-
Calcium silicate-based sealers remnants in isthmuses of mesial roots of mandibular molars: an in vitro evaluation
-
David Saldanha de Brito Alencar, Ana Cristina Padilha Janini, Lauter Eston Pelepenko, Brenda Fornazaro Moraes, Francisco Haiter Neto, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Marina Angélica Marciano
-
Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(3):e25. Published online July 15, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e25
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
Endodontic retreatment aims to address treatment failure through the removal of root canal filling materials. This in vitro study evaluated the presence of filling material remnants in the mesial root canals, specifically focusing on the isthmuses, of mandibular molars after retreatment.
Methods
One hundred extracted mandibular molar mesial roots with isthmuses were prepared with an R25 file, obturated with one of five calcium silicate-based sealers (BioRoot RCS [Septodont], MTApex [Ultradent Products Inc.], EndoSequence BC Sealer HiFlow [Brasseler USA], Bio-C Sealer [Angelus]) or an epoxy resin-based sealer (AH Plus Jet [Dentsply Maillefer]), all stained with rhodamine B, and stored at 37ºC for 30 days to allow for setting. Retreatment was subsequently performed using R40 and XP-endo Finisher R instruments (FKG Dentaire) with 2.5% sodium hypochlorite irrigation. The presence of remaining filling material was then assessed using confocal microscopy, and setting times were tested per ISO 6876:2012.
Results
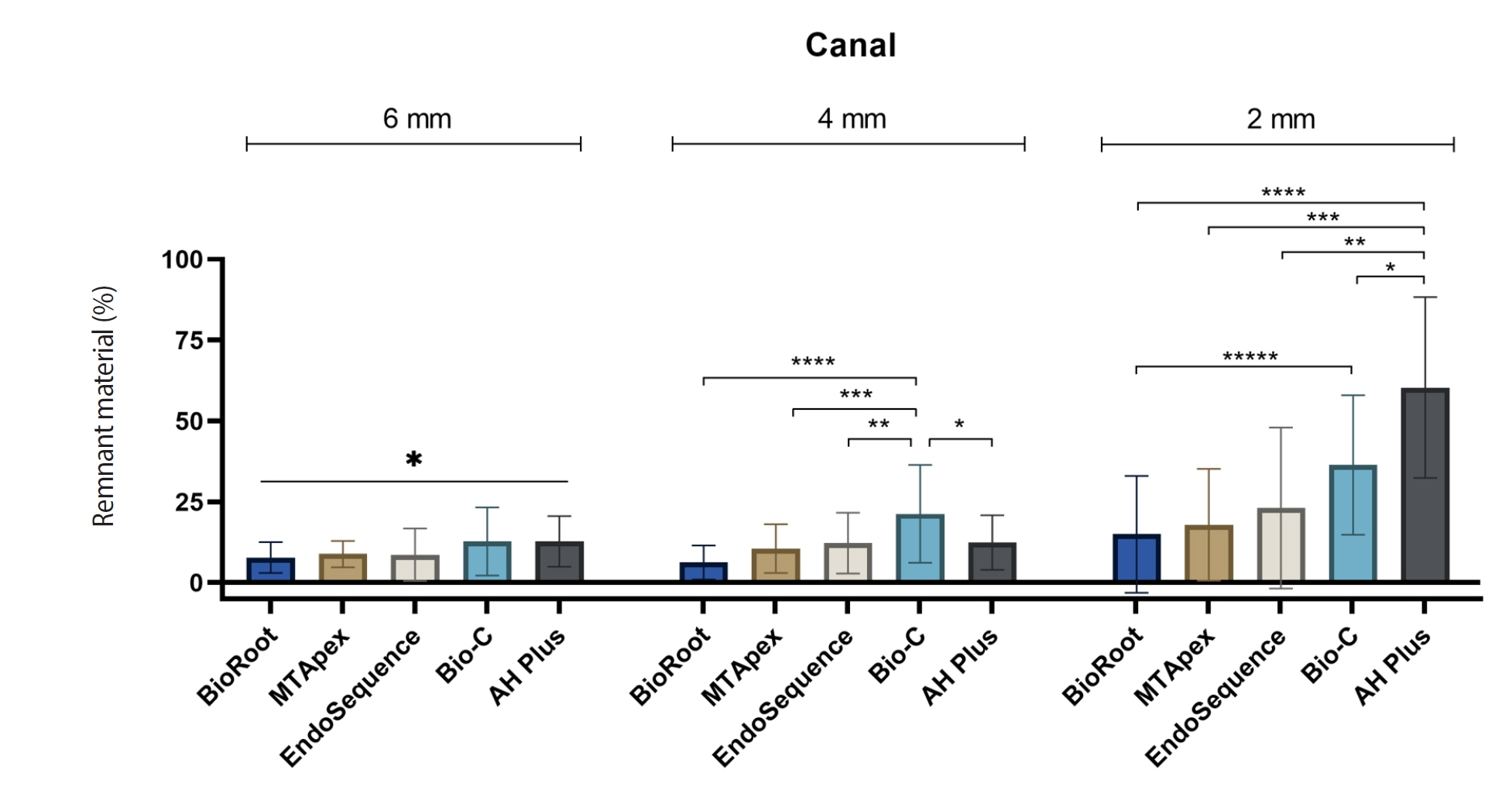
AH Plus Jet showed the most remnants at 2 mm and the longest retreatment time. Calcium silicate-based sealers exhibited prolonged setting times under dry conditions, with EndoSequence BC Sealer HiFlow showing a particularly extended setting period.
Conclusions
Despite retreatment, residues remained in all canals and isthmus regions, particularly Bio-C Sealer and AH Plus Jet in apical areas, emphasizing the difficulty of complete removal and the persistence of filling material.
-
Isolating design variables by assessing the impact of cross-section geometry on the mechanical performance of nickel-titanium rotary instruments: a comparative in vitro study
-
Anne Rafaella Tenório Vieira, Guilherme Ferreira da Silva, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, João Vitor Oliveira de Amorim, Thaine Oliveira Lima, Raimundo Sales de Oliveira Neto, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Murilo Priori Alcalde
-
Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(3):e28. Published online July 24, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e28
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
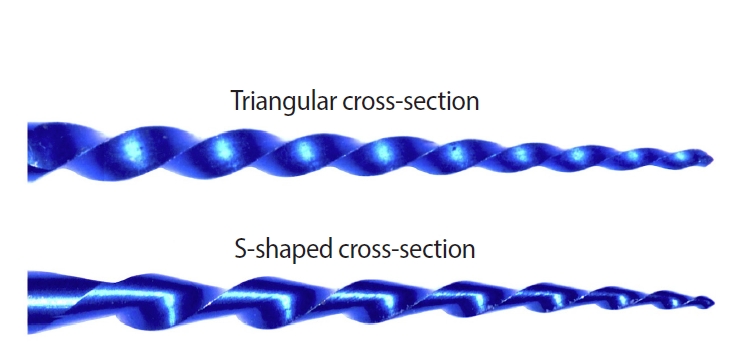
This study aimed to assess the effect of cross-section geometry on the mechanical properties of nickel-titanium (NiTi) instruments by comparing two instruments with identical tip size, taper, and thermal treatment but differing in cross-section design.
Methods
One hundred four NiTi rotary instruments, being S-shaped and triangular cross-section, manufactured with Blueish thermal treatment, were tested (n = 52 per group). Differential scanning calorimetry was employed, and the metal mass volume and cross-section area were assessed. The cyclic fatigue, torsional, and bending resistance tests were assessed. Data were analyzed using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov and Student t tests, and the level of significance was set at 5%.
Results
The instruments exhibited similar start and finish temperatures of phase transformation. The S-shaped instruments had significantly lower metal mass volume and cross-sectional area (p < 0.05). S-shaped instruments demonstrated superior cyclic fatigue resistance, greater angular deflection, and lower bending stiffness (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
Cross-section geometry significantly influences the mechanical properties of NiTi rotary instruments.
-
Impact of the use of high-power 810-nm diode laser as monotherapy on the clinical and tomographic success of the treatment of teeth with periapical lesions: an observational clinical study
-
Fabricio Hinojosa Pedraza, Abel Victor Isidro Teves-Cordova, Murilo Priori Alcalde, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte
-
Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(2):e15. Published online May 15, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e15
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
The aim of this study was to demonstrate the impact of a high-power 810-nm diode laser as monotherapy on the clinical and tomographic success of treating teeth with periapical lesions, through a series of 31 cases.
Methods
Teeth with apical lesions underwent endodontic treatment in which a high-power 810-nm diode laser with saline solution was used as monotherapy for disinfection. This type of therapy aimed to replace the traditional irrigation protocol with sodium hypochlorite. This research is the first to assess the clinical success of this alternative treatment, along with tomographic evaluations conducted over periods ranging from 2 to 7 years, analyzed using the periapical index based on cone-beam computed tomography (CBCTPAI). All cases were performed by a single clinician following the same laser protocol, which involved using 1 W of continuous power and four cycles of 20 seconds of laser activation.
Results
All teeth showed no clinical symptoms upon follow-up examination. However, the tomographic evaluation revealed that the success rates for teeth receiving primary treatment were 60% and 80% according to strict and loose criteria, respectively. For teeth requiring retreatment, the success rates were 12.5% and 37.5% using strict and loose criteria, respectively.
Conclusions
The teeth with apical lesions that underwent primary treatment did not present clinical symptoms, but they showed a moderate success rate on tomographic evaluation. However, despite lacking clinical symptoms, teeth with apical lesions that required retreatment had a very low success rate on tomographic evaluation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Diode Laser-Guided Protocol for Endo-Perio Lesions: Toward a Multi-Stage Therapeutic Strategy—A Case Series and Brief Literature Review
Ioana-Roxana Munteanu, George-Dumitru Constantin, Ruxandra-Elena Luca, Ioana Veja, Mariana-Ioana Miron
Medicina.2025; 61(12): 2157. CrossRef
-
3,712
View
-
180
Download
-
1
Web of Science
-
1
Crossref
-
Bibliometric analysis of the GentleWave system: trends, collaborations, and research gaps
-
Raimundo Sales de Oliveira Neto, Thais de Moraes Souza, João Vitor Oliveira de Amorim, Thaine Oliveira Lima, Guilherme Ferreira da Silva, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, Murilo Priori Alcalde, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte
-
Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(2):e17. Published online May 12, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e17
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
The study aimed to conduct a bibliometric analysis of the GentleWave system (Sonendo, Inc.).
Methods
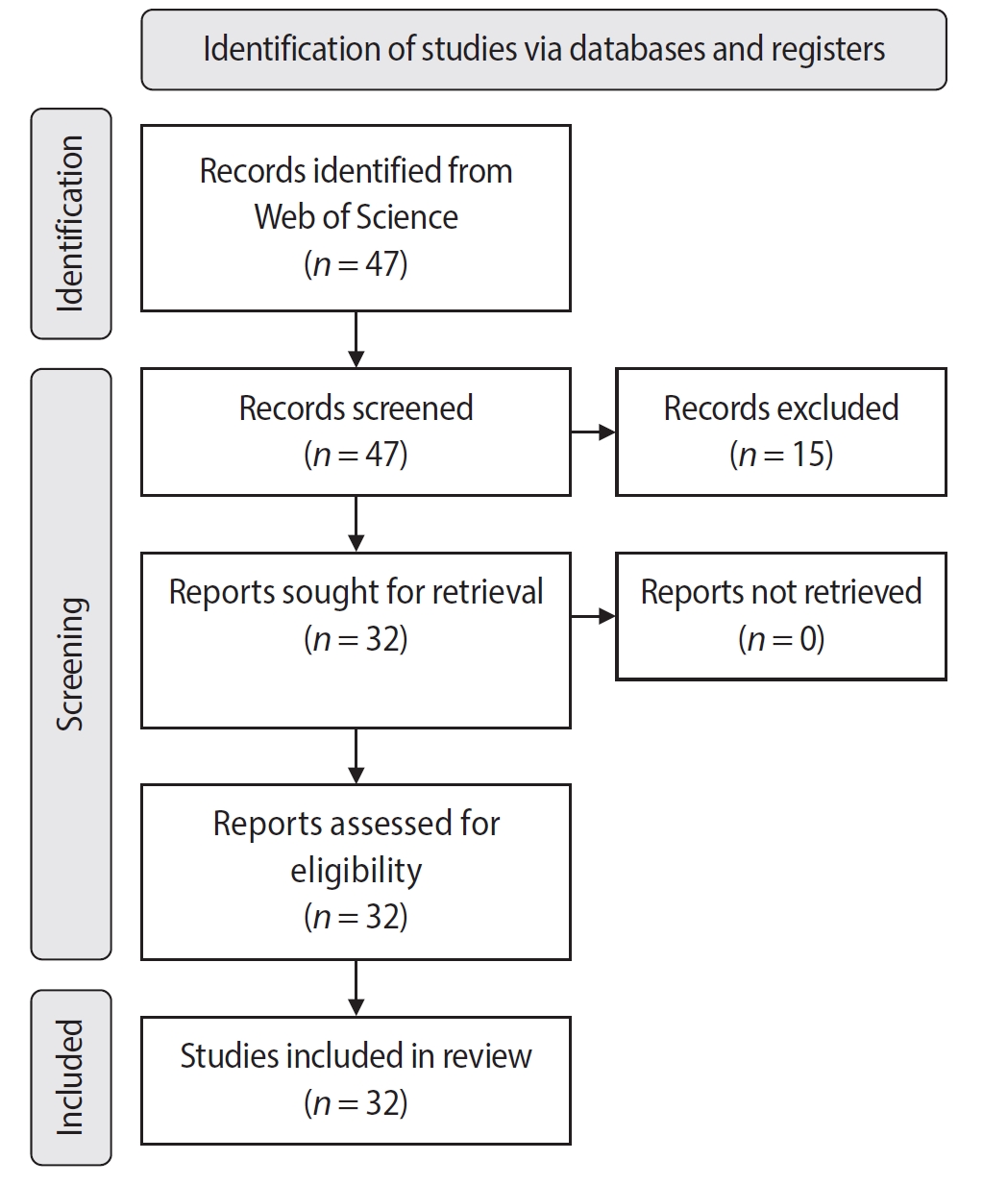
An electronic search was conducted in June 2024 using the Web of Science Collection database. Two reviewers independently screened publications, extracting data on authorship, publication details, study design, and citation metrics. Statistical analyses were performed in R to assess variable correlations, while the VOSviewer (Visualization of Similarities Viewer) software was used to map author and keyword networks.
Results
The search yielded 47 records, with 32 studies included. Publications spanned 2014 to 2024. The Journal of Endodontics published the highest number of studies (n = 15), and the International Endodontic Journal had the highest impact factor (5.4). The University of British Columbia and Sonendo, Inc. were the most frequent affiliations. Among the 32 articles, 28 were in vitro studies, primarily focusing on microbiology (n = 9). A total of 95 authors were identified, with Haapasalo and Shen being the most cited (n = 229). The articles accumulated 495 citations, demonstrating a strong positive correlation between the number of studies and citation counts (r = 0.98).
Conclusions
The analysis highlights a predominance of in vitro studies. Geographic concentration in the United States and Canada limits diversity, while the strong correlation between study numbers and citations suggests that increased publication volume enhances visibility.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Three-year Outcomes of Conventional Versus Minimally Invasive Endodontic Treatment Protocols: A Retrospective Study
Kiavash Hossini, He Liu, Ya Shen, Jolanta Aleksejuniene, Fahda Algahtani, Ahmed Hieawy
Journal of Endodontics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
-
3,273
View
-
79
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
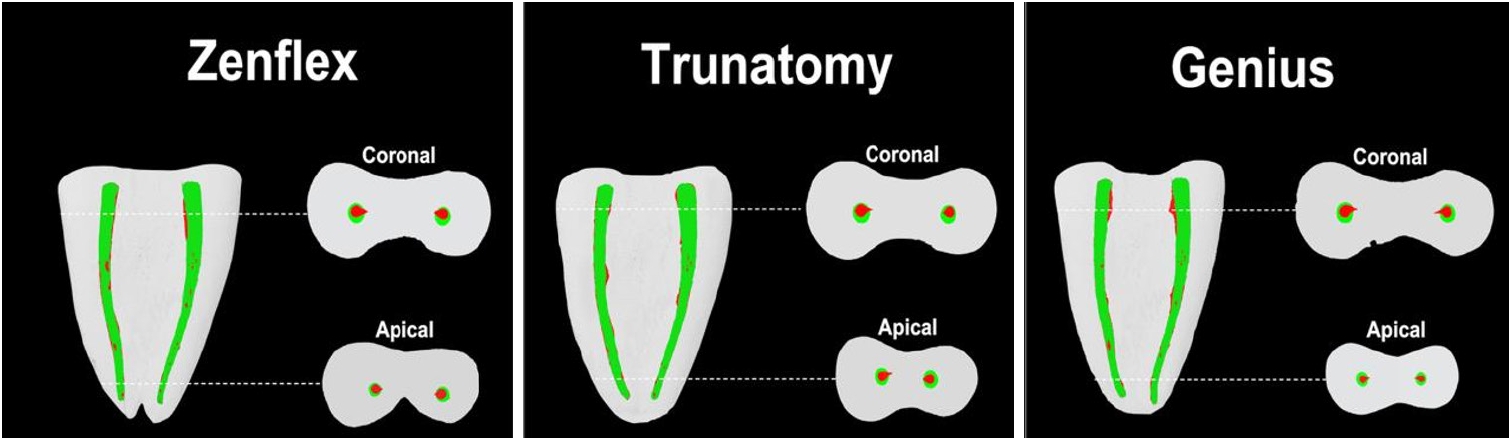
Shaping ability and cyclic fatigue resistance between Genius ProFlex, ZenFlex, and TruNatomy rotary systems: an experimental study
-
Raimundo Sales de Oliveira Neto, Murilo Priori Alcalde, Pedro Cesar Gomes Titato, Pedro Henrique Souza Calefi, Carlos Alberto Spironelli Ramos, Guilherme Ferreira da Silva, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte
-
Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(1):e9. Published online February 13, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e9
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
The aim of this study was to investigate the efficacy of three newly introduced rotary endodontic systems: Genius ProFlex (Medidenta), TruNatomy (Dentsply Maillefer), and ZenFlex (Kerr).
Methods
Forty-five mandibular molars with root canal curvatures <5° were utilized. Micro-computed tomography scans were performed pre- and post-preparation to assess apical transportation, centralization, percentage of dentin wear, and canal volume alterations. Eight instruments of each diameter underwent cyclic fatigue testing.
Results
The percentage of dentin wear on mesial and distal walls showed no significant differences among ZenFlex, TruNatomy, and Genius ProFlex at 1, 2, 3, and 4 mm from the apical foramen and root canal orifice (p > 0.05). Centering ability varied in the mesiolingual canal (p < 0.05). No notable differences were observed in transportation (p > 0.05). Genius ProFlex demonstrated lower volumetric changes (p < 0.05). There were significant differences in cyclic fatigue, with higher values for Genius ProFlex and lower values for TruNatomy (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
The three nickel-titanium rotary instruments are safe and efficient for root canal preparation, with Genius ProFlex exhibiting superior cyclic fatigue resistance.
-
Impact of different agitation methods on smear layer cleaning of mesial canals with accentuated curvature
-
Abel Teves Cordova, Murilo Priori Alcalde, Michel Espinosa Klymus, Leonardo Rigoldi Bonjardim, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte
-
Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(2):e12. Published online March 4, 2024
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e12
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
This study evaluated the impact of different methods of irrigant agitation on smear layer removal in the apical third of curved mesial canals of 3 dimensionally (D) printed mandibular molars. Materials and MethodsSixty 3D-printed mandibular second molars were used, presenting a 70° curvature and a Vertucci type II configuration in the mesial root. A round cavity was cut 2 mm from the apex using a trephine of 2 mm in diameter, 60 bovine dentin disks were made, and a smear layer was formed. The dentin disks had the adaptation checked in the apical third of the teeth with wax. The dentin disks were evaluated in environmental scanning electron microscope before and after the following irrigant agitation methods: G1(PIK Ultrasonic Tip), G2 (Passive Ultrasonic Irrigation with Irrisonic– PUI), G3 (Easy Clean), G4 (HBW Ultrasonic Tip), G5 (Ultramint X Ultrasonic tip), and G6 (conventional irrigation-CI) (n = 10). All groups were irrigated with 2.5% sodium hypochlorite and 17% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid. ResultsAll dentin disks were 100% covered by the smear layer before treatment, and all groups significantly reduced the percentage of the smear layer after treatment. After the irrigation protocols, the Ultra-X group showed the lowest coverage percentage, statistically differing from the conventional, PIK, and HBW groups (p < 0.05). There was no significant difference among Ultramint X, PUI-Irrisonic, and Easy Clean (p > 0.05). None of the agitation methods could remove the smear layer altogether. ConclusionsUltramint X resulted in the most significant number of completely clean specimens.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - A new cleaning protocol in minimally invasive endodontic surgery: RUA (“retro irrigant activation”)
Dina Abdellatif, Davide Mancino, Massimo Pisano, Sara De Fontaine, Alfredo Iandolo
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(3): 297. CrossRef - Impact of the use of high-power 810-nm diode laser as monotherapy on the clinical and tomographic success of the treatment of teeth with periapical lesions: an observational clinical study
Fabricio Hinojosa Pedraza, Abel Victor Isidro Teves-Cordova, Murilo Priori Alcalde, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2025; 50(2): e15. CrossRef - Smear layer removal comparing conventional irrigation, passive ultrasonic irrigation, EndoActivator System, and a new sonic device (Perfect Clean System) by scanning electron microscopy: An ex vivo study
Bruna Fernanda Alionço Gonçalves, Divya Reddy, Ricardo Machado, Paulo César Soares Júunior, Sérgio Aparecido Ignácio, Douglas Augusto Fernandes Couto, Karine Santos Frasquetti, Vânia Portela Ditzel Westphalen, Everdan Carneiro, Ulisses Xavier da Silva Net
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(12): e0314940. CrossRef
-
2,284
View
-
126
Download
-
2
Web of Science
-
3
Crossref
-
Effectiveness of endodontic retreatment using WaveOne Primary files in reciprocating and rotary motions
-
Patricia Marton Costa, Renata Maíra de Souza Leal, Guilherme Hiroshi Yamanari, Bruno Cavalini Cavenago, Marco Antônio Húngaro Duarte
-
Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(2):e15. Published online April 25, 2023
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e15
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
This study evaluated the efficiency of WaveOne Primary files (Dentsply Sirona) for removing root canal fillings with 2 types of movement: reciprocating (RCP) and continuous counterclockwise rotation (CCR). Materials and MethodsTwenty mandibular incisors were prepared with a RCP instrument (25.08) and filled using the Tagger hybrid obturation technique. The teeth were retreated with a WaveOne Primary file and randomly allocated to 2 experimental retreatment groups (n = 10) according to movement type: RCP and CCR. The root canals were emptied of filling material in the first 3 steps of insertion, until reaching the working length. The timing of retreatment and procedure errors were recorded for all samples. The specimens were scanned before and after the retreatment procedure with micro-computed tomography to calculate the percentage and volume (mm3) of the residual filling material. The results were statistically evaluated using paired and independent t-tests, with a significance level set at 5%. ResultsNo significant difference was found in the timing of filling removal between the groups, with a mean of 322 seconds (RCP) and 327 seconds (CCR) (p < 0.05). There were 6 instrument fractures: 1 in a RCP motion file and 5 in continuous rotation files. The volumes of residual filling material were similar (9.94% for RCP and 15.94% for CCR; p > 0.05). ConclusionsThe WaveOne Primary files used in retreatment performed similarly in both RCP and CCR movements. Neither movement type completely removed the obturation material, but the RCP movement provided greater safety.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Micro-CT evaluation of the removal of root fillings using rotary and reciprocating systems supplemented by XP-Endo Finisher, the Self-Adjusting File, or Er,Cr:YSGG laser
Gülsen Kiraz, Bulem Üreyen Kaya, Mert Ocak, Muhammet Bora Uzuner, Hakan Hamdi Çelik
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
-
2,279
View
-
51
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
Comparative analysis of torsional and cyclic fatigue resistance of ProGlider, WaveOne Gold Glider, and TruNatomy Glider in simulated curved canal
-
Pedro de Souza Dias, Augusto Shoji Kato, Carlos Eduardo da Silveira Bueno, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Pedro Henrique Souza Calefi, Rina Andréa Pelegrine
-
Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(1):e4. Published online December 8, 2022
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e4
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
This study aimed to compare the torsional and cyclic fatigue resistance of ProGlider (PG), WaveOne Gold Glider (WGG), and TruNatomy Glider (TNG). Materials and MethodsA total of 15 instruments of each glide path system (n = 15) were used for each test. A custom-made device simulating an angle of 90° and a radius of 5 millimeters was used to assess cyclic fatigue resistance, with calculation of number of cycles to failure. Torsional fatigue resistance was assessed by maximum torque and angle of rotation. Fractured instruments were examined by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Data were analyzed with Shapiro-Wilk and Kruskal-Wallis tests, and the significance level was set at 5%. ResultsThe WGG group showed greater cyclic fatigue resistance than the PG and TNG groups (p < 0.05). In the torsional fatigue test, the TNG group showed a higher angle of rotation, followed by the PG and WGG groups (p < 0.05). The TNG group was superior to the PG group in torsional resistance (p < 0.05). SEM analysis revealed ductile morphology, typical of the 2 fracture modes: cyclic fatigue and torsional fatigue. ConclusionsReciprocating WGG instruments showed greater cyclic fatigue resistance, while TNG instruments were better in torsional fatigue resistance. The significance of these findings lies in the identification of the instruments’ clinical applicability to guide the choice of the most appropriate instrument and enable the clinician to provide a more predictable glide path preparation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Buckling resistance of various pathfinding endodontic instruments: An in vitro study
Ujjwal Das, Rajesh Kumar Das, Kallol Kumar Saha, Lugu Buru Murmu, Srimanta Banerjee, Rishila Nag
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(4): 384. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of the remaining dentin volume following instrumentation with rotary, reciprocating, and hand files during root canal treatment in primary molars: An ex vivo study
İrem Eren, Berkant Sezer
Journal of Dental Sciences.2024; 19(4): 2126. CrossRef - Screw-in force, torque generation, and performance of glide-path files with three rotation kinetics
Jee-Yeon Woo, Ji-Hyun Jang, Seok Woo Chang, Soram Oh
Odontology.2024; 112(3): 761. CrossRef - Evaluation of shaping ability of different glide path instruments: a micro-computed tomography study
Merve Yeniçeri Özata, Seda Falakaloğlu, Ali Keleş, Özkan Adıgüzel, Mustafa Gündoğar
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
-
2,607
View
-
59
Download
-
3
Web of Science
-
4
Crossref
-
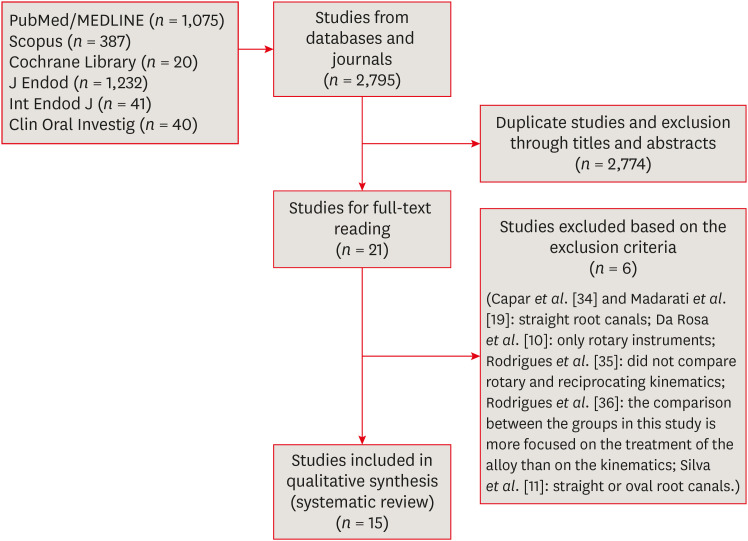
Effectiveness and safety of rotary and reciprocating kinematics for retreatment of curved root canals: a systematic review of in vitro studies
-
Lucas Pinho Simões, Alexandre Henrique dos Reis-Prado, Carlos Roberto Emerenciano Bueno, Ana Cecília Diniz Viana, Marco Antônio Húngaro Duarte, Luciano Tavares Angelo Cintra, Cleidiel Aparecido Araújo Lemos, Francine Benetti
-
Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(2):e22. Published online April 6, 2022
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e22
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
This systematic review (register-osf.io/wg7ba) compared the efficacy and safety of rotary and reciprocating kinematics in the removal of filling material from curved root canals. Materials and MethodsOnly in vitro studies evaluating both kinematics during retreatment were included. A systematic search (PubMed/MEDLINE, Scopus, and other databases, until January 2021), data extraction, and risk of bias analysis (Joanna Briggs Institute checklist) were performed. Efficacy in filling removal was the primary outcome. ResultsThe search resulted in 2,795 studies, of which 15 were included. Efficacy was measured in terms of the remaining filling material and the time required for this. Nine studies evaluated filling material removal, of which 7 found no significant differences between rotary and reciprocating kinematics. Regarding the time for filling removal, 5 studies showed no difference between both kinematics, 2 studies showed faster results with rotary systems, and other 2 showed the opposite. No significant differences were found in apical transportation, centering ability, instrument failure, dentin removed and extruded debris. A low risk of bias was observed. ConclusionsThis review suggests that the choice of rotary or reciprocating kinematics does not influence the efficacy of filling removal from curved root canals. Further studies are needed to compare the kinematics safety in curved root canals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - EVALUATION OF MICROLEAKAGE AFTER ENDODONTIC FILLING IN TEETH WITH APICAL WIDENING: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
Isabella da Costa Ferreira, Gabriela da Costa Ferreira, Isabella Figueiredo de Assis Macedo, Gustavo Oliveira Campos, Isabella Faria da Cunha Peixoto, Ana Cecília Diniz Viana, Rodrigo Rodrigues Amaral, Warley Luciano Fonseca Tavares
ARACÊ .2025; 7(10): e8792. CrossRef - Fifteen years of engine‐driven nickel–titanium reciprocating instruments, what do we know so far? An umbrella review
Felipe Immich, Lucas Peixoto de Araújo, Rafaella Rodrigues da Gama, Wellington Luiz de Oliveira da Rosa, Evandro Piva, Giampiero Rossi‐Fedele
Australian Endodontic Journal.2024; 50(2): 409. CrossRef - Efficacy of Various Heat-treated Retreatment File Systems on the Apical Deformity and Canal Centering Ability in a Single-rooted Teeth using Nano CT
Swathi S, Pradeep Solete, Ganesh Jeevanandan, Delphine Priscilla Antony S, Kavalipurapu Venkata Teja, Dona Sanju
The Open Dentistry Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Micro-CT evaluation of the removal of root fillings using rotary and reciprocating systems supplemented by XP-Endo Finisher, the Self-Adjusting File, or Er,Cr:YSGG laser
Gülsen Kiraz, Bulem Üreyen Kaya, Mert Ocak, Muhammet Bora Uzuner, Hakan Hamdi Çelik
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of sodium hypochlorite on cyclic fatigue resistance of nickel–titanium instruments: A systematic review and meta-analysis of in vitro studies
Alexandre Henrique dos Reis-Prado, Lucas Guimarães Abreu, Lara Cancella de Arantes, Kiani dos Santos de Paula, Sabrina de Castro Oliveira, Juliana Goto, Ana Cecília Diniz Viana, Francine Benetti
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(11): 6291. CrossRef - Retreatment of XP-endo Shaper and R-Endo files in curved root canals
Hayam Y. Hassan, Fahd M. Hadhoud, Ayman Mandorah
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Advancing Endodontics through Kinematics
Shilpa Bhandi, Dario Di Nardo, Francesco Pagnoni, Rosemary Abbagnale
World Journal of Dentistry.2023; 14(6): 479. CrossRef
-
3,158
View
-
58
Download
-
5
Web of Science
-
7
Crossref
-
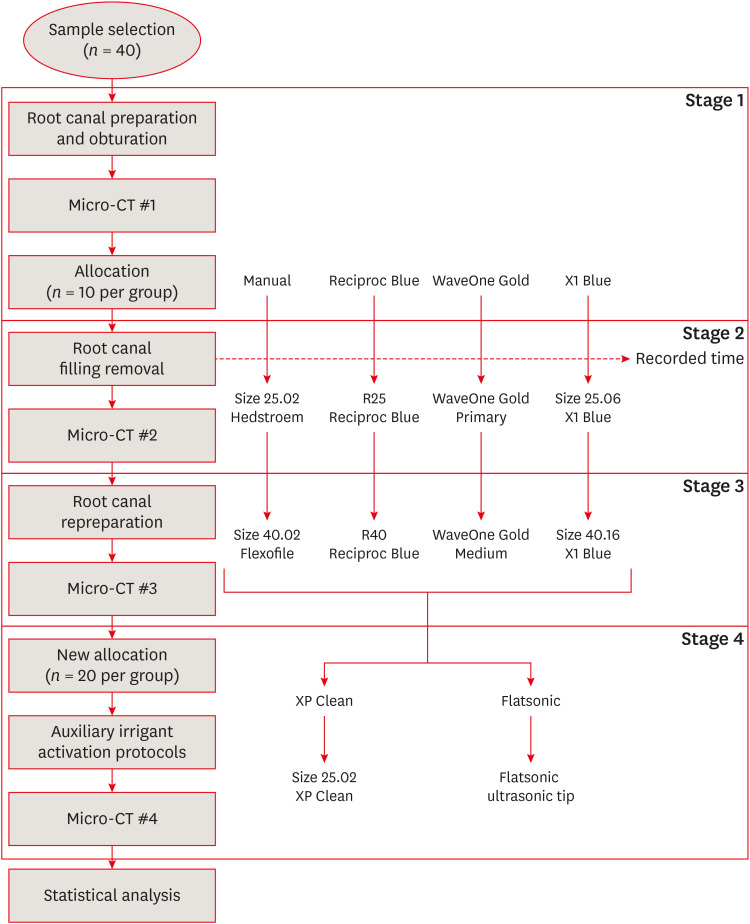
Efficacy of reciprocating instruments and final irrigant activation protocols on retreatment of mesiobuccal roots of maxillary molars: a micro-CT analysis
-
Lilian Tietz, Renan Diego Furlan, Ricardo Abreu da Rosa, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Murilo Priori Alcalde, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, Theodoro Weissheimer, Marcus Vinicius Reis Só
-
Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(1):e13. Published online February 15, 2022
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e13
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
This study evaluated the efficacy of 3 reciprocating systems and the effects of 2 instruments for irrigant activation on filling material removal. Materials and MethodsForty mesiobuccal roots of maxillary molars were prepared up to size 25.06 and obturated. Micro-computed tomography (micro-CT) examination #1 was performed. Teeth were then divided into 4 groups (n = 10), according to the retreatment protocol: (1) manual, (2) Reciproc Blue, (3) WaveOne Gold, and (4) X1 Blue. Micro-CT examinations #2 and #3 were performed after filling removal and repreparation, respectively. Next, all teeth were divided into 2 new groups (n = 20) according to the irrigant activation protocol: XP Clean (XP Clean size 25.02) and Flatsonic (Flatsonic ultrasonic tip). Micro-CT examination #4 was performed after irrigant activation. Statistical analysis was performed with a significance level set at 5%. ResultsWaveOne Gold removed a significantly greater amount of filling material than the manual group (p < 0.05). The time to reach the WL was similar for all reciprocating systems (p > 0.05). X1 Blue was faster than the manual group (p < 0.05). Only manual group improved the filling material removal after the repreparation stage (p < 0.05). Both activation protocols significantly improved the filling material removal (p < 0.05), without differences between them (p > 0.05). ConclusionsNone of the tested instruments completely removed the filling material. X1 Blue size 25.06 reached the working length in the shortest time. XP Clean and Flatsonic improved the filling material removal.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Supplementary instrumentation did not enhance the removal of residual gutta-percha: a micro-computed tomography study
Selin Nur Ayaz, Meltem Kucuk, Deniz Yanık Nalbantoğlu, Ali Keles, Amine Yigit, Fugen Dagli Comert Tasman, Bekir Karabucak
Odontology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Supplementary methods for filling material removal: A systematic review and meta-analysis of micro-CT imaging studies
Bruna Venzke Fischer, Taynara Santos Goulart, Filipe Colombo Vitali, Diego Leonardo de Souza, Cleonice da Silveira Teixeira, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
Journal of Dentistry.2024; 151: 105445. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Ability of 3 Reciprocating Instruments to Remove Obturation Material: A Micro–Computed Tomography Study
Fábio Luiz Cecagno, Alexandre Sigrist De Martin, Carlos Eduardo Fontana, Bruno Cavalini Cavenago, Wayne Martins Nascimento, Ana Grasiela da Silva Limoeiro, Carlos Eduardo da Silveira Bueno
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(3): 376. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of cleaning efficiency of single file NiTi rotary system during root canal treatment procedure - A scanning electron microscope study
Ruchi Vashisht, Umesh Kumar, Swaty Jhamb, Ruchi Singla
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2023; 26(3): 316. CrossRef - Influence of rotary and reciprocating kinematics on the accuracy of an integrated apex locator
Verônica de Almeida Gardelin, Júlia Itzel Acosta Moreno Vinholes, Renata Grazziotin‐Soares, Fernanda Geraldo Pappen, Fernando Branco Barletta
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(S1): 202. CrossRef
-
2,259
View
-
34
Download
-
4
Web of Science
-
5
Crossref
-
Effect of ultrasonic agitation on push-out bond strength and adaptation of root-end filling materials
-
Murilo Priori Alcalde, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, Marina Angélica Marciano, Jussaro Alves Duque, Samuel Lucas Fernandes, Mariana Bailo Rosseto, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte
-
Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(2):e23. Published online April 27, 2018
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e23
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
This study evaluated the effect of ultrasonic agitation of mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA), calcium silicate-based cement (CSC), and Sealer 26 (S26) on adaptation at the cement/dentin interface and push-out bond strength. Materials and MethodsSixty maxillary canines were divided into 6 groups (n = 10): MTA, S26, and CSC, with or without ultrasonic activation (US). After obturation, the apical portions of the teeth were sectioned, and retrograde cavities were prepared and filled with cement by hand condensation. In the US groups, the cement was activated for 60 seconds: 30 seconds in the mesio-distal direction and 30 seconds in the buccal-lingual direction, using a mini Irrisonic insert coupled with the ultrasound transducer. After the materials set, 1.5-mm thick sections were obtained from the apexes. The presence of gaps and the bond between cement and dentin were analyzed using low-vacuum scanning electron microscopy. Push-out bond strength was measured using a universal testing machine. ResultsUltrasonic agitation increased the interfacial adaptation of the cements. The S26 US group showed a higher adaptation value than MTA (p < 0.05). US improved the push-out bond strength for all the cements (p < 0.05). ConclusionsThe US of retrograde filling cements enhanced the bond to the dentin wall of the root-end filling materials tested.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effect of ultrasonic activation on setting time, pH and calcium ion release, solubility, and chemical structure of calcium silicate sealers
Simone Argenta Scalabrin, Lina Naomi Hashizume, Theodoro Weissheimer, Gabriel Barcelos Só, Jefferson Ricardo Pereira, Milton Carlos Kuga, Ricardo Abreu da Rosa, Marcus Vinicius Reis Só
Brazilian Dental Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of different disinfection protocols on the bond strength of NeoMTA 2 bioceramic sealer used as a root canal apical plug (in vitro study)
Nada Omar, Nihal Refaat Kabel, Muhammad Abbass Masoud, Tamer M. Hamdy
BDJ Open.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Endo-Z bur or Bladesonic ultrasonic tip on the adaptation of filling material. A micro-CT study
Pedro Henrique Fiorin de Souza, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Jáder Camilo Pinto, Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mário Tanomaru-Filho
Brazilian Dental Journal.2023; 34(5): 29. CrossRef - Effect of Different Mixing Methods on Physicochemical Properties of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate: A Systematic Review
Amin Salem Milani, Faraz Radmand, Behrad Rahbani, Mahdi Hadilou, Farnaz Haji Abbas Oghli, Fatemeh Salehnia, Milad Baseri, Stefano Pagano
International Journal of Dentistry.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Micro-CT comparative evaluation of porosity and dentin adaptation of root end filling materials applied with incremental, bulk, and ultrasonic activation techniques
Berkan Celikten, Aysenur Oncu, Mehrdad Koohnavard, Mert Ocak, Kaan Orhan
Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part H: Journal of Engineering in Medicine.2022; 236(8): 1209. CrossRef - Effect of ultrasonic activation of the adhesive system on dentin tubule penetration and the pushout bond strength of fiber posts
Isabel Verdum, Igor Abreu de Bem, Pedro Henrique Marks Duarte, Lucas Silveira Machado, Jefferson Ricardo Pereira, Marcus Vinícius Reis Só, Ricardo Abreu da Rosa
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2022; 127(2): 295. CrossRef - Influence of Ultrasonic Activation on the Physicochemical Properties of Calcium Silicate-Based Cements
Fredson Márcio Acris De Carvalho, Yara Teresinha Corrêa Silva-Sousa, Carlos Eduardo Saraiva Miranda, Paulo Henrique Miller Calderon, Ana Flávia Simões Barbosa, Luciana Martins Domingues De Macedo, Fuad Jacob Abi Rached-Junior, Boonlert Kukiattrakoon
International Journal of Dentistry.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of the flow and filling ability of endodontic materials using different test models
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Gisselle Moraima Chavez-Andrade, Jader Camilo Pinto, Fábio Luiz Camargo Villela Berbert, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Dental discoloration caused by Grey-MTAFlow cement: analysis of its physicochemical, biological and antimicrobial properties
Lauter Eston PELEPENKO, Flávia SAAVEDRA, Gabriela Fernanda BOMBARDA, Brenda Paula Figueiredo de Almeida GOMES, Adriana DE-JESUS-SOARES, Alexandre Augusto ZAIA, Marco Antonio Hungaro DUARTE, Mario TANOMARU-FILHO, Marina Angélica MARCIANO
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Ultrasonic Activation of Endodontic Sealers on Intratubular Penetration and Bond Strength to Root Dentin
Igor Abreu De Bem, Renata Aqel de Oliveira, Theodoro Weissheimer, Carlos Alexandre Souza Bier, Marcus Vinícius Reis Só, Ricardo Abreu da Rosa
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(9): 1302. CrossRef
-
1,534
View
-
9
Download
-
10
Crossref
-
Chelating and antibacterial properties of chitosan nanoparticles on dentin
-
Aldo del Carpio-Perochena, Clovis Monteiro Bramante, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Marcia Regina de Moura, Fauze Ahmad Aouada, Anil Kishen
-
Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(3):195-201. Published online March 30, 2015
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.3.195
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
The use of chitosan nanoparticles (CNPs) in endodontics is of interest due to their antibiofilm properties. This study was to investigate the ability of bioactive CNPs to remove the smear layer and inhibit bacterial recolonization on dentin. Materials and MethodsOne hundred bovine dentin sections were divided into five groups (n = 20 per group) according to the treatment. The irrigating solutions used were 2.5% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) for 20 min, 17% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) for 3 min and 1.29 mg/mL CNPs for 3 min. The samples were irrigated with either distilled water (control), NaOCl, NaOCl-EDTA, NaOCl-EDTA-CNPs or NaOCl-CNPs. After the treatment, half of the samples (n = 50) were used to assess the chelating effect of the solutions using portable scanning electronic microscopy, while the other half (n = 50) were infected intra-orally to examine the post-treatment bacterial biofilm forming capacity. The biovolume and cellular viability of the biofilms were analysed under confocal laser scanning microscopy. The Kappa test was performed for examiner calibration, and the non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis and Dunn tests (p < 0.05) were used for comparisons among the groups. ResultsThe smear layer was significantly reduced in all of the groups except the control and NaOCl groups (p < 0.05). The CNPs-treated samples were able to resist biofilm formation significantly better than other treatment groups (p < 0.05). ConclusionsCNPs could be used as a final irrigant during root canal treatment with the dual benefit of removing the smear layer and inhibiting bacterial recolonization on root dentin.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effect of experimental dentifrices containing epigallocatechin-3-gallate–loaded chitosan nanoparticles on permeability, tubule occlusion, microhardness, and wear in eroded dentin
Karen Pintado-Palomino, Letícia de Sousa Franco, Renata Siqueira Scatolin, Luiza Araújo Gusmão, Antonio Claudio Tedesco, Mario Sadaiti Ogasawara, Raissa Manoel Garcia, Tais Scaramucci, Silmara Aparecida Corona
JADA Foundational Science.2026; 5: 100057. CrossRef - Advanced nanoparticle-based antibacterial delivery for endodontic disinfection: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Kanwalpreet Kaur, Seerat Kaura, Ravinder S Saini, Maurya Manjunath, Shashit Shetty Bavabeedu, Mario Alberto Alarcón-Sánchez, Javier Flores-Fraile, Artak Heboyan
Journal of Dentistry.2026; 166: 106347. CrossRef - Comparison of Various Irrigation Techniques for the Removal of Silicone Oil-Based Calcium Hydroxide Intracanal Medicament from the Apical Third: An SEM Study
Shalin Ann Saji, Chitharanjan Shetty, Gurmeen Kaur, Sunheri Bajpe, Chandraprabha Chandraprabha, Rashi Shroff, Shazeena Qaiser, Surabhi Gupta
Journal of Health and Allied Sciences NU.2025; 15(01): 103. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of smear layer removal and dentin wettability using 1% phytic acid with and without 0.2% chitosan nanoparticles: An in vitro study
Rahul Halkai, Kiran R. Halkai, Syeda Uzma Mahveen
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2025; 15(1): 38. CrossRef - Chitosan’s Ability to Remove the Smear Layer—A Systematic Review of Ex Vivo Studies
Ana Ferreira-Reguera, Inês Ferreira, Irene Pina-Vaz, Benjamín Martín-Biedma, José Martín-Cruces
Medicina.2025; 61(1): 114. CrossRef - Nanoparticles modified bioceramic sealers on solubility, antimicrobial efficacy, pushout bond strength and marginal adaptation at apical-third of canal dentin
Basil Almutairi, Fahad Alkhudhairy
PeerJ.2025; 13: e18840. CrossRef - Optimization of chitosan nanoparticle dentin pretreatment with different concentrations and application times to improve bonding at resin-dentin interface
Rinki Meher, Rashmi Rekha Mallick, Priyanka Sarangi, Amit Jena, Shradha Suman, Gaurav Sharma
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(3): 248. CrossRef - Innovative strategy for chitosan nanoparticles biosynthesis using Gelidium amansii, statistical optimization, characterization, cytotoxicity and molecular docking against hepatocellular carcinoma
Noura El-Ahmady El-Naggar, Naglaa Elshafey, Hagar I. Alafifi, Manar A. Eltahy, Reem I. Haikl, Hagar A. ElShazly, Yasmin W. Ahmed, Hossam I. Hassan, Mohamed M. Safo, S.A. Haroun, Asmaa A. El-Sawah
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.2025; 311: 143687. CrossRef - Enhancing root canal sealing: Exploring the sealing potential of epoxy and calcium silicate-based sealers with chitosan nanoparticle enhancement
S. Harishma, Srilekha Jayakumar, K Shibani Shetty, Barkavi Panchatcharam, Jwaalaa Rajkumar, S. Harshini
Endodontology.2025; 37(3): 306. CrossRef - An in vitro comparative evaluation of silver and chitosan nanoparticles on shear bond strength of nanohybrid composite using different adhesion protocols
Roopadevi Garlapati, Nagesh Bolla, Mayana Aameena Banu, Anila Bandlapally Sreenivasa Guptha, Niharika Halder, Ram Chowdary Basam
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(6): 522. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of the effect of chitosan and titanium dioxide nanoparticles on the pushout bond strength of mineral trioxide aggregate: An in vitro comparative study
Garima Poddar, Suparna Ganguly Saha, Rolly S. Agarwal, Geetika Pable, Affrin Shaikh, Shakti Singh
Endodontology.2025; 37(3): 289. CrossRef - Antibacterial efficacy of chitosan nanoparticles against Enterococcus faecalis in planktonic and biofilm forms
Raras Ajeng Enggardipta, Minato Akizuki, Kazumitsu Sekine, Kenichi Hamada, Tomoko Sumitomo, Hiromichi Yumoto
Journal of Applied Microbiology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Corrosion Inhibition Properties of Chitosan Doped With Fe, Cu, Zn, and Co on the Fe(110) Surface: A Combined DFT and Monte Carlo Simulation Study
D. M. Mamand, Peshawa O. Hama, Rebaz Anwar Omer, Rebaz Obaid Kareem, Dana S. Muhammad, Sarkawt A. Hussen, Yousif Hussein Azeez
Surface and Interface Analysis.2025; 57(12): 936. CrossRef - Comparison of penetration depth of chitosan, zinc oxide, and silica-doped titanium novel nanoparticle irrigant solutions – A confocal laser scanning microscopic in vitro study
Sree Laksmi Bademela, T. B. V. G. Raju, Krishna Prasad Parvathaneni, Abitha Seshadri, Nadimpalli Mahendra Varma, Gowtam Dev Dondapati
Endodontology.2024; 36(3): 280. CrossRef - Combined use of XP-Endo Finisher and different chelating agents on the smear layer
Meenu Elizabeth Saju, Ramya Raghu, Ashish Shetty, Lekha Santhosh, Subhashini Rajasekhara, Priya C. Yadav
Endodontology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Therapeutic efficacy of chitosan-based hybrid nanomaterials to treat microbial biofilms and their infections – A review
Anisha Salim, Palanivel Sathishkumar
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.2024; 283: 137850. CrossRef - Local and systemic adverse effects of nanoparticles incorporated in dental materials- a critical review
Harini Karunakaran, Jogikalmat Krithikadatta, Mukesh Doble
The Saudi Dental Journal.2024; 36(1): 158. CrossRef - Effect of final irrigation protocols with chitosan nanoparticle and genipin on dentine against collagenase degradation: An ex‐vivo study
S. N. Şengül, S. Ozturk, K. Ulubayram, N. Pekel Bayramgil, S. Kucukkaya Eren
International Endodontic Journal.2024; 57(4): 477. CrossRef - Application of Nanomaterials in Endodontics
Farzaneh Afkhami, Yuan Chen, Laurence J. Walsh, Ove A. Peters, Chun Xu
BME Frontiers.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the Effect of Chitosan-Based Irrigation Solutions on the Bond Strength of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate to Bulk-Fill Composite
Arzu Şahin Mantı, Bağdagül Helvacıoğlu Kıvanç
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2024; 15(12): 370. CrossRef - In vitro analysis of compressive strength of root dentin on application of intracanal medicaments for different time periods
Kushal Kumar Ghosh, Sayantan Mukherjee, Paromita Mazumdar, Sahil Ali, Lovely Das
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(12): 1289. CrossRef - The comparative of chitosan and chitosan nanoparticle versus ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid on the smear layer removal: A systematic review and meta‐analysis of in vitro study
Hasan İlhan, Elif Bahar Cakici, Fatih Cakici
Microscopy Research and Technique.2024; 87(2): 181. CrossRef - Final Irrigant Temoporfin, Femtosecond Laser, and Chitosan Nanoparticles on Extrusion Bond Strength of Glass Fiber Post, Microhardness, and Modulus of Elasticity of Canal Dentin
Lujain Ibrahim N. Aldosari
Journal of Biomaterials and Tissue Engineering.2024; 14(2): 78. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of an epoxy resin-based and a premixed calcium silicate-based sealer’s push-out bond strength with and without incorporation of chitosan nanoparticles: An in vitro investigation
S. Harishma, K. B. Jeyalakshmi, K. Shibani Shetty, S. Harshini
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(9): 970. CrossRef - Chitosan: A Versatile Biomaterial Revolutionizing Endodontic Therapy
Akash Thakare, Shweta Sedani, Simran Kriplani , Aditya Patel, Utkarsh Umre
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the Effect of Farnesol and/or Chitosan as a Final Irrigation on Enterococcus faecalis Biofilm; An In-vitro Study
Ardavan Moinafshar, Hanieh Paik, Rashid Ramazanzadeh, Amjad Ahmadi, Mohammad Rastegar Khosravi
Scientific Journal of Kurdistan University of Medical Sciences.2024; 29(1): 85. CrossRef - Bionanomaterials an emerging field of nanotechnology
A.R. Shelin, S. Meenakshi
Archives of Materials Science and Engineering.2023; 121(1): 33. CrossRef - Bonding of chitosan and nanochitosan modified universal adhesive to dentin
Yasmin Ezz El-Din, Ahmed El-Banna, Tarek Salah Hussein
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2023; 125: 103432. CrossRef - Nanoparticles and Their Antibacterial Application in Endodontics
Nicoletta Capuano, Alessandra Amato, Federica Dell’Annunziata, Francesco Giordano, Veronica Folliero, Federica Di Spirito, Pragati Rajendra More, Anna De Filippis, Stefano Martina, Massimo Amato, Massimiliano Galdiero, Alfredo Iandolo, Gianluigi Franci
Antibiotics.2023; 12(12): 1690. CrossRef - In vitro techniques for evaluating smear layer removal by root canal irrigants: a literature review
Luis Hernán Carrillo Varguez, Aracely Serrano-Medina, Eduardo Alberto López Maldonado, Eustolia Rodríguez Velázquez, José Manuel Cornejo-Bravo
Horizon Interdisciplinary Journal.2023; 1(2): 58. CrossRef - Applicability of a Natural Nano-derivative as a Mouth Rinse on Salivary pH and S. mutans Count: An Ex Vivo Study
Raja S Prathigudupu, Deepthi N Gavarraju, Sai S Kallam, Sai Sankar J Avula, Chaitanya M Sattenapalli, Amrutha Valli Audipudi
World Journal of Dentistry.2023; 14(3): 207. CrossRef - Nanopartículas antimicrobianas en endodoncia: Revisión narrativa
Gustavo Adolfo Tovar Rangel , Fanny Mildred González Sáenz , Ingrid Ximena Zamora Córdoba , Lina María García Zapata
Revista Estomatología.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Quantification of Calcium Ions From the Irrigants Activated With Erbium-Doped Yttrium Aluminum Garnet (Er:YAG) Laser in the Root Dentin: An In Vitro Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer Study
Dhanalakshmi P, Kiran Kumar N, K Rashmi, Biji Brigit, Shwetha R S, Sourabh T J
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of chelating effect of chitosan as intracanal lubricant and an irrigant on smear layer removal – An in-vitro scanning electron microscope study
Thati Jyotsnanjali, M. A. Ranjini, G. R. Krishna Kumar, D. V. Swapna, S. N. Joshi, Roopa R. Nadig
Endodontology.2023; 35(3): 254. CrossRef - Assessment of the Effectiveness of Two Different Dentin Biomodifiers on Shear Bond Strength of Dentin and Resin Interface: A Comparative Study
Narendra V Penumatsa, AlWaleed Abushanan, Uthman S Uthman, Abdulhamid Al Ghwainem, Adel S Alqarni, Abdulfatah Alazmah
World Journal of Dentistry.2023; 14(1): 16. CrossRef - Scanning electron microscopy evaluation of smear layer removal using ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, etidronic acid, and chitosan nanoparticle solution as root canal irrigants
Sunheri Bajpe, Chitharanjan Shetty, Aditya Shetty, Gurmeen Kaur, Shalin Ann Saji, Chandra Prabha
Endodontology.2023; 35(1): 48. CrossRef - Green fabrication of chitosan nanoparticles using Lavendula angustifolia, optimization, characterization and in‑vitro antibiofilm activity
Noura El-Ahmady El-Naggar, Marwa Eltarahony, Elsayed E. Hafez, Shimaa I. Bashir
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Nanobiotechnology: Synthesis components and a few approaches for controlling plant diseases
Malavika Ram A K, Ramji Singh, Meenakshi Rana, S.A. Dwivedi, Kshitij Parmar, Abha Sharma, Chitranjan Kumar, Vineeta Pandey, Vikash Kumar, Shashank Mishra, Ajay Tomar
Plant Nano Biology.2023; 4: 100038. CrossRef - Physicochemical and biological properties of a biostimulating membrane (BBio) for pulp capping
Natalino Lourenço Neto, Luciana Lourenço Ribeiro Vitor, Silgia Aparecida da Costa, Sirlene Maria da Costa, Thiago Cruvinel, Thais Marchini Oliveira, Rodrigo Cardoso Oliveira, Maria Aparecida Andrade Moreira Machado
Materials Letters.2022; 308: 131186. CrossRef - In Vitro Study of Irrigation solution of Chitosan Nanoparticles to Inhibit the Adhesion and Biofilm Formation of Enterococcus faecalis in the Root Canal
Imelda Darmawi, Trimurni Abidin, Harry Agusnar, Basri A. Gani
Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology.2022; : 2691. CrossRef - Nanoparticles in Endodontics Disinfection: State of the Art
Xavier Roig-Soriano, Eliana B. Souto, Firas Elmsmari, Maria Luisa Garcia, Marta Espina, Fernando Duran-Sindreu, Elena Sánchez-López, Jose Antonio González Sánchez
Pharmaceutics.2022; 14(7): 1519. CrossRef - An In Vitro Study Comparing the Antimicrobial Efficacy of 0.2% Chitosan, 3% Sodium Hypochlorite, 2% Chlorhexidine against Enterococcus faecalis, Alone and in Conjunction with Diode Laser
Sameer Makkar, Tamanpreet Kaur, Pallavi Goel, Virat Galhotra, Jatinder Mohan, Neetu Bala
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2022; 15(1): 109. CrossRef - Chitosan-Based Carbon Dots with Applied Aspects: New Frontiers of International Interest in a Material of Marine Origin
Angel M. Villalba-Rodríguez, Reyna Berenice González-González, Manuel Martínez-Ruiz, Elda A. Flores-Contreras, María Fernanda Cárdenas-Alcaide, Hafiz M. N. Iqbal, Roberto Parra-Saldívar
Marine Drugs.2022; 20(12): 782. CrossRef - The Effect of Final Irrigation Protocols on the Apical Sealing Ability of Epoxy Resin-based and Bioceramic-based Root Canal Sealers
Anan Medhat, Angie Ghoneim, Nehal Nabil Roshdy
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.2022; 10(D): 458. CrossRef - Molecular docking reveals Chitosan nanoparticle protection mechanism for dentin against Collagen-binding bacteria
Ziliang Zhou, Yanyan Yang, Lu He, Junmei Wang, Jie Xiong
Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Free Available Chlorine of Sodium Hypochlorite When Admixed with 0.2% Chitosan: A Preliminary Study
Rupali Karale, Nithin K Shetty, Prashanth Bytarahosalli Rajachar, Mythreyee S Vidhya, Vinay Kumar Govindaraju
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2022; 22(10): 1171. CrossRef - Effect of chitosan irrigant solutions on the release of bioactive proteins from root dentin
Sara Quijano-Guauque, Lilia J. Bernal-Cepeda, Félix G. Delgado, Jaime E. Castellanos, Claudia García-Guerrero
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 27(2): 691. CrossRef - Chemical and morphological characterization of self-etch primers incorporated with nanochitosan
Pâmella Coelho Dias, Isabela Barbosa Quero, Juliana Jendiroba Faraoni, Regina Guenka Palma-Dibb
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2022; 118: 103215. CrossRef - The effects of different root canal irrigation protocols and artificial aging procedures on the bond strength between dentin and hybrid ceramic posts
Celalettin Topbaş, Şevki Çınar, Bike Altan, Dursun Ali Şirin, Mehmet Ali Fildişi
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of two different concentrations of chitosan irrigation on smear layer removal during root canal treatment
Doaa M. Abd El-latif, Abeer M. Darrag, Dalia A. Sherif
Tanta Dental Journal.2022; 19(4): 204. CrossRef - Impact of Dentin Conditioning and Sealer Modification With Chitosan-Hydroxyapatite Nanocomplexes on the Antibacterial and Mechanical Characteristics of Root Dentin
Aldo del Carpio-Perochena, Eric Nicholson, Chandra Veer Singh, Josette Camilleri, Anil Kishen
Journal of Endodontics.2022; 48(10): 1319. CrossRef - Assessment of Antimicrobial Efficacy of Nano Chitosan, Chlorhexidine, Chlorhexidine/Nano Chitosan Combination versus Sodium Hypochlorite Irrigation in Patients with Necrotic Mandibular Premolars: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Maha Nasr, Alaa Diab, Nehal Roshdy, Amira Farouk
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.2021; 9(D): 235. CrossRef - Enhanced visualization of the root canal morphology using a chitosan-based endo-radiopaque solution
Shashirekha Govind, Amit Jena, Satabdi Pattanaik, Mahaprasad Anarasi, Satyajit Mohapatra, Vinay Shivagange
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Chitosan-Based Biomaterial, Calcium Hydroxide and Chlorhexidine for Potential Use as Intracanal Medication
Bruna de Siqueira Nunes, Rosana Araújo Rosendo, Abrahão Alves de Oliveira Filho, Marcus Vinícius Lia Fook, Wladymyr Jefferson Bacalhau de Sousa, Rossemberg Cardoso Barbosa, Hermano de Vasconcelos Pina, João Emídio da Silva Neto, Solomon Kweku Sagoe Amoah,
Materials.2021; 14(3): 488. CrossRef - Nanostructures as Targeted Therapeutics for Combating Oral Bacterial Diseases
Shima Afrasiabi, Nasim Chiniforush, Hamid Reza Barikani, Alireza Partoazar, Ramin Goudarzi
Biomedicines.2021; 9(10): 1435. CrossRef - Microbiological Aspects of Root Canal Infections and Disinfection Strategies: An Update Review on the Current Knowledge and Challenges
Jasmine Wong, Daniel Manoil, Peggy Näsman, Georgios N. Belibasakis, Prasanna Neelakantan
Frontiers in Oral Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Nanomaterials Application in Endodontics
Wojciech Zakrzewski, Maciej Dobrzyński, Anna Zawadzka-Knefel, Adam Lubojański, Wojciech Dobrzyński, Mateusz Janecki, Karolina Kurek, Maria Szymonowicz, Rafał Jakub Wiglusz, Zbigniew Rybak
Materials.2021; 14(18): 5296. CrossRef - Preparation and application of chitosan biomaterials in dentistry
Chenxi Zhang, Didi Hui, Colin Du, Huan Sun, Wei Peng, Xiaobing Pu, Zhengyong Li, Jianxun Sun, Changchun Zhou
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.2021; 167: 1198. CrossRef - The Potential Translational Applications of Nanoparticles in Endodontics
Jasmine Wong, Ting Zou, Angeline Hui Cheng Lee, Chengfei Zhang
International Journal of Nanomedicine.2021; Volume 16: 2087. CrossRef - Chitosan Enhances the Anti-Biofilm Activity of Biodentine against an Interkingdom Biofilm Model
Sumaya Abusrewil, Jason L. Brown, Christopher Delaney, Mark C. Butcher, Mohammed Tiba, J. Alun Scott, Gordon Ramage, William McLean
Antibiotics.2021; 10(11): 1317. CrossRef - Evaluation of Anti-Biofilm Activity of Mouthrinses Containing Tannic Acid or Chitosan on Dentin In Situ
Anton Schestakow, Moritz S. Guth, Tobias A. Eisenmenger, Matthias Hannig
Molecules.2021; 26(5): 1351. CrossRef - An All-inclusive Estimation of Antibacterial and Antifungal Efficiencies of Propolis and Cetrimide Root Canal Irrigants against Enterococcus faecalis and Candida albicans: An In vitro (Original Research) Study
Sumita Giri Nishad
Journal of Research and Advancement in Dentistry.2021; 12(5): 185. CrossRef - Carbohydrate-containing nanoparticles as vaccine adjuvants
Xinyuan Zhang, Zhigang Zhang, Ningshao Xia, Qinjian Zhao
Expert Review of Vaccines.2021; 20(7): 797. CrossRef - RANDOMIZED CLINICAL TRIAL OF ANTIMICROBIAL EFFICACY OF TWO HERBAL PRODUCTS AS ROOT CANAL IRRIGANTS IN PRIMARY ENDODONTIC INFECTIONS.
Sonam Dhall, Rakesh Mittal, Monika Tandan
Journal of Indian Dental Association.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Preparation methods and applications of chitosan nanoparticles; with an outlook toward reinforcement of biodegradable packaging
Murat Yanat, Karin Schroën
Reactive and Functional Polymers.2021; 161: 104849. CrossRef -
Effect of the Incorporation of Chitosan and TiO
2
Nanoparticles on the Shear Bond Strength of an Orthodontic Adhesive: An In Vitro Study
Fahimeh Farzanegan, Hooman Shafaee, Majid Darroudi, Abdolrasoul Rangrazi
Journal of Advanced Oral Research.2021; 12(2): 261. CrossRef - Antibacterial effect of hyaluronan/chitosan nanofilm in the initial adhesion of Pseudomonas aeruginosa wild type, and IV pili and LPS mutant strains
Jacobo Hernandez-Montelongo, Gianlucca G. Nicastro, Thays de O. Pereira, Mariana Zavarize, Marisa M. Beppu, Waldemar A.A. Macedo, Regina L. Baldini, Monica A. Cotta
Surfaces and Interfaces.2021; 26: 101415. CrossRef - Randomized Clinical Trial of Antimicrobial Effi cacy of two Herbal Products as Root Canal Irrigants in Primary Endodontic Infections
Sonam Dhall, Rakesh Mittal, Monika Tandan
Journal of Indian Dental Association.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation Of Fracture Resistance Of Root Dentin To Different Intracanal Medicaments: In-Vitro Study
Anita Sanap-Tandale, Nikhil Borse, Kunal Kunjir, Karan Bhargava
Annals of Dental Specialty.2021; 9(2): 86. CrossRef - Engineering Polymeric Nanosystems against Oral Diseases
Valeria Mercadante, Edoardo Scarpa, Valeria De Matteis, Loris Rizzello, Alessandro Poma
Molecules.2021; 26(8): 2229. CrossRef - Chelation capability of chitosan and chitosan derivatives: Recent developments in sustainable corrosion inhibition and metal decontamination applications
Chandrabhan Verma, M.A. Quraishi
Current Research in Green and Sustainable Chemistry.2021; 4: 100184. CrossRef - Comparative effects of final canal irrigation with chitosan and EDTA
Polliana Vilaça Silva Antunes, Luis Eduardo Souza Flamini, Jardel Francisco Mazzi Chaves, Ricardo Gariba Silva, Antonio Miranda da Cruz Filho
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Antibacterial property of chitosan against E. faecalis standard strain and clinical isolates
Apimon SUPOTNGARMKUL, Anchana PANICHUTTRA, Chootima RATISOONTORN, Mettachit NAWACHINDA, Oranart MATANGKASOMBUT
Dental Materials Journal.2020; 39(3): 456. CrossRef - Polymeric and inorganic nanoscopical antimicrobial fillers in dentistry
Pooyan Makvandi, Jun Ting Gu, Ehsan Nazarzadeh Zare, Behnaz Ashtari, Arash Moeini, Franklin R. Tay, Li-na Niu
Acta Biomaterialia.2020; 101: 69. CrossRef - A chitosan-based irrigant improves the dislocation resistance of a mineral trioxide aggregate-resin hybrid root canal sealer
Esin Ozlek, Priti Pragati Rath, Anil Kishen, Prasanna Neelakantan
Clinical Oral Investigations.2020; 24(1): 151. CrossRef - Detection, treatment and prevention of endodontic biofilm infections: what’s new in 2020?
Sumaya Abusrewil, Om Alkhir Alshanta, Khawlah Albashaireh, Saeed Alqahtani, Christopher J. Nile, James Alun Scott, William McLean
Critical Reviews in Microbiology.2020; 46(2): 194. CrossRef - Cytotoxicity of Chelating Agents Used In Endodontics and Their Influence on MMPs of Cell Membranes
Kellin Pivatto, Fabio Luis Miranda Pedro, Orlando Aguirre Guedes, Adriana Fernandes da Silva, Evandro Piva, Thiago Machado Pereira, Welligton Luiz de Oliveira da Rosa, Alvaro Henrique Borges
Brazilian Dental Journal.2020; 31(1): 32. CrossRef - The Effect of Chitosan Nanoparticle as A Final Irrigation Solution on The Smear Layer Removal, Micro-hardness and Surface Roughness of Root Canal Dentin
Diatri Nari Ratih, Raras Ajeng Enggardipta, Aqilla Tiara Kartikaningtyas
The Open Dentistry Journal.2020; 14(1): 19. CrossRef - Time-Dependent Effect of Chitosan Nanoparticles as Final Irrigation on the Apical Sealing Ability and Push-Out Bond Strength of Root Canal Obturation
Diatri Nari Ratih, Nikita Ika Sari, Pribadi Santosa, Nofa Mardia Ningsih Kaswati
International Journal of Dentistry.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Targeting tuberculosis infection in macrophages using chitosan oligosaccharide nanoplexes
Uday Koli, Kayzad Nilgiriwala, Kalpana Sriraman, Ratnesh Jain, Prajakta Dandekar
Journal of Nanoparticle Research.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Application of Antimicrobial Nanoparticles in Dentistry
Wenjing Song, Shaohua Ge
Molecules.2019; 24(6): 1033. CrossRef - Assessment of antibacterial activity of 2.5% NaOCl, chitosan nano-particles against Enterococcus faecalis contaminating root canals with and without diode laser irradiation: an in vitro study
Nehal Nabil Roshdy, Engy M. Kataia, Neveen A. Helmy
Acta Odontologica Scandinavica.2019; 77(1): 39. CrossRef - In Vitro Antimicrobial Effect of Bioadhesive Oral Membrane with Chlorhexidine Gel
Annelyze Podolan Kloster, Natalino Lourenço Neto, Silgia Aparecida da Costa, Thais Marchini Oliveira, Rodrigo Cardoso de Oliveira, Maria Aparecida Andrade Moreira Machado
Brazilian Dental Journal.2018; 29(4): 354. CrossRef - How to improve root canal filling in teeth subjected to radiation therapy for cancer
Fabiana de Góes Paiola, Fabiane Carneiro Lopes, Jardel Francisco Mazzi-Chaves, Rodrigo Dantas Pereira, Harley Francisco Oliveira, Alexandra Mussolino de Queiroz, Manoel Damião de Sousa-Neto
Brazilian Oral Research.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of toxicity and oxidative DNA damage of sodium hypochlorite, chitosan and propolis on fibroblast cells
Zeliha Uğur Aydin, Kerem Engin Akpinar, Ceylan Hepokur, Demet Erdönmez
Brazilian Oral Research.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Recent developments in the use of nanoparticles for treatment of biofilms
Chendong Han, Nicholas Romero, Stephen Fischer, Julia Dookran, Aaron Berger, Amber L. Doiron
Nanotechnology Reviews.2017; 6(5): 383. CrossRef - Assessment of the Amount of Calcium Ions Released after the use of Different Chelating Agents and Agitation Protocols
Fábio Luis Miranda Pedro, Laura Maria Amorim Santana Costa, Gilberto Siebert Filho, Orlando Aguirre Guedes, Thiago Machado Pereira, Alvaro Henrique Borges
The Open Dentistry Journal.2017; 11(1): 133. CrossRef - Wettability and surface morphology of eroded dentin treated with chitosan
Mirian Saavedra Ururahy, Fabiana Almeida Curylofo-Zotti, Rodrigo Galo, Lucas Fabricio Bahia Nogueira, Ana Paula Ramos, Silmara Aparecida Milori Corona
Archives of Oral Biology.2017; 75: 68. CrossRef - Biophysical and biological characterization of intraoral multilayer membranes as potential carriers: A new drug delivery system for dentistry
Mariana dos Santos Silva, Natalino Lourenço Neto, Silgia Aparecida da Costa, Sirlene Maria da Costa, Thais Marchini Oliveira, Rodrigo Cardoso de Oliveira, Maria Aparecida Andrade Moreira Machado
Materials Science and Engineering: C.2017; 71: 498. CrossRef - Antibacterial Properties of Chitosan Nanoparticles and Propolis Associated with Calcium Hydroxide against Single- and Multispecies Biofilms: An In Vitro and In Situ Study
Aldo del Carpio-Perochena, Anil Kishen, Rafael Felitti, Anjali Y. Bhagirath, Manoj R. Medapati, Christopher Lai, Rodrigo S. Cunha
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(8): 1332. CrossRef - Analysis of the shelf life of chitosan stored in different types of packaging, using colorimetry and dentin microhardness
Antonio Miranda da Cruz-Filho, Angelo Rafael de Vito Bordin, Luis Eduardo Souza-Flamini, Débora Fernandes da Costa Guedes, Paulo César Saquy, Ricardo Gariba Silva, Jesus Djalma Pécora
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2017; 42(2): 87. CrossRef - Does nanobiotechnology create new tools to combat microorganisms?
Marlena K. Zielińska-Górska, Ewa Sawosz, Konrad Górski, André Chwalibog
Nanotechnology Reviews.2017; 6(2): 171. CrossRef - New frontiers for anti-biofilm drug development
Suzana M. Ribeiro, Mário R. Felício, Esther Vilas Boas, Sónia Gonçalves, Fabrício F. Costa, Ramar Perumal Samy, Nuno C. Santos, Octávio L. Franco
Pharmacology & Therapeutics.2016; 160: 133. CrossRef - The effect of combined use of chitosan and PIPS on push-out bond strength of root canal filling materials
Ugur Aydin, Fatih Aksoy, Samet Tosun, Abdul Semih Ozsevik
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2016; 30(18): 2024. CrossRef - Organic Nanomaterials and Their Applications in the Treatment of Oral Diseases
Maria Virlan, Daniela Miricescu, Radu Radulescu, Cristina Sabliov, Alexandra Totan, Bogdan Calenic, Maria Greabu
Molecules.2016; 21(2): 207. CrossRef
-
2,689
View
-
42
Download
-
95
Crossref
|