-
Observation of an extracted premolar 2.5 years after mineral trioxide aggregate apexification using micro-computed tomography
-
Gayeon Lee, Chooryung Chung, Sunil Kim, Su-Jung Shin
-
Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(2):e4. Published online November 22, 2019
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e4
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
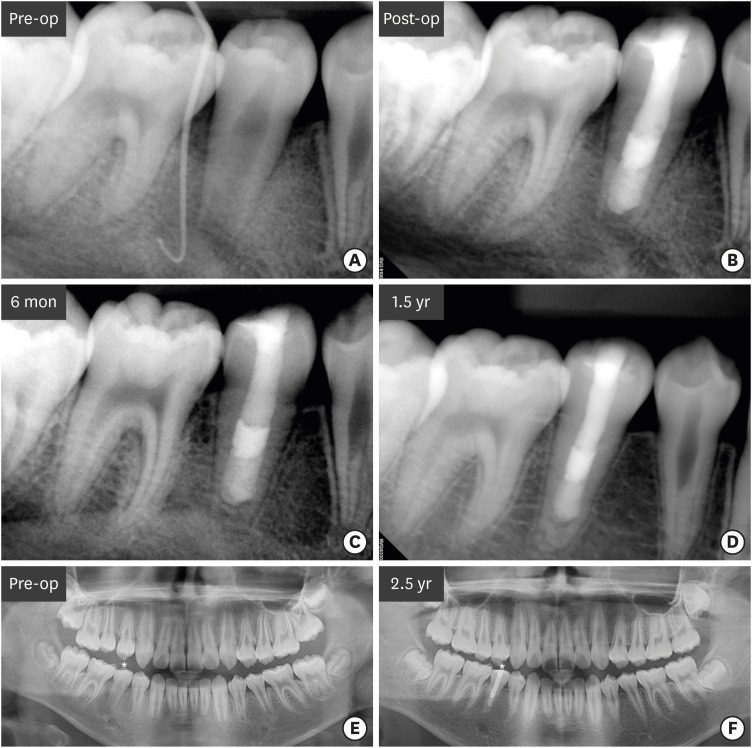
Although numerous studies have been conducted on apexification using mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA), direct observation of extracted human teeth after the procedure has been rarely reported. This case report describes a mandibular premolar treated 2.5 years ago and extracted recently for orthodontic treatment. The tubercle of the right mandibular premolar of a 12-year-old boy with dens evaginatus was fractured and the pulp was exposed. The tooth was diagnosed with pulp necrosis and asymptomatic periapical abscess. During the first visit, copious irrigation was performed with 2.5% sodium hypochlorite. Calcium hydroxide paste was placed as an intracanal medicament. The sinus tract had disappeared at the second visit after 3 weeks. MTA was applied on to the bleeding point as a 4-mm-thick layer, followed by a 3-mm-thick gutta-percha filling and resin core build-up. After 2.5 years, the tooth and three other premolars were extracted for orthodontic treatment. The right and left mandibular premolars were scanned with micro-computed tomography to determine the root shape and canal anatomy. Irregular root growth was observed and the root outline of the right mandibular premolar differed from that of the contralateral tooth. Apexification with MTA leads to the formation of roots with irregular morphology, without any pulpal space. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Incorporation of amoxicillin-loaded microspheres in mineral trioxide aggregate cement: an in vitro study
Fábio Rocha Bohns, Vicente Castelo Branco Leitune, Isadora Martini Garcia, Bruna Genari, Nélio Bairros Dornelles, Silvia Stanisçuaski Guterres, Fabrício Aulo Ogliari, Mary Anne Sampaio de Melo, Fabrício Mezzomo Collares
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
-
165
View
-
2
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
Progression of periapical cystic lesion after incomplete endodontic treatment
-
Jong-Ki Huh, Dong-Kyu Yang, Kug-Jin Jeon, Su-Jung Shin
-
Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(2):137-142. Published online February 22, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.2.137
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
We report a case of large radicular cyst progression related to endodontic origin to emphasize proper intervention and follow-up for endodontic pathosis. A 25 yr old man presented with an endodontically treated molar with radiolucency. He denied any intervention because of a lack of discomfort. Five years later, the patient returned. The previous periapical lesion had drastically enlarged and involved two adjacent teeth. Cystic lesion removal and apicoectomy were performed on the tooth. Histopathological analysis revealed that the lesion was an inflammatory radicular cyst. The patient did not report any discomfort except for moderate swelling 3 days after the surgical procedure. Although the patient had been asymptomatic, close follow-ups are critical to determine if any periapical lesions persist after root canal treatment. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Prognosis of Vital Teeth Involved in Large Cystic Lesions After a Surgical Intervention: A Longitudinal Ambidirectional Cohort Study
Khalid A. Merdad, Maha Shawky, Khalid A. Aljohani, Rawia Alghamdi, Saja Alzahrani, Omar R. Alkhattab, Abdulaziz Bakhsh
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(2): 83. CrossRef - Assessing the efficacy of apicoectomy without retrograde filling in treating periapical inflammatory cysts
Jeong-Kui Ku, Woo-Young Jeon, Seung-O Ko, Ji-Young Yoon
Journal of the Korean Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons.2024; 50(3): 140. CrossRef - Cystic lesion between a deciduous tooth and the succeeding permanent tooth: a retrospective analysis of 87 cases
Changmo Sohn, Jihye Ryu, Inhye Nam, Sang-Hun Shin, Jae-Yeol Lee
Journal of the Korean Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons.2022; 48(6): 342. CrossRef - The effectiveness of antibacterial treatment of the root canal in chronic apical periodontitis using an erbium-chromium laser
M. A. Postnikov, A. Yu. Rozenbaum, S. E. Chigarina, D. N. Kudryashov, M. B. Khaikin, I. V. Khramova, G. N. Belanov
Endodontics Today.2022; 20(2): 115. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Incomplete Endodontic Care
Carla Y. Falcon, Anthony R. Arena, Rebecca Hublall, Craig S. Hirschberg, Paul A. Falcon
Journal of Endodontics.2021; 47(9): 1398. CrossRef - Tratamento cirúrgico e conservador de cisto periapical de grande proporção: relato de caso
Maraísa Aparecida Pinto Resende, Neuza Maria Souza Picorelli Assis, Augusto César Sette-Dias, Evandro Guimarães de Aguiar, Bruno Salles Sotto-Maior
HU Revista.2018; 43(2): 191. CrossRef
-
299
View
-
0
Download
-
6
Crossref
-
Esthetic rehabilitation of single anterior edentulous space using fiber-reinforced composite
-
Hyeon Kim, Min-Ju Song, Su-Jung Shin, Yoon Lee, Jeong-Won Park
-
Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(3):220-225. Published online May 19, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.3.220
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
A fiber-reinforced composite (FRC) fixed prosthesis is an innovative alternative to a traditional metal restoration, as it is a conservative treatment method. This case report demonstrates a detailed procedure for restoring a missing anterior tooth with an FRC. A 44-year-old woman visited our department with an avulsed tooth that had fallen out on the previous day and was completely dry. This tooth was replanted, but it failed after one year. A semi-direct technique was used to fabricate a FRC fixed partial prosthesis for its replacement. The FRC framework and the pontic were fabricated using a duplicated cast model and nanofilled composite resin. Later on, interproximal contact, tooth shape, and shade were adjusted at chairside. This technique not only enables the clinician to replace a missing tooth immediately after extraction for minimizing esthetic problems, but it also decreases both tooth reduction and cost. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Anterior provisional fixed partial dentures: A finite element analysis
Nouf Almeganni, Rotana Abulaban, Ghada Naguib, Mohamed Tharwat, Hani M. Nassar
Journal of Prosthodontics.2024; 33(4): 367. CrossRef - FİBERLE GÜÇLENDİRİLMİŞ ADEZİV KÖPRÜLER VE UYGULAMA YÖNTEMLERİ
Gözde YALÇIN, Asude Dilek NALBANT
Atatürk Üniversitesi Diş Hekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi.2022; : 1. CrossRef - Fiber-reinforced composite resin bridges: an alternative method to treat root-fractured teeth
Gun Heo, Eun-Hye Lee, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho, Se-Hee Park
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - A New Technique for Direct Fabrication of Fiber-Reinforced Composite Bridge: A Long-Term Clinical Observation
Matías Ferrán Escobedo Martínez, Samuel Rodríguez López, Jairo Valdés Fontela, Sonsoles Olay García, Mario Mauvezín Quevedo
Dentistry Journal.2020; 8(2): 48. CrossRef - Customized Treatment Option for Malpositioned Dental Implant Placed in Aesthetic Zone
Priyanka N. Khungar, Trupti M. Dahane, Ramnath P. Revankar, Rupali Patel
Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences.2020; 9(39): 2930. CrossRef - Fiber reinforced composite bridge as a replacement for missing upper permanent lateral incisor – a case report
Ana Todorović, Danica Popović, Igor Djordjević, Vojkan Lazić
Stomatoloski glasnik Srbije.2016; 63(3): 133. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Viability of Rat Periodontal Ligament Cells after Storing at 0℃/2 MPa Condition up to One Week: In Vivo MTT Method
Sun Mi Jang, Sin-Yeon Cho, Eui-Seong Kim, Il-Young Jung, Seung Jong Lee
Journal of Korean Dental Science.2016; 9(1): 1. CrossRef - Semidirect Restorations in Multidisciplinary Treatment: Viable Option for Children and Teenagers
Mateus Rodrigues Tonetto, Milton Carlos Kuga, Fausto Frizzera, Matheus Coelho Bandeca, Shilpa H Bhandi, Célia Regina Maio Pinzan-Vercelino, Monica Barros da Silva, Kamila Figueiredo Pereira
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2015; 16(4): 280. CrossRef
-
218
View
-
2
Download
-
8
Crossref
-
Diagnosis and treatment of teeth with primary endodontic lesions mimicking periodontal disease: three cases with long-term follow ups
-
Jae-Hyung Lim, Ji-Hyun Lee, Su-Jung Shin
-
Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(1):56-62. Published online January 20, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.1.56
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
A tooth with primary endodontic disease that demonstrates a periodontal defect might be extracted because of misdiagnosis as severe periodontal disease or a vertical root fracture. The aim of this case report was to demonstrate the long-term survival of endodontically treated teeth, which had been initially considered unsavable. With meticulous evaluation including the patient's dental history, clinical and radiographic examinations, teeth with primary endodontic lesions could be differentiated and saved after proper root canal treatment. Pain history, vitality test, and radiographic examinations, as well as a general periodontal condition check with periodontal probing on an affected tooth, might be the key methods to differentiate endodontic pathosis from that of periodontal disease. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - The morphological and functional relationship between dental pulp and periodontal tissue in the aspect of endo-perio lesions
D. A. Moiseev, S. I. Volkov, A. A. Konov, M. A. Kulyukina
Parodontologiya.2022; 26(4): 289. CrossRef - Evaluation of root morphology of maxillary and mandibular second molars lost due to periodontitis
Akiko Kato, Toshimitsu Hishikawa, Koji Inagaki, Genta Yamamoto, Akio Mitani, Masaki Honda
Journal of Periodontal Research.2020; 55(5): 753. CrossRef - Clinical and Radiographic Characteristics of Endoperiodontitis in Patients with Chronic Generalized Periodontitis
L.N. Dedova, Yu.L. Denisova, N.I. Rossenik
Stomatologist. Minsk.2017; (3(26)): 13. CrossRef - The importance of correct diagnosis and treatment in endo-periodontal lesions: a two cases comparison
Sara Bernardi, Christian Frascarelli, Giulia Fantozzi, Silvia Caruso, Robert Gatto, Gianna Maria Nardi, Maria Adelaide Continenza
Dental Update.2016; 43(8): 766. CrossRef - Surgical management with intentional replantation on a tooth with palato-radicular groove
Jorge Forero-López, Luis Gamboa-Martínez, Laura Pico-Porras, Javier Laureano Niño-Barrera
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(2): 166. CrossRef - Subgingival microbiome in smokers and non‐smokers in Korean chronic periodontitis patients
J.‐H. Moon, J.‐H. Lee, J.‐Y. Lee
Molecular Oral Microbiology.2015; 30(3): 227. CrossRef
-
276
View
-
2
Download
-
6
Crossref
-
Misdiagnosis of florid cemento-osseous dysplasia leading to unnecessary root canal treatment: a case report
-
Jong-Ki Huh, Su-Jung Shin
-
Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(3):160-166. Published online August 23, 2013
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.3.160
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
This case report demonstrates an unnecessary endodontic treatment of teeth with florid cemento-osseous dysplasia (FCOD) due to a misdiagnosis as periapical pathosis and emphasizes the importance of correct diagnosis to avoid unnecessary treatment. A 30-year-old woman was referred to our institution for apicoectomies of the mandibular left canine and both the lateral incisors. The periapical lesions associated with these teeth had failed to resolve after root canal treatment over a 3-year period. Radiographic examinations revealed multiple lesions on the right canine, the second premolar, and both first molars as well as the anterior region of the mandible. Based on clinical, radiographic and histological evaluations, the patient condition was diagnosed as FCOD. The patient has been monitored for 2 years. To avoid unnecessary invasive treatment, accurate diagnosis is essential before treatment is carried out in managing FCOD. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Periapical cemento‐osseous dysplasia masquerading as asymptomatic chronic apical periodontitis in a Chinese woman: A case report
Yunjing Ma, Dong Fang, Mei Ji
Clinical Case Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Benign Fibro-Osseous Lesions of The Jaw: A Retrospective Analysis
Saim Yanık, Mehmet Emrah Polat
European Journal of Therapeutics.2024; 30(5): 760. CrossRef - Radiological follow-up of cemento-osseous dysplasia on cone-beam computed tomography
Stefan F. Nemec, Steffen Schneider, Klaus M. Friedrich, Michael Weber, Ursula Schwarz-Nemec
Journal of Cranio-Maxillofacial Surgery.2024; 52(5): 644. CrossRef - Cemento osseous dysplasia(COD) of the mandibular teeth misdiagnosed as periapical lesion; cone beam CT-based case report
Won-Jeong Han
The Journal of The Korean Dental Association.2024; 62(7): 432. CrossRef - Surgical Management of Infection Secondary to Cemento-osseous Dysplasia
Farin Ebrahimi, Faraz Ebrahimi, Jingang An
Journal of Craniofacial Surgery.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Florid osseous dysplasia mimicking odontogenic infections: A report of two cases and literature review
A. Wajdi Bin Mohammed, Mohammed Mubarak Aldosari, Osama A. Alharbi, Ahmed Alzahrani, Abdullah M. Alsoghier
Saudi Journal of Oral Sciences.2023; 10(3): 195. CrossRef - Radiolucent lesions that may resemble inflammatory periapical lesions: A review article
Hamad Albagieh, Mohammed Aldosari, Abdulmajeed Alkhathlan, Nawaf Alfawaz, Mohammed Almutairi
The Saudi Dental Journal.2023; 35(8): 916. CrossRef - Cemento-Osseous Dysplasia: A Detailed Comparison of the 2005 and 2017 WHO Classifications and Case Analysis
Jiankang Zhang, Yunbo Yu, Wei Tang, Jian Pan, Wei Jing
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The bony changes after mandibular incisors retraction on a severe skeletal Class II bimaxillary protrusion extraction patient with periapical cemento-osseous dysplasia
Huijuan Wang, Yiwen Zhou, Baochao Li, Ling Huang, Huang Li
AJO-DO Clinical Companion.2022; 2(5): 496. CrossRef - Cemento-ossøs dysplasi – en diagnostisk utfordring
Stig Løvold, Sivakami Rethnam Haug
Den norske tannlegeforenings Tidende.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A retrospective cone beam computed tomography analysis of cemento-osseous dysplasia
Birsay Gumru, Melda Pelin Akkitap, Sevilay Deveci, Ender Idman
Journal of Dental Sciences.2021; 16(4): 1154. CrossRef - Florid Cemento-osseous Dysplasia: A Report of Two Cases and Literature Review
Prashanth Panta, Imran Shahid, Mukund Seshadri
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2021; 22(3): 304. CrossRef - Natural history of florid osseous dysplasia of the jaws with important clinical implications
Camile S. Farah, Marie Anne T. Matias
Australian Endodontic Journal.2021; 47(3): 684. CrossRef - Clinical assessment of cemento‐osseous dysplasia based on three‐dimensional diagnostic imaging: A case report
Naoki Shibata, Kyoko Inamoto, Munetaka Naitoh, Eiichiro Ariji
Australian Endodontic Journal.2021; 47(1): 105. CrossRef - Odontogenic Cysts
Arvind Babu Rajendra Santosh
Dental Clinics of North America.2020; 64(1): 105. CrossRef - Difficulties in the diagnosis of periapical translucencies and in the classification of cemento-osseous dysplasia
Andrea Brody, Attila Zalatnai, Krisztian Csomo, Andrea Belik, Csaba Dobo-Nagy
BMC Oral Health.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Florid Cemento-Osseous Dysplasia of Osteolytic Stage Showing Cyst-Like Findings on CT and MRI: A Case Report
Kotaro Ito, Naohisa Hirahara, Norihito Iizuka, Eri Sawada, Shunya Okada, Masaaki Suemitsu, Kayo Kuyama, Takashi Kaneda
International Journal of Oral-Medical Sciences.2019; 17(3-4): 137. CrossRef - Oral management of a patient with cemento-osseous dysplasia: a case report
Camila de Nazaré Alves de Oliveira KATO, Juliana Diogo de Almeida SAMPAIO, Tânia Mara Pimenta do AMARAL, Lucas Guimarães ABREU, Cláudia Borges BRASILEIRO, Ricardo Alves MESQUITA
RGO - Revista Gaúcha de Odontologia.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Retrospective Study of 383 Cases of Fibro-Osseous Lesions of the Jaws
Camila de Nazaré Alves de Oliveira Kato, Laiz Fernandes Mendes Nunes, Loliza Luiz Figueiredo Houri Chalub, Adriana Etges, Tarcília Aparecida Silva, Ricardo Alves Mesquita
Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.2018; 76(11): 2348. CrossRef - Successful Implant Placement in a Case of Florid Cemento-Osseous Dysplasia: A Case Report and Literature Review
Nasrin Esfahanizadeh, Hila Yousefi
Journal of Oral Implantology.2018; 44(4): 275. CrossRef - Recurrent symptomatic cemento-osseous dysplasia: A case report
Chang-Ki Min, Kwang-Joon Koh, Kyoung-A Kim
Imaging Science in Dentistry.2018; 48(2): 131. CrossRef - Cemento-Osseous Dysplasias: Imaging Features Based on Cone Beam Computed Tomography Scans
Paulo Henrique Pereira Cavalcanti, Eduarda Helena Leandro Nascimento, Maria Luiza dos Anjos Pontual, Andréa dos Anjos Pontual, Priscylla Gonçalves Correia Leite de Marcelos, Danyel Elias da Cruz Perez, Flávia Maria de Moraes Ramos-Perez
Brazilian Dental Journal.2018; 29(1): 99. CrossRef - Florid cemento-osseous dysplasia: a contraindication to orthodontic treatment in compromised areas
Alberto Consolaro, Sergio Rafael Baggio Paschoal, Jose Burgos Ponce, Dario A. Oliveira Miranda
Dental Press Journal of Orthodontics.2018; 23(3): 26. CrossRef - Clinical, demographic, and radiographic analysis of 82 patients affected by florid osseous dysplasia: an international collaborative study
Débora Lima Pereira, Fábio Ramôa Pires, Márcio Ajudarte Lopes, Román Carlos, John Marshal Wright, Paras Patel, Willie van Heerden, Andre Uys, Pablo Agustin Vargas
Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology and Oral Radiology.2016; 122(2): 250. CrossRef - Cone beam CT as an aid to diagnosing mixed radiopaque radiolucent lesions in the mandibular incisor region
Unni Krishnan, Manal Al Maslamani, Alex J Moule
BMJ Case Reports.2015; : bcr2014207617. CrossRef - Benign Fibro-Osseous Lesions of the Craniofacial Area in Children and Adolescents: A Review
D.V. Rogozhin, F. Bertoni, D. Vanel, M. Gambarotti, A. Righi, I.V. Bulycheva, D.M. Konovalov, A.G. Talalaev, V.Yu. Roshin, A.P. Ektova, M.V. Bolotin, A.V. Lopatin
Arkhiv patologii.2015; 77(4): 63. CrossRef - Dysplasie osseuse floride mandibulaire : un cas de découverte fortuite et revue de la littérature
Eugénie Massereau, Ugo Ordioni, Maud Guivarc’h, Guillaume Royer, Jean-Hugues Catherine
Médecine Buccale Chirurgie Buccale.2015; 21(2): 101. CrossRef
-
314
View
-
5
Download
-
27
Crossref
-
Considerations during crown reattachment procedure over the pulpal exposure: case report
-
Bona Kim, Yoon Lee, Min-Ju Song, Su-Jung Shin, Jeong-Won Park
-
Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(4):240-244. Published online November 21, 2012
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.4.240
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
Crown reattachment is the most conservative treatment which can be used to restore fractured tooth, presumably with sufficient strength, while maintaining original contour, incisal translucency, and reducing chair time and cost. However, in case of crown fracture with pin-point pulp exposure, we should cautiously minimize the irritation to the pulp and consider pre-treatment pulpal status, choice of pulp capping materials, choice of bonding system and treatment sequence during crown reattachment procedures. This case reports the considerations while crown reattachment with direct pulp capping using calcium hydroxide (Dycal, Dentsply Caulk). -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - A Conservative Approach to the Management of a Dental Trauma for Immediate Natural Esthetics
Pallav Mahesh Patni, Pradeep Jain, Mona Jain Patni
Archives of Trauma Research.2016;[Epub] CrossRef
-
174
View
-
3
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
Prevention of tooth discoloration associated with triple antibiotics
-
Bona Kim, Min-Ju Song, Su-Jung Shin, Jeong-Won Park
-
Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(2):119-122. Published online May 18, 2012
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.2.119
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
Regenerative endodontics has a potential to heal a partially necrotic pulp, which can be beneficial for the continued root development and strengthening of immature teeth. For this purpose, triple antibiotic mixture of ciprofloxacin, metronidazole, and minocycline was recommended as intracanal medicament in an attempt to disinfect the root canal system for revascularization of a tooth with a necrotic pulp. However, discoloration of the tooth was reported after applying this. This case shows the idea for preventing the tooth discoloration using a delivery syringe (SW-O-01, Shinwoo dental) to avoid the contact between the clinical crown and the antibiotics. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Non-surgical Management of a Large Periapical Lesion: A Case Study of the Successful Application of a Modified Triple Antibacterial Paste
Srushti Awghad, Joyeeta Mahapatra, Amit Reche, Ankita Burse, Aradhana Kibe
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the antimicrobial efficacy of two combinations of drugs on bacteria taken from infected primary teeth (in vitro)
R. Rafatjou, R. Yousefimashouf, M. Farhadian, S. Afzalsoltani
European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry.2019; 20(6): 609. CrossRef - Triple antibiotic paste: momentous roles and applications in endodontics: a review
Ardavan Parhizkar, Hanieh Nojehdehian, Saeed Asgary
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical Effectiveness of Different Polishing Systems and Self-Etch Adhesives in Class V Composite Resin Restorations: Two-Year Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial
J-H Jang, H-Y Kim, S-M Shin, C-O Lee, DS Kim, K-K Choi, S-Y Kim
Operative Dentistry.2017; 42(1): 19. CrossRef - Revascularization of Necrotic Immature Permanent Teeth: An Update
N Velmurugan
Journal of Operative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 1(1): 18. CrossRef - Treatment of non-vital immature teeth with amoxicillin-containing triple antibiotic paste resulting in apexification
Hyon-Beom Park, Bin-Na Lee, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Hoon-Sang Chang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(4): 322. CrossRef
-
157
View
-
2
Download
-
6
Crossref
-
Morphological evaluation during in vitro chondrogenesis of dental pulp stromal cells
-
Choo-Ryung Chung, Ha-Na Kim, Yeul Park, Min-Jeong Kim, Young-Ju Oh, Su-Jung Shin, Yoon-Jeong Choi, Kyung-Ho Kim
-
Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(1):34-40. Published online March 2, 2012
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.1.34
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
-
Objectives
The aim was to confirm the stem cell-like properties of the dental pulp stromal cells and to evaluate the morphologic changes during in vitro chondrogenesis.
Materials and Methods
Stromal cells were outgrown from the dental pulp tissue of the premolars. Surface markers were investigated and cell proliferation rate was compared to other mesenchymal stem cells. Multipotency of the pulp cells was confirmed by inducing osteogenesis, adipogenesis and chondrogenesis. The morphologic changes in the chondrogenic pellet during the 21 day of induction were evaluated under light microscope and transmission electron microscope. TUNEL assay was used to evaluate apoptosis within the chondrogenic pellets.
Results
Pulp cells were CD90, 105 positive and CD31, 34 negative. They showed similar proliferation rate to other stem cells. Pulp cells differentiated to osteogenic, adipogenic and chondrogenic tissues. During chondrogenesis, 3-dimensional pellet was created with multi-layers, hypertrophic chondrocyte-like cells and cartilage-like extracellular matrix. However, cell morphology became irregular and apoptotic cells were increased after 7 day of chondrogenic induction.
Conclusions
Pulp cells indicated mesenchymal stem cell-like characteristics. During the in vitro chondrogenesis, cellular activity was superior during the earlier phase (within 7 day) of differentiation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Local myogenic pulp‐derived cell injection enhances craniofacial muscle regeneration in vivo
J. E. Jung, M. J. Song, S. Shin, Y. J. Choi, K. H. Kim, C. J. Chung
Orthodontics & Craniofacial Research.2017; 20(1): 35. CrossRef - Immune Tolerance of Human Dental Pulp-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Mediated by CD4+CD25+ FoxP3+ Regulatory T-Cells and Induced by TGF-β1 and IL-10
Jong Won Hong, Jung Hyun Lim, Chooryung J. Chung, Tae Jo Kang, Tae Yeon Kim, Young Seok Kim, Tae Suk Roh, Dae Hyun Lew
Yonsei Medical Journal.2017; 58(5): 1031. CrossRef - In vitrocharacterization of human dental pulp stem cells isolated by three different methods
Ji-Hyun Jang, Hyeon-Woo Lee, Kyu Min Cho, Hee-Woong Shin, Mo Kwan Kang, Sang Hyuk Park, Euiseong Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(4): 283. CrossRef - Effects of two fast-setting calcium-silicate cements on cell viability and angiogenic factor release in human pulp-derived cells
Chooryung J. Chung, Euiseong Kim, Minju Song, Jeong-Won Park, Su-Jung Shin
Odontology.2016; 104(2): 143. CrossRef - A Simplified Method for the Aspiration of Bone Marrow from Patients Undergoing Hip and Knee Joint Replacement for Isolating Mesenchymal Stem Cells andIn VitroChondrogenesis
Subhash C. Juneja, Sowmya Viswanathan, Milan Ganguly, Christian Veillette
Bone Marrow Research.2016; 2016: 1. CrossRef - Local Injection of Pulp Cells Enhances Wound Healing during the Initial Proliferative Phase through the Stimulation of Host Angiogenesis
Hyungjoo Yang, Sujung Shin, Jhiweon Ahn, YoonJeong Choi, Kyung-Ho Kim, Chooryung J. Chung
Journal of Endodontics.2013; 39(6): 788. CrossRef
-
175
View
-
1
Download
-
6
Crossref
-
Endodontic management of a maxillary lateral incisor with dens invaginatus and external root irregularity using cone-beam computed tomography
-
Young-Jun Lim, Sook-Hyun Nam, Sung-Ho Jung, Dong-Ryul Shin, Su-Jung Shin, Kyung-San Min
-
Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(1):50-53. Published online March 2, 2012
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.1.50
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
Cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) is a useful diagnostic tool for identification of both internal and external root configurations. This case report describes the endodontic management of a lateral incisor with both dens invaginatus and external root irregularity by using CBCT. Nonsurgical endodontic retreatment was performed on the lateral incisor with dens invaginatus. A perforation through the dens invaginatus and external concavity was repaired using mineral trioxide aggregate. After 18 mon of follow-up, there were no clinical symptoms. Recall radiographs appeared normal and showed healing of the periapical pathosis. The understanding of both internal root canal configuration and external root irregularity using CBCT can ensure predictable and successful results. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Cone-beam computed tomography for assessment of dens invaginatus in the Polish population
T. Katarzyna Różyło, Ingrid Różyło-Kalinowska, Magdalena Piskórz
Oral Radiology.2018; 34(2): 136. CrossRef - Nonsurgical Endodontic Management of a Molar-Incisor Malformation-affected Mandibular First Molar: A Case Report
Wonyoung Yue, Euiseong Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(4): 664. CrossRef - Three-year follow-up: Healing of a large periapical lesion related to a maxillary central incisor and two canalled lateral incisor after a single visit root canal treatment
Abu Mostafa Ammar
Journal of Dentistry and Oral Hygiene.2015; 7(4): 40. CrossRef - Dilemmas pertaining to three canals in the mesiobuccal root of a maxillary second molar: a case report
Ankit Arora, Shashi Rashmi Acharya, Muliya Vidya Saraswathi, Padmaja Sharma, Amber Ather
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(3): 172. CrossRef - Management of root canal perforation by using cone-beam computed tomography
Kyung-San Min
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(1): 55. CrossRef - Endodontic treatment of maxillary lateral incisors with anatomical variations
Moon-Hwan Lee, Jung-Hong Ha, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young-Kyung Kim, Sung-Kyo Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 253. CrossRef
-
180
View
-
2
Download
-
6
Crossref
-
Evaluation of canal preparation for apical sealing with various Ni-Ti rotary instruments
-
Yooseok Shin, Su-Jung Shin, Minju Song, Euiseong Kim
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(4):300-305. Published online July 31, 2011
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.4.300
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
-
Objectives
The aim of this study was to evaluate the various NiTi rotary instruments regarding their ability to provide a circular apical preparation.
Materials and Methods
50 single canal roots were selected, cut at the cementodentinal junction and the coronal 1/3 of the canals was flared using Gates Glidden burs. Samples were randomly divided into 5 experimental groups of 10 each. In group I, GT files, Profile 04 and Quantec #9 and #10 files were used. In Group II Lightspeed was used instead of Quantec. In Group III, Orifice shaper, Profile .06 series and Lightspeed were used. In Group IV, Quantec #9 and #10 files were used instead of Lightspeed. In Group V, the GT file and the Profile .04 series were used to prepare the entire canal length. All tooth samples were cut at 1 mm, 3 mm and 5 mm from the apex and were examined under the microscope.
Results
Groups II and III (Lightspeed) showed a more circular preparation in the apical 1mm samples than the groups that used Quantec (Group I & IV) or GT files and Profile .04 series.(Group V)(p < 0.05) There was no significant difference statistically among the apical 3, 5 mm samples. In 5 mm samples, most of the samples showed complete circularity and none of them showed irregular shape.
Conclusions
Lightspeed showed circular preparation at apical 1 mm more frequently than other instruments used in this study. However only 35% of samples showed circularity even in the Lightspeed Group which were enlarged 3 ISO size from the initial apical binding file (IAF) size. So it must be considered that enlarging 3 ISO size isn't enough to make round preparation.
-
Matrix metalloproteinase-8 and substance P levels in root canal exudates of nonvital teeth
-
Su-Jung Shin, Woocheol Lee, Jae-Il Lee, Seung-Ho Baek, Kee-Yeon Kum, Won-Jun Shon, Kwang-Shik Bae
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(3):196-202. Published online May 31, 2011
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.3.196
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
-
Objectives
The aim of this study was to investigate levels of matrix metalloproteinase-8 (MMP-8) and substance P (SP) in root canal exudates during root canal treatment (RCT) of nonvital, painful teeth.
Materials and Methods
Patients scheduled for nonsurgical RCT were prospectively selected; the study was performed after obtaining informed consent from the patients and was approved by the Institutional Review Board for Clinical Research of Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University (3-2008-0118). Canal exudates samples were collected using sterilized paper points from teeth scheduled for RCT across three different time periods. MMP-8 and SP levels were measured using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Data were analyzed using a mixed model analysis and the Pearson correlation analysis (p < 0.05).
Results
MMP-8 and SP levels in GCF were decreased during RCT (p < 0.0001), and they showed a weak positive correlation to each other (p < 0.05). Patients'subjective pain levels and the response from percussion test were significantly related to SP level.
Conclusions
This study demonstrated that periradicular inflammation endodontic origin can elevate SP and MMP-8 levels in root canal exudates. Interestingly, SP level of canal exudates showed a possibility of being used as an indicator of pain due to periapical pathosis.
-
Patients' perception and satisfaction with apicoectomy
-
Euiseong Kim, Seung-Jong Lee, Jeong-Won Park, Su-Jung Shin
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(2):114-118. Published online March 31, 2011
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.2.114
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
-
Objectives
This study was aimed to examine the patients' perception and satisfaction with the results of endodontic microsurgery which was apicoectomy with retrofilling.
Materials and Methods
A questionnaire was given to 109 patients, who were recalled after a minimum of 3 months upon endodontic microsurgery in the Department of Conservative Dentistry, Yonsei University. A contingency table and correlation analysis were used to determine if there were any correlations between age/gender and the patients' responses (p = 0.05).
Results
Approximately 60% of respondents answered they had never heard of surgical endodontic procedures. 63.3% of respondents chose the surgical option because they wanted to keep their natural teeth. If the patient required the same procedure on another tooth later, 100 out of 109 respondents answered they would choose microsurgery instead of extraction. Most patients (82.57%) appeared to be satisfied with the surgical procedure.
Conclusions
Endodontic microsurgery consisting of apicoectomy and retrofilling seems to appeal to majority of patients as a satisfactory and valuable treatment choice.
-
The evaluation of surface roughness and polishing time between polishing systems
-
Ye-Mi Kim, Su-Jung Shin, Min-Ju Song, Jeong-Won Park
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(2):119-124. Published online March 31, 2011
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.2.119
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
-
Objectives
The purpose of this experiment was to evaluate four different polishing systems of their polishability and polishing time.
Materials and Methods
4 mm diameter and 2 mm thickness Teflon mold was made. Z-250 (3M ESPE) hybrid composite resin was slightly overfilled and pressed with slide glass and cured with Optilux 501 for 40 sec each side. Then the surface roughness (glass pressed: control group) was measured with profilometer. One surface of the specimen was roughened by #320 grit sand paper and polished with one of the following polishing systems; Sof-Lex (3M ESPE), Jiffy (Ultradent), Enhance (Dentsply/Caulk), or Pogo (Dentsply/Caulk). The surface roughness and the total polishing time were measured. The results were analyzed with one-way ANOVA and Duncan's multiple range test.
Results
The surface roughness was lowest in Pogo, and highest in Sof-Lex. Polishing times were shortest with Pogo, and followed by the Sof-Lex, Enhance and Jiffy.
Conclusions
One-step polishing system (Pogo) is very effective to get the smooth surface in a short time, therefore it can be recommended for final polishing system of the restoration.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Observation of surface roughness on three types of resin based on grinding time of dental automatic barrel finishing
An-Na Jung, Hyeon-Jeong Ko, Yu-Jin Park
Journal of Korean Acedemy of Dental Technology.2021; 43(2): 56. CrossRef - Observations of surface roughness of Co-Cr alloys according to grinding time of dental barrel finishing
Hyeon-Jeong Ko, Yu-Jin Park, Sung-Min Choi
Journal of Korean Acedemy of Dental Technology.2021; 43(3): 93. CrossRef - Component and surface residue observation of barrel finishing media for grinding dental resins
An-Na Jung, Yu-Jin Park, Sung-Min Choi
Journal of Korean Acedemy of Dental Technology.2021; 43(4): 145. CrossRef - Performance of a novel polishing rubber wheel in improving surface roughness of feldspathic porcelain
Geum-Jun HAN, Jae-Hoon KIM, Mi-Ae LEE, So-Yeon CHAE, Yun-Hee LEE, Byeong-Hoon CHO
Dental Materials Journal.2014; 33(6): 739. CrossRef
-
157
View
-
4
Download
-
4
Crossref
-
Comparison of apical transportation and change of working length in K3, NRT AND PROFILE rotary instruments using transparent resin block
-
Min-Jung Yoon, Min-Ju Song, Su-Jung Shin, Euiseong Kim
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(1):59-65. Published online January 31, 2011
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.1.59
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
-
Objectives
The purpose of this study is to compare the apical transportation and working length change in curved root canals created in resin blocks, using 3 geometrically different types of Ni-Ti files, K3, NRT, and Profile.
Materials and Methods
The curvature of 30 resin blocks was measured by Schneider technique and each groups of Ni-Ti files were allocated with 10 resin blocks at random. The canals were shaped with Ni-Ti files by Crown-down technique. It was analyzed by Double radiograph superimposition method (Backman CA 1992), and for the accuracy and consistency, specially designed jig, digital X-ray, and CAD/CAM software for measurement of apical transportation were used. The amount of apical transportation was measured at 0, 1, 3, 5 mm from 'apical foramen - 0.5 mm' area, and the alteration of the working length before and after canal shaping was also measured. For statistics, Kruskal-Wallis One Way Analysis was used.
Results
There was no significant difference between the groups in the amount of working length change and apical transportation at 0, 1, and 3 mm area (p = 0.027), however, the amount of apical transportation at 5 mm area showed significant difference between K3 and Profile system (p = 0.924).
Conclusions
As a result of this study, the 3 geometrically different Ni-Ti files showed no significant difference in apical transportation and working length change and maintained the original root canal shape.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - A comparison of dimensional standard of several nickel-titanium rotary files
Ki-Won Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho, Se-Hee Park, Ki-Yeol Choi, Bekir Karabucak, Jin-Woo Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(1): 7. CrossRef
-
145
View
-
1
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
Biocompatibility of bioaggregate cement on human pulp and periodontal ligament (PDL) derived cells
-
Choo-Ryung Chung, Euiseong Kim, Su-Jung Shin
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(6):473-478. Published online November 30, 2010
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.6.473
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
-
Objectives
This study was performed to investigate the biocompatibility of newly introduced Bioaggregate on human pulp and PDL cells.
Materials and Methods
Cells were collected from human pulp and PDL tissue of extracted premolars. Cell culture plate was coated either with Bioaggregate or white MTA, then the same number of cells were poured to cell culture dishes. Cell attachment and growth was examined under a phase microscope after 1,3 and 7 days of seeding. Cell viability was measured and the data was analyzed using Student t-test and one way ANOVA.
Results
Both types of cells used in this study were well attached and grew healthy on Bioaggregate and MTA coated culture dishes. No cell inhibition zone was observed in Bioaggregate group. There was no statistical difference of viable cells between bioaggreagte and MTA groups.
Conclusions
Bioaggregate appeared to be biocompatible compared with white MTA on human pulp and PDL cells.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Evaluation of bioactivity, biocompatibility, and antibacterial properties of tricalcium silicate bone cement modified with wollastonite/ fluorapatite glass and glass-ceramic
H.K. Abd El-Hamid, A.M. Fayad, R.L. Elwan
Ceramics International.2024; 50(14): 25322. CrossRef - Influence of insulin on the healing of exposed dental pulp after pulp capping: An experimental study in a dog model
Mokhtar A. Al‐Anesi, Ashraf M. Abu‐Seida, Salma H. El Ashry, Abeer H. Mahran, Ehab S. Abd‐Elhamid
Special Care in Dentistry.2021; 41(1): 49. CrossRef - ROOT END FILLING MATERIALS – A REVIEW
Bynagari Chandra Shekar, Veerendra Uppin, Madhu Pujar
GLOBAL JOURNAL FOR RESEARCH ANALYSIS.2021; : 5. CrossRef - Effects of two fast-setting calcium-silicate cements on cell viability and angiogenic factor release in human pulp-derived cells
Chooryung J. Chung, Euiseong Kim, Minju Song, Jeong-Won Park, Su-Jung Shin
Odontology.2016; 104(2): 143. CrossRef - Cytotoxicity and physical properties of tricalcium silicate-based endodontic materials
Young-Eun Jang, Bin-Na Lee, Jeong-Tae Koh, Yeong-Joon Park, Nam-Eok Joo, Hoon-Sang Chang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Yun-Chan Hwang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(2): 89. CrossRef - Biocompatibility of root-end filling materials: recent update
Payal Saxena, Saurabh Kumar Gupta, Vilas Newaskar
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(3): 119. CrossRef
-
188
View
-
1
Download
-
6
Crossref
-
THE DYNAMIC CHANGE OF ARTIFICIALLY DEMINERALIZED ENAMEL BY DEGREE OF SATURATION OF REMINERALIZATION SOLUTION AT pH 4.3
-
Ji-Sook Yi, Bung-Duk Roh, Su-Jung Shin, Yoon Lee, Hyung-Kyu Gong, Chan-Young Lee
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(1):20-29. Published online January 14, 2009
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.1.020
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Abstract
The purpose of this study is to observe and compare the dynamic change of artificially demineralized enamel by remineralization solutions of different degrees of saturation at pH 4.3.
In this study, 30 enamel specimens were demineralized artificially by lactic acid buffered solution. Each of 10 specimens was immersed in pH 4.3 remineralization solution of three different degrees of saturation (0.22, 0.30, 0.35) for 10 days. After demineralization and remineralization, images were taken by a polarizing microscope (× 100). The density of lesion were determined from images taken after demineralization and remineralization.
During remineralization process, mineral deposition and mineral loss occurred at the same time. After remineralization, total mineral amount and width of surface lesion increased in all groups. The higher degree of saturation was, the more mineral deposition occurred in surface lesion and the amount of mineral deposition was not much in subsurface lesion. Total demineralized depth increased in all groups.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effect of fluoride concentration in pH 4.3 and pH 7.0 supersaturated solutions on the crystal growth of hydroxyapatite
Haneol Shin, Sung-Ho Park, Jeong-Won Park, Chan-Young Lee
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(1): 16. CrossRef
-
189
View
-
1
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
Evaluation of retrievability using a new soft resin based root canal filling material
-
Su-Jung Shin, Yoon Lee, Jeong-Won Park
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(4):323-329. Published online July 31, 2006
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.4.323
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The aim of this study was to evaluate the retrievability of Resilon as a root canal filling material. Twenty-seven human single-rooted extracted teeth were instrumented utilizing a crown down technique with Gates-Glidden burs and ProFile system. In group1 (n = 12) canals were obturated with gutta percha and AH-26 plus sealer using a continuous wave technique and backfilled. In group 2 (n = 15) Resilon was used as a filling material. Then teeth were sealed and kept in 37℃ and 100% humidity for 7 days. For retreatment, the samples were re-accessed and filling material was removed using Gates-Glidden burs and ProFiles. Teeth were sectioned longitudinally to compare the general cleanliness and amount of debris (× 75) using SEM. Chi-square test was used (α = 0.05) to analyze the data. The total time required for removal of filling materials was expressed as mean ± SD (min) and analyzed by the Student t-test (α = 0.05). Required time for retreatment was 3.25 ± 0.32 minutes for gutta percha/AH 26 plus sealer and 3.05 ± 0.34 minutes for Resilon. There was no statistically significant difference between the two experimental groups. There was no significant difference between the groups in the cleanliness of the root canal wall. This study showed that Resilon was effectively removed by Gates-Glidden burs and ProFiles. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - An in vitro evaluation of effectiveness of Xylene, Thyme oil and Orange oil in dissolving three different endodontic sealers
N Aiswarya, TN Girish, KC Ponnappa
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2023; 26(3): 305. CrossRef - A Comparative Evaluation of Two Commonly Used GP Solvents on Different Epoxy Resin-based Sealers: An In Vitro Study
Sakshi Tyagi, Ekta Choudhary, Rajat Chauhan, Ashish Choudhary
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2020; 13(1): 35. CrossRef - Evaluation of softening ability of Xylene & Endosolv-R on three different epoxy resin based sealers within 1 to 2 minutes - anin vitrostudy
Pratima Ramakrishna Shenoi, Gautam Pyarelal Badole, Rajiv Tarachand Khode
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(1): 17. CrossRef - Microleakage of resilon by methacrylate-based sealer and self-adhesive resin cement
Sun-Young Ham, Jin-Woo Kim, Hye-Jin Shin, Kyung-Mo Cho, Se-Hee Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2008; 33(3): 204. CrossRef - Microleakage of resilon: Effects of several self-etching primer
Jong-Hyeon O, Se-Hee Park, Hye-Jin Shin, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2008; 33(2): 133. CrossRef
-
168
View
-
0
Download
-
5
Crossref
|