Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
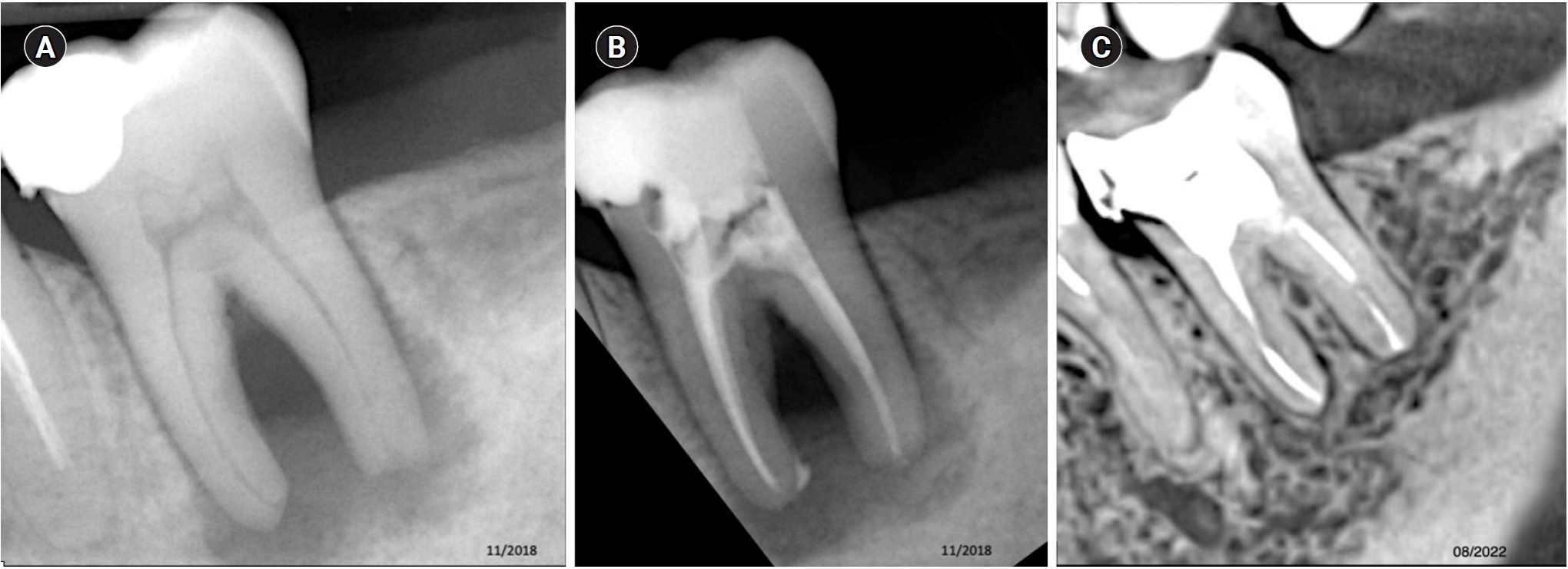
- Impact of the use of high-power 810-nm diode laser as monotherapy on the clinical and tomographic success of the treatment of teeth with periapical lesions: an observational clinical study
- Fabricio Hinojosa Pedraza, Abel Victor Isidro Teves-Cordova, Murilo Priori Alcalde, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(2):e15. Published online May 15, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e15
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
The aim of this study was to demonstrate the impact of a high-power 810-nm diode laser as monotherapy on the clinical and tomographic success of treating teeth with periapical lesions, through a series of 31 cases.
Methods
Teeth with apical lesions underwent endodontic treatment in which a high-power 810-nm diode laser with saline solution was used as monotherapy for disinfection. This type of therapy aimed to replace the traditional irrigation protocol with sodium hypochlorite. This research is the first to assess the clinical success of this alternative treatment, along with tomographic evaluations conducted over periods ranging from 2 to 7 years, analyzed using the periapical index based on cone-beam computed tomography (CBCTPAI). All cases were performed by a single clinician following the same laser protocol, which involved using 1 W of continuous power and four cycles of 20 seconds of laser activation.
Results
All teeth showed no clinical symptoms upon follow-up examination. However, the tomographic evaluation revealed that the success rates for teeth receiving primary treatment were 60% and 80% according to strict and loose criteria, respectively. For teeth requiring retreatment, the success rates were 12.5% and 37.5% using strict and loose criteria, respectively.
Conclusions
The teeth with apical lesions that underwent primary treatment did not present clinical symptoms, but they showed a moderate success rate on tomographic evaluation. However, despite lacking clinical symptoms, teeth with apical lesions that required retreatment had a very low success rate on tomographic evaluation. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diode Laser-Guided Protocol for Endo-Perio Lesions: Toward a Multi-Stage Therapeutic Strategy—A Case Series and Brief Literature Review
Ioana-Roxana Munteanu, George-Dumitru Constantin, Ruxandra-Elena Luca, Ioana Veja, Mariana-Ioana Miron
Medicina.2025; 61(12): 2157. CrossRef
- Diode Laser-Guided Protocol for Endo-Perio Lesions: Toward a Multi-Stage Therapeutic Strategy—A Case Series and Brief Literature Review
- 4,039 View
- 193 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

-
Influence of disinfecting solutions on the surface topography of gutta-percha cones: a systematic review of
in vitro studies - Lora Mishra, Gathani Dash, Naomi Ranjan Singh, Manoj Kumar, Saurav Panda, Franck Diemer, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska, Barbara Lapinska, Abdul Samad Khan
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(4):e42. Published online November 1, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e42
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The surface integrity of gutta-percha cones is a crucial factor in the success of endodontic procedures. Disinfecting solutions play a pivotal role in sterilizing gutta-percha cones, but their influence on gutta-percha surface topography remains a subject of concern. This systematic review aimed to present a qualitative synthesis of available laboratory studies assessing the influence of disinfecting solutions on the surface topography of gutta-percha and offers insights into the implications for clinical practice. The present review followed PRISMA 2020 guidelines. An advanced database search was performed in PubMed, Google Scholar, Embase, Scopus, LILAC, non-indexed citations and reference lists of eligible studies in May 2024. Laboratory studies, in English language, were considered for inclusion. The quality (risk of bias) of the included studies was assessed using parameters for
in vitro studies. A total of 28 studies were included in the qualitative synthesis. Based on the included in vitro studies, surface deposits and alterations in the physical properties of gutta-percha cones were observed after the disinfection protocol. A comprehensive review of the available literature indicates that the choice of disinfecting solution, its concentration, and immersion time significantly affect the surface topography of gutta-percha cones.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- In Vitro Evaluation of Disinfectants on Gutta-Percha Cones: Antimicrobial Efficacy Against Enterococcus faecalis and Candida albicans
Tringa Kelmendi, Donika Bajrami Shabani, Aida Meto, Hani Ounsi
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(19): 6846. CrossRef
- In Vitro Evaluation of Disinfectants on Gutta-Percha Cones: Antimicrobial Efficacy Against Enterococcus faecalis and Candida albicans
- 4,054 View
- 197 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Outcomes of the GentleWave system on root canal treatment: a narrative review
- Hernán Coaguila-Llerena, Eduarda Gaeta, Gisele Faria
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(1):e11. Published online February 14, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e11
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study aimed to describe the outcomes of the GentleWave system (GW) (Sonendo) on root canal treatment. Published articles were collected from scientific databases (MEDLINE/PubMed platform, Web of Science, Scopus, Science Direct and Embase). A total of 24 studies were collected from August/2014 to July/2021, 20
in vitro and 4 clinical. GW System was not associated with extrusion of the irrigant, promoted faster organic dissolution than conventional syringe irrigation (CSI), passive ultrasonic irrigation (PUI) continuous ultrasonic irrigation (CUI) and EndoVac, reduced more bacterial DNA and biofilm than PUI and CUI, promoted higher penetration of sodium hypochlorite into dentinal tubules than PUI and CUIin vitro , and removed more intracanal medication than CSI and PUI. GW was able to remove pulp tissue and calcifications. Moreover, its ability to remove hard-tissue debris and smear layer was better than that of CSI, and its ability to remove root canal obturation residues was lower or similar to that of PUI, and similar to that of CSI and EndoVac. Regarding root canal obturation of minimally instrumented molar canals, GW was associated with high-quality obturation. Clinically, the success rate of endodontic treatment using GW was 97.3%, and the short-term postoperative pain in the GW group was not different from CSI. Further research, mainly clinical, is needed to establish whether GW has any advantages over other available irrigation methods.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical and Laboratory Insights Into the GentleWave System: A Scoping Review
Lucas Peixoto de Araújo, Bruna Cavalcante Chaves de Araújo, Felipe Immich, Bruno das Neves Cavalcanti, Neville J. McDonald
Journal of Endodontics.2026; 52(2): 212. CrossRef - Effectiveness of the GentleWave system in root canal disinfection: a systematic review
Sıla Nur Usta, Eda Doğuş, Mustafa Gündoğar
BMC Oral Health.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - GentleWave versus Established Irrigation Techniques: Current Evidence from a Scoping Review
Mohmed Isaqali Karobari, Abdul Habeeb Adil, Niher Tabassum Snigdha, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva
Journal of Endodontics.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Endodontic bioceramics: current and futurity aspects
Roma M, Karthik Shetty, Laxmish Mallya, Krishna Prasad Shetty
Frontiers in Oral Health.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Use of the gentlewave system in endodonticsUse of the gentlewave system in endodontics
Daiana Jacobi Lazzarotto, Mayara Colpo Prado, Lara Dotto, Rafael Sarkis-Onofre
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2025; 24: e254250. CrossRef - A Comparison Between Multisonic and Ultrasonic Irrigant Activation Techniques for Multispecies Biofilm Removal During Root Canal Disinfection: A Systematic Review
Preethi Varadan, Sangavi Ra, Mathan R Rajendran
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Improving fluid dynamics during root canal irrigation
Geeta Asthana, Sadhna Manglani, Rajashree Tamuli
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(6): 595. CrossRef - Bibliometric analysis of the GentleWave system: trends, collaborations, and research gaps
Raimundo Sales de Oliveira Neto, Thais de Moraes Souza, João Vitor Oliveira de Amorim, Thaine Oliveira Lima, Guilherme Ferreira da Silva, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, Murilo Priori Alcalde, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2025; 50(2): e17. CrossRef - Effectiveness of the iVac System Compared to Conventional Irrigation and Ultrasonic Activation in Reducing Microbial Biofilm, Lipopolysaccharides and Apical Extrusion
Brenda P. F. A. Gomes, Ana B. S. Lopes, Emelly Aveiro, Lidiane M. Louzada, Ederaldo P. Godoi‐Junior, Pedro I. G. Fagundes, Esdras G. Alves‐Silva, Antônio A. L. Moura‐Filho, Rodrigo Arruda‐Vasconcelos, Juliana D. Bronzato
Australian Endodontic Journal.2025; 51(3): 598. CrossRef - Influence of Ultrasonic Activation of Endodontic Irrigants on Microbial Reduction and Postoperative Pain: A Scoping Review of In Vivo Studies
Jacob Marx, Corban Ward, Bayler Gunnell, Zachary Marx, Alicia Parry, Samuel Dyal, Amir Mohajeri, Man Hung
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(10): 459. CrossRef - Efficacy of Supplementary Irrigation Methods Against Bacterial Biofilm‐Infected Root Canals Prepared With Minimally Invasive and Conventional Techniques
Giuliana Soimu, Abhishek Parolia, Anelise V. Masiero, Fang Qian, Thomas Moninger, Jeffrey A. Banas, Fabricio B. Teixeira
Australian Endodontic Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of ultrasonic and multisonic irrigation on root canal microbial communities: An ex vivo study
Ki Hong Park, Ronald Ordinola‐Zapata, W. Craig Noblett, Bruno P. Lima, Christopher Staley
International Endodontic Journal.2024; 57(7): 895. CrossRef - An Experimental Anatomic CBCT Study on the Correlations Between MB1 and MB2 of the Mesio-Vestibular Root of the Upper First Molars
Luca Fiorillo, Cesare D’Amico, Giusy Rita Maria La Rosa, Francesco Calanna, Alfio Pappalardo, Eugenio Pedullà
Journal of Craniofacial Surgery.2024; 35(2): 672. CrossRef - Bioceramics in Endodontics: Updates and Future Perspectives
Xu Dong, Xin Xu
Bioengineering.2023; 10(3): 354. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of the effectiveness of modern irrigants activation techniques in the process of mechanical root canal system treatment (Literature review)
Anatoliy Potapchuk, Vasyl Almashi, Arsenii Horzov, Victor Buleza
InterConf.2023; (34(159)): 200. CrossRef - Evaluation of machine-assisted irrigation on removal of intracanal biofilm and extrusion of sodium hypochlorite using a three-dimensionally printed root canal model
Ji-Yoon Shin, Mi-Ah Kim, Hee-Jin Kim, Prasanna Neelakantan, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kyung-San Min
Journal of Oral Science.2023; 65(3): 158. CrossRef - Analysis of the efficiency of sound impact on the system of canals of the tooth root: A laboratory study
Anatolii A. Adamchik, Valerii V. Tairov, Irina O. Kamyshnikova, Ekaterina S. Zaporozhskaya-Abramova, Zhanna V. Solovyeva, Viktoria A. Ivashchenko, Natalia V. Lapina, Armenak V. Arutyunov, Olga N. Risovannaya, Ksenia D. Kirsch, Valeria D. Golubina
Russian Journal of Dentistry.2023; 27(4): 261. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of the effectiveness of modern irrigants activation techniques in the protocol of chemomechanical root canal system treatment (literature review)
A. Potapchuk, V. Almashi, Y. Rak, Y. Melnyk, V. Buleza, A. Horzov
SUCHASNA STOMATOLOHIYA.2023; 114(3): 4. CrossRef - Multispecies biofilm removal by a multisonic irrigation system in mandibular molars
Hernán Coaguila‐Llerena, Ronald Ordinola‐Zapata, Christopher Staley, Matthew Dietz, Ruoqiong Chen, Gisele Faria
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(11): 1252. CrossRef
- Clinical and Laboratory Insights Into the GentleWave System: A Scoping Review
- 4,346 View
- 76 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref

- Endodontic biofilms: contemporary and future treatment options
- Yeon-Jee Yoo, Hiran Perinpanayagam, Soram Oh, A-Reum Kim, Seung-Hyun Han, Kee-Yeon Kum
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(1):e7. Published online January 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e7
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Apical periodontitis is a biofilm-mediated infection. The biofilm protects bacteria from host defenses and increase their resistance to intracanal disinfecting protocols. Understanding the virulence of these endodontic microbiota within biofilm is essential for the development of novel therapeutic procedures for intracanal disinfection. Both the disruption of biofilms and the killing of their bacteria are necessary to effectively treat apical periodontitis. Accordingly, a review of endodontic biofilm types, antimicrobial resistance mechanisms, and current and future therapeutic procedures for endodontic biofilm is provided.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of Anti-Biofilm Property of Zirconium Oxide Nanoparticles on Streptococcus mutans and Enterococcus faecalis: An In Vitro Study
Anu Priya Guruswamy Pandian, Anil Kumar Ramachandran, Priyanka Kodaganallur Pitchumani, Blessy Mathai, Davis C Thomas
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Recent advances in antibacterial nanoformulations for endodontic applications
Tiago Dionísio, Pedro Brandão, Vanessa Machado, João Botelho, José João Mendes, Pedro Fonte
Expert Opinion on Drug Delivery.2025; 22(8): 1117. CrossRef - Physical–Chemical Assessment and Antimicrobial Activity of Chlortetracycline-Loaded Collagen Sponges
Graţiela Teodora Tihan, Camelia Ungureanu, Ileana Rău, Roxana Gabriela Zgârian, Răzvan Constantin Barbaresso, Mădălina Georgiana Albu Kaya, Cristina-Elena Dinu-Pîrvu, Mihaela Violeta Ghica
Materials.2025; 18(17): 4029. CrossRef - A Review of Chemical Approaches Inherent to Endodontic Disinfection Protocols: Part 1
Fatima Peer, Yahya E. Choonara, Pradeep Kumar
South African Dental Journal.2025; 80(07): 352. CrossRef - Self-Sacrificial Antibacterial Coating with Photothermal Response for Inhibiting Implant Infection
Jinglin Zhang, Aijian Cao, Lizhen Chen, Dongliang Huo, Jingxian Zhang, Langhuan Huang, Shaozao Tan
ACS Applied Nano Materials.2024; 7(23): 26907. CrossRef - Biofilm in Endodontic Infection and its Advanced Therapeutic Options – An Updated Review
Srilekha Jayakumar, Dinesh Sridhar, Bindu M. John, Karthikeyan Arumugam, Prashanth Ponnusamy, Hema Pulidindi
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2024; 16(Suppl 2): S1104. CrossRef - Analysis of the chemical interaction of polyhexanide with endodontic irrigants
Z. S. Zurab, Yu. A. Generalova, A. A. Kulikova, A. Yu. Umarov, F. V. Badalov, A. Wehbe, E. M. Kakabadze
Endodontics Today.2024; 22(4): 319. CrossRef - In vitro evaluation of three engineered multispecies endodontic biofilms on a dentinal disk substrate
Wajih Hage, Dolla Karam Sarkis, Mireille Kallasy, May Mallah, Carla Zogheib
Biomaterial Investigations in Dentistry.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - In vitro evaluation of enterococcus faecalis growth in different conditions on dentinal substrate
Wajih Hage, Dolla Karam Sarkis, Mireille Kallassy, May Mallah, Carla Zogheib
Biomaterial Investigations in Dentistry.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Bacteria associated with apical periodontitis promotes in vitro the differentiation of macrophages to osteoclasts
A. P. Torres-Monjarás, R. Sánchez-Gutiérrez, B. Hernández-Castro, L. González-Baranda, D. L. Alvarado-Hernández, A. Pozos-Guillén, A. Muñoz-Ruiz, V. Méndez-González, R. González-Amaro, M. Vitales-Noyola
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(6): 3139. CrossRef - Antimicrobial efficacy of Kerr pulp canal sealer (EWT) in combination with 10% amoxicillin on Enterococcus faecalis: A confocal laser scanning microscopic study
Madhureema De Sarkar, Kundabala Mala, Suchitra Shenoy Mala, Shama Prasada Kabekkodu, Srikant Natarajan, Neeta Shetty, Priyanka Madhav Kamath, Manuel Thomas
F1000Research.2023; 12: 725. CrossRef - Antimicrobial efficacy of Kerr pulp canal sealer (EWT) in combination with 10% amoxicillin on Enterococcus faecalis: A confocal laser scanning microscopic study
Madhureema De Sarkar, Kundabala Mala, Suchitra Shenoy Mala, Shama Prasada Kabekkodu, Srikant Natarajan, Neeta Shetty, Priyanka Madhav Kamath, Manuel Thomas
F1000Research.2023; 12: 725. CrossRef - Combined effect of electrical energy and graphene oxide on Enterococcus faecalis biofilms
Myung-Jin LEE, Mi-Ah KIM, Kyung-San MIN
Dental Materials Journal.2023; 42(6): 844. CrossRef - Innovative Curved-Tip Reactor for Non-Thermal Plasma and Plasma-Treated Water Generation: Synergistic Impact Comparison with Sodium Hypochlorite in Dental Root Canal Disinfection
Raúl Arguello-Sánchez, Régulo López-Callejas, Benjamín Gonzalo Rodríguez-Méndez, Rogelio Scougall-Vilchis, Ulises Velázquez-Enríquez, Antonio Mercado-Cabrera, Rosendo Peña-Eguiluz, Raúl Valencia-Alvarado, Carlo Eduardo Medina-Solís
Materials.2023; 16(22): 7204. CrossRef - Impact of antimicrobial photodynamic therapy on the bond-strength and penetration of endodontic sealers: A systematic review
Khalid H Almadi
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2023; 41: 103249. CrossRef - Apical periodontitis in mesiobuccal roots of maxillary molars: influence of anatomy and quality of root canal treatment, a CBCT study
Samantha Jannone Carrion, Marcelo Santos Coelho, Adriana de Jesus Soares, Marcos Frozoni
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Potential relationship between clinical symptoms and the root canal microbiomes of root filled teeth based on the next‐generation sequencing
Yajing Hou, Liu Wang, Lan Zhang, Xuelian Tan, Dingming Huang, Dongzhe Song
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(1): 18. CrossRef - Efficacy of 6% Sodium Hypochlorite on Infectious Content of Teeth with Symptomatic Irreversible Pulpitis
Rodrigo Arruda-Vasconcelos, Marlos Barbosa-Ribeiro, Lidiane M. Louzada, Beatriz I.N. Lemos, Adriana de-Jesus-Soares, Caio C.R. Ferraz, José F.A. Almeida, Marina A. Marciano, Brenda P.F. A. Gomes
Journal of Endodontics.2022; 48(2): 179. CrossRef - Specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators in endodontics: a narrative review
Davy Aubeux, Ove A. Peters, Sepanta Hosseinpour, Solène Tessier, Valérie Geoffroy, Fabienne Pérez, Alexis Gaudin
BMC Oral Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of curcumin-mediated antimicrobial photodynamic therapy associated to different chelators against Enterococcus faecalis biofilms
Daniela Alejandra Cusicanqui Méndez, Maricel Rosario Cardenas Cuéllar, Victor Feliz Pedrinha, Evelyn Giuliana Velásquez Espedilla, Flaviana Bombarda de Andrade, Patrícia de Almeida Rodrigues, Thiago Cruvinel
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2021; 35: 102464. CrossRef - Effectiveness of D,L‐2‐hydroxyisocaproic acid (HICA) and alpha‐mangostin against endodontopathogenic microorganisms in a multispecies bacterial–fungal biofilm in anex vivotooth model
Warat Leelapornpisid, Lilyann Novak‐Frazer, Alison Qualtrough, Riina Rautemaa‐Richardson
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(12): 2243. CrossRef - In Vitro Evaluation of a New Combination of Three Antibiotic Paste Against Common Endodontic Pathogens
Prasanna Dahake, Nilima Thosar
Journal of Islamic Dental Association of IRAN.2021; 33(3): 58. CrossRef - Effect of using diode laser on Enterococcus faecalis and its lipoteichoic acid (LTA) in chronic apical periodontitis
Zhaohui Zou, Junu Bhandari, Baiyan Xiao, Xiaoyue Liang, Yu Zhang, Guohui Yan
Lasers in Medical Science.2021; 36(5): 1059. CrossRef - Prevalence of Bacteria of Genus Actinomyces in Persistent Extraradicular Lesions—Systematic Review
Mario Dioguardi, Vito Crincoli, Luigi Laino, Mario Alovisi, Diego Sovereto, Lorenzo Lo Muzio, Giuseppe Troiano
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(2): 457. CrossRef - Evaluation of in vitro biofilm elimination of Enterococcus faecalis using a continuous ultrasonic irrigation device
Jennifer Galván-Pacheco, Marlen Vitales-Noyola, Ana M. González-Amaro, Heriberto Bujanda-Wong, Antonio Aragón-Piña, Verónica Méndez-González, Amaury Pozos-Guillén
Journal of Oral Science.2020; 62(4): 415. CrossRef - Comparison of the use of d-enantiomeric and l-enantiomeric antimicrobial peptides incorporated in a calcium-chelating irrigant against Enterococcus faecalis root canal wall biofilms
Wei-hu Ye, Lara Yeghiasarian, Christopher W. Cutler, Brian E. Bergeron, Stephanie Sidow, Hockin H.K. Xu, Li-na Niu, Jing-zhi Ma, Franklin R. Tay
Journal of Dentistry.2019; 91: 103231. CrossRef
- Evaluation of Anti-Biofilm Property of Zirconium Oxide Nanoparticles on Streptococcus mutans and Enterococcus faecalis: An In Vitro Study
- 4,640 View
- 127 Download
- 26 Crossref

- Evaluation of antimicrobial activity and efficacy of herbal oils and extracts in disinfection of gutta percha cones before obturation
- Chetana S. Makade, Pratima R. Shenoi, Elakshi Morey, Ameya V. Paralikar
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(4):264-272. Published online October 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.4.264
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Literature has shown that micro-organisms contaminate gutta percha (GP) during storage and manipulation. Till date herbal extracts are not explored as an alternative medicament for pre-operative chairside disinfection of GP cones. The purpose of our study was to evaluate the antimicrobial activity and efficacy of lemon grass oil (LG), basil oil (BO), and obicure tea extract (OT) in disinfecting GP cones before obturation.
Materials and Methods Agar diffusion method was used to evaluate the antimicrobial efficacy of LG, BO, OT, and sodium hypochlorite (control) against common contaminants, namely,
Enterococcus faecalis ,Staphylococcus aureus, andCandida albicans. One hundred and twenty GP cones were contaminated and cut into 2. First half was placed in the broth and incubated; whereas the second was treated with herbal extracts for 1 minute and then incubated for 24 hours in the broth. Any inhibition in bacterial growth was noted with presence/absence of turbidity. Two-way analysis of variance and χ2 test were used to assess the effectiveness of herbal extracts to decontaminate GP.Results LG showed the highest inhibition zones (29.9 ± 6.9 mm) for all tested organisms, followed by OT extract (16.3 ± 1.8 mm), sodium hypochlorite (16.0 ± 1.6 mm), and BO (14.5 ± 5.3 mm). Statistically significant difference was observed between LG and other herbal extracts (
p < 0.05).Conclusions All extracts proved to be potential rapid chairside disinfectants of GP cones with LG showing the highest antimicrobial activity.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of various disinfectant solutions on the tensile strength of gutta-percha using the rapid sterilization technique
Sandeep Rudranaik, Yoganatha Hanasoge Nagashetty, Sahadev Chikmagarvalli Krishna Gowda, Bharath Makonahalli Jaganath, K. B. Nirmala, M. C. Bharath Gowda
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(2): 154. CrossRef - Evaluation of antimicrobial efficacy of herbal extracts and their effect on the surface characteristics of gutta-percha cones: An in vitro study
Anshuman Shetty, Shivprasad Rai, Shetty Suhani Sudhakar
Endodontology.2023; 35(2): 142. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of various herbal agents for the disinfection of guttapercha cones – An in vitro study
Gunnam Anjany Chowdary
IP Indian Journal of Conservative and Endodontics.2023; 8(2): 86. CrossRef - Dynamics of herbal medicine processing and production in Benue State Nigeria
P. Adigwe Obi, F. Builders Philip, Alfa John, Oladosu Peter
African Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology.2022; 16(7): 110. CrossRef - Antimicrobial Efficacy of Acacia Nilotica (Babul) Extract and its Effectiveness in Disinfecting Gutta Percha Cones - An In Vitro Study
Dolly R. Jagyasi, Neelam D. Chandwani, Mohit K. Gunwal, Aastha S. Ranka
Indian Journal of Dental Research.2021; 32(2): 221. CrossRef - The Anti-Inflammatory and Antimicrobial Potential of Selected Ethnomedicinal Plants from Sri Lanka
Mayuri Napagoda, Jana Gerstmeier, Hannah Butschek, Sudhara De Soyza, Simona Pace, Sybille Lorenz, Mallique Qader, Sanjeeva Witharana, Ajith Nagahawatte, Gaya Wijayaratne, Aleš Svatoš, Lalith Jayasinghe, Andreas Koeberle, Oliver Werz
Molecules.2020; 25(8): 1894. CrossRef - Comparación de desinfección de diferentes marcas de punta de gutapercha con hipoclorito de sodio
Jorge Morales García, Mónica Badillo Barba, María Guadalupe Chávez García, Vanessa García Ruíz, Adolfo Gutiérrez García
Revista de la Asociación Dental Mexicana.2020; 77(4): 185. CrossRef - Current herbal medicine as an alternative treatment in dentistry: In vitro, in vivo and clinical studies
Ehsan Tafazoli Moghadam, Mohsen Yazdanian, Elahe Tahmasebi, Hamid Tebyanian, Reza Ranjbar, Alireza Yazdanian, Alexander Seifalian, Ali Tafazoli
European Journal of Pharmacology.2020; 889: 173665. CrossRef - Gutta-percha in endodontics - A comprehensive review of material science
Vijetha Vishwanath, HMurali Rao
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2019; 22(3): 216. CrossRef
- Effect of various disinfectant solutions on the tensile strength of gutta-percha using the rapid sterilization technique
- 1,996 View
- 13 Download
- 9 Crossref

-
Microorganism penetration in dentinal tubules of instrumented and retreated root canal walls.
In vitro SEM study - Saad Al-Nazhan, Alaa Al-Sulaiman, Fellwa Al-Rasheed, Fatimah Alnajjar, Bander Al-Abdulwahab, Abdulhakeem Al-Badah
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(4):258-264. Published online July 22, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.4.258
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This
in vitro study aimed to investigate the ability ofCandida albicans (C. albicans ) andEnterococcus faecalis (E. faecalis ) to penetrate dentinal tubules of instrumented and retreated root canal surface of split human teeth.Materials and Methods Sixty intact extracted human single-rooted teeth were divided into 4 groups, negative control, positive control without canal instrumentation, instrumented, and retreated. Root canals in the instrumented group were enlarged with endodontic instruments, while root canals in the retreated group were enlarged, filled, and then removed the canal filling materials. The teeth were split longitudinally after canal preparation in 3 groups except the negative control group. The teeth were inoculated with both microorganisms separately and in combination. Teeth specimens were examined by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and the depth of penetration into the dentinal tubules was assessed using the SMILE view software (JEOL Ltd).
Results Penetration of
C. albicans andE. faecalis into the dentinal tubules was observed in all 3 groups, although penetration was partially restricted by dentin debris of tubules in the instrumented group and remnants of canal filling materials in the retreated group. In all 3 groups,E. faecalis penetrated deeper into the dentinal tubules by way of cell division thanC. albicans which built colonies and penetrated by means of hyphae.Conclusions Microorganisms can easily penetrate dentinal tubules of root canals with different appearance based on the microorganism size and status of dentinal tubules.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Capped silver nanoparticle penetration in primary dentition: an in vitro SEM-EDS analysis
Amjad Almuqrin, Chaminda Jayampath Seneviratne, Jayanti Mendhi, Laurence J. Walsh, Sobia Zafar
BMC Oral Health.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of photobiomodulation therapy on regenerative potential of non-vital mature permanent teeth in healthy canine dogs
S. F. Khattab, Y. F. Gomaa, E. A. E. Abdelaziz, N. M. A. Khattab
European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry.2025; 26(3): 493. CrossRef - Evaluation of the effectiveness of different supplemental cleaning techniques in the retreatment of roots with small simulated internal resorption cavities: an in vitro comparative study
Sine Güngör Us, Özgür Uzun, Nazlı Merve Güngör
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A 12-month randomized controlled trial to assess the efficacy of revitalization of retreated mature incisors with periapical radiolucency in adolescents
Ahmad Abdel Hamid Elheeny, Osama Seif-Elnasr Hussien, Mahmoud Ahmed Abdelmotelb, Yassmin Mohamed ElMakawi, Norhan Khaled Omar Wahba
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Failed Regenerative Endodontic Case Treated by Modified Aspiration-irrigation Technique and Apexification
Loai Alsofi, Sara Almarzouki
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2024; 25(1): 92. CrossRef - Effectiveness of EndoActivator, PATS Vario system, and XP-endo Finisher files on smear layer removal under scanning electron microscope: A comparative study
Rishabh Patel, Gaurav Shinde, Prashant Bondarde, Aruna Vishwakarma, Madhuri Bhandare, Vaibhavi Pharne
Journal of Indian Society of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry.2024; 42(3): 195. CrossRef - Influence of root canal moisture on the penetration of TotalFill bioceramic sealer into the dentinal tubules: A confocal laser scanning microscopy study
Archika M Singh, Tarek M Elsewify, Walid S El-Sayed, Husam H Nuawafleh, Ranya F Elemam, Bassem M Eid
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2024; 14(2): 187. CrossRef - Fungi and bacteria occupy distinct spatial niches within carious dentin
Rosalyn M. Sulyanto, Clifford J. Beall, Kasey Ha, Joseph Montesano, Jason Juang, John R. Dickson, Shahr B. Hashmi, Seth Bradbury, Eugene J. Leys, Mira Edgerton, Sunita P. Ho, Ann L. Griffen, Alex Andrianopoulos
PLOS Pathogens.2024; 20(5): e1011865. CrossRef - The advancement in irrigation solution within the field of endodontics, A Review
Fatima Fahad , Raghad A Al-Hashimi , Munther J Hussain
Journal of Baghdad College of Dentistry.2024; 36(1): 54. CrossRef - Supplementary methods for filling material removal: A systematic review and meta-analysis of micro-CT imaging studies
Bruna Venzke Fischer, Taynara Santos Goulart, Filipe Colombo Vitali, Diego Leonardo de Souza, Cleonice da Silveira Teixeira, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
Journal of Dentistry.2024; 151: 105445. CrossRef - Impact of calcium hydroxide and 2-hydroxyisocaproic acid on the microhardness of root dentine: an in vitro study
Nandini T. Niranjan, Protim Ghosh Dastidar, Raghavendra Penukonda, Galvin Sim Siang Lin, Roopa Babannavar, Arun Jaysheel, Harshada Pattar
Odontology.2024; 112(3): 711. CrossRef - Fabrication of Rapidly Soluble Zn2+-Releasing Phosphate-Based Glass and Its Incorporation into Dental Resin
Fan Deng, Haruaki Kitagawa, Tomoki Kohno, Tingyi Wu, Naoya Funayama, Pasiree Thongthai, Hefei Li, Gabriela L. Abe, Ranna Kitagawa, Jun-Ichi Sasaki, Satoshi Imazato
Molecules.2024; 29(21): 5098. CrossRef - Combined effect of electrical energy and graphene oxide on Enterococcus faecalis biofilms
Myung-Jin LEE, Mi-Ah KIM, Kyung-San MIN
Dental Materials Journal.2023; 42(6): 844. CrossRef - Effect of Different Irrigant Activation Techniques on the Penetration of Calcium Hydroxide, an Intracanal Medicament: An In Vitro Study
Radha Kalyani Narla, Ravi kumar J, Tejosmita Chowdary Pavuluri, Krishna Chaitanya P, Ramesh Penumaka, Ratna Kamal Nagelli
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative assessment of antibacterial effect of two types of laser and their effect on morphology and mineral content of dentin
Soha Adel Abdou, Haythem S Moharrum, Elsayed Abdallah Eltayeb
Journal of The Arab Society for Medical Research.2023; 18(2): 117. CrossRef - Efficacy of Endodontic Disinfection Protocols in an E. faecalis Biofilm Model—Using DAPI Staining and SEM
Maria Dede, Sabine Basche, Jörg Neunzehn, Martin Dannemann, Christian Hannig, Marie-Theres Kühne
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2023; 14(4): 176. CrossRef - Antibacterial Effect of Matricaria chamomilla L. Extract Against Enterococcus faecalis
Ariana Kameri, Arben Haziri, Zeqir Hashani, Agime Dragidella, Kemajl Kurteshi, Arsim Kurti
Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dentistry.2023; Volume 15: 13. CrossRef - Efficacy of Smear Layer Removal at the Apical One-Third of the Root Using Different Protocols of Erbium-Doped Yttrium Aluminium Garnet (Er:YAG) Laser
Amel Yousif Habshi, Nausheen Aga, Khadija Yousif Habshi, Muna Eisa Mohamed Hassan, Ziaullah Choudhry, Muhammad Adeel Ahmed, Azeem Ul Yaqin Syed, Rizwan Jouhar
Medicina.2023; 59(3): 433. CrossRef - Minimally invasive management of vital teeth requiring root canal therapy
E. Karatas, M. Hadis, W. M. Palin, M. R. Milward, S. A. Kuehne, J. Camilleri
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Functionalized surface of PLGA nanoparticles in thermosensitive gel to enhance the efficacy of antibiotics against antibiotic resistant infections in endodontics: A randomized clinical trial
Mona G. Arafa, Hadeel A. Mousa, Mohamed Medhat Kataia, Shehabeldin M., Nagia N. Afifi
International Journal of Pharmaceutics: X.2023; 6: 100219. CrossRef - Critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study removal of root filling materials
Mahdi A. Ajina, Pratik K. Shah, Bun San Chong
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S1): 119. CrossRef - TREATMENT OF PERIODONTITIS WITH INCLUSIVE ANTIFUNGAL DRUGS
Lyudmila Tatintsyan, Janna Khachatryan, Sona Ambartsumyan, Arsen Mikaelyan, Valery Tatintsyan, Minas Pogosyan, Anna Hakobyan, Arsen Kupelyan, Armen Shahinyan
BULLETIN OF STOMATOLOGY AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY.2022; : 15. CrossRef - Antimicrobial action of photodynamic therapy on Enterococcus faecalis biofilm using curing light, curcumin and riboflavin
Mahsa Moradi, Mahta Fazlyab, Maryam Pourhajibagher, Nasim Chiniforush
Australian Endodontic Journal.2022; 48(2): 274. CrossRef - Candida albicans and Enterococcus faecalis biofilm frenemies: When the relationship sours
Om Alkhir Alshanta, Khawlah Albashaireh, Emily McKloud, Christopher Delaney, Ryan Kean, William McLean, Gordon Ramage
Biofilm.2022; 4: 100072. CrossRef - Calcium hydroxide/iodoform nanoparticles as an intracanal filling medication: synthesis, characterization, and in vitro study using a bovine primary tooth model
Arturo Garrocho-Rangel, Diana María Escobar-García, Mariana Gutiérrez-Sánchez, Denisse Herrera-Badillo, Fernanda Carranco-Rodríguez, Juan Carlos Flores-Arriaga, Amaury Pozos-Guillén
Odontology.2021; 109(3): 687. CrossRef - Dentin Disinfection Efficacy Using Four Different Irrigation Protocols
David Jaramillo, Jose L Ibarrola, Ana Arias, Phillipe Sleiman, Ali Naji, David E Jaramillo
Dental Research and Management.2021; : 33. CrossRef - Histologic, Radiographic, and Micro-Computed Tomography Evaluation of Experimentally Enlarged Root Apices in Dog Teeth with Apical Periodontitis after Regenerative Treatment
Mohammed S. Alenazy, Saad Al-Nazhan, Hezekiah A Mosadomi
Current Therapeutic Research.2021; 94: 100620. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of dentin volume removal and centralization of the root canal after shaping with the ProTaper Universal, ProTaper Gold, and One-Curve instruments using micro-CT
Hatice Yalniz, Mehrdad Koohnavard, Aysenur Oncu, Berkan Celikten, Ayse Isil Orhan, Kaan Orhan
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2021; 15(1): 47. CrossRef - The influence of centrifugation and inoculation time on the number, distribution, and viability of intratubular bacteria and surface biofilm in deciduous and permanent bovine dentin
Viktoria A. Dezhurko-Korol, Nina E. Novozhilova, Irina M. Makeeva, Anastasia Yu. Arkhipova, Mihail M. Moisenovich, Ludmila V. Akhmadishina, Alexander N. Lukashev, Alexander M. Semenov, Maria R. Leontieva, Svetlana F. Byakova
Archives of Oral Biology.2020; 114: 104716. CrossRef - Antimicrobial efficacy of synthetic and natural-derived novel endodontic irrigating solution – An In vitro study
Thangi Sowjanya, Sudhakar Naidu, MahendraVarma Nadimpalli, GowtamDev Dondapati, TB V G Raju, ParvathaneniKrishna Prasad
Journal of the International Clinical Dental Research Organization.2020; 12(1): 21. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Antimicrobial Efficacy of Three Different Intracanal Medicaments against Candida albicans: An In Vitro Study
Ravi Vaiyapuri, Jambai S Sivakumar, Chittrarasu Mathimaraiselvan, Andamuthu Sivakumar, Anjaneya Shiva Prasad, Sasmitha Chandrasekaran
Journal of Operative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020; 5(2): 79. CrossRef - Assessment of Nitrofurantoin as an Experimental Intracanal Medicament in Endodontics
Mewan Salahalddin A. Alrahman, Bestoon Muhammed Faraj, Kawa F. Dizaye, Abdelwahab Omri
BioMed Research International.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Conjugate of chitosan nanoparticles with chloroaluminium phthalocyanine: Synthesis, characterization and photoinactivation of Streptococcus mutans biofilm
Leonardo Lobo Ribeiro Cavalcante, Antonio Claudio Tedesco, Luandra Aparecida Unten Takahashi, Fabiana Almeida Curylofo-Zotti, Aline Evangelista Souza-Gabriel, Silmara Aparecida Milori Corona
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2020; 30: 101709. CrossRef - Effect of triple antibiotic loaded apatitic nanocarriers on Enterococcus faecalis biofilm – An In vitro study
S. Nagarathinam, V. Sujatha, K. Madhumathi, S. Mahalaxmi, P.Pranav Vanajassun, T.S.Sampath Kumar
Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology.2019; 51: 499. CrossRef - Wear profile of canal wall surfaces and bond strength of endodontic sealers after in situ acid challenge
R. D. Silva‐Neto, M. D. Sousa‐Neto, J. D. Pécora, R. G. Palma‐Dibb, A. E. Souza‐Gabriel
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(3): 364. CrossRef - Bacterial invasion of dentinal tubules from the external root surface with and without an intact cemental layer- a confocal laser scanning microscopic study
Jovita D’souza, Sneha Gokhale, Vikram Padbidri, Lovely M
Advances in Tissue Engineering & Regenerative Medicine: Open Access.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - AgCa-PLGA submicron particles inhibit the growth and colonization of E. Faecalis and P. Gingivalis on dentin through infiltration into dentinal tubules
Wei Fan, Danfeng Liu, Yanyun Li, Qing Sun, Bing Fan
International Journal of Pharmaceutics.2018; 552(1-2): 206. CrossRef - Antimicrobial Photodynamic Therapy Associated with Conventional Endodontic Treatment: A Clinical and Molecular Microbiological Study
Caroline C. da Silva, Sérgio P. Chaves Júnior, Gabriela L. D. Pereira, Karla B. F. da C. Fontes, Lívia A. A. Antunes, Helvécio C. C. Póvoa, Leonardo S. Antunes, Natalia L. P. P. Iorio
Photochemistry and Photobiology.2018; 94(2): 351. CrossRef - Human teeth biobank: Microbiological analysis of the teeth storage solution
Fabiana Almeida Curylofo‐Zotti, Francine Lorencetti‐Silva, Jéssica de Almeida Coelho, Rachel Maciel Monteiro, Evandro Watanabe, Silmara Aparecida Milori Corona
Microscopy Research and Technique.2018; 81(3): 332. CrossRef - Regenerative Endodontics by Cell Homing
Ling He, Juan Zhong, Qimei Gong, Bin Cheng, Sahng G. Kim, Junqi Ling, Jeremy J. Mao
Dental Clinics of North America.2017; 61(1): 143. CrossRef - Regenerative Endodontics for Adult Patients
Ling He, Sahng G. Kim, Qimei Gong, Juan Zhong, Sainan Wang, Xuedong Zhou, Ling Ye, Junqi Ling, Jeremy J. Mao
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(9): S57. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Sealing Ability of Three Obturation Techniques Using a Glucose Leakage Test
Katarzyna Olczak, Halina Pawlicka
BioMed Research International.2017; 2017: 1. CrossRef - Enterococcus faecium and Enterococcus faecalis in endodontic infections: antibiotic resistance profile and susceptibility to photodynamic therapy
Ana Carolina Chipoletti Prado, Patrícia Pimentel De Barros, Jéssica Diane Dos Santos, Luciane Dias De Oliveira, Claudio Antônio Talge Carvalho, Marcia Carneiro Valera, Antonio Olavo Cardoso Jorge, Juliana Campos Junqueira
Lasers in Dental Science.2017; 1(2-4): 91. CrossRef - Study of invasion and colonization of E. faecalis in microtubes by a novel device
Xiaoqiang Sun, Shujing Wang, Yue Yang, Chunxiong Luo, Benxiang Hou
Biomedical Microdevices.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Nail Damage (Severe Onychodystrophy) Induced by Acrylate Glue: Scanning Electron Microscopy and Energy Dispersive X-Ray Investigations
Tudor Pinteala, Anca Eduard Chiriac, Irina Rosca, Francesca Larese Filon, Mariana Pinteala, Anca Chiriac, Cristian Podoleanu, Simona Stolnicu, Marius Florin Coros, Adina Coroaba
Skin Appendage Disorders.2016; 2(3-4): 137. CrossRef -
Phage therapy against
Enterococcus faecalis
in dental root canals
Leron Khalifa, Mor Shlezinger, Shaul Beyth, Yael Houri-Haddad, Shunit Coppenhagen-Glazer, Nurit Beyth, Ronen Hazan
Journal of Oral Microbiology.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical Approach of High Technology Techniques for Control and Elimination of Endodontic Microbiota
Nasim Chiniforush, Maryam Pourhajibagher, Sima Shahabi, Abbas Bahador
Journal of lasers in medical sciences.2015; 6(4): 139. CrossRef - Evaluation of penetration depth of 2% chlorhexidine digluconate into root dentinal tubules using confocal laser scanning microscope
Sekar Vadhana, Jothi Latha, Natanasabapathy Velmurugan
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(2): 149. CrossRef
- Capped silver nanoparticle penetration in primary dentition: an in vitro SEM-EDS analysis
- 2,366 View
- 29 Download
- 48 Crossref

- Comparative efficacy of photo-activated disinfection and calcium hydroxide for disinfection of remaining carious dentin in deep cavities: a clinical study
- Sidhartha Sharma, Ajay Logani, Naseem Shah
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(3):195-200. Published online June 26, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.3.195
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives To comparatively evaluate the efficacy of photo-activated disinfection (PAD), calcium hydroxide (CH) and their combination on the treatment outcome of indirect pulp treatment (IPT).
Materials and Methods Institutional ethical clearance and informed consent of the patients were taken. The study was also registered with clinical registry of India. Sixty permanent molars exhibiting deep occlusal carious lesion in patients with the age range of 18 - 22 yr were included. Clinical and radiographic evaluation and set inclusion and exclusion criteria's were followed. Gross caries excavation was accomplished. In group I (
n = 20) PAD was applied for sixty seconds. In group II (n = 20), CH was applied to the remaining carious dentin, while in group III (n = 20), PAD application was followed by CH placement. The teeth were permanently restored. They were clinically and radiographically followed-up at 45 day, 6 mon and 12 mon. Relative density of the remaining affected dentin was measured by 'Radiovisiography (RVG) densitometric' analysis.Results Successful outcome with an increase in radiographic grey values were observed in all three groups. However, on inter-group comparison, this change was not significant (
p > 0.05).Conclusions PAD and CH both have equal disinfection efficacy in the treatment of deep carious dentin. PAD alone is as effective for treatment of deep carious lesion as calcium hydroxide and hence can be used as an alternative to CH. They can be used independently in IPT, since combining both does not offer any additional therapeutic benefits.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical and Radiographic Evaluation between Conventional Mineral Trioxide Aggregate and Gel-based Mineral Trioxide Aggregate in Indirect Pulp Therapy: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Yusuf Chunawala, BK Vanishree, Supriya S Dighe, Rooposhi Saha
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2025; 17(12): 1383. CrossRef - Potentialities of photoactivated disinfection in dentistry
E.I. Utkina, M.A. Gorbatova, A.M. Grjibovski, L.N. Gorbatova, A.A. Simakova
Stomatology.2023; 102(2): 84. CrossRef - Clinical and radiographic evaluation of diode laser and chemical disinfection in comparison to selective caries removal in management of patients with deep carious lesions
Mohamed Bahgat AbdelHamid, Ahmed Fawzy Abo Elezz, Ola M. Ibrahim Fahmy
Lasers in Dental Science.2022; 6(4): 219. CrossRef - Commercially Available Ion-Releasing Dental Materials and Cavitated Carious Lesions: Clinical Treatment Options
Amel Slimani, Salvatore Sauro, Patricia Gatón Hernández, Sevil Gurgan, Lezize Sebnem Turkun, Ivana Miletic, Avijit Banerjee, Hervé Tassery
Materials.2021; 14(21): 6272. CrossRef - Radiological Appraisal of Biodentine and Pulpotec Individually or in Combination with Photo-activated Disinfection as Pulp-capping Cements in Mature Teeth
Pratik Agrawal, Gaurav Patri, Surabhi Soumya, Prasanti K Pradhan, Vijeta Patri
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2021; 22(9): 1014. CrossRef - Clinical and radiographic evaluation of indirect pulp treatment of young permanent molars using photo-activated oral disinfection versus calcium hydroxide: a randomized controlled pilot trial
Marwa Aly Elchaghaby, Dalia Mohamed Moheb, Osama Ibrahim El Shahawy, Ahmed Mohamed Abd Alsamad, Mervat Abdel Moniem Rashed
BDJ Open.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Guidelines for the selection, use, and maintenance of LED light-curing units - Part 1
A. C. Shortall, R. B. Price, L. MacKenzie, F. J. T. Burke
British Dental Journal.2016; 221(8): 453. CrossRef
- Clinical and Radiographic Evaluation between Conventional Mineral Trioxide Aggregate and Gel-based Mineral Trioxide Aggregate in Indirect Pulp Therapy: A Randomized Clinical Trial
- 1,657 View
- 4 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Mental nerve paresthesia secondary to initiation of endodontic therapy: a case report
- Syed Mukhtar-Un-Nisar Andrabi, Sharique Alam, Afaf Zia, Masood Hasan Khan, Ashok Kumar
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(3):215-219. Published online May 8, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.3.215
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Whenever endodontic therapy is performed on mandibular posterior teeth, damage to the inferior alveolar nerve or any of its branches is possible. Acute periapical infection in mandibular posterior teeth may also sometimes disturb the normal functioning of the inferior alveolar nerve. The most common clinical manifestation of these insults is the paresthesia of the inferior alveolar nerve or mental nerve paresthesia. Paresthesia usually manifests as burning, prickling, tingling, numbness, itching or any deviation from normal sensation. Altered sensation and pain in the involved areas may interfere with speaking, eating, drinking, shaving, tooth brushing and other events of social interaction which will have a disturbing impact on the patient. Paresthesia can be short term, long term or even permanent. The duration of the paresthesia depends upon the extent of the nerve damage or persistence of the etiology. Permanent paresthesia is the result of nerve trunk laceration or actual total nerve damage. Paresthesia must be treated as soon as diagnosed to have better treatment outcomes. The present paper describes a case of mental nerve paresthesia arising after the start of the endodontic therapy in left mandibular first molar which was managed successfully by conservative treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evolving Paradigms in the Management of Trigeminal Nerve Injuries Post Oral Surgery: A Comprehensive Narrative Review
Saanvi Tank, Amit Patil, Tejal Patil, Minal M Kshirsagar, Aarti S Bedia, Sanpreet S Sachdev, Vyshnavi Mundada
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Separated Surgical Instrument During the Extraction of a Third Molar: A Case Report
Abdulaziz A Mahdi, Abdullah I Alkharji, Safa A Alburayh, Bader A Fatani, Osama A Alharbi
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Treatment of paresthesia induced by periapical lesions: a case report
Hyo Jin Jo, Jung-Hong Ha
Journal of Dental Rehabilitation and Applied Science.2024; 40(4): 305. CrossRef - İMPLANT CERRAHİSİ SONRASI HİPOESTEZİ-6 AYLIK TAKİP: VAKA SERİSİ
Sefa AYDINDOĞAN, Emine Elif MUTAFCİLAR VELİOĞLU, Yunus Emre BALABAN
Selcuk Dental Journal.2023; 10(4): 350. CrossRef - Mental Nerve Paraesthesia: A Report of Two Cases Associated with Endodontic Etiology
Neeta Patel, Akshayraj Langaliya, Shikha Kanodia, Aravind Kumbhar, Aastha Buch, Aarshvi Shah, Himani Bhatt, Drashti Panchal, Sharan Shah, Jinali Shah, Darko Macan
Case Reports in Dentistry.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Anatomic Danger Zones of the Head and Neck
Guy Talmor, Andy Trang, Omeed Ahadiat, Boris Paskhover, Ashley Wysong
Dermatologic Surgery.2020; 46(12): 1549. CrossRef - The anatomical relationship between the roots of erupted permanent teeth and the mandibular canal: a systematic review
Michał Puciło, Mariusz Lipski, Magdalena Sroczyk-Jaszczyńska, Aleksandra Puciło, Alicja Nowicka
Surgical and Radiologic Anatomy.2020; 42(5): 529. CrossRef - Endodontic-related inferior alveolar nerve injuries: A review and a therapeutic flow chart
R. Castro, M. Guivarc'h, J.M. Foletti, J.H. Catherine, C. Chossegros, L. Guyot
Journal of Stomatology, Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.2018; 119(5): 412. CrossRef - Neuropathy of Trigeminal Nerve Branches After Oral and Maxillofacial Treatment
Jimoh Olubanwo Agbaje, Elke Van de Casteele, Marjolein Hiel, Ciska Verbaanderd, Ivo Lambrichts, Constantinus Politis
Journal of Maxillofacial and Oral Surgery.2016; 15(3): 321. CrossRef - Facial nerve paralysis following endodontic treatment of lower first molar
Umut Demetoglu, Gokhan Ozkan, Hasan Onur Simsek
Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Medicine, and Pathology.2016; 28(3): 267. CrossRef - Broken Endodontic Instrument Caused Inferior Alveolar Nerve Paraesthesia: A Case Report.
M. Ozbek Selcuk, Kaman Süleyman, Ozgur Demiralp Kemal
Journal of Dentistry And Oral Implants.2016; 1(1): 21. CrossRef
- Evolving Paradigms in the Management of Trigeminal Nerve Injuries Post Oral Surgery: A Comprehensive Narrative Review
- 3,270 View
- 17 Download
- 11 Crossref

- Effect of infection control barrier thickness on light curing units
- Hoon-Sang Chang, Seok-Ryun Lee, Sung-Ok Hong, Hyun-Wook Ryu, Chang-Kyu Song, Kyung-San Min
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(5):368-373. Published online September 30, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.5.368
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study investigated the effect of infection control barrier thickness on power density, wavelength, and light diffusion of light curing units.
Materials and Methods Infection control barrier (Cleanwrap) in one-fold, two-fold, four-fold, and eight-fold, and a halogen light curing unit (Optilux 360) and a light emitting diode (LED) light curing unit (Elipar FreeLight 2) were used in this study. Power density of light curing units with infection control barriers covering the fiberoptic bundle was measured with a hand held dental radiometer (Cure Rite). Wavelength of light curing units fixed on a custom made optical breadboard was measured with a portable spectroradiometer (CS-1000). Light diffusion of light curing units was photographed with DSLR (Nikon D70s) as above.
Results Power density decreased significantly as the layer thickness of the infection control barrier increased, except the one-fold and two-fold in halogen light curing unit. Especially, when the barrier was four-fold and more in the halogen light curing unit, the decrease of power density was more prominent. The wavelength of light curing units was not affected by the barriers and almost no change was detected in the peak wavelength. Light diffusion of LED light curing unit was not affected by barriers, however, halogen light curing unit showed decrease in light diffusion angle when the barrier was four-fold and statistically different decrease when the barrier was eight-fold (
p < 0.05).Conclusions It could be assumed that the infection control barriers should be used as two-fold rather than one-fold to prevent tearing of the barriers and subsequent cross contamination between the patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Light curing infection control barriers: do some types jeopardize the concept of conventional bulk-fill composites?
Dalia I. Sherief, Mohamed M. Kandil, Dina Ahmed El-Refai
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Infection Control Barriers on Light Output from a Dental Light-Curing Unit Used in Various Positions
Jitte van der Zee, Andrew Tawse-Smith, Sunyoung Ma
Oral.2023; 3(2): 166. CrossRef - Evaluation of irradiance and spectral output of visible light curing units used in the laboratory
Yoorina Choi, Su-Beom Choi, Ji-Hye Jung, Hoon-Sang Chang
Oral Biology Research.2021; 45(4): 201. CrossRef - The Effectiveness of Clinical Sterilization Methods in Dental Air/water Syringes
Seyoung Shin, Yeonmi Yang, Miah Kim, Jaegon Kim, Byeongju Baik
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2013; 40(4): 268. CrossRef - Power density of various light curing units through resin inlays with modified layer thickness
Sung-Ok Hong, Yonghui Oh, Jeong-Bum Min, Jin-Woo Kim, Bin-Na Lee, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Hoon-Sang Chang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(3): 130. CrossRef - Effect of a multi-layer infection control barrier on the micro-hardness of a composite resin
In-Nam Hwang, Sung-Ok Hong, Bin-Na Lee, Yun-Chan Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Hoon-Sang Chang
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2012; 20(5): 576. CrossRef
- Light curing infection control barriers: do some types jeopardize the concept of conventional bulk-fill composites?
- 1,150 View
- 3 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Distribution of oral pathogens in infections of endodontic origin
- Seung-Yoon Kim, Ho-Young Choi, Sang-Hyuk Park, Gi-Woon Choi
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2003;28(4):303-313. Published online July 31, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.4.303
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub It has been documented that periodontopathic bacteria are also implicated in endodontic infections. 16S rDNA gene-directed PCR was to examine the prevalence of periodontopathic bacteria including
Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans (Aa ),Prevotella intermedia (Pi ),Prevotella nigrescens (Pn ),Porphyromonas gingivalis (Pg ),Porphyromonas endodontalis (Pe ), andTreponema denticola (Td ) in the root canals of 36 endodontically infected teeth having apical lesions with or without clinical symptoms like pain, swelling, and fistula.In 36 infected root canals, most frequently detected bacterial species was
Pg (61.1%), followed byTd (52.8%) andPe (38.9%).Of 36 infected root canals,
Aa was detected in 6 canals (16.7%) of the teeth, all of which showed clinical symptoms.Of 36 infected root canals,
Pi andPn were found in 4 (13.9%) and 5 (33.3%), respectively. Notably, prevalence ofPn in the symptomatic teeth was 50.0%.One of black-pigmented anaerobic bacteria (BPB) including
Pi ,Pn ,Pe , andPg was detected in all of the teeth that showed pain or especially swelling but not fistula. It was, however, found that prevalence of BPB in the asymptomatic teeth or the teeth with fistula was only 40%.Pe andPg were detected in the teeth regardless of the presence or absence of symptoms.Td was detected in the teeth regardless of the presence or absence of symptoms.High prevalence of BPB in the symptomatic teeth but low in the asymptomatic teeth suggests that BPB may play an important role in the pathogenesis of periapical lesions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Isolation of Propionibacterium acnes among the microbiota of primary endodontic infections with and without intraoral communication
Sadia Ambreen Niazi, Hana Suleiman Al Kharusi, Shanon Patel, Kenneth Bruce, David Beighton, Federico Foschi, Francesco Mannocci
Clinical Oral Investigations.2016; 20(8): 2149. CrossRef - Antimicrobial Activity of Isothiocyanates (ITCs) Extracted from Horseradish (Armoracia rusticana) Root against Oral Microorganisms
HO-WON PARK, KYU-DUCK CHOI, IL-SHIK SHIN
Biocontrol Science.2013; 18(3): 163. CrossRef - Microbial profile of asymptomatic and symptomatic teeth with primary endodontic infections by pyrosequencing
Sang-Min Lim, Tae-Kwon Lee, Eun-Jeong Kim, Jun-Hong Park, Yoon Lee, Kwang-Shik Bae, Kee-Yeon Kum
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(6): 498. CrossRef
- Isolation of Propionibacterium acnes among the microbiota of primary endodontic infections with and without intraoral communication
- 1,336 View
- 2 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Identification of putative pathogens in acute endodontic infections by PCR based on 16S rDNA
- Jee-Hoon Kim, So Young Yoo, Sun-A Lim, Joong-Ki Kook, Sang-Soo Lim, Seul-Hee Park, Ho-Keel Hwang
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2003;28(2):178-183. Published online March 31, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.2.178
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to investigate the frequency of 7 putative pathogens in endodontic infections. The specimens were collected from infected pulpal tissue of patients who were referred for root canal treatment to the department of conservative dentistry, Chosun University. Samples were collected aseptically using a barbed broach and a paper point. The cut barbed broaches and paper points were transferred to an eppendorf tube containing 500 ml of 1 X PBS. DNAs were extracted from the samples by direct DNA extraction method using lysis buffer (0.5% EDTA, 1% Triton X-100). Identification of 7 putative pathogens was performed by PCR based on 16S rDNA. The target species were as follows:
Porphyromonas endodontalis ,Porphyromonas gingivalis ,Prevotella intermedia ,Prevotella nigrescens ,Bacteroides forsythus ,Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans , andTreponema denticola . Our data revealed that the prevalence ofP. endodontalis was found in 88.6% (39/54),P. gingivalis 52.3% (23/44),P. nigrescens 18.2% (8/44),P. intermedia 15.9% (7/44),B. forsythus 18.2% (8/44),A. actinomycetemcomitans 2.3% (1/44),T. denticola 25% (11/44) of the samples. The high prevalence ofP. endodontalis andP. gingivalis suggests that they may play an important role in the etiology of endodontic infections.
- 915 View
- 0 Download


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


