-
Proximity of the mandibular molar root apex from the buccal bone surface: a cone-beam computed tomographic study
-
Dokyung Kim, Jung-Hong Ha, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young-Kyung Kim, Sung Kyo Kim
-
Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(3):182-188. Published online July 14, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.3.182
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
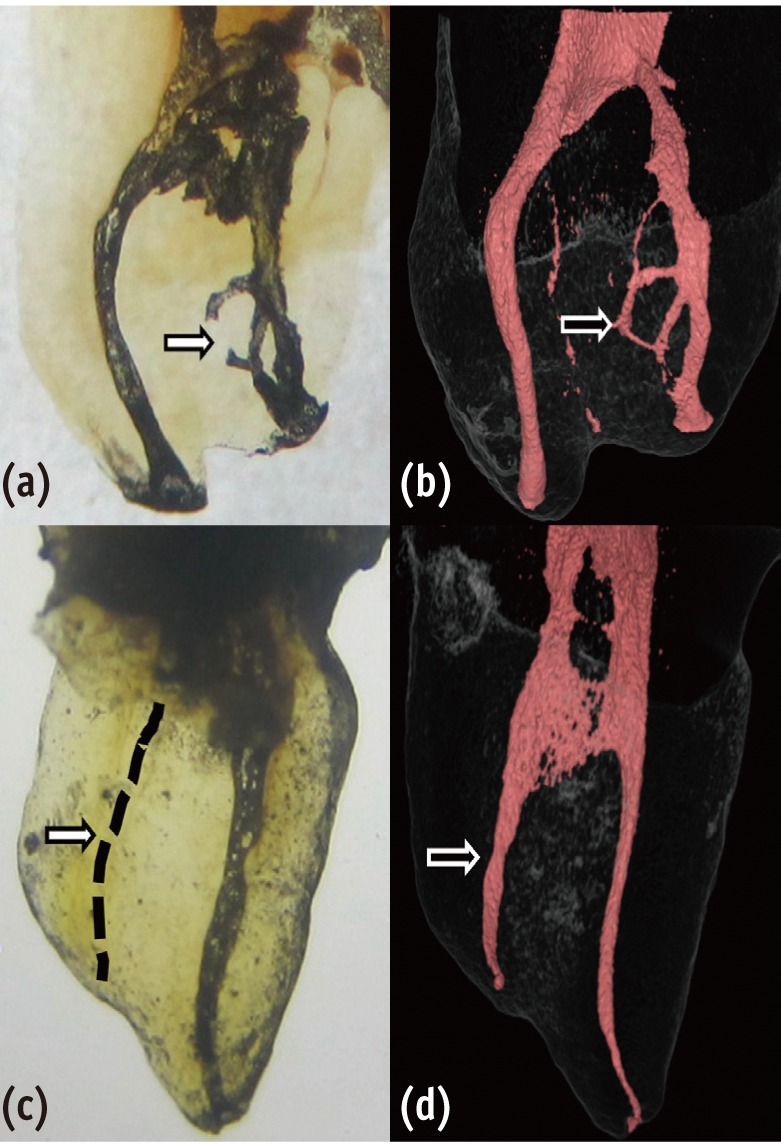
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the proximity of the mandibular molar apex to the buccal bone surface in order to provide anatomic information for apical surgery. Materials and MethodsCone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) images of 127 mandibular first molars and 153 mandibular second molars were analyzed from 160 patients' records. The distance was measured from the buccal bone surface to the root apex and the apical 3.0 mm on the cross-sectional view of CBCT. ResultsThe second molar apex and apical 3 mm were located significantly deeper relative to the buccal bone surface compared with the first molar (p < 0.01). For the mandibular second molars, the distance from the buccal bone surface to the root apex was significantly shorter in patients over 70 years of age (p < 0.05). Furthermore, this distance was significantly shorter when the first molar was missing compared to nonmissing cases (p < 0.05). For the mandibular first molars, the distance to the distal root apex of one distal-rooted tooth was significantly greater than the distance to the disto-buccal root apex (p < 0.01). In mandibular second molar, the distance to the apex of C-shaped roots was significantly greater than the distance to the mesial root apex of non-C-shaped roots (p < 0.01). ConclusionsFor apical surgery in mandibular molars, the distance from the buccal bone surface to the apex and apical 3 mm is significantly affected by the location, patient age, an adjacent missing anterior tooth, and root configuration.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Expert consensus on intentional tooth replantation
Zhengmei Lin, Dingming Huang, Shuheng Huang, Zhi Chen, Qing Yu, Benxiang Hou, Lihong Qiu, Wenxia Chen, Jiyao Li, Xiaoyan Wang, Zhengwei Huang, Jinhua Yu, Jin Zhao, Yihuai Pan, Shuang Pan, Deqin Yang, Weidong Niu, Qi Zhang, Shuli Deng, Jingzhi Ma, Xiuping
International Journal of Oral Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Outcome of intentional replantation of endodontically treated teeth with periapical pathosis: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Faizan Javed, Kamil Zafar, Farhan R. Khan
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(S1): 494. CrossRef - Proximity of maxillary molar apexes to the cortical bone surface and the maxillary sinus
Han Shin Lee, Dokyung Kim, Sung Kyo Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Alveolar bone thickness overlying healthy maxillary and mandibular teeth: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Marziyeh Shafizadeh, Azita Tehranchi, Armin Shirvani, Saeed Reza Motamedian
International Orthodontics.2021; 19(3): 389. CrossRef - Relationship between the anatomic structures and mandibular posterior teeth for endodontic surgery in a Turkish population: a cone-beam computed tomographic analysis
Zeliha Uğur Aydın, Duygu Göller Bulut
Clinical Oral Investigations.2019; 23(9): 3637. CrossRef
-
2,255
View
-
5
Download
-
5
Crossref
-
Esthetic enhancement of a traumatized anterior tooth with a combination of forced eruption and tooth alignment: a case report
-
So-Hee Kang, Jung-Hong Ha, Myoung-Uk Jin, Sung-Kyo Kim, Young-Kyung Kim
-
Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(3):210-217. Published online June 1, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.3.210
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
Exposing sound structure of a subgingivally fractured tooth using orthodontic extrusion is considered to be a conservative way to re-establish biologic width without sacrificing esthetics or jeopardizing periodontal support of neighboring teeth. When a misaligned tooth is traumatically involved, a more comprehensive approach combining tooth extrusion and re-alignment may be necessary for a successful restorative outcome. This case report describes a successful esthetic management of a patient with complicated crown-root fracture on the maxillary right central incisor and pre-existing malocclusion in the maxillary anterior region. Forced eruption along with re-alignment of teeth by orthodontic movement seems to allow re-positioning of the fracture line to a favorable position and correction of crowding, providing a better esthetic result. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effects of systematic bisphosphonate use in patients under orthodontic treatment: a systematic review
Vasileios F Zymperdikas, Maria P Yavropoulou, Eleftherios G Kaklamanos, Moschos A Papadopoulos
European Journal of Orthodontics.2020; 42(1): 60. CrossRef - In vitro retention efficiency of temporary type zinc oxide cement for orthodontic forced eruption
Renato Nieto-Aguilar, Deyanira Serrato-Ochoa, Rafael Medina-Navarro, Asdrúbal Aguilera-Méndez, Karina Denisse Morales-Soto, Juan Pablo Loyola-Rodriguez, Antonio Campos, Miguel Alaminos
International Orthodontics.2019; 17(1): 96. CrossRef
-
2,120
View
-
18
Download
-
2
Crossref
-
Endodontic treatment of maxillary lateral incisors with anatomical variations
-
Moon-Hwan Lee, Jung-Hong Ha, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young-Kyung Kim, Sung-Kyo Kim
-
Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(4):253-257. Published online November 12, 2013
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.4.253
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
Maxillary lateral incisors usually exhibit a single root with a single canal. However, maxillary lateral incisor teeth with unusual morphology of root canal system are frequently reported. These cases of variable root canal anatomy can be treated well by nonsurgical endodontic methods. A detailed description of root canal morphology is fundamental for successful endodontic treatment. Treatment using an operating microscope, radiographs from different angles, and cone-beam computerized tomography (CBCT) can produce more predictable endodontic outcomes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - An upper left lateral incisor with double roots and double root canals: A case report
Zhou-Bin Xia, Jing Ren, Jia-Xiang Chen, Yu Wei, Yan Yan, Liang-Ju Cao
Medicine.2025; 104(26): e42815. CrossRef - Retreatment of Mandibular Incisors Associated With Root Canal Variations and Periapical Cyst: A Case Report With 3‐Year Follow‐Up
Kai Chen, Ni Li
Clinical Case Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Endodnontic Management of a Maxillary Lateral Incisor with Two Roots
Pujan Kranti Kayastha, Merina Shakya, Laxman Poudel
Journal of Interdisciplinary Dentistry.2022; 12(1): 32. CrossRef - Non-surgical management of dens invaginatus type IIIB in maxillary lateral incisor with three root canals and 6-year follow-up: A case report and review of literature
Suraj Arora, Gurdeep Singh Gill, Shahabe Abullais Saquib, Priyanka Saluja, Suheel M Baba, Shafait Ullah Khateeb, Anshad M Abdulla, Shashit Shetty Bavabeedu, Ahmed Babiker Mohamed Ali, Mohamed Fadul A Elagib
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2022; 10(33): 12240. CrossRef - Endodontic management and follow-up of two rooted maxillary lateral incisor with open apex – A case report
R AnithaKumari, Sneha Jeetendra, Siddharth Rai, Sudhanva Eregowda
IP Indian Journal of Conservative and Endodontics.2020; 5(4): 200. CrossRef - Geminated Maxillary Lateral Incisor with Two Root Canals
Nayara Romano, Luis Eduardo Souza-Flamini, Isabela Lima Mendonça, Ricardo Gariba Silva, Antonio Miranda Cruz-Filho
Case Reports in Dentistry.2016; 2016: 1. CrossRef - Surgical management with intentional replantation on a tooth with palato-radicular groove
Jorge Forero-López, Luis Gamboa-Martínez, Laura Pico-Porras, Javier Laureano Niño-Barrera
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(2): 166. CrossRef - Use of cone-beam computed tomography and three-dimensional modeling for assessment of anomalous pulp canal configuration: a case report
Alper Sinanoglu, Dilek Helvacioglu-Yigit, Ibrahim Mutlu
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(2): 161. CrossRef - Endodontic management of a mandibular second molar with radix entomolaris: a case report
Rosaline Hannah, Deivanayagam Kandaswamy, Nachimuthu Jayaprakash
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(2): 132. CrossRef
-
3,219
View
-
28
Download
-
9
Crossref
-
Prepare the pre-heated composite resin
-
Myoung-Uk Jin
-
Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(2):103-104. Published online May 28, 2013
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.2.103
-
-
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effect of Preheating of Resin Composite on Microtensile Bond Strength In Vitro Study
M.A. Hanafy, O.M. Fahmy, A.F. Abo Elezz
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.2024; 12(1): 102. CrossRef - Preheated composite: Innovative approach for aesthetic restoration
Reema N Asani, Vandana J Gade, Kalyani G Umale, Rachana Gawande, Rohit R Amburle, Raksha R Kusumbe, Purva P Kale, Priya R Kosare
Archives of Dental Research.2021; 11(2): 103. CrossRef - Effect of Ultrasonic Vibration on Structural and Physical Properties of Resin-Based Dental Composites
Abdul Samad Khan
Polymers.2021; 13(13): 2054. CrossRef - Color Stability of Ceramic Veneers Luted With Resin Cements and Pre-Heated Composites: 12 Months Follow-Up
Brenda Procopiak Gugelmin, Luiz Carlos Machado Miguel, Flares Baratto Filho, Leonardo Fernandes da Cunha, Gisele Maria Correr, Carla Castiglia Gonzaga
Brazilian Dental Journal.2020; 31(1): 69. CrossRef
-
1,256
View
-
9
Download
-
4
Crossref
-
Diastema closure using direct bonding restorations combined with orthodontic treatment: a case report
-
Soon-Kong Hwang, Jung-Hong Ha, Myoung-Uk Jin, Sung-Kyo Kim, Young-Kyung Kim
-
Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(3):165-169. Published online August 29, 2012
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.3.165
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
Closure of interdental spaces using proximal build-ups with resin composite is considered to be practical and conservative. However, a comprehensive approach combining two or more treatment modalities may be needed to improve esthetics. This case report describes the management of a patient with multiple diastemas, a peg-shaped lateral incisor and midline deviation in the maxillary anterior area. Direct resin bonding along with orthodontic movement of teeth allows space closure and midline correction, consequently, creating a better esthetic result. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Gingival Conditioning with Provisional Composite Veneer Prior to Final Dental Restoration: Three-year Follow-up
B Mueller, GB Rauber, LA Linhares, JK Bernardon, E Santini, LF Pottmaier
Operative Dentistry.2023; 48(3): 237. CrossRef - Effectiveness, longevity, and color stability of in-office bleaching (6% H2O2 gel/Violet LED) and diastema closure with direct composite: 3-year follow-up
Ikejiri Larissa Luri Almeida Amorim, Álamo Larissa , Galli Mateus Zamora , Bombonatti Juliana Fraga Soares , de Amoêdo Campos Velo Marilia Mattar , Mondelli Rafael Francisco Lia
Journal of Clinical Advances in Dentistry.2023; 7(1): 001. CrossRef - Ortodontik Tedavi Bitiminden Sonra Polidiastemanın Kompozit Rezin Ile Rehabilitasyonu: Olgu Sunumu
Rümeysa BATTAL, Hacer Deniz ARISU
Selcuk Dental Journal.2022; 9(4): 127. CrossRef - Multidisciplinary Approach to Treatment of Midline Diastema With Edge-to-Edge Bite
Sumukh Nerurkar, Ranjit Kamble, Japneet Kaiser, Jeni Mathew
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - ÜST ANTERİOR DİŞLERDE BULUNAN ÇÜRÜKLERİN VE ESKİ RESTORASYONLARIN KOMPOZİT REZİNLER İLE ESTETİĞİNİN SAĞLANMASI: BİR VAKA SUNUMU
Abdulkadir HARMANKAYA, Hakan Yasin GÖNDER
Selcuk Dental Journal.2022; 9(4): 86. CrossRef - ANTERİOR DİASTEMALARIN DİREKT KOMPOZİT REZİN RESTORASYONLARLA ESTETİK REHABİLİTASYONU: 5 OLGU SUNUMU
Handan YILDIRIM, Esra ÖZYURT
Selcuk Dental Journal.2020; 7(2): 334. CrossRef - VAKUMLA ŞEKİLLENDİRİLEN ORTODONTİK PEKİŞTİRME APAREYLERİNİN KOMPOZİT RESTORASYONLARIN KLİNİK BAŞARISINA ETKİSİ
Serdar AKARSU, Sultan AKTUĞ KARADEMİR, Süleyman Kutalmış BÜYÜK
Atatürk Üniversitesi Diş Hekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi.2020; : 1. CrossRef - Aesthetic Smile Coming with Direct Composite Resin Laminate Restorations: Two Case Reports
Funda Demir, Elif Aybala Oktay, Numan Aydın, Fulya Toksoy Topçu, Ertürk Bilgeç
Ankara Medical Journal.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Different Demineralization‐Inhibiting Methods on the Shear Bond Strength of Glass‐Ceramics
Erhan Dilber, Mehmet Akın, Tevfik Yavuz, Ali Erdem
Journal of Prosthodontics.2015; 24(5): 407. CrossRef - Correction of Mandibular Prognathism in Combination with Polydiastema Using Rectangular Body Ostectomy: Literature Review and Case Report
Metin Sencimen, Abdullah Tugrul Coskun, Gurkan Rasit Bayar, Handan Altug, Hasan Ayberk Altug, Tamer Zerener
Case Reports in Clinical Medicine.2014; 03(11): 601. CrossRef - Predictable interproximal tissue removal with a surgical stent
Fausto Frizzera, Suzane Cristina Pigossi, Mateus Rodrigues Tonetto, William Kabbach, Elcio Marcantonio
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2014; 112(4): 727. CrossRef
-
2,224
View
-
21
Download
-
11
Crossref
-
Diagnostic challenges of nonodontogenic toothache
-
Hyung-Ok Park, Jung-Hong Ha, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young-Kyung Kim, Sung-Kyo Kim
-
Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(3):170-174. Published online August 29, 2012
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.3.170
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The objective of this article was to present two nonodontogenic conditions that may mimic odontogenic toothache: trigeminal neuralgia and burning mouth syndrome. Two cases are presented in which one is related to the upper left second premolar and the other is related to the upper left first molar. Both showed pain when chewing. These two cases highlight the complexities involved in diagnosing nonodontogenic toothache. This article demonstrates the importance of having a thorough knowledge of both odontogenic and nonodontogenic toothache, as well as the need for careful evaluation of the nature of the pain and history, clinical and radiographic examinations. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Analysis of Final Diagnosis of Patients with Suspected Nonodontogenic Toothache: A Retrospective Study
Jeong Yeop Chun, Young Joo Shim
Journal of Oral Medicine and Pain.2024; 49(3): 57. CrossRef - Interactions of Acetyl-11-Keto-Beta-Boswellic Acid on Catechol-O-Methyltransferase in the Management of Masticatory Myofascial Pain Syndrome
Ramya Suresh, Pradeep Kumar Yadalam, Ramya Ramadoss, Karthikeyan Ramalingam, Arvind Muthukrishnan
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of Concordance between Chairside Ultrasonography and Digital Palpation in Detecting Myofascial Trigger Points in Masticatory Myofascial Pain Syndrome
Mohamed Elbarbary, Michael Goldberg, Howard C. Tenenbaum, David K. Lam, Bruce V. Freeman, David J. Pustaka, David Mock, Joseph Beyene, Amir Azarpazhooh
Journal of Endodontics.2023; 49(2): 129. CrossRef - Masticatory Myofascial Pain Syndrome: Implications for Endodontists
Mohamed Elbarbary, Ariel Oren, Michael Goldberg, Bruce V. Freeman, David Mock, Howard C. Tenenbaum, Amir Azarpazhooh
Journal of Endodontics.2022; 48(1): 55. CrossRef - PRICE 2020 guidelines for reporting case reports in Endodontics: explanation and elaboration
V. Nagendrababu, B. S. Chong, P. McCabe, P. K. Shah, E. Priya, J. Jayaraman, S. J. Pulikkotil, P. M. H. Dummer
International Endodontic Journal.2020; 53(7): 922. CrossRef - Clinical Outline of Oral Diseases
Arvind Babu Rajendra Santosh, Doryck Boyd, Kumaraswamy Kikeri Laxminarayana
Dental Clinics of North America.2020; 64(1): 1. CrossRef - Nonodontogenic Sources of Dental Pain
Scott E. Schames, Michael Jordan, Hila Robbins, Lenard Katz, Kaitlyn Tarbert
Journal of the California Dental Association.2016; 44(8): 507. CrossRef - Nonodontogenic toothaches
Edward F. Wright
The Journal of the American Dental Association.2015; 146(6): 406. CrossRef - Síndrome de boca ardiente: claves diagnósticas y terapéuticas
Eduardo Chimenos-Küstner, Cristina Arcos-Guerra, Maria Sueli Marques-Soares
Medicina Clínica.2014; 142(8): 370. CrossRef
-
2,351
View
-
28
Download
-
9
Crossref
-
Comparison of screw-in effect for several nickel-titanium rotary instruments in simulated resin root canal
-
Jung-Hong Ha, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young-Kyung Kim, Sung-Kyo Kim
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(4):267-272. Published online July 31, 2010
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.4.267
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
Screw-in effect is one of the unintended phenomena that occurs during the root canal preparation with nickel-titanium rotary files. The aim of this study was to compare the screw-in effect among various nickel-titanium rotary file systems.
Six different nickel-titanium rotary instruments (ISO 20/.06 taper) were used: K3™ (SybronEndo, Glendora, CA, USA), Mtwo (VDW GmbH, München, Germany), NRT with safe-tip and with active tip (Mani Inc., Shioya-gun, Japan), ProFile® (Dentsply-Maillefer, Ballaigues, Switzerland) and ProTaper® (Dentsply-Maillefer, Ballaigues, Switzerland). For ProTaper®, S2 was selected because it has size 20. Root canal instrumentations were done in sixty simulated single-curved resin root canals with a rotational speed of 300 rpm and single pecking motion. A special device was designed to measure the force of screw-in effect. A dynamometer of the device recorded the screw-in force during simulated canal preparation and the recorded data was stored in a computer with designed software (LCV-USE-VS, Lorenz Messtechnik GmbH, Alfdorf, Germany). The data were subjected to one-way ANOVA and Tukey's multiple range test for post-hoc test. P value of less than 0.05 was regarded significant.
ProTaper® produced significantly more screw-in effects than any other instruments in the study (p < 0.001). K3™ produced significantly more screw-in effects than Mtwo, and ProFile® (p < 0.001). There was no significant difference among Mtwo, NRT, and ProFile® (p > 0.05), and between NRT with active tip and NRT with safe one neither (p > 0.05).
From the result of the present study, it was concluded, therefore, that there seems significant differences of screw-in effect among the tested nickel-titanium rotary instruments. The radial lands and rake angle of nickel-titanium rotary instrument might be the cause of the difference. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Impact of Radial Lands on the Reduction of Torque/Force Generation of a Heat-Treated Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instrument
Taro Nakatsukasa, Arata Ebihara, Moe Sandar Kyaw, Satoshi Omori, Hayate Unno, Shunsuke Kimura, Keiichiro Maki, Takashi Okiji
Applied Sciences.2022; 12(5): 2620. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of mechanical properties and shaping performance of heat-treated nickel titanium rotary instruments used in the single-length technique
Taro NAKATSUKASA, Arata EBIHARA, Shunsuke KIMURA, Keiichiro MAKI, Miki NISHIJO, Daisuke TOKITA, Takashi OKIJI
Dental Materials Journal.2021; 40(3): 743. CrossRef - Analysis of Torque and Force Induced by Rotary Nickel-Titanium Instruments during Root Canal Preparation: A Systematic Review
Myint Thu, Arata Ebihara, Sherif Adel, Takashi Okiji
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(7): 3079. CrossRef - Influence of rotational speed on torque/force generation and shaping ability during root canal instrumentation of extracted teeth with continuous rotation and optimum torque reverse motion
M. S. Kyaw, A. Ebihara, Y. Kasuga, K. Maki, S. Kimura, P. H. Htun, T. Nakatsukasa, T. Okiji
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(9): 1614. CrossRef - Influence of glide path on the screw-in effect and torque of nickel-titanium rotary files in simulated resin root canals
Jung-Hong Ha, Sang-Shin Park
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(4): 215. CrossRef - Influence of root canal curvature on the screw-in effect of nickel-titanium rotary files in simulated resin root canal
Ji-Young Son, Jung-Hong Ha, Young-Kyung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(5): 374. CrossRef - Influence of taper on the screw-in effect of nickel-titanium rotary files in simulated resin root canal
Hye-Jin Sung, Jung-Hong Ha, Sung-Kyo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(5): 380. CrossRef
-
1,897
View
-
6
Download
-
7
Crossref
-
Influence of additional etching on shear bond strength of self-etching adhesive system to enamel
-
Sun-Jin Yoo, Young-Kyung Kim, Jeong-Won Park, Myoung-Uk Jin, Sung Kyo Kim
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(4):263-268. Published online July 31, 2006
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.4.263
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
Recently, self-etching adhesive system has been introduced to simplify the clinical bonding procedures. It is less acidic compared to the phosphoric acid, thus there is doubt whether this system has enough bond strength to enamel. The purpose of this study was to investigate the influence of additional etching on the adhesion of resin composite to enamel.
Ninety extracted bovine permanent anterior teeth were used. The labial surfaces of the crown were ground with 600-grit abrasive paper under wet condition. The teeth were randomly divided into six groups of 15 teeth each. Clearfil SE Bond®, Adper™ Prompt L-Pop and Tyrian SPE™ were used as self-etching primers. Each self-etching primers were applied in both enamel specimens with and without additional etching. For additional etching groups, enamel surface was pretreated with 32% phosphoric acid (UNI-ETCH, Bisco, Inc., Schaumburg, IL, USA). Hybrid resin composite Clearfil AP-X, (Kuraray Co., Ltd., Osaka, Japan) was packed into the mold and light-cured for 40 seconds. Twenty-four hours after storage, the specimens were tested in shear bond strength. The data for each group were subjected to independent t - test at p < 0.01 to make comparisons among the groups.
In Clearfil SE Bond®, shear bond strength of additional etching group was higher than no additional etching group (p < 0.01). In Adper™ Prompt L-Pop and Tyrian SPE, there were no significant difference between additional etching and non-etching groups (p > 0.01).
In conclusion, self-etching adhesive system with weak acid seems to have higher bond strength to enamel with additional etching, while self-etching adhesive system with strong acid seems not. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Microtensile bond strength of silorane-based composite specific adhesive system using different bonding strategies
Laura Alves Bastos, Ana Beatriz Silva Sousa, Brahim Drubi-Filho, Fernanda de Carvalho Panzeri Pires-de-Souza, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(1): 23. CrossRef
-
1,402
View
-
0
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
The influence of AH-26 and zinc oxide-eugenol root canal sealer on the shear bond strength of composite resin to dentin
-
Ju-Yeon Cho, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young-Kyung Kim, Sung Kyo Kim
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(3):147-152. Published online May 31, 2006
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.3.147
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the influence of the AH-26 root canal sealer on the shear bond strength of composite resin to dentin.
One hundred and forty four (144) extracted, sound human molars were used. After embedding in a cylindrical mold, the occlusal part of the anatomical crown was cut away and trimmed in order to create a flat dentin surface. The teeth were randomly divided into three groups; the AH-26 sealer was applied to the AH-26 group, and zinc-oxide eugenol (ZOE) paste was applied to the ZOE group. The dentin surface of the control group did not receive any sealer.
A mount jig was placed against the surface of the teeth and the One-step dentin bonding agent was applied after acid etching. Charisma composite resin was packed into the mold and light cured. After polymerization, the alignment tube and mold were removed and the specimens were placed in distilled water at 37℃ for twenty four hours. The shear bond strength was measured by an Instron testing machine. The data for each group were subjected to one-way ANOVA and Tukey's studentized rank test so as to make comparisons between the groups.
The AH-26 group and the control group showed significantly higher shear bond strength than the ZOE group (p < 0.05).
There were no significant differences between the AH-26 group and the control one (p > 0.05).
Under the conditions of this study, the AH-26 root canal sealer did not seem to affect the shear bond strength of the composite resin to dentin while the ZOE sealer did. Therefore, there may be no decrease in bond strength when the composite resin core is built up immediately after a canal filling with AH-26 as a root canal sealer. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Is Zinc Oxide Eugenol Cement Still Impeding the Use of Resin-based Restoration? A Systematic Review
Fawaz Pullishery, Hajer Ayed Alhejoury, Mohammed Turkistani, Yasser Refay Souror
Dentistry and Medical Research.2021; 9(2): 59. CrossRef - A comparative evaluation of removal of gutta percha using two retreatment file system: An in vitro study
Shruthi Mary Sunil, Balakrishnan Rajkumar, Vishesh Gupta, Akanksha Bhatt, Pragyan Paliwal
IP Indian Journal of Conservative and Endodontics.2020; 5(2): 53. CrossRef - Evaluation of softening ability of Xylene & Endosolv-R on three different epoxy resin based sealers within 1 to 2 minutes - anin vitrostudy
Pratima Ramakrishna Shenoi, Gautam Pyarelal Badole, Rajiv Tarachand Khode
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(1): 17. CrossRef - Influence of Sodium Ascorbate on Microtensile Bond Strengths to Pulp Chamber Dentin treated with NaOCl
Soo-Yeon Jeon, Kwang-Won Lee, Mi-Kyung Yu
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2008; 33(6): 545. CrossRef
-
2,313
View
-
5
Download
-
4
Crossref
-
Effect of vital tooth bleaching agent on dentin bonding
-
Na-Young Jeong, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young-kyung Kim, Sung Kyo Kim
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(2):79-85. Published online March 31, 2006
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.2.079
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
To evaluate the effect of vital tooth bleaching agent and alcohol pretreatment on dentin bonding, flat dentin windows were produced on the buccal side of the crowns of fifty-five extracted, human premolars. A bleaching gel, Opalescence® with 10% of carbamide peroxide (Ultradent Product, USA) was daily applied on the teeth of three experimental groups for six hours for 10 consecutive days, while teeth of a control group were not bleached. After 6 hours of bleaching gel application, the specimens were washed and stored in saline until the next day application. After application of One-step® dentin bonding agent (Bisco, USA), Z-250® resin (3M-ESPE, USA) was bonded to dentin with a mount jig. Shear bond strength was measured with an Instron machine (Type 4202, Instron Corp., USA) after 24 hours. The results were analyzed using one-way ANOVA and Duncan's multiple range test at p < 0.05.
Immediate bonding group showed significantly lower bond strength than un-bleached control group (p < 0.05).
Ethanol-treated group showed significantly higher bond strength compared to immediate bonding group (p < 0.05). However, the bond strength of the ethanol treatment group was lower than that of the un-bleached control group (p < 0.05).
There were no significant difference in shear bond strength between the 2-week delayed bonding group and the ethanol-treated group (p > 0.05) and between delayed bonding group and un-bleached control group (p > 0.05).
In the condition of the present study, it seems that alcohol pretreatment after bleaching procedure can reduce the adverse effect of vital bleaching agent on dentin bonding. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effect of Applying Malatang Sauce by Type Before and After Expert Whitening Agent Treatment on Bovine Tooth Coloring
Chi-Yoon Sung, Hee-Jung Lim, Moon-Jin Jeong, Do-Seon Lim
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2025; 25(2): 79. CrossRef - Effect of the bleaching light on whitening efficacy
Jong-Hyun Park, Hye-Jin Shin, Deok-Young Park, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(2): 95. CrossRef
-
2,313
View
-
10
Download
-
2
Crossref
-
Change of working length in curved canals by various instrumentation techniques
-
Jeong-Im Jo, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young Kyung Kim, Sung Kyo Kim
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(1):30-35. Published online January 31, 2006
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.1.030
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
To evaluate the change of working length with various instrumentation techniques in curved canals, working length and canal curvature were determined before and after canal instrumentation in buccal or mesial canals of extracted human molars. Stainless steel K-files (MANI®, Matsutani Seisakusho Co. Takanezawa, Japan), nickel-titanium K-files (Naviflex NT™, Brassler, Savannah, USA), ProFile®, and ProTaper™ (Dentsply-Maillefer, Ballaigues, Switzerland) were used to prepare the canals with crown-down technique. In two hand instrumentation groups, coronal flaring was made with Gates Glidden burs. Apical canals were instrumented until apical diameter had attained a size of 30. Positional relation between the tooth apex and the #10 K-file tip was examined by using AutoCAD 2000 (Autodesk Corp., San Rafael. CA, USA) under a stereomicroscope before and after coronal flaring, and after apical instrumentation. Degree of canal curvature was also measured with Schneider's method in radiographs. Data of working length and canal curvature changes were statistically analyzed with one-way ANOVA and Tukey's studentized range test.
Working length and canal curvature were decreased significantly in each step in all instrumentation groups. Coronal flaring using Gates Glidden burs in hand instrument groups and whole canal instrumentation using stainless steel hand K-files caused significantly more working length change than in ProFile instrumentation group (p < 0.05).
The result of this study demonstrates that all of the above kinds of instrumentation in curved canals cause reduction of working length and canal curvature at each instrumentation steps, and hand instrumentation causes more working length change than ProFile. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Evaluation of the Accuracy of an Endomotor-Integrated Apex Locator Versus a Standalone Electronic Apex Locator in Teeth with Simulated Apical Root Resorption: An In Vitro Study
Yunus Emre Çakmak, Damla Erkal, Hatice Harorlı, Simay Koç
European Journal of Therapeutics.2025; 31(3): 173. CrossRef - Does Root Canal Shaping Effect the Accuracy of Electronic Apex Locators in Curved and Straight Root Canals?
Dide Tekinarslan, Damla Erkal, Esen Ercan, Simay Koc, Kürşat Er
Clinical and Experimental Health Sciences.2024; 14(3): 727. CrossRef - Comparative Study of Four Endodontic File Systems to Assess Changes in Working Length during Root Canal Instrumentation and the Effect of Canal Curvature on Working Length Change
Michelle Tien, Hermawan Tjoa, Maggie Zhou, Paul V. Abbott
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(1): 110. CrossRef - Study of endodontic working length of Korean posterior teeth
Jeong-Yeob Kim, Sang-Hoon Lee, Gwang-Hee Lee, Sang-Hyuk Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(6): 429. CrossRef
-
2,093
View
-
11
Download
-
4
Crossref
-
REGULATION OF PULPAL MICROCIRCULATION BY CALCITONIN GENE-RELATED PEPTIDE
-
Sung-Kyo Kim, Young-Kyung Kim, Myoung-Uk Jin
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(6):470-476. Published online January 14, 2005
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.6.470
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Abstract
The purpose of this study was to investigate the function of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) in regulatory mechanism of pulpal microcirculation with the aim of elucidating neurogenic inflammation.
Experiments were performed on twelve cats under general anesthesia. CGRP was administered through the femoral vein to see the systemic influence and through the external carotid artery to see the local effect. Sympathetic nerve to the dental pulp was stimulated electrically and pulpal blood flow (PBF) was measured with a laser Doppler flowmeter on the canine teeth to the drug administration. The paired variables of control and experimental data were compared by paired t-test and differences with p < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Systemic administration of CGRP (0.3 μg/kg) exerted decreases in systemic blood pressure and caused changes in PBF with an initial increase followed by decrease and a more marked second increase and decrease.
Close intra-arterial (i.a.) injection of CGRP (0.03 μ/kg) resulted in slight PBF increase. The effect of CGRP resulted in no significant increase in PBF in the presence of CGRP8-37.
The electrical stimulation of the sympathetic nerve alone resulted in PBF decreases. The i.a. administration of CGRP following the electrical stimulation of the sympathetic nerve compensated the decreased PBF. Therefore, CGRP effectively blocked the sympathetic nerve stimulation-induced PBF decrease.
Results of the present study have provided evidences that even though the local vasodilatory function of CGRP are weak, CGRP is effectively involved in blocking the vasoconstriction caused by sympathetic nerve stimulation in the feline dental pulp.
-
Shaping ability of four rotary nickel-titanium instruments to prepare root canal at danger zone
-
Seok-Dong Choi, Myoung-Uk Jin, Ki-Ok Kim, Sung-Kyo Kim
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(5):446-453. Published online September 30, 2004
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.5.446
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The aim of this study was to evaluate the shaping abilities of four different rotary nickel-titanium instruments with anticurvature motion to prepare root canal at danger zone by measuring the change of dentin thickness in order to have techniques of safe preparation of canals with nickel-titanium files.
Mesiobuccal and mesiolingual canals of forty mesial roots of extracted human lower molars were instrumented using the crown-down technique with ProFile, GT™ Rotary file, Quantec file and ProTaper™. In each root, one canal was prepared with a straight up-and-down motion and the other canal was with an anticurvature motion. Canals were instrumented until apical foramens were up to size of 30 by one operator. The muffle system was used to evaluate the root canal preparation. After superimposing the pre- and post-instrumentation canal, change in root dentin thickness was measured at the inner and outer sides of the canal at 1, 3, and 5 mm levels from the furcation. Data were analyzed using two-way ANOVA.
Root dentin thickness at danger zone was significantly thinner than that at safe zone at all levels (p < 0.05).
There was no significant difference in the change of root dentin thickness between the straight up-and-down and the anticurvature motions at both danger and safe zones in all groups (p > 0.05).
ProTaper removed significantly more dentin than other files especially at furcal 3 mm level of danger and safe zones (p < 0.05)
Therefore, it was concluded that anticurvature motion with nickel-titanium rotary instruments does not seem to be effective in danger zone of lower molars. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Conservation of dentin thickness in the root canals orifice following two preparation techniques
Ranjdar Talabani, Shawbo Ahmad, Arass Noori
Sulaimani Dental Journal.2014; 1(2): 6. CrossRef - Change of working length in curved canals by various instrumentation techniques
Jeong-Im Jo, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young Kyung Kim, Sung Kyo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2006; 31(1): 30. CrossRef - Effect of anticurvature filing method on preparation of the curved root canal using ProFile
Hyun-Ji Song, Juhea Chang, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2005; 30(4): 327. CrossRef
-
1,501
View
-
1
Download
-
3
Crossref
|