Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Pomegranate extract on eroded dentin: antioxidant action, bond strength and morphology of the adhesive interface after aging
- Thiago Vinícius Cortez, Nathália Mancioppi Cerqueira, Julia Adornes Gallas, Wanderley Pereira Oliveira, Silmara Aparecida Milori Corona, Aline Evangelista Souza-Gabriel
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(1):e9. Published online January 26, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e9
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
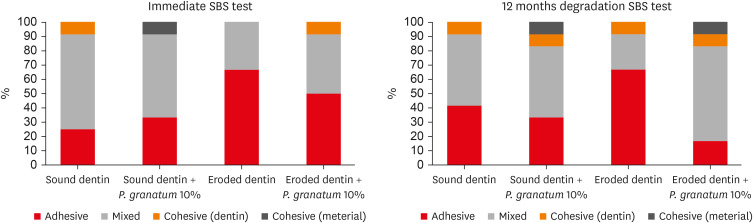
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the effect of pomegranate solution (
Punica granatum ) on eroded dentin through antioxidant action, shear bond strength (SBS) and interface morphology.Materials and Methods The 10% pomegranate peel extract was prepared by the lyophilization method. Punicalagin polyphenol was confirmed by high-performance liquid chromatography. Antioxidant activity was evaluated by capturing the 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical. For the SBS, 48 dentin fragments were divided into sound or eroded, and subdivided according to the pretreatment (
n = 12): water orP. granatum . The surfaces were restored with self-etch adhesive and a bulk-fill resin (Ecosite; DMG). The SBS was done immediately (24 hours) and after thermal cycling + water storage (12 months). For scanning electron microscopy, 48 dentin fragments (24 sound and 24 eroded) received the same treatments as for SBS (n = 6), and they were analyzed after 24 hours and 12 months.Results The
P. granatum had antioxidant action similar (p = 0.246) to the phenolic standard antioxidants. After 24 hours, eroded dentin had lower SBS than sound dentin (p < 0.001), regardless of the pretreatment. After 12 months,P. granatum maintained the SBS of sound dentin (13.46 ± 3.42 MPa) and eroded dentin (10.96 ± 1.90 MPa) statistically similar. The lowest values were found on eroded dentin treated with water (5.75 ± 1.65 MPa) (p < 0.001).P. granatum on eroded dentin caused peritubular demineralization and hybrid layer with resin tags.Conclusions The pomegranate extract had antioxidant action and preserved the adhesive interface of the eroded dentin.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Antibacterial Effects of Ethanolic Extractions of Aloe Vera, Black Tea, Pomegranate and Orange on Streptococcus mutans: An In-vitro Study
Bardia Vadiati Saberi, Soheil Taghavi Namin, Dina Maleki
Nutrition And Food In Health And Disease.2025; 12(2): 29. CrossRef - Protective effect of a novel antioxidant gel containing resveratrol and sodium fluoride on dentin erosion in the presence of acquired salivary pellicle: An in vitro study
Loraine Perez Manzoli, Luan Júlio Ruiz da Silva, George Clay dos Santos Caracas, Kalinca Furtado de Oliveira, Walessa Alana Braganca Aragão, Rafael Rodrigues Lima, Milton Carlos Kuga, Cristiane de Melo Alencar
Archives of Oral Biology.2025; 179: 106395. CrossRef - Effect of pomegranate solution alone or combined with chlorhexidine against oral multispecies biofilm
J. A. Gallas, L. L. Pelozo, S. A. M. Corona, Y. Shen, M. Haapasalo, M. D. Sousa‐Neto, A. E. Souza‐Gabriel
International Endodontic Journal.2024; 57(12): 1819. CrossRef - The effect of resveratrol application on the micro-shear bond strength of adhesive to bleached enamel
Esra Cengiz-Yanardag, Izgen Karakaya
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Antibacterial Effects of Ethanolic Extractions of Aloe Vera, Black Tea, Pomegranate and Orange on Streptococcus mutans: An In-vitro Study
- 2,620 View
- 91 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Is dentin biomodification with collagen cross-linking agents effective for improving dentin adhesion? A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Julianne Coelho Silva, Edson Luiz Cetira Filho, Paulo Goberlânio de Barros Silva, Fábio Wildson Gurgel Costa, Vicente de Paulo Aragão Saboia
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(2):e23. Published online May 6, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e23
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
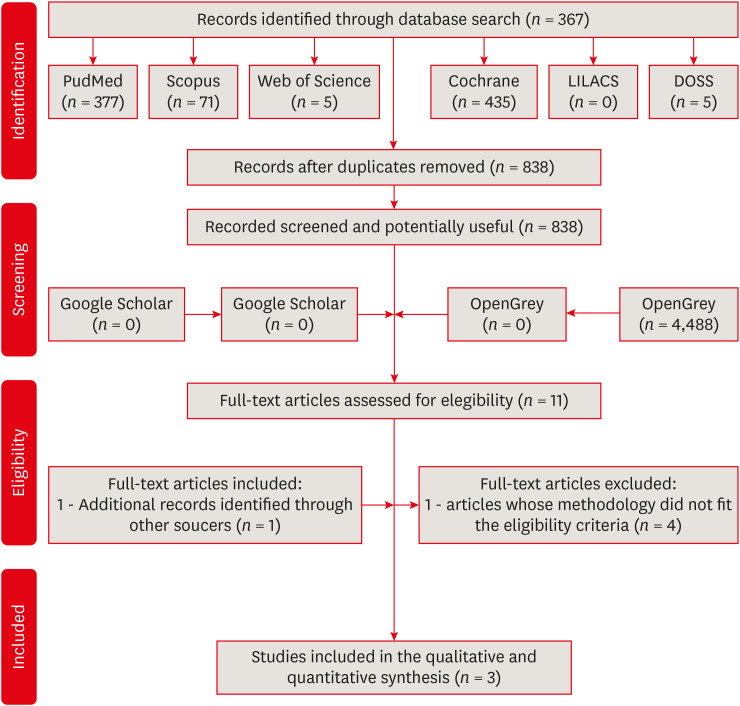
ePub Objectives The aim of this investigation was to evaluate the effectiveness of collagen cross-linking agents (CCLAs) used in combination with the adhesive technique in restorative procedures.
Materials and Methods In this systematic review, the authors followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses checklist. An electronic search was performed using PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, LILACS, and DOSS, up to October 2020. The gray literature was also researched. Only randomized clinical trials were selected.
Results The selection process yielded 3 studies from the 838 retrieved. The addition of CCLAs in the retention of restorations increased the number of events. The postoperative sensitivity scores and marginal adaptation scores showed no significant difference between the CCLA and control groups, and the marginal pigmentation scores showed a significant increase in the CCLA group. There were no caries events in any group throughout the evaluation period.
Conclusions This systematic review showed that there is no clinical efficacy to justify the use of CCLAs in the protocols performed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Riboflavin-ultraviolet-A collagen crosslinking treatments in improving dentin bonding and resistance to enzymatic digestion
Yung-Show Chiang, Ping-Ju Chen, Chun-Chan Ting, Yuh-Ling Chen, Shu-Fen Chuang
Journal of Dental Sciences.2025; 20(1): 109. CrossRef - Effect of dentin bio modifications and matrix metalloproteinase activity on bond strength – A systematic review and meta-analysis
D. Agarwal, S. R. Srinidhi, S. D. Aggarwal, P. Ingle, S. Tandon
Endodontics Today.2025; 23(1): 71. CrossRef - O USO DE ADESIVO AUTOCONDICIONANTE E RESINA FLOW COMO INTERFACE ADESIVA PROTETORA DA DENTINA FRENTE À IRRIGAÇÃO COM NaClO NO TRATAMENTO ENDODÔNTICO: ESTUDO IN-VITRO
Luís Daniel Ramos de Oliveira, Leandro Botelho Hanna, José Augusto Rodrigues
RECIMA21 - Revista Científica Multidisciplinar - ISSN 2675-6218.2025; 6(12): e6127063. CrossRef - Stability of dentin matrix treated with caffeic acid phenethyl ester at different concentrations
Aline Honorato Damázio, Rosanna Tarkany Basting, Enrico Coser Bridi, Fabiana Mantovani Gomes França, Flávia Lucisano Botelho do Amaral, Cecilia Pedroso Turssi, Waldemir Francisco Vieira Junior, Roberta Tarkany Basting
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2024; 23: e244006. CrossRef - Effect of Collagen Crosslinkers on Dentin Bond Strength of Adhesive Systems: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Louis Hardan, Umer Daood, Rim Bourgi, Carlos Enrique Cuevas-Suárez, Walter Devoto, Maciej Zarow, Natalia Jakubowicz, Juan Eliezer Zamarripa-Calderón, Mateusz Radwanski, Giovana Orsini, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska
Cells.2022; 11(15): 2417. CrossRef
- Riboflavin-ultraviolet-A collagen crosslinking treatments in improving dentin bonding and resistance to enzymatic digestion
- 2,248 View
- 59 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- Do universal adhesives promote bonding to dentin? A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Ali A. Elkaffas, Hamdi H. H. Hamama, Salah H. Mahmoud
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(3):e29. Published online June 18, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e29
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
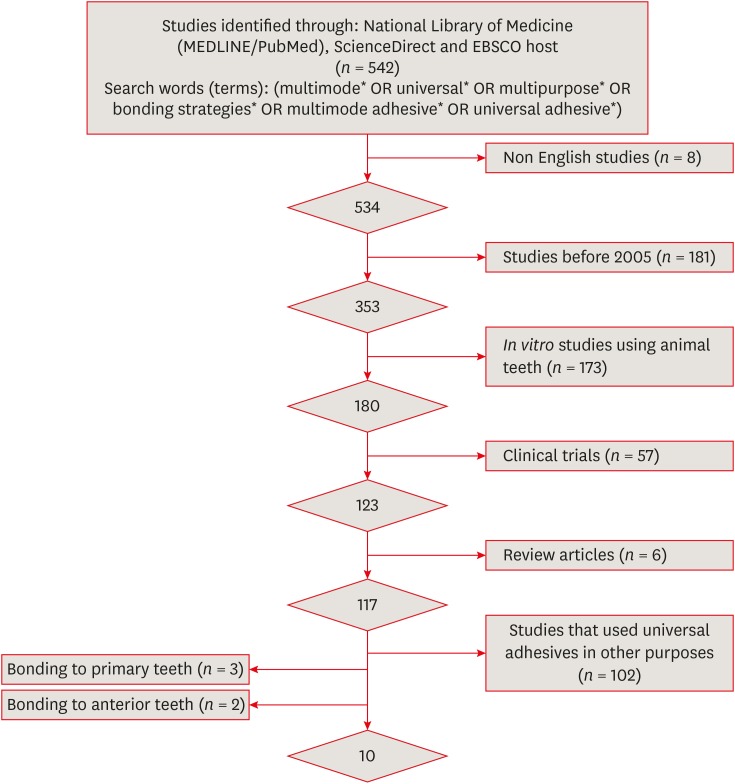
ePub Objectives The aims of this study were to conduct a systematic review of the microtensile bond strength (µTBS) of multi-mode adhesives to dentin and to perform a meta-analysis to assess the significance of differences in the µTBS of one of the most commonly used universal adhesives (Scotchbond Universal, 3M ESPE) depending on whether the etch-and-rinse or self-etch mode was used.
Materials and Methods An electronic search was performed of MEDLINE/PubMed, ScienceDirect, and EBSCOhost. Laboratory studies that evaluated the µTBS of multi-mode adhesives to dentin using either the etch-and-rinse or self-etch mode were selected. A meta-analysis was conducted of the reviewed studies to quantify the differences in the µTBS of Scotchbond Universal adhesive.
Results Only 10 studies fulfilled the inclusion criteria for the systematic review. Extensive variation was found in the restorative materials, testing methodologies, and failure mode in the reviewed articles. Furthermore, variation was also observed in the dimensions of the microtensile testing beams. The meta-analysis showed no statistically significant difference between the etch-and-rinse and self-etch modes for Scotchbond Universal adhesive (
p > 0.05).Conclusions Multi-mode ‘universal’ adhesives can achieve substantial bonding to dentin, regardless of the used modes (either etch-and-rinse or self-etch).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The potential cytotoxic effect of recent universal adhesives with modified monomeric compositions on human gingival epithelial cells
Omar Abd El-Maksoud, Nessma Sultan, Hoda Saleh Ismail, Ramy Ahmed Wafaie, Hamdi H. Hamama, Salah Hasab Mahmoud
Scientific Reports.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Proximal-Cervical Undermined Enamel Areas on Marginal Quality and Enamel Integrity of Laboratory and CAD/CAM Ceramic Inlays and Partial Crowns
Roland Frankenberger, Katharina Friedrich, Marie-Christine Dudek, Julia Winter, Norbert Krämer, Matthias J. Roggendorf
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2025; 16(3): 82. CrossRef - Improving Bonding Protocols: The Effect of Selective Dentin Etching with Two Different Universal Adhesives—An In Vitro Study
Sandro Ferreira, Tiago Rodrigues, Mariana Nunes, Ana Mano Azul, José João Mendes, Ana Filipa Chasqueira, Joana Costa
Polymers.2025; 17(9): 1215. CrossRef - Effect of surface treatment on glass ionomers in sandwich restorations: a systematic review and meta-analysis of laboratory studies
Hoda S. Ismail, Ashraf Ibrahim Ali, Franklin Garcia-Godoy
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2025; 50(2): e13. CrossRef - Wet vs. Dry Dentin Bonding: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Adhesive Performance and Hybrid Layer Integrity
Mircea Popescu, Mădălina Malița, Andrei Vorovenci, Andreea Angela Ștețiu, Viorel Ștefan Perieanu, Radu Cătălin Costea, Mihai David, Raluca Mariana Costea, Maria Antonia Ștețiu, Andi Ciprian Drăguș, Cristina Maria Șerbănescu, Andrei Burlibașa, Oana Eftene,
Oral.2025; 5(3): 63. CrossRef - The Effect of Different Multimode Adhesives On Microleakage of Class V Composite Restorations in Three Etching Modes
Fatma Yılmaz, Sevgi Kurşun, Zeliha Öztürk
ADO Klinik Bilimler Dergisi.2025; 14(3): 177. CrossRef - Controversies about refrigeration of dental adhesives: a review
Omar Abd El-Maksoud, Hamdi Hosni Hamdan Hamama, Ramy Ahmed Wafaie, Salah Hasab Mahmoud
BDJ Open.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Tooth-composite bond failure with a universal and an etch-and-rinse adhesive depending on mode and frequency of application
Ellen Schulz-Kornas, Mathilde Tittel, Hartmut Schneider, Maximilian Bemmann, Marco Pellino, Tobias Meissner, Florian Fuchs, Christian Hannig, Florian Tetschke, Kyung-Jin Park, Michaela Strumpski, Rainer Haak
Dental Materials.2024; 40(2): 359. CrossRef - Comparison of postoperative hypersensitivity between Total-etch and Universal adhesive system: a randomized clinical trial
Kiran Javed, Nouman Noor, Muhammad Zubair Nasir, Manzoor Ahmed Manzoor
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Adhesion and sealing of different universal adhesive systems associated with bulk‐fill resins after using endodontic irrigation solutions: An in vitro study
Érika Mayumi Omoto, Anderson Catelan, Paulo Henrique dos Santos, Luciano Tavares Angelo Cintra, Fernanda de Souza e Silva Ramos, Caio César Pavani, André Luiz Fraga Briso, Ticiane Cestari Fagundes
Australian Endodontic Journal.2024; 50(2): 309. CrossRef - Evaluation of the effects of combined application of dimethylaminohexadecyl methacrylate and MDP on dentin bonding and antimicrobial properties
Jiadi Shen, Ming Ma, Yun Huang, Haochen Miao, Xin Wei
Journal of Materials Science.2023; 58(31): 12685. CrossRef - Efficacy of adhesive strategies for restorative dentistry: A systematic review and network meta-analysis of double-blind randomized controlled trials over 12 months of follow-up
Kevin Sheng-Kai Ma, Li-Tzu Wang, Markus B. Blatz
Journal of Prosthodontic Research.2023; 67(1): 35. CrossRef - Impact of Preceded Tumor Therapeutic Irradiation on the Microtensile Bond Strength of Universal Adhesives Applied in Self-Etch Mode to Human Dentin In Vitro
Sina Broscheit, Dirk Vordermark, Reinhard Gerlach, Christian Ralf Gernhardt
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(13): 7873. CrossRef - Effect of the Adhesive Strategy on Clinical Performance and Marginal Integrity of a Universal Adhesive in Non-Carious Cervical Lesions in a Randomized 36-Month Study
Rainer Haak, Gesa Stache, Hartmut Schneider, Matthias Häfer, Gerhard Schmalz, Ellen Schulz-Kornas
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(18): 5776. CrossRef - Universal Adhesives in Clinical Dentistry
Fusun Ozer, Shilpa Patnaikuni
Science, Art and Religion.2023; 2(1--2): 6. CrossRef - Deep proximal margin rebuilding with direct esthetic restorations: a systematic review of marginal adaptation and bond strength
Hoda S. Ismail, Ashraf I. Ali, Rabab El. Mehesen, Jelena Juloski, Franklin Garcia-Godoy, Salah H. Mahmoud
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Improving Properties of an Experimental Universal Adhesive by Adding a Multifunctional Dendrimer (G-IEMA): Bond Strength and Nanoleakage Evaluation
Joana Vasconcelos e Cruz, António H. S. Delgado, Samuel Félix, José Brito, Luísa Gonçalves, Mário Polido
Polymers.2022; 14(7): 1462. CrossRef - Scoping review of trials evaluating adhesive strategies in pediatric dentistry: where do simplified strategies lie?
António H. S. Delgado, Hasan Jamal, Anne Young, Paul Ashley
BMC Oral Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Does acid etching prior to applying universal adhesives affect the bond strength of glass fiber post to root dentin?
Helder Callegaro Velho, Eduardo Trindade Dalence, Pablo Soares Machado, Marília Pivetta Rippe, Jovito Adiel Skupien, Vinícius Felipe Wandscher
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2021; 105: 102795. CrossRef - Does Adhesive Layer Thickness and Tag Length Influence Short/Long-Term Bond Strength of Universal Adhesive Systems? An In-Vitro Study
Naji Kharouf, Tarek Ashi, Ammar Eid, Levi Maguina, Jihed Zghal, Nairy Sekayan, Rim Bourgi, Louis Hardan, Salvatore Sauro, Youssef Haikel, Davide Mancino
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(6): 2635. CrossRef - Chronological history and current advancements of dental adhesive systems development: a narrative review
Maicon Sebold, Carolina Bosso André, Beatriz Ometto Sahadi, Lorenzo Breschi, Marcelo Giannini
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2021; 35(18): 1941. CrossRef - Laboratory methods for measuring adhesive bond strength between restoration materials and hard tooth tissues
I.Ya. Poyurovskaya, A.P. Polikarpova, F.S. Rusanov
Stomatologiya.2021; 100(5): 88. CrossRef - Effect of Curcumin Suspension and Vitamin C on Dentin Shear Bond Strength and Durability. A Pilot Study
Dalia A. Abuelenain, Ensanya A. Abou Neel, Tariq S. Abuhaimed, Amal M. Alamri, Hanan S. Ammar, Sahar M. N. Bukhary
The Open Dentistry Journal.2021; 15(1): 540. CrossRef - Effect of 9.3 μm CO2 and 2.94 μm Er:YAG Laser vs. Bur Preparations on Marginal Adaptation in Enamel and Dentin of Mixed Class V Cavities Restored With Different Restorative Systems
Clara Isabel Anton y Otero, Enrico Di Bella, Ivo Krejci, Tissiana Bortolotto
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Adhesion strategy and curing mode of a universal adhesive influence the bonding of dual-cured core build-up resin composite to dentin
Ahmed Eid Elsayed, Mohamed Amr Kamel, Farid Sabry El-Askary
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2021; 35(1): 52. CrossRef - Influence of etching mode and composite resin type on bond strength to dentin using universal adhesive system
Stefan Dačić, Milan Miljković, Aleksandar Mitić, Goran Radenković, Marija Anđelković‐Apostolović, Milica Jovanović
Microscopy Research and Technique.2021; 84(6): 1212. CrossRef - Universal adhesives - a new direction in the development of adhesive systems
A. Tichý, K. Hosaka, J. Tagami
Česká stomatologie a praktické zubní lékařství.2020; 120(1): 4. CrossRef - Effect of Over-Etching and Prolonged Application Time of a Universal Adhesive on Dentin Bond Strength
Phoebe Burrer, Hoang Dang, Matej Par, Thomas Attin, Tobias T. Tauböck
Polymers.2020; 12(12): 2902. CrossRef - Profile of a 10-MDP-based universal adhesive system associated with chlorhexidine: Dentin bond strength and in situ zymography performance
Marina Ciccone Giacomini, Polliana Mendes Candia Scaffa, Rafael Simões Gonçalves, Giovanna Speranza Zabeu, Cristina de Mattos Pimenta Vidal, Marcela Rocha de Oliveira Carrilho, Heitor Marques Honório, Linda Wang
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2020; 110: 103925. CrossRef - Universal dental adhesives: Current status, laboratory testing, and clinical performance
Sanket Nagarkar, Nicole Theis‐Mahon, Jorge Perdigão
Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials.2019; 107(6): 2121. CrossRef - Modifying Adhesive Materials to Improve the Longevity of Resinous Restorations
Wen Zhou, Shiyu Liu, Xuedong Zhou, Matthias Hannig, Stefan Rupf, Jin Feng, Xian Peng, Lei Cheng
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2019; 20(3): 723. CrossRef
- The potential cytotoxic effect of recent universal adhesives with modified monomeric compositions on human gingival epithelial cells
- 5,518 View
- 53 Download
- 31 Crossref

- Effects of solvent volatilization time on the bond strength of etch-and-rinse adhesive to dentin using conventional or deproteinization bonding techniques
- José Aginaldo de Sousa Júnior, Márcia Luciana Carregosa Santana, Fabricio Eneas Diniz de Figueiredo, André Luis Faria-e-Silva
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(3):202-208. Published online March 17, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.3.202
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study determined the effect of the air-stream application time and the bonding technique on the dentin bond strength of adhesives with different solvents. Furthermore, the content and volatilization rate of the solvents contained in the adhesives were also evaluated.
Materials and Methods Three adhesive systems with different solvents (Stae, SDI, acetone; XP Bond, Dentsply De Trey, butanol; Ambar, FGM, ethanol) were evaluated. The concentrations and evaporation rates of each adhesive were measured using an analytical balance. After acid-etching and rinsing, medium occlusal dentin surfaces of human molars were kept moist (conventional) or were treated with 10% sodium hypochlorite for deproteinization. After applying adhesives over the dentin, slight air-stream was applied for 10, 30 or 60 sec. Composite cylinders were built up and submitted to shear testing. The data were submitted to ANOVA and Tukey's test (α = 0.05).
Results Stae showed the highest solvent content and Ambar the lowest. Acetone presented the highest evaporation rate, followed by butanol. Shear bond strengths were significantly affected only by the factors of 'adhesive' and 'bonding technique' (
p < 0.05), while the factor 'duration of air-stream' was not significant. Deproteinization of dentin increased the bond strength (p < 0.05). Stae showed the lowest bond strength values (p < 0.05), while no significant difference was observed between XP Bond and Ambar.Conclusions Despite the differences in content and evaporation rate of the solvents, the duration of air-stream application did not affect the bond strength to dentin irrespective of the bonding technique.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of solvent evaporation and photo-irradiation strategy of contact-cure adhesive system on bonding to root canal
Wahyuni Suci Dwiandhany, Kittisak Sanon, Yasushi Shimada, Ahmed Abdou
Odontology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of adhesive air-drying time on bond strength to dentin: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Mohamed M. Awad, Ali Alrahlah, Jukka P. Matinlinna, Hamdi Hosni Hamama
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2019; 90: 154. CrossRef
- Effect of solvent evaporation and photo-irradiation strategy of contact-cure adhesive system on bonding to root canal
- 1,670 View
- 6 Download
- 2 Crossref

- The effects of dentin bonding agent thickness on stress distribution of composite-tooth interface : Finite element method
- Sang-Il Park, Yemi Kim, Byoung-Duk Roh
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(5):442-449. Published online September 30, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.5.442
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The aim of this study was to examine that thick dentin bonding agent application or low modulus composite restoration could reduce stresses on dentin bonding agent layer.
A mandibular first premolar with abfraction lesion was modeled by finite element method. The lesion was restored by different composite resins with variable dentin bonding agent thickness (50µm, 100µm, 150µm). 170N of occlusal loading was applied buccally or lingually. Von Mises stress on dentin bonding agent layer were measured.
When thickness of dentin bonding agent was increased von Mises stresses at dentin bonding agent were decreased in both composites. Lower elastic modulus composite restoration showed decreased von Mises stresses. On root dentin margin more stresses were generated than enamel margin.
For occlusal stress relief at dentin boning agent layer to applicate thick dentin bonding agent or to choose low elastic modulus composite is recommended.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of application methods of one-step self-etching adhesives on microtensile bond strength
Chul-Kyu Choi, Sung-Ae Son, Jin-Hee Ha, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Yong-Hun Kwon, Jeong-Kil Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(3): 203. CrossRef
- Influence of application methods of one-step self-etching adhesives on microtensile bond strength
- 1,401 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The influence of cavity configuration on the microtensile bond strength between composite resin and dentin
- Yemi Kim, Jeong-won Park, Chan young Lee, Yoon jung Song, Deok Kyu Seo, Byoung-Duck Roh
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(5):472-480. Published online September 30, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.5.472
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study was conducted to evaluate the influence of the C-factor on the bond strength of a 6th generation self-etching system by measuring the microtensile bond strength of four types of restorations classified by different C-factors with an identical depth of dentin.
Eighty human molars were divided into four experimental groups, each of which had a C-factor of 0.25, 2, 3 or 4. Each group was then further divided into four subgroups based on the adhesive and composite resin used. The adhesives used for this study were AQ Bond Plus (Sun Medical, Japan) and Xeno III (DENTSPLY, Germany). And composite resins used were Fantasista (Sun Medical, Japan) and Ceram-X mono (DENTSPLY, Germany).
The results were then analyzed using one-way ANOVA, a Tukey's test, and a Pearson's correlation test and were as follows.
There was no significant difference among C-factor groups with the exception of groups of Xeno III and Ceram-X mono (p < 0.05).
There was no significant difference between any of the adhesives and composite resins in groups with C-factor 0.25, 2 and 4.
There was no correlation between the change in C-factor and microtensile bond strength in the Fantasista groups.
It was concluded that the C-factor of cavities does not have a significant effect on the microtensile bond strength of the restorations when cavities of the same depth of dentin are restored using composite resin in conjunction with the 6th generation self-etching system.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of different chlorhexidine application times on microtensile bond strength to dentin in Class I cavities
Hyun-Jung Kang, Ho-Jin Moon, Dong-Hoon Shin
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(1): 9. CrossRef - Effect of Er:YAG lasing on the dentin bonding strength of two-step adhesives
Byeong-Choon Song, Young-Gon Cho, Myung-Seon Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(5): 409. CrossRef - Effect of Chlorhexidine Application Methods on Microtensile Bond Strength to Dentin in Class I Cavities
Y-E. Chang, D-H. Shin
Operative Dentistry.2010; 35(6): 618. CrossRef - Difference in bond strength according to filling techniques and cavity walls in box-type occlusal composite resin restoration
Eun-Joo Ko, Dong-Hoon Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(4): 350. CrossRef
- Effect of different chlorhexidine application times on microtensile bond strength to dentin in Class I cavities
- 1,095 View
- 1 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Influence of adhesive application on shear bond strength of the resin cement to indirect resin composite
- Mi-Hae Song, Su-Jung Park, Hyun-Gu Cho, Yun-Chan Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, In-Nam Hwang
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(5):419-427. Published online September 30, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.5.419
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study analyzed the influence of dental adhesive/primer on the bond strength between indirect resin composite and the resin cement.
Seventy disc specimens of indirect resin composite (Tescera Dentin, Bisco) were fabricated. And bonding area of all specimens were sandblasted and silane treated for one minute. The resin cements were used with or without application of adhesive/primer to bonding area of indirect resin restoration: Variolink-II (Ivoclar-Vivadent): Exite DSC, Panavia-F (Kuraray): ED-Primer, RelyX Unicem (3M ESPE): Single-Bond, Duolink (Bisco): One-step, Mulitlink (Ivoclar-Vivadent): Multilinh Primer.
Shear bond strength was measured by Instron universal testing machine.
Adhesive application improved shear bond strength (p < 0.05). But Variolink II and Panavia-F showed no statistically significant difference according to the adhesive application.
With the above results, when resin inlay is luted by resin cement it seems that application of dental adhesive/primer is necessary in order to improve the bond strength.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Shear bond strength of a self-adhesive resin cement to resin-coated dentin
Jee-Youn Hong, Cheol-Woo Park, Jeong-Uk Heo, Min-Ki Bang, Jae-Jun Ryu
The Journal of Korean Academy of Prosthodontics.2013; 51(1): 27. CrossRef - Microtensile bond strength of self-etching and self-adhesive resin cements to dentin and indirect composite resin
Jae-Gu Park, Young-Gon Cho, Il-Sin Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(2): 106. CrossRef - Effect of a desensitizer on dentinal bond strength in cementation of composite resin inlay
Sae-Hee Han, Young-Gon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(3): 223. CrossRef - Effect of curing methods of resin cements on bond strength and adhesive interface of post
Mun-Hong Kim, Hae-Jung Kim, Young-Gon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(2): 103. CrossRef - Effect of dentin surface wetness on tensile bond strength of self adhesive resin cements
Sung-Young Yoon, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(2): 113. CrossRef
- Shear bond strength of a self-adhesive resin cement to resin-coated dentin
- 1,214 View
- 3 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Shear bond strength of dentin bonding agents cured with a Plasma Arc curing light
- Youngchul Kwon, Sun-Young Kim, Sae-Joon Chung, Young-Chul Han, In-Bog Lee, Ho-Hyun Son, Chung-Moon Um, Byeong-Hoon Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(3):213-223. Published online May 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.3.213
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The objective of this study was to compare dentin shear bond strength (DSBS) of dentin bonding agents (DBAs) cured with a plasma arc (PAC) light curing unit (LCU) and those cured with a light emitting diode (LED) LCU. Optical properties were also analyzed for Elipar freelight 2 (3M ESPE); LED LCU, Apollo 95E (DMT Systems); PAC LCU and VIP Junior (Bisco); Halogen LCU. The DBAs used for DSBS test were Scotchbond Multipurpose (3M ESPE), Singlebond 2 (3M ESPE) and Clearfil SE Bond (Kuraray). After DSBS testing, fractured specimens were analyzed for failure modes with SEM.
The total irradiance and irradiance between 450 nm and 490 nm of the LCUs were different. LED LCU showed narrow spectral distribution around its peak at 462 nm whereas PAC and Halogen LCU showed a broad spectrum. There were no significant differences in mean shear bond strength among different LCUs (P > 0.05) but were significant differences among different DBAs (P < 0.001)
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Temperature changes under demineralized dentin during polymerization of three resin-based restorative materials using QTH and LED units
Sayed-Mostafa Mousavinasab, Maryam Khoroushi, Mohammadreza Moharreri, Mohammad Atai
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(3): 155. CrossRef
- Temperature changes under demineralized dentin during polymerization of three resin-based restorative materials using QTH and LED units
- 1,313 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- A study on fractural behavior of dentin-resin interface
- Gil-Joo Ryu, Gi-Woon Choi, Sang-Jin Park, Kyung-Kyu Choi
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(3):208-221. Published online May 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.3.208
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The fracture toughness test is believed as a clinically relevant method for assessing the fracture resistance of the dentinal restoratives. The objectives of this study were to measure the fracture toughness (K1C) and microtensile bond strength of dentin-resin composite interface and compare their relationship for their use in evaluation of the integrity of the dentin-resin bond.
A minimum of six short-rod specimens for fracture toughness test and fifteen specimens for microtensile bond strength test was fabricated for each group of materials used. After all specimens storing for 24 hours in distilled water at 37℃, they were tensile-loaded with an EZ tester universal testing machin. Statistical analysis was performed using ANOVA and Tukey's test at the 95% confidence level, Pearson's coefficient was used to verify the correlation between the mean of fracture toughness and microtensile bond strength. FE-SEM was employed on fractured surface to describe the crack propagation.
Fracture toughness value of Clearfil SE Bond (SE) was the highest, followed by Adper Single Bond 2 (SB), OptiBond Solo (OB), ONE-STEP PLUS (OS), ScotchBond Multi-purpose (SM) and there was significant difference between SE and other 4 groups (p < 0.05). There were, however, no significant difference among SB, OB, OS, SM (p > 0.05). Microtensile bond strength of SE was the highest, followed by SB, OB, SM, OS and OS only showed significant lower value (p < 0.05). There was no correlation between fracture toughness and microtensile bond strength values. FE-SEM examination revealed that dentin bonding agent showed different film thickness and different failure pattern according to the film thickness.
From the limited results of this study, it was noted that there was statistically no correlation between K1C and µTBS. We can conclude that for obtaining the reliability of bond strength test of dentin bonding agent, we must pay more attention to the test procedure and its profound scrutiny.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The study of fractural behavior of repaired composite
Sang-Soon Park, Wook Nam, Ah-Hyang Eom, Duck-Su Kim, Gi-Woon Choi, Kyoung-Kyu Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(6): 461. CrossRef
- The study of fractural behavior of repaired composite
- 1,203 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The effect of cavity wall property on the shear bond strength test using iris method
- Dong-Hwan Kim, Ji-Hyun Bae, Byeong-Hoon Cho, In-Bog Lee, Seung-Ho Baek, Hyun-Mi Ryu, Ho-Hyun Son, Chung-Moon Um, Hyuck-Choon Kwon
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(2):170-176. Published online March 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.2.170
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives In the unique metal iris method, the developing interfacial gap at the cavity floor resulting from the cavity wall property during polymerizing composite resin might affect the nominal shear bond strength values. The aim of this study is to evaluate that the iris method reduces the cohesive failure in the substrates and the cavity wall property effects on the shear bond strength tests using iris method.
Materials and Methods The occlusal dentin of 64 extracted human molars were randomly divided into 4 groups to simulate two different levels of cavity wall property (metal and dentin iris) and two different materials (ONE-STEP® and ALL-BOND® 2) for each wall property. After positioning the iris on the dentin surface, composite resin was packed and light-cured. After 24 hours the shear bond strength was measured at a crosshead speed of 0.5 mm/min. Fracture analysis was performed using a microscope and SEM. The data was analyzed statistically by a two-way ANOVA and t-test.
Results The shear bond strength with metal iris was significant higher than those with dentin iris (p = 0.034). Using ONE-STEP®, the shear bond strength with metal iris was significant higher than those with dentin iris (p = 0.005), but not in ALL-BOND® 2 (p = 0.774). The incidence of cohesive failure was very lower than other shear bond strength tests that did not use iris method.
Conclusions The iris method may significantly reduce the cohesive failures in the substrates. According to the bonding agent systems, the shear bond strength was affected by the cavity wall property.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of infection control barrier thickness on light curing units
Hoon-Sang Chang, Seok-Ryun Lee, Sung-Ok Hong, Hyun-Wook Ryu, Chang-Kyu Song, Kyung-San Min
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(5): 368. CrossRef
- Effect of infection control barrier thickness on light curing units
- 1,414 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Comparison of shear bond strength of different bonding systems on bleached enamel
- Kwang-Keun Kim, Jeong-Won Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(1):30-35. Published online January 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.1.030
-
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of concentration and application time of hydrogen peroxide on the microtensile bond strength of resin restorations to the dentin at different depths
Jeong-Lyong Son, Gye-Young Lee, Yu-Mi Kang, Young-Taek Oh, Kwang-Won Lee, Tae-Gun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(5): 406. CrossRef - Effect of vital tooth bleaching agent on dentin bonding
Na-Young Jeong, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young-kyung Kim, Sung Kyo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2006; 31(2): 79. CrossRef
- The effect of concentration and application time of hydrogen peroxide on the microtensile bond strength of resin restorations to the dentin at different depths
- 1,288 View
- 5 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Dentin bond strength of bonding agents cured with Light Emitting Diode
- Sun-Young Kim, In-Bog Lee, Byeong-Hoon Cho, Ho-Hyun Son, Mi-Ja Kim, Chang-In Seok, Chung-Moon Um
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(6):504-514. Published online January 14, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.6.504
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub ABSTRACT This study compared the dentin shear bond strengths of currently used dentin bonding agents that were irradiated with an LED (Elipar FreeLight, 3M-ESPE) and a halogen light (VIP, BISCO). The optical characteristics of two light curing units were evaluated. Extracted human third molars were prepared to expose the occlusal dentin and the bonding procedures were performed under the irradiation with each light curing unit. The dentin bonding agents used in this study were Scotchbond Multipurpose (3M ESPE), Single Bond (3M ESPE), One-Step (Bisco), Clearfil SE bond (Kuraray), and Adper Prompt (3M ESPE). The shear test was performed by employing the design of a chisel-on-iris supported with a Teflon wall. The fractured dentin surface was observed with SEM to determine the failure mode.
The spectral appearance of the LED light curing unit was different from that of the halogen light curing unit in terms of maximum peak and distribution. The LED LCU (maximum peak in 465 ㎚) shows a narrower spectral distribution than the halogen LCU (maximum peak in 487 ㎚). With the exception of the Clearfil SE bond (
P < 0.05), each 4 dentin bonding agents showed no significant difference between the halogen light-cured group and the LED light-cured group in the mean shear bond strength (P > 0.05).The results can be explained by the strong correlation between the absorption spectrum of cam-phoroquinone and the narrow emission spectrum of LED.
- 1,095 View
- 0 Download

- Effect of dentinal tubules orientation on penetration pattern of dentin adhesives using confocal laser scanning microscopy
- Dong-Jun Kim, Yun-Chan Hwang, Sun-Ho Kim, Won-Mann Oh, In-Nam Hwang
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2003;28(5):392-401. Published online September 30, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.5.392
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the penetration pattern of dentin adhesives according to the orientation of dentinal tubules with confocal laser scanning microscopy. Specimens having perpendicular, parallel and oblique surface to dentinal tubules were fabricated. The primer of dentin adhesives (ALL BOND® 2, CLEARFIL™ SE BOND and PQ1) was mixed with fluorescent material, rhodamine B isothiocyanate (Aldrich Chem. CO., Milw., USA). It was applied to the specimens according to the instructions of manufactures. The specimens were covered with composite resin (Estelite, shade A2) and then cut to a thickness of 500 µm with low speed saw (Isomet™, Buehler, USA). The adhesive pattern of dentin adhesives were observed by fluorescence image using confocal laser scanning microscopy.
The results were as follows.
For the groups with tubules perpendicular to bonded surface, funnel shape of resin tag was observed in all specimen. However, resin tags were more prominent in phosphoric acid etching system (ALL BOND® 2 and PQ1) than self etching system (CLEARFIL™ SE BOND).
For the groups with tubules parallel to bonded surface, rhodamine-labeled primer penetrated into peritubular dentin parallel to the orientation of dentinal tubules. But rhodamine-labeled primer of PQ1 diffused more radially into surrounding intertubular dentin than other dentin adhesive systems.
For the groups with tubules oblique to bonded surface, resin tags appeared irregular and discontinuous. But they penetrated deeper into dentinal tubules than other groups.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bonding efficacy of cured or uncured dentin adhesives in indirect resin
Ji-Hyun Jang, Bin-Na Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang, Yun-Chan Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, In-Nam Hwang
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(6): 490. CrossRef
- Bonding efficacy of cured or uncured dentin adhesives in indirect resin
- 1,285 View
- 9 Download
- 1 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


