Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Concentrated growth factor scaffold-based pulpotomy of permanent molars with symptomatic irreversible pulpitis
- Arthi K. Harith, Vishnupriya Koteeswaran, Dinesh Kowsky, Natanasabapathy Velmurugan, Suresh Nandini
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(1):e1. Published online January 17, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
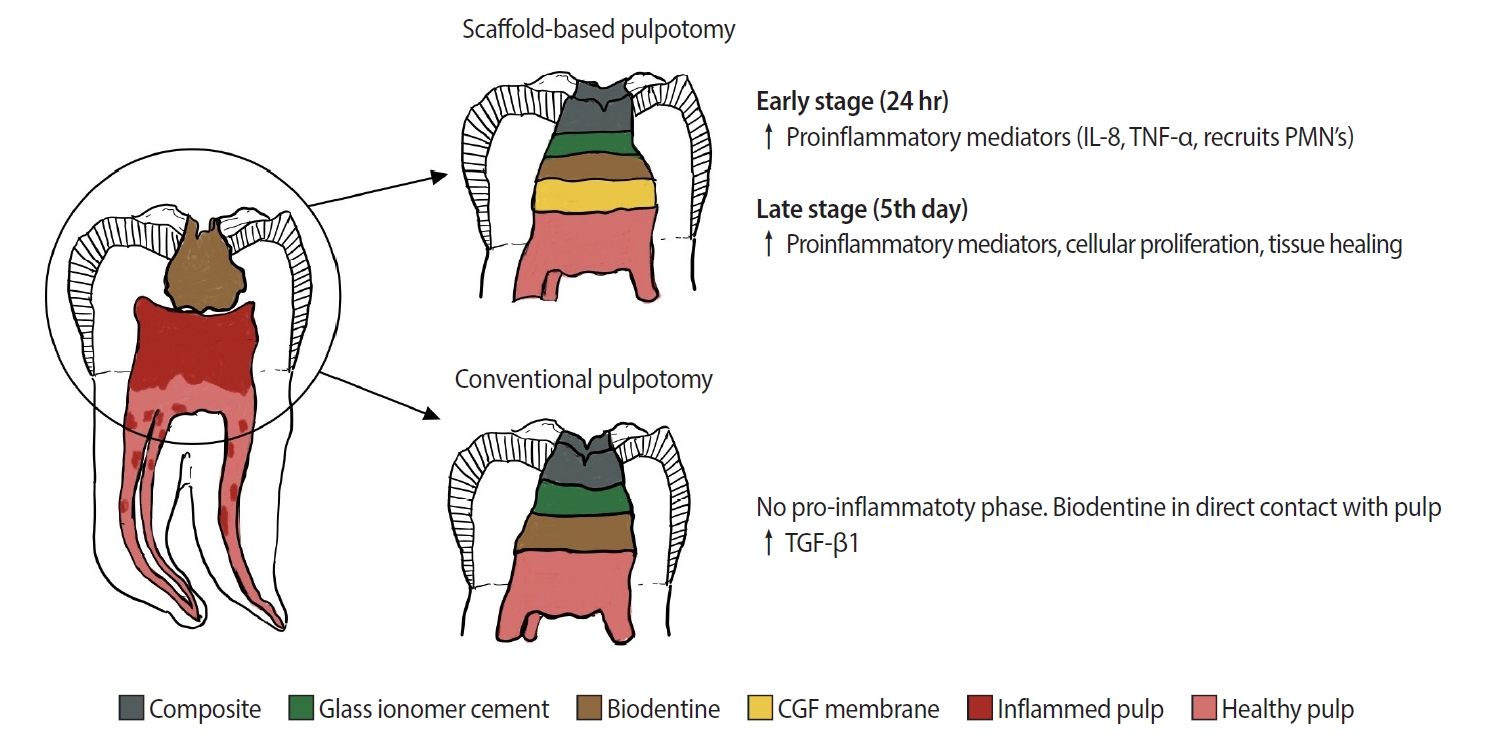
Pulpotomy is a minimally invasive procedure that aims to retain the vitality of the radicular pulp by removing the inflamed coronal pulp tissue. This case series presents the successful management of symptomatic irreversible pulpitis by pulpotomy with concentrated growth factor (CGF) scaffolds.
Methods
Six permanent mandibular molars with a diagnosis of symptomatic irreversible pulpitis were included. Under Local anesthesia and rubber dam isolation, caries were excavated using high-speed bur under coolant. Full coronal pulpotomy was done and hemostasis was achieved. CGF membrane was prepared and placed over the radicular pulp and layered with Biodentine (Septodont). Final restoration of type IX glass ionomer cement and bulk fill composite resin was placed. Patients were assessed for various clinical and radiographic parameters at intervals of 1 week and 3, 6, and 12 months. Five patients fulfilled the success criteria at the end of 1 year.
Results
Pulpotomy is considered an alternative treatment modality for root canal treatment in symptomatic irreversible pulpitis aiming at alleviating symptoms and maintaining vitality. CGF scaffold when used as a capping material acts as a reservoir for growth factors with anti-inflammatory properties and enhances healing.
Conclusions
Scaffold-based pulpotomy can be considered a biological approach to healing inflamed pulp.
- 4,585 View
- 469 Download

- Assessment of mechanical allodynia in healthy teeth adjacent and contralateral to endodontically diseased teeth: a clinical study
- Vaishnavi Ratnakar Patankar, Ashish K Jain, Rahul D Rao, Prajakta R Rao
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(3):e31. Published online July 29, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e31
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
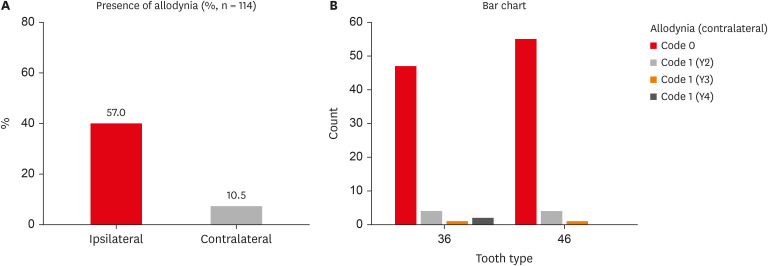
ePub Objectives The present study investigated the prevalence of mechanical allodynia (MA) in healthy teeth adjacent and contralateral to endodontically diseased teeth.
Materials and Methods This cross-sectional study included 114 patients with symptomatic irreversible pulpitis and apical periodontitis in permanent mandibular first molars who possessed healthy teeth adjacent and contralateral to the endodontically diseased tooth. The mechanical sensitivity of the teeth was determined by percussion testing. The presence or absence of pain on percussion in the teeth adjacent and contralateral to the endodontically diseased tooth and the tooth distal to the contralateral symmetrical tooth was recorded according to coding criteria. The prevalence of MA was computed as a percentage, and binary logistic regression analysis was done. The Fisher exact test and Mann-Whitney
U test were used for binary and ordinal data.Results Age and sex did not influence the prevalence of MA. An increased prevalence of MA was found in patients with higher levels of spontaneous pain (
p < 0.001). The prevalence of allodynia was 57% in teeth adjacent to endodontically diseased teeth and 10.5% in teeth contralateral to endodontically diseased teeth. In addition, on the ipsilateral side, there were more painful sensations distal to the diseased tooth than mesially.Conclusions Despite being disease-free, teeth adjacent and contralateral to endodontically diseased teeth exhibited pain on percussion. There was a direct association between the severity of the patient’s pain and the presence of MA.
- 3,008 View
- 91 Download

- Efficacy of buccal piroxicam infiltration and inferior alveolar nerve block in patients with irreversible pulpitis: a prospective, double-blind, randomized clinical trial
- Saurav Paul, Sridevi Nandamuri, Aakrati Raina, Mukta Bansal
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(1):e9. Published online January 26, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e9
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
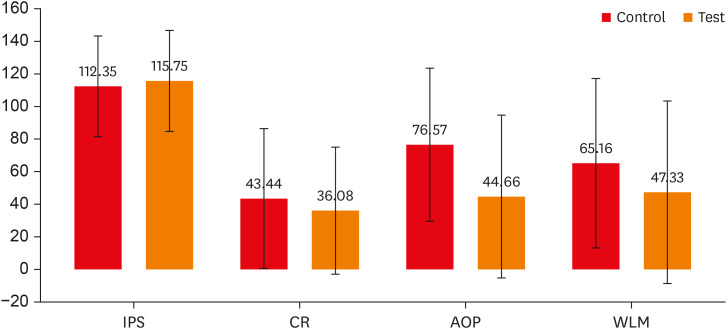
ePub Objectives This randomized clinical trial aimed to assess the effectiveness of buccal infiltration with piroxicam on the anesthetic efficacy of inferior alveolar nerve block (IANB) with buccal infiltration in irreversible pulpitis, with pain assessed using the Heft-Parker visual analogue scale (HP-VAS).
Materials and Methods This study included 56 patients with irreversible pulpitis in mandibular molars, randomly distributed between 2 groups (
n = 28). After evaluating the initial pain score with the HP-VAS, each patient received IANB followed by buccal infiltration of 2% lignocaine with adrenaline (1:80,000). Five minutes later, the patients in groups 1 and 2 were given buccal infiltration with 40 mg/2 mL of piroxicam or normal saline, respectively. An access opening procedure (AOP) was performed 15 minutes post-IANB once the individual showed signs of lip numbness as well as 2 negative responses to electric pulp testing. The HP-VAS was used to grade the patient's pain during caries removal (CR), AOP, and working length measurement (WLM). Successful anesthesia was identified either by the absence of pain or slight pain through CR, AOP, and WLM, with no requirement of a further anesthetic dose. A statistical analysis was done using the Shapiro-Wilk and Mann-WhitneyU tests.Results The piroxicam group presented a significantly lower (
p < 0.05) mean pain score than the saline group during AOP.Conclusions Buccal infiltration with piroxicam enhanced the efficacy of anesthesia with IANB and buccal infiltration with lignocaine in patients with irreversible pulpitis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Inferior alveolar nerve block success of 2% mepivacaine versus 4% articaine in patients with symptomatic irreversible pulpitis in mandibular molars: A randomized double‐blind single‐centre clinical trial
Mohammed Fawzy Omar Mohammed Habib, Sovana Tarek, Sara Mohamed Elsayed Teama, Khaled Ezzat, Randa Mohamed El Boghdadi, Abeer Marzouk, Manar Yehia Fouda, Shaimaa Ismail Gawdat, Marwa Mahmoud Bedier, Suzan Abdul Wanees Amin
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(11): 1177. CrossRef - Present status and future directions—Mechanisms and management of local anaesthetic failures
Masoud Parirokh, Paul V. Abbott
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S4): 951. CrossRef
- Inferior alveolar nerve block success of 2% mepivacaine versus 4% articaine in patients with symptomatic irreversible pulpitis in mandibular molars: A randomized double‐blind single‐centre clinical trial
- 2,252 View
- 23 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Development of a mouse model for pulp-dentin complex regeneration research: a preliminary study
- Sunil Kim, Sukjoon Lee, Han-Sung Jung, Sun-Young Kim, Euiseong Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(2):e20. Published online May 7, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e20
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
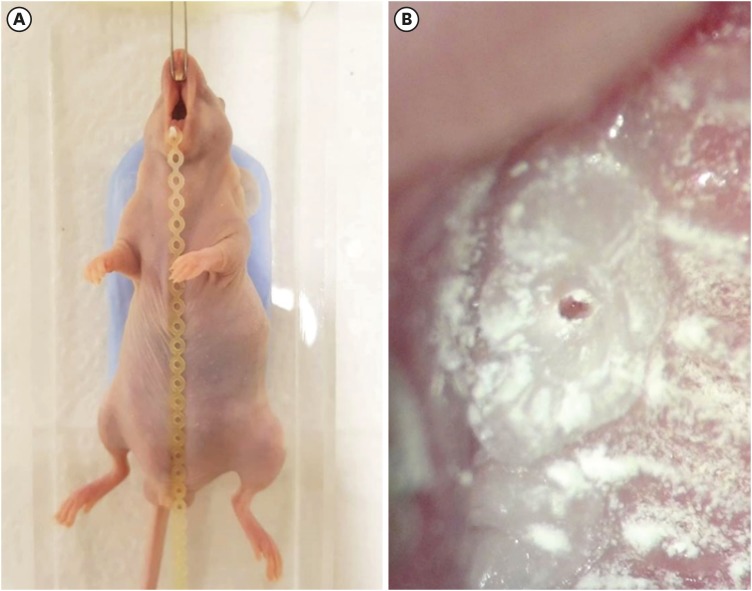
ePub Objectives To achieve pulp-dentin complex regeneration with tissue engineering, treatment efficacies and safeties should be evaluated using
in vivo orthotopic transplantation in a sufficient number of animals. Mice have been a species of choice in which to study stem cell biology in mammals. However, most pulp-dentin complex regeneration studies have used large animals because the mouse tooth is too small. The purpose of this study was to demonstrate the utility of the mouse tooth as a transplantation model for pulp-dentin complex regeneration research.Materials and Methods Experiments were performed using 7-week-old male Institute of Cancer Research (ICR) mice; a total of 35 mice had their pulp exposed, and 5 mice each were sacrificed at 1, 2, 4, 7, 9, 12 and 14 days after pulp exposure. After decalcification in 5% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, the samples were embedded and cut with a microtome and then stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Slides were observed under a high-magnification light microscope.
Results Until 1 week postoperatively, the tissue below the pulp chamber orifice appeared normal. The remaining coronal portion of the pulp tissue was inflammatory and necrotic. After 1 week postoperatively, inflammation and necrosis were apparent in the root canals inferior to the orifices. The specimens obtained after experimental day 14 showed necrosis of all tissue in the root canals.
Conclusions This study could provide opportunities for researchers performing
in vivo orthotopic transplantation experiments with mice.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Is dental pulp inflammation capable of causing central inflammation, behavioral, and sensory alterations? A pre-clinical study
Iago Ramirez, Igor Bassi Ferreira Petean, Francisco Wanderley Garcia de Paula-Silva, Aline Aparecida Ferraresi Tiballi, Manoel Damião Sousa-Neto, Fabiane Carneiro Lopes-Olhê, Christie Ramos Andrade Leite-Panissi, Jardel Francisco Mazzi-Chaves
Archives of Oral Biology.2025; 177: 106320. CrossRef - PRIASE 2021 guidelines for reporting animal studies in Endodontology: explanation and elaboration
V. Nagendrababu, A. Kishen, P. E. Murray, M. H. Nekoofar, J. A. P. de Figueiredo, E. Priya, J. Jayaraman, S. J. Pulikkotil, A. Jakovljevic, P. M. H. Dummer
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(6): 858. CrossRef
- Is dental pulp inflammation capable of causing central inflammation, behavioral, and sensory alterations? A pre-clinical study
- 1,766 View
- 10 Download
- 2 Crossref

-
Identification of
Enterococcus faecalis antigens specifically expressedin vivo - Seok-Woo Lee, Uttom K. Shet, Sang-Won Park, Hyun-Pil Lim, Kwi-Dug Yun, Seong Soo Kang, Se Eun Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(4):306-311. Published online October 5, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.4.306
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Molecular mechanism of the pathogenicity of
Enterococcus faecalis (E. faecalis ), a suspected endodontic pathogen, has not yet been adequately elucidated due to limited information on its virulence factors. Here we report the identification ofin vivo expressed antigens ofE. faecalis by using a novel immunoscreening technique called change-mediated antigen technology (CMAT) and an experimental animal model of endodontic infection.Materials and Methods Among 4,500
E. coli recombinant clones screened, 19 positive clones reacted reproducibly with hyperimmune sera obtained from rabbits immunized withE. faecalis cells isolated from an experimental endodontic infection. DNA sequences from 16 of thesein vivo -induced (IVI) genes were determined.Results Identified protein antigens of
E. faecalis included enzymes involved in housekeeping functions, copper resistance protein, putative outer membrane proteins, and proteins of unknown function.Conclusions In vivo expressed antigens ofE. faecalis could be identified by using a novel immune-screening technique CMAT and an experimental animal model of endodontic infection. Detailed analysis of these IVI genes will lead to a better understanding of the molecular mechanisms involved in the endodontic infection ofE. faecalis .-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by-
Insights into ecology, pathogenesis, and biofilm formation of
Enterococcus faecalis
from functional genomics
Julia L. E. Willett, Gary M. Dunny, Corrella S. Detweiler
Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Antibody-based Screening of Porphyromonas gingivalis Proteins Specifically Produced in Patients with Chronic Periodontitis
Hye-Jung Kim, Seok-Woo Lee
International Journal of Oral Biology.2018; 43(4): 201. CrossRef - The controversial role of Enterococcus faecalis in colorectal cancer
Carolina Vieira de Almeida, Antonio Taddei, Amedeo Amedei
Therapeutic Advances in Gastroenterology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Model systems for the study of Enterococcal colonization and infection
H. M. Sharon Goh, M. H. Adeline Yong, Kelvin Kian Long Chong, Kimberly A. Kline
Virulence.2017; 8(8): 1525. CrossRef
-
Insights into ecology, pathogenesis, and biofilm formation of
Enterococcus faecalis
from functional genomics
- 1,596 View
- 3 Download
- 4 Crossref

- The success rate of bupivacaine and lidocaine as anesthetic agents in inferior alveolar nerve block in teeth with irreversible pulpitis without spontaneous pain
- Masoud Parirokh, Mohammad Hosein Yosefi, Nouzar Nakhaee, Paul V. Abbott, Hamed Manochehrifar
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(2):155-160. Published online March 16, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.2.155
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Achieving adequate anesthesia with inferior alveolar nerve blocks (IANB) is of great importance during dental procedures. The aim of the present study was to assess the success rate of two anesthetic agents (bupivacaine and lidocaine) for IANB when treating teeth with irreversible pulpitis.
Materials and Methods Sixty volunteer male and female patients who required root canal treatment of a mandibular molar due to caries participated in the present study. The inclusion criteria included prolonged pain to thermal stimulus but no spontaneous pain. The patients were randomly allocated to receive either 2% lidocaine with 1:80,000 epinephrine or 0.5% bupivacaine with 1:200,000 epinephrine as an IANB injection. The sensitivity of the teeth to a cold test as well as the amount of pain during access cavity preparation and root canal instrumentation were recorded. Results were statistically analyzed with the Chi-Square and Fischer's exact tests.
Results At the final step, fifty-nine patients were included in the study. The success rate for bupivacaine and lidocaine groups were 20.0% and 24.1%, respectively. There was no significant difference between the two groups at any stage of the treatment procedure.
Conclusions There was no difference in success rates of anesthesia when bupivacaine and lidocaine were used for IANB injections to treat mandibular molar teeth with irreversible pulpitis. Neither agent was able to completely anesthetize the teeth effectively. Therefore, practitioners should be prepared to administer supplemental anesthesia to overcome pain during root canal treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Morphometric Study of the Mandibular Foramen, Lingula, and the Incidence of Accessory Mandibular Foramina in Dry Mandibles
Yashaswi Singh, Pratibha Shakya, Noor Us Saba, Heena Singh, Navneet Kumar
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A Comparative Evaluation of the Effect of Photobiomodulation on the Depth of Anaesthesia During Endodontic Treatment of Teeth with Symptomatic Irreversible Pulpitis—A Prospective Clinical Trial
Akshita Balivada, R Vinay Chandra, D Krithika, B Arvind, Mrinalini Jaichander, Priyanka Girish
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2025; 17(Suppl 2): S1359. CrossRef - Is there a direct relationship between the cost and effectiveness of local anesthetics in lower molars with irreversible pulpitis? Systematic review, meta-analysis and cost-effectiveness evaluation
Luísa Figueredo de Carvalho, Adriana Poli Castilho Dugaich, Alexandra Maria de Melo Schiefler, Letícia Cristine Ramos Ribeiro, Andressa da Silva Barboza, Sheila Cristina Stolf, Rafael Guerra Lund, Juliana Silva Ribeiro de Andrade
Journal of Dentistry.2025; 163: 106175. CrossRef - Effect of topical application of amitriptyline and nortriptyline on irreversible pulpitis pain in teeth with failed pulpal anesthesia after a successful inferior alveolar nerve block: A randomized clinical trial
Armita Vali Sichani, Hossein Baharian, Navid Yaraghi, Zahra Khosravani, Asana Vali Sichani
Dental Research Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of the Anatomic Variables on the Success Rate of Anesthesia in Maxillary Molars with Irreversible Pulpitis
Masoud Parirokh, Sina Kakooei, Nouzar Nakhaee, Hamed Manochehrifar, Paul Abbott
Journal of Endodontics.2022; 48(6): 707. CrossRef - Present status and future directions—Mechanisms and management of local anaesthetic failures
Masoud Parirokh, Paul V. Abbott
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S4): 951. CrossRef - Local anesthesia in oral and maxillofacial surgery: A review of current opinion
Yu-Hao Wang, Dian-Ri Wang, Ji-Yuan Liu, Jian Pan
Journal of Dental Sciences.2021; 16(4): 1055. CrossRef - ANATOMICAL STUDY OF MANDIBULAR FORAMEN IN DRY ADULT HUMAN MANDIBLES IN BIHAR STATE REGION
Vijay Kumar Singh, Md. Zahid Hussain, Subodh Kumar
GLOBAL JOURNAL FOR RESEARCH ANALYSIS.2021; : 34. CrossRef - Efficacy of buccal piroxicam infiltration and inferior alveolar nerve block in patients with irreversible pulpitis: a prospective, double-blind, randomized clinical trial
Saurav Paul, Sridevi Nandamuri, Aakrati Raina, Mukta Bansal
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Different anesthetics on the efficacy of inferior alveolar nerve block in patients with irreversible pulpitis
Juliana Larocca de Geus, Jane Kenya Nogueira da Costa, Letícia Maíra Wambier, Bianca Medeiros Maran, Alessandro Dourado Loguercio, Alessandra Reis
The Journal of the American Dental Association.2020; 151(2): 87. CrossRef - Efficacy of local anaesthetic solutions on the success of inferior alveolar nerve block in patients with irreversible pulpitis: a systematic review and network meta‐analysis of randomized clinical trials
V. Nagendrababu, S. J. Pulikkotil, A. Suresh, S. K. Veettil, S. Bhatia, F. C. Setzer
International Endodontic Journal.2019; 52(6): 779. CrossRef - The Effect of Sphenopalatine Block on the Postoperative Pain of Endoscopic Sinus Surgery: A Meta‐analysis
Do Hyun Kim, Haram Kang, Se Hwan Hwang
Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery.2019; 160(2): 223. CrossRef - Effect of four local anesthetics (tetracaine, proparacaine, lidocaine, and bupivacaine) on intraocular pressure in dogs
Ali Asghar Sarchahi, Mehdi Eskandari
International Ophthalmology.2019; 39(7): 1467. CrossRef - Strategies for managing pain during endodontic treatment
Paul V. Abbott, Masoud Parirokh
Australian Endodontic Journal.2018; 44(2): 99. CrossRef - Is mepivacaine as effective as lidocaine during inferior alveolar nerve blocks in patients with symptomatic irreversible pulpitis? A systematic review and meta‐analysis
W. A. Vieira, L. R. Paranhos, G. O. Cericato, A. Franco, M. A. G. Ribeiro
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(10): 1104. CrossRef - Injectable local anaesthetic agents for dental anaesthesia
Geoffrey St George, Alyn Morgan, John Meechan, David R Moles, Ian Needleman, Yuan-Ling Ng, Aviva Petrie
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Successful pulpal anesthesia for symptomatic irreversible pulpitis
Melissa Drum, Al Reader, John Nusstein, Sara Fowler
The Journal of the American Dental Association.2017; 148(4): 267. CrossRef - The Effect of Photobiomodulation on the Depth of Anesthesia During Endodontic Treatment of Teeth With Symptomatic Irreversible Pulpitis (Double Blind Randomized Clinical Trial)
Sholeh Ghabraei, Nasim Chiniforush, Behnam Bolhari, Mohsen Aminsobhani, Abbas Khosarvi
Journal of Lasers in Medical Sciences.2017; 9(1): 11. CrossRef - Morphometric study on mandibular foramen and incidence of accessory mandibular foramen in mandibles of south Indian population and its clinical implications in inferior alveolar nerve block
R. Shalini, C. RaviVarman, R. Manoranjitham, M. Veeramuthu
Anatomy & Cell Biology.2016; 49(4): 241. CrossRef - The Effect of Maxillary First Molar Root Length on the Success Rate of Buccal Infiltration Anesthesia
Ehsan Moradi Askari, Masoud Parirokh, Nouzar Nakhaee, Hamid Reza Hosseini, Paul V. Abbott
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(10): 1462. CrossRef - Efficacy of Ketorolac Buccal Infiltrations and Inferior Alveolar Nerve Blocks in Patients with Irreversible Pulpitis: A Prospective, Double-blind, Randomized Clinical Trial
Nahid Mohammadzadeh Akhlaghi, Behnoush Hormozi, Paul V. Abbott, Zohreh Khalilak
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(5): 691. CrossRef
- A Morphometric Study of the Mandibular Foramen, Lingula, and the Incidence of Accessory Mandibular Foramina in Dry Mandibles
- 3,000 View
- 9 Download
- 21 Crossref

- Conservative approach of a symptomatic carious immature permanent tooth using a tricalcium silicate cement (Biodentine): a case report
- Cyril Villat, Brigitte Grosgogeat, Dominique Seux, Pierre Farge
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(4):258-262. Published online November 12, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.4.258
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The restorative management of deep carious lesions and the preservation of pulp vitality of immature teeth present real challenges for dental practitioners. New tricalcium silicate cements are of interest in the treatment of such cases. This case describes the immediate management and the follow-up of an extensive carious lesion on an immature second right mandibular premolar. Following anesthesia and rubber dam isolation, the carious lesion was removed and a partial pulpotomy was performed. After obtaining hemostasis, the exposed pulp was covered with a tricalcium silicate cement (Biodentine, Septodont) and a glass ionomer cement (Fuji IX extra, GC Corp.) restoration was placed over the tricalcium silicate cement. A review appointment was arranged after seven days, where the tooth was asymptomatic with the patient reporting no pain during the intervening period. At both 3 and 6 mon follow up, it was noted that the tooth was vital, with normal responses to thermal tests. Radiographic examination of the tooth indicated dentin-bridge formation in the pulp chamber and the continuous root formation. This case report demonstrates a fast tissue response both at the pulpal and root dentin level. The use of tricalcium silicate cement should be considered as a conservative intervention in the treatment of symptomatic immature teeth.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bioceramic Pulpotomy and Direct Pulp
Capping on Complicated Fractures
Reattachment of Young Mature
Permanent Teeth: Case Series
A. Lavanya
The Traumaxilla.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical and radiographic outcomes of pulpotomy materials in permanent teeth: a systematic review of calcium hydroxide, MTA, biodentine, and iRoot BP plus
Anggi Putri Riandani, Arief Cahyanto, Rana Abdelbaset Lotfy Diab, Ratih Widyasari, Atia Nurul Sidiqa, Hendra Dian Adhita Dharsono, Myrna Nurlatifah Zakaria
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - How Does Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid Irrigation Affect Biodentine? A Multimethod Ex Vivo Study
Katarzyna Dąbrowska, Aleksandra Palatyńska-Ulatowska, Leszek Klimek
Materials.2024; 17(6): 1230. CrossRef - Evaluation of Biodentine Tricalcium Silicate-Based Cement after Chlorhexidine Irrigation
Katarzyna Dąbrowska, Aleksandra Palatyńska-Ulatowska, Leszek Klimek
Applied Sciences.2024; 14(19): 8702. CrossRef - Evaluation of the chemical, physical, and biological properties of a newly developed bioceramic cement derived from cockle shells: an in vitro study
Monthip Wannakajeepiboon, Chankhrit Sathorn, Chatvadee Kornsuthisopon, Busayarat Santiwong, Thanakorn Wasanapiarnpong, Pairoj Linsuwanont
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Protección pulpar directa y posterior apexogénesis. Informe de un caso clínico / Direct pulp capping followed by apexogenesis. A clinical case report
Osvaldo Zmener, Ana C. Boetto
Revista de la Asociación Odontológica Argentina.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of Irrigation with Citric Acid on Biodentine Tricalcium Silicate-Based Cement: SEM-EDS In Vitro Study
Katarzyna Dąbrowska, Aleksandra Palatyńska-Ulatowska, Leszek Klimek
Materials.2022; 15(10): 3467. CrossRef - The Immunomodulatory and Regenerative Effect of Biodentine™ on Human THP‐1 Cells and Dental Pulp Stem Cells: In Vitro Study
Duaa Abuarqoub, Nazneen Aslam, Rand Zaza, Hanan Jafar, Suzan Zalloum, Renata Atoom, Walhan Alshaer, Mairvat Al-Mrahleh, Abdalla Awidi, Bruna Sinjari
BioMed Research International.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Biodentine: Material of choice for apexification
Himanshu Aeran, Mahema Sharma, Avantika Tuli
International Journal of Oral Health Dentistry.2021; 7(1): 54. CrossRef - Minimal Intervention in Dentistry: A Literature Review on Biodentine as a Bioactive Pulp Capping Material
Naji Ziad Arandi, Mohammad Thabet, Mona Abbassy
BioMed Research International.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Biodentine Pulpotomies on Permanent Traumatized Teeth with Complicated Crown Fractures
Léa Haikal, Beatriz Ferraz dos Santos, Duy-Dat Vu, Marina Braniste, Basma Dabbagh
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(9): 1204. CrossRef - Influence of sodium hypochlorite and ultrasounds on surface features and chemical composition of Biodentine tricalcium silicate-based material
Aleksandra PALATYŃSKA-ULATOWSKA, Katarzyna BUŁA, Leszek KLIMEK
Dental Materials Journal.2020; 39(4): 587. CrossRef - Effects of two fast-setting pulp-capping materials on cell viability and osteogenic differentiation in human dental pulp stem cells: An in vitro study
Yan Sun, Jun Liu, Tao Luo, Ya Shen, Ling Zou
Archives of Oral Biology.2019; 100: 100. CrossRef - Healing Capacity of Autologous Bone Marrow–derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Partially Pulpotomized Dogs' Teeth
Mona H. El-Zekrid, Salah H. Mahmoud, Fawzy A. Ali, Mohamed E. Helal, Mohammed E. Grawish
Journal of Endodontics.2019; 45(3): 287. CrossRef - Large Periapical or Cystic Lesions in Association with Roots Having Open Apices Managed Nonsurgically Using 1-step Apexification Based on Platelet-rich Fibrin Matrix and Biodentine Apical Barrier: A Case Series
Sarang Sharma, Vivek Sharma, Deepak Passi, Dhirendra Srivastava, Shibani Grover, Shubha Ranjan Dutta
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(1): 179. CrossRef - Microleakage and Shear Bond Strength of Biodentine at Different Setting Time
Yong Ho Song, Nanyoung Lee, Sangho Lee, Myeongkwan Jih
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2018; 45(3): 344. CrossRef - Biodentine™ material characteristics and clinical applications: a 3 year literature review and update
S. Rajasekharan, L. C. Martens, R. G. E. C. Cauwels, R. P. Anthonappa
European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry.2018; 19(1): 1. CrossRef - Case Report: Immediate pain relief after partial pulpotomy of cariously exposed young permanent molar using mineral trioxide aggregate and root maturation, with two years follow-up
Passant Nagi, Nevine Waly, Adel Elbardissy, Mohammed Khalifa
F1000Research.2018; 7: 1616. CrossRef - Factors affecting the outcomes of direct pulp capping using Biodentine
Mariusz Lipski, Alicja Nowicka, Katarzyna Kot, Lidia Postek-Stefańska, Iwona Wysoczańska-Jankowicz, Lech Borkowski, Paweł Andersz, Anna Jarząbek, Katarzyna Grocholewicz, Ewa Sobolewska, Krzysztof Woźniak, Agnieszka Droździk
Clinical Oral Investigations.2018; 22(5): 2021. CrossRef - Mineral trioxide aggregate and other bioactive endodontic cements: an updated overview – part I: vital pulp therapy
M. Parirokh, M. Torabinejad, P. M. H. Dummer
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(2): 177. CrossRef - Effect of iRoot Fast Set root repair material on the proliferation, migration and differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells in vitro
Yan Sun, Tao Luo, Ya Shen, Markus Haapasalo, Ling Zou, Jun Liu, Gianpaolo Papaccio
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(10): e0186848. CrossRef - Dislodgement resistance of calcium silicate‐based materials from root canals with varying thickness of dentine
Ö. İ. Ulusoy, Y. N. Paltun, N. Güven, B. Çelik
International Endodontic Journal.2016; 49(12): 1188. CrossRef - Expression of Mineralization Markers during Pulp Response to Biodentine and Mineral Trioxide Aggregate
Mariana O. Daltoé, Francisco Wanderley G. Paula-Silva, Lúcia H. Faccioli, Patrícia M. Gatón-Hernández, Andiara De Rossi, Léa Assed Bezerra Silva
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(4): 596. CrossRef - Biodentine Reduces Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha–induced TRPA1 Expression in Odontoblastlike Cells
Ikhlas A. El Karim, Maelíosa T.C. McCrudden, Mary K. McGahon, Tim M. Curtis, Charlotte Jeanneau, Thomas Giraud, Chris R. Irwin, Gerard J. Linden, Fionnuala T. Lundy, Imad About
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(4): 589. CrossRef - Coronal Pulpotomy Technique Analysis as an Alternative to Pulpectomy for Preserving the Tooth Vitality, in the Context of Tissue Regeneration: A Correlated Clinical Study across 4 Adult Permanent Molars
Raji Viola Solomon, Umrana Faizuddin, Parupalli Karunakar, Grandhala Deepthi Sarvani, Sevvana Sree Soumya, Jiiang H. Jeng
Case Reports in Dentistry.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - A Review on Biodentine, a Contemporary Dentine Replacement and Repair Material
Özlem Malkondu, Meriç Karapinar Kazandağ, Ender Kazazoğlu
BioMed Research International.2014; 2014: 1. CrossRef - The use of platelet rich plasma in the treatment of immature tooth with periapical lesion: a case report
Günseli Güven Polat, Ceren Yıldırım, Özlem Martı Akgün, Ceyhan Altun, Didem Dinçer, Cansel Köse Özkan
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(3): 230. CrossRef - Biodentine-a novel dentinal substitute for single visit apexification
Gurudutt Nayak, Mohammad Faiz Hasan
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(2): 120. CrossRef
- Bioceramic Pulpotomy and Direct Pulp
Capping on Complicated Fractures
Reattachment of Young Mature
Permanent Teeth: Case Series
- 2,102 View
- 5 Download
- 28 Crossref

- Endodontic treatment of mandibular molar with root dilaceration using Reciproc single-file system
- Daniely Amorin Meireles, Mariana Mena Barreto Bastos, André Augusto Franco Marques, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia, Emílio Carlos Sponchiado
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(3):167-171. Published online August 23, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.3.167
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Biomechanical preparation of root canals with accentuated curvature is challenging. New rotatory systems, such as Reciproc, require a shorter period of time to prepare curved canals, and became a viable alternative for endodontic treatment of teeth with root dilaceration. Thus, this study aimed to report a clinical case of endodontic therapy of root with accentuated dilaceration using Reciproc single-file system. Mandibular right second molar was diagnosed as asymptomatic irreversible pulpitis. Pulp chamber access was performed, and glide path was created with #10 K-file (Dentsply Maillefer) and PathFile #13, #16 and #19 (Dentsply Maillefer) up to the temporary working length. The working length measured corresponded to 20 mm in the mesio-buccal and mesio-lingual canals, and 22 mm in the distal canal. The R25 file (VDW GmbH) was used in all the canals for instrumentation and final preparation, followed by filling with Reciproc gutta-percha cones (VDW GmbH) and AH Plus sealer (Dentsply Maillefer), using thermal compaction technique. The case has been receiving follow-up for 6 mon and no painful symptomatology or periapical lesions have been found. Despite the difficulties, the treatment could be performed in a shorter period of time than the conventional methods.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Surface Characteristics of Reciprocating Instruments Before and After Use - A SEM Analysis
Aida Rene Assayag Hanan, Daniely Amorin de Meireles, Emílio Carlos Sponchiado Júnior, Simone Hanan, Milton Carlos Kuga, Idomeo Bonetti Filho
Brazilian Dental Journal.2015; 26(2): 121. CrossRef - Endodontic Treatment of an Anomalous Anterior Tooth with the Aid of a 3-dimensional Printed Physical Tooth Model
Chanhee Byun, Changhwan Kim, Seungryong Cho, Seung Hoon Baek, Gyutae Kim, Sahng G. Kim, Sun-Young Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(6): 961. CrossRef
- Surface Characteristics of Reciprocating Instruments Before and After Use - A SEM Analysis
- 1,570 View
- 3 Download
- 2 Crossref

- The relationship between the level of salivary alpha amylase activity and pain severity in patients with symptomatic irreversible pulpitis
- Fatemeh Ahmadi-Motamayel, Shahriar Shahriari, Mohammad Taghi Goodarzi, Abbas Moghimbeigi, Mina Jazaeri, Parisa Babaei
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(3):141-145. Published online August 23, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.3.141
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Assessment of dental pain severity is very challenging in dentistry. Previous studies have suggested that elevated salivary alpha amylase may contribute to increased physical stresses. There is a close association between salivary alpha amylase and plasma norepinephrine under stressful physical conditions. The aim of this study was to evaluate the relationship between pain severity and salivary alpha amylase levels in patients with symptomatic irreversible pulpitis.
Materials and Methods Thirty-six patients (20 females and 16 males) with severe tooth pain due to symptomatic irreversible pulpitis were selected. The visual analogue scale (VAS) score was used to assess the pain severity in each patient. Unstimulated whole saliva was collected, and the level of alpha amylase activity was assessed by the spectrophotometric method. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS 13.
Results The level of alpha amylase was significantly increased in the saliva in association with pain severity assessed by VAS. The salivary alpha amylase was also elevated with increased age and in males.
Conclusions There was a significant correlation between the VAS pain scale and salivary alpha amylase level, which indicates this biomarker may be a good index for the objective assessment of pain intensity.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Long COVID-19 effect on Prevalence of Dental Caries and Periodontal Disease and Correlation with Salivary Total Antioxidant Capacity and Alpha Amylase Levels among Subpopulation of North Karnataka Region of India
Kiran R Halkai, Rahul Halkai
Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology.2025; : 3880. CrossRef - Diagnosis of Pain Deception Using Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory-2 Based on XGBoost Machine Learning Algorithm: A Single-Blinded Randomized Controlled Trial
Hyewon Chung, Kihwan Nam, Subin Lee, Ami Woo, Joongbaek Kim, Eunhye Park, Hosik Moon
Medicina.2024; 60(12): 1989. CrossRef - Utilizing Saliva Biomarkers for Diagnostic Purposes
Fatemeh Ahmadi -Motamayel, Ali Mahdavinezhad, Seyedeh Sareh Hendi
Avicenna Journal of Dental Research.2024; 16(1): 46. CrossRef - Clinical correlation of salivary alpha-amylase levels with pain intensity in patients undergoing emergency endodontic treatment
Kavalipurapu Venkata Teja, Sindhu Ramesh, Krishnamachari Janani, Kumar Chandan Srivastava, Deepti Shrivastava, Valentino Natoli, Marco Di Blasio, Marco Cicciù, Giuseppe Minervini
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Statherin and alpha-amylase levels in saliva from patients with gingivitis and periodontitis
Hanife Merva Parlak, Esra Buber, Ali Tugrul Gur, Erdem Karabulut, Ferda Alev Akalin
Archives of Oral Biology.2023; 145: 105574. CrossRef - Topical review – salivary biomarkers in chronic muscle pain
Hajer Jasim
Scandinavian Journal of Pain.2023; 23(1): 3. CrossRef - Relationship between salivary alpha-amylase activity and pain relief scale score after low level laser therapy: a prospective interventional pilot study
Ryoji Iida, Junpei Konishi, Takahiro Suzuki
Lasers in Medical Science.2022; 37(1): 681. CrossRef - Assessment of salivary stress and pain biomarkers and their relation to self-reported pain intensity during orthodontic tooth movement: a longitudinal and prospective study
Nehir Canigur Bavbek, Erdal Bozkaya, Sila Cagri Isler, Sehri Elbeg, Ahu Uraz, Sema Yuksel
Journal of Orofacial Orthopedics / Fortschritte der Kieferorthopädie.2022; 83(5): 339. CrossRef - Pain intensity and salivary α‐amylase activity in patients following mandibular third molar surgery
Wanvipa Surin, Piyanart Chatiketu, Nuntouchaporn Hutachok, Somdet Srichairatanakool, Vuttinun Chatupos
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2022; 8(5): 1082. CrossRef - Application of Salivary Biomarkers in the Diagnosis of Fibromyalgia
Rebeca Illescas-Montes, Víctor J. Costela-Ruiz, Lucía Melguizo-Rodríguez, Elvira De Luna-Bertos, Concepción Ruiz, Javier Ramos-Torrecillas
Diagnostics.2021; 11(1): 63. CrossRef - The Correlation between Pain, Stress, and Oral Function in Oral and Maxillofacial Infection and Trauma Patients
Medyannisa Shafira, Tantry Maulina, Nurnayly Putri Lyana, Endang Sjamsudin, Andri Hardianto
The Open Dentistry Journal.2021; 15(1): 266. CrossRef - Comparison of the Zurich Observation Pain Assessment with the Behavioural Pain Scale and the Critical Care Pain Observation Tool in nonverbal patients in the intensive care unit: A prospective observational study
Martin R. Fröhlich, Gabriele Meyer, Rebecca Spirig, Lucas M. Bachmann
Intensive and Critical Care Nursing.2020; 60: 102874. CrossRef - Salivary Alpha-Amylase in Experimentally-Induced Muscle Pain
Nikolaos Christidis, Pegah Baghernejad, Aylin Deyhim, Hajer Jasim
Diagnostics.2020; 10(9): 722. CrossRef - Protein Signature in Saliva of Temporomandibular Disorders Myalgia
Hajer Jasim, Malin Ernberg, Anders Carlsson, Björn Gerdle, Bijar Ghafouri
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(7): 2569. CrossRef - The Relationship Between Salivary Alpha Amylase Activity and Score of McGill Pain Questionnaire in Patients With Tension Type Headache
Mohammad Vahedi, Mehrdokht Mazdeh, Mehrdad Hajilooi, Maryam Farhadian, Yasamin Barakian, Parastoo Sadr
Basic and Clinical Neuroscience Journal.2018; 9(1): 59. CrossRef - Salivary Stress-Related Responses in Tinnitus: A Preliminary Study in Young Male Subjects with Tinnitus
Ola A. Alsalman, Denise Tucker, Sven Vanneste
Frontiers in Neuroscience.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Pain during embryo transfer is independently associated with clinical pregnancy in fresh/frozen assisted reproductive technology cycles
Sotirios H. Saravelos, Alice WY. Wong, Grace WS. Kong, Jin Huang, Robert Klitzman, Tin‐Chiu Li
Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research.2016; 42(6): 684. CrossRef
- Long COVID-19 effect on Prevalence of Dental Caries and Periodontal Disease and Correlation with Salivary Total Antioxidant Capacity and Alpha Amylase Levels among Subpopulation of North Karnataka Region of India
- 1,966 View
- 9 Download
- 17 Crossref

- Isolation and identification of bacteria from the root canal of the teeth diagnosed as the acute pulpitis and acute periapical abscess
- Yeon-Jae Lee, Mi-Kwang Kim, Ho-Keel Hwang, Joong-Ki Kook
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(5):409-422. Published online September 30, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.5.409
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The aim of this study was to identify the bacteria isolated from acute endodontic lesions by cell culture and 16S rDNA sequencing. The necrotic pulpal tissue was collected from 17 infected root canals, which were diagnosed as being either an acute pulpitis or acute periapical abscess. Samples were collected aseptically from the infected pulpal tissue of the infected root canals using a barbed broach and a paper point. The cut barbed broaches and paper points were transferred to an eppendorf tube containing 500 ul of 1 X PBS. The sample solution was briefly mixed and plated onto a BHI-agar plate containing 5% sheep blood. The agar plates were incubated in a 37℃ anaerobic chamber for 7 days. The bacteria growing on the agar plate were identified by 16S rRNA coding gene (rDNA) cloning and sequencing at the species level. Among the 71 colonies grown on the agar plates, 56 strains survived and were identified. In dental caries involving the root canals,
Streptococcus spp. were mainly isolated.Actinomyces ,Clostridia ,Bacteroides andFusobacteria were isolated in the periapical lesion without dental caries. Interestingly, two newActinomyces spp. (ChDC B639 and ChDC B631) were isolated in this study. These results showed that there was diversity among the species in endodontic lesions. This suggests that an endodontic infection is a mixed infection with a polymicrobial etiology. These results may offer the bacterial strains for pathogenesis studies related to an endodontic infection.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Microorganism penetration in dentinal tubules of instrumented and retreated root canal walls.In vitroSEM study
Saad Al-Nazhan, Alaa Al-Sulaiman, Fellwa Al-Rasheed, Fatimah Alnajjar, Bander Al-Abdulwahab, Abdulhakeem Al-Badah
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(4): 258. CrossRef - Microbial profile of asymptomatic and symptomatic teeth with primary endodontic infections by pyrosequencing
Sang-Min Lim, Tae-Kwon Lee, Eun-Jeong Kim, Jun-Hong Park, Yoon Lee, Kwang-Shik Bae, Kee-Yeon Kum
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(6): 498. CrossRef
- Microorganism penetration in dentinal tubules of instrumented and retreated root canal walls.In vitroSEM study
- 1,415 View
- 11 Download
- 2 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


