-
Proximity of maxillary molar apexes to the cortical bone surface and the maxillary sinus
-
Han Shin Lee, Dokyung Kim, Sung Kyo Kim
-
Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(3):e33. Published online August 8, 2022
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e33
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
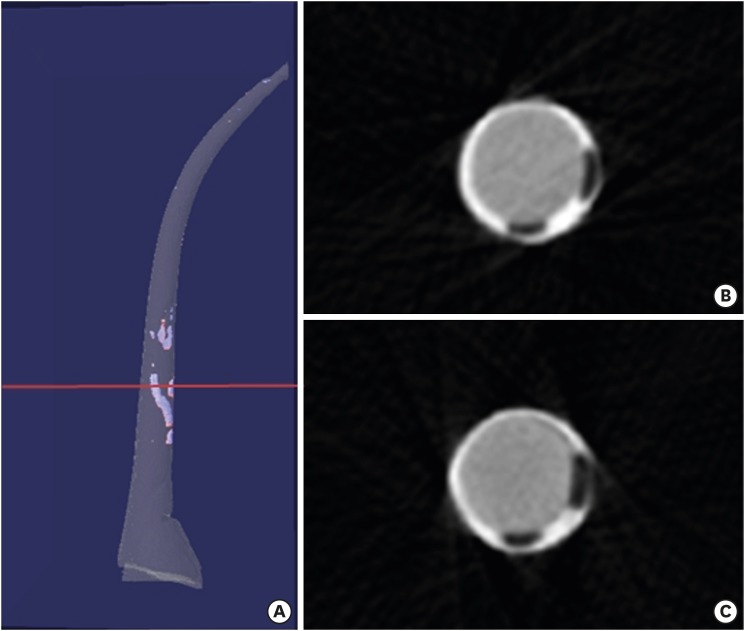
This study aimed to analyze the proximity of maxillary molar roots to their overlying cortical bone surfaces and the maxillary sinus. Materials and MethodsCone-beam computed tomographic images of 151 patients with completely erupted upper molars that had 3 separate roots were studied. The following distances were measured: from the root apex to the cortical plate and maxillary sinus floor, and from the apical 3-mm level of the root to the cortical plate. Differences between groups were analyzed with 1-way analysis of variance and the Scheffé post hoc test, the significance of differences between cone-beam computed tomography views with the paired t-test, and the significance of differences among age groups with linear regression analysis. The significance level was set at p < 0.05. ResultsThe mesiobuccal and distobuccal root apexes of maxillary second molars were more distant from the buccal cortical plate than the maxillary first molars (p < 0.05). The apical 3-mm level of the mesiobuccal root of the first molar was closer to the buccal cortical bone than the second molar (p < 0.05). In the maxillary first molars, the thickness of the buccal cortical bone decreased in all roots with age (p < 0.05). In all root apexes of both molars, the difference in the vertical level between the maxillary sinus floor and the root apex increased with age (p < 0.05). ConclusionsAwareness of the anatomical profile of maxillary molar apices in relation to the cortical bones and maxillary sinus will be beneficial for apical surgery.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Proximity of maxillary molar palatal roots to adjacent structures for endodontic microsurgery: a cone-beam computed tomography study
Xiaoxiang Huang, Jun Xu, Benxiang Hou, Ying Wang
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
-
226
View
-
7
Download
-
1
Web of Science
-
1
Crossref
-
A micro-computed tomographic evaluation of root canal filling with a single gutta-percha cone and calcium silicate sealer
-
Jong Cheon Kim, Maung Maung Kyaw Moe, Sung Kyo Kim
-
Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(2):e18. Published online February 12, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e18
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the void of root canal filling over time when a calcium silicate sealer was used in the single gutta-percha cone technique. Materials and MethodsTwenty-four J-shaped simulated root canals and twenty-four palatal root canals from extracted human maxillary molars were instrumented with ProFile Ni-Ti rotary instruments up to size 35/0.06 or size 40/0.06, respectively. Half of the canals were filled with Endoseal MTA and the other half were with AH Plus Jet using the single gutta-percha cone technique. Immediately after and 4 weeks after the root canal filling, the samples were scanned using micro-computed tomography at a resolution of 12.8 μm. The scanned images were reconstructed using the NRecon software and the void percentages were calculated using the CTan software, and statistically analyzed by 1-way analysis of variance, paired t-test and Tukey post hoc test. ResultsAfter 4 weeks, there were no significant changes in the void percentages at all levels in both material groups (p > 0.05), except at the apical level of the AH Plus Jet group (p < 0.05) in the simulated root canal showing more void percentage compared to other groups. Immediately after filling the extracted human root canals, the Endoseal MTA group showed significantly less void percentage compared to the AH Plus Jet group (p < 0.05). ConclusionsUnder the limitations of this study, the Endoseal MTA does not seem to reduce the voids over time.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Evaluation of various obturation techniques with bioceramic sealers in 3D-printed C-shaped canals
Maryam Gharechahi, Melika Hoseinzadeh, Saeed Moradi, Mina Mehrjouei
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of obturation quality in natural and replica teeth root-filled using different sealers and techniques
Chuta Kooanantkul, Richard M Shelton, Josette Camilleri
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(5): 2407. CrossRef - Obturation canalaire
N. Linas, M.-L. Munoz-Sanchez, N. Decerle, P.-Y. Cousson
EMC - Médecine buccale.2023; 16(5): 1. CrossRef - The Effect of Sealer Application Methods on Voids Volume after Aging of Three Calcium Silicate-Based Sealers: A Micro-Computed Tomography Study
Amre R. Atmeh, Rakan Alharbi, Ibrahim Aljamaan, Abdulrahman Alahmari, Ashwin C. Shetty, Ahmed Jamleh, Imran Farooq
Tomography.2022; 8(2): 778. CrossRef - Clinical Efficacy of Sealer-based Obturation Using Calcium Silicate Sealers: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Ji-hyung Kim, Sin-Yeon Cho, Yoonwoo Choi, Do-hyun Kim, Su-Jung Shin, Il-Young Jung
Journal of Endodontics.2022; 48(2): 144. CrossRef - A critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study root canal fillings
Gustavo De‐Deus, Erick Miranda Souza, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Marco Simões‐Carvalho, Daniele Moreira Cavalcante, Marco Aurélio Versiani
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S2): 384. CrossRef - Calcium Silicate Cements vs. Epoxy Resin Based Cements: Narrative Review
Mario Dioguardi, Cristian Quarta, Diego Sovereto, Giuseppe Troiano, Khrystyna Zhurakivska, Maria Bizzoca, Lorenzo Lo Muzio, Lucio Lo Russo
Oral.2021; 1(1): 23. CrossRef - Physico-Chemical Properties of Calcium-Silicate vs. Resin Based Sealers—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Laboratory-Based Studies
Viresh Chopra, Graham Davis, Aylin Baysan
Materials.2021; 15(1): 229. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomography in preventive and restorative dental research: A review
Mehrsima Ghavami-Lahiji, Reza Tayefeh Davalloo, Gelareh Tajziehchi, Paria Shams
Imaging Science in Dentistry.2021; 51(4): 341. CrossRef - Main and Accessory Canal Filling Quality of a Premixed Calcium Silicate Endodontic Sealer According to Different Obturation Techniques
Su-Yeon Ko, Hae Won Choi, E-Deun Jeong, Vinicius Rosa, Yun-Chan Hwang, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kyung-San Min
Materials.2020; 13(19): 4389. CrossRef
-
218
View
-
4
Download
-
10
Crossref
-
Preference of undergraduate students after first experience on nickel-titanium endodontic instruments
-
Sang Won Kwak, Gary Shun-Pan Cheung, Jung-Hong Ha, Sung Kyo Kim, Hyojin Lee, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
-
Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(3):176-181. Published online June 23, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.3.176
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
This study aimed to compare two nickel-titanium systems (rotary vs. reciprocating) for their acceptance by undergraduate students who experienced nickel-titanium (NiTi) instruments for the first time. Materials and MethodsEighty-one sophomore dental students were first taught on manual root canal preparation with stainless-steel files. After that, they were instructed on the use of ProTaper Universal system (PTU, Dentsply Maillefer), then the WaveOne (WO, Dentsply Maillefer). They practiced with each system on 2 extracted molars, before using those files to shape the buccal or mesial canals of additional first molars. A questionnaire was completed after using each file system, seeking students' perception about 'Ease of use', 'Flexibility', 'Cutting-efficiency', 'Screwing-effect', 'Feeling-safety', and 'Instrumentation-time' of the NiTi files, relative to stainless-steel instrumentation, on a 5-point Likert-type scale. They were also requested to indicate their preference between the two systems. Data was compared between groups using t-test, and with Chi-square test for correlation of each perception value with the preferred choice (p = 0.05). ResultsAmong the 81 students, 55 indicated their preferred file system as WO and 22 as PTU. All scores were greater than 4 (better) for both systems, compared with stainless-steel files, except for 'Screwing-effect' for PTU. The scores for WO in the categories of 'Flexibility', 'Screwing-effect', and 'Feeling-safety' were significantly higher scores than those of PTU. A significant association between the 'Screwing-effect' and students' preference for WO was observed. ConclusionsNovice operators preferred nickel-titanium instruments to stainless-steel, and majority of them opted for reciprocating file instead of continuous rotating system.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Endodontic Procedural Errors and Associated Factors among Undergraduate Dental Students: A Cross-sectional Study
Vivek Padmanabhan, Md Sofiqul Islam, Mohamed A Elsayed, Duaa R Saleh, Amal M Alnahdi
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2024; 24(12): 998. CrossRef - Clinicians’ perspectives, inducements, preferences, and clinical experiences regarding the use of electronic apex locator and apex locator integrated engine-driven instrumentation: a cross-sectional study
Sena Kaşıkçı, Sena Kolunsağ Özbek, Ebru Şirinoğlu, Olcay Özdemir
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation and Comparison of Manual and Mechanical Endodontic Instrumentation Completed by Undergraduate Dental Students on Endodontic Blocks
António Ginjeira, Abayomi O. Baruwa, Karla Baumotte
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(11): 363. CrossRef - The first experiences of preclinical dentistry students with rotary instruments: A pilot study
Işıl Kaya Büyükbayram, Gizem Çolakoğlu, Sana Mahroos Al-Shammari, Katia Stoicefidis
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2024; 14(2): 205. CrossRef - First Experience of an Undergraduate Dental Student with a Reciprocating System in Simulated Root Canals—A Pilot Study
Ana Rita Arede, Inês Ferreira, Ana Cristina Braga, Irene Pina-Vaz
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(8): 4848. CrossRef - Effect on undergraduate student self-confidence in using 3D printed primary molars for root canal treatment simulation training
C. Delfosse, T. Marquillier, S. Ndoye, P.-Y. Cousson, M. Hennequin, C. Catteau
European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry.2023; 24(1): 105. CrossRef - Influence of operator expertise on glide path and root canal preparation of curved root canals with rotary and reciprocating motions
Ana Belén Dablanca‐Blanco, Ana Arias, María José Ginzo‐Villamayor, María Consuelo Pérez, Pablo Castelo‐Baz, Benjamín Martín‐Biedma
Australian Endodontic Journal.2022; 48(1): 37. CrossRef - Quality of root canal treatment performed by undergraduate students using nickel‐titanium reciprocating versus hand instruments
Seniha Miçooğulları Kurt, Gözde Kandemir Demirci, Burcu Serefoglu, Mehmet Emin Kaval, Pelin Güneri, Mehmet Kemal Çalışkan
Journal of Dental Education.2022; 86(12): 1662. CrossRef - Radiographic assessment of endodontic mishaps in an undergraduate student clinic: a 2-year retrospective study
Manal Matoug-Elwerfelli, Ahmed Abdou, Wejdan Almutairi, Malak Alhuthayli, Shaikhah Aloyaynaa, Rahaf Almohareb
PeerJ.2022; 10: e13858. CrossRef - Ex vivo shaping ability of reciprocating instruments operated by new users: Reciproc versus WaveOne
Mary S. H. Lam, Jeffrey W. W. Chang, Gary S. P. Cheung
Clinical Oral Investigations.2021; 25(5): 2791. CrossRef - Body temperature fatigue behaviour of reciprocating and rotary glide path instruments in sodium hypochlorite solutions alone or combined with etidronate
Dario Perez‐Villalba, José C. Macorra, Juan J. Perez‐Higueras, Ove A. Peters, Ana Arias
Australian Endodontic Journal.2021; 47(3): 450. CrossRef - Undergraduate Students’ Acceptance of a Reciprocating One-File System for Endodontic Treatment
Benjamin Mahmoodi, Adriano Azaripour, Kawe Sagheb, Keyvan Sagheb, Brita Willershausen, Jens Weusmann
European Journal of Dentistry.2020; 14(03): 393. CrossRef - Fracture of endodontic instruments - Part 1: Literature review on factors that influence instrument breakage
Maheshan Pillay, Martin Vorster, Peet J Van der Vyver
South African Dental Journal.2020; 75(10): 553. CrossRef - A comparative study of root canal shaping using protaper universal and protaper next rotary files in preclinical dental education
Gül Çelik, Feyza Özdemir Kısacık, Emir Faruk Yılmaz, Arife Mersinlioğlu, İhsan Furkan Ertuğrul, Hikmet Orhan
PeerJ.2019; 7: e7419. CrossRef - Undergraduate dentistry students’ perception of difficulties regarding endodontic treatment
Lorrane G. Tavares, Stella M. F. Lima, Miriane G. Lima, Marcos P. Arruda, Thiago C. Menegazzi, Taia M. B. Rezende
Australian Endodontic Journal.2019; 45(1): 98. CrossRef - First Experience of Rotary Nickel Titanium Root Canal Instrumentation Performed by Undergraduate Students and General Dentists
marwa sharaan, Noreen Kamel, Dimitrios Tziafas
Journal of Dentistry and Oral Care.2017; 3(2): 1. CrossRef
-
204
View
-
2
Download
-
16
Crossref
-
Proximity of the mandibular molar root apex from the buccal bone surface: a cone-beam computed tomographic study
-
Dokyung Kim, Jung-Hong Ha, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young-Kyung Kim, Sung Kyo Kim
-
Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(3):182-188. Published online July 14, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.3.182
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the proximity of the mandibular molar apex to the buccal bone surface in order to provide anatomic information for apical surgery. Materials and MethodsCone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) images of 127 mandibular first molars and 153 mandibular second molars were analyzed from 160 patients' records. The distance was measured from the buccal bone surface to the root apex and the apical 3.0 mm on the cross-sectional view of CBCT. ResultsThe second molar apex and apical 3 mm were located significantly deeper relative to the buccal bone surface compared with the first molar (p < 0.01). For the mandibular second molars, the distance from the buccal bone surface to the root apex was significantly shorter in patients over 70 years of age (p < 0.05). Furthermore, this distance was significantly shorter when the first molar was missing compared to nonmissing cases (p < 0.05). For the mandibular first molars, the distance to the distal root apex of one distal-rooted tooth was significantly greater than the distance to the disto-buccal root apex (p < 0.01). In mandibular second molar, the distance to the apex of C-shaped roots was significantly greater than the distance to the mesial root apex of non-C-shaped roots (p < 0.01). ConclusionsFor apical surgery in mandibular molars, the distance from the buccal bone surface to the apex and apical 3 mm is significantly affected by the location, patient age, an adjacent missing anterior tooth, and root configuration.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Expert consensus on intentional tooth replantation
Zhengmei Lin, Dingming Huang, Shuheng Huang, Zhi Chen, Qing Yu, Benxiang Hou, Lihong Qiu, Wenxia Chen, Jiyao Li, Xiaoyan Wang, Zhengwei Huang, Jinhua Yu, Jin Zhao, Yihuai Pan, Shuang Pan, Deqin Yang, Weidong Niu, Qi Zhang, Shuli Deng, Jingzhi Ma, Xiuping
International Journal of Oral Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Outcome of intentional replantation of endodontically treated teeth with periapical pathosis: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Faizan Javed, Kamil Zafar, Farhan R. Khan
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(S1): 494. CrossRef - Proximity of maxillary molar apexes to the cortical bone surface and the maxillary sinus
Han Shin Lee, Dokyung Kim, Sung Kyo Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Alveolar bone thickness overlying healthy maxillary and mandibular teeth: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Marziyeh Shafizadeh, Azita Tehranchi, Armin Shirvani, Saeed Reza Motamedian
International Orthodontics.2021; 19(3): 389. CrossRef - Relationship between the anatomic structures and mandibular posterior teeth for endodontic surgery in a Turkish population: a cone-beam computed tomographic analysis
Zeliha Uğur Aydın, Duygu Göller Bulut
Clinical Oral Investigations.2019; 23(9): 3637. CrossRef
-
238
View
-
2
Download
-
5
Crossref
-
Involvement of TRPA1 in the cinnamaldehyde-induced pulpal blood flow change in the feline dental pulp
-
Dokyung Kim, Moon-Hwan Lee, Sung Kyo Kim
-
Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(3):202-209. Published online July 29, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.3.202
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
The purpose of this study was to investigate the involvement of TRPA1 in the cinnamaldehyde-induced pulpal blood flow (PBF) change in the feline dental pulp. Materials and MethodsMandibles of eight cats were immobilized and PBF was monitored with a laser Doppler flowmetry at the mandibular canine tooth. To evaluate the effect of cinnamaldehyde on PBF, cinnamaldehyde was injected into the pulp through the lingual artery at a constant rate for 60 seconds. As a control, a mixture of 70% ethanol and 30% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO, vehicle) was used. To evaluate the involvement of transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 (TRPA1) in PBF change, AP18, a specific TRPA1 antagonist, was applied into the pulp through the Class V dentinal cavity followed by cinnamaldehyde-administration 3 minutes later. The paired variables of experimental data were statistically analyzed using paired t-test. A p value of less than 0.05 was considered as statistically significant. ResultsAdministration of cinnamaldehyde (0.5 mg/kg, intra-arterial [i.a.]) induced significant increases in PBF (p < 0.05). While administration of a TRPA1 antagonist, AP18 (2.5 - 3.0 mM, into the dentinal cavity [i.c.]) caused insignificant change of PBF (p > 0.05), administration of cinnamaldehyde (0.5 mg/kg, i.a.) following the application of AP18 (2.5 - 3.0 mM, i.c.) resulted in an attenuation of PBF increase from the control level (p < 0.05). As a result, a TRPA1 antagonist, AP18 effectively inhibited the vasodilative effect of cinnamaldehyde (p < 0.05). ConclusionsThe result of the present study provided a functional evidence that TRPA1 is involved in the mechanism of cinnamaldehyde-induced vasodilation in the feline dental pulp.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - A simple model for the assessment of the agonistic activity of dibenzazepine derivatives by molecular moieties
Mohammad Hossein Keshavarz, Hossein Fakhraian, Norollah Saedi
Medicinal Chemistry Research.2021; 30(1): 215. CrossRef
-
189
View
-
1
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
Effect of pre-heating on some physical properties of composite resin
-
Myoung Uk Jin, Sung Kyo Kim
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(1):30-37. Published online January 31, 2009
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.1.030
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of pre-heating on some physical properties of composite resin.
Eighty extracted, noncarious human molars were used in the present study. Four different temperatures of composite resin were used: 4℃, 17℃, 48℃, and 56℃. The 4℃ and 17℃ values represented the refrigerator storage temperature and room temperature respectively. For 48℃ and 56℃, composite resin was heated to the temperatures. As physical properties of composite resin, shear bond strength, microhardness, and degree of conversion were measured. The data for each group were subjected to one-way ANOVAs followed by the Tukey's HSD test at 95% confidence level.
Both in enamel and dentin, among composite resin of 4℃, 17℃, 48℃, and 56℃, the pre-heated composite resin up to 56℃ revealed the highest shear bond strength, and pre-heated composite resin to the higher temperature revealed higher shear bond strength.
Microhardness value was also higher with composite resin of higher temperature.
Degree of conversion was also higher with composite resin of the higher temperature.
In this study, it seems that pre-heating composite resin up to the higher temperature may show higher shear bond strength, higher microhardness value, and higher degree of conversion. Therefore, when using composite resin in the clinic, preheating the composite resin could be recommended to have enhanced physical properties of it. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Evaluation of Shear Bond Strength of Lithium Disilicate Veneers Using Pre-heated Resin Composite With Two Conventional Resin Cements: An In Vitro Study
Ghalia Akyle, Hassan Achour
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The different effects of preheating and heat treatment on the surface microhardness of nanohybrid resin composite
Brelian Elok Septyarini, Irfan Dwiandhono, Dian N. Agus Imam
Dental Journal.2020; 53(1): 6. CrossRef
-
180
View
-
1
Download
-
2
Crossref
-
Polymerization of dual cured composites by different thickness
-
Yun Ju Kim, Myoung Uk Jin, Sung Kyo Kim, Tae-Yub Kwon, Young Kyung Kim
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(3):169-176. Published online May 31, 2008
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.3.169
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of thickness, filling methods and curing methods on the polymerization of dual cured core materials by means of microhardness test.
Two dual cured core materials, MultiCore Flow (Ivoclar Vivadent AG, Schaan, Liechtenstein) and Bis-Core (Bisco Inc., Schaumburg, IL, USA) were used in this study. 2 mm (bulky filled), 4 mm (bulky filled), 6 mm (bulky and incrementally filled) and 8 mm (bulky and incrementally filled)-thickness specimens were prepared with light cure or self cure mode. After storage at 37℃ for 24 hours, the Knoop hardness values (KHN) of top and bottom surfaces were measured and the microhardness ratio of top and bottom surfaces was calculated. The data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA and Scheffe multiple comparison test, with α = 0.05.
The effect of thickness on the polymerization of dual cured composites showed material specific results. In 2, 4 and 6 mm groups, the KHN of two materials were not affected by thickness. However, in 8 mm group of MultiCore Flow, the KHN of the bottom surface was lower than those of other groups (p < 0.05). The effect of filling methods on the polymerization of dual cured composites was different by their thickness or materials. In 6 mm thickness, there was no significant difference between bulk and incremental filling groups. In 8 mm thickness, Bis-Core showed no significant difference between groups. However, in MultiCore Flow, the microhardness ratio of bulk filling group was lower than that of incremental filling group (p < 0.05). The effect of curing methods on the polymerization of dual cured composites showed material specific results. In Bis-Core, the KHN of dual cured group were higher than those of self cured group at both surfaces (p < 0.05). However, in MultiCore Flow, the results were not similar at both surfaces. At the top surface, dual cured group showed higher KHN than that of self cured group (p < 0.05). However, in the bottom surface, dual cured group showed lower value than that of self cured group (p < 0.05). -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effect of curing modes on micro-hardness of dual-cure resin cements
Ki-Deok Lee, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(2): 132. CrossRef
-
165
View
-
2
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
Expression of P2X3 and its colocalization with trpv1 in the human dental pulp
-
Young Kyung Kim, Sung Kyo Kim
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(6):514-521. Published online November 30, 2007
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.6.514
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The purinoreceptor, P2X3 is a ligand-gated cation channel activated by extracellular ATP. It has been reported that ATP can be released during inflammation and tissue damage, which in turn may activate P2X3 receptors to initiate nociceptive signals. However, little is known about the contribution of P2X3 to the dental pain during pulpal inflammation. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to investigate the expression of P2X3 and its colocalization with TRPV1 to understand the mechanism of pain transmission through P2X3 in the human dental pulp with double labeling immunofluorescence method.
In the human dental pulp, intense P2X3 immunoreactivity was observed throughout the coronal and radicular pulp. Of all P2X3-positive fibers examined, 79.4% coexpressed TRPV1.
This result suggests that P2X3 along with TRPV1 may be involved in the transmission of pain and potentiation of noxious stimuli during pulpal inflammation.
-
Effect of local anesthesia on pulpal blood flow in mechanically stimulated teeth
-
Wan-Sik Chu, Seung-Ho Park, Dong-Kuk Ahn, Sung Kyo Kim
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(4):257-262. Published online January 14, 2006
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.4.257
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Abstract
The aims of the study were to evaluate the effect of epinephrine-containing local anesthetics on pulpal blood flow (PBF) and to investigate its effect on cavity preparation-induced PBF change. PBF was recorded using a laser Doppler flowmeter (Perimed Co., Sweden) from canines of nine cats under general anesthesia before and after injection of local anesthetics and after cavity preparation. 2% lidocaine hydrochloride with 1 : 100,000 epinephrine was administered by local infiltration given apical to the mandibular canine at the vestibular area and the same volume of isotonic saline was injected on the contralateral tooth as a control. A round carbide bur was operated at slow speed with isotonic saline flushing to grind spherical cavities with increasing depth through the enamel and into the dentin on both teeth. The obtained data was analyzed with paired t-test.
Cavity preparation caused significant increase of PBF (n = 9, p < 0.05). Local infiltration of lidocaine with epinephrine resulted in decreases of PBF (n = 9, p < 0.05), whereas there was no significant change of PBF with the physiologic saline as a control. Cavity preparation on tooth anesthetized with lidocaine with epinephrine caused significantly less increase of PBF than in control tooth (p < 0.05).
Therefore, the result of the present study demonstrates that local infiltration of 2% lidocaine with 1 : 100,000 epinephrine effectively reduces PBF increase caused by cavity preparation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Systematic Injection Patterned-Technique of One-Per-Mil Tumescent Solution for Perforator-Based Skin Flap: Is it Better Than the Random Patterned-Technique?
Theddeus O. H. Prasetyono, Sweety Pribadi
International Surgery.2015; 100(9-10): 1308. CrossRef - Biologic response of local hemostatic agents used in endodontic microsurgery
Youngjune Jang, Hyeon Kim, Byoung-Duck Roh, Euiseong Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(2): 79. CrossRef - Change in Pulpal Blood Flow of Heat-induced Neurogenic Inflammation in Feline Dental Plup
Min-Kyoung Park
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2013; 14(12): 6340. CrossRef - Cardiovascular effect of epinephrine in endodontic microsurgery: a review
Youngjune Jang, Euiseong Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 187. CrossRef
-
193
View
-
4
Download
-
4
Crossref
-
Influence of additional etching on shear bond strength of self-etching adhesive system to enamel
-
Sun-Jin Yoo, Young-Kyung Kim, Jeong-Won Park, Myoung-Uk Jin, Sung Kyo Kim
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(4):263-268. Published online July 31, 2006
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.4.263
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
Recently, self-etching adhesive system has been introduced to simplify the clinical bonding procedures. It is less acidic compared to the phosphoric acid, thus there is doubt whether this system has enough bond strength to enamel. The purpose of this study was to investigate the influence of additional etching on the adhesion of resin composite to enamel.
Ninety extracted bovine permanent anterior teeth were used. The labial surfaces of the crown were ground with 600-grit abrasive paper under wet condition. The teeth were randomly divided into six groups of 15 teeth each. Clearfil SE Bond®, Adper™ Prompt L-Pop and Tyrian SPE™ were used as self-etching primers. Each self-etching primers were applied in both enamel specimens with and without additional etching. For additional etching groups, enamel surface was pretreated with 32% phosphoric acid (UNI-ETCH, Bisco, Inc., Schaumburg, IL, USA). Hybrid resin composite Clearfil AP-X, (Kuraray Co., Ltd., Osaka, Japan) was packed into the mold and light-cured for 40 seconds. Twenty-four hours after storage, the specimens were tested in shear bond strength. The data for each group were subjected to independent t - test at p < 0.01 to make comparisons among the groups.
In Clearfil SE Bond®, shear bond strength of additional etching group was higher than no additional etching group (p < 0.01). In Adper™ Prompt L-Pop and Tyrian SPE, there were no significant difference between additional etching and non-etching groups (p > 0.01).
In conclusion, self-etching adhesive system with weak acid seems to have higher bond strength to enamel with additional etching, while self-etching adhesive system with strong acid seems not. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Microtensile bond strength of silorane-based composite specific adhesive system using different bonding strategies
Laura Alves Bastos, Ana Beatriz Silva Sousa, Brahim Drubi-Filho, Fernanda de Carvalho Panzeri Pires-de-Souza, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(1): 23. CrossRef
-
134
View
-
0
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
The influence of AH-26 and zinc oxide-eugenol root canal sealer on the shear bond strength of composite resin to dentin
-
Ju-Yeon Cho, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young-Kyung Kim, Sung Kyo Kim
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(3):147-152. Published online May 31, 2006
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.3.147
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the influence of the AH-26 root canal sealer on the shear bond strength of composite resin to dentin.
One hundred and forty four (144) extracted, sound human molars were used. After embedding in a cylindrical mold, the occlusal part of the anatomical crown was cut away and trimmed in order to create a flat dentin surface. The teeth were randomly divided into three groups; the AH-26 sealer was applied to the AH-26 group, and zinc-oxide eugenol (ZOE) paste was applied to the ZOE group. The dentin surface of the control group did not receive any sealer.
A mount jig was placed against the surface of the teeth and the One-step dentin bonding agent was applied after acid etching. Charisma composite resin was packed into the mold and light cured. After polymerization, the alignment tube and mold were removed and the specimens were placed in distilled water at 37℃ for twenty four hours. The shear bond strength was measured by an Instron testing machine. The data for each group were subjected to one-way ANOVA and Tukey's studentized rank test so as to make comparisons between the groups.
The AH-26 group and the control group showed significantly higher shear bond strength than the ZOE group (p < 0.05).
There were no significant differences between the AH-26 group and the control one (p > 0.05).
Under the conditions of this study, the AH-26 root canal sealer did not seem to affect the shear bond strength of the composite resin to dentin while the ZOE sealer did. Therefore, there may be no decrease in bond strength when the composite resin core is built up immediately after a canal filling with AH-26 as a root canal sealer. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Is Zinc Oxide Eugenol Cement Still Impeding the Use of Resin-based Restoration? A Systematic Review
Fawaz Pullishery, Hajer Ayed Alhejoury, Mohammed Turkistani, Yasser Refay Souror
Dentistry and Medical Research.2021; 9(2): 59. CrossRef - A comparative evaluation of removal of gutta percha using two retreatment file system: An in vitro study
Shruthi Mary Sunil, Balakrishnan Rajkumar, Vishesh Gupta, Akanksha Bhatt, Pragyan Paliwal
IP Indian Journal of Conservative and Endodontics.2020; 5(2): 53. CrossRef - Evaluation of softening ability of Xylene & Endosolv-R on three different epoxy resin based sealers within 1 to 2 minutes - anin vitrostudy
Pratima Ramakrishna Shenoi, Gautam Pyarelal Badole, Rajiv Tarachand Khode
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(1): 17. CrossRef - Influence of Sodium Ascorbate on Microtensile Bond Strengths to Pulp Chamber Dentin treated with NaOCl
Soo-Yeon Jeon, Kwang-Won Lee, Mi-Kyung Yu
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2008; 33(6): 545. CrossRef
-
187
View
-
1
Download
-
4
Crossref
-
Effect of vital tooth bleaching agent on dentin bonding
-
Na-Young Jeong, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young-kyung Kim, Sung Kyo Kim
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(2):79-85. Published online March 31, 2006
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.2.079
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
To evaluate the effect of vital tooth bleaching agent and alcohol pretreatment on dentin bonding, flat dentin windows were produced on the buccal side of the crowns of fifty-five extracted, human premolars. A bleaching gel, Opalescence® with 10% of carbamide peroxide (Ultradent Product, USA) was daily applied on the teeth of three experimental groups for six hours for 10 consecutive days, while teeth of a control group were not bleached. After 6 hours of bleaching gel application, the specimens were washed and stored in saline until the next day application. After application of One-step® dentin bonding agent (Bisco, USA), Z-250® resin (3M-ESPE, USA) was bonded to dentin with a mount jig. Shear bond strength was measured with an Instron machine (Type 4202, Instron Corp., USA) after 24 hours. The results were analyzed using one-way ANOVA and Duncan's multiple range test at p < 0.05.
Immediate bonding group showed significantly lower bond strength than un-bleached control group (p < 0.05).
Ethanol-treated group showed significantly higher bond strength compared to immediate bonding group (p < 0.05). However, the bond strength of the ethanol treatment group was lower than that of the un-bleached control group (p < 0.05).
There were no significant difference in shear bond strength between the 2-week delayed bonding group and the ethanol-treated group (p > 0.05) and between delayed bonding group and un-bleached control group (p > 0.05).
In the condition of the present study, it seems that alcohol pretreatment after bleaching procedure can reduce the adverse effect of vital bleaching agent on dentin bonding. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effect of the bleaching light on whitening efficacy
Jong-Hyun Park, Hye-Jin Shin, Deok-Young Park, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(2): 95. CrossRef
-
140
View
-
0
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
Change of working length in curved canals by various instrumentation techniques
-
Jeong-Im Jo, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young Kyung Kim, Sung Kyo Kim
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(1):30-35. Published online January 31, 2006
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.1.030
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
To evaluate the change of working length with various instrumentation techniques in curved canals, working length and canal curvature were determined before and after canal instrumentation in buccal or mesial canals of extracted human molars. Stainless steel K-files (MANI®, Matsutani Seisakusho Co. Takanezawa, Japan), nickel-titanium K-files (Naviflex NT™, Brassler, Savannah, USA), ProFile®, and ProTaper™ (Dentsply-Maillefer, Ballaigues, Switzerland) were used to prepare the canals with crown-down technique. In two hand instrumentation groups, coronal flaring was made with Gates Glidden burs. Apical canals were instrumented until apical diameter had attained a size of 30. Positional relation between the tooth apex and the #10 K-file tip was examined by using AutoCAD 2000 (Autodesk Corp., San Rafael. CA, USA) under a stereomicroscope before and after coronal flaring, and after apical instrumentation. Degree of canal curvature was also measured with Schneider's method in radiographs. Data of working length and canal curvature changes were statistically analyzed with one-way ANOVA and Tukey's studentized range test.
Working length and canal curvature were decreased significantly in each step in all instrumentation groups. Coronal flaring using Gates Glidden burs in hand instrument groups and whole canal instrumentation using stainless steel hand K-files caused significantly more working length change than in ProFile instrumentation group (p < 0.05).
The result of this study demonstrates that all of the above kinds of instrumentation in curved canals cause reduction of working length and canal curvature at each instrumentation steps, and hand instrumentation causes more working length change than ProFile. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Does Root Canal Shaping Effect the Accuracy of Electronic Apex Locators in Curved and Straight Root Canals?
Dide Tekinarslan, Damla Erkal, Esen Ercan, Simay Koc, Kürşat Er
Clinical and Experimental Health Sciences.2024; 14(3): 727. CrossRef - Comparative Study of Four Endodontic File Systems to Assess Changes in Working Length during Root Canal Instrumentation and the Effect of Canal Curvature on Working Length Change
Michelle Tien, Hermawan Tjoa, Maggie Zhou, Paul V. Abbott
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(1): 110. CrossRef - Study of endodontic working length of Korean posterior teeth
Jeong-Yeob Kim, Sang-Hoon Lee, Gwang-Hee Lee, Sang-Hyuk Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(6): 429. CrossRef
-
178
View
-
0
Download
-
3
Crossref
-
Influence of plugger penetration depth on the area of the canal space occupied by gutta-percha
-
Young Mi Lee, Ho-young So, Young Kyung Kim, Sung Kyo Kim
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(1):66-71. Published online January 31, 2006
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.1.066
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
To evaluate the ratio of gutta-percha area in the canal after canal obturation with Continuous Wave of Condensation Technique (CWCT) with varying depths of plugger penetration, forty root canals of extracted human teeth were prepared up to size 40 of 0.06 taper with ProFile®. Canals of three groups were filled with CWCT with System B™ (Analytic Tech., USA) and different plugger penetration depths of 3, 5, or 7 mm from the apex. Canals of one group were filled with lateral condensation technique as a control. The filled teeth were cross-sectioned at 1, 2, and 3 mm levels from the apical foramen. The ratio of gutta-percha area in the canal was analyzed using Auto®Cad 2000. Data were analyzed with one-way ANOVA and Duncan's multiple range test.
At all levels, higher gutta-percha area ratio was found with deeper plugger penetration depth in CWCT, and cold lateral condensation group showed higher ratio than group of plugger penetration to apical 7 mm in CWCT.
At apical 1 mm and 2 mm levels, group of plugger penetration to apical 3 mm showed significantly higher gutta-percha area ratio than those of apical 7 mm and lateral condensation (p < 0.05).
It is concluded therefore that, under the conditions of the present study, deeper plugger penetration depth results in more favorable and efficient obturation in CWCT.
|