Previous issues
- Page Path
- HOME > Browse articles > Previous issues
-
Restorative Dentistry and Endodontics is indexed in Web of Science and Scopus, marking the start of a new era - Kyung-San Min
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(1):e11. Published online February 20, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e11
- 2,258 View
- 64 Download

- Cone-beam computed tomography in endodontics: from the specific technical considerations of acquisition parameters and interpretation to advanced clinical applications
- Néstor Ríos-Osorio, Sara Quijano-Guauque, Sandra Briñez-Rodríguez, Gustavo Velasco-Flechas, Antonieta Muñoz-Solís, Carlos Chávez, Rafael Fernandez-Grisales
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(1):e1. Published online December 11, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
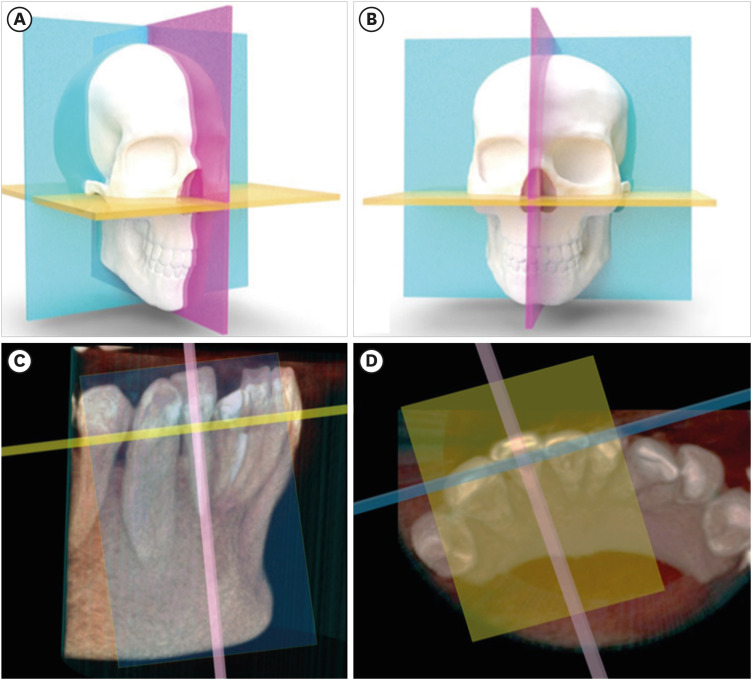
ePub The implementation of imaging methods that enable sensitive and specific observation of anatomical structures has been a constant in the evolution of endodontic therapy. Cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) enables 3-dimensional (3D) spatial anatomical navigation in the 3 volumetric planes (sagittal, coronal and axial) which translates into great accuracy for the identification of endodontic pathologies/conditions. CBCT interpretation consists of 2 main components: (i) the generation of specific tasks of the image and (ii) the subsequent interpretation report. A systematic and reproducible method to review CBCT scans can improve the accuracy of the interpretation process, translating into greater precision in terms of diagnosis and planning of endodontic clinical procedures. MEDLINE (PubMed), Web of Science, Google Scholar, Embase and Scopus were searched from inception to March 2023. This narrative review addresses the theoretical concepts, elements of interpretation and applications of the CBCT scan in endodontics. In addition, the contents and rationale for reporting 3D endodontic imaging are discussed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative Evaluation of the Accuracy of Two-Dimensional and Three-Dimensional Radiographic Assessment of Bony Defects Before and After Endodontic Surgery
Aishwarya Talakeri, Pravin Kumar, Soundharrajan P, Vinay Kumar Chugh , Rajat Sharma, Arun Patnana
Cureus.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence and morphometric assessment of the middle mesial canal in mandibular first molars in a turkish population: A CBCT study
Elif Solakoğlu, Özge Kurt
Odontology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Maxillary Sinus Pathologies in Children and Adolescents with Cleft Lip and Palate Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography: A Retrospective Study
Ayşe Çelik, Nilüfer Ersan, Senem Selvi-Kuvvetli
The Cleft Palate Craniofacial Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Machine Learning Models in the Detection of MB2 Canal Orifice in CBCT Images
Shishir Shetty, Meliz Yuvali, Ilker Ozsahin, Saad Al-Bayatti, Sangeetha Narasimhan, Mohammed Alsaegh, Hiba Al-Daghestani, Raghavendra Shetty, Renita Castelino, Leena R David, Dilber Uzun Ozsahin
International Dental Journal.2025; 75(3): 1640. CrossRef - Early diagnosis of acute lymphoblastic leukemia utilizing clinical, radiographic, and dental age indicators
Rehab F Ghouraba, Shaimaa S. EL-Desouky, Mohamed R. El-Shanshory, Ibrahim A. Kabbash, Nancy M. Metwally
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Tomographic evaluation of apexogenesis with human treated dentin matrix in young permanent molars: a split-mouth randomized controlled clinical trial
Nora M. Abo Shanady, Nahed A. Abo Hamila, Gamal M. El Maghraby, Rehab F. Ghouraba
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Integration of Cone Beam Computed Tomography, Artificial Intelligence, Augmented Reality, and Virtual Reality in Dental Diagnostics, Surgical Planning, and Education: A Narrative Review
Aida Meto, Gerta Halilaj
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(11): 6308. CrossRef - Healing Outcomes of Through‐And‐Through Bone Defects in Periapical Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta‐Analysis
Bibi Fatima, Farhan Raza Khan, Syeda Abeerah Tanveer
Australian Endodontic Journal.2025; 51(2): 518. CrossRef - Genotoxic and cytotoxic effects of cone beam computed tomography on exfoliated epithelial cells in different age groups
Maged Bakr, Fatma Ata, Asmaa Saleh Elmahdy, Bassant Mowafey
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Bridging the gap in aberrant root canal systems: Case series
Seethalakshmi Tamizhselvan, Diana Davidson, Srinivasan Manali Ramakrishnan
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(8): 833. CrossRef - IMAGING TECHNIQUES IN ENDODONTIC DIAGNOSIS: A REVIEW OF LITERATURE
Mihaela Salceanu, Anca Melian , Tudor Hamburda , Cristina Antohi , Corina Concita , Claudiu Topoliceanu , Cristian Levente Giuroiu
Romanian Journal of Oral Rehabilitation.2025; 17(1): 705. CrossRef - A Three-rooted Deciduous Second Molar in a 13-year-old Caucasian Female
Daniel Traub, Robert Walsh, Colleen Ahern
International Journal of Medical Case Reports.2025; 4(3): 51. CrossRef - Critical success factors for digital transformation in government organizations using a structural model approach
Abdalla Al Maazmi, Zehra Canan Araci, Sujan Piya
Discover Applied Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - AGE ESTIMATION BASED ON PULP / TOOTH VOLUME BY CONE BEAM COMPUTERIZED TOMOGRAPHY IMAGE
Ramadhan Rasheed, Salah Faraj
BULLETIN OF STOMATOLOGY AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY.2025; : 288. CrossRef - Clinical Benefits and Limitations of Cone-Beam Computed Tomography in Endodontic Practice: A Contemporary Evidence-Based Review
Jasmine Wong, Chengfei Zhang, Angeline Hui Cheng Lee
Diagnostics.2025; 15(24): 3117. CrossRef - On the Causes of Persistent Apical Periodontitis. Findings From Endodontic Microsurgery: A Case Report
Mateo José Pesántez-Ibarra, Carolina Berruecos-Orozco, Jeimmy Katherine Molina-Barrera, Néstor Ríos-Osorio, Rafael Fernández-Grisales
Journal of Endodontic Microsurgery.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Bildgebung im ZMK-Bereich – aber in welcher Reihenfolge?
Rainer Lutz
Zahnmedizin up2date.2024; 18(04): 297. CrossRef - Cone-beam computed tomography evaluation of shaping ability of kedo-S square and fanta AF™ baby rotary files compared to manual K-files in root canal preparation of primary anterior teeth
Shaimaa S. El-Desouky, Bassem N. El Fahl, Ibrahim A. Kabbash, Shimaa M. Hadwa
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of Endodontic Successes and Failures in the Removal of Fractured Endodontic Instruments during Retreatment: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Trial Sequential Analysis
Mario Dioguardi, Corrado Dello Russo, Filippo Scarano, Fariba Esperouz, Andrea Ballini, Diego Sovereto, Mario Alovisi, Angelo Martella, Lorenzo Lo Muzio
Healthcare.2024; 12(14): 1390. CrossRef
- Comparative Evaluation of the Accuracy of Two-Dimensional and Three-Dimensional Radiographic Assessment of Bony Defects Before and After Endodontic Surgery
- 17,181 View
- 706 Download
- 18 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref

- Predictor factors of 1-rooted mandibular second molars on complicated root and canal anatomies of other mandibular teeth
- Hakan Aydın, Hatice Harorlı
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(1):e2. Published online January 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e2
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
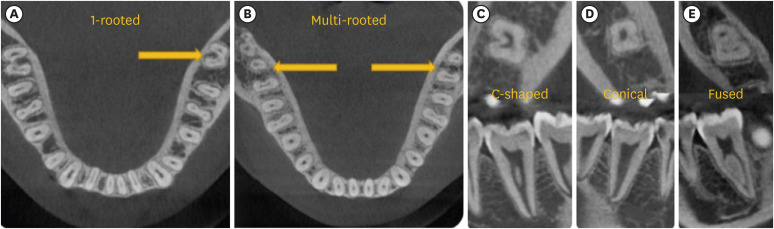
ePub Objectives This study aimed to determine the effects of 1-rooted mandibular second molar (MnSM) teeth on root canal anatomy complexities of the mandibular central incisor (MnCI), mandibular lateral incisor (MnLI), mandibular canine (MnCn), mandibular first premolar (MnFP), mandibular second premolar (MnSP), and mandibular first molar (MnFM) teeth.
Materials and Methods Cone-beam computed tomography images of 600 patients with full lower dentition were examined. Individuals with 1-rooted MnSMs were determined, and the complexity of root canal anatomy of other teeth was compared with individuals without 1-rooted MnSMs (Group-1; subjects with at least one 1-rooted MnSM, Group-2; subjects with more than a single root in both MnSMs). A second canal in MnCIs, MnLIs, MnCns, MnFPs, and MnSPs indicated a complicated root canal. The presence of a third root in MnFMs was recorded as complicated.
Results The prevalence of 1-rooted MnSMs was 12.2%, with the C-shaped root type being the most prevalent (9%). There were fewer complicated root canals in MnCIs (
p = 0.02), MnLIs (p < 0.001), and MnFPs (p < 0.001) in Group 1. The other teeth showed no difference between the groups (p > 0.05). According to logistic regression analysis, 1-rooted right MnSMs had a negative effect on having complex canal systems of MnLIs and MnFPs. Left MnSMs were explanatory variables on left MnLIs and both MnFPs.Conclusions In individuals with single-rooted MnSMs, a less complicated root canal system was observed in all teeth except the MnFMs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Repair of furcal perforations using different calcium silicate cements: An in vitro study
Ariana Esperanza Apolo Aguilar, Maria Soledad Peñaherrera Manosalvas, Henry Paul Valverde Haro
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(10): 1007. CrossRef
- Repair of furcal perforations using different calcium silicate cements: An in vitro study
- 1,955 View
- 62 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Prevalence of salivary microbial load and lactic acid presence in diabetic and non-diabetic individuals with different dental caries stages
- Monika Mohanty, Shashirekha Govind, Shakti Rath
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(1):e4. Published online January 12, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e4
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
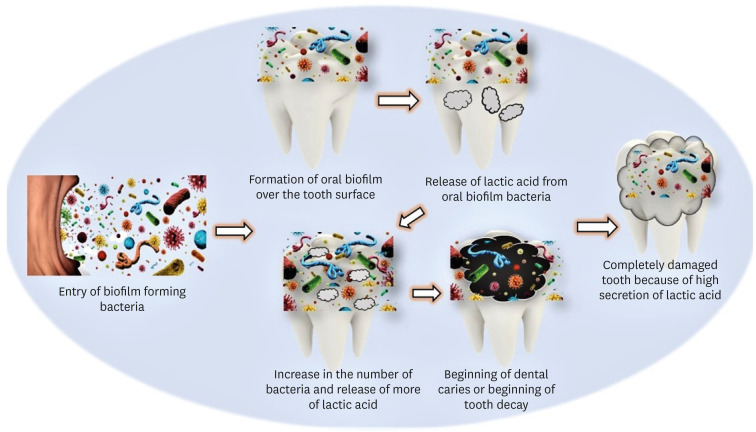
ePub Objectives This study aims to correlate caries-causing microorganism load, lactic acid estimation, and blood groups to high caries risk in diabetic and non-diabetic individuals and low caries risk in healthy individuals.
Materials and Methods This study includes 30 participants divided into 3 groups: Group A, High-risk caries diabetic individuals; Group B, High-risk caries non-diabetic individuals; and Group C, Low-risk caries individuals. The medical condition, oral hygiene, and caries risk assessment (American Dental Association classification and International Caries Detection and Assessment System scoring) were documented. Each individual’s 3 mL of saliva was analyzed for microbial load and lactic acid as follows: Part I: 2 mL for microbial quantity estimation using nutrient agar and blood agar medium, biochemical investigation, and carbohydrate fermentation tests; Part II: 0.5 mL for lactic acid estimation using spectrophotometric analysis. Among the selected individuals, blood group correlation was assessed. The χ2 test, Kruskal-Wallis test, and
post hoc analysis were done using Dunn’s test (p < 0.05).Results Group A had the highest microbial load and lactic acid concentration, followed by Groups B and C. The predominant bacteria were
Lactobacilli (63.00 ± 15.49) andStreptococcus mutans (76.00 ± 13.90) in saliva. Blood Group B is prevalent in diabetic and non-diabetic high-risk caries patients but statistically insignificant.Conclusions Diabetic individuals are more susceptible to dental caries due to high microbial loads and increased lactic acid production. These factors also lower the executing tendency of neutrophils, which accelerates microbial accumulation and increases the risk of caries in diabetic individuals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Oral Health Disparities in Type 2 Diabetes: Examining the Elevated Risk for Dental Caries—A Comparative Study
José Frias-Bulhosa, Maria Conceição Manso, Carla Lopes Mota, Paulo Melo
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(6): 258. CrossRef - Exploring the photosensitizing potential of Nanoliposome Loaded Improved Toluidine Blue O (NLITBO) Against Streptococcus mutans: An in-vitro feasibility study
Swagatika Panda, Lipsa Rout, Neeta Mohanty, Anurag Satpathy, Bhabani Sankar Satapathy, Shakti Rath, Divya Gopinath, Geelsu Hwang
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(10): e0312521. CrossRef - Altered salivary microbiota associated with high-sugar beverage consumption
Xiaozhou Fan, Kelsey R. Monson, Brandilyn A. Peters, Jennifer M. Whittington, Caroline Y. Um, Paul E. Oberstein, Marjorie L. McCullough, Neal D. Freedman, Wen-Yi Huang, Jiyoung Ahn, Richard B. Hayes
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Oral Health Disparities in Type 2 Diabetes: Examining the Elevated Risk for Dental Caries—A Comparative Study
- 3,315 View
- 86 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- The status of clinical trials regarding root canal sealers
- Ahmad AL Malak, Yasmina EL Masri, Mira Al Ziab, Nancy Zrara, Tarek Baroud, Pascale Salameh
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(1):e5. Published online January 15, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e5
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
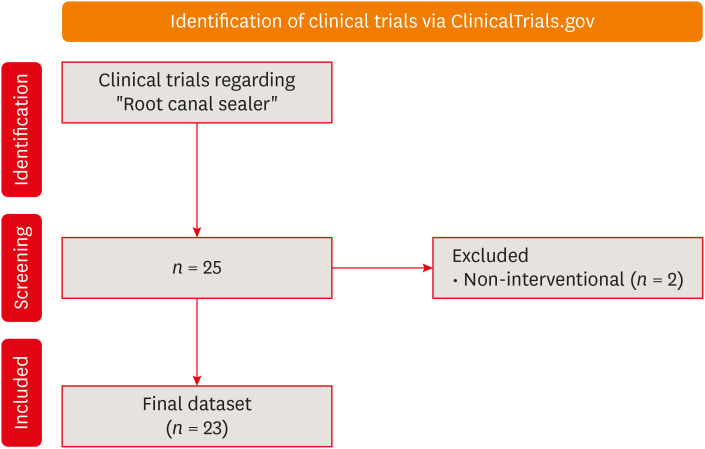
ePub Objectives This study aimed to present the results and analyses of clinical trials, including updates on the different functions of root canal sealers.
Materials and Methods In June 2023, we performed a comprehensive search of ClinicalTrials.gov to identify interventional clinical trials pertaining to root canal sealers. In total, 23 clinical trials conducted up to June 2023 were included in this study.
Results Approximately half of the trials (11 out of 23) were completed, while none were terminated or withdrawn. Each included trial had a minimum of 10 participants, with 11 trials having more than 100 participants. None of the assessed trials provided outcomes, and the majority (17 out of 23) lacked associated publications. In terms of geographic distribution, the USA and Canada did not contribute to any root canal sealer trials.
Conclusions This study highlights the lack of diversity in trial locations, the absence of reported results, and a scarcity of clinical trials examining the physicochemical properties of different sealers. Most published trials primarily focused on assessing the post-operative pain effect of these sealers, but no significant difference was found regarding post-operative pain control.
- 3,954 View
- 55 Download

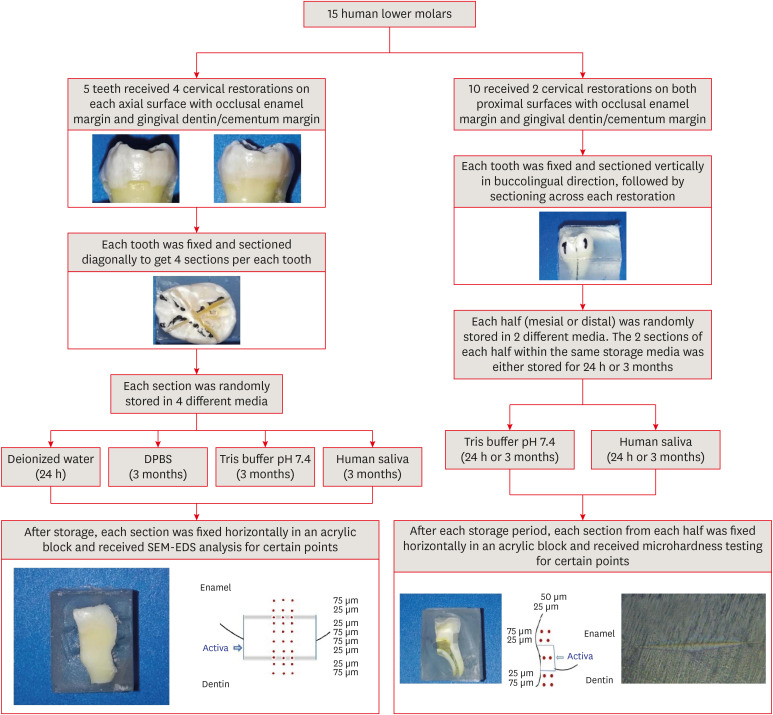
- Effect of different storage media on elemental analysis and microhardness of cervical cavity margins restored with a bioactive material
- Hoda Saleh Ismail, Brian Ray Morrow, Ashraf Ibrahim Ali, Rabab Elsayed Elaraby Mehesen, Salah Hasab Mahmoud, Franklin Garcia-Godoy
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(1):e6. Published online January 17, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e6
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to investigate the elemental analysis and microhardness of a bioactive material (Activa) and marginal tooth structure after storage in different media.
Materials and Methods Fifteen teeth received cervical restorations with occlusal enamel and gingival dentin margins using the tested material bonded with a universal adhesive, 5 of them on the 4 axial surfaces and the other 10 on only the 2 proximal surfaces. The first 5 teeth were sectioned into 4 restorations each, then stored in 4 different media; deionized water, Dulbecco's phosphate buffered saline (DPBS), Tris buffer, and saliva. The storage period for deionized water was 24 hours while it was 3 months for the other media. Each part was analyzed by scanning electron microscopy-energy dispersive spectroscopy (SEM-EDS) analysis for different substrates/distances and the wt% of calcium, phosphorus, silica, and fluoride were calculated. The other 10 teeth were sectioned across the restoration, stored in either Tris buffer or saliva for 24 hours or 3 months, and were evaluated for microhardness of different substrates/areas. Data were analyzed using analysis of variance and Tukey’s
post hoc test.Results Enamel and dentin interfaces in the DPBS group exhibited a significant increase in calcium and phosphorus wt%. Both silica and fluoride significantly increased in tooth structure up to a distance of 75 μm in the 3-month-media groups than the immediate group. Storage media did not affect the microhardness values.
Conclusions SEM-EDS analysis suggests an ion movement between Activa and tooth structure through a universal adhesive while stored in DPBS.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Elemental and micromorphological analysis of ion releasing restoration/carious dentin interface
Alaa Esmat Abdelsalam, Hoda Saleh Ismail, Hamdi Hosni Hamama
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of curing mode and aging on the bonding performance of universal adhesives in coronal and root dentin
Hoda Saleh Ismail, Ashraf Ibrahim Ali, Mohamed Elshirbeny Elawsya
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Elemental and micromorphological analysis of ion releasing restoration/carious dentin interface
- 2,215 View
- 101 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

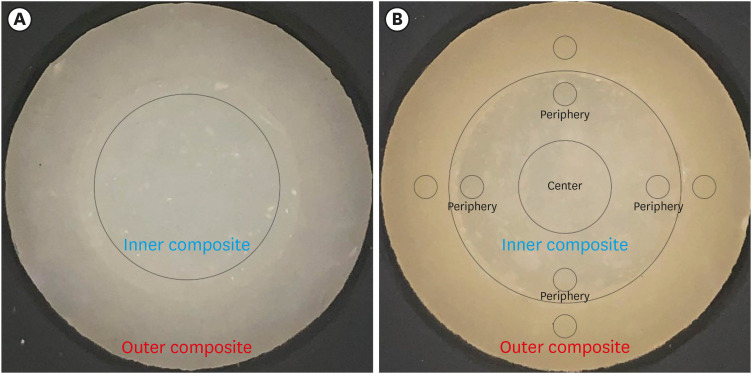
- Color discrepancy of single-shade composites at different distances from the interface measured using cell phone images
- Márcia Luciana Carregosa Santana, Gabriella de Jesus Santos Livi, André Luis Faria-e-Silva
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(1):e7. Published online January 24, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e7
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the impact of substrate color and interface distance on the color adjustment of 2 single-shade composites, Vittra APS Unique and Charisma Diamond One.
Materials and Methods Dual disc-shaped specimens were created using Vittra APS Unique or Charisma Diamond One as the center composite, surrounded by shaded composites (A1 or A3). Color measurements were taken with a spectrophotometer against a gray background, recording the color coordinates in the CIELAB color space. Illumination with a light-correcting device and image acquisition using a polarizing filter-equipped cell phone were performed on specimens over the same background. Image processing software was used to measure the color coordinates in the center and periphery of the inner composite and in the outer composite. The color data were then converted to CIELAB coordinates and adjusted using data from the spectrophotometer. Color differences (ΔE00) between the center/periphery of single-shade and outer composites were calculated, along with color changes in single-shade composites caused by different outer composites. Color differences for the inner composites surrounded by A1 and A3 were also calculated. Data were analyzed using repeated-measures analysis of variance (α = 0.05).
Results The results showed that color discrepancies were lowest near the interface and when the outer composite was whiter (A1). Additionally, Charisma Diamond One exhibited better color adjustment ability than Vittra APS Unique.
Conclusions Color discrepancies between the investigated single-shade composites diminished towards the interface with the surrounding composite, particularly when the latter exhibited a lighter shade.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of color stability in single-shade composite resins using spectrophotometer and cross-polarized mobile photography
Hatice Tepe, Ozge Celiksoz, Batu Can Yaman
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of the Staining Resistance of Two Single-Shade Composites in Coffee and Chlorhexidine: A Spectrophotometric Analysis
Unmesh Khanvilkar, Shrinath D Kulkarni, Siddhesh Bandekar, Ved M Talathi, Oshin Baghel, Priyanka Razdan, Seema Gupta
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical Implications of Color Adjustment in Single-Shade Resins Post-Dental Bleaching: A Systematic Review
Samille Biasi Miranda, Caroline de Farias Charamba Leal, Rodrigo Barros Esteves Lins, Marcos Antonio Japiassu Resende Montes
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(9): 3194. CrossRef - Accuracy and Reliability of Smartphone Versus Mirrorless Camera Images-Assisted Digital Shade Guides: An In Vitro Study
Soo Teng Chew, Suet Yeo Soo, Mohd Zulkifli Kassim, Khai Yin Lim, In Meei Tew
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(14): 8070. CrossRef
- Evaluation of color stability in single-shade composite resins using spectrophotometer and cross-polarized mobile photography
- 2,387 View
- 77 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Effect of Dental Practicality Index training using an online video on decision-making and confidence level in treatment planning by dental undergraduates
- Zhai Wei See, Ming Sern Lee, Abhishek Parolia, Shalini Kanagasingam, Shilpa Gunjal, Shanon Patel
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(1):e8. Published online January 24, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e8

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of Dental Practicality Index (DPI) training using an online video on the treatment planning decisions and confidence level of dental undergraduates (DUs).
Materials and Methods Ninety-four DUs were shown 15 clinical case scenarios and asked to decide on treatment plans based on 4 treatment options. The most appropriate treatment plan had been decided by a consensus panel of experienced dentists. DUs then underwent DPI training using an online video. In a post-DPI-training test, DUs were shown the same clinical case scenarios and asked to assign the best treatment option. After 6 weeks, DUs were retested to assess their knowledge retention. In all 3 tests, DUs completed the confidence level scale questionnaire. Data were analyzed using the related-samples Wilcoxon signed rank test and the independent-samples Mann-Whitney
U test with the level of significance set atp < 0.05.Results DPI training significantly improved the mean scores of the DUs from 7.53 in the pre-DPI-training test to 9.01 in the post-DPI-training test (
p < 0.001). After 6 weeks, the mean scores decreased marginally to 8.87 in the retention test (p = 0.563). DPI training increased their confidence level from 5.68 pre-DPI training to 7.09 post-DPI training.Conclusions Training DUs using DPI with an online video improved their decision-making and confidence level in treatment planning.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- STUDY OF THE EFFECTIVENESS OF THE USE OF DIRECT AND INDIRECT RESTORATION OVER TIME IN THE TREATMENT OF DEFECTS OF HARD DENTAL TISSUES AFTER ENDODONTIC INTERVENTION
V. V. Fedoriuk, М. М. Rozhko
Art of Medicine.2025; : 94. CrossRef
- STUDY OF THE EFFECTIVENESS OF THE USE OF DIRECT AND INDIRECT RESTORATION OVER TIME IN THE TREATMENT OF DEFECTS OF HARD DENTAL TISSUES AFTER ENDODONTIC INTERVENTION
- 2,845 View
- 68 Download
- 1 Crossref

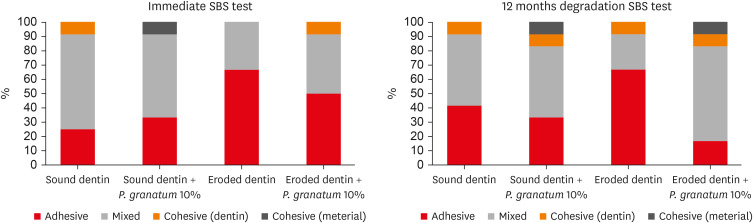
- Pomegranate extract on eroded dentin: antioxidant action, bond strength and morphology of the adhesive interface after aging
- Thiago Vinícius Cortez, Nathália Mancioppi Cerqueira, Julia Adornes Gallas, Wanderley Pereira Oliveira, Silmara Aparecida Milori Corona, Aline Evangelista Souza-Gabriel
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(1):e9. Published online January 26, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e9
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the effect of pomegranate solution (
Punica granatum ) on eroded dentin through antioxidant action, shear bond strength (SBS) and interface morphology.Materials and Methods The 10% pomegranate peel extract was prepared by the lyophilization method. Punicalagin polyphenol was confirmed by high-performance liquid chromatography. Antioxidant activity was evaluated by capturing the 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical. For the SBS, 48 dentin fragments were divided into sound or eroded, and subdivided according to the pretreatment (
n = 12): water orP. granatum . The surfaces were restored with self-etch adhesive and a bulk-fill resin (Ecosite; DMG). The SBS was done immediately (24 hours) and after thermal cycling + water storage (12 months). For scanning electron microscopy, 48 dentin fragments (24 sound and 24 eroded) received the same treatments as for SBS (n = 6), and they were analyzed after 24 hours and 12 months.Results The
P. granatum had antioxidant action similar (p = 0.246) to the phenolic standard antioxidants. After 24 hours, eroded dentin had lower SBS than sound dentin (p < 0.001), regardless of the pretreatment. After 12 months,P. granatum maintained the SBS of sound dentin (13.46 ± 3.42 MPa) and eroded dentin (10.96 ± 1.90 MPa) statistically similar. The lowest values were found on eroded dentin treated with water (5.75 ± 1.65 MPa) (p < 0.001).P. granatum on eroded dentin caused peritubular demineralization and hybrid layer with resin tags.Conclusions The pomegranate extract had antioxidant action and preserved the adhesive interface of the eroded dentin.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Antibacterial Effects of Ethanolic Extractions of Aloe Vera, Black Tea, Pomegranate and Orange on Streptococcus mutans: An In-vitro Study
Bardia Vadiati Saberi, Soheil Taghavi Namin, Dina Maleki
Nutrition And Food In Health And Disease.2025; 12(2): 29. CrossRef - Protective effect of a novel antioxidant gel containing resveratrol and sodium fluoride on dentin erosion in the presence of acquired salivary pellicle: An in vitro study
Loraine Perez Manzoli, Luan Júlio Ruiz da Silva, George Clay dos Santos Caracas, Kalinca Furtado de Oliveira, Walessa Alana Braganca Aragão, Rafael Rodrigues Lima, Milton Carlos Kuga, Cristiane de Melo Alencar
Archives of Oral Biology.2025; 179: 106395. CrossRef - Effect of pomegranate solution alone or combined with chlorhexidine against oral multispecies biofilm
J. A. Gallas, L. L. Pelozo, S. A. M. Corona, Y. Shen, M. Haapasalo, M. D. Sousa‐Neto, A. E. Souza‐Gabriel
International Endodontic Journal.2024; 57(12): 1819. CrossRef - The effect of resveratrol application on the micro-shear bond strength of adhesive to bleached enamel
Esra Cengiz-Yanardag, Izgen Karakaya
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Antibacterial Effects of Ethanolic Extractions of Aloe Vera, Black Tea, Pomegranate and Orange on Streptococcus mutans: An In-vitro Study
- 2,620 View
- 91 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- YouTube as a source of information about rubber dam: quality and content analysis
- Gülsen Kiraz, Arzu Kaya Mumcu, Safa Kurnaz
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(1):e10. Published online February 5, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e10
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the content, quality and demographics of YouTube videos about rubber dam as an information source for clinicians and dental students.
Materials and Methods “Rubber dam,” “rubber dam application,” “dental isolation,” “rubber dam isolation,” and “dental dam” were determined as keywords for the detection of YouTube videos related to rubber dam. Seventy 3 videos were evaluated and a total of 34 videos met the inclusion criteria. All selected videos were evaluated according to 8 parameters. The videos were scored 1 if the videos contained information about the selected parameter, but if the videos did not contain enough information, they were scored 0. The data were statistically analyzed with the analysis of variance and
post hoc Tukey test (p < 0.05).Results We found that 41% of the videos have poor, 47% have moderate, and 12% have good information. There is a statistically significant difference in time between poor and good information content (
p < 0.05). There is a statistically significant difference between the poor and good information in the video information and quality index 1.Conclusions Rubber dam-related videos available on YouTube are generally moderately informed and insufficient. YouTube is currently not sufficient as a source of information for patients and clinicians at the moment. The YouTube platform should be developed and enriched with quality information on current and dental issues.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Assessing the Quality of YouTube® Videos on Nitrous Oxide/Oxygen Inhalation: A Multi-Dimensional Approach for Pediatric Dentists
Sanaa N. Al-Haj Ali, Nehal AlHarbi, Hessah H. Almutairi
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessing the reliability and educational value of YouTube videos on computer-controlled local anesthesia in dentistry
Hulya Cerci Akcay, Erdal Cem Kargu, Nefise Seker, Tanay Chaubal
PLOS One.2025; 20(8): e0329291. CrossRef - Evaluation of Endodontic Retreatment Videos on The Youtube Platform: Quality and Content Analysis
Birgül Özaşır, Tufan Özaşır, Derin Buğu Yüzer, Deniz İmamoğlu, Kamran Gülşahı
European Annals of Dental Sciences.2025; 52(2): 103. CrossRef - Assessing the usefulness of educational videos on endodontic irrigation for dental students: a pilot study
Jin Wey Kock, Shahmin Kar Sze Yeap, Naveen Chhabra, Philip Yuan-Ho Chien, Shekhar Bhatia
BMC Medical Education.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Assessing the Quality of YouTube® Videos on Nitrous Oxide/Oxygen Inhalation: A Multi-Dimensional Approach for Pediatric Dentists
- 3,026 View
- 55 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Sample size determination for conducting a pilot study to assess reliability of a questionnaire
- Mohamad Adam Bujang, Evi Diana Omar, Diana Hui Ping Foo, Yoon Khee Hon
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(1):e3. Published online January 10, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e3
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This article is a narrative review that discusses the recommended sample size requirements to design a pilot study to assess the reliability of a questionnaire. A list of various sample size tables that are based on the kappa agreement test, intra-class correlation test and Cronbach’s alpha test has been compiled together. For all calculations, type I error (alpha) was set at a maximum value of 0.05, and power was set at a minimum value of 80.0%. For the kappa agreement test, intra-class correlation test, and Cronbach’s alpha test, the recommended minimum sample size requirement based on the ideal effect sizes shall be at least 15, 22, and 24 subjects respectively. By making allowances for a non-response rate of 20.0%, a minimum sample size of 30 respondents will be sufficient to assess the reliability of the questionnaire. The clear guideline of minimum sample size requirement for the pilot study to assess the reliability of a questionnaire is discussed and this will ease researchers in preparation for the pilot study. This study provides justification for a minimum requirement of a sample size of 30 respondents specifically to test the reliability of a questionnaire.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Preliminary efficacy of an online intervention based on Acceptance and Commitment Therapy for family caregivers of people with dementia: a feasibility study
Golnaz L. Atefi, Rosalie J. M. van Knippenberg, Sara Laureen Bartels, Andrés Losada-Baltar, María Márquez-González, Frans R. J. Verhey, Marjolein E. de Vugt
Cognitive Behaviour Therapy.2026; 55(1): 74. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of the Turkish Adaptation of the Feeling Safe During Surgery Scale
Hatice Çakır, Seda Cansu Yeniğün, Seçil Taylan
Journal of PeriAnesthesia Nursing.2026; 41(1): 116. CrossRef - Development of immersive radiotherapy clinical learning experience prototype (IRCLEP)
Nur Najihah Binti Hamzaini, Gunalan A.L. Ramachandran, Tavaneethan A.L. Mogan, Nur Liyana Shuib, Abdul Khaliq Mohd Saparudin, Nur Khalis Sukiman, Noraini Ahmad Wahid, Saiful Izzuan Hussin, Nor Aniza Azmi
Journal of Medical Imaging and Radiation Sciences.2026; 57(2): 102167. CrossRef - Developing and validating the augmented reality-enabled e-commerce questionnaire (ARECQ): an extended technology acceptance model for Gen Z
Alfia Sayed, Asish Oommen Mathew, Lewlyn L. R. Rodrigues
Cogent Social Sciences.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - School-based interventions of menstrual hygiene management in Indonesia: systematic literature review
Aldilia Wyasti Pratama, Erni Rosita Dewi, Kusmayra Ambarwati
BMC Women's Health.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Cultural Adaptation and Reliability Testing of the Coeliac Disease Food Attitudes and Behaviours Scale in Brazil
Camila dos Santos Ribeiro, Eduardo Yoshio Nakano, Renata Puppin Zandonadi
Nutrients.2026; 18(1): 162. CrossRef - Pilot study: Training bilingual Hmong caregivers using the pain assessment information visualization tool for effective communication in healthcare
Maichou Lor, Betty Chewning, Linkai Wu
Patient Education and Counseling.2026; 145: 109476. CrossRef - Occupants’ perceived importance and satisfaction towards indoor environmental quality of a Malaysian green campus
Agnes Tien Tien Wong, Shi Yee Wong, Nor Nazihah Chuweni, Chih Siong Wong, Ai Chen Tay
Property Management.2026; : 1. CrossRef - Veterinarians' attitudes, knowledge, and practices about antibiotic use in animals: questionnaire design and reliability
Ana Filipa Pereira, Leonardo de Rago, Jacinta Oliveira Pinho, Ana Isabel Plácido, Adolfo Figueiras, Fátima Roque, Maria Teresa Herdeiro, Ana Cláudia Coelho, Paula Alexandra Oliveira
Frontiers in Veterinary Science.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessing biopsychosocial status in people living with HIV: validity, reliability, and responsiveness of BETY-BQ
Sinan Buran, Orkun Tüfekçi, Erkin Oğuz Sarı, Süreyya Damar-Örenler, Tuba Damar-Çakırca, Ayşen Akgöz, Ayşenur Besler-Tuncer, Yavuz Yakut, Nur Banu Karaca, Mertcan Uzun, Meliha Çağla Sönmezer, Ahmet Çağkan İnkaya, Serhat Ünal, Edibe Ünal
BMC Infectious Diseases.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Pesticide Exposure and Mucocutaneous Symptoms Among Thai Agricultural Workers: A Cross-Sectional Study
Warin Intana, Chime Eden, Weeratian Tawanwongsri
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2026; 23(1): 97. CrossRef - Climate-smart radiography in Ghana: training needs of diagnostic radiographers mapped to the WHO operational framework and UNFCCC Action for Climate Empowerment (ACE)
Christian Ven Emery, Eric Akpabli, Bernard Amedzoame, Tretu Beracah, Jeffery Gameli Amlalo, Hayford Insidey, Isaac Tigbee, Joseph Amihere Ackah, Wuni Abdul-Razak
BMC Health Services Research.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Longing for Another: Extradyadic Infatuation and Its Associations with Features of the Primary Relationship and Infidelity
Teodora-Elena Huţanu, Andrei Corneliu Holman
Journal of Pacific Rim Psychology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Level of community collaboration in the implementation of wildlife conservation and management policy in King’wal Wildlife Conservancy, Nandi County, Kenya
Josphat K. Koech, Edmond M. Were, Daniel Rotich Kandagor
African Journal of Empirical Research.2026; 7(1): 215. CrossRef - Patient Adherence to Splint Therapy and Counselling Programmes in Temporomandibular Disorders: Development and Validation of a New Questionnaire
Soaad Tolba Badawy, Amal T. Badawi, Mai Ahmed Haggag
Journal of Oral Rehabilitation.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Modeling sustainable environmental responsibility behavior of students in private university
Shaohua Ben, Wenjun Zheng, Mohamad Bin Bilal Ali
Journal of Environmental Engineering and Landscape Management.2026; 34(1): 19. CrossRef - Reliability and validity of stroke self-efficacy questionnaire: a Vietnamese version
Tinh Thi Thanh Nguyen, Thanh Tran Ngoc Dang, Vien Truong Nguyen, Hong Thuy Phuong Huynh
Topics in Stroke Rehabilitation.2026; : 1. CrossRef - Comprehensive mental and cognitive health screening: A novel approach
Sejal K. Vyas
Current Psychology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychometric testing of the teacher food and nutrition-related health and wellbeing questionnaire
Tammie Jakstas, Andrew Miller, Vanessa A. Shrewsbury, Tamara Bucher, Clare E. Collins
BMC Public Health.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Behavioural and Systemic Determinants of Pesticide Waste Disposal Among Nigerian Cocoa Farmers: Insights from Mixed-Methods Research
Oluseye Oludoye, Charles C. Okolo, Opeyemi Adebanjo-Aina, Koleayo Omoyajowo, Lanrewaju Ogunyebi
Pollutants.2026; 6(1): 8. CrossRef - Validation of the Iranian version of the work-family guilt scale
Seyedeh-Bahare Safavi, Mahnaz Joukar, Farahnaz Kamali, Khatoon Samsami, Razieh Bagherzadeh
BMC Psychology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Dark triad with green attitude influence green intentions towards employee health and well-being
Mohammed Ashrafunnisa, D. Lakshmi Narasimha Prasad, Karthikeya Gattupalli, Jangili Siva Rama Krishna, Md Asadul Haque, A. V. S. Kamesh, Kirubaharan Boobalan
Discover Sustainability.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Preliminary Validation of a Knowledge, Attitude, and Practice Questionnaire Assessing Parental Self-Healthcare for Respiratory Tract Infections in Children With Cerebral Palsy in Malaysia
Riham M. K Abualeinein, Sazlina Kamaralzaman, Nur Zakiah Mohd Saat
Cureus.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Public perceptions of community pharmacists' evolving role in health promotion and pharmaceutical care: A cross-sectional study in Indonesia
Didiek Hardiyanto Soegiantoro, Fortunata Narwadan, Joyce Nadia Clarita Ndruru, Oktaviana Koa, Yunita Susanti Mahemba, Betriks Utang Palunggu, Debora Olivke, Mikha Adyatama Putra, Nikodemus Yeingo, Gregory Hope Soegiantoro
Currents in Pharmacy Teaching and Learning.2026; 18(5): 102600. CrossRef - A validated Arabic version of the clinical learning evaluation questionnaire for medical students and interns
Ahmed Amir Samir, Kerollos Abdelsayed, Hebatalla Abdelmaksoud Abdelmonsef Ahmed, Ahmed Almahdy Mohamed, Ahmed Reda Bahr, Naji Al-bawah, Ali Malik Tiryag, Alla' Khirfan, Mohamed Yacoub, Ramy Mohamed Ghazy
Medical Education Online.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessing Human Emotional Responses to Urban Sound Environments: Evidence from Web Questionnaire and EEG Survey
Neng Zhao, Weishi Li, Xiaoxia Wang, Lin Liu, Qing Wu, Wei Liao
Buildings.2026; 16(4): 874. CrossRef - Assessing active thumb palmar and radial abduction in persons with thumb carpometacarpal osteoarthritis via intermetacarpal distance methods: an exploration of validity, reliability, and precision
Halil Ibrahim Ergen, Karl Dischinger, Corey W. McGee
Clinical Rheumatology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Construction and validation of a short spirituality scale on a French population: SPI-8
Océane Agli, Christine-Vanessa Cuervo-Lombard, Nathalie Bailly
Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics Plus.2026; 3(2): 100265. CrossRef - Determinants of honey production among smallholder beekeepers: evidence from Baringo County, Kenya
Naftali Kiprono, Naomi Chebiwot Chelang’a, Raphael Gitau
Frontiers in Sustainable Food Systems.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Construct Validity and Reliability of the Effective Early Childhood Physical Literacy Pedagogue (ECE-PLP) Self-Report Instrument
Jaime Barratt, Dean Dudley, Michalis Stylianou, George Thomas, Kai Wheeler, John Cairney
Measurement in Physical Education and Exercise Science.2025; 29(2): 145. CrossRef - Enhancing energy resilience in manufacturing enterprises: A systematic mapping of challenges to strategies
P. Lebepe, T.N.D. Mathaba
Journal of Economy and Technology.2025; 3: 82. CrossRef - Impact of digital device utilization on public health surveillance to enhance city resilience during the public health emergency response: A case study of SARS-CoV-2 response in Thailand (2020–2023)
Watcharaporn Chutarong, Roongaroon Thammalikhit, Rungwasun Kraiklang, Anurak Sawangwong, Orachorn Saechang, Yuqian Guo, Weiwen Zhang
DIGITAL HEALTH.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Quality of Life and the Role of Gender in Patients With Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer in Greece
Nikolitsa S Dareioti, Christos Τ Lampropoulos, Balasis B Stavros, Sophia Georgiou, Philippos Gourzis, Nicholas S Mastronikolis
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring public perspectives on solar energy adoption in Mexico
Ana Sofia Andrade-Arias, Golam Kabir, Mehdi Mirmohammadsadeghi, Angappa Gunasekaran, Armando Elizondo-Noriega
Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews.2025; 212: 115410. CrossRef - Development and Initial Validation of the Psychosocial Stress Scale for Dancers
Yuqianqian Dong, Young-Eun Noh, Siqi Liu, Eliza Hafiz
SSRN Electronic Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Analyzing factors influencing students’ decisions to adopt smart classrooms in higher education
Long Kim, Rungrawee Jitpakdee, Wasin Praditsilp, Sook Fern Yeo
Education and Information Technologies.2025; 30(10): 14335. CrossRef - Collaborative Working Relationships Between Community Prevention Coalitions and Their Technical Assistance Providers: A Mixed Methods Approach for the Development of an Innovative Implementation Measure
Sarah M. Chilenski, Meg Small, Jochebed G. Gayles, Brittany Rhoades Cooper, Louis D. Brown
Prevention Science.2025; 26(2): 193. CrossRef - Intentions of hospital pharmacists to use digital technology in their daily practice: a cross-sectional survey using the Theory of Planned Behaviour
Kamer Tecen-Yucel, Nesligül Ozdemir-Ayduran, Emre Kara, Kutay Demirkan, Betul Okuyan
International Journal of Clinical Pharmacy.2025; 47(4): 1024. CrossRef - Development and validation of the nurses’ touch comfort evaluation scale in China
Yaohong Liu, Sainan Qiu, Hao Li, Chong Chen, Renhe Yu, Su’e Yuan
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Sequential mediator and moderator model of intention for the implementation of chatbots in Malaysian government agencies
Ramizatunnisah Jais, Abdul Hafaz Ngah
Journal of Decision Systems.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Freshmen’s Perceptions of the Effect of Technology on Learning English: A Case Study at the National University of Battambang, Cambodia
Keo Vireak, Sam Rany, Lan Bunrosy, Rouet Wen
Journal of Social Knowledge Education (JSKE).2025; 6(1): 54. CrossRef - Exploring EFL students’ challenges in oral presentations at National University of Battambang
Vireak Keo, Bunrosy Lan, Rany Sam, Wen Rouet
International Journal of Professional Development, Learners and Learning.2025; 7(2): e2513. CrossRef - Development and validation of the Persian Prosthesis Embodiment Scale for Lower Limb Amputees
Alireza Khani, Robin Bekrater-Bodmann, Zahra Fattahi, Vahideh Moradi, Mehdi Rezaee, Taher Babaee
Disability and Rehabilitation.2025; 47(20): 5368. CrossRef - Psychometric properties of the Persian version of the treatment satisfaction questionnaire for medication (TSQM) among Iranian hypertensive patients
Ali Khalooei, Mohadeseh Ghasemi, Sahar Salehi, Farshid Sharifi, Mehran Nakhaeizadeh
Chronic Illness.2025; 21(3): 390. CrossRef - The SCIEPR checklist: A tool for standardizing chest X-ray interpretation in resource-constrained settings – A pilot study
K.M. Sethole, N. Mshunqane
Radiography.2025; 31(3): 102912. CrossRef - Extracurricular physical activities and academic achievement in Saudi female physical education students: the mediating effect of motivation, enjoyment, and BMI
Mohamed Frikha
Frontiers in Psychology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Frailty as a Predictor of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder After Advance Care Planning Communication Intervention by Trained Care Managers in Long-Term Care Service Users in Japan: A Secondary Analysis
Mariko Miyamichi, Kyoko Oshiro, Shozo Okochi, Noriyasu Takeuchi, Tomoe Nakamura, Terumi Matsushima, Masako Okada, Yoshimi Kudo, Takehiro Ishiyama, Tomoyasu Kinoshita, Hideki Kojima, Mitsunori Nishikawa
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2025; 15(4): 159. CrossRef - Cross-cultural Adaptation and Validation of the Italian Version of the Revised Perceived Perioperative Competence Scale
Chiara Giammaria, Nicolò Panattoni, Irene Terrenato, Alessandro Spano, Aurora De Leo, Bernardino Tomei, Emanuele Di Simone, Fabrizio Petrone
Journal of PeriAnesthesia Nursing.2025; 40(5): 1230. CrossRef - Assessing ChatGPT for Clinical Decision-Making in Radiation Oncology, With Open-Ended Questions and Images
Wei-Kai Chuang, Yung-Shuo Kao, Yen-Ting Liu, Cho-Yin Lee
Practical Radiation Oncology.2025; 15(5): e412. CrossRef - Accuracy of a self-report questionnaire to predict peri-implant disease: a pilot study
Drew M. Young, Debora C. Matthews, Haider Al-Waeli
Periodontal and Implant Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Sport-specific relationship problems: Turkish adaptation of an evaluation method
Sabriye Ercan, Esma Arslan, Elif Şahi̇n, Esra Şahi̇n, Aydan Örsçeli̇k, Gökhan Büyüklüoğlu, Nihan Büyüklüoğlu, Hasan Kaya
BMC Sports Science, Medicine and Rehabilitation.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Multidimensional evaluation of the clinical efficacy and potential mechanisms of acupuncture combined with rehabilitation training in the treatment of stroke: a study based on multiple evaluation indicators
Jingjun Xie, Jinxia Li, Qi Sun, Jie Jiang
Frontiers in Neurology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Validation of Chinese version of the familiar tools use test for assessing limb apraxia in stroke patients
Jinni Wang, Jingxin Wei, Meilian Chen, Lu Gao, Xiaoyan Liao
Frontiers in Neurology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Sağlık Sigortası Okuryazarlığı Düzeyinin Ölçümüne Yönelik Bir Model Çalışması
Doğancan Çavmak
Akademik Araştırmalar ve Çalışmalar Dergisi (AKAD).2025; 17(32): 219. CrossRef - Pain self-efficacy scale for children and adolescents aged 8 to 17 years (SPaSE): Translation, adaptation and psychometric properties into Turkish
Bahar Aksoy, Seda Cansu Yeniğün, Adem Sümen
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2025; 84: 188. CrossRef - Validity and reliability of the Box and Block Test for individuals with schizophrenia spectrum disorder
Jing-Wen Su, Hsiang-Yu Chen, Kuan-Yi Li
Frontiers in Psychiatry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Arabic version of the patient education materials assessment tool (PEMAT): translation and validation
Marwan A. Alrasheed, Aliyah Almobarak, Hisham M. Alfayyadh, Abdulelah Alkahtani, Bander Balkhi
Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison between self-reported and pedometer-measured physical activity in Vietnamese adolescents: A reliability and agreement study
Tram T. N. Truong, Van-Anh N. Huynh, Kien G. To, Julia Robinson
PLOS Global Public Health.2025; 5(6): e0004725. CrossRef - Psychological Burden and Coping Strategies Among Pakistani Adults: A Cross-Sectional Survey Study
Madeeha Malik, Humaira Rehman, Azhar Hussain, Ayisha Hashmi, Khalid Ahmad Al-Sunaidar, Georgina Balogh, Márió Gajdács, Shazia Jamshed
Epidemiologia.2025; 6(3): 30. CrossRef - Psychometric properties of an Iranian instrument for assessing adherence to ethical principles in the use of artificial intelligence among healthcare providers
Mohsen Khosravi, Yasaman Herandi, Sedighe Sadat Tabatabaei Far, Ghasem Rajabi Vasokolaei, Fatemeh Yousefi Nejad, Hossein Bouzarjomehri, Reyhane Izadi, Zahra Zare, Marzie Abdollahzade, Hojjat Rahmani, Milad Ahmadi Marzaleh
International Journal of Medical Informatics.2025; 203: 106019. CrossRef - Development and reproducibility of a questionnaire to assess drivers and barriers to consuming plant-based alternatives to dairy foods
Beatriz Philippi Rosane, Julia Batalha, Eduardo Yoshio Nakano, Derek V. Byrne, Susanne Gjdested Bügel, Barbara Vad Andersen, Renata Puppin Zandonadi, Raquel Braz Assunção Botelho
International Journal of Gastronomy and Food Science.2025; 41: 101231. CrossRef - Development of the SCI-BodyMap—Measuring Mental Body Representations in Adults With Spinal Cord Injury: Protocol for Item Generation, Reliability, and Validity Testing
Sydney Carpentier, Sara Bottale, Nicole Cenci, Mauro Cracchiolo, Daniele De Patre, Julian Pablo Gorosito, Ilaria Grimaldi, Mara Melo, Bianca Polinelli, Marco Rigoni, Fortunata Romeo, Marina Zernitz, Ann Van de Winckel
JMIR Research Protocols.2025; 14: e72370. CrossRef - Inter-Rater Reliability of Griffiths III in a Multi-lingual Community
Nur Alfreena Alfie, Jeffrey Soon-Yit Lee, Siew-Ming Ting, Teck-Hock Toh
Malaysian Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health.2025; 31(S1): 25. CrossRef - Mediating effects of sustainability-oriented innovation on the relationship between organizational creativity and sustainable performance among Chinese manufacturing SMEs
Xie Qiong, Mohd Hizam Hanafiah, Hu Yang, Roshayati Abdul Hamid, Noor Hasni Juhdi
Multidisciplinary Reviews.2025; 8(12): 2025373. CrossRef - A study of knowledge, awareness and eating habits of Orang Asli children at Sg Rual primary school, Jeli, Kelantan, Malaysia
Muhamad Azahar Abas, Ameer Sabrin Muhammad Shukri, Mohamad Faiz Mohd Amin, Mohd Sukhairi Mat Rasat, Noor Janatun Naim Jemali
Multidisciplinary Reviews.2025; 8(12): 2025344. CrossRef - Quality Management Systems (QMSs): Exploring the Effect of Risk Factors and Developing the Risk Management Framework for QMS Effectiveness in Service Institutions
Simon Emmanuel, Ismail W. R. Taifa
Quality and Reliability Engineering International.2025; 41(7): 3176. CrossRef - Selection of Resin-Based Dental Restorative Materials: A Pilot Study on Professional Characteristics, Knowledge, and Selection Criteria
Anna Kontakou Zoniou, Maria Antoniadou, Sofia Saridou
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(14): 7987. CrossRef - Perceptions and Procedural Errors in the Use of a Patient‐Specific 3D‐Printed Model for MTA Apexification Technique Training
H. Plascencia, M. A. Contreras‐Preciado, J. F. Brito‐Ortiz, M. Díaz, R. Solis, G. Gascón
International Endodontic Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of eHealth Literacy in Healthcare Service Users: Construction and Validation of a Measurement Instrument
Juan Morales, César Augusto Eguia
Clinical Practice & Epidemiology in Mental Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring Sidewalk Built Environment Design Strategies to Promote Walkability in Tropical Humid Climates
Pakin Anuntavachakorn, Purinat Pawarana, Tarid Wongvorachan, Chaniporn Thampanichwat, Suphat Bunyarittikit
Buildings.2025; 15(15): 2659. CrossRef - Impact of freight logistics supply chain management on supply chain robustness and financial performance: Post-COVID-19 era
Valentine Muradzikwa, Chengedzai Mafini, Douglas Zvinowanda
International Journal of Research in Business and Social Science (2147- 4478).2025; 14(5): 32. CrossRef - Management of maxillofacial trauma in patients with alcohol use disorder : a cross-sectional study on awareness, practices and gaps
Elavenil Panneerselvam, Rajkumar Krishnan
Clinical Oral Investigations.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Adaptation of the Child Coeliac Disease Food Attitudes and Behaviours Scale (Child CD-FAB) into Brazilian Portuguese: Translation and Evaluation of Reproducibility and Internal Consistency
Marina de Cesaro Schwantes, Heather Maddison-Roberts, Eduardo Yoshio Nakano, Raquel Braz Assunção Botelho, Renata Puppin Zandonadi
Nutrients.2025; 17(16): 2704. CrossRef - Validation of the consumer health activation index (CHAI) among community-dwelling adults in primary care clinics in Singapore
Justin Guang Jie Lee, Qin Xiang Ng, Nan Luo, Gerald Choon Huat Koh, Ling Jie Cheng
Population Health Metrics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Maternal satisfaction with childbirth and its implications for maternity care quality: A cross-sectional study
Mirko Prosen, Sabina Ličen
Journal of Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Role of Media in the E-Government Adoption in Morocco: A Diffusion of Innovation and Technology Acceptance Model Perspective Using PLS-SEM
Oumaima El Harim, Nouh El Harmouzi
Digital.2025; 5(3): 39. CrossRef - The effect of segmented-interactive video demonstration on student performance in procedural skills among healthcare students
Nurul Rimadhayanti Hamzah, Mohd Fadzil Abdul Hanid, Mohamad Ikram Zakaria
Advances in Health Sciences Education.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Purchase intention towards products on wildberries: an empirical study among Gen Z in Russia with customer attitude as mediator
Anna Orelskaia, Arumugam G Sithamparam, Daniel Ruiz De Garibay Ponce, Ruslan V. Ozarnov
Cogent Business & Management.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring the Impact of Servitization and Digitalization on Firm Competitiveness and Performance: The Moderating Role of Government Support
Hendri Ginting, Hamidah Nayati Utami, Riyadi Riyadi, Benny Hutahayan
Sustainability.2025; 17(19): 8756. CrossRef - Assessing food label literacy: development and validation of a psychometric scale for adults
Güldane Yildirim, Muhammet Ali Çakır
Nutrition & Food Science.2025; 55(8): 1280. CrossRef - Building Resilience in Sandwich-Generation Families: Financial Literacy and Emergency Fund Ownership from an Islamic Socio-Cultural Perspective
Irni Rahmayani Johan, Sifa Nabila Azzahra, Megawati Simanjuntak, Mohamad Fazli Sabri
Fikri : Jurnal Kajian Agama, Sosial dan Budaya.2025; 10(2): 521. CrossRef - Phase one preliminary validation of a psychologically informed scale for faith based organisational effectiveness
Abraham Nyako Jnr, Ramakrushna Mahapatra
Discover Psychology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Home-Based Exercise and Fall Prevention in Older Adults: Development, Validation and Usability of the Mais Equilíbrio Mobile App
Mateus Medeiros Leite, Alessandro de Oliveira Silva, Silvana Schwerz Funghetto, Luciano Ramos de Lima, Samuel Barbosa Mezavila Abdelmur, Hudson Azevedo Pinheiro, Calliandra Maria de Souza Silva, Maurílio Tiradentes Dutra, Marina Morato Stival
JMIR Aging.2025; 8: e80724. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Antenatal Care Attendance among Pregnant Women in Mogadishu, Somalia
Walid Abdulkadir Osman, Aweis Ahmed Moallim Abdullahi, Hassan Muse Ahmed, Khalid Abdukadir Osman, Abdiwali Abdullahi Abdiwali, Ahmed Mohamud Hussein
Sage Open Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychometric evaluation of an instrument measuring artificial intelligence utilization in decision-making domains of healthcare organizations
Zahra Zare, Mohsen Khosravi, Milad Ahmadi Marzaleh, Faride Sadat Jalali, Reyhane Izadi, Homeira Naseh
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The effects of stressors on readiness for clinical practice in novice nursing students: a path analysis
Nur Guven Ozdemir, Berna Kokturk Dalcali, Soner Berse
BMC Medical Education.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychometric properties of the operationalized ICF Core Sets for autism and ADHD: item metrics, reliability, and validity
Lovisa Alehagen, John Hasslinger, Melissa H. Black, Elina Wessman, Sven Bölte
Disability and Rehabilitation.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Sun protection behaviors and knowledge of skin cancer and sun exposure among Emirati undergraduate students
Huda Anshasi, Hajer Almazrouei, Nojoud Rashed, Reem Salem, Mareyah Suhail, Amal Abdulla
BMC Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Validation of the ASSU Model for Age-Friendly E-Service Quality: An Independent Research Aligned With the ISO 25556:2025 Evidence From Senior Tourists in Guilin, China
Fan Yang, Ahmad Albattat
Sage Open.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Validation of the Adult Interpersonal Acceptance-Rejection Scale to measure parents, best friend, and romantic partner acceptance in Bangladeshi young adults
Rumana Aktar, Mohammad Ifaz Uddin, Md. Imran Hossain, Md. Robiul Hossain
Acta Psychologica.2025; 261: 105899. CrossRef - Bridging the divide between projected hydroclimatic variability and agricultural ecosystem sustainability through Life Cycle Assessment–Geographic Information System
Haseeb Akbar, Shabbir H. Gheewala
Sustainable Production and Consumption.2025; 61: 194. CrossRef - Development and validation of an instrument to assess the maturity of digital transformation in higher education institutions
Carlos Valdivia-Salazar, Oscar Serquén, Laurita Guevara, Jessie Bravo-Jaico, Roger Alarcón, Nilton Germán, Janet Aquino, Gisella Luisa Elena Maquen-Niño, Armando Moreno Heredia
Frontiers in Education.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Relationship Between Religiosity and Happiness Among Students of the Pancasila and Civic Education Study Program at the Faculty of Teacher Training and Education, Pamulang University
Adam Sugiarto, Rachmatullah Rusli
Journal of Smart Pedagogy and Education.2025; 1(1): 12. CrossRef - Development and psychometric evaluation of the Osteoporosis Preventing Behaviors Questionnaire (OPBQ) based on pender’s health promotion model
Mahsa Askarian, Ali Baloochi, Fatemeh Vizeshfar, Fatemeh Mohammadizadeh, Mobin Mottahedi, Farzad Abaszadeh
BMC Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - From Planting to Participation: Early-Phase Resident Attachment in an Urban Fruit Orchard
Jiri Remr, Jiri Sedlák
Urban Science.2025; 9(12): 492. CrossRef - The risk of occupational anaphylaxis in beekeepers: an educational public health intervention
Tea Močnik, Mihaela Zidarn, Nina Frelih, Sabina Ličen
Frontiers in Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Understanding Financial and Access Factors in Housing Decisions: An Economic Education Perspective from Phnom Penh
Berna Ou, Por Narith, Sario T Pio
Journal of Social Knowledge Education (JSKE).2025; 6(4): 438. CrossRef - Evaluating the quality-of-life for patient surviving with breast cancer diseases
Nor Intan Shamimi Abdul Aziz, Mass Hareeza Ali, Ahmad Taufik Jamil, Yuhanis Ab Aziz
International Journal of Healthcare Management.2025; : 1. CrossRef - ДОСВІД УКРАЇНОМОВНОЇ АДАПТАЦІЇ ОСОБИСТІСНОГО ОПИТУВАЛЬНИКА HEXACO M. C. ASHTON & K. LEE
Зіновія Карпенко , Арсен Климпуш
Psychological Prospects Journal.2025; (46): 39. CrossRef - Prevalence and Contributing Factors of Illicit Drug Use Among Youth Aged 18–24 Years in South Korea
Chaehee Kim, Kihye Han, Jieun Kim, Alison M. Trinkoff, Sihyun Park, Hyejin Kim
Asian Nursing Research.2025; 19(5): 433. CrossRef - Knowledge, attitudes, and practices regarding mosquito-borne diseases in an urban sector of southwestern Colombia
Francisco Javier Bedoya-Rodríguez, Carlos Eduardo Guevara-Fletcher, Jonathan S. Pelegrin
Frontiers in Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Patient perspectives on follow-up CT scans after treatment for renal cell carcinoma (RCC): a cross-sectional questionnaire study
Marlin A. A. Reijerink, Jaap Stoker, Patricia J. Zondervan, Shandra Bipat
Abdominal Radiology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effectiveness of Technology Transfer Within the China–Laos Economic Corridor on Industrial SME Performance: A Configurational Approach
Ying Xong Thanongsack, Muhammad Kamil, Souvanhxay Paovangsa, Ke Xing
Sage Open.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Movement and Function Assessment Kit (MFAK) for Children with Specific Learning Disabilities
Nur Sakinah Baharudin, Dzalani Harun, Suhaili Ibrahim, Hanif Farhan Mohd Rasdi, Masne Kadar
Environment-Behaviour Proceedings Journal.2025; 10(SI35): 43. CrossRef - Religiosity and LGBTQ+ Affirmative Practice Among Filipino Mental Health Professionals
Rolf Gian Marcos, John Manuel R. Kliatchko, Marc Eric S. Reyes
Sexuality & Culture.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictive Cultural Model for Family Caregivers of Older People with Musculoskeletal Pain in East Coast Malaysia: A Pilot Validation Study
Nurin Syafiqah Mohd Jaias, Che Azunie Che Abdullah, Muhammad Kamil Che Hasan, Mohd Khairul Zul Hasymi Firdaus, Nur Ain Mahat
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CARE SCHOLARS .2025; 8(3): 64. CrossRef - MRI safety knowledge and attitudes among nursing students in the UAE
Mohamed Zakaria El-Sayed, Mohammad Rawashdeh, Mohammed Muhussin, Ayesha Bibi, Magdi A. Ali
Health Education.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Development and Pilot Validation of the Sexual Satisfaction and Emotional Impact After Cesarean Section Scale (SSEI-CS-24): A Pilot Study
Ana-Maria Brezeanu, Dragos Brezeanu, Stase Simona, Dan Cozmei, Vlad I Tica
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Procurement Skills and Organizational Performance of the Procurement Department of the County Government of Nakuru, Kenya.
Teresiah Wanjiru Kibe, Duncan Nyakundi Nyaberi
International Journal of Social Science and Humanities Research (IJSSHR) ISSN 2959-7056 (o); 2959-7048 (p).2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Design of Luxury Train Seat Integrating Emotional Perception and Local Wisdom Approaches
Afif Hakim, Bambang Suhardi, Pringgo Widyo Laksono, Mirwan Ushada, Jafri Mohd Rohani
Jurnal Optimasi Sistem Industri.2025; 24(2): 234. CrossRef - Psychometric of the Ferrer-Urbina multidimensional scale of sexual self concept (MSSSC) in the Iranian population
Yeganeh Dadashzadeh Sangary, Mohammad Hassan Asayesh, Ali Asgharzadeh, Zahra Naghsh
BMC Psychology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Content validity, practicality and testing of the reliability of various tools for the detection and screening of delirium in residents with dementia in German nursing homes: a study protocol
Johanna Christina Seiters, Vincent Molitor, Alessandro Morandi, Tania Zieschang, Martin N Dichter, Burkhard Haastert, Maria Erdmann, Falk Hoffmann, Rebecca Palm
BMJ Open.2025; 15(12): e112357. CrossRef - Development and validation of Transtheoretical model-based questionnaire on micronutrients for adolescents: Psychometric properties
Priyanka Pareek, Aparna Thorat, Chethana Chandrasekar, Poonam Khanna, Rashmi Kulkarni, Shravya Karkera
Journal of Education and Health Promotion.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Critical success factors for digital transformation in government organizations using a structural model approach
Abdalla Al Maazmi, Zehra Canan Araci, Sujan Piya
Discover Applied Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and validation of the Thai Halitosis Associated Life-Quality Test (T-HALT): an evaluation of psychometric properties
Yodhathai Satravaha, Katkarn Thitiwatpalakarn, Supakit Peanchitlertkajorn, Supatchai Boonpratham, Chaiyapol Chaweewannakorn, Kawin Sipiyaruk
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Developing and validating a culturally tailored questionnaire to assess COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy in Israel’s ultraorthodox Jewish population
Imanuel Ber, Wasef Na’amnih, Saritte Perlman, Ben Kasstan, Yehuda Lerman, Khitam Muhsen
Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring Blood Lead Level Determinants in Refinery Workers: A Cross-Sectional Study
Luay M Mohammed , Manoochehr Karami, Yadollah Mehrabi , Seyed S Hashemi, Somayeh Farhang Dehghan, Mohammed Rafiee, Hasan Baiee
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of intervention by trained care managers on advance care planning engagement among long-term care service users in Japan: a pre- and post-pilot comparative study across multiple institutions
Shozo Okochi, Kyoko Oshiro, Noriyasu Takeuchi, Mariko Miyamichi, Tomoe Nakamura, Terumi Matsushima, Masako Okada, Yoshimi Kudo, Takehiro Ishiyama, Tomoyasu Kinoshita, Hideki Kojima, Mitsunori Nishikawa
Palliative Care and Social Practice.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Cross-cultural adaptation and validation of the Arabic version of the knee and hip health-related quality of life (Mini-OAKHQOL) questionnaire in male Saudi patients with osteoarthritis: a methodological observational design
Madi Talal Alharbi, Mahamed Ateef, Ahmad Alanazi, Msaad Alzhrani
PeerJ.2024; 12: e18122. CrossRef - The psychometric properties of the Turkish version of the parents' perception of satisfaction with care from pediatric nurse practitioners instrument
Dilek Demir Kösem, Şenay Demir, Murat Bektaş, Frances DiAnna Kinder
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2024; 78: e75. CrossRef - Advanced Work Packaging (AWP): Implementation and Challenges in the Malaysian Oil and Gas Sector
Muhammad Ali Musarat, Wesam Salah Alaloul, Mohd Al-Azahary bin Abdullah Sani, Ng Wei Chong
Sustainability.2024; 16(23): 10234. CrossRef - The assessment of reliability and validity of the Thai Versions of the Thirst Distress Scale for patients with Heart Failure and the Simplified Nutritional Appetite Questionnaire in heart failure patients
Jenjiratchaya Thanapholsart, Ehsan Khan, Satit Janwanishstaporn, Porntipa Thongma, Saowanee Naowapanich, Pornpoj Pramyothin, Srisakul Chirakarnjanakorn, Porntera Sethalao, Thitipong Tankumpuan, Nana Waldréus, Geraldine A. Lee
Journal of Research in Nursing.2024; 29(8): 622. CrossRef - Measuring internalized health-related stigma across health conditions: development and validation of the I-HEARTS Scale
Rebecca L. Pearl, Yulin Li, Laurie C. Groshon, Marian Hernandez, Danielle Saunders, Miriam Sheynblyum, Kimberly A. Driscoll, Joel M. Gelfand, Preeti Manavalan, Marjorie Montanez-Wiscovich, Deidre B. Pereira, Rebecca M. Puhl, Thomas A. Wadden, Lori B. Waxe
BMC Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A Modular XR Collaborative Platform for Occupational Safety and Health Training: A Case Study in Circular Logistics Facilities
Ali Vatankhah Barenji, Jorge E. Garcia, Benoit Montreuil
Information.2024; 15(9): 570. CrossRef
- Preliminary efficacy of an online intervention based on Acceptance and Commitment Therapy for family caregivers of people with dementia: a feasibility study
- 57,841 View
- 2,041 Download
- 103 Web of Science
- 124 Crossref


 KACD
KACD



 First
First Prev
Prev


