Previous issues
- Page Path
- HOME > Browse articles > Previous issues
- Statistical notes for clinical researchers: simple linear regression 3 – residual analysis
- Hae-Young Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(1):e11. Published online February 12, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e11
-
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Anomaly detection using different types of machine learning models in the context of “smart maintenance technologies in the manufacturing industry”
San Giliyana
Procedia Computer Science.2025; 253: 942. CrossRef - Investigation of the effect of flocculation and pulp parameters on the performance of vacuum filtration of Moroccan phosphate slurry using novel definitive screening design
Ahmed Alalou, Zouhair Hafid, Bouali Ali, El Yazghi Ezzaher Amine, Mohammed El Asri, Ahmed Boulahna
Chemical Papers.2025; 79(8): 5139. CrossRef - A Scale Development Study on the Expectation of a Disabled Friendly Hotel in the Context of Accessible Tourism
Ayşe Himmetoğlu, Beril Erkaya, Zeki Akıncı, Gülseren Yurcu, Edina Ajanovic, Gürkan Aybek, Didem Kutlu
Advances in Hospitality and Tourism Research (AHTR).2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinically significant bradycardia in children with respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis receiving dexmedetomidine: effect modification by mechanical ventilation
Rasha S Farag, Aditya S Kalluri, Geetha Iyer, Jennifer P Stevens, Carly E Milliren, James Brian McAlvin
BMJ Paediatrics Open.2025; 9(1): e003625. CrossRef - Evaluation of the influence of mixtures of nonionic surfactants on the rheology of bituminous coal-water slurry using simplex centroid mixture design
Ahmed Alalou, Abiodun A. Saka, Mohammed El Asri, Ahmed Boulahna, Monday U. Okoronkwo, Muthanna H. Al-Dahhan
Journal of Dispersion Science and Technology.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Investigating the effect of mixtures of anionic surfactants on the potential stability and rheology of coal-water slurry using the mixture design methodology
Ahmed Alalou, Abiodun A. Saka, Mohammed El Asri, Ahmed Boulahna, Monday U. Okoronkwo, Muthanna H Al-Dahhan
International Journal of Coal Preparation and Utilization.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Assessment of physical and psychological function factors and central sensitization-related symptoms associated with the Oswestry disability index in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis
Subaru Hirotsu, Teppei Abiko, Akinori Tatsuda, Satoshi Makio, Tomohisa Harada, Shin Murata
European Spine Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Correlation Analysis of the Effectiveness of Electric Energy Production at PT PLN (Persero) based on Panel Data Regression Method
Agista Surya Bawana, Nurcahya Yulian Ashar, Humam Rosyadi, Arya Wicaksana
International Journal of Research and Review.2025; : 338. CrossRef - A usability study on mobile EMG-guided wrist extension training in subacute stroke patients-MyoGuide
Hao-Ping Lin, Yang Xu, Xue Zhang, Daniel Woolley, Lina Zhao, Weidi Liang, Mengdi Huang, Hsiao-ju Cheng, Lixin Zhang, Nicole Wenderoth
Journal of NeuroEngineering and Rehabilitation.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Prediction of high-performance concrete strength using machine learning with hierarchical regression
Iman Kattoof Harith, Wissam Nadir, Mustafa S. Salah, Mohammed L. Hussien
Multiscale and Multidisciplinary Modeling, Experiments and Design.2024; 7(5): 4911. CrossRef - Influence of the radius of Monson’s sphere and excursive occlusal contacts on masticatory function of dentate subjects
Dominique Ellen Carneiro, Luiz Ricardo Marafigo Zander, Carolina Ruppel, Giancarlo De La Torre Canales, Rubén Auccaise-Estrada, Alfonso Sánchez-Ayala
Archives of Oral Biology.2024; 159: 105879. CrossRef - Fish oil supplementation modifies the associations between genetically predicted and observed concentrations of blood lipids: a cross-sectional gene-diet interaction study in UK Biobank
Yitang Sun, Tryggvi McDonald, Abigail Baur, Huifang Xu, Naveen Brahman Bateman, Ye Shen, Changwei Li, Kaixiong Ye
The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.2024; 120(3): 540. CrossRef - Associations between Dietary Sugar and Fiber with Infant Gut Microbiome Colonization at 6 Mo of Age
Pari Mokhtari, Elizabeth A. Holzhausen, Bridget N. Chalifour, Kelsey A. Schmidt, Mahsa Babaei, Christopher J. Machle, Shana Adise, Tanya L. Alderete, Michael I. Goran
The Journal of Nutrition.2024; 154(1): 152. CrossRef - A machine-learned model for predicting weight loss success using weight change features early in treatment
Farzad Shahabi, Samuel L. Battalio, Angela Fidler Pfammatter, Donald Hedeker, Bonnie Spring, Nabil Alshurafa
npj Digital Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Response surface methodology optimization of the effect of pH, contact time, and microbial concentration on chemical oxygen removal potential of vegetable oil industrial effluents
Abiodun Onadeji, Badruddeen Saulawa Sani, Umar Alfa Abubakar
Water Environment Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Selecting, optimizing and externally validating a preexisting machine-learning regression algorithm for estimating waist circumference
Bryan V. Phillips-Farfán
Computers in Biology and Medicine.2024; 169: 107909. CrossRef - QUALITY CONTROL ASSESSMENT OF DUTASTERIDE AND SILODOSIN IN CAPSULES AND TABLETS EMPLOYING A NOVEL DEVELOPED HPLC TECHNIQUE; EVALUATION OF STABILITIES OF DUTASTERIDE AND SILODOSIN IN ACCELERATED DEGRADATION
KADALI JAGADEESH, K. GANESH KADIYALA, B. N. SURESH VARMA DENDUKURI, RAMA SWAMY GUTTULA, V. L. N. BALAJI GUPTA TIRUVEEDHI, PEDDINTI VAMSI, RAJYA LAKSHMI CHAVAKULA
International Journal of Applied Pharmaceutics.2023; : 98. CrossRef - Statistical Estimation of Soil Carbon Stocks in Chungcheong Province through Digital Soil Mapping and Multiple Linear Regression
Yun-Gu Kang, Jae-Han Lee, Jun-Yeong Lee, Taek-Keun Oh
Korean Journal of Soil Science and Fertilizer.2023; 56(3): 209. CrossRef - Modelling of Low-Voltage Varistors’ Responses under Slow-Front Overvoltages
Lutendo Muremi, Pitshou N. Bokoro, Wesley Doorsamy
Electronic Materials.2023; 4(2): 62. CrossRef - Evaluating Changes in Trauma Epidemiology during the COVID-19 Lockdown: Insights and Implications for Public Health and Disaster Preparedness
Mariusz Jojczuk, Jakub Pawlikowski, Piotr Kamiński, Dariusz Głuchowski, Katarzyna Naylor, Jakub Gajewski, Robert Karpiński, Przemysław Krakowski, Józef Jonak, Adam Nogalski, Dariusz Czerwiński
Healthcare.2023; 11(17): 2436. CrossRef - Impact of Regional Development Strategy on the Productivity of Polluting Firms:Evidence From China
Jianmin Dou, Zhipeng Tao, Yongbao Ji
Frontiers in Environmental Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Associated with Japanese Nurses’ Support on End-of-life Decision-making: A Cross-sectional Study
Asahiko Higashitsuji, Tomoko Majima
Journal of Community Health Nursing.2022; 39(3): 139. CrossRef - Postnatal exposure to ambient air pollutants is associated with the composition of the infant gut microbiota at 6-months of age
Maximilian J. Bailey, Elizabeth A. Holzhausen, Zachariah E. M. Morgan, Noopur Naik, Justin P. Shaffer, Donghai Liang, Howard H. Chang, Jeremy Sarnat, Shan Sun, Paige K. Berger, Kelsey A. Schmidt, Frederick Lurmann, Michael I. Goran, Tanya L. Alderete
Gut Microbes.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Forecasting surgical costs: Towards informed financial consent and financial risk reduction
Savio George Barreto, Norma Bulamu, Adarsh Chaudhary, Gang Chen, Kazuki Kawakami, Laura Maggino, Giuseppe Malleo, Sayali Pendharkar, Maxwell T. Trudeau, Roberto Salvia, Charles M. Vollmer, John A. Windsor
Pancreatology.2021; 21(1): 253. CrossRef
- Anomaly detection using different types of machine learning models in the context of “smart maintenance technologies in the manufacturing industry”
- 5,049 View
- 94 Download
- 24 Crossref

-
Appreciations to peer reviewers in 2018: contributions to the journal,
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics - Byeong-Hoon Cho, Su-Jung Shin
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(1):e12. Published online February 18, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e12
- 706 View
- 6 Download

- Endodontic biofilms: contemporary and future treatment options
- Yeon-Jee Yoo, Hiran Perinpanayagam, Soram Oh, A-Reum Kim, Seung-Hyun Han, Kee-Yeon Kum
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(1):e7. Published online January 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e7
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Apical periodontitis is a biofilm-mediated infection. The biofilm protects bacteria from host defenses and increase their resistance to intracanal disinfecting protocols. Understanding the virulence of these endodontic microbiota within biofilm is essential for the development of novel therapeutic procedures for intracanal disinfection. Both the disruption of biofilms and the killing of their bacteria are necessary to effectively treat apical periodontitis. Accordingly, a review of endodontic biofilm types, antimicrobial resistance mechanisms, and current and future therapeutic procedures for endodontic biofilm is provided.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of Anti-Biofilm Property of Zirconium Oxide Nanoparticles on Streptococcus mutans and Enterococcus faecalis: An In Vitro Study
Anu Priya Guruswamy Pandian, Anil Kumar Ramachandran, Priyanka Kodaganallur Pitchumani, Blessy Mathai, Davis C Thomas
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Recent advances in antibacterial nanoformulations for endodontic applications
Tiago Dionísio, Pedro Brandão, Vanessa Machado, João Botelho, José João Mendes, Pedro Fonte
Expert Opinion on Drug Delivery.2025; 22(8): 1117. CrossRef - Physical–Chemical Assessment and Antimicrobial Activity of Chlortetracycline-Loaded Collagen Sponges
Graţiela Teodora Tihan, Camelia Ungureanu, Ileana Rău, Roxana Gabriela Zgârian, Răzvan Constantin Barbaresso, Mădălina Georgiana Albu Kaya, Cristina-Elena Dinu-Pîrvu, Mihaela Violeta Ghica
Materials.2025; 18(17): 4029. CrossRef - A Review of Chemical Approaches Inherent to Endodontic Disinfection Protocols: Part 1
Fatima Peer, Yahya E. Choonara, Pradeep Kumar
South African Dental Journal.2025; 80(07): 352. CrossRef - Self-Sacrificial Antibacterial Coating with Photothermal Response for Inhibiting Implant Infection
Jinglin Zhang, Aijian Cao, Lizhen Chen, Dongliang Huo, Jingxian Zhang, Langhuan Huang, Shaozao Tan
ACS Applied Nano Materials.2024; 7(23): 26907. CrossRef - Biofilm in Endodontic Infection and its Advanced Therapeutic Options – An Updated Review
Srilekha Jayakumar, Dinesh Sridhar, Bindu M. John, Karthikeyan Arumugam, Prashanth Ponnusamy, Hema Pulidindi
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2024; 16(Suppl 2): S1104. CrossRef - Analysis of the chemical interaction of polyhexanide with endodontic irrigants
Z. S. Zurab, Yu. A. Generalova, A. A. Kulikova, A. Yu. Umarov, F. V. Badalov, A. Wehbe, E. M. Kakabadze
Endodontics Today.2024; 22(4): 319. CrossRef - In vitro evaluation of three engineered multispecies endodontic biofilms on a dentinal disk substrate
Wajih Hage, Dolla Karam Sarkis, Mireille Kallasy, May Mallah, Carla Zogheib
Biomaterial Investigations in Dentistry.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - In vitro evaluation of enterococcus faecalis growth in different conditions on dentinal substrate
Wajih Hage, Dolla Karam Sarkis, Mireille Kallassy, May Mallah, Carla Zogheib
Biomaterial Investigations in Dentistry.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Bacteria associated with apical periodontitis promotes in vitro the differentiation of macrophages to osteoclasts
A. P. Torres-Monjarás, R. Sánchez-Gutiérrez, B. Hernández-Castro, L. González-Baranda, D. L. Alvarado-Hernández, A. Pozos-Guillén, A. Muñoz-Ruiz, V. Méndez-González, R. González-Amaro, M. Vitales-Noyola
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(6): 3139. CrossRef - Antimicrobial efficacy of Kerr pulp canal sealer (EWT) in combination with 10% amoxicillin on Enterococcus faecalis: A confocal laser scanning microscopic study
Madhureema De Sarkar, Kundabala Mala, Suchitra Shenoy Mala, Shama Prasada Kabekkodu, Srikant Natarajan, Neeta Shetty, Priyanka Madhav Kamath, Manuel Thomas
F1000Research.2023; 12: 725. CrossRef - Antimicrobial efficacy of Kerr pulp canal sealer (EWT) in combination with 10% amoxicillin on Enterococcus faecalis: A confocal laser scanning microscopic study
Madhureema De Sarkar, Kundabala Mala, Suchitra Shenoy Mala, Shama Prasada Kabekkodu, Srikant Natarajan, Neeta Shetty, Priyanka Madhav Kamath, Manuel Thomas
F1000Research.2023; 12: 725. CrossRef - Combined effect of electrical energy and graphene oxide on Enterococcus faecalis biofilms
Myung-Jin LEE, Mi-Ah KIM, Kyung-San MIN
Dental Materials Journal.2023; 42(6): 844. CrossRef - Innovative Curved-Tip Reactor for Non-Thermal Plasma and Plasma-Treated Water Generation: Synergistic Impact Comparison with Sodium Hypochlorite in Dental Root Canal Disinfection
Raúl Arguello-Sánchez, Régulo López-Callejas, Benjamín Gonzalo Rodríguez-Méndez, Rogelio Scougall-Vilchis, Ulises Velázquez-Enríquez, Antonio Mercado-Cabrera, Rosendo Peña-Eguiluz, Raúl Valencia-Alvarado, Carlo Eduardo Medina-Solís
Materials.2023; 16(22): 7204. CrossRef - Impact of antimicrobial photodynamic therapy on the bond-strength and penetration of endodontic sealers: A systematic review
Khalid H Almadi
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2023; 41: 103249. CrossRef - Apical periodontitis in mesiobuccal roots of maxillary molars: influence of anatomy and quality of root canal treatment, a CBCT study
Samantha Jannone Carrion, Marcelo Santos Coelho, Adriana de Jesus Soares, Marcos Frozoni
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Potential relationship between clinical symptoms and the root canal microbiomes of root filled teeth based on the next‐generation sequencing
Yajing Hou, Liu Wang, Lan Zhang, Xuelian Tan, Dingming Huang, Dongzhe Song
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(1): 18. CrossRef - Efficacy of 6% Sodium Hypochlorite on Infectious Content of Teeth with Symptomatic Irreversible Pulpitis
Rodrigo Arruda-Vasconcelos, Marlos Barbosa-Ribeiro, Lidiane M. Louzada, Beatriz I.N. Lemos, Adriana de-Jesus-Soares, Caio C.R. Ferraz, José F.A. Almeida, Marina A. Marciano, Brenda P.F. A. Gomes
Journal of Endodontics.2022; 48(2): 179. CrossRef - Specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators in endodontics: a narrative review
Davy Aubeux, Ove A. Peters, Sepanta Hosseinpour, Solène Tessier, Valérie Geoffroy, Fabienne Pérez, Alexis Gaudin
BMC Oral Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of curcumin-mediated antimicrobial photodynamic therapy associated to different chelators against Enterococcus faecalis biofilms
Daniela Alejandra Cusicanqui Méndez, Maricel Rosario Cardenas Cuéllar, Victor Feliz Pedrinha, Evelyn Giuliana Velásquez Espedilla, Flaviana Bombarda de Andrade, Patrícia de Almeida Rodrigues, Thiago Cruvinel
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2021; 35: 102464. CrossRef - Effectiveness of D,L‐2‐hydroxyisocaproic acid (HICA) and alpha‐mangostin against endodontopathogenic microorganisms in a multispecies bacterial–fungal biofilm in anex vivotooth model
Warat Leelapornpisid, Lilyann Novak‐Frazer, Alison Qualtrough, Riina Rautemaa‐Richardson
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(12): 2243. CrossRef - In Vitro Evaluation of a New Combination of Three Antibiotic Paste Against Common Endodontic Pathogens
Prasanna Dahake, Nilima Thosar
Journal of Islamic Dental Association of IRAN.2021; 33(3): 58. CrossRef - Effect of using diode laser on Enterococcus faecalis and its lipoteichoic acid (LTA) in chronic apical periodontitis
Zhaohui Zou, Junu Bhandari, Baiyan Xiao, Xiaoyue Liang, Yu Zhang, Guohui Yan
Lasers in Medical Science.2021; 36(5): 1059. CrossRef - Prevalence of Bacteria of Genus Actinomyces in Persistent Extraradicular Lesions—Systematic Review
Mario Dioguardi, Vito Crincoli, Luigi Laino, Mario Alovisi, Diego Sovereto, Lorenzo Lo Muzio, Giuseppe Troiano
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(2): 457. CrossRef - Evaluation of in vitro biofilm elimination of Enterococcus faecalis using a continuous ultrasonic irrigation device
Jennifer Galván-Pacheco, Marlen Vitales-Noyola, Ana M. González-Amaro, Heriberto Bujanda-Wong, Antonio Aragón-Piña, Verónica Méndez-González, Amaury Pozos-Guillén
Journal of Oral Science.2020; 62(4): 415. CrossRef - Comparison of the use of d-enantiomeric and l-enantiomeric antimicrobial peptides incorporated in a calcium-chelating irrigant against Enterococcus faecalis root canal wall biofilms
Wei-hu Ye, Lara Yeghiasarian, Christopher W. Cutler, Brian E. Bergeron, Stephanie Sidow, Hockin H.K. Xu, Li-na Niu, Jing-zhi Ma, Franklin R. Tay
Journal of Dentistry.2019; 91: 103231. CrossRef
- Evaluation of Anti-Biofilm Property of Zirconium Oxide Nanoparticles on Streptococcus mutans and Enterococcus faecalis: An In Vitro Study
- 4,589 View
- 125 Download
- 26 Crossref

- Finishing and polishing effects of multiblade burs on the surface texture of 5 resin composites: microhardness and roughness testing
- Elodie Ehrmann, Etienne Medioni, Nathalie Brulat-Bouchard
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(1):e1. Published online November 26, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e1

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this
in vitro study was to test the effect of 2 finishing–polishing sequences (QB, combining a 12/15-fluted finishing bur and an EVO-Light polisher; QWB, adding a 30-fluted polishing bur after the 12/15-fluted finishing bur used in the QB sequence) on 5 nanotech-based resin composites (Filtek Z500, Ceram X Mono, Ceram X Duo, Tetric Evoceram, and Tetric Evoceram Bulk Fill) by comparing their final surface roughness and hardness values to those of a Mylar strip control group (MS).Materials and Methods Twelve specimens of each nanocomposite were prepared in Teflon moulds. The surface of each resin composite was finished with QB (5 samples), QWB (5 samples), or MS (2 samples), and then evaluated (60 samples). Roughness was analysed with an optical profilometer, microhardness was tested with a Vickers indenter, and the surfaces were examined by optical and scanning electron microscopy. Data were analysed using the Kruskal-Wallis test (
p < 0.05) followed by the Dunn test.Results For the hardness and roughness of nanocomposite resin, the QWB sequence was significantly more effective than QB (
p < 0.05). The Filtek Z500 showed significantly harder surfaces regardless of the finishing–polishing sequence (p < 0.05).Conclusions QWB yielded the best values of surface roughness and hardness. The hardness and roughness of the 5 nanocomposites presented less significant differences when QWB was used.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of modeling liquid application on color stability and surface roughness of single-shade composites
Melek Güven Bekdaş, Ihsan Hubbezoglu
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of different charcoal-containing whitening toothpastes on color and surface roughness of a supra-nanofilled composite resin
Meltem Nermin Polan, Sevil Gurgan
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of different polishing techniques on surface roughness, gloss, and microhardness of zirconium oxide reinforced flowable bulk-fill resin composite: an in vitro study
Amr Elsayed Elnahas, Mohamed Elshirbeny Elawsya, Abeer ElSayed ElEmbaby
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Tek Renkli Monokromatik Kompozit Rezinlerle İlgili Bir Durum Değerlendirmesi
Kubra Nur Yeşilova, Sebnem Turkun
Selcuk Dental Journal.2025; 12(2): 331. CrossRef - Effect of different finishing and polishing systems on surface properties of universal single shade resin-based composites
Ghada Alharbi, Hend NA Al Nahedh, Loulwa M. Al-Saud, Nourah Shono, Ahmed Maawadh
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A comparative study of polishing systems on optical properties and surface roughness of additively manufactured and conventional resin based composites
Ayse Tugba Erturk-Avunduk, Sevim Atılan-Yavuz, Hande Filiz, Esra Cengiz-Yanardag
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Instrument Lubricant on Mechanical Properties of Restorative Composite
G Pippin, D Tantbirojn, M Wolfgang, JS Nordin, A Versluis
Operative Dentistry.2024; 49(4): 475. CrossRef - An In Vitro Study regarding the Wear of Composite Materials Following the Use of Dental Bleaching Protocols
Alexandru Dan Popescu, Mihaela Jana Ţuculină, Lelia Mihaela Gheorghiță, Andrei Osman, Claudiu Nicolicescu, Smaranda Adelina Bugălă, Mihaela Ionescu, Jaqueline Abdul-Razzak, Oana Andreea Diaconu, Bogdan Dimitriu
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2023; 14(10): 532. CrossRef - Akıllı Kromatik Teknolojili Kompozit Rezinlerin Farklı pH Değerlerindeki Sıvılarda Bekletilmesi Sonrası Oluşan Yüzey Pürüzlülüğü ve Renk Değişimlerinin Değerlendirilmesi
Fatih ÖZNURHAN, Aylin ÖZEL
Farabi Tıp Dergisi.2023; 2(4): 17. CrossRef - Enamel surface roughness evaluation after debonding and residual resin removal using four different burs
Rapeti Madhu Vanya, Anil Chirla, Uday Kumar Digumarthi, Tarakesh Karri, Bommareddy Radhika, Sanapala Manojna
Journal of Contemporary Orthodontics.2023; 7(3): 173. CrossRef - Finishing and Polishing of Composite Restoration: Assessment of Knowledge, Attitude and Practice Among Various Dental Professionals in India
Sankar Vishwanath, Sadasiva Kadandale, Senthil kumar Kumarappan, Anupama Ramachandran, Manu Unnikrishnan, Honap manjiri Nagesh
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of different composite resin finishing and polishing protocols by confocal laser scan microscopy
Kayo Matheus Rodrigues de Souza, Roberto Victor de Melo Silva, Marlon Ferreira Dias, Paulo Cardoso Lins-Filho, Claudio Heliomar Vicente da Silva, Renata Pedrosa Guimarães
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2022; 21: e225334. CrossRef - Laboratory methods to simulate the mechanical degradation of resin composite restorations
Veronica P. Lima, Jaqueline B. Machado, Yu Zhang, Bas A.C. Loomans, Rafael R. Moraes
Dental Materials.2022; 38(1): 214. CrossRef - FARKLI POLİSAJ SİSTEMLERİNİN POSTERİOR BÖLGEDE KULLANILAN KOMPOZİT REZİNLERİN YÜZEY PÜRÜZLÜLÜĞÜ ÜZERİNE ETKİSİ
Meltem Nermin DURSUN, Cansu ATALAY
Atatürk Üniversitesi Diş Hekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi.2022; : 1. CrossRef - The Effect of Additional Finishing and Polishing Sequences on Hardness and Roughness of Two Different Dental Composites: An In Vitro Study
Kıvanç Dülger
Journal of Advanced Oral Research.2022; 13(2): 216. CrossRef - Effect of immediate and delayed finishing and polishing procedure on Streptococcal mutans adhesion and micro-hardness of composite resin surface: An in-vitro study
Tushar Kanti Majumdar, Moumita Khatua, Paromita Mazumdar, Sayantan Mukherjee
International Dental Journal of Student's Research.2022; 10(1): 5. CrossRef - Comparison of Polishing Systems on the Surface Roughness of Resin Based Composites Containing Different Monomers
Marina Gullo Augusto, Guilherme Schmitt de Andrade, Ingrid Fernandes Mathias-Santamaria, Amanda Maria de Oliveira Dal Piva, João Paulo Mendes Tribst
Journal of Composites Science.2022; 6(5): 146. CrossRef - THE EFFECT OF PH-CYCLING AND TOOTHBRUSHING SIMULATIONS ON SURFACE ROUGHNESS OF BULK-FILL COMPOSITES
Tuğba MİSİLLİ, Nihan GONULOL, Özge Gizem CABADAĞ, Lena ALMASIFAR, Derya DİNÇ
Clinical and Experimental Health Sciences.2021; 11(3): 487. CrossRef - A three-year randomized clinical trial evaluating direct posterior composite restorations placed with three self-etch adhesives
Joseph Sabbagh, Layal El Masri, Jean Claude Fahd, Paul Nahas
Biomaterial Investigations in Dentistry.2021; 8(1): 92. CrossRef - Press-On Force Effect on the Efficiency of Composite Restorations Final Polishing—Preliminary In Vitro Study
Anna Lehmann, Kacper Nijakowski, Natalia Potempa, Paweł Sieradzki, Mateusz Król, Olaf Czyż, Agnieszka Radziszewska, Anna Surdacka
Coatings.2021; 11(6): 705. CrossRef - Surface evaluations of a nanocomposite after different finishing and polishing systems for anterior and posterior restorations
Riccardo Monterubbianesi, Vincenzo Tosco, Giulia Orilisi, Simone Grandini, Giovanna Orsini, Angelo Putignano
Microscopy Research and Technique.2021; 84(12): 2922. CrossRef - Wear, roughness and microhardness analyses of single increment restorative materials submitted to different challenges in vitro
L. C. Oliveira, P. H. dos Santos, F. S. S. Ramos, M. D. Moda, A. L. F. Briso, T. C. Fagundes
European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry.2021; 22(2): 247. CrossRef - Neurotic personality trait as a predictor in the prognosis of composite restorations: A 24-month clinical follow up study
Sulthan Ibrahim Raja Khan, Dinesh Rao, Anupama Ramachandran, Bhaskaran Veni Ashok, Jagan Kumar Baskaradoss
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of Finishing and Polishing Sequences on The Surface Roughness of Three Different Nanocomposites and Composite/Enamel and Composite/Cementum Interfaces
Ksenia Babina, Maria Polyakova, Inna Sokhova, Vladlena Doroshina, Marianna Arakelyan, Nina Novozhilova
Nanomaterials.2020; 10(7): 1339. CrossRef - Surface Geometry of Four Conventional Nanohybrid Resin‐Based Composites and Four Regular Viscosity Bulk Fill Resin‐Based Composites after Two‐Step Polishing Procedure
Mateusz Granat, Janusz Cieloszyk, Urszula Kowalska, Jadwiga Buczkowska-Radlińska, Ryta Łagocka, Ali Nokhodchi
BioMed Research International.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Effect of modeling liquid application on color stability and surface roughness of single-shade composites
- 2,456 View
- 24 Download
- 25 Crossref

- The top 10 most-cited articles on the management of fractured instruments: a bibliometric analysis
- Lora Mishra, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Naomi Ranjan Singh, Priti Pragati Rath
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(1):e2. Published online December 26, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e2
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this research was to identify the top 10 most-cited articles on the management of fractured or broken instruments and to perform a bibliometric analysis thereof.
Materials and Methods Published articles related to fractured instruments were screened from online databases, such as Web of Science, Scopus, PubMed, and ScienceDirect, and highly cited papers, with at least 50 citations since publication, were identified. The most-cited articles were selected and analysed with regard to publication title, authorship, the journal of publication, year, institution, country of origin, article type, and number of citations.
Results The top 10 most-cited articles were from various journals. Most were published in the
Journal of Endodontics , followed by theInternational Endodontic Journal , andDental Traumatology . The leading countries were Australia, Israel, Switzerland, the USA, and Germany, and the leading institution was the University of Melbourne. The majority of articles among the top 10 articles were clinical research studies (n = 8), followed by a basic research article and a non-systematic review article.Conclusions This bibliometric analysis revealed interesting information about scientific progress in endodontics regarding fractured instruments. Overall, clinical research studies and basic research articles published in high-impact endodontic journals had the highest citation rates.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bibliometric analysis of the publications that list the most-cited articles in endodontics
Oscar Alejandro Gutiérrez-Alvarez, Luis Alberto Pantoja-Villa, Benigno Miguel Calderón-Rojas
Endodontology.2025; 37(2): 128. CrossRef - Endodontide Mikro-Bilgisayarlı Tomografinin Kullanımı Konusunda Yayımlanan Makalelerin Bibliyometrik Analizi: Nicel Araştırma
Özge Kurt, Emine Şimşek
Mersin Üniversitesi Sağlık Bilimleri Dergisi.2025; 18(3): 309. CrossRef - A Bibliometric Analysis of the 100 Top-Cited Articles on Vertical Root Fractures
Pillai Arun Gopinathan , Ikram UI Haq, Nawaf Alfahad, Saleh Alwatban, Abdullah Alghamdi, Amal Alamri, Kiran Iyer
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictive factors in the retrieval of endodontic instruments: the relationship between the fragment length and location
Ricardo Portigliatti, Eugenia Pilar Consoli Lizzi, Pablo Alejandro Rodríguez
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A bibliometric analysis of the top 100 most‐cited case reports and case series in Endodontic journals
Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Jelena Jacimovic, Aleksandar Jakovljevic, Giampiero Rossi‐Fedele, Paul M. H. Dummer
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(3): 185. CrossRef - The Most Highly Cited Publications on Basketball Originate From English-Speaking Countries, Are Published After 2000, Are Focused on Medicine-Related Topics, and Are Level III Evidence
Zachary D. Griffin, Jordan R. Pollock, M. Lane Moore, Kade S. McQuivey, Jaymeson R. Arthur, Anikar Chhabra
Arthroscopy, Sports Medicine, and Rehabilitation.2022; 4(3): e891. CrossRef - Ten years of minimally invasive access cavities in Endodontics: a bibliometric analysis of the 25 most-cited studies
Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Karem Paula Pinto, Natasha C. Ajuz, Luciana Moura Sassone
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Publication trends in micro‐CT endodontic research: a bibliometric analysis over a 25‐year period
U. Aksoy, M. Küçük, M. A. Versiani, K. Orhan
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(3): 343. CrossRef
- Bibliometric analysis of the publications that list the most-cited articles in endodontics
- 1,604 View
- 10 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Effect of cooling water temperature on the temperature changes in pulp chamber and at handpiece head during high-speed tooth preparation
- Ra'fat I. Farah
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(1):e3. Published online December 24, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e3
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives It was the aim of this study to evaluate the effect of cooling water temperature on the temperature changes in the pulp chamber and at the handpiece head during high-speed tooth preparation using an electric handpiece.
Materials and Methods Twenty-eight intact human molars received a standardized occlusal preparation for 60 seconds using a diamond bur in an electric handpiece, and one of four treatments were applied that varied in the temperature of cooling water applied (control, with no cooling water, 10°C, 23°C, and 35°C). The temperature changes in the pulp chamber and at the handpiece head were recorded using K-type thermocouples connected to a digital thermometer.
Results The average temperature changes within the pulp chamber and at the handpiece head during preparation increased substantially when no cooling water was applied (6.8°C and 11.0°C, respectively), but decreased significantly when cooling water was added. The most substantial drop in temperature occurred with 10°C water (−16.3°C and −10.2ºC), but reductions were also seen at 23°C (−8.6°C and −4.9°C). With 35°C cooling water, temperatures increased slightly, but still remained lower than the no cooling water group (1.6°C and 6.7ºC).
Conclusions The temperature changes in the pulp chamber and at the handpiece head were above harmful thresholds when tooth preparation was performed without cooling water. However, cooling water of all temperatures prevented harmful critical temperature changes even though water at 35°C raised temperatures slightly above baseline.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficacy Assessment of a Novel Device for Dental Aerosol Capture and Inactivation: An In Vitro Study
Yan Sun, Jia-Chun Li, Yu-Gang Li, Xiao-Yan Yu, Jie Hu, Zhe Li, Ji-Chao Cao
International Dental Journal.2026; 76(2): 109331. CrossRef - Comparison of Two Fiber Post Removal Techniques Evaluating Dentin Removal, Efficiency, and Heat Production
Matthew Fenigstein, Mazin Askar, Ahmad Maalhagh-Fard, Susan Paurazas
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(6): 234. CrossRef - Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA): An Overview of Its Biological Activities, Properties, Polymerization, Modifications, and Dental and Industrial Applications
Great Iruoghene Edo, Emad Yousif, Mohammed H. Al-Mashhadani
Regenerative Engineering and Translational Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of Water Coolant and Bur Type on Pulp Temperature When Removing Tooth Structure and Restorative Dental Materials
C Mafrici, M Kingston, R Grice, PV Abbott
Operative Dentistry.2024; 49(1): 91. CrossRef - A Finite Element Method Study on a Simulation of the Thermal Behaviour of Four Methods for the Restoration of Class II Cavities
Adela Nicoleta Staicu, Mihaela Jana Țuculină, Cristian Niky Cumpătă, Ana Maria Rîcă, Maria Cristina Beznă, Dragoș Laurențiu Popa, Alexandru Dan Popescu, Oana Andreea Diaconu
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2024; 15(4): 86. CrossRef - In vitro comparison of guide planes for removable partial dentures prepared with CAD-CAM-assisted templates, guiding rod templates, and freehand
Ni Cheng, Hai Yu, Wenxi Shan, Jiang Wu
Journal of Dentistry.2024; 149: 105322. CrossRef - Comparison of antimicrobial efficacy of different disinfectants on the biofilm formation in dental unit water systems using dip slide and conventional methods: A pilot study
Pelin Özmen, Hilal Erdoğan, Aslıhan Güngördü, Bülent Pişkin, Funda Kont Çobankara, Serdar Sütcü, Nesrin Şahin
Microscopy Research and Technique.2024; 87(6): 1241. CrossRef - Analysis of the Pulpal Blood Flow Microdynamics during Prosthetic Tooth Preparation Using Diamond Burs with Different Degrees of Wear
Edmond Ciora, Mariana Miron, Diana Lungeanu, Andreea Igna, Anca Jivanescu
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(6): 178. CrossRef - Bacterial contamination potential of personal protective equipment itself in dental aerosol-producing treatments
Madline Priska Gund, Jusef Naim, Stefan Rupf, Barbara Gärtner, Matthias Hannig
Odontology.2024; 112(2): 309. CrossRef - Patient satisfaction before and after occlusal adjustment using a visual analog scale
Ha-Rim Lee, Sun-Haeng Lee, Gyeong-Je Lee
Oral Biology Research.2023; 47(1): 8. CrossRef - Heat generated during dental treatments affecting intrapulpal temperature: a review
Xin Er Lau, Xiaoyun Liu, Helene Chua, Wendy Jingwen Wang, Maykon Dias, Joanne Jung Eun Choi
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(5): 2277. CrossRef - “The effect of diode laser 940 nm and 445 nm on the rise in temperature of a pulp simulating material: in vitro study”
Basant Bahaaeldin, Ola Ibrahim Fahmy, Amira Zoghaby, Rene Franzen
Lasers in Dental Science.2023; 7(3): 147. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Pulp Chamber Temperature during Tooth Veneer Preparation Using Burs with Different Degrees of Wear—A Preliminary In Vitro Study
Edmond Ciora, Mariana Miron, Daliana Bojoga, Diana Lungeanu, Anca Jivanescu
Dentistry Journal.2023; 11(8): 197. CrossRef - Effect of spray air settings of speed-increasing contra-angle handpieces on intrapulpal temperatures, drilling times, and coolant spray pattern
Edina Lempel, József Szalma
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 26(1): 523. CrossRef - Preparing guiding planes for removable partial dentures: an in vitro comparison between assisted CAD-CAM template procedure and freehand preparation
Hefei Bai, Hongqiang Ye, Hu Chen, Yong Wang, Yongsheng Zhou, Yuchun Sun
Journal of Dentistry.2022; 123: 104166. CrossRef - Yeni Tip Koronavirüs (COVID-19) Salgınının Diş Hekimlerinin Tedavi Kliniği Düzeni Üzerine Etkisi
Onur Altuğ SAKALLI, Sedanur SAKALLI, Aleyna Öykü AKBAŞAK, Selim ERKUT
ADO Klinik Bilimler Dergisi.2022; 11(2): 140. CrossRef - Aerosol suppression from a handpiece using viscoelastic solution in confined dental office
Yong Il Kim, Seongpil An, Jungwoo Huh, Yang-Soo Kim, Jihye Heo, In-Seok Song, Alexander L. Yarin, Sam S. Yoon
Physics of Fluids.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Transmission through Aerosols in Restorative and Endodontic Practice
Ambar W. Raut, Priyatama V. Meshram, Radha A. Raut
Annals of African Medicine.2022; 21(1): 1. CrossRef - Redefining aerosol in dentistry during COVID-19 pandemic
Kanupriya Rathore, HarshvardhanSingh Rathore, Pranshu Singh, Pravin Kumar
Dental Research Journal.2022; 19(1): 53. CrossRef - Different grinding speeds affect induced regeneration capacity of human treated dentin matrix
Min Li, Sen Yang, Jinlin Song, Tiwei Fu, Panpan Liang, Zhi Gao, Jing Tang, Lijuan Guo
Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials.2022; 110(4): 755. CrossRef -
In Vivo Pulp Temperature Changes During Class V Cavity Preparation and Resin Composite Restoration in Premolars
DC Zarpellon, P Runnacles, C Maucoski, DJ Gross, U Coelho, FA Rueggeberg, CAG Arrais
Operative Dentistry.2021; 46(4): 374. CrossRef - In vivo evaluation of the virucidal efficacy of chlorhexidine and povidone-iodine mouthwashes against salivary SARS-CoV-2. A randomized-controlled clinical trial
Rola Elzein, Fadi Abdel-Sater, Soha Fakhreddine, Pierre Abi Hanna, Rita Feghali, Hassan Hamad, Fouad Ayoub
Journal of Evidence Based Dental Practice.2021; 21(3): 101584. CrossRef - Possible transmission of Covid-19 & precautions in a dental setting: A review
Sonali Gholap, Amit Mani, Shubhangi Mani, Shivani Sachdeva, Jasleen Kaur Sodhi, Hiral Vora
IP International Journal of Periodontology and Implantology.2021; 6(2): 98. CrossRef - An Evaluation of Two Systems for the Management of the Microbiological Quality of Water in Dental Unit Waterlines: Hygowater® and IGN Calbénium®
Damien Offner, Anne-Marie Musset
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(10): 5477. CrossRef - Restoration of dental services after COVID-19: The fallow time determination with laser light scattering
Xiujie Li, Cheuk Ming Mak, Kuen Wai Ma, Hai Ming Wong
Sustainable Cities and Society.2021; 74: 103134. CrossRef - Possible aerosol transmission of COVID-19 and special precautions in dentistry
Zi-yu Ge, Lu-ming Yang, Jia-jia Xia, Xiao-hui Fu, Yan-zhen Zhang
Journal of Zhejiang University-SCIENCE B.2020; 21(5): 361. CrossRef - Yeni Koronavirüs Salgını ve Diş Hekimliği Tedavileri Üzerine Etkileri
Elif Ballıkaya, Gülce Esentürk, Gizem Erbaş Ünverdi, Zafer Cehreli
Hacettepe University Faculty of Health Sciences Journal.2020; 7(2): 92. CrossRef
- Efficacy Assessment of a Novel Device for Dental Aerosol Capture and Inactivation: An In Vitro Study
- 5,168 View
- 52 Download
- 27 Crossref

-
Inhibition of nicotine-induced
Streptococcus mutans biofilm formation by salts solutions intended for mouthrinses - Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad, Mary Anne S. Melo, Richard L. Gregory
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(1):e4. Published online January 16, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e4
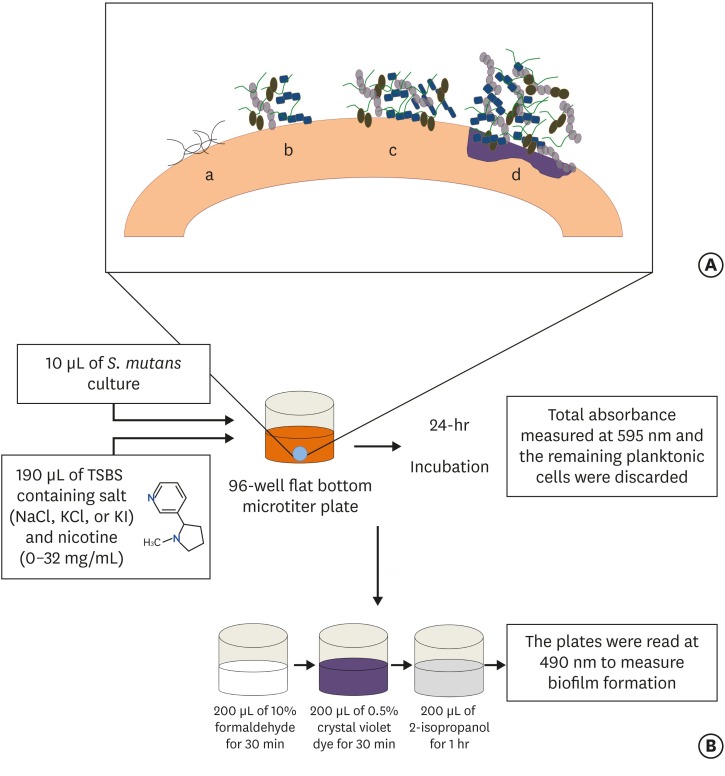
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Biofilm formation is critical to dental caries initiation and development. The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of nicotine exposure on
Streptococcus mutans (S. mutans ) biofilm formation concomitantly with the inhibitory effects of sodium chloride (NaCl), potassium chloride (KCl) and potassium iodide (KI) salts. This study examined bacterial growth with varying concentrations of NaCl, KCl, and KI salts and nicotine levels consistent with primary levels of nicotine exposure.Materials and Methods A preliminary screening experiment was performed to investigate the appropriate concentrations of NaCl, KCl, and KI to use with nicotine. With the data, a
S. mutans biofilm growth assay was conducted using nicotine (0–32 mg/mL) in Tryptic Soy broth supplemented with 1% sucrose with and without 0.45 M of NaCl, 0.23 M of KCl, and 0.113 M of KI. The biofilm was stained with crystal violet dye and the absorbance measured to determine biofilm formation.Results The presence of 0.45 M of NaCl, 0.23 M of KCl, and 0.113 M of KI significantly inhibited (
p < 0.05) nicotine-inducedS. mutans biofilm formation by 52%, 79.7%, and 64.1%, respectively.Conclusions The results provide additional evidence regarding the biofilm-enhancing effects of nicotine and demonstrate the inhibitory influence of these salts in reducing the nicotine-induced biofilm formation. A short-term exposure to these salts may inhibit
S. mutans biofilm formation.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Biofilm forming and swarming activities of Bacillus cereus modulated by multiclass compounds
Abdul Rafay Rafiq, Mohsin Tariq, Syeda Tahseen Zahra, Temoor Ahmed
The Microbe.2026; 10: 100644. CrossRef - The Influence of Nicotine on Collagen Binding in Streptococcus mutans Serotype C Strains: An In Vitro Study
Naif N Abogazalah, Richard L Gregory, Mohammed M Al Moaleem
World Journal of Dentistry.2026; 16(11): 967. CrossRef - The Inhibition of Streptococcus mutans Biofilms following Exposure to Different Chocolate Ingredients
Hadi A. Almoabid, Leen Saleh Almutairi, Abdul Samad Khan, Mohammed A. Aljaffary, Rasha AlSheikh, Khalid S. Almulhim, Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad
European Journal of Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The impact of Caralluma munbyana extracts on Streptococcus mutans biofilm formation
Turki Alshehri, Israa Alkhalifah, Areeb Alotaibi, Alaa F. Alsulaiman, Abdullah Al Madani, Basil Almutairi, Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Tobacco‐enhanced biofilm formation by Porphyromonas gingivalis and other oral microbes
Jinlian Tan, Gwyneth J. Lamont, David A. Scott
Molecular Oral Microbiology.2024; 39(5): 270. CrossRef - Nicotine is a potent extracellular polysaccharide inducer in Fusobacterium nucleatum biofilms
Adaias Oliveira Matos, Valentim Adelino Ricardo Barão, Richard Lee Gregory
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of eucalyptus oil on Streptococcus mutans and Enterococcus faecalis growth
Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad, Rasha N. AlSheikh
BDJ Open.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Microorganisms: crucial players of smokeless tobacco for several health attributes
Akanksha Vishwakarma, Digvijay Verma
Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology.2021; 105(16-17): 6123. CrossRef - Microbiology of the American Smokeless Tobacco
A. J. Rivera, R. E. Tyx
Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology.2021; 105(12): 4843. CrossRef - The Impact of Photosensitizer Selection on Bactericidal Efficacy Of PDT against Cariogenic Biofilms: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Maurício Ítalo Silva Teófilo, Teresa Maria Amorim Zaranza de Carvalho Russi, Paulo Goberlanio de Barros Silva, Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad, Mary Anne S. Melo, Juliana P.M.L. Rolim
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2021; 33: 102046. CrossRef - Antibacterial Activities of Methanol and Aqueous Extracts of Salvadora persica against Streptococcus mutans Biofilms: An In Vitro Study
Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad, Lamia Mokeem, Mary Anne S. Melo, Richard L. Gregory
Dentistry Journal.2021; 9(12): 143. CrossRef - The burden of root caries: Updated perspectives and advances on management strategies
Mohammed S. AlQranei, Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad, Mary A.S. Melo
Gerodontology.2021; 38(2): 136. CrossRef - Emerging Contact-Killing Antibacterial Strategies for Developing Anti-Biofilm Dental Polymeric Restorative Materials
Heba Mitwalli, Rashed Alsahafi, Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad, Michael D. Weir, Hockin H. K. Xu, Mary Anne S. Melo
Bioengineering.2020; 7(3): 83. CrossRef - In-Vitro Model of Scardovia wiggsiae Biofilm Formation and Effect of Nicotine
Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad, Hadeel M. Ayoub, Richard L. Gregory
Brazilian Dental Journal.2020; 31(5): 471. CrossRef - Antibacterial efficacy and remineralization capacity of glycyrrhizic acid added casein phosphopeptide‐amorphous calcium phosphate
Feride Sahin, Fatih Oznurhan
Microscopy Research and Technique.2020; 83(7): 744. CrossRef - Concentration dependence of quaternary ammonium monomer on the design of high-performance bioactive composite for root caries restorations
Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad, Maria S. Ibrahim, Michael D. Weir, Hockin H.K. Xu, Mary Anne S. Melo
Dental Materials.2020; 36(8): e266. CrossRef
- Biofilm forming and swarming activities of Bacillus cereus modulated by multiclass compounds
- 1,796 View
- 13 Download
- 16 Crossref

- The push-out bond strength of BIOfactor mineral trioxide aggregate, a novel root repair material
- Makbule Bilge Akbulut, Durmus Alperen Bozkurt, Arslan Terlemez, Melek Akman
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(1):e5. Published online January 28, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e5
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this
in vitro study was to evaluate the push-out bond strength of a novel calcium silicate-based root repair material-BIOfactor MTA to root canal dentin in comparison with white MTA-Angelus (Angelus) and Biodentine (Septodont).Materials and Methods The coronal parts of 12 central incisors were removed and the roots were embedded in acrylic resin blocks. Midroot dentin of each sample was horizontally sectioned into 1.1 mm slices and 3 slices were obtained from each root. Three canal-like standardized holes having 1 mm in diameter were created parallel to the root canal on each dentin slice with a diamond bur. The holes were filled with MTA-Angelus, Biodentine, or BIOfactor MTA. Wet gauze was placed over the specimens and samples were stored in an incubator at 37°C for 7 days to allow complete setting. Then samples were subjected to the push-out test method using a universal test machine with the loading speed of 1 mm/min. Data was statistically analyzed using Friedman test and
post hoc Wilcoxon signed rank test with Bonferroni correction.Results There were no significant differences among the push-out bond strength values of MTA-Angelus, Biodentine, and BIOfactor MTA (
p > 0.017). Most of the specimens exhibited cohesive failure in all groups, with the highest rate found in Biodentine group.Conclusions Based on the results of this study, MTA-Angelus, Biodentine, and BIOfactor MTA showed similar resistances to the push-out testing.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of marginal adaptation and bond strength of apical root canal plugs using different bioceramic cements
Michel Sena Fernandes Faria Lima, Alberto Nogueira da Gama Antunes, Kênia Maria Pereira Soares de Toubes, Fábio Fernandes Borém Bruzinga, Camila de Sousa Caneschi, Luís Fernando dos Santos Alves Morgan, Frank Ferreira Silveira
BMC Oral Health.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Examination of the Bond Strength of Retrograde Filling in Teeth with Failed Apical Resection After Retreatment
Sevda Tok, Leyla Benan Ayranci
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(7): 3441. CrossRef - Comparative Analysis of Physicocomechanical Properties of MTA and Biodentine with Addition of Graphene Oxide to MTA and Biodentine: An In-vitro Study
Tanvi Arvind Jagtap, Budhabhushan A. Sonvane, Guruprasad Handal, Jayashri Nimba Bhangare, Kedar Vilas Saraf, Abhishek Mulay
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2025; 17(Suppl 1): S608. CrossRef - Influence of Incubation Duration on Bond Strength and Microhardness of Calcium Silicate‐Based Materials
Emine Şimşek, Makbule Bilge Akbulut
Australian Endodontic Journal.2025; 51(2): 438. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of push-out bond strength after root perforation repair using recently introduced bioceramic and calcium silicate-based materials – An in vitro study
Gurinder Kaur, Deepak Kurup, Deepyanti Dubey, Ajit Hindlekar, Ganesh Ranganath Jadhav, Priya Mittal, Siddharth Shinde
Endodontology.2025; 37(2): 194. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Push-out Bond Strength of Conventional Mineral Trioxide Aggregate, Biodentine, and Two Novel Antibacterial-enhanced Mineral Trioxide Aggregates
Sanjeev Khanagar, Suman Panda, Prabhadevi C Maganur, Ganesh Jeevanandan, Satish Vishwanathaiah, Ather A Syed, Sara Kalagi, Arokia RS Merlin, Vignesh Ravindran, Aram AlShehri
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2024; 25(2): 168. CrossRef - Influence of Phase Composition and Morphology on the Calcium Ion Release of Several Classical and Hybrid Endodontic Cements
Ivanka Dimitrova, Galia Gentscheva, Ivanka Spassova, Daniela Kovacheva
Materials.2024; 17(22): 5568. CrossRef - The Effect of Two Different MTA (Mineral Trioxide Aggregate) On Thermal Insulation
Gizem Akkus, Ecem Salmaz, Didem Oner Ozdas
The Open Dentistry Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of push‐out bond strength and apical microleakage of different calcium silicate‐based cements after using EDTA, chitosan and phytic acid irrigations
Tutku Koçak Şahin, Murat Ünal
Microscopy Research and Technique.2024; 87(9): 2072. CrossRef - In vitro evaluation of the physical characteristics and push-out bond strength of new experimental nano-MTA
Nada Omar, Yousra Aly, Haidy N. Salem
Bulletin of the National Research Centre.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Interfacial characteristics of BIOfactor MTA and Biodentine with dentin
Makbule Bilge Akbulut, Şeref Nur Mutlu, Mehmet Ali Soylu, Emine Şimşek
Microscopy Research and Technique.2023; 86(2): 258. CrossRef - Systemic effect of calcium silicate-based cements with different radiopacifiers-histopathological analysis in rats
Osman Ataş, Kubra Bılge, Semsettin Yıldız, Serkan Dundar, Ilknur Calik, Asime Gezer Ataş, Alihan Bozoglan
PeerJ.2023; 11: e15376. CrossRef - The push-out bond strength of three root canal materials used in primary teeth: in vitro study
Hazal Özer, Merve Abaklı İnci, Sevcihan Açar Tuzluca
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of different irrigation protocols on push-out bond strength of pre-mixed calcium silicate-based cements
Sabiha Ceren İlisulu, Aliye Tugce Gürcan, Soner Sismanoglu
Journal of the Australian Ceramic Society.2023; 59(5): 1381. CrossRef - Micro-Computed Tomographic Evaluation of the Sealing Quality and Bond Strength of Different MTA Apical Plugs
Taibe Tokgöz Kaplan, Murat Selim Botsalı
European Journal of Therapeutics.2023; 30(1): 29. CrossRef - Kan kontaminasyonunun farklı kök ucu dolgu materyallerinin dentine bağlanma dayanımına etkisi
Şeyma Nur GERÇEKCİOĞLU, Melike BAYRAM, Emre BAYRAM
Acta Odontologica Turcica.2023; 40(1): 9. CrossRef - Tooth Discoloration Effect of BIOfactor Mineral Trioxide Aggregate: A 6-Month In Vitro Study
Şeref Nur Mutlu, Makbule Bilge Akbulut
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(15): 8914. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of the Push-Out Bond Strength of Root-End Filling Materials by Using Different Condensation Methods
Pelin Tüfenkçi, Sevinç Sevgi, Ayşenur Öncü, Fatma Semra Sevimay, Berkan Çelikten
Cyprus Journal of Medical Sciences.2022; 7(7): 115. CrossRef - Effect of Different Adhesive Strategies on the Microshear Bond Strength of Calcium-Silicate-Based Materials
Aliye Tuğçe Gürcan, Soner Şişmanoğlu, Görkem Sengez
Journal of Advanced Oral Research.2022; 13(2): 191. CrossRef - BIOfactor MTA’nın Radyoopasitesinin Dijital Radyografi ile Değerlendirilmesi
Şeref Nur MUTLU, Makbule Bilge AKBULUT
Selcuk Dental Journal.2022; 9(2): 520. CrossRef - Morphological and Chemical Analysis of Different Types of Calcium Silicate‐Based Cements
Okba Mahmoud, Nashwan Abdullah Al-Afifi, Mohideen Salihu Farook, Maysara Adnan Ibrahim, Saaid Al Shehadat, Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, Sandrine Bittencourt Berger
International Journal of Dentistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Blood Contamination on Push-Out Bond Strength of Three Calcium Silicate-Based Materials to Root Dentin
Cristina Rodrigues Paulo, Joana A. Marques, Diana B. Sequeira, Patrícia Diogo, Rui Paiva, Paulo J. Palma, João Miguel Santos
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(15): 6849. CrossRef - An In vitro comparative evaluation of effect of novel irrigant Qmix and 17% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid on the push-out bond strength of biodentine and endosequence bioceramic root repair material
VandanaJ Gade, Aparajita Gangrade, JaykumarR Gade, Neelam Rahul
Journal of the International Clinical Dental Research Organization.2021; 13(2): 124. CrossRef - A micro-computed tomographic study using a novel test model to assess the filling ability and volumetric changes of bioceramic root repair materials
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Jader Camilo Pinto, Gabriella Oliveira Figueira, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of the flow and filling ability of endodontic materials using different test models
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Gisselle Moraima Chavez-Andrade, Jader Camilo Pinto, Fábio Luiz Camargo Villela Berbert, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Evaluation of marginal adaptation and bond strength of apical root canal plugs using different bioceramic cements
- 2,067 View
- 12 Download
- 25 Crossref

- Evaluation of the effects of whitening mouth rinses combined with conventional tooth bleaching treatments
- Jaqueline Costa Favaro, Omar Geha, Ricardo Danil Guiraldo, Murilo Baena Lopes, Andreza Maria Fábio Aranha, Sandrine Bittencourt Berger
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(1):e6. Published online January 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e6
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
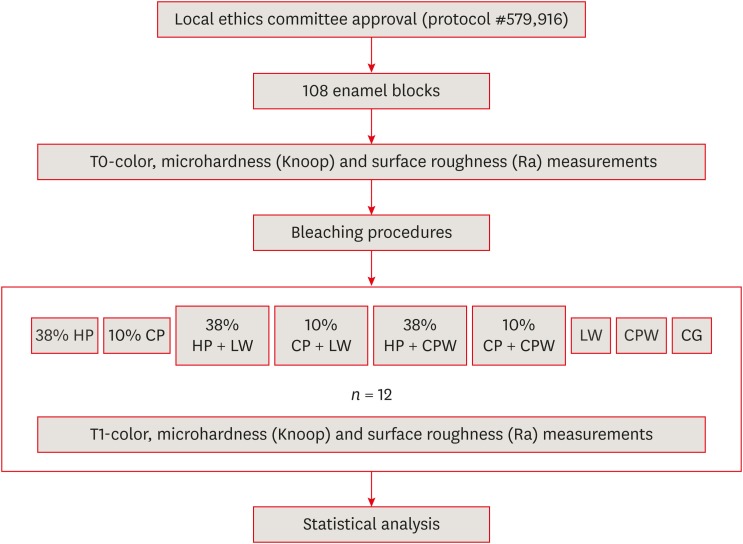
ePub Objectives The aim of the present study was to evaluate the effect of whitening mouth rinses alone and in combination with conventional whitening treatments on color, microhardness, and surface roughness changes in enamel specimens.
Materials and Methods A total of 108 enamel specimens were collected from human third molars and divided into 9 groups (
n = 12): 38% hydrogen peroxide (HP), 10% carbamide peroxide (CP), 38% HP + Listerine Whitening (LW), 10% CP + LW, 38% HP + Colgate Plax Whitening (CPW), 10% CP + CPW, LW, CPW, and the control group (CG). The initial color of the specimens was measured, followed by microhardness and roughness tests. Next, the samples were bleached, and their color, microhardness, and roughness were assessed. Data were analyzed through 2-way analysis of variance (ANOVA; microhardness and roughness) and 1-way ANOVA (color change), followed by the Tukeypost hoc test. The Dunnett test was used to compare the roughness and microhardness data of the CG to those of the treated groups.Results Statistically significant color change was observed in all groups compared to the CG. All groups, except the LW group, showed statistically significant decreases in microhardness. Roughness showed a statistically significant increase after the treatments, except for the 38% HP group.
Conclusions Whitening mouth rinses led to a whitening effect when they were used after conventional treatments; however, this process caused major changes on the surface of the enamel specimens.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Property changes in resin composite exposed to mouth rinses during 10% carbamide peroxide bleaching
Mariana Ferreira da Silva, Giovana Contin Germinari, Carolina Meneghin Barbosa, Tatiane Cristina Dotta, Renata Siqueira Scatolin, Waldemir Francisco Vieira Júnior, Laura Nobre Ferraz
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2026; 25: e260366. CrossRef - Which Whitening Mouthwash With Different Ingredients Is More Effective on Color and Bond Strength of Enamel?
Elif Varli Tekingur, Fatih Bedir, Muhammet Karadas, Rahime Zeynep Erdem
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2025; 37(4): 960. CrossRef - Do Different Tooth Bleaching–Remineralizing Regimens Affect the Bleaching Effectiveness and Enamel Microhardness In Vitro?
Hamideh Sadat Mohammadipour, Parnian Shokrollahi, Sima Gholami, Hosein Bagheri, Fatemeh Namdar, Salehe Sekandari, Cesar Rogério Pucci
International Journal of Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of hydrogen peroxide versus charcoal-based whitening mouthwashes on color, surface roughness, and color stability of enamel
Mayada S. Sultan
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of online marketplace-sourced over-the-counter tooth whitening products on the colour, microhardness, and surface topography of enamel: an in vitro study
Radhika Agarwal, Nikki Vasani, Urmila Sachin Mense, Niharika Prasad, Aditya Shetty, Srikant Natarajan, Arindam Dutta, Manuel S. Thomas
BDJ Open.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Whitening Mouthwashes on Color Change and Enamel Mineralization: An In Vitro Study
Rosa Josefina Roncal Espinoza, José Alberto Castañeda Vía, Alexandra Mena-Serrano, Lidia Yileng Tay
World Journal of Dentistry.2023; 14(9): 739. CrossRef - Effectiveness and Adverse Effects of Over-the-Counter Whitening Products on Dental Tissues
Maiara Rodrigues de Freitas, Marynara Mathias de Carvalho, Priscila Christiane Suzy Liporoni, Ana Clara Borges Fort, Rodrigo de Morais e Moura, Rayssa Ferreira Zanatta
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Renklendirilmiş kompozit rezinin renk değişimine ve yüzey pürüzlülüğüne beyazlatıcı ağız gargarasının etkisi
Şeref Nur MUTLU, Makbule Tuğba TUNCDEMIR
Selcuk Dental Journal.2020; 7(3): 435. CrossRef
- Property changes in resin composite exposed to mouth rinses during 10% carbamide peroxide bleaching
- 1,667 View
- 14 Download
- 8 Crossref

-
In vitro evaluation of octenidine as an antimicrobial agent againstStaphylococcus epidermidis in disinfecting the root canal system - Jia Da Chum, Darryl Jun Zhi Lim, Sultan Omer Sheriff, Shaju Jacob Pulikkotil, Anand Suresh, Fabian Davamani
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(1):e8. Published online February 8, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e8
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
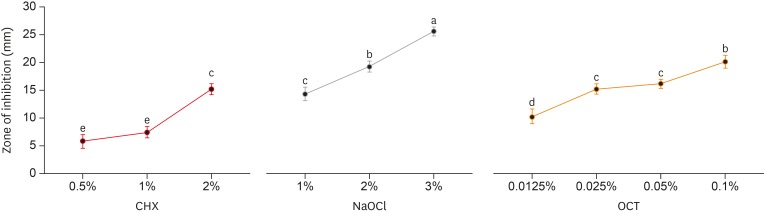
ePub Objectives Irrigants are imperative in endodontic therapy for the elimination of pathogens from the infected root canal. The present study compared the antimicrobial efficacy of octenidine dihydrochloride (OCT) with chlorhexidine (CHX) and sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) against
Staphylococcus epidermidis (S. epidermidis ) for root canal disinfection.Materials and Methods The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) was obtained using serial dilution method. The agar diffusion method was then used to determine the zones of inhibition for each irrigant. Lastly, forty 6-mm dentin blocks were prepared from human mandibular premolars and inoculated with
S. epidermidis . Samples were randomly divided into 4 groups of 10 blocks and irrigated for 3 minutes with saline (control), 2% CHX, 3% NaOCl, or 0.1% OCT. Dentin samples were then collected immediately for microbial analysis, including an analysis of colony-forming units (CFUs).Results The MICs of each tested irrigant were 0.05% for CHX, 0.25% for NaOCl, and 0.0125% for OCT. All tested irrigants showed concentration-dependent increase in zones of inhibition, and 3% NaOCl showed the largest zone of inhibition amongst all tested irrigants (
p < 0.05). There were no significant differences among the CFU measurements of 2% CHX, 3% NaOCl, and 0.1% OCT showing complete elimination ofS. epidermidis in all samples.Conclusions This study showed that OCT was comparable to or even more effective than CHX and NaOCl, demonstrating antimicrobial activity at low concentrations against
S. epidermidis .-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of final irrigation protocols on the bond strength and dentinal tubule penetration of root canal sealers: an ex vivo laboratory study
Sevinc Askerbeyli Örs, Gülgün Atay Yılmaz, Nihan Şengül, Ahmet Keleş, Selen Küçükkaya Eren
BMC Oral Health.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - WITHDRAWN: Substantivity of different antiseptic oral gels. An In vitro study
Nirit Tagger Green, Roni Kolerman, Carlos Nemcovsky, Shlomo Matalon, Dan Gaukhman, Liat Chaushu
Heliyon.2025; : e42654. CrossRef - Antimicrobial and anti-biofilm activity of crustacean-derived chitosan against Salmonella Typhimurium, Staphylococcus aureus and Listeria monocytogenes
Sivainesh Devi Remesh, Pratheep Sandrasaigaran, Santhaniswarman Remesh, Veeradasan Perumal, Joshua Yap Lip Vun, Sivasangkary Gandhi, Hanan Hasan
Food Bioscience.2025; : 106697. CrossRef - Glycerol-Enhanced Gum Karaya Hydrogel Films with a Sandwich-like Structure Enriched with Octenidine for Antibacterial Action against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria
Eva Černá, Vilém Neděla, Eva Tihlařiková, Jana Brtníková, Zdenka Fohlerová, Břetislav Lipový, Lukáš Vacek, Filip Růžička, Jana Matulová, Lucy Vojtová
ACS Omega.2025; 10(27): 29530. CrossRef - Effect of Mouth Rinsing and Antiseptic Solutions on Periodontitis Bacteria in an In Vitro Oral Human Biofilm Model
Jan Tinson Strenge, Ralf Smeets, Maria Geffken, Thomas Beikler, Ewa Klara Stuermer
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(7): 324. CrossRef - In Vitro Investigation of the Effects of Octenidine Dihydrochloride on Nasal Septum Squamous Carcinoma Cells
Ihsan Hakki Ciftci, Asuman Deveci Ozkan, Gulay Erman, Elmas Pinar Kahraman Kilbas, Mehmet Koroglu
Biomedicines.2025; 13(11): 2668. CrossRef - Peptidoglycan Recognition Protein-S as a Dual-Action Antimicrobial and Immunomodulatory Agent Against Staphylococcus aureus
Priya Verma, Priyanka Swaroop, Surabhi Pandit, Ved Prakash, Surender Kumar Sharawat, T. P. Singh, Sujata Sharma, Pradeep Sharma
Probiotics and Antimicrobial Proteins.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - In Vitro Evaluation of Antimicrobial Effects of Endodontic Irrigants Containing Disodium Edetate and Chlorhexidine Gluconate, Octenidine Dihydrochloride, and Benzalkonium Bromide Against Intracanal Enterococcus faecalis
Anna Siemińska, Katarzyna Kot, Ewa Marek, Agnieszka Chamarczuk, Magdalena Kaczała, Joanna Rasławska-Socha, Laurentia Schuster, Till Dammaschke, Liliana Szyszka-Sommerfeld, Mariusz Lipski
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(19): 7100. CrossRef - Evaluation of postoperative pain in endodontic retreatment with apical periodontitis using ozonated 2% chlorhexidine and 0.1% octenidine application: A randomized clinical trial
Nidhi Sinha, Geeta Asthana, Girish Parmar, Akshayraj Langaliya, Jinali Shah, Bijay Singh
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(6): 654. CrossRef - Research on NiTi instruments combined with ultrasonic irrigation and multiantibiotic paste in root canal therapy of periapical inflammation in deciduous teeth
Zongxia Zhu, Guangli Fu
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of antimicrobial efficacy of 0.1% octenidine dihydrochloride, superoxidized solution, ozonated water, 0.1% silver nanoparticle solution, and Q mix™ 2 in 1 in root canals infected with Enterococcus faecalis
Mahenaz Salam Inamdar, Dayanand G. Chole, Shrinivas S. Bakle, Preeti B. Vaprani, Neha P. Gandhi, Nikhil R. Hatte
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(10): 1059. CrossRef - Causal relationship, shared genes between rheumatoid arthritis and pulp and periapical disease: evidence from GWAS and transcriptome data
Huili Wu, Lijuan Wang, Chenjie Qiu
Frontiers in Immunology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of octenidine dihydrochloride on the antibacterial activity of a formulated resin composite: an in vitro study
Mahitab Mansour, Tarek Salah, Haidy N. Salem
Bulletin of the National Research Centre.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between pulp and periapical disease with type 2 diabetes: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization
Yuqiang Wang, Jiakang Zhu, Ying Tang, Cui Huang
International Endodontic Journal.2024; 57(5): 566. CrossRef - New Insights Regarding the Use of Relevant Synthetic Compounds in Dentistry
Stefania-Irina Dumitrel, Anamaria Matichescu, Stefania Dinu, Roxana Buzatu, Ramona Popovici, Dorin Dinu, Dana Bratu
Molecules.2024; 29(16): 3802. CrossRef - Formulation and Characterization of a Novel Palm-Oil-Based α-Mangostin Nano-Emulsion (PO-AMNE) as an Antimicrobial Endodontic Irrigant: An In Vitro Study
Omer Sheriff Sultan, Haresh Kumar A/L Kantilal, Khoo Suan Phaik, Hira Choudhury, Fabian Davamani
Processes.2023; 11(3): 798. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Antimicrobial Efficacy of Herbal Formulations of Septilin and Triphala with Conventional 2% Chlorhexidine on Root Canal and Oral Commensal Bacteria using Kirby Bauer Method
Shadab Ahmed, Kamil Shahnawaz, Tapan Kumar Mandal, Mamnoon Ghafir, Shiva Shankar Gummaluri, Gaurav Vishal
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2022; 13(4): 383. CrossRef - A comparative assessment of pomegranate extract, sodium hypochlorite, chlorhexidine, Myrrh (Commiphora molmol), tulsi extract against Enterococcus faecalis, Fusobacterium nucleatum and Staphylococci epidermidis
Mallwika Sisodiya, Shadab Ahmed, Ranjan Sengupta, Priyanka, Ankit Kumar Saha, Gourav Verma
Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology.2021; 25(2): 369. CrossRef - Effects of Octenidine on the Formation and Disruption of Dental Biofilms: An Exploratory In Situ Study in Healthy Subjects
B. Reda, J. Dudek, M. Martínez-Hernández, M. Hannig
Journal of Dental Research.2021; 100(9): 950. CrossRef - Does Cavity Disinfectant Affect Sealing Ability of Universal Self-etch Adhesive?
S Lata, Prasanti Kumari Pradhan, Gaurav Patri, Subhasmita Bhol, Kanhu C Sahoo, Khushboo Ghosh
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2021; 22(3): 273. CrossRef - Effect of duration and dilution on antimicrobial efficacy of octenidine hydrochloride as an intracanal medicament with chitosan carrier against Enterococcus faecalis – A modified direct contact test
VinayaSusan Varghese, Nirmal Kurian
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2020; 23(5): 463. CrossRef
- Effect of final irrigation protocols on the bond strength and dentinal tubule penetration of root canal sealers: an ex vivo laboratory study
- 2,572 View
- 20 Download
- 21 Crossref

- Comparison of postoperative pain intensity after using reciprocating and continuous rotary glide path systems: a randomized clinical trial
- Mehmet Adıgüzel, Koray Yılmaz, Pelin Tüfenkçi
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(1):e9. Published online February 12, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e9
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
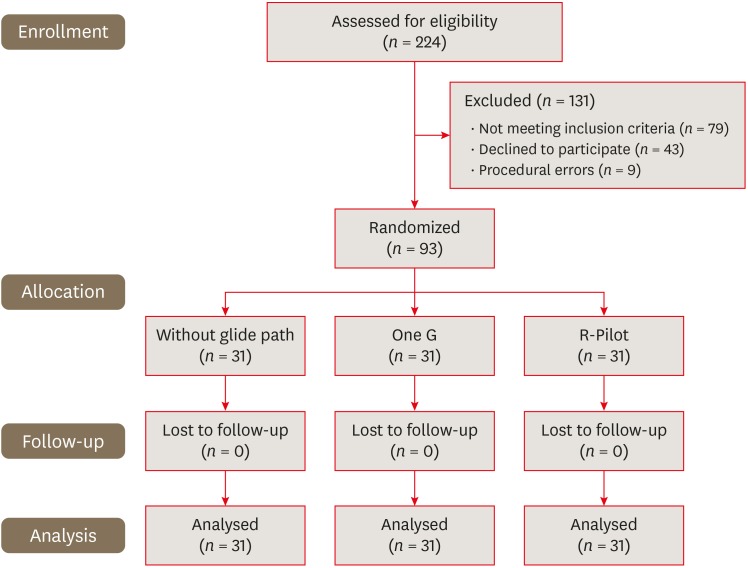
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to compare postoperative pain intensity after root canal treatment with One G (OG) vs. R-Pilot (RP) files used for glide path preparation.
Materials and Methods Ninety-three single-canaled mandibular premolar teeth with asymptomatic non-vital pulp were randomly assigned into 3 groups (
n = 31): OG, RP, or without glide path (WGP). After creating the glide path, the root canals were prepared using sequential Mtwo rotary files to size 30/0.05. One endodontic specialist carried out single-visit endodontic treatment. The patients were asked to rate the severity of postoperative pain on a visual analogue scale at 24, 48, and 72 hours after the visit. They were also asked to record their intake of prescribed analgesics taken. The data were analyzed using the χ2, Friedman, Kruskal-Wallis, and Mann-WhitneyU tests.Results In all 3 groups, postoperative pain decreased significantly at each time interval (
p < 0.05). At 24 hours, the OG group had less postoperative pain than the WGP group (p < 0.05). However, no significant difference was found between the RP group and the others. No statistically significant difference was found among the WGP, OG, and RP groups in postoperative pain intensity at 48 or 72 hours or in analgesic tablet intake at the 3 assessed time intervals.Conclusions The OG group had less postoperative pain than the WGP group in the first 24 hours. The OG and RP systems were similar regarding postoperative pain intensity and analgesic intake.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of glide path preparation on postoperative pain using TruNatomy and Reciproc Blue in single-visit root canal therapy: A randomized clinical trial
Fatima Siddiqui, Sajid Ali, Huma Iftekhar, Rajendra Kumar Tewari, Ashok Kumar, Sharique Alam
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(12): 1222. CrossRef - Postoperative pain in patients following endodontic treatment by XP-endo Shaper files: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Henal Nilesh Dedhia, Vibha R. Hegde, Maitri B. Bhayani, Sanitra R. Hegde
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(11): 1168. CrossRef - Postoperative Pain Following Single Visit Root Canal Treatment With Reciproc Blue And Hyflex EDM Instrumentation; A Prospective Randomized Clinical Trial
Nimet Gençoğlu, Anıl Özgün Karatekin, Mustafa Gündoğar
Meandros Medical And Dental Journal.2024; 25(1): 78. CrossRef - Glide Path in Endodontics: A Literature Review of Current Knowledge
Vlad Mircea Lup, Giulia Malvicini, Carlo Gaeta, Simone Grandini, Gabriela Ciavoi
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(8): 257. CrossRef - Post-Operative Pain in Reciprocating Versus Rotary Kinematics Post-Endodontic Treatment: A Systematic Review
Youssef Algarni
Archives of Pharmacy Practice.2024; 15(2): 53. CrossRef - Evaluation of Pain Following the Use of Different Single-file Glide Path Systems: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Zeliha Danaci, Kübra Yeşildal Yeter
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(2): 120. CrossRef - Incidence of postoperative pain after using single continuous, single reciprocating, and full sequence continuous rotary file system: a prospective randomized clinical trial
Umesh Kumar, Pragnesh Parmar, Ruchi Vashisht, Namita Tandon, Charan Kamal Kaur
Journal of Dental Anesthesia and Pain Medicine.2023; 23(2): 91. CrossRef - Impact of kinematics on the efficiency and safety of an engine-driven file for glide path preparation in MB2 canals of maxillary molars
Larissa B. B. Araújo, Pedro H. S. Calefi, Murilo P. Alcalde, Giulio Gavini, Rodrigo R. Vivan, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 27(3): 1153. CrossRef - Evaluation of Postoperative Pain after Pulpectomy using Different File Systems in Primary Teeth
Lakshimi Lakshmanan, Sujatha Somasundaram, Ganesh Jeevanandan, EMG Subramanian
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2021; 12(1): 3. CrossRef - Evaluation of type of kinematics on glide path procedures and torsional fatigue resistance after preparation of moderately curved canals
Murilo Priori Alcalde, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Pedro Henrique Souza Calefi, Victor de Moraes Cruz, Bruno Carvalho de Vasconcelos, Marcus Vinícius Reis Só, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan
Brazilian Oral Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of glide path kinematics during endodontic treatment on the occurrence and intensity of intraoperative and postoperative pain: a systematic review of randomized clinical trials
Thaís Christina Cunha, Felipe de Souza Matos, Luiz Renato Paranhos, Ítalo de Macedo Bernardino, Camilla Christian Gomes Moura
BMC Oral Health.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Effect of glide path preparation on postoperative pain using TruNatomy and Reciproc Blue in single-visit root canal therapy: A randomized clinical trial
- 3,197 View
- 23 Download
- 11 Crossref

- Discoloration of teeth due to different intracanal medicaments
- Farzaneh Afkhami, Sadaf Elahy, Alireza Mahmoudi Nahavandi, Mohamad Javad Kharazifard, Aidin Sooratgar
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(1):e10. Published online February 12, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e10

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The objective of this study was to assess coronal discoloration induced by the following intracanal medicaments: calcium hydroxide (CH), a mixture of CH paste and chlorhexidine gel (CH/CHX), and triple antibiotic paste (3Mix).
Materials and Methods Seventy extracted single-canal teeth were selected. Access cavities were prepared and each canal was instrumented with a rotary ProTaper system. The specimens were randomly assigned to CH, CH/CHX, and 3Mix paste experimental groups (
n = 20 each) or a control group (n = 10). Each experimental group was randomly divided into 2 subgroups (A and B). In subgroup A, medicaments were only applied to the root canals, while in subgroup B, the root canals were completely filled with medicaments and a cotton pellet dipped in medicament was also placed in the pulp chamber. Spectrophotometric readings were obtained from the mid-buccal surface of the tooth crowns immediately after placing the medicaments (T1) and at 1 week (T2), 1 month (T3), and 3 months (T4) after filling. The ∆E was then calculated. Data were analyzed using 2-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), 3-way ANOVA, and the Scheffépost hoc test.Results The greatest color change (ΔE) was observed at 3 months (
p < 0.0001) and in 3Mix subgroup B (p = 0.0057). No significant color change occurred in the CH (p = 0.7865) or CH/CHX (p = 0.1367) groups over time, but the 3Mix group showed a significant ΔE (p = 0.0164).Conclusion Intracanal medicaments may induce tooth discoloration. Use of 3Mix must be short and it must be carefully applied only to the root canals; the access cavity should be thoroughly cleaned afterwards.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Time-dependent Tooth Color Changes Following Conventional, Silver-based, and Photodynamic Root Canal Irrigants: An In Vitro Study
Laila Mohamed Mohamed Kenawi, Mohamed Fattouh, Khaled Abid Althaqafi, Abla Arafa
The Open Dentistry Journal.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative analysis of tooth discoloration induced by different intracanal medicaments in regenerative endodontics: A systematic review and network meta-analysis
Ashlesha Nageshwar Madankar, Sulabha Radke, Shanmuga Priya, Darshan Dakshindas
Endodontology.2026; 38(1): 8. CrossRef - Effects of Intra-canal Medicaments on Infrared Light Energy Transmission Through Enamel and Dentin During Photobiomodulation: An In Vitro Study
Sachin Kulkarni, Laurence J. Walsh, Yash Bhurani, Roy George
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(5): 616. CrossRef - Tooth discoloration caused by nanographene oxide as an irrigant and intracanal medicament in the endodontic treatment of extracted single-rooted teeth: An ex-vivo study
Abbas Abbaszadegan, Zeinab Rafiee, Bahar Asheghi, Ahmad Gholami, Mohmed Isaqali Karobari
PLOS One.2025; 20(6): e0325430. CrossRef - Investigation of Discoloration of Anterior Teeth With Three Types of Substances Used in Endodontic Treatment
Sahar Soltani, Eshagh Ali Saberi, Nazanin Shahradnia, Pedram Abdollahzade Sangrodi, Elham Majidi
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A New Disinfection Approach Using a Chitosan-Based Endodontic Irrigant
Alejandra Itzel Lopez-Flores, Ulises Velazquez-Enriquez, Rogelio Jose Scougall-Vilchis, Laura Susana Acosta-Torres, Laura Emma Rodriguez-Vilchis, Rosalía Contreras-Bulnes, Paloma Netzayeli Serrano-Diaz, Rene Garcia-Contreras
Materials.2025; 18(24): 5552. CrossRef - Spectrophotometric Analysis of Intracoronal Bleaching on Crown Discoloration Induced by Various Antibiotic Pastes: An In Vitro Study
Avneet Kaur, Harshit Srivastava, Deepak Raisingani, Ashwini B Prasad, Dileep Soni, Poorva R Sharma
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2025; 18(12): 1443. CrossRef - Effect of Calcium Hydroxide Versus Double Antibiotic Paste on Endodontic Treatment Outcomes in Teeth With Large Periapical Lesions: A Triple‐Blind Randomized Clinical Trial
Afsaneh Rahmati, Farshad Seyedein, Omid Dianat, Sara Saedi, Golriz Rostami, Alireza Akbarzadeh Baghban, Shima Sabertahan, Majid Kazem, Kee Y. Kum
International Journal of Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of different intracanal irrigants on the push-out bond strength of dentin in damaged anterior primary teeth
Leila Bassir, Shirin Taravati, Farzad Nouri, Saeide Rahimi
Journal of Medicine and Life.2024; 17(5): 536. CrossRef - In Vıtro Evaluatıon of Dıscoloratıon Caused by Root Canal Sealers and Color Changes after Bleachıng
Emre Bodrumlu, Esma Dinger
Annals of Dental Specialty.2024; 12(1): 77. CrossRef - Assessment of Discoloration Induced by Root Canal Sealers and Color Alterations Post-Bleaching
T.P. Van der Burgt, T.P. Mullaney, A.J.M. Plasschaert
International Journal of Dental Research and Allied Sciences.2024; 4(1): 1. CrossRef - The effect of four different intracanal medicaments on the push-out bond strength of root canal sealers
Shalu Maan, Vijaya Dhar Bhatt, Rohit Singh, Sayak Gupta, Syed Alay Noorain, Aashna Gill, Pradeep Kumar, Sushil Yadav, Preeti Sharma
Journal of Medicine and Life.2022; 15(4): 448. CrossRef - Effect of hydrogel-based antibiotic intracanal medicaments on crown discoloration
Rayan B. Yaghmoor, Jeffrey A. Platt, Kenneth J. Spolnik, Tien Min Gabriel Chu, Ghaeth H. Yassen
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Time-dependent Tooth Color Changes Following Conventional, Silver-based, and Photodynamic Root Canal Irrigants: An In Vitro Study
- 3,131 View
- 58 Download
- 13 Crossref


 KACD
KACD



 First
First Prev
Prev


