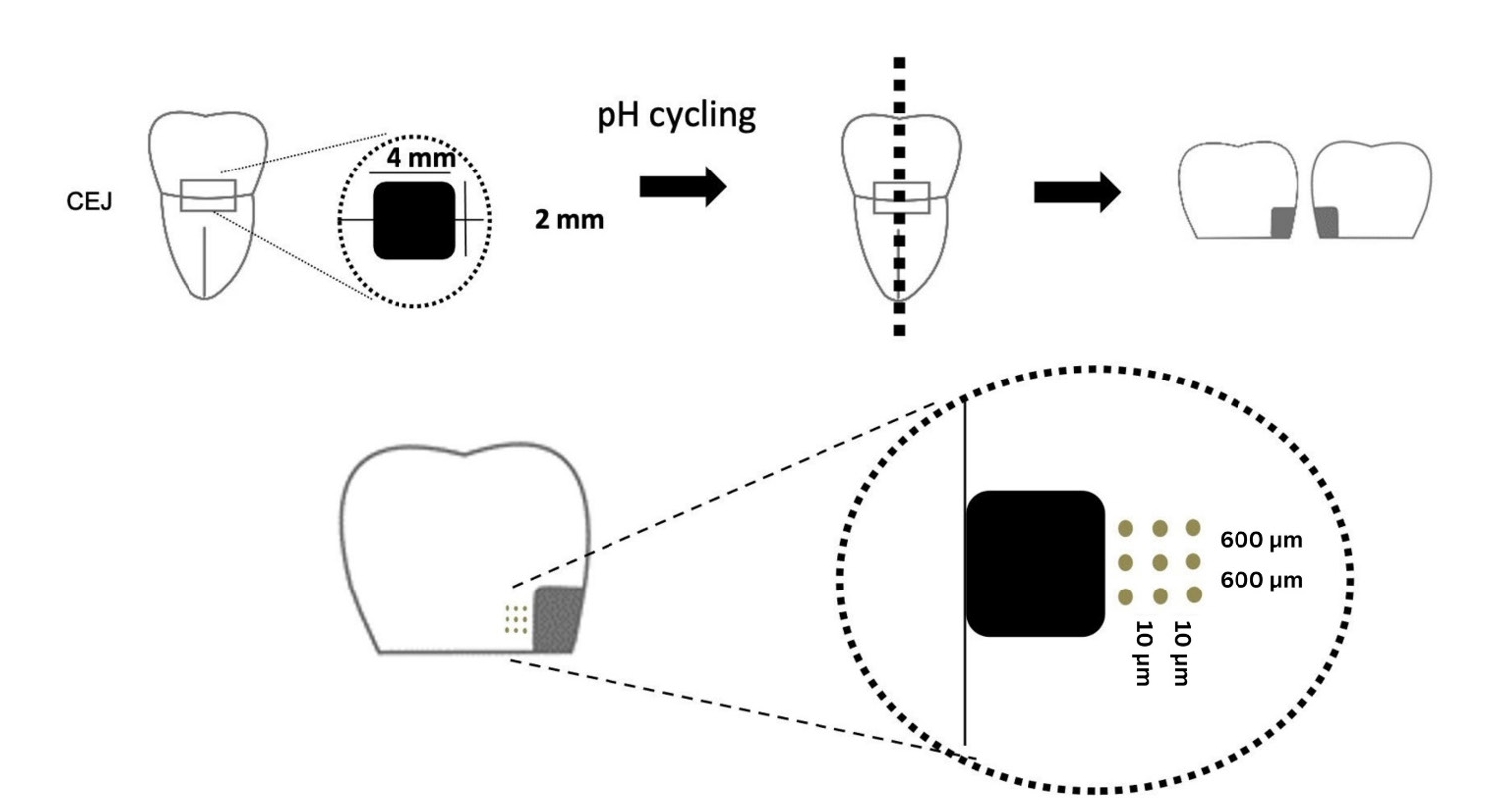
Twenty-five class V cavities were prepared on extracted human third molars. Twenty teeth underwent artificial caries induction. The remaining five teeth with sound dentin serve as the positive control. The twenty demineralized teeth were subdivided into four groups (n = 5): carious dentin without restoration (negative control [NC]), carious dentin restored with CSC (Biodentine, Septodont), carious dentin restored with GI (Fuji IX, GC Corporation), and carious dentin restored with RMGIC (Fuji II LC, GC Corporation). Following restoration, the specimens were stored in artificial saliva for 7 days. The elastic modulus was evaluated by a nanoindentation test. The mineral composition was analyzed by scanning electron microscopy-energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM-EDX), and the mineral composition at the dentin-material interface.
Results
CSC had a higher modulus of elasticity compared to GI, RMGI, and NC groups (p < 0.05). Higher calcium and phosphorus content was observed under CSC restorations, as indicated by SEM-EDX examination, which may lead to better remineralization.
Conclusions
Compared to GI and RMGI, CSC showed the best remineralization and mechanical reinforcement in caries-affected dentin, indicating CSC for use in minimally invasive restorative dentistry.
- 1,226 View
- 163 Download

- Prevalence of salivary microbial load and lactic acid presence in diabetic and non-diabetic individuals with different dental caries stages
- Monika Mohanty, Shashirekha Govind, Shakti Rath
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(1):e4. Published online January 12, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e4
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aims to correlate caries-causing microorganism load, lactic acid estimation, and blood groups to high caries risk in diabetic and non-diabetic individuals and low caries risk in healthy individuals.
Materials and Methods This study includes 30 participants divided into 3 groups: Group A, High-risk caries diabetic individuals; Group B, High-risk caries non-diabetic individuals; and Group C, Low-risk caries individuals. The medical condition, oral hygiene, and caries risk assessment (American Dental Association classification and International Caries Detection and Assessment System scoring) were documented. Each individual’s 3 mL of saliva was analyzed for microbial load and lactic acid as follows: Part I: 2 mL for microbial quantity estimation using nutrient agar and blood agar medium, biochemical investigation, and carbohydrate fermentation tests; Part II: 0.5 mL for lactic acid estimation using spectrophotometric analysis. Among the selected individuals, blood group correlation was assessed. The χ2 test, Kruskal-Wallis test, and
post hoc analysis were done using Dunn’s test (p < 0.05).Results Group A had the highest microbial load and lactic acid concentration, followed by Groups B and C. The predominant bacteria were
Lactobacilli (63.00 ± 15.49) andStreptococcus mutans (76.00 ± 13.90) in saliva. Blood Group B is prevalent in diabetic and non-diabetic high-risk caries patients but statistically insignificant.Conclusions Diabetic individuals are more susceptible to dental caries due to high microbial loads and increased lactic acid production. These factors also lower the executing tendency of neutrophils, which accelerates microbial accumulation and increases the risk of caries in diabetic individuals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Oral Health Disparities in Type 2 Diabetes: Examining the Elevated Risk for Dental Caries—A Comparative Study
José Frias-Bulhosa, Maria Conceição Manso, Carla Lopes Mota, Paulo Melo
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(6): 258. CrossRef - Exploring the photosensitizing potential of Nanoliposome Loaded Improved Toluidine Blue O (NLITBO) Against Streptococcus mutans: An in-vitro feasibility study
Swagatika Panda, Lipsa Rout, Neeta Mohanty, Anurag Satpathy, Bhabani Sankar Satapathy, Shakti Rath, Divya Gopinath, Geelsu Hwang
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(10): e0312521. CrossRef - Altered salivary microbiota associated with high-sugar beverage consumption
Xiaozhou Fan, Kelsey R. Monson, Brandilyn A. Peters, Jennifer M. Whittington, Caroline Y. Um, Paul E. Oberstein, Marjorie L. McCullough, Neal D. Freedman, Wen-Yi Huang, Jiyoung Ahn, Richard B. Hayes
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Oral Health Disparities in Type 2 Diabetes: Examining the Elevated Risk for Dental Caries—A Comparative Study
- 2,930 View
- 79 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Can silver diamine fluoride or silver nanoparticle-based anticaries agents to affect enamel bond strength?
- Jaqueline Costa Favaro, Yana Cosendey Toledo de Mello Peixoto, Omar Geha, Flaviana Alves Dias, Ricardo Danil Guiraldo, Murilo Baena Lopes, Sandrine Bittencourt Berger
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(1):e7. Published online January 12, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e7
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of the current study is to investigate the effect of different anticaries agents, such as experimental agents based on silver nanoparticles (SNPs) and silver diamine fluoride (SDF), on the micro-shear bond strength (μ-SBS) of composite resin applied to intact enamel (IE) or demineralized enamel (DE).
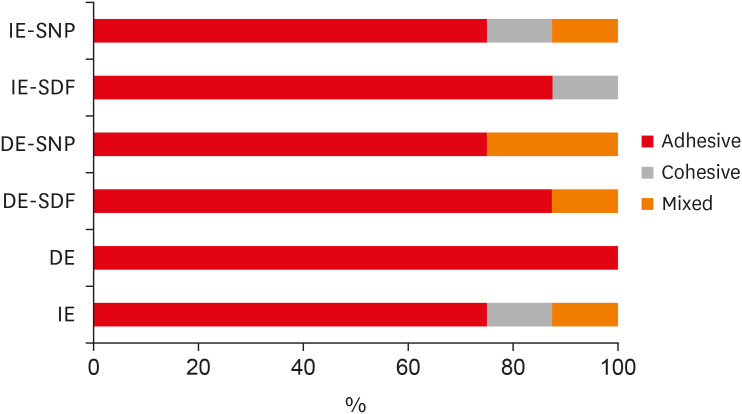
Materials and Methods Sixty dental enamel fragments were collected from human third molars and categorized into 6 groups (
n = 10): positive control (IE), negative control (DE), IE + SDF, DE + SDF, IE + SNP and DE + SNP. Samples from DE, DE + SDF and DE + SNP groups were subjected to pH cycling; superficial microhardness test was performed to confirm demineralization. Resin composite build-ups were applied to the samples (0.75-mm diameter and 1-mm height) after the treatments (except for IE and DE groups); μ-SBS was also evaluated. Samples were analyzed under a stereomicroscope at 40× magnification to identify failure patterns. Data were subjected to one-way analysis of variance, followed by Tukey's and Dunnett's tests (p < 0.05).Results There was no significant difference among the IE, IE + SNP, DE + SDF, and DE + SNP groups. The IE + SDF and DE groups recorded the highest and the lowest μ-SBS values, respectively. Adhesive-type failures were the most frequent for all treatments.
Conclusions Anticaries agents did not have a negative effect on the μ-SBS of composite resin when it was used on IE or DE.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of Incorporating Nanoparticles to Adhesive Resin on the Demineralization of Enamel: A Systematic Review
Naif Almosa
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(3): 89. CrossRef - Preventing white spot lesions around orthodontic brackets: efficacy of pre-reacted glass-ionomer barrier coat versus silver diamine fluoride: an in vitro study
Enas A. Elshenawy, Safa B. Alawy, Wafaa Yahia Alghonemy, Ahmed Ibrahime El dosoky
BDJ Open.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Research Status of Silver Nanoparticles for Dental Applications
Yanyan Guo, Xiaomei Hou, Sanjun Fan, Chanyuan Jin
Inorganics.2025; 13(5): 168. CrossRef - The use of silver diamine fluoride to prevent/treat enamel carious lesions: a narrative review
Rasha N. AlSheikh
PeerJ.2024; 12: e17897. CrossRef - Phosphoric Acid Etch Partially Restores the Initial Bond Strength of Composite to Silver Diamine Fluoride–Treated Enamel Using Universal Adhesives
Zaher Jabbour, Mijoo Kim, Marc Hayashi, Reuben Kim
Dentistry Journal.2023; 11(7): 161. CrossRef - Efficacy of Nano Silver Fluoride and/or Diode Laser In Enhancing Enamel Anticariogenicity around orthodontic brackets
Aya Anwar Alsherif, Mohamed Ali Farag, Mai Badreldin Helal
BDJ Open.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Amelioration Strategies for Silver Diamine Fluoride: Moving from Black to White
Amjad Almuqrin, Inder Preet Kaur, Laurence J. Walsh, Chaminda Jayampath Seneviratne, Sobia Zafar
Antibiotics.2023; 12(2): 298. CrossRef - The Effect of Loading Time on Color Stability of Various Restorative Materials Bonded to Silver Diamine Fluoride-Treated Demineralized Dentin
Mohammed M Aldosari, Fares S Al-Sehaibany
Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dentistry.2022; Volume 14: 123. CrossRef - In vitro study of the effect of nanosilver fluoride on shear bond strength of orthodontic brackets and demineralization of enamel
Mariam H. El-Toukhy, Eman M. El-Shourbagy, Neveen M. Fakhry
Tanta Dental Journal.2022; 19(4): 281. CrossRef
- Impact of Incorporating Nanoparticles to Adhesive Resin on the Demineralization of Enamel: A Systematic Review
- 1,751 View
- 22 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref

- Functional and aesthetic rehabilitation in posterior tooth with bulk-fill resin composite and occlusal matrix
- Luciana Fávaro Francisconi-dos-Rios, Johnny Alexandre Oliveira Tavares, Luanderson Oliveira, Jefferson Chaves Moreira, Flavia Pardo Salata Nahsan
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(1):e9. Published online January 3, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e9
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The restorative procedure in posterior teeth involves clinical steps related to professional skill, especially when using the incremental technique, which may fail in the long term. A recent alternative is bulk-fill resins, which can reduce polymerization shrinkage, decreasing clinical problems such as marginal leakage, secondary caries, and fracture. This scientific study aims to report a clinical case using bulk-fill resin with an occlusal matrix. As determined in the treatment plan, an acrylic resin matrix was produced to establish an improved oral and aesthetic rehabilitation of the right mandibular first molar, which presented a carious lesion with dentin involvement. The occlusal matrix is a simple technique that maintains the original dental anatomy, showing satisfactory results regarding function and aesthetic rehabilitation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mastery of Aesthetic and Functional Restoration of Maxillary Molars Using the Technique of Direct Restoration (Clinical Case)
Yu. Kolenko
SUCHASNA STOMATOLOHIYA.2025; (2): 67. CrossRef - Color stability of bulk‐fill compared to conventional resin‐based composites: A scoping review
Gaetano Paolone, Mauro Mandurino, Nicola Scotti, Giuseppe Cantatore, Markus B. Blatz
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2023; 35(4): 657. CrossRef - Evaluation of Abfraction Lesions Restored with Three Dental Materials: A Comparative Study
Bogdan Constantin Costăchel, Anamaria Bechir, Alexandru Burcea, Laurența Lelia Mihai, Tudor Ionescu, Olivia Andreea Marcu, Edwin Sever Bechir
Clinics and Practice.2023; 13(5): 1043. CrossRef - Aesthetic restoration of posterior teeth using different occlusal matrix techniques
Elsa Reis Carneiro, Anabela Paula, José Saraiva, Ana Coelho, Inês Amaro, Carlos Miguel Marto, Manuel Marques Ferreira, Eunice Carrilho
British Dental Journal.2021; 231(2): 88. CrossRef
- Mastery of Aesthetic and Functional Restoration of Maxillary Molars Using the Technique of Direct Restoration (Clinical Case)
- 1,458 View
- 20 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Management of large class II lesions in molars: how to restore and when to perform surgical crown lengthening?
- Ana Belén Dablanca-Blanco, Juan Blanco-Carrión, Benjamín Martín-Biedma, Purificación Varela-Patiño, Alba Bello-Castro, Pablo Castelo-Baz
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(3):240-252. Published online August 3, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.3.240
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The restoration of endodontic tooth is always a challenge for the clinician, not only due to excessive loss of tooth structure but also invasion of the biological width due to large decayed lesions. In this paper, the 7 most common clinical scenarios in molars with class II lesions ever deeper were examined. This includes both the type of restoration (direct or indirect) and the management of the cavity margin, such as the need for deep margin elevation (DME) or crown lengthening. It is necessary to have the DME when the healthy tooth remnant is in the sulcus or at the epithelium level. For caries that reaches the connective tissue or the bone crest, crown lengthening is required. Endocrowns are a good treatment option in the endodontically treated tooth when the loss of structure is advanced.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Awareness and Practice of Deep Margin Elevation among Dental Practitioners in India: A Cross-Sectional Survey
Mythri Padaru, Preethesh Shetty, Namith Rai, Raksha Bhat
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Rubber dam isolation to optimise intraoral scanning and the restoration of teeth with subgingival margins
Renato Lardin Sartori Sanchez, Gisele Lie Fukuoka, Nathália Pereira Censi Stapani, Isabella Neme Ribeiro dos Reis
BMJ Case Reports.2025; 18(4): e264082. CrossRef - Impact of spacers and thermocycling on porosity and gaps in class II endodontic temporary restorations evaluated by microcomputed tomography
Fahda N. Algahtani, Manal Alkadi, Hiba R. Talic, Sarah S. AlShalawi, Lujain M. Alqarni, Reem M. Barakat, Rasha Haridy, Sara M. ElKhateeb, Rahaf A. Almohareb
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Deep Margin Elevation: Current Evidence and a Critical Approach to Clinical Protocols—A Narrative Review
Athanasios Karageorgiou, Maria Fostiropoulou, Maria Antoniadou, Eftychia Pappa
Adhesives.2025; 1(3): 10. CrossRef - Deep margin elevation in restorative dentistry: A scoping review
Anna Taylor, Lorna Burns
Journal of Dentistry.2024; 146: 105066. CrossRef - Effect of cervical margin relocation on marginal adaptation and microleakage of indirect ceramic restorations
Marwa Adel, Amina Hamdy, Ahmed Sabet, Kamal Ebeid
Journal of Prosthodontics.2024; 33(4): 374. CrossRef - Application of one-piece endodontic crowns fabricated with CAD-CAM system to molars
Haruto Hiraba, Kensuke Nishio, Yoshimasa Takeuchi, Takashi Ito, Tetsuo Yamamori, Atsushi Kamimoto
Japanese Dental Science Review.2024; 60: 81. CrossRef - Structurally compromised teeth. Part II: A novel approach to peripheral build up procedures
Guido Fichera, Claudia Mazzitelli, Vincenzo Picciariello, Tatjana Maravic, Uros Josic, Annalisa Mazzoni, Lorenzo Breschi
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2024; 36(1): 20. CrossRef - Biomimetic Restorative Dentistry: an evidence-based discussion of common myths
Alessandra REIS, Victor Pinheiro FEITOSA, Ana Cláudia CHIBINSKI, Michael Willian FAVORETO, Mario Felipe GUTIERREZ, Alessandro Dourado LOGUERCIO
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative clinical evaluation of correct anatomic contour and tight contact in Class II direct composite restoration using two newer contact forming instruments
Jaimini Patel, Nimisha C. Shah, Meetkumar Dedania, Deebah Choudhary, Nidhi Bharti, Aishwarya Jain
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(11): 1135. CrossRef - Effect of Deep Margin Elevation on the Pulpal and Periodontal Health of Teeth: A Systematic Review
S Srirama, S Jain, B Arul, K Prabakar, V Natanasabapathy
Operative Dentistry.2024; 49(4): 388. CrossRef - New Technique for Wedge Selection in Direct Class II Restorations: A Pilot Study
Tania Gancedo-Gancedo, Benjamín Martín-Biedma, Javier Domínguez-Cachón, Sara Garrido-Parada, Victoria Ababii, Patricia Pereira-Lores, Sandra García-Varela, Pablo Castelo-Baz
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(5): 1324. CrossRef - Different Designs of Deep Marginal Elevation and Its Influence on Fracture Resistance of Teeth with Monolith Zirconia Full-Contour Crowns
Ali Robaian, Abdullah Alqahtani, Khalid Alanazi, Abdulrhman Alanazi, Meshal Almalki, Anas Aljarad, Refal Albaijan, Ahmed Maawadh, Aref Sufyan, Mubashir Baig Mirza
Medicina.2023; 59(4): 661. CrossRef - M-i-M for DME: matrix-in-a-matrix technique for deep margin elevation
Pascal Magne
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2023; 130(4): 434. CrossRef - A New Concept of Posterior Mini-invasive Restorations: Clinical Procedures and Requirements—Case Report
Zeineb Riahi, Belhassen Harzallah, Mounir Cherif, Dalenda Hadyaoui, Imen Kalghoum, Oumayma Mejri
CODS - Journal of Dentistry.2023; 14(2): 61. CrossRef - Evaluation of biologic width re-establishment using CHU aesthetic gauges in crown lengthening cases- a clinical study
Avantika Rani, Shiva Shankar Gummaluri, Hirak S. Bhattacharya, Preeti Bhattacharya, Sumbul Saifi, saummya singh
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2023; 13(2): 138. CrossRef - Interfacial integrity of bulk-fill resin composite restorations in deep Class-II cavities
Rana Abdelrehim SEDKY, Hooi Pin CHEW, Khaled Aly NOUR, Shaimaa Mohamed ABUELSADAT, Dina ELSHERBINI, Alex Siu Lun FOK
Dental Materials Journal.2023; 42(5): 692. CrossRef - Biological evaluation of indirect restorations in endodontically treated posterior teeth with deeply located proximal margins following deep margin elevation versus surgical crown lengthening: a randomized controlled trial
Ahmed Tarek Farouk, Olfat El Sayed Hassanein, Ola Ibrahim Fahmy, Ahmed M. Elkady, Hani ElNahass
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Deep Margin Elevation: Current Concepts and Clinical Considerations: A Review
Majed Aldakheel, Khalid Aldosary, Shatha Alnafissah, Rahaf Alaamer, Anwar Alqahtani, Nora Almuhtab
Medicina.2022; 58(10): 1482. CrossRef - Deep Margin Elevation: A Literature Review
Theodora Kalliopi Samartzi, Dimokritos Papalexopoulos, Panagiotis Ntovas, Christos Rahiotis, Markus B. Blatz
Dentistry Journal.2022; 10(3): 48. CrossRef - Examination of caries‐affected dentin and composite‐resin interface after different caries removal methods: A scanning electron microscope study
Nazmiye Donmez, Magrur Kazak, Zeynep Buket Kaynar, Yesim Sesen Uslu
Microscopy Research and Technique.2022; 85(6): 2212. CrossRef - Clinical performance of indirect restorations with cervical margin relocation in posterior teeth: A systematic review
Ghaida Alhumaidan, Raghad Alammar, Dhafer Al Asmari, Ali Alenezi
Dentistry Review.2022; 2(1): 100034. CrossRef - Current Strategies to Control Recurrent and Residual Caries with Resin Composite Restorations: Operator- and Material-Related Factors
Moataz Elgezawi, Rasha Haridy, Moamen A. Abdalla, Katrin Heck, Miriam Draenert, Dalia Kaisarly
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(21): 6591. CrossRef - Survival and success of endocrowns: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Raghad A. Al-Dabbagh
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2021; 125(3): 415.e1. CrossRef - The Relationships Between Tooth‐Supported Fixed Dental Prostheses and Restorations and the Periodontium
Carlo Ercoli, Dennis Tarnow, Carlo E. Poggio, Alexandra Tsigarida, Marco Ferrari, Jack G. Caton, Konstantinos Chochlidakis
Journal of Prosthodontics.2021; 30(4): 305. CrossRef - Placement of Posterior Composite Restorations: A Cross-Sectional Study of Dental Practitioners in Al-Kharj, Saudi Arabia
Mohamed M. Awad, Mansour Alradan, Nawaf Alshalan, Ali Alqahtani, Feras Alhalabi, Mohammed Ali Salem, Ahmed Rabah, Ali Alrahlah
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(23): 12408. CrossRef - Microleakage of Direct Restorations-Comparisonbetween Bulk-Fill and Traditional Composite Resins:Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Francesca Zotti, Edoardo Falavigna, Giorgia Capocasale, Daniele De Santis, Massimo Albanese
European Journal of Dentistry.2021; 15(04): 755. CrossRef - Assessment of knowledge, attitude, and practice regarding Deep Margin Elevation (DME) among dental practitioners in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
Sultan R. Binalrimal, Weam M. Banjar, Sara H. Alyousef, Mada I. Alawad, Ghalia I. Alawad
Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.2021; 10(5): 1931. CrossRef - Treatment Prognosis of Restored Teeth with Crown Lengthening vs. Deep Margin Elevation: A Systematic Review
Maryam H. Mugri, Mohammed E. Sayed, Binoy Mathews Nedumgottil, Shilpa Bhandi, A. Thirumal Raj, Luca Testarelli, Zohaib Khurshid, Saurabh Jain, Shankargouda Patil
Materials.2021; 14(21): 6733. CrossRef - Direct resin composite restoration of endodontically-treated permanent molars in adolescents: bite force and patient-specific finite element analysis
Monise de Paula RODRIGUES, Priscilla Barbosa Ferreira SOARES, Márcio Alex Barros GOMES, Renata Afonso PEREIRA, Daranee TANTBIROJN, Antheunis VERSLUIS, Carlos Jose SOARES
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Up to 12 years clinical evaluation of 197 partial indirect restorations with deep margin elevation in the posterior region
R.A. Bresser, D. Gerdolle, I.A. van den Heijkant, L.M.A. Sluiter-Pouwels, M.S. Cune, M.M.M. Gresnigt
Journal of Dentistry.2019; 91: 103227. CrossRef - How biomechanics can affect the endodontic treated teeth and their restorative procedures?
Carlos José Soares, Monise de Paula Rodrigues, André Luis Faria-e-Silva, Paulo Cesar Freitas Santos-Filho, Crisnicaw Veríssimo, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Antheunis Versluis
Brazilian Oral Research.2018;[Epub] CrossRef
- Awareness and Practice of Deep Margin Elevation among Dental Practitioners in India: A Cross-Sectional Survey
- 2,953 View
- 100 Download
- 32 Crossref

- Comparison of two different methods of detecting residual caries
- Uzay Koç Vural, Zeynep Bilge Kütük, Esra Ergin, Filiz Yalçın Çakır, Sevil Gürgan
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(1):48-53. Published online January 25, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.1.48

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to investigate the ability of the fluorescence-aided caries excavation (FACE) device to detect residual caries by comparing conventional methods
in vivo .Materials and Methods A total of 301 females and 202 males with carious teeth participated in this study. The cavity preparations were done by grade 4 (Group 1, 154 teeth), grade 5 (Group 2, 176 teeth), and postgraduate (Group 3, 173 teeth) students. After caries excavation using a handpiece and hand instruments, the presence of residual caries was evaluated by 2 investigators who were previously calibrated for visual-tactile assessment with and without magnifying glasses and trained in the use of a FACE device. The tooth number, cavity type, and presence or absence of residual caries were recorded. The data were analyzed using the Chi-square test, the Fisher's Exact test, or the McNemar test as appropriate. Kappa statistics was used for calibration. In all tests, the level of significance was set at
p = 0.05.Results Almost half of the cavities prepared were Class II (Class I, 20.9%; Class II, 48.9%; Class III, 20.1%; Class IV, 3.4%; Class V, 6.8%). Higher numbers of cavities left with caries were observed in Groups 1 and 2 than in Group 3 for all examination methods. Significant differences were found between visual inspection with or without magnifying glasses and inspection with a FACE device for all groups (
p < 0.001). More residual caries were detected through inspection with a FACE device (46.5%) than through either visual inspection (31.8%) or inspection with a magnifying glass (37.6%).Conclusions Within the limitations of this study, the FACE device may be an effective method for the detection of residual caries.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- CariesXplainer: enhancing dental caries detection using Gradient-weighted Class Activation Mapping and transfer learning
Saira Asghar, Junaid Rashid, Anum Masood
Multimedia Tools and Applications.2025; 84(38): 46647. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of caries detector dyes and laser fluorescence systems for intraoperative diagnosis during selective caries removal: a scoping review
Ana Iglesias-Poveda, Javier Flores-Fraile, Diego González-Gil, Joaquín López-Marcos
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Fluorescence as a Quantitative Indicator of Cariogenic Bacteria During Chemo-Mechanical Caries Excavation with BRIX 3000 in Primary Teeth
Zornitsa Lazarova, Raina Gergova, Nadezhda Mitova
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2025; 16(12): 453. CrossRef - Examining the Efficacy of a 405 nm Wavelength Diode Laser as a Diagnostic Tool in Routine Dental Practice
Marwan El Mobader, Samir Nammour
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Diş Çürüğünün Teşhisi ve Bu Amaçla Kullanılan Güncel Yöntemler
Oya BALA, Sümeyye KANLIDERE
Türk Diş Hekimliği Araştırma Dergisi.2023; 2(2): 219. CrossRef - Longitudinal study for dental caries calibration of dentists unexperienced in epidemiological surveys
Mariana NABARRETTE, Patrícia Rafaela dos SANTOS, Andréa Videira ASSAF, Glaucia Maria Bovi AMBROSANO, Marcelo de Castro MENEGHIM, Silvia Amélia Scudeler VEDOVELLO, Karine Laura CORTELLAZZI
Brazilian Oral Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - CURRENT CONCEPTS AND TECHNIQUES IN CARIES EXCAVATION: A REVIEW
Priyanka Aggarwal, Shivani Mathur, Tanya Batra
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH.2022; : 26. CrossRef - Current Strategies to Control Recurrent and Residual Caries with Resin Composite Restorations: Operator- and Material-Related Factors
Moataz Elgezawi, Rasha Haridy, Moamen A. Abdalla, Katrin Heck, Miriam Draenert, Dalia Kaisarly
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(21): 6591. CrossRef - Rezidüel Çürük Tespitinde Kullanılan Geleneksel Yöntemin Farklı Yöntemlerle Klinik Olarak Doğrulanması
Fatma SAĞ GÜNGÖR
Selcuk Dental Journal.2021; 8(2): 402. CrossRef
- CariesXplainer: enhancing dental caries detection using Gradient-weighted Class Activation Mapping and transfer learning
- 1,814 View
- 11 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Elemental analysis of caries-affected root dentin and artificially demineralized dentin
- Young-Hye Sung, Ho-Hyun Son, Keewook Yi, Juhea Chang
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(4):255-261. Published online August 19, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.4.255
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to analyze the mineral composition of naturally- and artificially-produced caries-affected root dentin and to determine the elemental incorporation of resin-modified glass ionomer (RMGI) into the demineralized dentin.
Materials and Methods Box-formed cavities were prepared on buccal and lingual root surfaces of sound human premolars (
n = 15). One cavity was exposed to a microbial caries model using a strain of Streptococcus mutans. The other cavity was subjected to a chemical model under pH cycling. Premolars and molars with root surface caries were used as a natural caries model (n = 15). Outer caries lesion was removed using a carbide bur and a hand excavator under a dyeing technique and restored with RMGI (FujiII LC, GC Corp.). The weight percentages of calcium (Ca), phosphate (P), and strontium (Sr) and the widths of demineralized dentin were determined by electron probe microanalysis and compared among the groups using ANOVA and Tukey test (p < 0.05).Results There was a pattern of demineralization in all models, as visualized with scanning electron microscopy. Artificial models induced greater losses of Ca and P and larger widths of demineralized dentin than did a natural caries model (
p < 0.05). Sr was diffused into the demineralized dentin layer from RMGI.Conclusions Both microbial and chemical caries models produced similar patterns of mineral composition on the caries-affected dentin. However, the artificial lesions had a relatively larger extent of demineralization than did the natural lesions. RMGI was incorporated into the superficial layer of the caries-affected dentin.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- 3D Multi-modal Imaging of demineralised dentine using combined synchrotron µ-XRD-CT and STXM-CT
Nathanael Leung, Robert A. Harper, Bin Zhu, Stuart A. Bartlett, Konstantin Ignatyev, Richard M. Shelton, Gabriel Landini, Tan Sui
Journal of Structural Biology.2025; 217(2): 108208. CrossRef - A dynamic microcosm biofilm model for root carious-like lesion development: analysis of demineralization and microbiological characterization
Tamires Timm Maske, Glenda Ávila Marques, Bruna Dalongaro Fritsch, Bruna Moraes Kremer, Maximiliano Sérgio Cenci, Pabulo Henrique Rampelotto, Rodrigo Alex Arthur
Biofouling.2025; 41(5): 536. CrossRef - Bond strength durability of three bioactive restorative materials to silver diamine fluoride treated artificially demineralized dentine
Mostafa A. Abdelshafi, Hanan A.N. Soliman, Dina Abdelaziz
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Frontiers of Global Research Trend on Root Caries: A Bibliometric Analysis
Grace Yuchan Xu, Irene Shuping Zhao, Christie Ying Kei Lung, Iris Xiaoxue Yin, Edward Chin Man Lo, Chun Hung Chu
International Dental Journal.2024; 74(6): 1197. CrossRef - Effects of NaF versus SDF treatment on microhardness of artificial radiation caries at cervical and root areas
Pipop SAIKAEW, Karis KATEKOVIT, Anocha BURANARACHADA, Nattapat SAIMALA, Anussara PRAYONGRAT, Pornpoj FUANGTHARNTHIP
Dental Materials Journal.2024; 43(4): 591. CrossRef - Degradable polycaprolactone/buffer composites as pH regulating carrier materials for drug delivery and 3D printed biomaterials
Therese Schüler, Celine Guder, Franziska Alt, Katrin Lorenz, Torsten Sterzenbach, Christian Hannig, Hans-Peter Wiesmann, Benjamin Kruppke
Materialia.2024; 34: 102087. CrossRef - The Effect of Oral Care Foams and a Spray on Salivary pH Changes after Exposure to Acidic Beverages in Young Adults
Maria Polyakova, Anna Egiazaryan, Vladlena Doroshina, Alexandr Zaytsev, Alexey Malashin, Ksenia Babina, Nina Novozhilova
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(4): 93. CrossRef - In Vitro Models Used in the Formation of Root Caries Lesions—A Review of the Literature
Zaid Dohan, Lara T. Friedlander, Paul R. Cooper, Kai-Chun Li, Jithendra T. Ratnayake, May L. Mei
Dentistry Journal.2023; 11(12): 269. CrossRef - Yttrium Trifluoride as a Marker of Infiltration Rate of Decalcified Root Cementum: An In Vitro Study
Anna Nowak-Wachol, Anna Korytkowska-Wałach, Bartosz Chmiela, Kacper Wachol, Maciej Łopaciński, Magdalena Wyszyńska, Yousuf Al-Dulaimi, Małgorzata Skucha-Nowak
Polymers.2022; 14(4): 780. CrossRef - Effect of fluoride, chlorhexidine or Nd:YAG on the progression of root dentin demineralization after removal of the demineralized organic matrix
Andrea Maselli, Tânia Mara da Silva, Lucélia Lemes Gonçalves, Aline Silva Braga, Eduardo Bresciani, Ana Carolina Magalhães, Sérgio Eduardo de Paiva Gonçalves
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of ionizing radiation and cariogenic biofilm challenge on root-dentin caries
Camila de Carvalho Almança Lopes, Renata Borges Rodrigues, Maximiliano Sérgio Cenci, Juliana Lays Stolfo Uehara, Tamires Timm Maske, Pedro Henrique Justino Oliveira Limirio, Priscilla Barbosa Ferreira Soares, Veridiana Resende Novais
Clinical Oral Investigations.2021; 25(6): 4059. CrossRef - Silver diamine fluoride treatment of active root caries lesions in older adults: A case series
Chelsea Mitchell, Andrew J Gross, Peter Milgrom, Lloyd Mancl, David B Prince
Journal of Dentistry.2021; 105: 103561. CrossRef - A Hydrogel Drink With High Fructose Content Generates Higher Exogenous Carbohydrate Oxidation and a Reduced Drop in Dental Biofilm pH Compared to Two Other, Commercially Available, Carbohydrate Sports Drinks
Stefan Pettersson, Martin Ahnoff, Fredrik Edin, Peter Lingström, Charlotte Simark Mattsson, Ulrika Andersson-Hall
Frontiers in Nutrition.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- 3D Multi-modal Imaging of demineralised dentine using combined synchrotron µ-XRD-CT and STXM-CT
- 1,612 View
- 9 Download
- 13 Crossref

- The effect of different fluoride application methods on the remineralization of initial carious lesions
- Seon Mi Byeon, Min Ho Lee, Tae Sung Bae
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(2):121-129. Published online May 10, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.2.121
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to assess the effect of single and combined applications of fluoride on the amount of fluoride release, and the remineralization and physical properties of enamel.
Materials and Methods Each of four fluoride varnish and gel products (Fluor Protector, FP, Ivoclar Vivadent; Tooth Mousse Plus, TM, GC; 60 Second Gel, A, Germiphene; CavityShield, CS, 3M ESPE) and two fluoride solutions (2% sodium fluoride, N; 8% tin(ii) fluoride, S) were applied on bovine teeth using single and combined methods (10 per group), and then the amount of fluoride release was measured for 4 wk. The electron probe microanalysis and the Vickers microhardness measurements were conducted to assess the effect of fluoride application on the surface properties of bovine teeth.
Results The amount of fluoride release was higher in combined applications than in single application (
p < 0.05). Microhardness values were higher after combined applications of N with FP, TM, and CS than single application of them, and these values were also higher after combined applications of S than single application of A (p < 0.05). Ca and P values were higher in combined applications of N with TM and CS than single application of them (p < 0.05). They were also increased after combined applications of the S with A than after single application (p < 0.05).Conclusions Combined applications of fluoride could be used as a basis to design more effective methods of fluoride application to provide enhanced remineralization.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Different Topical Fluorides on the Microhardness of Bleached Enamel: In Vitro Study
Soumyashri Das, Mansi Jain, HP Suma Sogi, Sonali Sukesh K, Apurva Gambhir, FNU Gagandeep
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2025; 18(11): 1365. CrossRef - Therapeutic effect of ozone gel on the initial carious lesions
Maha A. Alsharqawy, Wedad M Etman, Mirvat M Salama, Reda G. Saleh
Tanta Dental Journal.2023; 20(3): 203. CrossRef - Evaluation of Remineralization Potential of Natural Substances on Artificially Induced Carious Lesions in Primary Teeth: An In Vitro Study
Kavitha Ramar, Pooja V Ravi, Rajakumar Sekar
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2023; 16(2): 244. CrossRef - Upaya Preventif Kesehatan Gigi dan Mulut dengan Aplikasi Fluor pada Gigi Siswa SMPN 77 Jakarta
Agus Ardinansyah, Mochammad Atmaji Windrianto, Nur Hidayati Nosi Prastiyani
Info Abdi Cendekia.2023; 6(2): 74. CrossRef - Evaluation of the antibacterial activity of Enamelast® and Fluor defender® fluoride varnishes against Streptococcus mutans biofilm: an in vitro study in primary teeth
M. A. Matar, S. S. Darwish, R. S. Salma, W. A. Lotfy
European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry.2023; 24(5): 549. CrossRef - In-vitro evaluation of the anti-cariogenic effect of a hybrid coating associated with encapsulated sodium fluoride and stannous chloride in nanoclays on enamel
Sávio José Cardoso BEZERRA, Ítallo Emídio Lira VIANA, Idalina Vieira AOKI, Simone DUARTE, Anderson Takeo HARA, Taís SCARAMUCCI
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Salivary Fluoride Concentration after Topical Application of Silver Diamine Fluoride and Sodium Fluoride: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Nidhi Agarwal, V Vishnu Priya, Zohra Jabin, Iffat Nasim
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2022; 15(3): 371. CrossRef - Release and Recharge of Fluoride Ions from Acrylic Resin Modified with Bioactive Glass
Zbigniew Raszewski, Danuta Nowakowska, Wlodzimierz Wieckiewicz, Agnieszka Nowakowska-Toporowska
Polymers.2021; 13(7): 1054. CrossRef - Enamel remineralisation-inducing materials for caries prevention
Sri Kunarti, Widya Saraswati, Dur Muhammad Lashari, Nadhifa Salma, Tasya Nafatila
Dental Journal.2021; 54(3): 165. CrossRef - Fluoride Concentration in Saliva following Professional Topical Application of 2% Sodium Fluoride Solution
Manjit Talwar, Amrit Tewari, H. S. Chawla, Vinod Sachdev, Suresh Sharma
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2019; 10(3): 423. CrossRef - Clinical and laboratory evaluation of the Elgydium Protection caries toothpaste effectiveness in patients with high intensity of dental caries
O. A. Zorina, N. B. Petruhina, A. Z. M, O. A. Boriskina, A. A. Tupicin, V. A. Prohodnaja
Stomatologiya.2019; 98(3): 21. CrossRef - Bleaching of simulated stained-remineralized caries lesions in vitro
Sarah S. Al-Angari, Frank Lippert, Jeffrey A. Platt, George J. Eckert, Carlos González-Cabezas, Yiming Li, Anderson T. Hara
Clinical Oral Investigations.2019; 23(4): 1785. CrossRef - Short-Time Antibacterial Effects of Dimethylaminododecyl Methacrylate on Oral Multispecies Biofilm In Vitro
Yujie Zhou, Suping Wang, Xuedong Zhou, Yiran Zou, Mingyun Li, Xian Peng, Biao Ren, Hockin H. K. Xu, Michael D. Weir, Lei Cheng, Yu Chen, Qi Han
BioMed Research International.2019; 2019: 1. CrossRef - Comparison of the Application of Different Fluoride Supplements on Enamel Demineralization Adjacent to Orthodontic Brackets: An In Vitro Study
Arman Mohammadi Shayan, Monireh Rassouli, Soodabeh Kimyai, Hadi Valizadeh, Mohammad Hossein Ahangar Atashi, Sahand Rikhtegaran
Iranian Journal of Orthodontics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of nicomethanol hydrofluoride on dental enamel and synthetic apatites: a role for anti-caries protection
N. Sharkov
European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry.2017; 18(6): 411. CrossRef - Intérêt prophylactique et thérapeutique des chewing-gums sans sucre en orthodontie. Une étude menée auprès de professionnels de santé et de patients
Pauline Ferney, François Clauss, Damien Offner, Delphine Wagner
L'Orthodontie Française.2017; 88(3): 275. CrossRef - Silver Diamine Fluoride Has Efficacy in Controlling Caries Progression in Primary Teeth: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Ana Cláudia Chibinski, Letícia Maíra Wambier, Juliana Feltrin, Alessandro Dourado Loguercio, Denise Stadler Wambier, Alessandra Reis
Caries Research.2017; 51(5): 527. CrossRef - Dental Caries Management of a Patient with a High Caries Risk Based on the Caries Risk Assessment: a Case Peport
Dong-Hyun Lee, Sung-Ok Hong, Seok-Ryun Lee
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2016; 43(3): 231. CrossRef
- Effect of Different Topical Fluorides on the Microhardness of Bleached Enamel: In Vitro Study
- 2,029 View
- 13 Download
- 18 Crossref

-
How to design
in situ studies: an evaluation of experimental protocols - Young-Hye Sung, Hae-Young Kim, Ho-Hyun Son, Juhea Chang
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(3):164-171. Published online May 13, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.3.164
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Designing
in situ models for caries research is a demanding procedure, as both clinical and laboratory parameters need to be incorporated in a single study. This study aimed to construct an informative guideline for planningin situ models relevant to preexisting caries studies.Materials and Methods An electronic literature search of the PubMed database was performed. A total 191 of full articles written in English were included and data were extracted from materials and methods. Multiple variables were analyzed in relation to the publication types, participant characteristics, specimen and appliance factors, and other conditions. Frequencies and percentages were displayed to summarize the data and the Pearson's chi-square test was used to assess a statistical significance (
p < 0.05).Results There were many parameters commonly included in the majority of
in situ models such as inclusion criteria, sample sizes, sample allocation methods, tooth types, intraoral appliance types, sterilization methods, study periods, outcome measures, experimental interventions, etc. Interrelationships existed between the main research topics and some parameters (outcome measures and sample allocation methods) among the evaluated articles.Conclusions It will be possible to establish standardized
in situ protocols according to the research topics. Furthermore, data collaboration from comparable studies would be enhanced by homogeneous study designs.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- What is the effectiveness of titanium tetrafluoride to prevent or treat dental caries and tooth erosion? A systematic review
Ana Beatriz Chevitarese, Karla Lorene de França Leite, Guido A. Marañón-Vásquez, Danielle Masterson, Matheus Pithon, Lucianne Cople Maia
Acta Odontologica Scandinavica.2022; 80(6): 441. CrossRef - Effect of fluoride group on dental erosion associated or not with abrasion in human enamel: A systematic review with network metanalysis
Bruna Machado da Silva, Daniela Rios, Gerson Aparecido Foratori-Junior, Ana Carolina Magalhães, Marília Afonso Rabelo Buzalaf, Silvia De Carvalho Sales Peres, Heitor Marques Honório
Archives of Oral Biology.2022; 144: 105568. CrossRef - Multimodal Human and Environmental Sensing for Longitudinal Behavioral Studies in Naturalistic Settings: Framework for Sensor Selection, Deployment, and Management
Brandon M Booth, Karel Mundnich, Tiantian Feng, Amrutha Nadarajan, Tiago H Falk, Jennifer L Villatte, Emilio Ferrara, Shrikanth Narayanan
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2019; 21(8): e12832. CrossRef - Evaluation of an antibacterial orthodontic adhesive incorporated with niobium-based bioglass: an in situ study
Felipe Weidenbach DEGRAZIA, Aline Segatto Pires ALTMANN, Carolina Jung FERREIRA, Rodrigo Alex ARTHUR, Vicente Castelo Branco LEITUNE, Susana Maria Werner SAMUEL, Fabrício Mezzomo COLLARES
Brazilian Oral Research.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - A Review of the Common Models Used in Mechanistic Studies on Demineralization-Remineralization for Cariology Research
Ollie Yiru Yu, Irene Shuping Zhao, May Lei Mei, Edward Chin-Man Lo, Chun-Hung Chu
Dentistry Journal.2017; 5(2): 20. CrossRef - Effects of rinsing with arginine bicarbonate and urea solutions on initial enamel lesions in situ
Y Yu, X Wang, C Ge, B Wang, C Cheng, Y‐H Gan
Oral Diseases.2017; 23(3): 353. CrossRef - The cariogenicity of commercial infant formulas: a systematic review
S. F. Tan, H. J. Tong, X. Y. Lin, B. Mok, C. H. Hong
European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry.2016; 17(3): 145. CrossRef - In situ antibiofilm effect of glass-ionomer cement containing dimethylaminododecyl methacrylate
Jin Feng, Lei Cheng, Xuedong Zhou, Hockin H.K. Xu, Michael D. Weir, Markus Meyer, Hans Maurer, Qian Li, Matthias Hannig, Stefan Rupf
Dental Materials.2015; 31(8): 992. CrossRef
- What is the effectiveness of titanium tetrafluoride to prevent or treat dental caries and tooth erosion? A systematic review
- 1,321 View
- 4 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Early caries detection using optical coherence tomography: a review of the literature
- Young-Seok Park, Byeong-Hoon Cho, Seung-Pyo Lee, Won-Jun Shon
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(5):367-376. Published online September 14, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.5.367
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Abstract Early detection of carious lesions increases the possibility of treatment without the need for surgical intervention. Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is an emerging three-dimensional imaging technique that has been successfully used in other medical fields, such as ophthalmology for optical biopsy, and is a prospective candidate for early caries detection. The technique is based on low coherence interferometry and is advantageous in that it is non-invasive, does not use ionizing radiation, and can render three-dimensional images. A brief history of the development of this technique and its principles are discussed in this paper. There have been numerous studies on caries detection, which were mostly
in vitro orex vivo experiments. Through these studies, the feasibility of OCT for caries detection was confirmed. However, further research should be performed, includingin vivo studies of OCT applications, in order to prove the clinical usefulness of this technique. In addition, some technological problems must be resolved in the near future to allow for the use of OCT in everyday practice.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Differential diagnosis of periapical cyst using collagen birefringence pattern of the cyst wall
Hyo Jin Ji, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho, Suk Keun Lee, Jin Woo Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2017; 42(2): 111. CrossRef - How to designin situstudies: an evaluation of experimental protocols
Young-Hye Sung, Hae-Young Kim, Ho-Hyun Son, Juhea Chang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(3): 164. CrossRef
- Differential diagnosis of periapical cyst using collagen birefringence pattern of the cyst wall
- 2,239 View
- 14 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Elemental analysis of the fluoride varnish effects on root caries initiation
- Se-Eun Park, Keewook Yi, Hae-Young Kim, Ho-Hyun Son, Juhea Chang
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(4):290-299. Published online July 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.4.290
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The usage of fluoride varnish for a moderate to low caries-risk group has not been well validated. This study aimed to evaluate the preventive and therapeutic efficacies of fluoride varnish on the initiated root caries.
Materials and Methods Ten premolars were sectioned into quarters, further divided into two windows, one of which was painted with Fluor Protector (1,000 ppm fluoride, Ivoclar Vivadent). An initial lesion with a well-preserved surface layer was produced by pH cycling. Scanned line analysis using energy dispersive spectrometry determined the weight percentages of Ca and P in the demineralized layer. Scanning Electron microscopy and confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) evaluated the varnish-applied root surfaces.
Results The mean lesion depth (SD) was 12.3 (2.6) µm (single cycling) and 19.6 (3.8) µm (double cycling). Double cycling extended the lesion depth, but induced no more mineral loss than single cycling (
p < 0.05). The mean weight percentages of Ca and P between groups with and without varnish were not significantly different (p < 0.05). A CLSM showed varnish remained within 15 µm of the surface layer.Conclusions When a mild acid challenge initiated root tissue demineralization, the application of low-concentration fluoride varnish did not influence the lesion depth or the mineral composition of the subsurface lesion.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The combined occluding effect of sodium fluoride varnish and Nd:YAG laser irradiation on dentinal tubules—A CLSM and SEM study
Samet Tosun, Emre Culha, Ugur Aydin, Abdul Semih Ozsevik
Scanning.2016; 38(6): 619. CrossRef - How to designin situstudies: an evaluation of experimental protocols
Young-Hye Sung, Hae-Young Kim, Ho-Hyun Son, Juhea Chang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(3): 164. CrossRef - Evaluation of release of fluoride from dental varnishes marketed in Korea
Han-Na Kim, Myung-Su Jeong, Se-Yeon Kim, Jin-Bom Kim, Seung-Hwa Jeong
Journal of Korean Academy of Oral Health.2014; 38(3): 131. CrossRef
- The combined occluding effect of sodium fluoride varnish and Nd:YAG laser irradiation on dentinal tubules—A CLSM and SEM study
- 1,522 View
- 4 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Theory of X-ray microcomputed tomography in dental research: application for the caries research
- Young-Seok Park, Kwang-Hak Bae, Juhea Chang, Won-Jun Shon
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(2):98-107. Published online March 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.2.98
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Caries remains prevalent throughout modern society and is the main disease in the field of dentistry. Although studies of this disease have used diverse methodology, recently, X-ray microtomography has gained popularity as a non-destructive, 3-dimensional (3D) analytical technique, and has several advantages over the conventional methods. According to X-ray source, it is classified as monochromatic or polychromatic with the latter being more widely used due to the high cost of the monochromatic source despite some advantages. The determination of mineral density profiles based on changes in X-ray attenuation is the principle of this method and calibration and image processing procedures are needed for the better image and reproducible measurements. Using this tool, 3D reconstruction is also possible and it enables to visualize the internal structures of dental caries. With the advances in the computer technology, more diverse applications are being studied, such automated caries assessment algorithms.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Synchrotron X-ray Studies of the Structural and Functional Hierarchies in Mineralised Human Dental Enamel: A State-of-the-Art Review
Cyril Besnard, Ali Marie, Sisini Sasidharan, Robert A. Harper, Richard M. Shelton, Gabriel Landini, Alexander M. Korsunsky
Dentistry Journal.2023; 11(4): 98. CrossRef - Revelation of microcracks as tooth structural element by X-ray tomography and machine learning
Irma Dumbryte, Donatas Narbutis, Arturas Vailionis, Saulius Juodkazis, Mangirdas Malinauskas
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Three-dimensional non-destructive visualization of teeth enamel microcracks using X-ray micro-computed tomography
Irma Dumbryte, Arturas Vailionis, Edvinas Skliutas, Saulius Juodkazis, Mangirdas Malinauskas
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Radiological Appraisal of Biodentine and Pulpotec Individually or in Combination with Photo-activated Disinfection as Pulp-capping Cements in Mature Teeth
Pratik Agrawal, Gaurav Patri, Surabhi Soumya, Prasanti K Pradhan, Vijeta Patri
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2021; 22(9): 1014. CrossRef - Ex vivoevaluation of new 2D and 3D dental radiographic technology for detecting caries
Laurence Gaalaas, Donald Tyndall, André Mol, Eric T Everett, Ananta Bangdiwala
Dentomaxillofacial Radiology.2016; 45(3): 20150281. CrossRef - Stationary intraoral digital tomosynthesis using a carbon nanotube X-ray source array
J Shan, A W Tucker, L R Gaalaas, G Wu, E Platin, A Mol, J Lu, O Zhou
Dentomaxillofacial Radiology.2015; 44(9): 20150098. CrossRef - Comparative efficacy of photo-activated disinfection and calcium hydroxide for disinfection of remaining carious dentin in deep cavities: a clinical study
Sidhartha Sharma, Ajay Logani, Naseem Shah
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(3): 195. CrossRef - Current status of dental caries diagnosis using cone beam computed tomography
Young-Seok Park, Jin-Soo Ahn, Ho-Beom Kwon, Seung-Pyo Lee
Imaging Science in Dentistry.2011; 41(2): 43. CrossRef
- Synchrotron X-ray Studies of the Structural and Functional Hierarchies in Mineralised Human Dental Enamel: A State-of-the-Art Review
- 2,389 View
- 11 Download
- 8 Crossref

- The effect of lactic acid concentration and ph of lactic acid buffer solutions on enamel remineralization
- Jung-Won Kwon, Duk-Gyu Suh, Yun-Jung Song, Yun Lee, Chan-Young Lee
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(6):507-517. Published online November 30, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.6.507
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub There are considerable in vitro and in vivo evidences for remineralization and demineralization occurring simultaneously in incipient enamel caries. In order to "heal"the incipient dental caries, many experiments have been carried out to determine the optimal conditions for remineralization. It was shown that remineralization is affected by different pH, lactic acid concentrations, chemical composition of the enamel, fluoride concentrations, etc.
Eighty specimens from sound permanent teeth without demineralization or cracks, 0.15 mm in thickness, were immersed in lactic acid buffered demineralization solutions for 3 days. Dental caries with a surface zone and subsurface lesion were artificially produced. Groups of 10 specimens were immersed for 10 or 12 days in lactic acid buffered remineralization solutions consisting of pH 4.3 or pH 6.0, and 100, 50, 25, or 10 mM lactic acid. After demineralization and remineralization, images were taken by polarizing microscopy (x100) and micro-computed tomography. The results were obtained by observing images of the specimens and the density of the caries lesions was determined.
As the lactic acid concentration of the remineralization solutions with pH 4.3 was higher, the surface zone of the carious enamel increased and an isotropic zone of the subsurface lesion was found. However, the total decalcification depth increased at the same time.
In the remineralization solutions with pH 6.0, only the surface zone increased slightly but there was no significant change in the total decalcification depth and subsurface zone.
In the lactic acid buffer solutions with the lower pH and higher lactic acid concentration, there were dynamic changes at the deep area of the dental carious lesion.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of fluoride concentration in pH 4.3 and pH 7.0 supersaturated solutions on the crystal growth of hydroxyapatite
Haneol Shin, Sung-Ho Park, Jeong-Won Park, Chan-Young Lee
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(1): 16. CrossRef
- Effect of fluoride concentration in pH 4.3 and pH 7.0 supersaturated solutions on the crystal growth of hydroxyapatite
- 1,379 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The influence of pH and lactic acid concentration on the formation of artificial root caries in acid buffer solution
- Hyun-Suk Oh, Byoung-Duck Roh, Chan-Young Lee
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(1):47-60. Published online January 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.1.047
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study is to compare and to evaluate the effect of pH and lactic acid concentration on the progression of artificial root caries lesion using polarizing microscope, and to evaluate the morphological changes of hydroxyapatite crystals of the demineralized area and to investigate the process of demineralization using scanning electron microscope.
Artificial root caries lesion was created by dividing specimens into 3 pH groups (pH 4.3, 5.0, 5.5), and each pH group was divided into 3 lactic acid concentration groups (25 mM, 50 mM, 100 mM). Each group was immersed in acid buffer solution for 5 days and examined. The results were as follows:
1. Under polarized microscope, the depth of lesion was more effected by the lactic acid concentration rather than the pH.
2. Under scanning electron microscope, dissolution of hydroxyapatite crystals were increased as the lactic acid concentration increased and the pH decreased.
3. Demineralized hydroxyapatite crystals showed peripheral dissolution and decreased size and number within cluster of hydroxyapatite crystals and widening of intercluster and intercrystal spaces as the pH decreased and the lactic acid concentration increased.
4. Under scanning electron microscope evaluation of the surface zone, clusters of hydroxyapatite crystals were dissolved, and dissolution and reattachment of crystals on the surface of collagen fibrils were observed as the lactic acid concentration increased.
5. Under scanning electron microscope, demineralization of dentin occurred not only independently but also with remineralization simultaneously.
In conclusion, the study showed that pH and lactic acid concentration influenced the rate of progression of the lesion in artificial root caries. Demineralization process was progressed from the surface of the cluster of hydroxyapatite crystals and the morphology of hydroxyapatite crystals changed from round or elliptical shape into irregular shape as time elapsed.
- 903 View
- 7 Download

- The efficacy of chemo-mechanical removal of dentin carious lesion
- Soon-Bin Lim, Kyung-Kyu Choi, Sang-Jin Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(3):149-157. Published online May 31, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.3.149
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Mechanical removals in decayed teeth have been performed using drill and sharp hand instruments. These methods have some disadvantages such as pain, local anesthesia and overextended cavities. Therefore chemo-mechanical excavation of dentin carious lesions has been introduced. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the efficacy of traditional mechanical methods using burs and chemo-mechanical methods (Carisolv) of caries dentin.
Mechanical caries removal was carried with low speed round bur. Chemo-mechanical caries excavation was performed with Carisolv (Medi-team), using the Carisolv hand instruments. The mean time to remove caries with two different methods was evaluated and the data analyzed with SPSS software (ver 11.5) by t-test (p < 0.05). For histomorphometry of caries removal were also carried with mechanical or chemo-mechanical (Carisolv) methods from 20 extracted caries permanent molars. Complete caries removal was verified with a #23 sharp explorers, Caries Detector (Kuraray Co. Japan), and standard apical radiography.
1. Chemo-mechanical method was taken more times than mechanical method (1.5 fold) (p < 0.05).
2. Excavation for caries took more time for molar lesion than premolar lesion, and the least time was taken to remove the caries in incisor lesion (p < 0.05).
3. There were no significant differences to remove the caries between the maxilla and mandible (p > 0.05).
4. The remaining carious dentin was detected after the chemo-mechanical removal of the carious dentin, and no smear layer were seen after the mechanical and chemo-mechanical removal of the carious dentin.
- 716 View
- 2 Download

- Microtensile bond strength of all-in-one adhesive to caries-affected dentin
- Ji-Deok Moon, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(1):49-57. Published online January 31, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.1.049
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of multiple application of all-in-one dentin adhesive system on microtensile bond strength to caries-affected dentin.
Twenty one extracted human molars with occlusal caries extending into mid-dentin were prepared by grinding the occlusal surface flat. The carious lesions were excavated with the aid of caries detector dye. The following adhesives were applied to caries-affected dentin according to manufacturer's directions; Scotchbond™ Multi-Purpose in SM group, Adper Prompt L-Pop™ 1 coat in LP1 group, 2 coats in LP2 group, 3 coats in LP3 group, Xeno® III 1 coat in XN1 group, 2 coats in XN2 group, and 3 coats in XN3 group. After application of the adhesives, a cylinder of resin-based composite was built up on the occlusal surface. Each tooth was sectioned vertically to obtain the 1 × 1 mm2 sticks. The microtensile bond strength was determined. Each specimen was observed under SEM to examine the failure mode. Data were analyzed with one-way ANOVA.
The results of this study were as follows;
1. The microtensile bond strength values were; SM (14.38 ± 2.01 MPa), LP1 (9.15 ± 1.81 MPa), LP2 (14.08 ± 1.75 MPa), LP3 (14.06 ± 1.45 MPa), XN1 (13.65 ± 1.95 MPa), XN2 (13.98 ± 1.60 MPa), XN3 (13.88 ± 1.66 MPa). LP1 was significantly lower than the other groups in bond strength (p < 0.05). All groups except LP1 were not significantly different in bond strength (p > 0.05).
2. In LP1, there were a higher number of specimens showing adhesive failure. Most specimens of all groups except LP1 showed mixed failure.
- 883 View
- 4 Download

-
In vivo quantitative analysis of remineralization effect of remineralization solution "R" of incipient enamel dental caries - Myung-Eun Kim, Il-young Jung, Kee-Yeon Kum, Chang-young Lee, Byoung-Duck Roh
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2002;27(2):175-182. Published online March 31, 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2002.27.2.175
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Dental caries is a chronic disease that causes the destruction of tooth structure by the interaction of plaque bacteria, food debris, and saliva.
There has been attempts to induce remineralization by supersaturating the intra-oral environment around the surface enamel, where there is incipient caries.
In this study, supersaturated remineralized solution "R" was applied to specimens with incipient enamel caries, and the quantitative ananlysis of remineralization was evaluated using microradiography. Thirty subjects volunteered to participate in this study. Removable appliances were constructed for the subjects, and the enamel specimen with incipient caries were embedded in the appliances. The subjects wore the intra-oral appliance for 15 days except while eating and sleeping.
The removable appliance were soaked in supersaturated solution "R", saline, or Senstime® to expose the specimen to those solutions three times a day, 5 minutes each time. After 15 days, microradiography was retaken to compare and evaluate remineralization.
The results were as the following:
1. The ratio of remineralized area to demineralized area was significantly higher in the supersaturated solution "R" and Senstime® than in the saline. (p<0.05)
2. Remineralization in the supersaturated buffer solution "R" occurred in the significantly deeper parts of the tooth, compared to the Senstime® group containing high concentration of fluoride.(p<0.05)
As in the above results, the remineralization effect of remineralized buffer solution "R" on incipient enamel caries has been proven. For clinical utilization, further studies on soft tissue reaction and the effect on dentin and cementum are necessary.
In conclusion compared to commercially available fluoride solution, remineralization solution "R" showed better remineralization effect on early enamel caries lesion, so it is considered as effecient solution for clinical application.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Color and hardness changes in artificial white spot lesions after resin infiltration
Ji-Hoon Kim, Ho-Hyun Son, Juhea Chang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(2): 90. CrossRef - Changes in surface content and crystal structure after fluoride gel or hydroxyapatite paste application on stripped enamel
Sang-Cheol Kim, Hyun-Sil Hong, Young-Cheol Hwang
The Korean Journal of Orthodontics.2008; 38(6): 407. CrossRef
- Color and hardness changes in artificial white spot lesions after resin infiltration
- 1,065 View
- 9 Download
- 2 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


