Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Effects of a relined fiberglass post with conventional and self-adhesive resin cement
- Wilton Lima dos Santos Junior, Marina Rodrigues Santi, Rodrigo Barros Esteves Lins, Luís Roberto Marcondes Martins
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(2):e18. Published online March 27, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e18
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
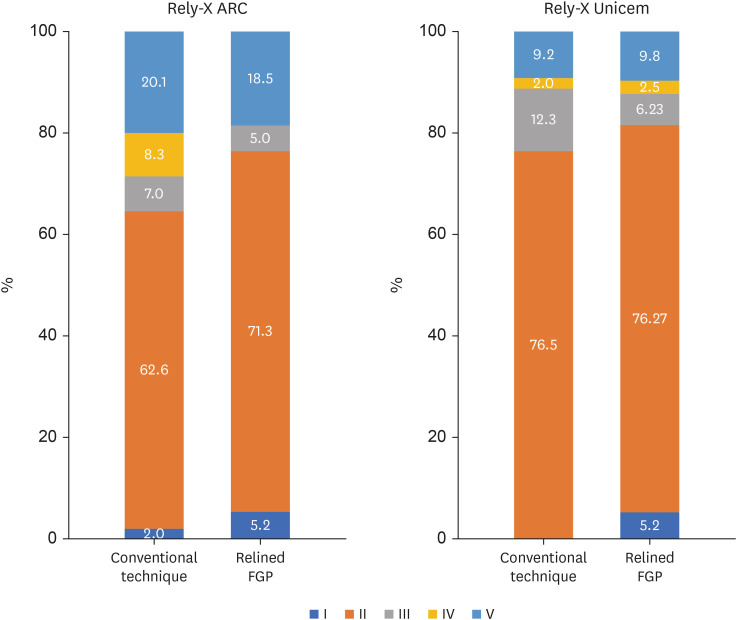
ePub Objectives This study was conducted to evaluate the mechanical properties of relined and non-relined fiberglass posts when cemented to root canal dentin using a conventional dual-cure resin cement or a self-adhesive resin cement.
Materials and Methods Two types of resin cements were utilized: conventional and self-adhesive. Additionally, 2 cementation protocols were employed, involving relined and non-relined fiberglass posts. In total, 72 bovine incisors were cemented and subjected to push-out bond strength testing (
n = 10) followed by failure mode analysis. The cross-sectional microhardness (n = 5) was assessed along the root canal, and interface analyses (n = 3) were conducted using scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Data from the push-out bond strength and cross-sectional microhardness tests were analyzed via 3-way analysis of variance and the Bonferronipost-hoc test (α = 0.05).Results For non-relined fiberglass posts, conventional resin cement exhibited higher push-out bond strength than self-adhesive cement. Relined fiberglass posts yielded comparable results between the resin cements. Type II failure was the most common failure mode for both resin cements, regardless of cementation protocol. The use of relined fiberglass posts improved the cross-sectional microhardness values for both cements. SEM images revealed voids and bubbles in the incisors with non-relined fiberglass posts.
Conclusions Mechanical properties were impacted by the cementation protocol. Relined fiberglass posts presented the highest push-out bond strength and cross-sectional microhardness values, regardless of the resin cement used (conventional dual-cure or self-adhesive). Conversely, for non-relined fiberglass posts, the conventional dual-cure resin cement yielded superior results to the self-adhesive resin cement.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Push-Out Bond Strength of Different Luting Cements Following Post Space Irrigation with 2% Chitosan: An In Vitro Study
Shimaa Rifaat, Ahmed Rahoma, Hind Muneer Alharbi, Sawsan Jamal Kazim, Shrouq Ali Aljuaid, Basmah Omar Alakloby, Faraz A. Farooqi, Noha Taymour
Prosthesis.2025; 7(1): 18. CrossRef
- Push-Out Bond Strength of Different Luting Cements Following Post Space Irrigation with 2% Chitosan: An In Vitro Study
- 4,842 View
- 130 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

-
Effectiveness and safety of rotary and reciprocating kinematics for retreatment of curved root canals: a systematic review of
in vitro studies - Lucas Pinho Simões, Alexandre Henrique dos Reis-Prado, Carlos Roberto Emerenciano Bueno, Ana Cecília Diniz Viana, Marco Antônio Húngaro Duarte, Luciano Tavares Angelo Cintra, Cleidiel Aparecido Araújo Lemos, Francine Benetti
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(2):e22. Published online April 6, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e22
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
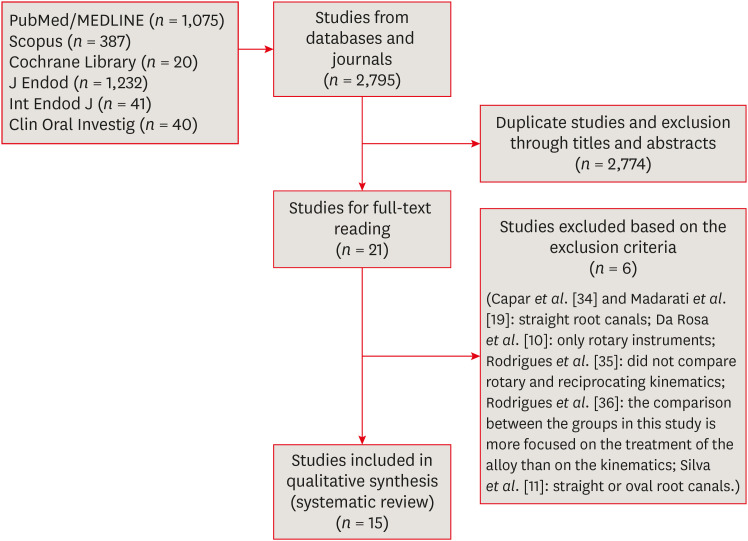
ePub Objectives This systematic review (register-osf.io/wg7ba) compared the efficacy and safety of rotary and reciprocating kinematics in the removal of filling material from curved root canals.
Materials and Methods Only
in vitro studies evaluating both kinematics during retreatment were included. A systematic search (PubMed/MEDLINE, Scopus, and other databases, until January 2021), data extraction, and risk of bias analysis (Joanna Briggs Institute checklist) were performed. Efficacy in filling removal was the primary outcome.Results The search resulted in 2,795 studies, of which 15 were included. Efficacy was measured in terms of the remaining filling material and the time required for this. Nine studies evaluated filling material removal, of which 7 found no significant differences between rotary and reciprocating kinematics. Regarding the time for filling removal, 5 studies showed no difference between both kinematics, 2 studies showed faster results with rotary systems, and other 2 showed the opposite. No significant differences were found in apical transportation, centering ability, instrument failure, dentin removed and extruded debris. A low risk of bias was observed.
Conclusions This review suggests that the choice of rotary or reciprocating kinematics does not influence the efficacy of filling removal from curved root canals. Further studies are needed to compare the kinematics safety in curved root canals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- EVALUATION OF MICROLEAKAGE AFTER ENDODONTIC FILLING IN TEETH WITH APICAL WIDENING: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
Isabella da Costa Ferreira, Gabriela da Costa Ferreira, Isabella Figueiredo de Assis Macedo, Gustavo Oliveira Campos, Isabella Faria da Cunha Peixoto, Ana Cecília Diniz Viana, Rodrigo Rodrigues Amaral, Warley Luciano Fonseca Tavares
ARACÊ .2025; 7(10): e8792. CrossRef - Fifteen years of engine‐driven nickel–titanium reciprocating instruments, what do we know so far? An umbrella review
Felipe Immich, Lucas Peixoto de Araújo, Rafaella Rodrigues da Gama, Wellington Luiz de Oliveira da Rosa, Evandro Piva, Giampiero Rossi‐Fedele
Australian Endodontic Journal.2024; 50(2): 409. CrossRef - Efficacy of Various Heat-treated Retreatment File Systems on the Apical Deformity and Canal Centering Ability in a Single-rooted Teeth using Nano CT
Swathi S, Pradeep Solete, Ganesh Jeevanandan, Delphine Priscilla Antony S, Kavalipurapu Venkata Teja, Dona Sanju
The Open Dentistry Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Micro-CT evaluation of the removal of root fillings using rotary and reciprocating systems supplemented by XP-Endo Finisher, the Self-Adjusting File, or Er,Cr:YSGG laser
Gülsen Kiraz, Bulem Üreyen Kaya, Mert Ocak, Muhammet Bora Uzuner, Hakan Hamdi Çelik
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of sodium hypochlorite on cyclic fatigue resistance of nickel–titanium instruments: A systematic review and meta-analysis of in vitro studies
Alexandre Henrique dos Reis-Prado, Lucas Guimarães Abreu, Lara Cancella de Arantes, Kiani dos Santos de Paula, Sabrina de Castro Oliveira, Juliana Goto, Ana Cecília Diniz Viana, Francine Benetti
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(11): 6291. CrossRef - Retreatment of XP-endo Shaper and R-Endo files in curved root canals
Hayam Y. Hassan, Fahd M. Hadhoud, Ayman Mandorah
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Advancing Endodontics through Kinematics
Shilpa Bhandi, Dario Di Nardo, Francesco Pagnoni, Rosemary Abbagnale
World Journal of Dentistry.2023; 14(6): 479. CrossRef
- EVALUATION OF MICROLEAKAGE AFTER ENDODONTIC FILLING IN TEETH WITH APICAL WIDENING: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
- 3,160 View
- 58 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref

-
Cyclic fatigue resistance of M-Pro and RaCe Ni-Ti rotary endodontic instruments in artificial curved canals: a comparative
in vitro study - Hadeer Mostafa El Feky, Khalid Mohammed Ezzat, Marwa Mahmoud Ali Bedier
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(4):e44. Published online November 7, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e44

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
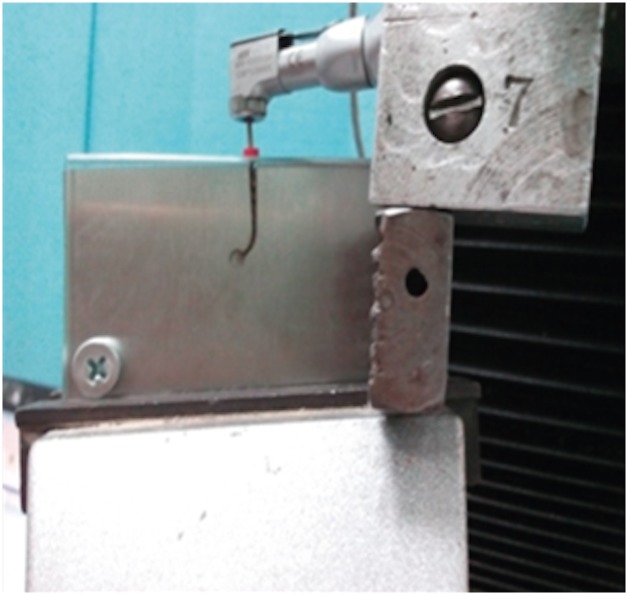
ePub Objectives To compare the flexural cyclic fatigue resistance and the length of the fractured segments (FLs) of recently introduced M-Pro rotary files with that of RaCe rotary files in curved canals and to evaluate the fracture surface by scanning electron microscopy (SEM).
Materials and Methods Thirty-six endodontic files with the same tip size and taper (size 25, 0.06 taper) were used. The samples were classified into 2 groups (n = 18): the M-Pro group (M-Pro IMD) and the RaCe group (FKG). A custom-made simulated canal model was fabricated to evaluate the total number of cycles to failure and the FL. SEM was used to examine the fracture surfaces of the fragmented segments. The data were statistically analyzed and comparisons between the 2 groups for normally distributed numerical variables were carried out using the independent Student's
t -test. Ap value less than 0.05 was considered to indicate statistical significance.Results The M-Pro group showed significantly higher resistance to flexural cyclic fatigue than the RaCe group (
p < 0.05), but there was no significant difference in the FLs between the 2 groups (p ≥ 0.05).Conclusions Thermal treatment of nickel-titanium instruments can improve the flexural cyclic fatigue resistance of rotary endodontic files, and the M-Pro rotary system seems to be a promising rotary endodontic file.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of Canal Curvature and Different Manufacturing Processes of Five Different NiTi Rotary Files on Cyclic Fatigue Resistance
Panupat Phumpatrakom, Awiruth Klaisiri, Sukitti Techapatiphandee, Thippawan Saekow, Panuroot Aguilar
European Journal of General Dentistry.2025; 14(03): 264. CrossRef - EndoMagic Gold M06 Eğelerinde Boyut ve Konikliğin Döngüsel Yorgunluğa Etkisi: Bir İn Vitro Çalışma
Bircan Kuloğlu, Ayşe Çoban, Hatice Büyüközer Özkan
Akdeniz Diş Hekimliği Dergisi.2025; 4(3): 212. CrossRef - Evaluatation of two nickle-titanium systems’ (Neolix and X Pro Gold) resistance to fracture after immersion in sodium hypochlorite.
Solmaz Araghi, Abbas Delvarani, Faeze dehghan, Parisa Kaghazloo
journal of research in dental sciences.2024; 21(1): 17. CrossRef - Endodontic Ni–Ti Rotary Instruments for Glide-path, Are They Still Necessary and How to Think about the Ideal Instrument?
Shilpa Bhandi, Rodolfo Reda, Luca Testarelli, Elisa Maccari
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2024; 25(6): 505. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of cyclic fatigue resistance of thermomechanically treated NiTi rotary instruments in simulated curved canals with two different radii of curvature: An in vitro Study
Tahira Hamid, Azhar Malik, Ajay Kumar, Shamim Anjum
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(4): 393. CrossRef - New heat-treated vs electropolished nickel-titanium instruments used in root canal treatment: Influence of autoclave sterilization on surface roughness
Rahaf A. Almohareb, Reem Barakat, Fatimah Albohairy, Hannes C. Schniepp
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(3): e0265226. CrossRef - The Effect of Taper and Apical Diameter on the Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Rotary Endodontic Files Using an Experimental Electronic Device
Vicente Faus-Llácer, Nirmine Hamoud Kharrat, Celia Ruiz-Sánchez, Ignacio Faus-Matoses, Álvaro Zubizarreta-Macho, Vicente Faus-Matoses
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(2): 863. CrossRef
- The Effect of Canal Curvature and Different Manufacturing Processes of Five Different NiTi Rotary Files on Cyclic Fatigue Resistance
- 2,134 View
- 10 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Comparison of the shaping ability of novel thermally treated reciprocating instruments
- Cangül Keskin, Murat Demiral, Evren Sarıyılmaz
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(2):e15. Published online March 3, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e15
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
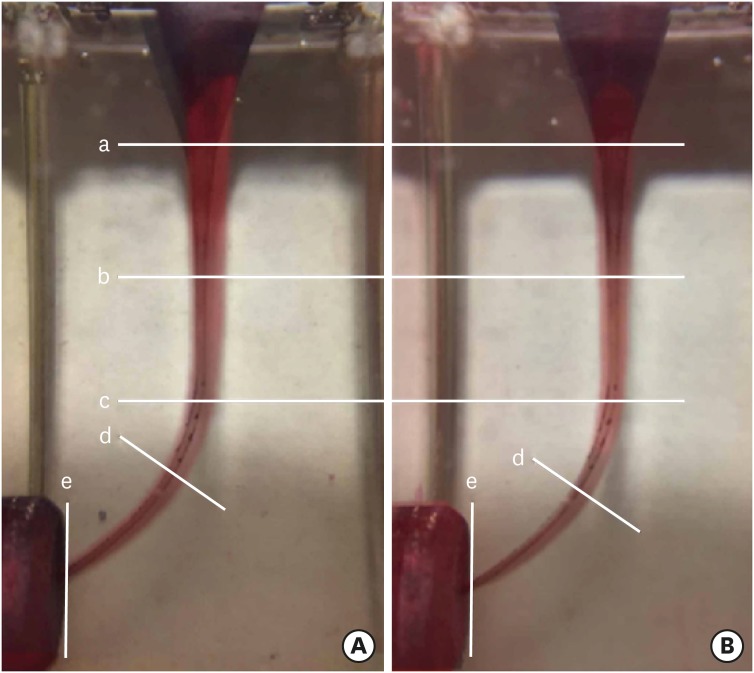
ePub Objectives The present study aimed to evaluate the shaping ability of 2 thermally treated nickel-titanium reciprocating systems in simulated curved canals.
Materials and Methods Forty simulated canals were prepared to apical size 25 using Reciproc Blue R25 (VDW) and WaveOne Gold Primary (Dentsply Sirona) instruments. Standard pre- and post-preparation images were taken and superimposed. The removal of resin material was measured at 5 standard points: the canal orifice, halfway between the canal orifice and the beginning of the curve, the beginning of the curve, the apex of the curve, and the end-point of the simulated canal. The data were analysed using the independent sample
t -test with a 5% significance threshold.Results The canals in which Reciproc Blue R25 was used showed a significantly greater widening than those in which WaveOne Gold was used at 4 of the 5 measurement points (
p < 0.05). The Reciproc Blue R25 instrument removed significantly more resin from the inner aspect of the curve at 2 of the 5 points and similar amounts at the remaining 3 points. At the 2 apical points, there was no significant difference between the Reciproc Blue R25 and WaveOne Gold Primary instruments.Conclusion Both instruments respected the original canal anatomy; however, WaveOne Gold resulted in a more conservative shape with less transportation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Centering Ability and Canal Transportation of Nickel-Titanium (NiTi) Single-File Systems With and Without Glide Path in Extracted Natural Teeth: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Indumathi Manoharan, Deblina Basu, Mathan Rajan
Cureus.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Shaping Ability of the Root Canal System Using Reciproc and Reciproc Blue in Preparation of Artificial Canals
Hawazin Majdi, Khalid Merdad, Tariq Abuhaimed, Lujain Mirdad, Omar Alkhattab, Abdulaziz Bakhsh
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of four different file systems in terms of transportation in S-shaped canals and apically extruded debris
Mustafa Alrahhal, Fatma Tunç
Journal of Oral Science.2024; 66(4): 226. CrossRef - Assessment of Debris Extrusion in Curved Canals: An In Vitro Analysis of Various Single‐File Endodontic Instrumentation Systems
Muhammad Zubair Ahmad, Boonlert Kukiattrakoon
International Journal of Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Shaping ability of rotary and reciprocating single-file systems in combination with and without different glide path techniques in simulated curved canals
Lu Shi, Yunfei Yang, Jie Wan, Wen Xie, Ruiming Yang, Ying Yao
Journal of Dental Sciences.2022; 17(4): 1520. CrossRef - An Investigation of the Accuracy and Reproducibility of 3D Printed Transparent Endodontic Blocks
Martin Smutný, Martin Kopeček, Aleš Bezrouk
Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove, Czech Republic).2022; 65(2): 59. CrossRef - Shaping Ability of Reciprocating Single-file Systems in Simulated Canals: Reciproc versus Reciproc Blue
İrem ÇETİNKAYA, Mukadder İnci BAŞER KOLCU
SDÜ Tıp Fakültesi Dergisi.2021; 28(1): 145. CrossRef - Combination of a new ultrasonic tip with rotary systems for the preparation of flattened root canals
Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Jáder Camilo Pinto, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Apical extrusion of debris with different rotary and reciprocating single-file endodontic instrumentation systems: a systematic review and meta-analysis protocol
Muhammad Zubair Ahmad, Durre Sadaf, Marcy McCall MacBain, Ahmed Nabil Mohamed
BMJ Open.2020; 10(9): e038502. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic assessment of the shaping ability of the One Curve, One Shape, and ProTaper Next nickel-titanium rotary systems
Pelin Tufenkci, Kaan Orhan, Berkan Celikten, Burak Bilecenoglu, Gurkan Gur, Semra Sevimay
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Changes in Geometry and Transportation of Root Canals with Severe Curvature Prepared by Different Heat-treated Nickel-titanium Instruments: A Micro–computed Tomographic Study
Daniel José Filizola de Oliveira, Graziela Bianchi Leoni, Rafael da Silva Goulart, Manoel Damião de Sousa-Neto, Yara Teresinha Correa Silva Sousa, Ricardo Gariba Silva
Journal of Endodontics.2019; 45(6): 768. CrossRef - Several factors can affect the root canal transportation of MB2 canals in extracted maxillary first molars
R. R. Vivan, M. P. Alcalde, E. J de Camargo, V. A. S. Marques, M. V. R. Só, J. A. Duque, M. A. H. Duarte
International Endodontic Journal.2019; 52(4): 551. CrossRef - Effect of larger apical size on the quality of preparation in curved canals using reciprocating instruments with different heat thermal treatments
J. A. Duque, R. R. Vivan, M. A. H. Duarte, M. P. Alcalde, V. M. Cruz, M. M. B. Borges, C. M. Bramante
International Endodontic Journal.2019; 52(11): 1652. CrossRef
- Centering Ability and Canal Transportation of Nickel-Titanium (NiTi) Single-File Systems With and Without Glide Path in Extracted Natural Teeth: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- 1,346 View
- 7 Download
- 13 Crossref

- Endodontic treatment of a C-shaped mandibular second premolar with four root canals and three apical foramina: a case report
- Thikamphaa Bertrand, Sahng Gyoon Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(1):68-73. Published online January 19, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.1.68

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This case report describes a unique C-shaped mandibular second premolar with four canals and three apical foramina and its endodontic management with the aid of cone-beam computer tomography (CBCT). C-shaped root canal morphology with four canals was identified under a dental operating microscope. A CBCT scan was taken to evaluate the aberrant root canal anatomy and devise a better instrumentation strategy based on the anatomy. All canals were instrumented to have a 0.05 taper using 1.0 mm step-back filing with appropriate apical sizes determined from the CBCT scan images and filled using a warm vertical compaction technique. A C-shaped mandibular second premolar with multiple canals is an anatomically rare case for clinicians, yet its endodontic treatment may require a careful instrumentation strategy due to the difficulty in disinfecting the canals in the thin root area without compromising the root structure.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Unique root anatomy of mandibular second premolars: clinical strategies for effective disinfection and preservation of dentine structure in root canal treatment—a case report
Ji Wook Jeong, Erika Silguero Gonzalez, Scott R. Makins, Timothy Kirkpatrick
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - PRICE 2020 guidelines for reporting case reports in Endodontics: explanation and elaboration
V. Nagendrababu, B. S. Chong, P. McCabe, P. K. Shah, E. Priya, J. Jayaraman, S. J. Pulikkotil, P. M. H. Dummer
International Endodontic Journal.2020; 53(7): 922. CrossRef - A cone-beam computed tomography study of C-shaped root canal systems in mandibular second premolars in a Taiwan Chinese subpopulation
Yi-Chin Chen, Chia-Lun Tsai, Yi-Chen Chen, Gin Chen, Shue-Fen Yang
Journal of the Formosan Medical Association.2018; 117(12): 1086. CrossRef - Anatomic Comparison of Contralateral Premolars
Gaute Floer Johnsen, Sazan Dara, Sameenah Asjad, Pia Titterud Sunde, Håvard Jostein Haugen
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(6): 956. CrossRef - Endodontic Management of Dilacerated Maxillary Central Incisor fused to a Supernumerary Tooth using Cone Beam Computed Tomography: An Unusual Clinical Presentation
Thilla S Vinothkumar, Deivanayagam Kandaswamy, Ganesh Arathi, Sathishkumar Ramkumar, Gnanasekaran Felsypremila
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2017; 18(6): 522. CrossRef
- Unique root anatomy of mandibular second premolars: clinical strategies for effective disinfection and preservation of dentine structure in root canal treatment—a case report
- 2,502 View
- 12 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Endodontic management of a maxillary first molar with three roots and seven root canals with the aid of cone-beam computed tomography
- Gurudutt Nayak, Kamal Krishan Singh, Rhitu Shekhar
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(3):241-248. Published online June 3, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.3.241
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Variation in root canal morphology, especially in maxillary first molar presents a constant challenge for a clinician in their detection and management. This case report describes the successful root canal treatment of a three rooted right maxillary first molar presenting with three canals each in the mesiobuccal and distobuccal roots and one canal in the palatal root. The clinical detection of this morphologic aberration was made using a dental operating microscope, and the canal configuration was established after correlating and computing the clinical, radiographic and cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) scan findings. CBCT images confirmed the configuration of the canals in the mesiobuccal and distobuccal roots to be Al-Qudah and Awawdeh type (3-2) and type (3-2-1), respectively, whereas the palatal root had a Vertucci type I canal pattern. This report reaffirms the importance of careful examination of the floor of the pulp chamber with a dental operating microscope and the use of multiangled preoperative radiographs along with advanced diagnostic aids such as CBCT in identification and successful management of aberrant canal morphologies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Inhibition potential of rhamnolipid biosurfactant against Corynespora cassiicola – a phytopathogen of king chilli
Nilam Sarma, Suresh Deka, Hemen Deka
Studia Biologica.2025; 19(3): 153. CrossRef - Endodontic Management of Maxillary First Molar with Seven Root Canals Diagnosed Using Cone-beam Computed Tomography: A Case Report
Ravindranath Megha, Venkatachalam Prakash
World Journal of Dentistry.2021; 12(1): 89. CrossRef - The MB3 canal in maxillary molars: a micro-CT study
Ronald Ordinola-Zapata, Jorge N. R. Martins, Hugo Plascencia, Marco A. Versiani, Clovis M. Bramante
Clinical Oral Investigations.2020; 24(11): 4109. CrossRef - Maxillary first molar with 7 root canals diagnosed using cone-beam computed tomography
Evaldo Rodrigues, Antônio Henrique Braitt, Bruno Ferraz Galvão, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2017; 42(1): 60. CrossRef - Endodontic management of a maxillary first molar with seven root canal systems evaluated using cone-beam computed tomography scanning
VijayReddy Venumuddala, Sridhar Moturi, SV Satish, BKalyan Chakravarthy, Sudhakar Malapati
Journal of International Society of Preventive and Community Dentistry.2017; 7(5): 297. CrossRef
- Inhibition potential of rhamnolipid biosurfactant against Corynespora cassiicola – a phytopathogen of king chilli
- 2,065 View
- 11 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Endodontic treatment of a mandibular first molar with 8 canals: a case report
- Ankit Arora, Shashi Rashmi Acharya, Padmaja Sharma
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(1):75-78. Published online October 13, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.1.75
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Presented here is a case where 8 canals were located in a mandibular first molar. A patient with continuing pain in mandibular left first molar even after completion of biomechanical preparation was referred by a dentist. Following basic laws of the pulp chamber floor anatomy, 8 canals were located in three steps with 4 canals in each root. In both of the roots, 4 separate canals commenced which joined into two canals and exited as two separate foramina. At 6 mon follow-up visit, the tooth was found to be asymptomatic and revealed normal radiographic periapical area. The case stresses on the fact that understanding the laws of pulp chamber anatomy and complying with them while attempting to locate additional canals can prevent missing canals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- How Do Different Image Modules Impact the Accuracy of Working Length Measurements in Digital Periapical Radiography? An In Vitro Study
Vahide Hazal Abat, Rabia Figen Kaptan
Diagnostics.2025; 15(3): 305. CrossRef - Determinants of the Number of Main Canals in a Tooth: Deciphering Potential Mechanisms
Andrea Alejandra Moreno Robalino, José Luis Álvarez Vásquez
Universitas Odontologica.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Application Of Cone-Beam Computed Tomography In Diagnosis And Treatment Of Multiple Canals– A Case Report
Gyanendra Pratap Singh, Shruthi H Attavar, Sivaji Kavuri
Annals of Dental Specialty.2022; 10(2): 15. CrossRef - Four distal root canals in a two-rooted permanent mandibular first molar
Urvashi M. Ujariya, Foram H. Patel, Rajendra P. Bharatiya, Anjali K. Kothari
Endodontology.2022; 34(3): 212. CrossRef - Utilizing Cone-Beam Computed Tomography for Identifying and Managing Multiple Canals: A Case Report
Gyanendra Pratap Singh, Shruthi H Attavar, Sivaji Kavuri
Journal of Current Research in Oral Surgery.2022; 2(1): 37. CrossRef - Morphology and prevalence of middle canals in the mandibular molars: A systematic review
Rashmi Bansal, Sapna Hegde, Madhusudan Astekar
Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology.2018; 22(2): 216. CrossRef - Endodontic management of a permanent mandibular first molar with unusual root canal configurations: Two case reports
Mohammad Ahmad Alenezi, Mustafa Aldajani, Hind O. Al-Qathami, Seraj Al-Shommrani
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2017; 7(3): 181. CrossRef
- How Do Different Image Modules Impact the Accuracy of Working Length Measurements in Digital Periapical Radiography? An In Vitro Study
- 4,082 View
- 26 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Endodontic treatment of maxillary lateral incisors with anatomical variations
- Moon-Hwan Lee, Jung-Hong Ha, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young-Kyung Kim, Sung-Kyo Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(4):253-257. Published online November 12, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.4.253
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Maxillary lateral incisors usually exhibit a single root with a single canal. However, maxillary lateral incisor teeth with unusual morphology of root canal system are frequently reported. These cases of variable root canal anatomy can be treated well by nonsurgical endodontic methods. A detailed description of root canal morphology is fundamental for successful endodontic treatment. Treatment using an operating microscope, radiographs from different angles, and cone-beam computerized tomography (CBCT) can produce more predictable endodontic outcomes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An upper left lateral incisor with double roots and double root canals: A case report
Zhou-Bin Xia, Jing Ren, Jia-Xiang Chen, Yu Wei, Yan Yan, Liang-Ju Cao
Medicine.2025; 104(26): e42815. CrossRef - Retreatment of Mandibular Incisors Associated With Root Canal Variations and Periapical Cyst: A Case Report With 3‐Year Follow‐Up
Kai Chen, Ni Li
Clinical Case Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Endodnontic Management of a Maxillary Lateral Incisor with Two Roots
Pujan Kranti Kayastha, Merina Shakya, Laxman Poudel
Journal of Interdisciplinary Dentistry.2022; 12(1): 32. CrossRef - Non-surgical management of dens invaginatus type IIIB in maxillary lateral incisor with three root canals and 6-year follow-up: A case report and review of literature
Suraj Arora, Gurdeep Singh Gill, Shahabe Abullais Saquib, Priyanka Saluja, Suheel M Baba, Shafait Ullah Khateeb, Anshad M Abdulla, Shashit Shetty Bavabeedu, Ahmed Babiker Mohamed Ali, Mohamed Fadul A Elagib
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2022; 10(33): 12240. CrossRef - Endodontic management and follow-up of two rooted maxillary lateral incisor with open apex – A case report
R AnithaKumari, Sneha Jeetendra, Siddharth Rai, Sudhanva Eregowda
IP Indian Journal of Conservative and Endodontics.2020; 5(4): 200. CrossRef - Geminated Maxillary Lateral Incisor with Two Root Canals
Nayara Romano, Luis Eduardo Souza-Flamini, Isabela Lima Mendonça, Ricardo Gariba Silva, Antonio Miranda Cruz-Filho
Case Reports in Dentistry.2016; 2016: 1. CrossRef - Surgical management with intentional replantation on a tooth with palato-radicular groove
Jorge Forero-López, Luis Gamboa-Martínez, Laura Pico-Porras, Javier Laureano Niño-Barrera
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(2): 166. CrossRef - Use of cone-beam computed tomography and three-dimensional modeling for assessment of anomalous pulp canal configuration: a case report
Alper Sinanoglu, Dilek Helvacioglu-Yigit, Ibrahim Mutlu
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(2): 161. CrossRef - Endodontic management of a mandibular second molar with radix entomolaris: a case report
Rosaline Hannah, Deivanayagam Kandaswamy, Nachimuthu Jayaprakash
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(2): 132. CrossRef
- An upper left lateral incisor with double roots and double root canals: A case report
- 2,931 View
- 25 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Dilemmas pertaining to three canals in the mesiobuccal root of a maxillary second molar: a case report
- Ankit Arora, Shashi Rashmi Acharya, Muliya Vidya Saraswathi, Padmaja Sharma, Amber Ather
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(3):172-177. Published online August 23, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.3.172
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The mesiobuccal root of the maxillary molars is well known to pose a hindrance during endodontic therapy. Presented here is a case of a maxillary left second molar where three canals were located in its mesiobuccal root with the use of visual and diagnostic aids. Difficulties encountered during the process of unveiling the tooth's internal anatomy were discussed. The dilemmas encountered pertained to the root canal configuration, the nomenclature of the extra canals, and the justification for the presence of a third canal. The root canal configuration of 3-2-1 was confirmed for the mesiobuccal root using information gained from clinical, radiographic, and multi-detector computed tomography (MDCT) scan findings. This case demonstrates the need for efforts to locate extra canals in the mesiobuccal root of the maxillary molars as their internal anatomy remains a mystery.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical Significance of Mesiobuccal and Distobuccal Canal Variations in Maxillary Molars: A Case Series and a Mini Review
Mohsen Aminsobhani, Somayeh Majidi, Vlaho Brailo
Case Reports in Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A case report on endodontic management of the rarest Vertucci's Type VIII configuration in maxillary second molar with three mesiobuccal canals
ShrustiAjay Govil, Geeta Asthana, Shikha Kanodia, Abhishek Parmar
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2021; 24(4): 404. CrossRef - The MB3 canal in maxillary molars: a micro-CT study
Ronald Ordinola-Zapata, Jorge N. R. Martins, Hugo Plascencia, Marco A. Versiani, Clovis M. Bramante
Clinical Oral Investigations.2020; 24(11): 4109. CrossRef - Three Root Canals in the Mesiobuccal Root of Maxillary Molars: Case Reports and Literature Review
Ibrahim Ali Ahmad, Anas Al-Jadaa
Journal of Endodontics.2014; 40(12): 2087. CrossRef
- Clinical Significance of Mesiobuccal and Distobuccal Canal Variations in Maxillary Molars: A Case Series and a Mini Review
- 1,470 View
- 7 Download
- 4 Crossref

- A maxillary canine with two separated root canals: a case report
- Dong-Ryul Shin, Jin-Man Kim, Duck-Su Kim, Sun-Young Kim, Paul V Abbott, Sang-Hyuk Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(5):431-435. Published online September 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.5.431
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Maxillary canines have less anatomical diversities than other teeth. They usually have a single root and root canal. This report describes an endodontic treatment of a maxillary canine with two separated root canals which have not been reported through the demonstration of radiography and computerized tomography (CT).
Even though appropriated endodontic treatment has been performed, the severe pain could happen due to lack of consideration of anatomical variations of the teeth. Therefore, the clinicians should be well aware of the possibility of anatomical variations in the root canal system during endodontic treatment even if the number of root canals is obvious such as in this case.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Management of an Unusual Maxillary Canine: A Rare Entity
Jaya Nagendra Krishna Muppalla, Krishnamurthy Kavuda, Rajani Punna, Amulya Vanapatla, Malka Ashkenazi
Case Reports in Dentistry.2015;[Epub] CrossRef
- Management of an Unusual Maxillary Canine: A Rare Entity
- 1,617 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Root canal treatment of a mandibular second premolar with three separate root canals
- Seok-Ryun Lee, Seol-Hee Shin, Sung-Ok Hong, Chang-Kyu Song, Hoon-Sang Chang, Kyung-San Min
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(4):302-305. Published online July 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.4.302
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Mandibular premolars show a wide variety of root canal anatomy. Especially, the occurrence of three canals with three separate foramina in mandibular second premolars is very rare. This case report describes the root canal treatment of an unusual morphological configuration of the root canal system and supplements previous reports of the existence of such configuration in mandibular second premolar.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effective management of mandibular second premolar with root anomalies
Ashwaq Faia Asiri
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2023; 13(1): 28. CrossRef
- Effective management of mandibular second premolar with root anomalies
- 1,716 View
- 9 Download
- 1 Crossref

- A study on the C-shaped root canal system of mandibular second molar
- Dong-Gyun Lee, Jun-Mo Park, Ho-Keel Hwang
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(4):335-342. Published online July 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.4.335
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub C-shaped canals are known to present a complex canal anatomy with numerous fins connecting individual canals, thus requiring supplementary effort to accomplish a successful root canal treatment. This study examined the frequency of the C-shaped mandibular second molars and interrelation between the clinical records and radiographs to recognize them treated in the Department of Conservative Dentistry of the Chosun University Dental Hospital during a six-year period (1998 - 2004). This study reviewed the clinical records of 227 patients who underwent root canal treatment of the mandibular second molars. After opening the chamber, those cases with C-shaped orifices in the pulpal floor were selected, and the C-shaped root canal types were classified according to Melton's criteria. Three experienced dentists evaluated the radiographs of the C-shaped mandibular second molar on a viewer using a magnifying glass in order to determine if the root apex was fused or separated, the distal root canal was either centered or mesial shifted in the distal root, and if there was bilateral symmetry in a panorama. In conclusion, there is a high frequency of C-shaped mandibular second molars in Koreans. Simultaneous interpretation of the root shape and distal root canal using the preoperative, working length and post-treatment radiographs is important for diagnosing a C-shaped mandibular second molar.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An evaluation of canal curvature at the apical one third in type II mesial canals of mandibular molars
Hye-Rim Yun, Dong-Kyun Lee, Ho-Keel Hwang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(2): 104. CrossRef - A retrospective study on incidence of C-shaped canals in mandibular second molars
Hee-Sun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(4): 346. CrossRef
- An evaluation of canal curvature at the apical one third in type II mesial canals of mandibular molars
- 1,801 View
- 12 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Time-dependent effects of EDTA application on removal of smear layer in the root canal system
- Ja-Kyong Lee, Sang-Hyuk Park, Gi-Woon Choi
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(3):169-178. Published online May 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.3.169
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study was to verify that the combined application of NaOCl and EDTA was more effective in removal of smear layer than the application of NaOCl alone. Furthermore it was aimed to find out the optimal time for the application of EDTA.
Thirty five single rooted teeth were cleaned and shaped. NaOCl solution was used as an irrigant during instrumentation. After instrumentation, root canals of the control group were irrigated with 5 ml of NaOCl for 2 minutes. 30 sec, 1 min, and 2 min group were irrigated with 5 ml of 17% EDTA for 30 sec, 1 min, and 2 min respectively. Then the roots were examined with scanning electron microscopy for evaluating removal of smear layer and erosion of dentinal tubule.
The results were as follows;
The control group:
The smear layer was not removed at all.
The other groups:
1) Middle⅓: All groups showed almost no smear layer. And the erosion occurred more frequently as increasing irrigation time.
2) Apical⅓: The cleaning effect of 2 min group was better than the others.
The results suggest that 2 min application of 17% EDTA should be adequate to remove smear layer on both apical⅓ and middle⅓.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enhancing the Antibacterial Effect of Erythrosine-Mediated Photodynamic Therapy with Ethylenediamine Tetraacetic Acid
MinKi Choi, Haeni Kim, Siyoung Lee, Juhyun Lee
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2024; 51(1): 32. CrossRef - Apical foramen morphology according to the length of merged canal at the apex
Hee-Ho Kim, Jeong-Bum Min, Ho-Keel Hwang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(1): 26. CrossRef - Effect of moisture on sealing ability of root canal filling with different types of sealer through the glucose penetration model
Jin-Ah Jang, Hee-Lyang Kim, Mi-Ja Her, Kwang-Won Lee, Mi-Kyung Yu
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(5): 335. CrossRef
- Enhancing the Antibacterial Effect of Erythrosine-Mediated Photodynamic Therapy with Ethylenediamine Tetraacetic Acid
- 1,559 View
- 5 Download
- 3 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


