Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Concentrated growth factor scaffold-based pulpotomy of permanent molars with symptomatic irreversible pulpitis
- Arthi K. Harith, Vishnupriya Koteeswaran, Dinesh Kowsky, Natanasabapathy Velmurugan, Suresh Nandini
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(1):e1. Published online January 17, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
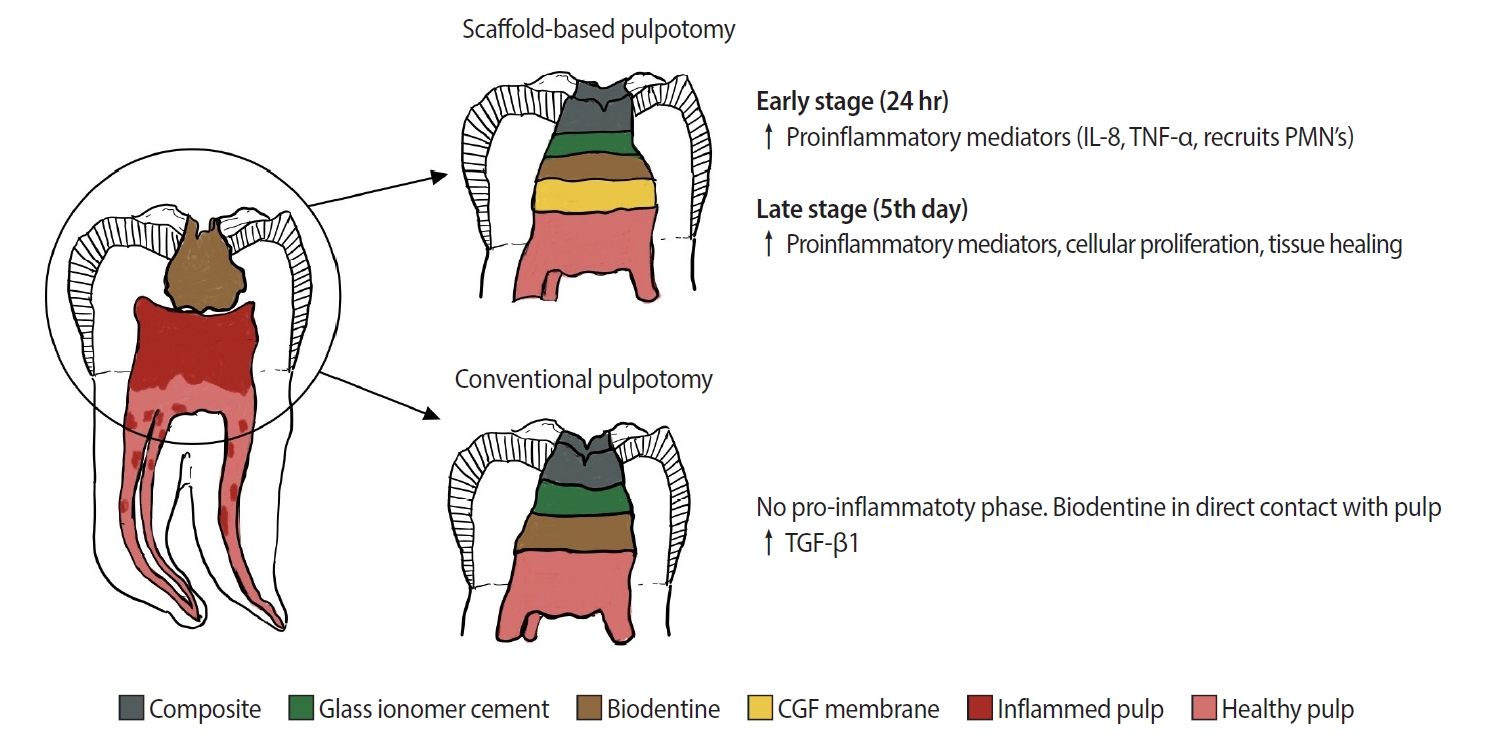
Pulpotomy is a minimally invasive procedure that aims to retain the vitality of the radicular pulp by removing the inflamed coronal pulp tissue. This case series presents the successful management of symptomatic irreversible pulpitis by pulpotomy with concentrated growth factor (CGF) scaffolds.
Methods
Six permanent mandibular molars with a diagnosis of symptomatic irreversible pulpitis were included. Under Local anesthesia and rubber dam isolation, caries were excavated using high-speed bur under coolant. Full coronal pulpotomy was done and hemostasis was achieved. CGF membrane was prepared and placed over the radicular pulp and layered with Biodentine (Septodont). Final restoration of type IX glass ionomer cement and bulk fill composite resin was placed. Patients were assessed for various clinical and radiographic parameters at intervals of 1 week and 3, 6, and 12 months. Five patients fulfilled the success criteria at the end of 1 year.
Results
Pulpotomy is considered an alternative treatment modality for root canal treatment in symptomatic irreversible pulpitis aiming at alleviating symptoms and maintaining vitality. CGF scaffold when used as a capping material acts as a reservoir for growth factors with anti-inflammatory properties and enhances healing.
Conclusions
Scaffold-based pulpotomy can be considered a biological approach to healing inflamed pulp.
- 798 View
- 130 Download

- A novel antimicrobial-containing nanocellulose scaffold for regenerative endodontics
- Victoria Kichler, Lucas Soares Teixeira, Maick Meneguzzo Prado, Guilherme Colla, Daniela Peressoni Vieira Schuldt, Beatriz Serrato Coelho, Luismar Marques Porto, Josiane de Almeida
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(2):e20. Published online March 16, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e20
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
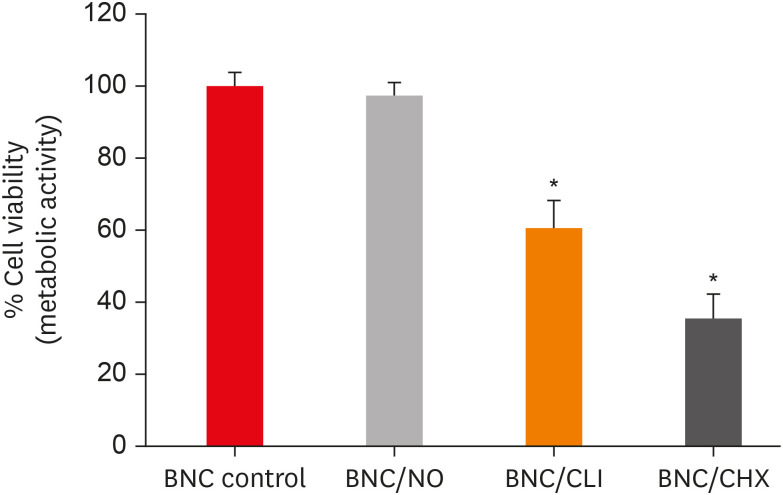
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to evaluate bacterial nanocellulose (BNC) membranes incorporated with antimicrobial agents regarding cytotoxicity in fibroblasts of the periodontal ligament (PDLF), antimicrobial activity, and inhibition of multispecies biofilm formation.
Materials and Methods The tested BNC membranes were BNC + 1% clindamycin (BNC/CLI); BNC + 0.12% chlorhexidine (BNC/CHX); BNC + nitric oxide (BNC/NO); and conventional BNC (BNC; control). After PDLF culture, the BNC membranes were positioned in the wells and maintained for 24 hours. Cell viability was then evaluated using the MTS calorimetric test. Antimicrobial activity against
Enterococcus faecalis ,Actinomyces naeslundii , andStreptococcus sanguinis (S. sanguinis ) was evaluated using the agar diffusion test. To assess the antibiofilm activity, BNC membranes were exposed for 24 hours to the mixed culture. After sonicating the BNC membranes to remove the remaining biofilm and plating the suspension on agar, the number of colony-forming units (CFU)/mL was determined. Data were analyzed by 1-way analysis of variance and the Tukey, Kruskal-Wallis, and Dunn tests (α = 5%).Results PDLF metabolic activity after contact with BNC/CHX, BNC/CLI, and BNC/NO was 35%, 61% and 97%, respectively, compared to BNC. BNC/NO showed biocompatibility similar to that of BNC (
p = 0.78). BNC/CLI showed the largest inhibition halos, and was superior to the other BNC membranes againstS. sanguinis (p < 0.05). The experimental BNC membranes inhibited biofilm formation, with about a 3-fold log CFU reduction compared to BNC (p < 0.05).Conclusions BNC/NO showed excellent biocompatibility and inhibited multispecies biofilm formation, similarly to BNC/CLI and BNC/CHX.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Topic: Perspectives on Success and Failure of Endodontic Treatments
Ilma Robo, Manola Kelmendi, Eva Habazaj, Kleves Elezi, Rialda Xhizdari, Nevila Alliu
SN Comprehensive Clinical Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Prospective and applications of bacterial nanocellulose in dentistry
Yasmin Alimardani, Esmaeel Mirzakhani, Fereshteh Ansari, Hadi Pourjafar, Nadia Sadeghi
Cellulose.2024; 31(13): 7819. CrossRef - Bacterial nanocelluloses as sustainable biomaterials for advanced wound healing and dressings
Atefeh Zarepour, Bahar Gok, Yasemin Budama-Kilinc, Arezoo Khosravi, Siavash Iravani, Ali Zarrabi
Journal of Materials Chemistry B.2024; 12(48): 12489. CrossRef - Sulfated endospermic nanocellulose crystals prevent the transmission of SARS-CoV-2 and HIV-1
Enrique Javier Carvajal-Barriga, Wendy Fitzgerald, Emilios K. Dimitriadis, Leonid Margolis, R. Douglas Fields
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A Novel Approach for the Fabrication of 3D-Printed Dental Membrane Scaffolds including Antimicrobial Pomegranate Extract
Hatice Karabulut, Songul Ulag, Basak Dalbayrak, Elif Arisan, Turgut Taskin, Mehmet Guncu, Burak Aksu, Alireza Valanezhad, Oguzhan Gunduz
Pharmaceutics.2023; 15(3): 737. CrossRef - Current advances of nanocellulose application in biomedical field
M.Y. Leong, Y.L. Kong, M.Y. Harun, C.Y. Looi, W.F. Wong
Carbohydrate Research.2023; 532: 108899. CrossRef - Bacterial cellulose as a potential biopolymer in biomedical applications: a state-of-the-art review
Prachi Shrivastav, Sheersha Pramanik, Gayatri Vaidya, Mohamed A. Abdelgawad, Mohammed M. Ghoneim, Ajeet Singh, Bassam M. Abualsoud, Larissa Souza Amaral, Mohammed A. S. Abourehab
Journal of Materials Chemistry B.2022; 10(17): 3199. CrossRef - Nanocelluloses as new generation materials: natural resources, structure-related properties, engineering nanostructures, and technical challenges
Ahmed Barhoum, Vibhore K. Rastogi, Bhupender K. Mahur, Amit Rastogi, Fatehy M. Abdel-Haleem, Pieter Samyn
Materials Today Chemistry.2022; 26: 101247. CrossRef - The current natural/chemical materials and innovative technologies in periodontal diseases therapy and regeneration: A narrative review
Peyman Esmaeili Fard Barzegar, Reza Ranjbar, Mohsen Yazdanian, Elahe Tahmasebi, Mostafa Alam, Kamyar Abbasi, Hamid Tebyaniyan, Keyvan Esmaeili Fard Barzegar
Materials Today Communications.2022; 32: 104099. CrossRef
- Topic: Perspectives on Success and Failure of Endodontic Treatments
- 328 View
- 9 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref

-
Coronal tooth discoloration induced by regenerative endodontic treatment using different scaffolds and intracanal coronal barriers: a 6-month
ex vivo study - Noushin Shokouhinejad, Hassan Razmi, Maryam Farbod, Marzieh Alikhasi, Josette Camilleri
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(3):e25. Published online July 16, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e25
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
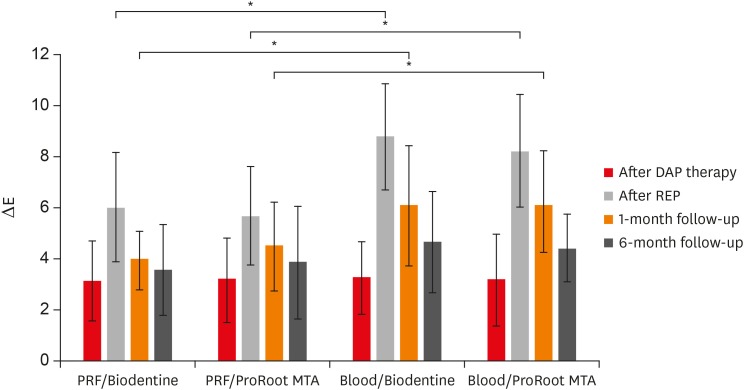
ePub Objective The aim of this study was to evaluate discoloration of teeth undergoing regenerative endodontic procedures (REPs) using blood clot or platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) as the scaffolds and different calcium silicate-based materials as the intracanal coronal barriers in an
ex vivo model.Materials and Methods Forty-eight bovine incisors were prepared and disinfected using 1 mg/mL double antibiotic paste (DAP). The specimens were then randomly divided into 2 groups (
n = 24) according to the scaffolds (blood or PRF). After placement of scaffolds each group was divided into 2 subgroups (n = 12) according to the intracanal coronal barriers (ProRoot MTA or Biodentine). The pulp chamber walls were sealed with dentin bonding agent before placement of DAP and before placement of scaffolds. The color changes (∆E) were measured at different steps. The data were analyzed using 2-way analysis of variance.Results Coronal discoloration induced by DAP was not clinically perceptible (ΔE ≤ 3.3). Regarding the type of the scaffold, coronal discoloration was significantly higher in blood groups compared with PRF groups at the end of REP and after 1 month (
p < 0.05). However, no significant difference was found between PRF and blood clot after 6 months (p > 0.05). Considering the type of intracanal coronal barrier, no significant difference existed between ProRoot MTA and Biodentine (p > 0.05).Conclusions With sealing the dentinal tubules of pulp chamber with a dentin bonding agent and application of DAP as an intracanal medicament, coronal color change of the teeth following the use of PRF and blood sealed with either ProRoot MTA or Biodentine was not different at 6-month follow-up.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of pH on the solubility and volumetric change of ready-to-use Bio-C Repair bioceramic material
Luana Raphael da SILVA, Jader Camilo PINTO, Juliane Maria GUERREIRO-TANOMARU, Mário TANOMARU-FILHO
Brazilian Oral Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of Potassium Iodide and Glutathione for Correlation of Dentin Discoloration Caused by Silver Diamine Fluoride
Mahsa Samani, Hamid Majzoub, Faramarz Zakavi, Ayyub Mojaddami
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Intracanal medicaments and coronal sealing materials influence on root fracture resistance and coronal discoloration: An in vitro study
Rasoul Sahebalam, Marzie Boskabady, Maryam Naghavi, Samira Dehghanitafti
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2024; 14(2): 199. CrossRef - Potential Crown Discoloration Induced by the Combination of Various Intracanal Medicaments and Scaffolds Applied in Regenerative Endodontic Therapy
NB Altun, A Turkyilmaz
Nigerian Journal of Clinical Practice.2024; 27(7): 897. CrossRef - Evaluation of the effectiveness of different treatment approaches in preventing coronal discoloration caused by regenerative endodontic treatment
Melis Oya Ateş, Zeliha Uğur Aydın
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(8): 4595. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Laser-Assisted Bleaching of the Teeth Discolored due to Regenerative Endodontic Treatment
Noushin Shokouhinejad, Mehrfam Khoshkhounejad, Fatemeh Hamidzadeh, Murilo Baena Lopes
International Journal of Dentistry.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Teeth Whitening after Regenerative Endodontics Procedures: An In Vitro Study
Irini Fagogeni, Joanna Metlerska, Tomasz Falgowski, Maciej Górski, Mariusz Lipski, Alicja Nowicka
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(23): 7016. CrossRef - Microstructure and color stability of calcium silicate-based dental materials exposed to blood or platelet-rich fibrin
Noushin Shokouhinejad, Ibrahim Abu Tahun, Shima Saber Tahan, Fatemeh Mohandes, Mohammad H. Nekoofar, Paul M. H. Dummer
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 27(3): 1193. CrossRef - Spectrophotometric analysis of internal bleaching of traumatized teeth with coronal discoloration following regenerative endodontic procedures
Jaqueline Lazzari, Walbert Vieira, Vanessa Pecorari, Brenda Paula Figueiredo de Almeida Gomes, José Flávio Affonso de Almeida, Adriana De-Jesus-Soares
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Biological parameters, discolouration and radiopacity of calcium silicate‐based materials in a simulated model of partial pulpotomy
Lilian Vieira Oliveira, Gabriela Leite de Souza, Gisele Rodrigues da Silva, Thamara Eduarda Alves Magalhães, Gabrielle Alves Nunes Freitas, Ana Paula Turrioni, Gabriella Lopes de Rezende Barbosa, Camilla Christian Gomes Moura
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(11): 2133. CrossRef - Effect of hydrogel-based antibiotic intracanal medicaments on crown discoloration
Rayan B. Yaghmoor, Jeffrey A. Platt, Kenneth J. Spolnik, Tien Min Gabriel Chu, Ghaeth H. Yassen
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of different calcium silicate-based pulp capping materials on tooth discoloration: an in vitro study
Ahmad S. Al-Hiyasat, Dana M. Ahmad, Yousef S. Khader
BMC Oral Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Knowledge, attitudes, and practices of undergraduate students concerning Regenerative Endodontics
Ligia B. da Silva, Mariana Gabriel, Márcia M. Marques, Fernanda C. Carrer, Flávia Gonçalves, Giovanna Sarra, Giovanna L. Carvalho, Ana Armas-Vega, Maria S. Moreira
Minerva Stomatologica.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Coronal Discoloration Related to Bioceramic and Mineral Trioxide Aggregate Coronal Barrier in Non-vital Mature Teeth Undergoing Regenerative Endodontic Procedures
Mazen Doumani, Mohammad Yaman Seirawan, Kinda Layous, Mohammad Kinan Seirawan
World Journal of Dentistry.2020; 11(1): 52. CrossRef
- Effect of pH on the solubility and volumetric change of ready-to-use Bio-C Repair bioceramic material
- 281 View
- 7 Download
- 14 Crossref

- Biocompatibility of two experimental scaffolds for regenerative endodontics
- Dephne Jack Xin Leong, Frank C. Setzer, Martin Trope, Bekir Karabucak
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(2):98-105. Published online March 28, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.2.98
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The biocompatibility of two experimental scaffolds for potential use in revascularization or pulp regeneration was evaluated.
Materials and Methods One resilient lyophilized collagen scaffold (COLL), releasing metronidazole and clindamycin, was compared to an experimental injectable poly(lactic-co-glycolic) acid scaffold (PLGA), releasing clindamycin. Human dental pulp stem cells (hDPSCs) were seeded at densities of 1.0 × 104, 2.5 × 104, and 5.0 × 104. The cells were investigated by light microscopy (cell morphology), MTT assay (cell proliferation) and a cytokine (IL-8) ELISA test (biocompatibility).
Results Under microscope, the morphology of cells coincubated for 7 days with the scaffolds appeared healthy with COLL. Cells in contact with PLGA showed signs of degeneration and apoptosis. MTT assay showed that at 5.0 × 104 hDPSCs, COLL demonstrated significantly higher cell proliferation rates than cells in media only (control,
p < 0.01) or cells co-incubated with PLGA (p < 0.01). In ELISA test, no significant differences were observed between cells with media only and COLL at 1, 3, and 6 days. Cells incubated with PLGA expressed significantly higher IL-8 than the control at all time points (p < 0.01) and compared to COLL after 1 and 3 days (p < 0.01).Conclusions The COLL showed superior biocompatibility and thus may be suitable for endodontic regeneration purposes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Advances in scaffolds used forpulp–dentinecomplex tissue engineering: A narrative review
Parisa Noohi, Mohammad J. Abdekhodaie, Mohammad H. Nekoofar, Kerstin M. Galler, Paul M. H. Dummer
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(12): 1277. CrossRef - In vitro performance of a nanobiocomposite scaffold containing boron-modified bioactive glass nanoparticles for dentin regeneration
Reza Moonesi Rad, Engin Pazarçeviren, Elif Ece Akgün, Zafer Evis, Dilek Keskin, Sıla Şahin, Ayşen Tezcaner
Journal of Biomaterials Applications.2019; 33(6): 834. CrossRef - Biological effects of silk fibroin 3D scaffolds on stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth (SHEDs)
M. Collado-González, M. P. Pecci-Lloret, D. García-Bernal, S. Aznar-Cervantes, R. E. Oñate-Sánchez, J. M. Moraleda, J. L. Cenis, F. J. Rodríguez-Lozano
Odontology.2018; 106(2): 125. CrossRef - Pulp Regeneration Concepts for Nonvital Teeth: From Tissue Engineering to Clinical Approaches
Valérie Orti, Pierre-Yves Collart-Dutilleul, Sofía Piglionico, Orsolya Pall, Frédéric Cuisinier, Ivan Panayotov
Tissue Engineering Part B: Reviews.2018; 24(6): 419. CrossRef - Investigation of Human Dental Pulp Cells on a Potential Injectable Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) Microsphere Scaffold
Huiru Zou, Guanhua Wang, Fang Song, Xudong Shi
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(5): 745. CrossRef - Biocompatibility of hydrogel-based scaffolds for tissue engineering applications
Sheva Naahidi, Mousa Jafari, Megan Logan, Yujie Wang, Yongfang Yuan, Hojae Bae, Brian Dixon, P. Chen
Biotechnology Advances.2017; 35(5): 530. CrossRef
- Advances in scaffolds used forpulp–dentinecomplex tissue engineering: A narrative review
- 220 View
- 2 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Platelet rich fibrin - a novel acumen into regenerative endodontic therapy
- Kavita Hotwani, Krishna Sharma
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(1):1-6. Published online January 20, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Research into regenerative dentistry has added impetus onto the field of molecular biology. It can be documented as a prototype shift in the therapeutic armamentarium for dental disease. Regenerative endodontic procedures are widely being added to the current armamentarium of pulp therapy procedures. The regenerative potential of platelets has been deliberated. A new family of platelet concentrates called the platelet rich fibrin (PRF) has been recently used by several investigators and has shown application in diverse disciplines of dentistry. This paper is intended to add light on the various prospects of PRF and clinical insights to regenerative endodontic therapy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Apicoectomy versus apical curettage in combination with or without L-PRF application: a randomized clinical trial
Serap Gulsever, Seyda Ersahan, Yelda Erdem Hepsenoglu, Alperen Tekin
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Pulp regeneration treatment using different bioactive materials in permanent teeth of pediatric subjects
Dina Abdellatif, Alfredo Iandolo, Giuseppina De Benedetto, Francesco Giordano, Davide Mancino, Edouard Euvrard, Massimo Pisano
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(5): 458. CrossRef - Analysis of Pulp Tissue Viability and Cytotoxicity of Pulp Capping Agents
Pratima Panda, Shashirekha Govind, Sanjit Kumar Sahoo, Satabdi Pattanaik, Rachappa M. Mallikarjuna, Triveni Nalawade, Sanjay Saraf, Naseer Al Khaldi, Salma Al Jahdhami, Vinay Shivagange, Amit Jena
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(2): 539. CrossRef - Implantation Effect of a Fibrin Matrix Associated with Mesenchymal Wharton’s Jelly Stromal Cells on the Course of an Experimental Spinal Cord Injury
V. V. Medvediev, N. P. Oleksenko, L. D. Pichkur, S. A. Verbovska, S. I. Savosko, N. G. Draguntsova, Yu. A. Lontkovskyi, V. V. Vaslovych, V. I. Tsymbalyuk
Cytology and Genetics.2023; 57(1): 19. CrossRef - Advanced Platelet-rich Fibrin-mediated Regeneration of Necrotic Immature Permanent Teeth: A Clinico-radiographic Observational Study
Ashi Chug, Sagrika Shukla, Tulika Wakhloo, Mridul Dhar
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2022; 15(4): 402. CrossRef - Effect of Implantation of a Fibrin Matrix Associated with Neonatal Brain Cells on the Course of an Experimental Spinal Cord Injury
V. V. Medvediev, N. P. Oleksenko, L. D. Pichkur, S. A. Verbovska, S. I. Savosko, N. G. Draguntsova, Yu. A. Lontkovskiy, V. V. Vaslovych, V. I. Tsymbalyuk
Cytology and Genetics.2022; 56(2): 125. CrossRef - Comparison of Autologous Platelet-Rich Fibrin Matrix and Transplantation of Autologous Noncultured Epidermal Cell Suspension in the Treatment of Chronic Non Healing Ulcer
Satyendra K. Singh, Sri Rupa
Indian Journal of Dermatology.2022; 67(4): 334. CrossRef - Effect of amniotic membrane and platelet‐rich fibrin membrane on bone healing post endodontic surgery: An ultrasonographic, randomized controlled study
Saumya Johri, Promila Verma, Aseem Prakash Tikku, Rhythm Bains, Neera Kohli
Journal of Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine.2022; 16(12): 1208. CrossRef - Effect of biodentine coated with emdogain on proliferation and differentiation of human stem cells from the apical papilla
Hamed Karkehabadi, Erfan Ahmadyani, Rezvan Najafi, Elham Khoshbin
Molecular Biology Reports.2022; 49(5): 3685. CrossRef - SINGLE VISIT- APEXIFICATION USING MTA AND AUTOLOGOUS PRF AS AN INTERNAL MATRIX. A CASE SERIES.
Deepika Deepika, Abhishek Sharma, Ajay Kumar Nagpal, Muhammad Mutiur Rahman
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH.2022; : 61. CrossRef - COMPARATIVE CLINICAL, RADIOGRAPHICAL AND HISTOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF CORONAL PULPOTOMY TECHNIQUE WITH PRF AND A NOVEL CROSSLINKED PRF AS AN ALTERNATIVE TO PULPECTOMY FOR PRESERVING THE TOOTH VITALITY IN CONTEXT OF TISSUE ENGINEERING.
Suman Kar, R. R. Paul, H. D. Adhikari, Swagata Gayen, Sandip Sinha
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH.2022; : 84. CrossRef - Clinical Application of Platelet-Rich Fibrin in Pediatric Dentistry
Sowndarya Gunasekaran, Soundarya Sakthivel, Shanthala B. M., George Babu, Vidhya Vijayan
Journal of Health and Allied Sciences NU.2022; 12(02): 186. CrossRef - Platelet-Rich Fibrin Used as a Scaffold in Pulp Regeneration: Case Series
Ceren ÇİMEN, Selin ŞEN, Elif ŞENAY, Tuğba BEZGİN
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2021; 24(1): 113. CrossRef - Treatment of Miller I Mandibular Gingival Recessions Using PRF vs. Connective Graft
Hernan S. Garzon, Camilo Alfonso, Francisco J. Vega, Andrea García, Ana Muñoz, Gustavo Jaimes, Katherine Isaza, Katherine Rivera, Gaetano Isola
International Journal of Dentistry.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Over Platelet Rich Fibrin Scaffold for Mandibular Cartilage Defects Regenerative Medicine
Ni Putu Mira Sumarta, David Buntoro Kamadjaja, Nike Hendrijantini, Coen Pramono Danudiningrat, Fedik Abdul Rantam
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Platelet-Rich Fibrin Enhances Surgical Wound Healing in Total Laryngectomy
Mirta H. Reksodiputro, Syahrial M. Hutauruk, Dini W. Widodo, Fauziah Fardizza, Dita Mutia
Facial Plastic Surgery.2021; 37(03): 325. CrossRef - Role of Platelet-Rich Fibrin (PRF) and Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) in Oro-Facial Tissue Regeneration: A Narrative Review
Modhi Al Deeb
Journal of Advanced Oral Research.2020; 11(1): 5. CrossRef - Efficacy of Autologous Platelet Concentrates in Regenerative Endodontic Treatment: A Systematic Review of Human Studies
Joanna Metlerska, Irini Fagogeni, Alicja Nowicka
Journal of Endodontics.2019; 45(1): 20. CrossRef - Autologous platelet-rich-fibrin-induced revascularization sequelae: Two case reports
Ahmed M Eltawila, Rania El Backly
World Journal of Stomatology.2019; 7(3): 28. CrossRef - Revascularization of a Nonvital, Immature Permanent Tooth Using Amniotic Membrane: A Novel Approach
Meghna Bajaj, Ashu J Soni
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2019; 12(2): 150. CrossRef - Biomimetics in Endodontics: A Review of the Changing Trends in Endodontics
Jalak Patel, Tejal Sheth, Dhwanit Thakore, Dharmesh Dhamat
Journal of Advanced Oral Research.2018; 9(1-2): 11. CrossRef - Regenerative in endodontics: how, when and where
AL Ahmar Rima, Bassam Sanaa, Salloum Sarah, El Husseini Hassan, AL Ahmar Rima
Journal of Dental Health, Oral Disorders & Therapy.2018; 9(6): 531. CrossRef - Effects of the nitric oxide releasing biomimetic nanomatrix gel on pulp-dentin regeneration: Pilot study
Chan-Yang Moon, Ok Hyung Nam, Misun Kim, Hyo-Seol Lee, Sagar N. Kaushik, David A. Cruz Walma, Ho-Wook Jun, Kyounga Cheon, Sung Chul Choi, Jinkee Hong
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(10): e0205534. CrossRef - Growth Factors and Cell Homing in Dental Tissue Regeneration
Henry F. Duncan, Yoshifumi Kobayashi, Emi Shimizu
Current Oral Health Reports.2018; 5(4): 276. CrossRef - Use of Leukocyte Platelet (L-PRF) Rich Fibrin in Diabetic Foot Ulcer with Osteomyelitis (Three Clinical Cases Report)
Alessandro Crisci, Giuseppe Marotta, Anna Licito, Edda Serra, Giulio Benincasa, Michela Crisci
Diseases.2018; 6(2): 30. CrossRef - Pulp Regeneration Concepts for Nonvital Teeth: From Tissue Engineering to Clinical Approaches
Valérie Orti, Pierre-Yves Collart-Dutilleul, Sofía Piglionico, Orsolya Pall, Frédéric Cuisinier, Ivan Panayotov
Tissue Engineering Part B: Reviews.2018; 24(6): 419. CrossRef - Long-term cytokine and growth factor release from equine platelet-rich fibrin clots obtained with two different centrifugation protocols
Román F. Jiménez-Aristizabal, Catalina López, María E. Álvarez, Carlos Giraldo, Marta Prades, Jorge U. Carmona
Cytokine.2017; 97: 149. CrossRef - Rejeneratif Pulpa Tedavilerine Genel Bir Bakış
Elif Sungurtekin Ekçi
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2017; 19(3): 238. CrossRef - Three-dimensional structure and cytokine distribution of platelet-rich fibrin
Meng-Yi Bai, Ching-Wei Wang, Jyun-Yi Wang, Ming-Fang Lin, Wing P Chan
Clinics.2017; 72(2): 116. CrossRef - The impact of autologous platelet concentrates on endodontic healing: a systematic review
Nastaran Meschi, Ana B. Castro, Katleen Vandamme, Marc Quirynen, Paul Lambrechts
Platelets.2016; 27(7): 613. CrossRef - Platelet concentrates for revitalization of immature necrotic teeth: a systematic review of the clinical studies
Alessandra Lolato, Cristina Bucchi, Silvio Taschieri, Ahmed El Kabbaney, Massimo Del Fabbro
Platelets.2016; 27(5): 383. CrossRef - Endodontie in der unreifen bleibenden Dentition — Maßnahmen zur Vitalerhaltung, Apexifikation und Regeneration der Pulpa
Martin Jung
Oralprophylaxe & Kinderzahnheilkunde.2016; 38(1): 29. CrossRef - A review of the regenerative endodontic treatment procedure
Bin-Na Lee, Jong-Wook Moon, Hoon-Sang Chang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Yun-Chan Hwang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(3): 179. CrossRef - Platelet preparations in dentistry: How? Why? Where? When?
Luigi Fabrizio Rodella
World Journal of Stomatology.2015; 4(2): 39. CrossRef - The use of platelet rich plasma in the treatment of immature tooth with periapical lesion: a case report
Günseli Güven Polat, Ceren Yıldırım, Özlem Martı Akgün, Ceyhan Altun, Didem Dinçer, Cansel Köse Özkan
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(3): 230. CrossRef
- Apicoectomy versus apical curettage in combination with or without L-PRF application: a randomized clinical trial
- 300 View
- 4 Download
- 35 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


