Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Marginal adaptation of three root-end filling materials in cavities prepared with laser and ultrasonic tips: an in vitro comparative study
- Busra Zengin, Seda Aydemir, Nicholas Paul Chandler
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(4):e32. Published online September 9, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e32

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
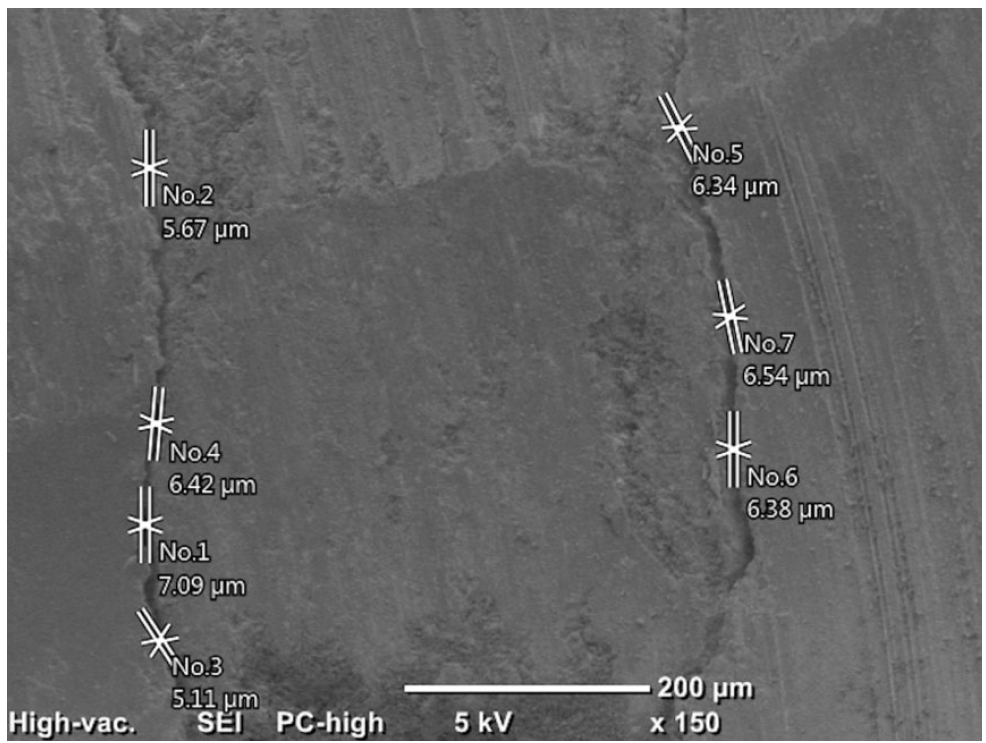
This study evaluated the marginal adaptation of ProRoot MTA (Dentsply Tulsa Dental), Biodentine (Septodont), and TotalFill BC RRM (FKG) placed in root-end cavities prepared with ultrasonic or Er,Cr:YSGG laser tips, using scanning electron microscopy.
Methods
The canals of 90 extracted maxillary central incisors were prepared and obturated and their roots resected. Six groups of 15 specimens were allocated as follows: ultrasonic + ProRoot MTA, ultrasonic + Biodentine, ultrasonic + TotalFill, laser + ProRoot MTA, laser + Biodentine, and laser + TotalFill. Roots were sectioned longitudinally to expose the filling material. Apical and coronal micrographs were taken, and the greatest distance between dentin and filling material was measured. The total gap area was also calculated using further micrographs.
Results
Cavities prepared with the ultrasonic tips and filled with Biodentine showed significantly greater gap dimensions compared with TotalFill (p < 0.001) and ProRoot MTA (p = 0.007) in the apical region. The ultrasonic group showed significantly higher void values compared to the laser group for ProRoot MTA (p = 0.026), when comparing the total values of void. The Biodentine group was significantly higher than the TotalFill group in root-end cavities prepared with ultrasonic tips (p < 0.001). The Biodentine group was significantly higher than the ProRoot MTA group in root-end cavities prepared with the laser tip (p = 0.002).
Conclusions
Under the conditions of this study, it was determined that the root-end cavity preparation technique had an effect on the amount of gaps formed between the dentin and the three filling materials. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Marginal Adaptability of Harvard MTA and Biodentine Used as Root-End Filling Material: A Comparative SEM Study
Yaneta Kouzmanova, Ivanka Dimitrova
Materials.2025; 18(19): 4598. CrossRef
- Marginal Adaptability of Harvard MTA and Biodentine Used as Root-End Filling Material: A Comparative SEM Study
- 2,988 View
- 250 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

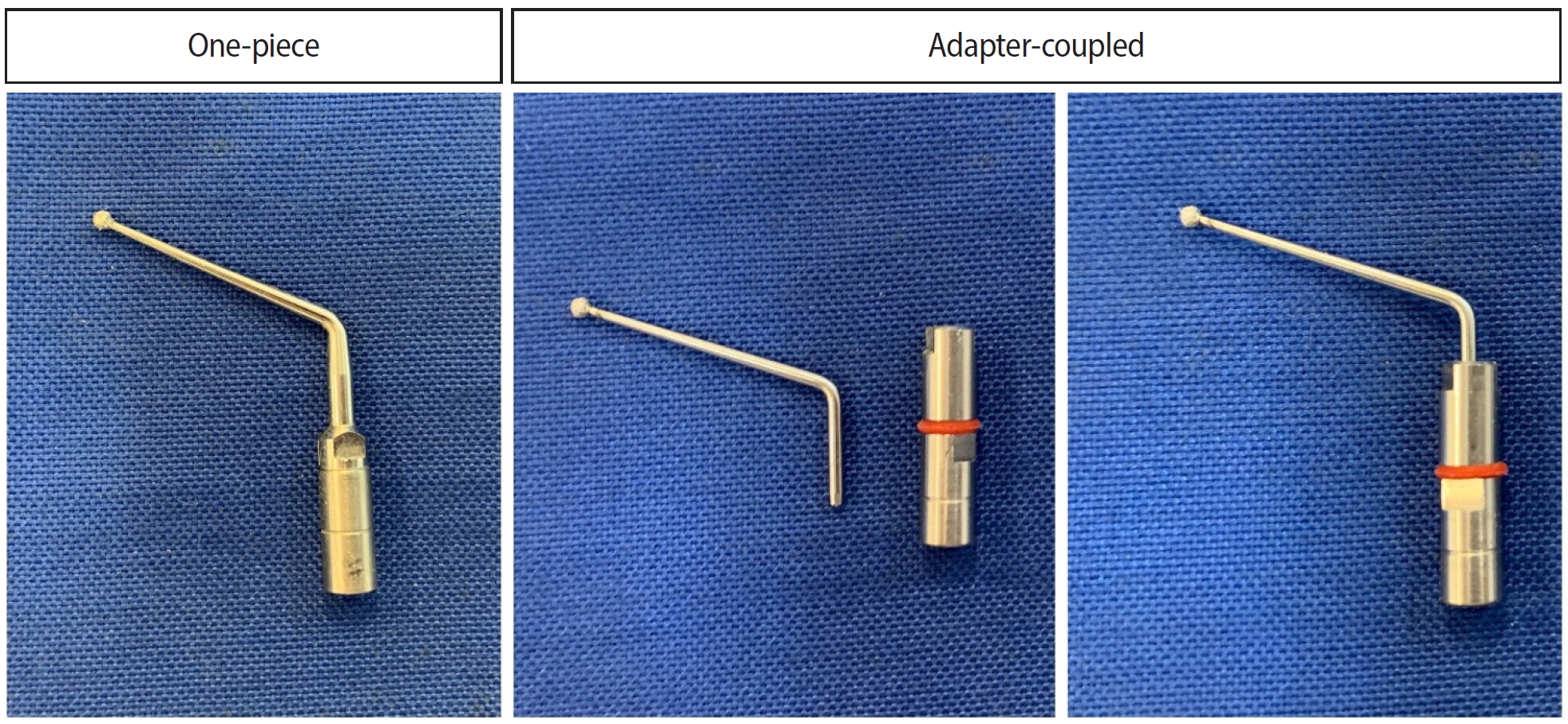
- Analysis of thermal profiles on tooth structure and insert during one-piece or adapter-coupled ultrasonic insert use: an in vitro experimental study
- Gabriela Loewen Brotto, Bruno Monguilhott Crozeta, Bruno Marques-da-Silva, Alysson Nunes Diógenes, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva, Flávia Sens Fagundes Tomazinho
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(3):e24. Published online July 11, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e24
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This in vitro study aimed to evaluate temperature variation on the external surface of mandibular molars and within ultrasonic inserts when using adapter-coupled versus one-piece inserts.
Methods
Twenty-four extracted human mandibular molars were divided into two groups based on the type of ultrasonic insert used: adapter-coupled and one-piece inserts. Temperature on the external surface of each tooth was measured with a thermocouple probe positioned in the furcation area, capturing data continuously. The temperature of the ultrasonic inserts was monitored in real-time using a thermal imaging camera. Measurements were taken in a controlled environment without cooling for over 120 seconds. Statistical analysis was conducted using analysis of variance (ANOVA) and two-way ANOVA with repeated measures to evaluate temperature variations between groups and over time, with significance set at 5%.
Results
In the external tooth surface temperature measurements, no significant differences were observed between the groups during the initial 15 seconds (p = 0.185) and 30 seconds (p = 0.067). However, significant differences emerged at 60 seconds (p = 0.025), 90 seconds (p = 0.024), and 120 seconds (p = 0.020), with the one-piece insert group demonstrating higher temperatures in the furcation region. Thermal imaging of the inserts revealed a significant difference at all time points (p < 0.001), with adapter-coupled inserts showing greater heating.
Conclusions
The use of ultrasonic inserts leads to a gradual rise in temperature on the external tooth surface. One-piece inserts generated higher temperatures on the tooth, while adapter-coupled inserts exhibited greater heating within the insert.
- 1,816 View
- 96 Download

- Pattern of endodontic instrument separation and factors affecting its retrieval: a 10-year retrospective observational study in a postgraduate institute
- Velmurugan Natanasabapathy, Aswathi Varghese, Paul Kevin Abishek Karthikeyan, Srinivasan Narasimhan
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(1):e7. Published online February 19, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e7
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study aimed to assess the pattern of endodontic instrument separation, their retrievability, and factors affecting its retrieval, in a postgraduate institute.
Methods
Cases referred for the management of separated endodontic instruments (SEI) from 2013 to 2023 were considered for this study. Data related to demographics, tooth type, file type, and retrieval were documented in an Excel sheet. Eight prognostic factors assumed to influence the retrieval were analyzed in this study. The secondary aim was to compare the pattern of SEI and retrievability between conventional nickel-titanium files and newer generation heat-treated nickel-titanium files. Retrieval was attempted by a senior endodontist under the dental operating microscope. Various ultrasonic tips and a Broken Tool Removal loop system were used during retrieval. Simple descriptive statistics were performed. Binomial logistic regression was done to identify the effect of the eight prognostic factors on the retrieval outcome.
Results
A total of 190 SEI was reported. SEI occurred more often in posterior teeth than anterior teeth, mandibular arch than maxillary arch, and in larger files than smaller files. Separation occurred more often in the apical third compared to the other levels. Retrieval was attempted in 88 cases and successful in 70 cases (79.5%). The larger taper and apical position of the SEI negatively influenced the retrieval by 1.4 and 8.7 times, respectively.
Conclusions
Retrieval of SEI was successful in the majority of the cases. An increase in taper and apically placed SEI negatively impacted the retrieval. There was no difference in the pattern of separation nor retrievability between conventional nickel-titanium files and newer generation heat-treated nickel-titanium files. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk Factors for Failure of Separated Instrument Removal: A Systematic Review and Meta‐Analysis
Le Zhao, WangYu Luo, Yue Shen, WanNing Yu, Liu Yang, Xiaolei Zhang
Australian Endodontic Journal.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of microscope-assisted root canal treatment in permanent posterior teeth: A retrospective cohort study
Ya-Ching Chang, Ting-Ya Wang
Journal of Dentistry.2025; 157: 105771. CrossRef - Deep Learning-Based Detection of Separated Root Canal Instruments in Panoramic Radiographs Using a U2-Net Architecture
Nildem İnönü, Umut Aksoy, Dilan Kırmızı, Seçil Aksoy, Nurullah Akkaya, Kaan Orhan
Diagnostics.2025; 15(14): 1744. CrossRef - MANAGEMENT OF INTRACANAL SEPARATED INSTRUMENTS: FACTORS CONTRIBUTING TO ENDODONTIC FILE SEPARATION — A NARRATIVE REVIEW
Tareq Hajaj, Paul Freiman , Serban Talpos Niculescu , Mihai Rominu , Tiberiu Hosszu , Ioana Veja
Romanian Journal of Oral Rehabilitation.2025; 17(2): 993. CrossRef
- Risk Factors for Failure of Separated Instrument Removal: A Systematic Review and Meta‐Analysis
- 7,763 View
- 368 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Comparative evaluation of the effectiveness of ultrasonic tips versus the Terauchi file retrieval kit for the removal of separated endodontic instruments
- Preeti Jain Pruthi, Ruchika Roongta Nawal, Sangeeta Talwar, Mahesh Verma
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(2):e14. Published online February 6, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e14
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objective The aim of this study was to perform a comparative evaluation of the effectiveness of ultrasonic tips versus the Terauchi file retrieval kit (TFRK) for the removal of broken endodontic instruments.
Materials and Methods A total of 80 extracted human first mandibular molars with moderate root canal curvature were selected. Following access cavity preparation canal patency was established with a size 10/15 K-file in the mesiobuccal canals of all teeth. The teeth were divided into 2 groups of 40 teeth each: the P group (ProUltra tips) and the T group (TFRK). Each group was further subdivided into 2 smaller groups of 20 teeth each according to whether ProTaper F1 rotary instruments were fractured in either the coronal third (C constituting the PC and TC groups) or the middle third (M constituting the PM and TM groups). Instrument retrieval was performed using either ProUltra tips or the TFRK.
Results The overall success rate at removing the separated instrument was 90% in group P and 95% in group T (
p > 0.05) The mean time for instrument removal was higher with the ultrasonic tips than with the TFRK (p > 0.05).Conclusion Both systems are acceptable clinical tools for instrument retrieval but the loop device in the TFRK requires slightly more dexterity than is needed for the ProUltra tips.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative evaluation of success rate and operator variability in loop.based versus ultrasonic retrieval of fractured endodontic instruments: An ex vivo study
Tanushree Saxena, Vivek Devidas Mahale, Manish Ranjan, Sanyuta Singh, E. Aparna Mohan, M. Hema
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2026; 16(1): 73. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of time efficiency and dentin preservation in ultrasonic versus loop retrieval of separated endodontic files: An ex vivo study with pilot nano-computed tomography analysis
Tanushree Saxena, Vivek Devidas Mahale, Manish Ranjan, M. Hema, Sanyukta Singh, E. Aparna Mohan
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2026; 16(1): 90. CrossRef - Comparison of the pull-out force of different microtube-based methods in fractured endodontic instrument removal: An in-vitro study
Nasim Hashemi, Mohsen Aminsobhani, Mohammad Javad Kharazifard, Fatemeh Hamidzadeh, Pegah Sarraf
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Fracture resistance and volumetric dentin change after management of broken instrument using static navigation – An in vitro study
Shady Atef Adeeb Yassa, Mohamed Nabeel, Ahmed M. Ghobashy, Moataz B. Alkhawas
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(4): 319. CrossRef - Remoção de instrumento fraturado com a técnica do laço: relato de caso
Larissa Sousa Rangel, Ryhan Menezes Cardoso, Thayane Kelly Trajano da Silva, Robeci Alves Macêdo Filho, Andressa Cartaxo de Almeida, Mariana Camilly Tavares Ferreira, Thalles Gabriel Germano Lima, Diana Santana de Albuquerque
Caderno Pedagógico.2025; 22(7): e16332. CrossRef - Would It Necessarily Require Retrieving Endodontic Files on Every Instance? Implementing Separated Files with the Bypass Technique: Report of Three Cases
Mohit S. Zarekar, Apurva S. Satpute, Mohini S. Zarekar
Journal of Primary Care Dentistry and Oral Health.2025; 6(2): 118. CrossRef - Novel electromagnetic device to retrieve fractured stainless steel endodontic files: an in-vitro investigation
Ashraf Mohammed Alhumaidi, Mubashir Baig Mirza, Ahmed A. Alelyani, Raid A. Almnea, Amal S. Shaiban, Ahmed Altuwalah, Riyadh Alroomy, Ahmed Abdullah Al Malwi, Ahmad Jabali, Mohammed M. Al Moaleem
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficiency of Root Canal Treatment Using Loops While Endodontic Treatment: A Clinical Study
Chitharanjan Shetty, Kodithala Sravya, Abhilasha Bhawalkar, Alok Dubey, Tejaswi Kala, Prachi Sethy
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2025; 17(Suppl 5): S3735. CrossRef - Efficiency of fractured file retrieval according to different nickel-titanium alloys and fragment lengths
Joon Hyuk Yoon, Yoshitsugu Terauchi, Jae-Hoon Kim, Sang Won Kwak, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Broken Instrument Removal Methods with a Minireview of the Literature
Mohsen Aminsobhani, Nasim Hashemi, Fatemeh Hamidzadeh, Pegah Sarraf, Giovanni Mergoni
Case Reports in Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comprehensive Assessment of Cyclic Fatigue Strength in Five Multiple-File Nickel–Titanium Endodontic Systems
Jorge N. R. Martins, Emmanuel J. N. L. Silva, Duarte Marques, Francisco M. Braz Fernandes, Marco A. Versiani
Materials.2024; 17(10): 2345. CrossRef - Management of an Intracanal Separated Instrument in the Lower Right First Molar: A Case Report
Pratik Rathod, Aditya Patel, Anuja Ikhar, Manoj Chandak, Joyeeta Mahapatra, Tejas Suryawanshi, Jay Patil, Priti Mahale
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictive factors in the retrieval of endodontic instruments: the relationship between the fragment length and location
Ricardo Portigliatti, Eugenia Pilar Consoli Lizzi, Pablo Alejandro Rodríguez
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of two instrument retrieval techniques in removing separated rotary and reciprocating nickel-titanium files in mandibular molars – An in vitro study
S. Jitesh, Smita Surendran, Velmurugan Natanasabapathy
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(12): 1240. CrossRef - Effect of Heat Treatment on Mechanical Properties of Nickel-Titanium Instruments
Eunmi Kim, Jung-Hong Ha, Samuel O. Dorn, Ya Shen, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Sang Won Kwak
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(2): 213. CrossRef - Efficacy of instrument removal techniques in root canal treatment: a literature review
Rómulo Guillermo López Torres, Jairo Romario Moreno Ochoa, Verónica Alejandra Salame Ortiz
Salud, Ciencia y Tecnología - Serie de Conferencias.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of the HBW Ultrasonic Ring for retrieval of fragmented manual or rotatory instruments
Jennifer Galván-Pacheco, Verónica Méndez-González, Ana González-Amaro, Heriberto Bujanda-Wong, Amaury Pozos-Guillén, Arturo Garrocho-Rangel
Journal of Oral Science.2023; 65(4): 278. CrossRef - Retrieving Fragments
Swayangprabha Sarangi, Manoj Ghanshyamdasji Chandak, Kajol Naresh Relan, Payal Sandeep Chaudhari, Pooja Chandak, Anuja Ikhar
Journal of Datta Meghe Institute of Medical Sciences University.2022; 17(2): 429. CrossRef - A novel approach for retrieval of separated endodontic instrument: Two case reports
Tanvi Kohli, Syed Shahid Hilal
IP Indian Journal of Conservative and Endodontics.2022; 7(3): 143. CrossRef - A novel endodontic extractor needle for separated instrument retrieval
Saaid Al Shehadat, Colin Alexander Murray, Sunaina Shetty Yadadi
Advances in Biomedical and Health Sciences.2022; 1(2): 116. CrossRef - Present status and future directions: Removal of fractured instruments
Yoshi Terauchi, Wagih Tarek Ali, Mohamed Mohsen Abielhassan
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S3): 685. CrossRef - Ultrasonic Use in Endodontic Management Approach, Review Article
Bakheet Mohammed Al-Ghannam, Khalid Abdulmohsen Almuhrij, Rund Talal Basfar, Raghad Omar Alamoudi, Aseel Mohammed Alqahtani, Ahmed Atef Sait, Ahmed Loay Ghannam, Sultan Khalid Abdoun
World Journal of Environmental Biosciences.2021; 10(1): 61. CrossRef - The Time Taken for Retrieval of Separated Instrument and the Change in Root Canal Volume after Two Different Techniques Using Cbct
Balu Santhosh Kumar, Sridevi Krishnamoorthy, Sandhya Shanmugam, Angambakkam Rajasekharan PradeepKumar
Indian Journal of Dental Research.2021; 32(4): 489. CrossRef
- Comparative evaluation of success rate and operator variability in loop.based versus ultrasonic retrieval of fractured endodontic instruments: An ex vivo study
- 4,074 View
- 119 Download
- 23 Crossref

- Effect of ultrasonic agitation on push-out bond strength and adaptation of root-end filling materials
- Murilo Priori Alcalde, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, Marina Angélica Marciano, Jussaro Alves Duque, Samuel Lucas Fernandes, Mariana Bailo Rosseto, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(2):e23. Published online April 27, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e23
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the effect of ultrasonic agitation of mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA), calcium silicate-based cement (CSC), and Sealer 26 (S26) on adaptation at the cement/dentin interface and push-out bond strength.
Materials and Methods Sixty maxillary canines were divided into 6 groups (
n = 10): MTA, S26, and CSC, with or without ultrasonic activation (US). After obturation, the apical portions of the teeth were sectioned, and retrograde cavities were prepared and filled with cement by hand condensation. In the US groups, the cement was activated for 60 seconds: 30 seconds in the mesio-distal direction and 30 seconds in the buccal-lingual direction, using a mini Irrisonic insert coupled with the ultrasound transducer. After the materials set, 1.5-mm thick sections were obtained from the apexes. The presence of gaps and the bond between cement and dentin were analyzed using low-vacuum scanning electron microscopy. Push-out bond strength was measured using a universal testing machine.Results Ultrasonic agitation increased the interfacial adaptation of the cements. The S26 US group showed a higher adaptation value than MTA (
p < 0.05). US improved the push-out bond strength for all the cements (p < 0.05).Conclusions The US of retrograde filling cements enhanced the bond to the dentin wall of the root-end filling materials tested.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of ultrasonic activation on setting time, pH and calcium ion release, solubility, and chemical structure of calcium silicate sealers
Simone Argenta Scalabrin, Lina Naomi Hashizume, Theodoro Weissheimer, Gabriel Barcelos Só, Jefferson Ricardo Pereira, Milton Carlos Kuga, Ricardo Abreu da Rosa, Marcus Vinicius Reis Só
Brazilian Dental Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of different disinfection protocols on the bond strength of NeoMTA 2 bioceramic sealer used as a root canal apical plug (in vitro study)
Nada Omar, Nihal Refaat Kabel, Muhammad Abbass Masoud, Tamer M. Hamdy
BDJ Open.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Endo-Z bur or Bladesonic ultrasonic tip on the adaptation of filling material. A micro-CT study
Pedro Henrique Fiorin de Souza, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Jáder Camilo Pinto, Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mário Tanomaru-Filho
Brazilian Dental Journal.2023; 34(5): 29. CrossRef - Effect of Different Mixing Methods on Physicochemical Properties of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate: A Systematic Review
Amin Salem Milani, Faraz Radmand, Behrad Rahbani, Mahdi Hadilou, Farnaz Haji Abbas Oghli, Fatemeh Salehnia, Milad Baseri, Stefano Pagano
International Journal of Dentistry.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Micro-CT comparative evaluation of porosity and dentin adaptation of root end filling materials applied with incremental, bulk, and ultrasonic activation techniques
Berkan Celikten, Aysenur Oncu, Mehrdad Koohnavard, Mert Ocak, Kaan Orhan
Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part H: Journal of Engineering in Medicine.2022; 236(8): 1209. CrossRef - Effect of ultrasonic activation of the adhesive system on dentin tubule penetration and the pushout bond strength of fiber posts
Isabel Verdum, Igor Abreu de Bem, Pedro Henrique Marks Duarte, Lucas Silveira Machado, Jefferson Ricardo Pereira, Marcus Vinícius Reis Só, Ricardo Abreu da Rosa
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2022; 127(2): 295. CrossRef - Influence of Ultrasonic Activation on the Physicochemical Properties of Calcium Silicate-Based Cements
Fredson Márcio Acris De Carvalho, Yara Teresinha Corrêa Silva-Sousa, Carlos Eduardo Saraiva Miranda, Paulo Henrique Miller Calderon, Ana Flávia Simões Barbosa, Luciana Martins Domingues De Macedo, Fuad Jacob Abi Rached-Junior, Boonlert Kukiattrakoon
International Journal of Dentistry.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of the flow and filling ability of endodontic materials using different test models
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Gisselle Moraima Chavez-Andrade, Jader Camilo Pinto, Fábio Luiz Camargo Villela Berbert, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Dental discoloration caused by Grey-MTAFlow cement: analysis of its physicochemical, biological and antimicrobial properties
Lauter Eston PELEPENKO, Flávia SAAVEDRA, Gabriela Fernanda BOMBARDA, Brenda Paula Figueiredo de Almeida GOMES, Adriana DE-JESUS-SOARES, Alexandre Augusto ZAIA, Marco Antonio Hungaro DUARTE, Mario TANOMARU-FILHO, Marina Angélica MARCIANO
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Ultrasonic Activation of Endodontic Sealers on Intratubular Penetration and Bond Strength to Root Dentin
Igor Abreu De Bem, Renata Aqel de Oliveira, Theodoro Weissheimer, Carlos Alexandre Souza Bier, Marcus Vinícius Reis Só, Ricardo Abreu da Rosa
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(9): 1302. CrossRef
- Effect of ultrasonic activation on setting time, pH and calcium ion release, solubility, and chemical structure of calcium silicate sealers
- 1,707 View
- 12 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Smear layer removal by different chemical solutions used with or without ultrasonic activation after post preparation
- Daniel Poletto, Ana Claudia Poletto, Andressa Cavalaro, Ricardo Machado, Leopoldo Cosme-Silva, Cássia Cilene Dezan Garbelini, Márcio Grama Hoeppner
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(4):324-331. Published online November 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.4.324
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated smear layer removal by different chemical solutions used with or without ultrasonic activation after post preparation.
Materials and Methods Forty-five extracted uniradicular human mandibular premolars with single canals were treated endodontically. The cervical and middle thirds of the fillings were then removed, and the specimens were divided into 9 groups: G1, saline solution (NaCl); G2, 2.5% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl); G3, 2% chlorhexidine (CHX); G4, 11.5% polyacrylic acid (PAA); G5, 17% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA). For the groups 6, 7, 8, and 9, the same solutions used in the groups 2, 3, 4, and 5 were used, respectively, but activated with ultrasonic activation. Afterwards, the roots were analyzed by a score considering the images obtained from a scanning electron microscope.
Results EDTA achieved the best performance compared with the other solutions evaluated regardless of the irrigation method (
p < 0.05).Conclusions Ultrasonic activation did not significantly influence smear layer removal.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cerium Oxide Nanoparticle Loaded with Toluidine Blue as Cavity Disinfectant Activated via Light-Emitting Diode on the Shear Bond Strength and Resin Tag Length of Universal Adhesive: A Scanning Electron Microscope-EDX Study
Amer M. Alanazi, Syed Hussain Askary, Ibrahim Warsi, Aamir Afzal, Muhammad Omar Niaz, Ambrina Qureshi
Photobiomodulation, Photomedicine, and Laser Surgery.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - O papel do ultrassom no tratamento e retratamento de canais radiculares: Revisão de literatura
Carlos Roberto Souza Hipp, Joaquim Carlos Fest da Silveira, Luiz Felipe Gilson de Oliveira Rangel, Tatiana Federici de Souza Fest da Silveira, Carla Minozzo Mello, Rodrigo Simões de Oliveira
Research, Society and Development.2025; 14(8): e1314849323. CrossRef - Effect of sodium hypochlorite, ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, and dual-rinse irrigation on dentin adhesion using an etch-and-rinse or self-etch approach
Matej Par, Tobias Steffen, Selinay Dogan, Noah Walser, Tobias T. Tauböck
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Effect of Poloxamer on Smear Layer Removal Using Apical Negative Pressure: An In Vitro Scanning Electron Microscopy Study
Chandra Prabha, Chitharanjan Shetty, Aditya Shetty
Journal of International Oral Health.2024; 16(6): 498. CrossRef - Laboratory Assessment of Antibacterial Efficacy of Five Different Herbal-based Potential Endodontic Irrigants
Anjali A Oak, Kailash Attur, Kamal Bagda, Nitish Mathur, Lubna Mohammad, Nikhat M Attar
Advances in Human Biology.2023; 13(4): 350. CrossRef - Dental Surface Conditioning Techniques to Increase the Micromechanical Retention to Fiberglass Posts: A Literature Review
Paulina Leticia Moreno-Sánchez, Maricela Ramírez-Álvarez, Alfredo del Rosario Ayala-Ham, Erika de Lourdes Silva-Benítez, Miguel Ángel Casillas-Santana, Diana Leyva del Rio, León Francisco Espinosa-Cristóbal, Erik Lizárraga-Verdugo, Mariana Melisa Avendaño
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(14): 8083. CrossRef - Effect of irrigation protocols on smear layer removal, bond strength and nanoleakage of fiber posts using a self-adhesive resin cement
Rodrigo Stadler Alessi, Renata Terumi Jitumori, Bruna Fortes Bittencourt, Giovana Mongruel Gomes, João Carlos Gomes
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of using different root canal sealers and protocols for cleaning intraradicular dentin on the bond strength of a composite resin used to reinforce weakened roots
Luiz Pascoal Vansan, Ricardo Machado, Celso Bernardes de Souza, Ricardo Gariba, Antônio Miranda da Cruz, Cinara Muniz, Jardel FranciscoX Jardel Francisco Mazzi-Chaves, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
Journal of Oral Research.2022; 11(6): 1. CrossRef - Influence of the use of chelating agents as final irrigant on the push‐out bond strength of epoxy resin‐based root canal sealers: A systematic review
Carla M. Augusto, Miguel A. Cunha Neto, Karem P. Pinto, Ana Flavia A. Barbosa, Emmanuel J. N. L. Silva, Ana Paula P. dos Santos, Luciana M. Sassone
Australian Endodontic Journal.2022; 48(2): 347. CrossRef - Adhesion and whitening efficacy of P11-4 self-assembling peptide and HAP suspension after using NaOCl as a pre-treatment agent
Niloofar Hojabri, Karl-Heinz Kunzelmann
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of resin cements and root canal disinfection techniques on the adhesive bond strength of fibre reinforced composite post to radicular dentin
Zaid A. Al Jeaidi
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2021; 33: 102108. CrossRef - The Antibacterial Efficacy and In Vivo Toxicity of Sodium Hypochlorite and Electrolyzed Oxidizing (EO) Water-Based Endodontic Irrigating Solutions
Sung-Chih Hsieh, Nai-Chia Teng, Chia Chun Chu, You-Tai Chu, Chung-He Chen, Liang-Yu Chang, Chieh-Yun Hsu, Ching-Shuan Huang, Grace Ying-Wen Hsiao, Jen-Chang Yang
Materials.2020; 13(2): 260. CrossRef
- Cerium Oxide Nanoparticle Loaded with Toluidine Blue as Cavity Disinfectant Activated via Light-Emitting Diode on the Shear Bond Strength and Resin Tag Length of Universal Adhesive: A Scanning Electron Microscope-EDX Study
- 2,641 View
- 19 Download
- 12 Crossref

- The use of auxiliary devices during irrigation to increase the cleaning ability of a chelating agent
- Marina Carvalho Prado, Fernanda Leal, Renata Antoun Simão, Heloisa Gusman, Maíra do Prado
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(2):105-110. Published online February 3, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.2.105
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study investigated the cleaning ability of ultrasonically activated irrigation (UAI) and a novel activation system with reciprocating motion (EC, EasyClean, Easy Equipamentos Odontológicos) when used with a relatively new chelating agent (QMix, Dentsply). In addition, the effect of QMix solution when used for a shorter (1 minute) and a longer application time (3 minutes) was investigated.
Materials and Methods Fifty permanent human teeth were prepared with K3 rotary system and 6% sodium hypochlorite. Samples were randomly assigned to five groups (
n = 10) according to the final irrigation protocol: G1, negative control (distilled water); G2, positive control (QMix 1 minute); G3, QMix 1 minute/UAI; G4, QMix 1 minute/EC; G5, QMix 3 minutes. Subsequently the teeth were prepared and three photomicrographs were obtained in each root third of root walls, by scanning electron microscopy. Two blinded and pre-calibrated examiners evaluated the images using a four-category scoring system. Data were statistically analyzed using Kruskal-Wallis and Dunn tests (p < 0.05).Results There were differences among groups (
p < 0.05). UAI showed better cleaning ability than EC (p < 0.05). There were improvements when QMix was used with auxiliary devices in comparison with conventional irrigation (p < 0.05). Conventional irrigation for 3 minutes presented significantly better results than its use for 1 minute (p < 0.05).Conclusions QMix should be used for 1 minute when it is used with UAI, since this final irrigation protocol showed the best performance and also allowed clinical optimization of this procedure.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative Evaluation of Different Methods of Activation of Chelating Solution for Smear Layer Removal in the Apical Portion of the Root Canal Using a Scanning Electron Microscopy: An In Vitro Study
Mrunal B Alhat, Sudha B Mattigatti, Rushikesh R Mahaparale, Kapil D Wahane, Apoorva Jadhav
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Impact of Laser-Activated and Conventional Irrigation Techniques on Sealer Penetration into Dentinal Tubules
Dilara Koruk, Fatma Basmacı, Dilan Kırmızı, Umut Aksoy
Photobiomodulation, Photomedicine, and Laser Surgery.2022; 40(8): 565. CrossRef - Utilização dos atuais métodos de agitação de soluções endodônticas no canal radicular
Lívia Rodrigues Schneider, Larissa Giovanella
Revista Científica Multidisciplinar Núcleo do Conhecimento.2022; : 135. CrossRef - Smear layer removal by passive ultrasonic irrigation and 2 new mechanical methods for activation of the chelating solution
Ricardo Machado, Isadora da Silva, Daniel Comparin, Bianca Araujo Marques de Mattos, Luiz Rômulo Alberton, Ulisses Xavier da Silva Neto
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Proteomic analysis of human dental pulp in different clinical diagnosis
Poliana Amanda Oliveira Silva, Stella Maris de Freitas Lima, Mirna de Souza Freire, André Melro Murad, Octávio Luiz Franco, Taia Maria Berto Rezende
Clinical Oral Investigations.2021; 25(5): 3285. CrossRef - Effect of QMix irrigant in removal of smear layer in root canal system: a systematic review of in vitro studies
Margaret Soo Yee Chia, Abhishek Parolia, Benjamin Syek Hur Lim, Jayakumar Jayaraman, Isabel Cristina Celerino de Moraes Porto
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of 17% EDTA and QMiX ultrasonic activation on smear layer removal and sealer penetration: ex vivo study
Felipe de Souza Matos, Fabrício Rutz da Silva, Luiz Renato Paranhos, Camilla Christian Gomes Moura, Eduardo Bresciani, Marcia Carneiro Valera
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Micro-CT evaluation of different final irrigation protocols on the removal of hard-tissue debris from isthmus-containing mesial root of mandibular molars
Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Carla Rodrigues Carvalho, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Marina Carvalho Prado, Ricardo Tadeu Lopes, Gustavo De-Deus, Edson Jorge Lima Moreira
Clinical Oral Investigations.2019; 23(2): 681. CrossRef
- Comparative Evaluation of Different Methods of Activation of Chelating Solution for Smear Layer Removal in the Apical Portion of the Root Canal Using a Scanning Electron Microscopy: An In Vitro Study
- 1,403 View
- 7 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Multivariate analysis of the cleaning efficacy of different final irrigation techniques in the canal and isthmus of mandibular posterior teeth
- Yeon-Jee Yoo, WooCheol Lee, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Won-Jun Shon, Seung-Ho Baek
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(3):154-159. Published online August 23, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.3.154
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to compare the cleaning efficacy of different final irrigation regimens in canal and isthmus of mandibular molars, and to evaluate the influence of related variables on cleaning efficacy of the irrigation systems.
Materials and Methods Mesial root canals from 60 mandibular molars were prepared and divided into 4 experimental groups according to the final irrigation technique: Group C, syringe irrigation; Group U, ultrasonics activation; Group SC, VPro StreamClean irrigation; Group EV, EndoVac irrigation. Cross-sections at 1, 3 and 5 mm levels from the apex were examined to calculate remaining debris area in the canal and isthmus spaces. Statistical analysis was completed by using Kruskal-Wallis test and Mann-Whitney U test for comparison among groups, and multivariate linear analysis to identify the significant variables (regular replenishment of irrigant, vapor lock management, and ultrasonic activation of irrigant) affecting the cleaning efficacy of the experimental groups.
Results Group SC and EV showed significantly higher canal cleanliness values than group C and U at 1 mm level (
p < 0.05), and higher isthmus cleanliness values than group U at 3 mm and all levels of group C (p < 0.05). Multivariate linear regression analysis demonstrated that all variables had independent positive correlation at 1 mm level of canal and at all levels of isthmus with statistical significances.Conclusions Both VPro StreamClean and EndoVac system showed favorable result as final irrigation regimens for cleaning debris in the complicated root canal system having curved canal and/or isthmus. The debridement of the isthmi significantly depends on the variables rather than the canals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficacy of different irrigant activation techniques for cleaning root canal anastomosis
O. K. Montaser, D. M. Fayyad, N. Abdelsalam
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Activación ultrasónica durante la preparación bio químico mecánica del tratamiento endodóntico no quirúrgico. Revisión de la literatura
Gisselle Cantanzaro, Nelsin Villaroel, Diana Dorta
ODOUS Científica .2022; 22(2): 135. CrossRef - Heated distilled water with or without continuous ultrasonic irrigation improves final irrigation efficacy and reduces dentine erosion
Michelli Cássia dos Santos, Cleonice da Silveira Teixeira, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia, Bruno Henriques, Franklin R. Tay, Eduardo Antunes Bortoluzzi
Journal of Dentistry.2020; 103: 103507. CrossRef - Ultrasonic Irrigant Activation during Root Canal Treatment: A Systematic Review
Petruţa E. Căpută, Anastasios Retsas, Lydwien Kuijk, Luis E. Chávez de Paz, Christos Boutsioukis
Journal of Endodontics.2019; 45(1): 31. CrossRef - Irrigation effectiveness of continuous ultrasonic irrigation system: An ex vivo study
Ahmed JAMLEH, Hideaki SUDA, Carlos G. ADORNO
Dental Materials Journal.2018; 37(1): 1. CrossRef - Apical negative pressure irrigation versus syringe irrigation: a systematic review of cleaning and disinfection of the root canal system
E. Konstantinidi, Z. Psimma, L. E. Chávez de Paz, C. Boutsioukis
International Endodontic Journal.2017; 50(11): 1034. CrossRef - Effect of Different Agitation Techniques on the Penetration of Irrigant and Sealer into Dentinal Tubules
Yu Gu, Hiran Perinpanayagam, David J.W. Jin, Yeon-Jee Yoo, Jin-Sun Jeong, Sang-Min Lim, Seok-Woo Chang, Seung-Ho Baek, Qiang Zhu, Kee-Yeon Kum
Photomedicine and Laser Surgery.2017; 35(2): 71. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Sonic, Ultrasonic, and Photon-Induced Photoacoustic Streaming Activation of NaOCl on Filling Material Removal Following Retreatment in Oval Canal Anatomy
Shan Jiang, Ting Zou, Dongxia Li, Jeffery W.W. Chang, Xiaojing Huang, Chengfei Zhang
Photomedicine and Laser Surgery.2016; 34(1): 3. CrossRef -
Efficacy of Needle, Ultrasonic, and Endoactivator Irrigation and Photon-Induced Photoacoustic Streaming in Removing Calcium Hydroxide from the Main Canal and Isthmus: An
In Vitro
Micro-Computed Tomography and Scanning
Dongxia Li, Shan Jiang, Xingzhe Yin, Jeffrey Wen Wei Chang, Jie Ke, Chengfei Zhang
Photomedicine and Laser Surgery.2015; 33(6): 330. CrossRef - Effect of three different irrigation solutions applied by passive ultrasonic irrigation
Carmen Llena, Leopoldo Forner, Raquel Cambralla, Adrian Lozano
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(2): 143. CrossRef
- Efficacy of different irrigant activation techniques for cleaning root canal anastomosis
- 1,275 View
- 1 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Review of root canal irrigant delivery techniques and devices
- Yeon-Jee Yoo, Su-Jeong Shin, Seung-Ho Baek
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(3):180-187. Published online May 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.3.180
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Introduction Eliminating the residual debris and bacteria in the root canal system is one of the main purposes of the endodontic treatment. However, the complexity on the anatomy of the root canal system makes it difficult to eliminate the bacterial biofilm existing along the root canal surface and necrotic pulp tissue by mechanical instrumentation and chemical irrigation. Recently, more effective irrigant delivery systems for root canal irrigation have been developed. The purpose of this review was to present an overview of root canal irrigant delivery techniques and devices available in endodontics.
Review The contents of this paper include as follows;
- syringe-needle irrigation, manual dynamic irrigation, brushes
- sonic and ultrasonic irrigation, passive ultrasonic irrigation, rotary brush, RinsEndo, EndoVac, Laser
Conclusion Though technological advances during the last decade have brought to fruition new agitation devices that rely on various mechanisms, there are few evidence based study to correlate the clinical efficacy of these devices with improved outcomes except syringe irrigation with needle and ultrasonic irrigation.
The clinicians should try their best efforts to deliver antimicrobial and tissue solvent solutions in predictable volumes safely to working length.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and performance test of a micro bubble irrigation system for root canal cleaning of tooth
Gilhwan Sung, Jaeyong Sung, Myeong Ho Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Visualization.2016; 14(1): 40. CrossRef
- Development and performance test of a micro bubble irrigation system for root canal cleaning of tooth
- 1,727 View
- 34 Download
- 1 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


