Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Pattern of endodontic instrument separation and factors affecting its retrieval: a 10-year retrospective observational study in a postgraduate institute
- Velmurugan Natanasabapathy, Aswathi Varghese, Paul Kevin Abishek Karthikeyan, Srinivasan Narasimhan
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(1):e7. Published online February 19, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e7
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
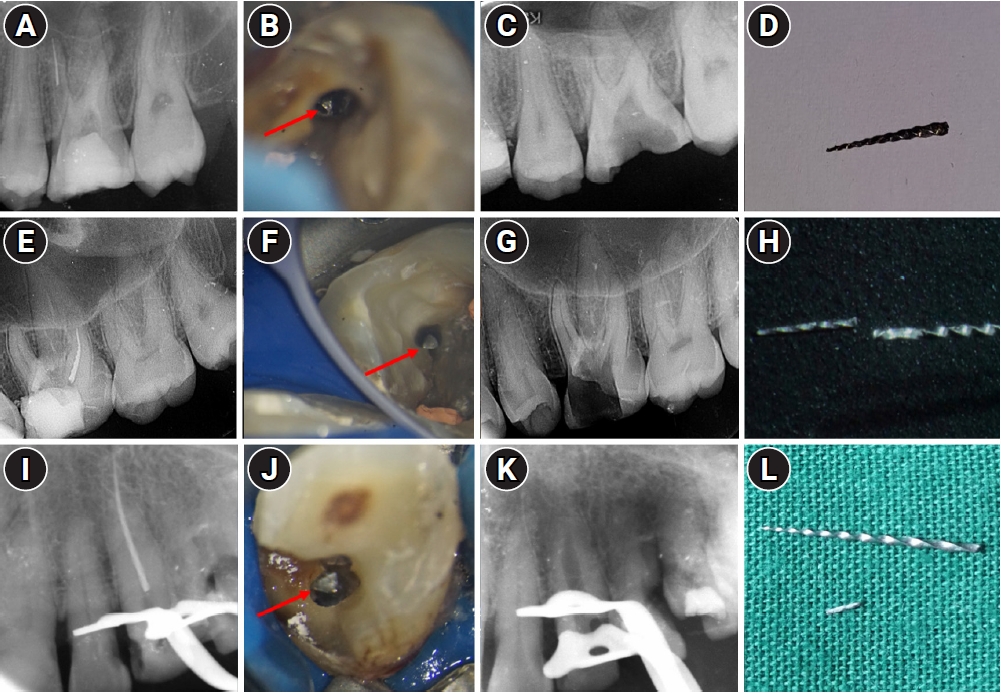
This study aimed to assess the pattern of endodontic instrument separation, their retrievability, and factors affecting its retrieval, in a postgraduate institute.
Methods
Cases referred for the management of separated endodontic instruments (SEI) from 2013 to 2023 were considered for this study. Data related to demographics, tooth type, file type, and retrieval were documented in an Excel sheet. Eight prognostic factors assumed to influence the retrieval were analyzed in this study. The secondary aim was to compare the pattern of SEI and retrievability between conventional nickel-titanium files and newer generation heat-treated nickel-titanium files. Retrieval was attempted by a senior endodontist under the dental operating microscope. Various ultrasonic tips and a Broken Tool Removal loop system were used during retrieval. Simple descriptive statistics were performed. Binomial logistic regression was done to identify the effect of the eight prognostic factors on the retrieval outcome.
Results
A total of 190 SEI was reported. SEI occurred more often in posterior teeth than anterior teeth, mandibular arch than maxillary arch, and in larger files than smaller files. Separation occurred more often in the apical third compared to the other levels. Retrieval was attempted in 88 cases and successful in 70 cases (79.5%). The larger taper and apical position of the SEI negatively influenced the retrieval by 1.4 and 8.7 times, respectively.
Conclusions
Retrieval of SEI was successful in the majority of the cases. An increase in taper and apically placed SEI negatively impacted the retrieval. There was no difference in the pattern of separation nor retrievability between conventional nickel-titanium files and newer generation heat-treated nickel-titanium files. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk Factors for Failure of Separated Instrument Removal: A Systematic Review and Meta‐Analysis
Le Zhao, WangYu Luo, Yue Shen, WanNing Yu, Liu Yang, Xiaolei Zhang
Australian Endodontic Journal.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of microscope-assisted root canal treatment in permanent posterior teeth: A retrospective cohort study
Ya-Ching Chang, Ting-Ya Wang
Journal of Dentistry.2025; 157: 105771. CrossRef - Deep Learning-Based Detection of Separated Root Canal Instruments in Panoramic Radiographs Using a U2-Net Architecture
Nildem İnönü, Umut Aksoy, Dilan Kırmızı, Seçil Aksoy, Nurullah Akkaya, Kaan Orhan
Diagnostics.2025; 15(14): 1744. CrossRef - MANAGEMENT OF INTRACANAL SEPARATED INSTRUMENTS: FACTORS CONTRIBUTING TO ENDODONTIC FILE SEPARATION — A NARRATIVE REVIEW
Tareq Hajaj, Paul Freiman , Serban Talpos Niculescu , Mihai Rominu , Tiberiu Hosszu , Ioana Veja
Romanian Journal of Oral Rehabilitation.2025; 17(2): 993. CrossRef
- Risk Factors for Failure of Separated Instrument Removal: A Systematic Review and Meta‐Analysis
- 7,806 View
- 370 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Shaping ability and cyclic fatigue resistance between Genius ProFlex, ZenFlex, and TruNatomy rotary systems: an experimental study
- Raimundo Sales de Oliveira Neto, Murilo Priori Alcalde, Pedro Cesar Gomes Titato, Pedro Henrique Souza Calefi, Carlos Alberto Spironelli Ramos, Guilherme Ferreira da Silva, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(1):e9. Published online February 13, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e9
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
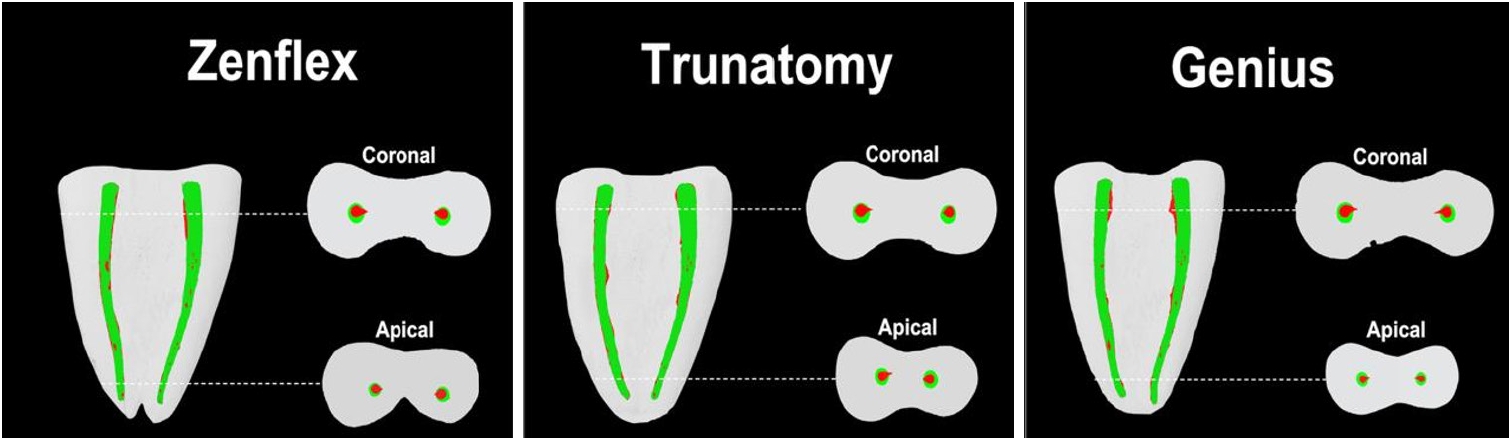
The aim of this study was to investigate the efficacy of three newly introduced rotary endodontic systems: Genius ProFlex (Medidenta), TruNatomy (Dentsply Maillefer), and ZenFlex (Kerr).
Methods
Forty-five mandibular molars with root canal curvatures <5° were utilized. Micro-computed tomography scans were performed pre- and post-preparation to assess apical transportation, centralization, percentage of dentin wear, and canal volume alterations. Eight instruments of each diameter underwent cyclic fatigue testing.
Results
The percentage of dentin wear on mesial and distal walls showed no significant differences among ZenFlex, TruNatomy, and Genius ProFlex at 1, 2, 3, and 4 mm from the apical foramen and root canal orifice (p > 0.05). Centering ability varied in the mesiolingual canal (p < 0.05). No notable differences were observed in transportation (p > 0.05). Genius ProFlex demonstrated lower volumetric changes (p < 0.05). There were significant differences in cyclic fatigue, with higher values for Genius ProFlex and lower values for TruNatomy (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
The three nickel-titanium rotary instruments are safe and efficient for root canal preparation, with Genius ProFlex exhibiting superior cyclic fatigue resistance. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of Shaping Ability and Apical Debris Extrusion Using 4 Different Nickel–Titanium Single‐File Systems
Siyu Li, Mengzhen Tang, Xi Wang, Jian Yang, Hyun-Do Jung
International Journal of Biomaterials.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Comparison of Shaping Ability and Apical Debris Extrusion Using 4 Different Nickel–Titanium Single‐File Systems
- 3,141 View
- 175 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Predictive factors in the retrieval of endodontic instruments: the relationship between the fragment length and location
- Ricardo Portigliatti, Eugenia Pilar Consoli Lizzi, Pablo Alejandro Rodríguez
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(4):e35. Published online September 9, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e35
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
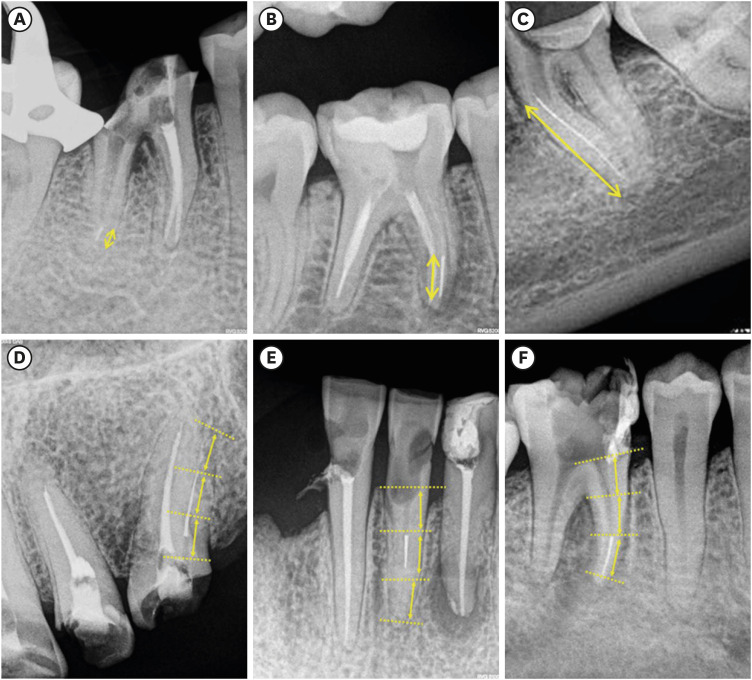
ePub Objectives This study aimed to relate the file fragment length and location in the root canal to the retrieval chances, the clinical time required and the occurrence of secondary fractures.
Materials and Methods Sixty clinical cases of fractured instruments were included in this study. They were classified according to the instrument length and the location of the root canal. In each group, the success rate in the instrument retrieval, the clinical time required and the occurrence of secondary fractures were evaluated. The collected data were analyzed using the Kruskal-Wallis test on the basis of a 0.05 significance level.
Results The fragment length showed no significant influence on the assessed variables (
p > 0.05). The root third where the instrument was located resulted in an increased clinical time, with statistically significant differences (p < 0.05). However, the procedure success rate and the occurrence of secondary fractures showed no association with these variables.Conclusions In accordance with the findings of this study, the fractured fragment length did not influence any of the variables assessed, but it is suggested to focus on the fragment location inside the root canal to decide the retrieval of a fractured instrument.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Study of Adverse Events Associated with Endodontic Files Utilizing the Manufacturer and User Facility Device Experience (MAUDE) Database
Luaibi S, Timban SA, Boopalan K, Nalliah RP
Journal of Dental Health and Oral Research.2026; 7(1): 1. CrossRef - Neodymium-Doped Yttrium Aluminum Perovskite (Nd:YAP) Laser in the Elimination of Endodontic Nickel-Titanium Files Fractured in Rooted Canals (Part 2: Teeth With Significant Root Curvature)
Amaury Namour, Marwan El Mobadder, Clément Cerfontaine, Patrick Matamba, Lucia Misoaga, Delphine Magnin , Praveen Arany, Samir Nammour
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- A Study of Adverse Events Associated with Endodontic Files Utilizing the Manufacturer and User Facility Device Experience (MAUDE) Database
- 3,391 View
- 261 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Micro-CT evaluation of the removal of root fillings using rotary and reciprocating systems supplemented by XP-Endo Finisher, the Self-Adjusting File, or Er,Cr:YSGG laser
- Gülsen Kiraz, Bulem Üreyen Kaya, Mert Ocak, Muhammet Bora Uzuner, Hakan Hamdi Çelik
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(4):e36. Published online October 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e36
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
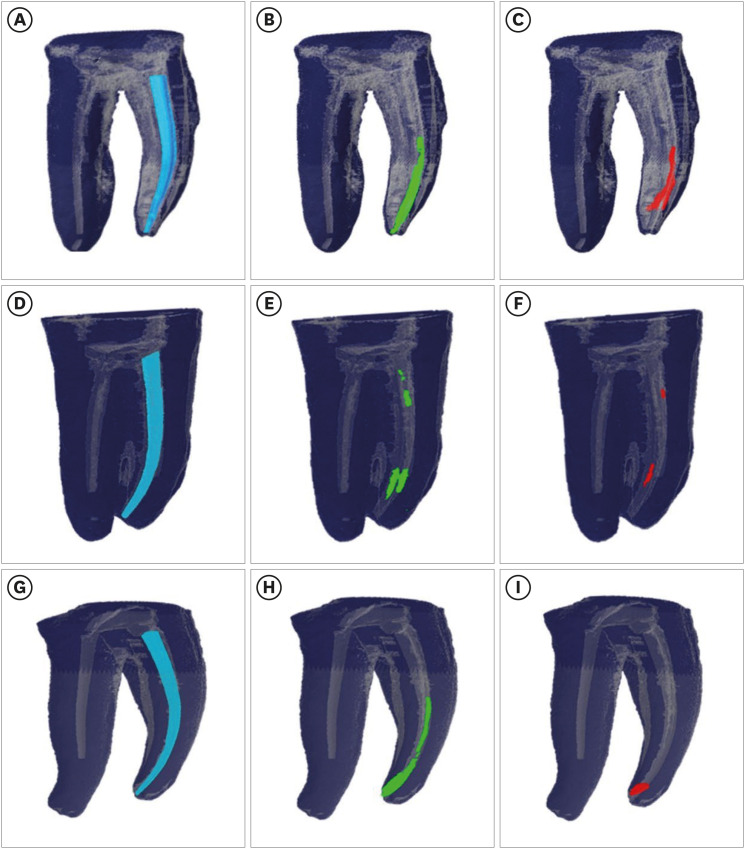
ePub Objectives This study aimed to compare the effectiveness of a single-file reciprocating system (WaveOne Gold, WOG) and a multi-file rotary system (ProTaper Universal Retreatment, PTUR) in removing canal filling from severely curved canals and to evaluate the possible adjunctive effects of XP-Endo Finisher (XPF), the Self-Adjusting File (SAF), and an erbium, chromium: yttrium, scandium, gallium garnet (Er,Cr:YSGG) laser using micro-computed tomography (μCT).
Materials and Methods Sixty-six curved mandibular molars were divided into 2 groups based on the retreatment technique and then into 3 based on the supplementary method. The residual filling volumes and root canals were evaluated with μCT before and after retreatment, and after the supplementary steps. The data were statistically analyzed with the
t -test, Mann-WhitneyU test, analysis of covariance, and factorial analysis of variance (p < 0.05).Results PTUR and WOG showed no significant difference in removing filling materials (
p > 0.05). The supplementary techniques were significantly more effective than reciprocating or rotary systems only (p < 0.01). The supplementary steps showed no significant differences in canal filling removal effectiveness (p > 0.05), but XPF showed less dentin reduction than the SAF and Er,Cr:YSGG laser (p < 0.01).Conclusions The supplementary methods significantly decreased the volume of residual filling materials. XPF caused minimal changes in root canal volume and might be preferred for retreatment in curved root canals. Supplementary approaches after retreatment procedures may improve root canal cleanliness.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Trends in dentomaxillofacial radiology
Kıvanç Kamburoğlu
World Journal of Radiology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Retrieval of AH Plus Bioceramic and Ceraseal Versus AH Plus in Endodontic Retreatment
Eurok Shim, Jee Woo Son, Jiyoung Kwon, Hyun-Jung Kim, Ji-Hyun Jang, Seok Woo Chang, Soram Oh
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(6): 1826. CrossRef - Characteristics and Effectiveness of XP‐Endo Files and Systems: A Narrative Review
Sarah M. Alkahtany, Rana Alfadhel, Aseel AlOmair, Sarah Bin Durayhim, Kee Y. Kum
International Journal of Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of the filling technique on the filling removal from oval-shaped canals
Lislaine Valerio, Lisa Yurie Oda, Felipe Andretta Copelli, Clarissa Teles Rodrigues, Everdan Carneiro, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Bruno Cavalini Cavenago
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Trends in dentomaxillofacial radiology
- 4,134 View
- 99 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

-
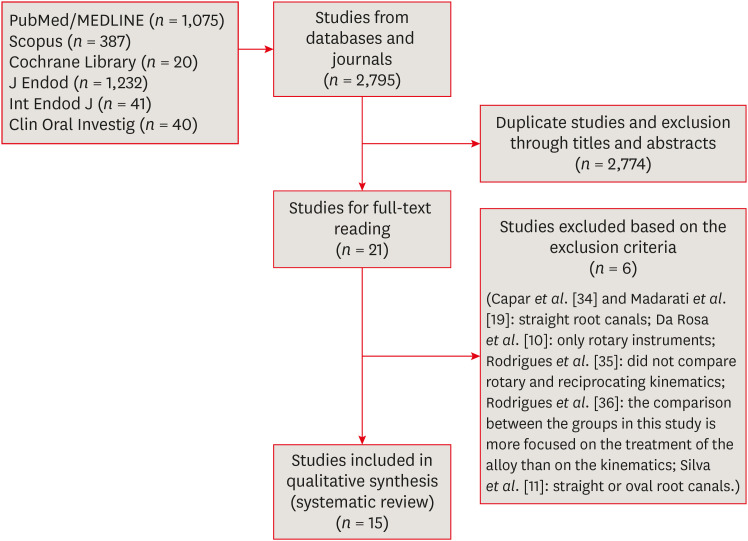
Effectiveness and safety of rotary and reciprocating kinematics for retreatment of curved root canals: a systematic review of
in vitro studies - Lucas Pinho Simões, Alexandre Henrique dos Reis-Prado, Carlos Roberto Emerenciano Bueno, Ana Cecília Diniz Viana, Marco Antônio Húngaro Duarte, Luciano Tavares Angelo Cintra, Cleidiel Aparecido Araújo Lemos, Francine Benetti
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(2):e22. Published online April 6, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e22
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This systematic review (register-osf.io/wg7ba) compared the efficacy and safety of rotary and reciprocating kinematics in the removal of filling material from curved root canals.
Materials and Methods Only
in vitro studies evaluating both kinematics during retreatment were included. A systematic search (PubMed/MEDLINE, Scopus, and other databases, until January 2021), data extraction, and risk of bias analysis (Joanna Briggs Institute checklist) were performed. Efficacy in filling removal was the primary outcome.Results The search resulted in 2,795 studies, of which 15 were included. Efficacy was measured in terms of the remaining filling material and the time required for this. Nine studies evaluated filling material removal, of which 7 found no significant differences between rotary and reciprocating kinematics. Regarding the time for filling removal, 5 studies showed no difference between both kinematics, 2 studies showed faster results with rotary systems, and other 2 showed the opposite. No significant differences were found in apical transportation, centering ability, instrument failure, dentin removed and extruded debris. A low risk of bias was observed.
Conclusions This review suggests that the choice of rotary or reciprocating kinematics does not influence the efficacy of filling removal from curved root canals. Further studies are needed to compare the kinematics safety in curved root canals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Apical Third Cleaning Efficiency of Hand, Rotary, and Reciprocating Root Canal Instrumentation: A Quantitative In Vitro Scanning Electron Microscopic Study
B. Sai Krishna, Sita Mahalakshmi Koppu, Dilip Katakam, Sahithi Nammaniwar, Ambika Belam, Akshita Balivada, Divakar K. P.
Cureus.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Selective Nonsurgical Endodontic Retreatment: Relevant Aspects for Clinical Application—A Scoping Review
Tomás Manuel Braz Marinho, Luiz Renato Paranhos, Anne Caroline Brito Cabral dos Santos, Djessyca Miranda‐e‐Paulo, Rui Barbosa de Brito Júnior, João Marcos da Costa Ribeiro, Felipe de Souza Matos
Australian Endodontic Journal.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - EVALUATION OF MICROLEAKAGE AFTER ENDODONTIC FILLING IN TEETH WITH APICAL WIDENING: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
Isabella da Costa Ferreira, Gabriela da Costa Ferreira, Isabella Figueiredo de Assis Macedo, Gustavo Oliveira Campos, Isabella Faria da Cunha Peixoto, Ana Cecília Diniz Viana, Rodrigo Rodrigues Amaral, Warley Luciano Fonseca Tavares
ARACÊ .2025; 7(10): e8792. CrossRef - Fifteen years of engine‐driven nickel–titanium reciprocating instruments, what do we know so far? An umbrella review
Felipe Immich, Lucas Peixoto de Araújo, Rafaella Rodrigues da Gama, Wellington Luiz de Oliveira da Rosa, Evandro Piva, Giampiero Rossi‐Fedele
Australian Endodontic Journal.2024; 50(2): 409. CrossRef - Efficacy of Various Heat-treated Retreatment File Systems on the Apical Deformity and Canal Centering Ability in a Single-rooted Teeth using Nano CT
Swathi S, Pradeep Solete, Ganesh Jeevanandan, Delphine Priscilla Antony S, Kavalipurapu Venkata Teja, Dona Sanju
The Open Dentistry Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Micro-CT evaluation of the removal of root fillings using rotary and reciprocating systems supplemented by XP-Endo Finisher, the Self-Adjusting File, or Er,Cr:YSGG laser
Gülsen Kiraz, Bulem Üreyen Kaya, Mert Ocak, Muhammet Bora Uzuner, Hakan Hamdi Çelik
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of sodium hypochlorite on cyclic fatigue resistance of nickel–titanium instruments: A systematic review and meta-analysis of in vitro studies
Alexandre Henrique dos Reis-Prado, Lucas Guimarães Abreu, Lara Cancella de Arantes, Kiani dos Santos de Paula, Sabrina de Castro Oliveira, Juliana Goto, Ana Cecília Diniz Viana, Francine Benetti
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(11): 6291. CrossRef - Retreatment of XP-endo Shaper and R-Endo files in curved root canals
Hayam Y. Hassan, Fahd M. Hadhoud, Ayman Mandorah
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Advancing Endodontics through Kinematics
Shilpa Bhandi, Dario Di Nardo, Francesco Pagnoni, Rosemary Abbagnale
World Journal of Dentistry.2023; 14(6): 479. CrossRef
- Apical Third Cleaning Efficiency of Hand, Rotary, and Reciprocating Root Canal Instrumentation: A Quantitative In Vitro Scanning Electron Microscopic Study
- 3,467 View
- 68 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref

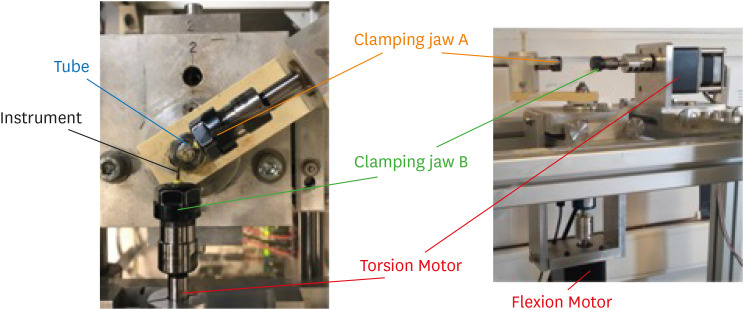
- Comparison of the cyclic fatigue resistance of One Curve, F6 Skytaper, Protaper Next, and Hyflex CM endodontic files
- Charlotte Gouédard, Laurent Pino, Reza Arbab-Chirani, Shabnam Arbab-Chirani, Valérie Chevalier
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(2):e16. Published online March 4, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e16
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study compared the cyclic fatigue resistance of One Curve (C wire) and F6 Skytaper (conventional austenite nickel-titanium [NiTi]), and 2 instruments with thermo-mechanically treated NiTi: Protaper Next X2 (M wire) and Hyflex CM (CM wire).
Materials and Methods Ten new instruments of each group (size: 0.25 mm, 6% taper in the 3 mm tip region) were tested using a rotary bending machine with a 60° curvature angle and a 5 mm curvature radius, at room temperature. The number of cycles until fracture was recorded. The length of the fractured instruments was measured. The fracture surface of each fragment was examined with a scanning electron microscope (SEM). The data were analyzed using one-way analysis of variance and the
post hoc Tukey test. The significance level was set at 0.05.Results At 60°, One Curve, F6 Skytaper and Hyflex CM had significantly longer fatigue lives than Protaper Next X2 (
p < 0.05). No statistically significant differences were found in the cyclic fatigue lives of One Curve, F6 Skytaper, and Hyflex CM (p > 0.05). SEM images of the fracture surfaces of the different instruments showed typical features of fatigue failure.Conclusions Within the conditions of this study, at 60° and with a 5 mm curvature radius, the cyclic fatigue life of One Curve was not significantly different from those of F6 Skytaper and Hyflex CM. The cyclic fatigue lives of these 3 instruments were statistically significantly longer than that of Protaper Next.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of Canal Shaping and Transportation Between the Protaper Next and Protaper Ultimate in Simulated Double-curved Canals
Seher Pelda Biçer, Betül Aycan Uysal
ADO Klinik Bilimler Dergisi.2026; 15(1): 47. CrossRef - Evaluation of cyclic fatigue in three pediatric endodontic rotary file systems in root canals of primary molars: A finite element analysis (FEA)
Monika sri S.S., K.C. Vignesh, K. Vivek, Kavitha Swaminathan, Selvakumar Haridoss
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2025; 15(2): 310. CrossRef - Stress analysis of different experimental finite element models of rotary endodontic instruments
Manar M. Galal, Amira Galal Ismail, Nada Omar
Bulletin of the National Research Centre.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Understanding Cyclic Fatigue in Three Nickel–Titanium Pediatric Files: An In Vitro Study for Enhanced Patient Care
Alwaleed Abushanan, Rajashekhara Bhari Sharanesha, Fahd Aljarbou, Hadi Alamri, Mohammed Hamad Almasud, Abdulfatah AlAzmah, Sara Alghamdi, Mubashir Baig Mirza
Medicina.2025; 61(5): 830. CrossRef - Analyzing Surface Morphology Changes Induced by Cyclic Fatigue in Three Different Nickel–Titanium Rotary Files Using Scanning Electron Microscopy Analysis
Chintan Joshi, Mahima P Jain, Sweety M Thumar, Jay H Dave, Applu R Bhatt, Juhi I Dholani
World Journal of Dentistry.2024; 15(7): 579. CrossRef - Nickel ion release and surface analyses on instrument fragments fractured beyond the apex: a laboratory investigation
Sıdıka Mine Toker, Ekim Onur Orhan, Arzu Beklen
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Comparison of Canal Shaping and Transportation Between the Protaper Next and Protaper Ultimate in Simulated Double-curved Canals
- 3,457 View
- 47 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

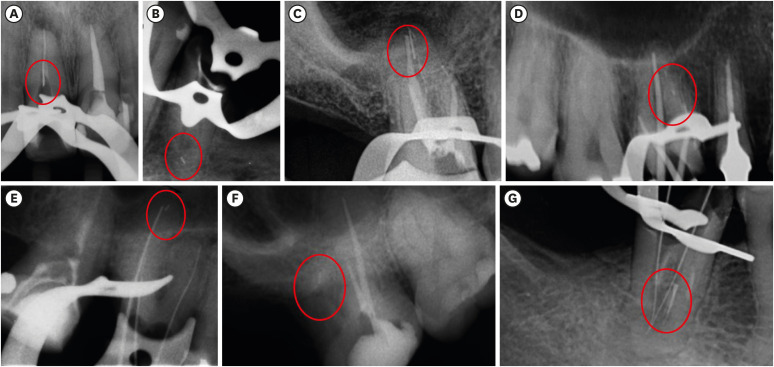
- Fracture incidence of Reciproc instruments during root canal retreatment performed by postgraduate students: a cross-sectional retrospective clinical study
- Liliana Machado Ruivo, Marcos de Azevedo Rios, Alexandre Mascarenhas Villela, Alexandre Sigrist de Martin, Augusto Shoji Kato, Rina Andrea Pelegrine, Ana Flávia Almeida Barbosa, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Carlos Eduardo da Silveira Bueno
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(4):e49. Published online September 9, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e49
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives To evaluate the fracture incidence of Reciproc R25 instruments (VDW) used during non-surgical root canal retreatments performed by students in a postgraduate endodontic program.
Materials and Methods From the analysis of clinical record cards and periapical radiographs of root canal retreatments performed by postgraduate students using the Reciproc R25, a total of 1,016 teeth (2,544 root canals) were selected. The instruments were discarded after a single use. The general incidence of instrument fractures and its frequency was analyzed considering the group of teeth and the root thirds where the fractures occurred. Statistical analysis was performed using the χ2 test (
p < 0.01).Results Seven instruments were separated during the procedures. The percentage of fracture in relation to the number of instrumented canals was 0.27% and 0.68% in relation to the number of instrumented teeth. Four fractures occurred in maxillary molars, 1 in a mandibular molar, 1 in a mandibular premolar and 1 in a maxillary incisor. A greater number of fractures was observed in molars when compared with the number of fractures observed in the other dental groups (
p < 0.01). Considering all of the instrument fractures, 71.43% were located in the apical third and 28.57% in the middle third (p < 0.01). One instrument fragment was removed, one bypassed, while in 5 cases, the instrument fragment remained inside the root canal.Conclusions The use of Reciproc R25 instruments in root canal retreatments carried out by postgraduate students was associated with a low incidence of fractures.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Reciprocating Torsional Fatigue and Mechanical Tests of Thermal-Treated Nickel Titanium Instruments
Victor Talarico Leal Vieira, Alejandro Jaime, Carlos Garcia Puente, Giuliana Soimu, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Carlos Nelson Elias, Gustavo de Deus
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(3): 359. CrossRef - Neodymium-Doped Yttrium Aluminum Perovskite (Nd:YAP) Laser in the Elimination of Endodontic Nickel-Titanium Files Fractured in Rooted Canals (Part 2: Teeth With Significant Root Curvature)
Amaury Namour, Marwan El Mobadder, Clément Cerfontaine, Patrick Matamba, Lucia Misoaga, Delphine Magnin , Praveen Arany, Samir Nammour
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Temperature-Dependent Effects on Cyclic Fatigue Resistance in Three Reciprocating Endodontic Systems: An In Vitro Study
Marcela Salamanca Ramos, José Aranguren, Giulia Malvicini, Cesar De Gregorio, Carmen Bonilla, Alejandro R. Perez
Materials.2025; 18(5): 952. CrossRef - The Cost of Instrument Retrieval on the Root Integrity
Marco A. Versiani, Hugo Sousa Dias, Emmanuel J. N. L. Silva, Felipe G. Belladonna, Jorge N. R. Martins, Gustavo De‐Deus
International Endodontic Journal.2025; 58(12): 1948. CrossRef - Multimethod analysis of large‐ and low‐tapered single file reciprocating instruments: Design, metallurgy, mechanical performance, and irrigation flow
Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Fernando Peña‐Bengoa, Natasha C. Ajuz, Victor T. L. Vieira, Jorge N. R. Martins, Duarte Marques, Ricardo Pinto, Mario Rito Pereira, Francisco Manuel Braz‐Fernandes, Marco A. Versiani
International Endodontic Journal.2024; 57(5): 601. CrossRef - Nd: YAP Laser in the Elimination of Endodontic Nickel-Titanium Files Fractured in Rooted Canals (Part 1: Teeth With Minimal Root Curvature)
Amaury Namour, Marwan El Mobadder, Patrick Matamba, Lucia Misoaga, Delphine Magnin , Praveen Arany, Samir Nammour
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue of Different Reciprocating Endodontic Instruments Using Matching Artificial Root Canals at Body Temperature In Vitro
Sebastian Bürklein, Paul Maßmann, Edgar Schäfer, David Donnermeyer
Materials.2024; 17(4): 827. CrossRef - Endodontic Orthograde Retreatments: Challenges and Solutions
Alessio Zanza, Rodolfo Reda, Luca Testarelli
Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dentistry.2023; Volume 15: 245. CrossRef - Design, metallurgy, mechanical properties, and shaping ability of 3 heat-treated reciprocating systems: a multimethod investigation
Emmanuel J. N. L. Silva, Jorge N. R. Martins, Natasha C. Ajuz, Henrique dos Santos Antunes, Victor Talarico Leal Vieira, Francisco Manuel Braz-Fernandes, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Marco Aurélio Versiani
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(5): 2427. CrossRef - Noncontact 3D evaluation of surface topography of reciprocating instruments after retreatment procedures
Miriam Fatima Zaccaro-Scelza, Renato Lenoir Cardoso Henrique Martinez, Sandro Oliveira Tavares, Fabiano Palmeira Gonçalves, Marcelo Montagnana, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva, Pantaleo Scelza
Brazilian Dental Journal.2022; 33(3): 38. CrossRef
- Reciprocating Torsional Fatigue and Mechanical Tests of Thermal-Treated Nickel Titanium Instruments
- 2,648 View
- 23 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref

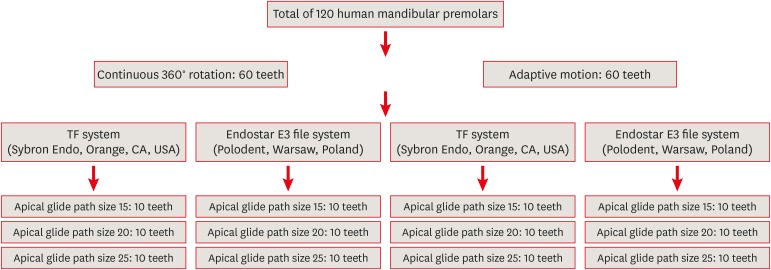
- Influence of glide path size and operating kinetics on time to reach working length and fracture resistance of Twisted File adaptive and Endostar E3 nickel-titanium file systems
- Tamilkumaran Ramyadharshini, Inbaraj Anand Sherwood, V Shanmugham Vigneshwar, Prakasam Ernest Prince, Murugadoss Vaanjay
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(2):e22. Published online March 5, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e22
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study investigated the influence of glide path size and operating kinetics on the time to reach the working length and the fracture resistance of Twisted File (TF) and Endostar E3 files.
Materials and Methods A total of 120 mandibular single-rooted premolars were selected. Two methods of kinetic motion (TF adaptive and continuous rotary motion) and file systems (TF and Endostar E3) were employed. The files were used in root canals prepared to apical glide path sizes of 15, 20, and 25. The time taken to reach the working length and the number of canals used before the instrument deformed or fractured were noted. Fractured instruments were examined with scanning electron microscopy.
Results The TF system took significantly more time to reach the working length than the Endostar E3 system. Both systems required significantly more time to reach the working length at the size 15 glide path than at sizes 20 and 25. A greater number of TFs than Endostar E3 files exhibited deformation, and a higher incidence of instrument deformation was observed in adaptive than in continuous rotary motion; more deformation was also observed with the size 15 glide path. One TF was fractured while undergoing adaptive motion.
Conclusions No significant difference was observed between continuous rotary and adaptive motion. The TF system and adaptive motion were associated with a higher incidence of deformation and fracture. Apical glide path sizes of 20 and 25 required significantly less time to reach the working length than size 15.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of the Adaptive Torque Control Motion on the Ability of Neolix EDMax to Reach Working Length When Used as a Single Shaping File—An In Vitro Study
Vlad Mircea Lup, Carlo Gaeta, Ashkan Tavakkoli, Andreas Louloudiadis, Simone Grandini, Gabriela Ciavoi
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(6): 262. CrossRef - Glide Path in Endodontics: A Literature Review of Current Knowledge
Vlad Mircea Lup, Giulia Malvicini, Carlo Gaeta, Simone Grandini, Gabriela Ciavoi
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(8): 257. CrossRef - Assessment of Different File Systems for Working Time Based on Glide Path, Operating Kinetics, and the Fracture Resistance
Ruchika Gupta, Divya Batra, Debkant Jena, Nandita Bansal, Alka Arora, Divya Gaurav Dudulwar
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2021; 22(1): 69. CrossRef
- Influence of the Adaptive Torque Control Motion on the Ability of Neolix EDMax to Reach Working Length When Used as a Single Shaping File—An In Vitro Study
- 1,903 View
- 13 Download
- 3 Crossref

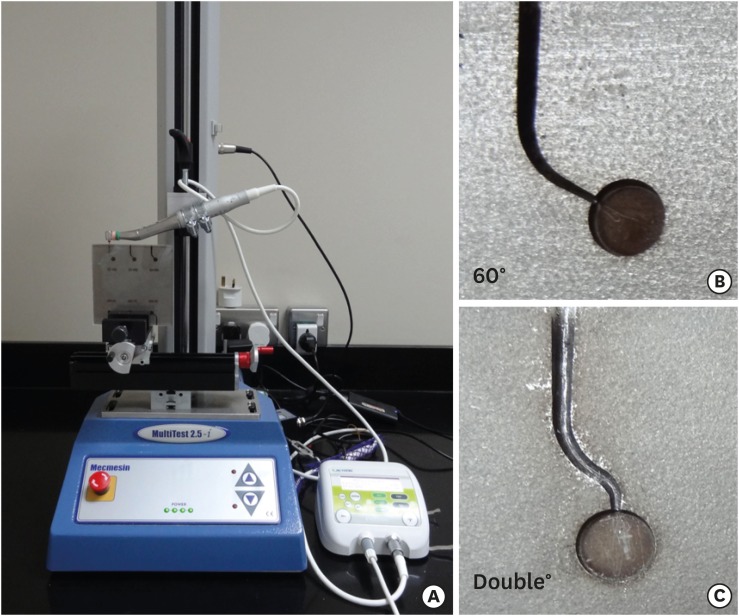
- Cyclic fatigue, bending resistance, and surface roughness of ProTaper Gold and EdgeEvolve files in canals with single- and double-curvature
- Wafaa A. Khalil, Zuhair S. Natto
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(2):e19. Published online April 26, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e19
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to evaluate the cyclic fatigue, bending resistance, and surface roughness of EdgeEvolve (EdgeEndo) and ProTaper Gold (Dentsply Tulsa Dental Specialties) nickel-titanium (NiTi) rotary files.
Materials and Methods The instruments (
n = 15/each) were tested for cyclic fatigue in single- (60° curvature, 5-mm radius) and double-curved (coronal curvature 60°, 5-mm radius, and apical curvature of 30° and 2-mm radius) artificial canals. The number of cycles to fracture was calculated. The bending resistance of both files were tested using a universal testing machine where the files were bent until reach 45°. Scanning electron microscopy and x-ray energy-dispersive spectrometric analysis were used for imaging the fractured segments, while the atomic force microscope was used to quantify the surface roughness average (Ra).Results EdgeEvolve files exhibited higher cyclic fatigue resistance than ProTaper Gold files in single- and double-curved canals (
p < 0.05) and both files were more resistant to cyclic fatigue in single-curved canals than double-curved canals (p < 0.05). EdgeEvolve files exhibited significantly more flexibility than did ProTaper Gold files (p < 0.05). Both files had approximately similar Ni and Ti contents (p > 0.05). EdgeEvolve files showed significantly lower Ra values than ProTaper Gold files (p < 0.05).Conclusions Within the limitation of this study, EdgeEvolve files exhibited significantly higher cyclic fatigue resistance than ProTaper Gold files in both single- and double-curved canals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of Design, Cyclic Fatigue Resistance, and Metallurgical Properties of Original, Replica‐Like, and Counterfeit Nickel‐Titanium Files
Mert Unal, Elif Bahar Cakici
Microscopy Research and Technique.2026; 89(1): 87. CrossRef - An in vitro comparison of alterations in surface topographies of three different rotary files after root canal preparation with different irrigating solutions: Atomic force microscopic study
PremSai Parepalli, TB. V G. Raju, PKrishna Prasad, GowtamDev Dondapati, VenkataSrija Kintada, Alekhya Mediboyina
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2023; 26(3): 299. CrossRef - Assessment of surface topographic changes of nickel–titanium rotary endodontic file at repeated usage: An in vitro study
E. Viswas, VSS Krishna, E. Sridevi, A. J. Sai Sankar, K. Siva Sankar, B. Nagesh
Endodontology.2023; 35(2): 149. CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue Resistance and Surface Roughness of Rotary NiTi Instruments after Simulated Clinical Use in Curved Root Canals – An Atomic Force Microscopy Study
Raksha Bhat, Arjun Kini, Preethesh Shetty, Payalben Kansara, Bapanaiah Penugonda
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Metallurgical Tests in Endodontics: A Narrative Review
Alessio Zanza, Marco Seracchiani, Rodolfo Reda, Gabriele Miccoli, Luca Testarelli, Dario Di Nardo
Bioengineering.2022; 9(1): 30. CrossRef - Influence of nickel-titanium rotary systems with varying cross-sectional, pitch, and rotational speed on deflection and cyclic fatigue: a finite element analysis study
Wignyo Hadriyanto, Lukita Wardani, Christina Nugrohowati, Ananto Alhasyimi, Rachmat Sriwijaya, Margareta Rinastiti, Widowati Siswomihardjo, Gunadi, T. Yamada, A.A.C. Pramana, Y. Ophinni, A. Gusnanto, W.A. Kusuma, J. Yunus, Afiahayati, R. Dharmastiti, T.
BIO Web of Conferences.2021; 41: 05005. CrossRef - Can the Separated Instrument be Removed From the Root Canal System out by Magnetism? A Hypothesis
Mohammad Daryaeian, Sanjay Miglani, AbdolMahmood Davarpanah, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Mohsen Ramazani
Dental Hypotheses.2019; 10(4): 108. CrossRef - Resistance to cyclic fatigue of reciprocating instruments determined at body temperature and phase transformation analysis
Raymond Scott, Ana Arias, José C. Macorra, Sanjay Govindjee, Ove A. Peters
Australian Endodontic Journal.2019; 45(3): 400. CrossRef
- Comparison of Design, Cyclic Fatigue Resistance, and Metallurgical Properties of Original, Replica‐Like, and Counterfeit Nickel‐Titanium Files
- 1,582 View
- 9 Download
- 8 Crossref

- The top 10 most-cited articles on the management of fractured instruments: a bibliometric analysis
- Lora Mishra, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Naomi Ranjan Singh, Priti Pragati Rath
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(1):e2. Published online December 26, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e2
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this research was to identify the top 10 most-cited articles on the management of fractured or broken instruments and to perform a bibliometric analysis thereof.
Materials and Methods Published articles related to fractured instruments were screened from online databases, such as Web of Science, Scopus, PubMed, and ScienceDirect, and highly cited papers, with at least 50 citations since publication, were identified. The most-cited articles were selected and analysed with regard to publication title, authorship, the journal of publication, year, institution, country of origin, article type, and number of citations.
Results The top 10 most-cited articles were from various journals. Most were published in the
Journal of Endodontics , followed by theInternational Endodontic Journal , andDental Traumatology . The leading countries were Australia, Israel, Switzerland, the USA, and Germany, and the leading institution was the University of Melbourne. The majority of articles among the top 10 articles were clinical research studies (n = 8), followed by a basic research article and a non-systematic review article.Conclusions This bibliometric analysis revealed interesting information about scientific progress in endodontics regarding fractured instruments. Overall, clinical research studies and basic research articles published in high-impact endodontic journals had the highest citation rates.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bibliometric analysis of the publications that list the most-cited articles in endodontics
Oscar Alejandro Gutiérrez-Alvarez, Luis Alberto Pantoja-Villa, Benigno Miguel Calderón-Rojas
Endodontology.2025; 37(2): 128. CrossRef - Endodontide Mikro-Bilgisayarlı Tomografinin Kullanımı Konusunda Yayımlanan Makalelerin Bibliyometrik Analizi: Nicel Araştırma
Özge Kurt, Emine Şimşek
Mersin Üniversitesi Sağlık Bilimleri Dergisi.2025; 18(3): 309. CrossRef - A Bibliometric Analysis of the 100 Top-Cited Articles on Vertical Root Fractures
Pillai Arun Gopinathan , Ikram UI Haq, Nawaf Alfahad, Saleh Alwatban, Abdullah Alghamdi, Amal Alamri, Kiran Iyer
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictive factors in the retrieval of endodontic instruments: the relationship between the fragment length and location
Ricardo Portigliatti, Eugenia Pilar Consoli Lizzi, Pablo Alejandro Rodríguez
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A bibliometric analysis of the top 100 most‐cited case reports and case series in Endodontic journals
Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Jelena Jacimovic, Aleksandar Jakovljevic, Giampiero Rossi‐Fedele, Paul M. H. Dummer
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(3): 185. CrossRef - The Most Highly Cited Publications on Basketball Originate From English-Speaking Countries, Are Published After 2000, Are Focused on Medicine-Related Topics, and Are Level III Evidence
Zachary D. Griffin, Jordan R. Pollock, M. Lane Moore, Kade S. McQuivey, Jaymeson R. Arthur, Anikar Chhabra
Arthroscopy, Sports Medicine, and Rehabilitation.2022; 4(3): e891. CrossRef - Ten years of minimally invasive access cavities in Endodontics: a bibliometric analysis of the 25 most-cited studies
Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Karem Paula Pinto, Natasha C. Ajuz, Luciana Moura Sassone
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Publication trends in micro‐CT endodontic research: a bibliometric analysis over a 25‐year period
U. Aksoy, M. Küçük, M. A. Versiani, K. Orhan
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(3): 343. CrossRef
- Bibliometric analysis of the publications that list the most-cited articles in endodontics
- 1,635 View
- 10 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Comparison of the shaping ability of novel thermally treated reciprocating instruments
- Cangül Keskin, Murat Demiral, Evren Sarıyılmaz
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(2):e15. Published online March 3, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e15
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The present study aimed to evaluate the shaping ability of 2 thermally treated nickel-titanium reciprocating systems in simulated curved canals.
Materials and Methods Forty simulated canals were prepared to apical size 25 using Reciproc Blue R25 (VDW) and WaveOne Gold Primary (Dentsply Sirona) instruments. Standard pre- and post-preparation images were taken and superimposed. The removal of resin material was measured at 5 standard points: the canal orifice, halfway between the canal orifice and the beginning of the curve, the beginning of the curve, the apex of the curve, and the end-point of the simulated canal. The data were analysed using the independent sample
t -test with a 5% significance threshold.Results The canals in which Reciproc Blue R25 was used showed a significantly greater widening than those in which WaveOne Gold was used at 4 of the 5 measurement points (
p < 0.05). The Reciproc Blue R25 instrument removed significantly more resin from the inner aspect of the curve at 2 of the 5 points and similar amounts at the remaining 3 points. At the 2 apical points, there was no significant difference between the Reciproc Blue R25 and WaveOne Gold Primary instruments.Conclusion Both instruments respected the original canal anatomy; however, WaveOne Gold resulted in a more conservative shape with less transportation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Centering Ability and Canal Transportation of Nickel-Titanium (NiTi) Single-File Systems With and Without Glide Path in Extracted Natural Teeth: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Indumathi Manoharan, Deblina Basu, Mathan Rajan
Cureus.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Shaping Ability of the Root Canal System Using Reciproc and Reciproc Blue in Preparation of Artificial Canals
Hawazin Majdi, Khalid Merdad, Tariq Abuhaimed, Lujain Mirdad, Omar Alkhattab, Abdulaziz Bakhsh
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of four different file systems in terms of transportation in S-shaped canals and apically extruded debris
Mustafa Alrahhal, Fatma Tunç
Journal of Oral Science.2024; 66(4): 226. CrossRef - Assessment of Debris Extrusion in Curved Canals: An In Vitro Analysis of Various Single‐File Endodontic Instrumentation Systems
Muhammad Zubair Ahmad, Boonlert Kukiattrakoon
International Journal of Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Shaping ability of rotary and reciprocating single-file systems in combination with and without different glide path techniques in simulated curved canals
Lu Shi, Yunfei Yang, Jie Wan, Wen Xie, Ruiming Yang, Ying Yao
Journal of Dental Sciences.2022; 17(4): 1520. CrossRef - An Investigation of the Accuracy and Reproducibility of 3D Printed Transparent Endodontic Blocks
Martin Smutný, Martin Kopeček, Aleš Bezrouk
Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove, Czech Republic).2022; 65(2): 59. CrossRef - Shaping Ability of Reciprocating Single-file Systems in Simulated Canals: Reciproc versus Reciproc Blue
İrem ÇETİNKAYA, Mukadder İnci BAŞER KOLCU
SDÜ Tıp Fakültesi Dergisi.2021; 28(1): 145. CrossRef - Combination of a new ultrasonic tip with rotary systems for the preparation of flattened root canals
Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Jáder Camilo Pinto, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Apical extrusion of debris with different rotary and reciprocating single-file endodontic instrumentation systems: a systematic review and meta-analysis protocol
Muhammad Zubair Ahmad, Durre Sadaf, Marcy McCall MacBain, Ahmed Nabil Mohamed
BMJ Open.2020; 10(9): e038502. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic assessment of the shaping ability of the One Curve, One Shape, and ProTaper Next nickel-titanium rotary systems
Pelin Tufenkci, Kaan Orhan, Berkan Celikten, Burak Bilecenoglu, Gurkan Gur, Semra Sevimay
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Changes in Geometry and Transportation of Root Canals with Severe Curvature Prepared by Different Heat-treated Nickel-titanium Instruments: A Micro–computed Tomographic Study
Daniel José Filizola de Oliveira, Graziela Bianchi Leoni, Rafael da Silva Goulart, Manoel Damião de Sousa-Neto, Yara Teresinha Correa Silva Sousa, Ricardo Gariba Silva
Journal of Endodontics.2019; 45(6): 768. CrossRef - Several factors can affect the root canal transportation of MB2 canals in extracted maxillary first molars
R. R. Vivan, M. P. Alcalde, E. J de Camargo, V. A. S. Marques, M. V. R. Só, J. A. Duque, M. A. H. Duarte
International Endodontic Journal.2019; 52(4): 551. CrossRef - Effect of larger apical size on the quality of preparation in curved canals using reciprocating instruments with different heat thermal treatments
J. A. Duque, R. R. Vivan, M. A. H. Duarte, M. P. Alcalde, V. M. Cruz, M. M. B. Borges, C. M. Bramante
International Endodontic Journal.2019; 52(11): 1652. CrossRef
- Centering Ability and Canal Transportation of Nickel-Titanium (NiTi) Single-File Systems With and Without Glide Path in Extracted Natural Teeth: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- 1,494 View
- 7 Download
- 13 Crossref

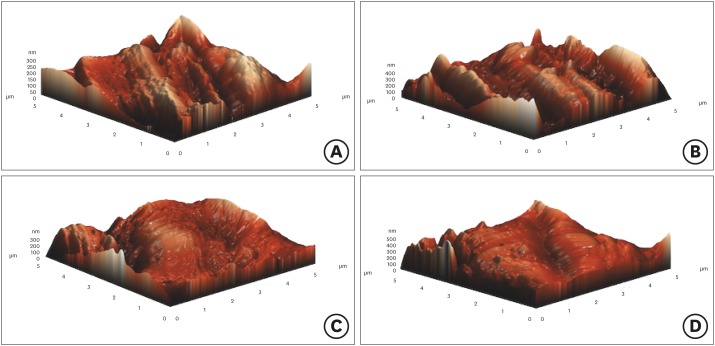
- The effect of root canal preparation on the surface roughness of WaveOne and WaveOne Gold files: atomic force microscopy study
- Taha Özyürek, Koray Yılmaz, Gülşah Uslu, Gianluca Plotino
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(1):e10. Published online February 2, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e10
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives To examine the surface topography of intact WaveOne (WO; Dentsply Sirona Endodontics) and WaveOne Gold (WOG; Dentsply Sirona Endodontics) nickel-titanium rotary files and to evaluate the presence of alterations to the surface topography after root canal preparations of severely curved root canals in molar teeth.
Materials and Methods Forty-eight severely curved canals of extracted molar teeth were divided into 2 groups (
n = 24/each group). In group 1, the canals were prepared using WO and in group 2, the canals were prepared using WOG files. After the preparation of 3 root canals, instruments were subjected to atomic force microscopy analysis. Average roughness and root mean square values were chosen to investigate the surface features of endodontic files. The data was analyzed using one-way analysis of variance andpost hoc Tamhane's tests at 5% significant level.Results The surface roughness values of WO and WOG files significantly changed after use in root canals (
p < 0.05). The used WOG files exhibited higher surface roughness change when compared with the used WO files (p < 0.05).Conclusions Using WO and WOG Primary files in 3 root canals affected the surface topography of the files. After being used in root canals, the WOG files showed a higher level of surface porosity value than the WO files.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative Analysis of Surface Roughness and Plastic Deformation of Reciprocating Instruments after Clinical Use
Ángel Herrera, Magdalena Azabal, Jesús R. Jimenez-Octavio, Juan C. del Real-Romero, Sara López de Armentia, Juan M. Asensio-Gil, Ana Arias
Materials.2024; 17(16): 3978. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Surface Roughness of Different Rotary Nickel-Titanium (NiTi) Files After Autoclaving: An Atomic Force Microscopic Study
Angela Alex, Ranjith Kumar Sivarajan, Vijay Venkatesh
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of endodontic irrigants on surface roughness of various nickel-titanium rotary endodontic instruments
Tamer M. Hamdy, Yasmine Mohsen Alkabani, Amira Galal Ismail, Manar M. Galal
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Metallurgical Tests in Endodontics: A Narrative Review
Alessio Zanza, Marco Seracchiani, Rodolfo Reda, Gabriele Miccoli, Luca Testarelli, Dario Di Nardo
Bioengineering.2022; 9(1): 30. CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue Resistance and Surface Roughness of Rotary NiTi Instruments after Simulated Clinical Use in Curved Root Canals – An Atomic Force Microscopy Study
Raksha Bhat, Arjun Kini, Preethesh Shetty, Payalben Kansara, Bapanaiah Penugonda
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - In Vitro Study of Irrigation solution of Chitosan Nanoparticles to Inhibit the Adhesion and Biofilm Formation of Enterococcus faecalis in the Root Canal
Imelda Darmawi, Trimurni Abidin, Harry Agusnar, Basri A. Gani
Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology.2022; : 2691. CrossRef - Alteration in surface roughness of reciprocating endodontic instruments
Khoa Van Pham
F1000Research.2021; 10: 875. CrossRef - Surface profile of different heat-treated nickel-titanium files before and after root canal preparation
Iandara de Lima Scardini, Denise Maria Zezell, Juliana Lisboa Couto Marques, Laila Gonzales Freire, Marcelo dos Santos
Brazilian Dental Journal.2021; 32(6): 8. CrossRef - Impact of Endodontic Instrumentation on Surface Roughness of Various Nickel-Titanium Rotary Files
Muhammad Sohail Zafar
European Journal of Dentistry.2021; 15(02): 273. CrossRef - A new method for assessment of nickel-titanium endodontic instrument surface roughness using field emission scanning electronic microscope
Khoa Van Pham, Canh Quang Vo
BMC Oral Health.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Surface Alterations Induced on Endodontic Instruments by Sterilization Processes, Analyzed with Atomic Force Microscopy: A Systematic Review
Mario Dioguardi, Vito Crincoli, Luigi Laino, Mario Alovisi, Enrica Laneve, Diego Sovereto, Bruna Raddato, Khrystyna Zhurakivska, Filiberto Mastrangelo, Domenico Ciavarella, Lucio Lo Russo, Lorenzo Lo Muzio
Applied Sciences.2019; 9(22): 4948. CrossRef - Atomic force microscopy and energy dispersive X‐ray spectrophotometry analysis of reciprocating and continuous rotary nickel‐titanium instruments following root canal retreatment
Bulem Üreyen Kaya, Cevat Emre Erik, Gülsen Kiraz
Microscopy Research and Technique.2019; 82(7): 1157. CrossRef - Influence of heat treatment on torsional resistance and surface roughness of nickel‐titanium instruments
E. J. N. L. Silva, J. F. N. Giraldes, C. O. de Lima, V. T. L. Vieira, C. N. Elias, H. S. Antunes
International Endodontic Journal.2019; 52(11): 1645. CrossRef
- Comparative Analysis of Surface Roughness and Plastic Deformation of Reciprocating Instruments after Clinical Use
- 1,772 View
- 12 Download
- 13 Crossref

- Incidence of apical crack formation and propagation during removal of root canal filling materials with different engine driven nickel-titanium instruments
- Taha Özyürek, Vildan Tek, Koray Yılmaz, Gülşah Uslu
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(4):332-341. Published online November 4, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.4.332
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives To determine the incidence of crack formation and propagation in apical root dentin after retreatment procedures performed using ProTaper Universal Retreatment (PTR), Mtwo-R, ProTaper Next (PTN), and Twisted File Adaptive (TFA) systems.
Materials and Methods The study consisted of 120 extracted mandibular premolars. One millimeter from the apex of each tooth was ground perpendicular to the long axis of the tooth, and the apical surface was polished. Twenty teeth served as the negative control group. One hundred teeth were prepared, obturated, and then divided into 5 retreatment groups. The retreatment procedures were performed using the following files: PTR, Mtwo-R, PTN, TFA, and hand files. After filling material removal, apical enlargement was done using apical size 0.50 mm ProTaper Universal (PTU), Mtwo, PTN, TFA, and hand files. Digital images of the apical root surfaces were recorded before preparation, after preparation, after obturation, after filling removal, and after apical enlargement using a stereomicroscope. The images were then inspected for the presence of new apical cracks and crack propagation. Data were analyzed with χ2 tests using SPSS 21.0 software.
Results New cracks and crack propagation occurred in all the experimental groups during the retreatment process. Nickel-titanium rotary file systems caused significantly more apical crack formation and propagation than the hand files. The PTU system caused significantly more apical cracks than the other groups after the apical enlargement stage.
Conclusions This study showed that retreatment procedures and apical enlargement after the use of retreatment files can cause crack formation and propagation in apical dentin.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Microcracks induced by XP-endo retreatment system in root canals filled with bioceramic sealer: A micro-computed tomographic analysis
Sarah M. Alkahtany
The Saudi Dental Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A comparative evaluation of different retreatment methods on apical root microcracks initiation and propagation: An in vitro study
Shweta Lodha, Zinnie Nanda
Endodontology.2025; 37(2): 175. CrossRef - Efficacy of Endodontic Files in Root Canal Retreatment: A Systematic Review of In Vitro Studies
Anna Soler-Doria, José Luis Sanz, Marcello Maddalone, Leopoldo Forner
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2025; 16(8): 293. CrossRef - Efficacy of Various Heat-treated Retreatment File Systems on Dentin Removal and Crack Analysis: An in vitro Study
Swathi Suresh, Pradeep Solete, Delphine Priscilla Antony, Kavalipurapu Venkata Teja, Adimulapu Hima Sandeep, Sruthi Sairaman, Marco Cicciù, Giuseppe Minervini
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A comparative evaluation of the dentinal microcracks formed and propagated during the removal of gutta-percha using hand and three rotary retreatment file systems: A micro-computed tomography study
Srivastava Sanjeev, Rita Gupta, Dubey Sandeep, Tewari Tanu, Shukla Namita, Singh Arohan
Endodontology.2023; 35(2): 155. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of incidence of dentinal defects after root canal preparation using hand, rotary, and reciprocating files: An ex vivo study
Debanjan Das, Sudipto Barai, Rohit Kumar, Sourav Bhattacharyya, AsimB Maity, Pushpa Shankarappa
Journal of International Oral Health.2022; 14(1): 78. CrossRef - Critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study removal of root filling materials
Mahdi A. Ajina, Pratik K. Shah, Bun San Chong
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S1): 119. CrossRef - Evaluation of Dentinal Crack Propagation, Amount of Gutta Percha Remaining and Time Required During Removal of Gutta Percha Using Two Different Rotary Instruments and Hand Instruments - An In vitro Study
S Tejaswi, A Singh, S Manglekar, UK Ambikathanaya, S Shetty
Nigerian Journal of Clinical Practice.2022; 25(4): 524. CrossRef - The Influence of Root Canal Preparation with ProTaper Next, WaveOne Gold, and Twisted Files on Dentine Crack Formation
Wojciech Eliasz, Beata Czarnecka, Anna Surdacka
Machines.2021; 9(12): 332. CrossRef - The potential effect of instrumentation with different nickel titanium rotary systems on dentinal crack formation—An in vitro study
Márk Fráter, András Jakab, Gábor Braunitzer, Zsolt Tóth, Katalin Nagy, Andrej M. Kielbassa
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(9): e0238790. CrossRef - Micro–computed Tomographic Assessment of the Residual Filling Volume, Apical Transportation, and Crack Formation after Retreatment with Reciproc and Reciproc Blue Systems in Curved Root Canals
Damla Kırıcı, Sezer Demirbuga, Ertuğrul Karataş
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(2): 238. CrossRef - Force and vibration generated in apical direction by three endodontic files of different kinematics during simulated canal preparation: An in vitro analytical study
Ankit Nayak, PK Kankar, Prashant K Jain, Niharika Jain
Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part H: Journal of Engineering in Medicine.2019; 233(8): 839. CrossRef - Effect of Aging on Dentinal Crack Formation after Treatment and Retreatment Procedures: a Micro-CT Study
Lilian Rachel de Lima Aboud, Bernardo Camargo dos Santos, Ricardo Tadeu Lopes, Leonardo Aboud Costa Viana, Miriam Fátima Zaccaro Scelza
Brazilian Dental Journal.2018; 29(6): 530. CrossRef
- Microcracks induced by XP-endo retreatment system in root canals filled with bioceramic sealer: A micro-computed tomographic analysis
- 1,896 View
- 12 Download
- 13 Crossref

- The effects of autoclave sterilization on the cyclic fatigue resistance of ProTaper Universal, ProTaper Next, and ProTaper Gold nickel-titanium instruments
- Taha Özyürek, Koray Yılmaz, Gülşah Uslu
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(4):301-308. Published online November 2, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.4.301
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives It was aimed to compare the cyclic fatigue resistances of ProTaper Universal (PTU), ProTaper Next (PTN), and ProTaper Gold (PTG) and the effects of sterilization by autoclave on the cyclic fatigue life of nickel-titanium (NiTi) instruments.
Materials and Methods Eighty PTU, 80 PTN, and 80 PTG were included to the present study. Files were tested in a simulated canal. Each brand of the NiTi files were divided into 4 subgroups: group 1, as received condition; group 2, pre-sterilized instruments exposed to 10 times sterilization by autoclave; group 3, instruments tested were sterilized after being exposed to 25%, 50%, and 75% of the mean cycles to failure, then cycled fatigue test was performed; group 4, instruments exposed to the same experiment with group 3 without sterilization. The number of cycles to failure (NCF) was calculated. The data was statistically analyzed by using one-way analysis of variance and
post hoc Tukey tests.Results PTG showed significantly higher NCF than PTU and PTN in group 1 (
p < 0.05). Sterilization significantly increased the NCF of PTN and PTG (p < 0.05) in group 2. PTN in group 3 had significantly higher cyclic fatigue resistance than PTN group 4 (p < 0.05). Also, significantly higher NCF was observed for PTG in group 2 than in groups 3 and 4 (p < 0.05).Conclusions PTG instrument made of new gold alloy was more resistant to fatigue failure than PTN and PTU. Autoclaving increased the cyclic fatigue resistances of PTN and PTG.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of Autoclaving on the Mechanical Performance and Metallurgical Behavior of ProTaper Ultimate, BlueShaper, and ZenFlex Nickel–Titanium Systems
Fatima Bardan, Mohamed El-Kishawi, Ensanya Ali Abou Neel, Saaid Al Shehadat, Rashid El Abed, Ahmed Jamleh
Journal of Endodontics.2026; 52(2): 292. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of fracture resistance of Hyflex EDM OGSF file system, Protaper Ultimate and RACE EVO file system: an in vitro study
N. Maiti, V. M. Lup, R. Chawla, P. Agrawal
Endodontics Today.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue Evaluation of Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instruments Using an Electrical Resistance-based Method
Congyu Yang, Yi Min, Wei Fan
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(10): 1471. CrossRef - The influence of autoclave sterilization on the cyclic fatigue of M-wire rotary endodontic instruments
Nenad Stosic, Jelena Popovic, Antonije Stankovic, Aleksandar Mitic, Marija Nikolic, Kosta Todorovic
Vojnosanitetski pregled.2024; 81(10): 642. CrossRef - Evaluatation of two nickle-titanium systems’ (Neolix and X Pro Gold) resistance to fracture after immersion in sodium hypochlorite.
Solmaz Araghi, Abbas Delvarani, Faeze dehghan, Parisa Kaghazloo
journal of research in dental sciences.2024; 21(1): 17. CrossRef - Comparing the EdgeFile X3, GenEndo, HeroGold, and ProTaper Gold Rotary Instruments Regarding the Effect of Different Concentrations and Temperature of NaOCl on Cyclic Fatigue Resistance
Garima Tyagi, Parul Shakarwal, Prakash Kumar, Annu Kumari, Aditya Singh, Pallavi Kusum
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2023; 24(9): 715. CrossRef - Cyclic fatigue resistance of EdgeTaper Platinum, Protaper Gold, and TruNatomy Prime rotary files before and after autoclave sterilization
Rahaf A. Almohareb, Reem M. Barakat, Fahda N. Algahtani, Manal F. Alkadi
PeerJ.2023; 11: e14656. CrossRef - Comparison of the fracture resistance of the teeth prepared with ProTaper Universal, ProTaper Next, and ProTaper Gold rotary files
Amin Salem Milani, Shabnam Ganjpour, Fatemeh Dehghani, Saeed Rahimi, Pouya Sabanik
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2022; 8(6): 1421. CrossRef - Impacts of NaOCl and Irritrol irrigation solutions with/without autoclave sterilisation on the cyclic fatigue resistance of different nickel‐titanium files
Fatma Kermeoglu, Mohamad Abduljalil
Australian Endodontic Journal.2022; 48(3): 392. CrossRef - Fracture Resistance of Heat-Treated Nickel-Titanium Rotary Files After Usage and Autoclave Sterilization: An In Vitro Study
Rashid El Abed, Aisha Alshehhi, Yoo Jung Kang, Dana Al Raeesi, Amar H. Khamis, Mohamed Jamal, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2022; 48(11): 1428. CrossRef - Nitinol Type Alloys General Characteristics and Applications in Endodontics
Leszek A. Dobrzański, Lech B. Dobrzański, Anna D. Dobrzańska-Danikiewicz, Joanna Dobrzańska
Processes.2022; 10(1): 101. CrossRef - The Impact of Multiple Autoclave Cycles on the Surface Roughness of Thermally Treated Nickel-Titanium Endodontic Files
Raidan Ba-Hattab, Rahaf A. Almohareb, Rana Alkhalaf, Shikhah Binnjefan, Meral Sulayem, Reem M. Barakat, Ismail Demir
Advances in Materials Science and Engineering.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Effect of autoclave sterilisation and heat activated sodium hypochlorite irrigation on the performance of nickel-titanium rotary files against cyclic fatigue
Zuha Ayad Jaber, Sattar Jabbar Abdul-Zahra Al-Hmedat, Sarmad Adel Hameed, Suhad Jabbar Hamed Al-Nasrawi, Abtesam Imhemed Aljdaimi, Julfikar Haider
Advances in Materials and Processing Technologies.2022; 8(1): 1071. CrossRef - Effect of different axial speed patterns on cyclic fatigue resistance of rotary nickel-titanium instruments
Myint Thu, Arata Ebihara, Keiichiro Maki, Miki Nishijo, Shunsuke Kimura, Taro Nakatsukasa, Moe Sandar Kyaw, Takashi Okiji
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue Resistance and Shaping Ability of Heat-Treated Nickel-Titanium Instruments after Repeated Use
SG Kamali, D Turkaydin
Nigerian Journal of Clinical Practice.2021; 24(2): 247. CrossRef - Effects of repeated sterilization cycles on the surface alterations of ProTaper Next, TF Adaptive, HyFlex CM, and 2Shape instruments
Olcay Özdemir, Sibel Koçak, Mustafa Murat Koçak, Baran Can Sağlam
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2021; 15(2): 76. CrossRef - Cleaning of endodontic files with and without enzymatic detergent by means of the manual method versus the ultrasonic method
César F Cayo-Rojas, Estefany Brito-Ávila, Ana S Aliaga-Mariñas, Karen K Hernández-Caba, Emylain D Saenz-Cazorla, Marysela I Ladera-Castañeda, Luis A Cervantes-Ganoza
Journal of International Society of Preventive and Community Dentistry.2021; 11(3): 307. CrossRef - Effect of number of uses and sterilization on the instrumented area and resistance of reciprocating instruments
Victor de Ornelas Peraça, Samantha Rodrigues Xavier, Fabio de Almeida Gomes, Luciane Geanini Pena dos Santos, Erick Miranda Souza, Fernanda Geraldo Pappen
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of sterilization procedures on the physical and mechanical properties of rotating endodontic instruments: a systematic review and network meta-analysis
Mario Dioguardi, Claudia Arena, Diego Sovereto, Riccardo Aiuto, Luigi Laino, Gaetano Illuzzi, Enrica Laneve, Bruna Raddato, Vito Carlo Alberto Caponio, Antonio Dioguardi, Khrystyna Zhurakivska, Giuseppe Troiano, Lorenzo Lo Muzio
Frontiers in Bioscience-Landmark.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - EFFECTS OF SODIUM HYPOCHLORIDE ON CYCLIC FATIGUE RESISTANCE OF BIORACE ROTARY INSTRUMENT WITH DIFFERENT TIP SIZES
Ayfer ATAV ATEŞ, Burçin ARICAN
Atatürk Üniversitesi Diş Hekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi.2021; : 1. CrossRef - The Influence of NiTi Alloy on the Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Endodontic Files
Celia Ruiz-Sánchez, Vicente Faus-Llácer, Ignacio Faus-Matoses, Álvaro Zubizarreta-Macho, Salvatore Sauro, Vicente Faus-Matoses
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(11): 3755. CrossRef - Novel Electronic Device to Quantify the Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Endodontic Reciprocating Files after Using and Sterilization
Álvaro Zubizarreta-Macho, Óscar Alonso-Ezpeleta, Alberto Albaladejo Martínez, Vicente Faus Matoses, Javier Caviedes Brucheli, Rubén Agustín-Panadero, Jesús Mena Álvarez, Fernando Vizmanos Martínez-Berganza
Applied Sciences.2020; 10(14): 4962. CrossRef - Influence of autoclave sterilization procedures on the cyclic fatigue resistance of heat-treated nickel-titanium instruments: a systematic review
Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Mayara Zanon, Fernanda Hecksher, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Rafaela Andrade de Vasconcelos, Tatiana Kelly da Silva Fidalgo
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Management of Instrument Sterilization Workflow in Endodontics: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Mario Dioguardi, Diego Sovereto, Gaetano Illuzzi, Enrica Laneve, Bruna Raddato, Claudia Arena, Vito Carlo Alberto Caponio, Giorgia Apollonia Caloro, Khrystyna Zhurakivska, Giuseppe Troiano, Lorenzo Lo Muzio
International Journal of Dentistry.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Effect of autoclave sterilization on cyclic fatigue and torsional fracture resistance of NiTi rotary instruments
Wooyoung Kim, Soram Oh, Gil-Joo Ryu, Tae-Hwan Kim, Sung-Jae Kim, Dong-Hyung Kim, Bin-Na Lee, Kee-Yeon Kum, Seok Woo Chang, Ji-Hyun Jang
Odontology.2020; 108(2): 194. CrossRef - Effects of Sodium Hypochlorite Concentration and Temperature on the Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Heat-treated Nickel-titanium Rotary Instruments
Hussam Alfawaz, Abdullah Alqedairi, Hala Alsharekh, Eman Almuzaini, Shahd Alzahrani, Ahmed Jamleh
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(10): 1563. CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Heat-treated Nickel-titanium Instruments after Immersion in Sodium Hypochlorite and/or Sterilization
Eugenio Pedullà, Angela Benites, Giusy M. La Rosa, Gianluca Plotino, Nicola M. Grande, Ernesto Rapisarda, Luigi Generali
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(4): 648. CrossRef
- Impact of Autoclaving on the Mechanical Performance and Metallurgical Behavior of ProTaper Ultimate, BlueShaper, and ZenFlex Nickel–Titanium Systems
- 1,808 View
- 27 Download
- 27 Crossref

-
Comparison of apical extrusion of intracanal bacteria by various glide-path establishing systems: an
in vitro study - Alberto Dagna, Rashid El Abed, Sameeha Hussain, Ibrahim H Abu-Tahun, Livia Visai, Federico Bertoglio, Floriana Bosco, Riccardo Beltrami, Claudio Poggio, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(4):316-323. Published online October 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.4.316
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study compared the amount of apically extruded bacteria during the glide-path preparation by using multi-file and single-file glide-path establishing nickel-titanium (NiTi) rotary systems.
Materials and Methods Sixty mandibular first molar teeth were used to prepare the test apparatus. They were decoronated, blocked into glass vials, sterilized in ethylene oxide gas, infected with a pure culture of
Enterococcus faecalis, randomly assigned to 5 experimental groups, and then prepared using manual stainless-steel files (group KF) and glide-path establishing NiTi rotary files (group PF with PathFiles, group GF with G-Files, group PG with ProGlider, and group OG with One G). At the end of canal preparation, 0.01 mL NaCl solution was taken from the experimental vials. The suspension was plated on brain heart infusion agar and colonies of bacteria were counted, and the results were given as number of colony-forming units (CFU).Results The manual instrumentation technique tested in group KF extruded the highest number of bacteria compared to the other 4 groups (
p < 0.05). The 4 groups using rotary glide-path establishing instruments extruded similar amounts of bacteria.Conclusions All glide-path establishment instrument systems tested caused a measurable apical extrusion of bacteria. The manual glide-path preparation showed the highest number of bacteria extruded compared to the other NiTi glide-path establishing instruments.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Apical Extrusion of Bacteria during Canal Preparation: A Systematic Review of Laboratory Studies
Thamyres M. Monteiro, Warley O. Silva, Jeferson O. Marques, Ana Carolina S.P. Guerra, Flávio R.F. Alves
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(7): 866. CrossRef - Glide Path in Endodontics: A Literature Review of Current Knowledge
Vlad Mircea Lup, Giulia Malvicini, Carlo Gaeta, Simone Grandini, Gabriela Ciavoi
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(8): 257. CrossRef - Evaluation of apically extruded debris using protaper universal, protaper next, one curve, Xp shaper, and edge file: An in vitro study
Murtada Qadir Muhaibes, Shatha Abdulkareem Alwakeel
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2024; 14(1): 31. CrossRef - Effect of Multiple Glide Path Files on Apical Debris Extrusion in Severely Curved Mesial Roots of Mandibular Molars: An In Vitro Study
Niranjan Desai, Ashish S Bhadane, Nishant K Vyavahare, Dipali Y Shah, Akash S Kale, Simran K Chaudhari
Journal of Operative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024; 8(1): 1. CrossRef - Evaluation of Pain Following the Use of Different Single-file Glide Path Systems: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Zeliha Danaci, Kübra Yeşildal Yeter
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(2): 120. CrossRef - Impact of Different Glidepath Techniques on the Overall Performance of WaveOne Gold in an Artificial S-Shape Canal
Vlad Mircea Lup, Olivia Andreea Marcu, Carlo Gaeta, Gabriela Ciavoi
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(6): 182. CrossRef - Influence of different irrigant activation methods on apical debris extrusion and bacterial elimination from infected root canals
KSadia Ada, Shibani Shetty, KB Jayalakshmi, PrasannaLatha Nadig, PG Manje Gowda, ArulK Selvan
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2023; 26(1): 31. CrossRef - A Comparative Evaluation of the Apically Extruded Debris from Root Canals Prepared by R-Motion NiTi File System
Farah B. Al-Saffar, Hikmet A. Al-Gharrawi, Luca Testarelli
International Journal of Dentistry.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Effect of glide path files with different metallurgy on intracanal bacterial extrusion by HyFlex electrical discharge machining file
Priyanka Soni, Pragya Kumar, Sonali Taneja, Anshi Jain
Endodontology.2022; 34(3): 168. CrossRef - Impact of kinematics on the efficiency and safety of an engine-driven file for glide path preparation in MB2 canals of maxillary molars
Larissa B. B. Araújo, Pedro H. S. Calefi, Murilo P. Alcalde, Giulio Gavini, Rodrigo R. Vivan, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 27(3): 1153. CrossRef - Critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study removal of root filling materials
Mahdi A. Ajina, Pratik K. Shah, Bun San Chong
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S1): 119. CrossRef - A Comparative Evaluation of Apically Extruded Debris using Three Rotary and One Reciprocating Instrumentation Ni-Ti Systems
Maha Adnan Habeeb
Journal of Orofacial Sciences.2022; 14(2): 93. CrossRef - A critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study apical extrusion of debris and irrigants
Jale Tanalp
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S1): 153. CrossRef - Evaluation of type of kinematics on glide path procedures and torsional fatigue resistance after preparation of moderately curved canals
Murilo Priori Alcalde, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Pedro Henrique Souza Calefi, Victor de Moraes Cruz, Bruno Carvalho de Vasconcelos, Marcus Vinícius Reis Só, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan
Brazilian Oral Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of a glide path creation necessity at the initial stages of endodontic treatment
Z. S. Khabadze, Yu. A. Generalova
Endodontics Today.2021; 19(1): 39. CrossRef - Influence of glide path kinematics during endodontic treatment on the occurrence and intensity of intraoperative and postoperative pain: a systematic review of randomized clinical trials
Thaís Christina Cunha, Felipe de Souza Matos, Luiz Renato Paranhos, Ítalo de Macedo Bernardino, Camilla Christian Gomes Moura
BMC Oral Health.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Apically extruded debris produced during glide path preparation using R‐Pilot, WaveOne Gold Glider and ProGlider in curved root canals
Cangül Keskin, Özlem Sivas Yilmaz, Uğur Inan
Australian Endodontic Journal.2020; 46(3): 439. CrossRef - Influence of Negotiation, Glide Path, and Preflaring Procedures on Root Canal Shaping—Terminology, Basic Concepts, and a Systematic Review
Gianluca Plotino, Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Frederic Bukiet, Nicola M. Grande, Sajesh K. Veettil, Gustavo De-Deus, Hany Mohamed Aly Ahmed
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(6): 707. CrossRef - Mechanical Properties of Various Glide Path Preparation Nickel-titanium Rotary Instruments
Joo-Yeong Lee, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Ibrahim H. Abu-Tahun, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2019; 45(2): 199. CrossRef - Effective Establishment of Glide-Path to Reduce Torsional Stress during Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instrumentation
Ibrahim H. Abu-Tahun, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Asgeir Sigurdsson, Mehmet Baybora Kayahan, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Materials.2019; 12(3): 493. CrossRef - Postoperative pain after glide path preparation using manual, reciprocating and continuous rotary instruments: a randomized clinical trial
C. Keskin, Ö. Sivas Yilmaz, U. Inan, Ö. Özdemir
International Endodontic Journal.2019; 52(5): 579. CrossRef - Intraoperative Pain During Glide Path Creation with the Use of a Rotary or Reciprocating System
Pelin TUFENKCİ, Mehmet ADIGUZEL, Koray YILMAZ
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2019; 22(1): 66. CrossRef - Effects of Different Glide Path Files on Apical Debris Extrusion in Curved Root Canals
Betul Gunes, Kubra Yesildal Yeter
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(7): 1191. CrossRef
- Apical Extrusion of Bacteria during Canal Preparation: A Systematic Review of Laboratory Studies
- 1,690 View
- 13 Download
- 23 Crossref

- Effect of surface treatment on the mechanical properties of nickel-titanium files with a similar cross-section
- Sang Won Kwak, Joo Yeong Lee, Hye-Jin Goo, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(3):216-223. Published online June 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.3.216
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to compare the mechanical properties of various nickel-titanium (NiTi) files with similar tapers and cross-sectional areas depending on whether they were surface-treated.
Materials and Methods Three NiTi file systems with a similar convex triangular cross-section and the same ISO #25 tip size were selected for this study: G6 (G6), ProTaper Universal (PTU), and Dia-PT (DPT). To test torsional resistance, 5 mm of the straightened file's tip was fixed between polycarbonate blocks (
n = 15/group) and continuous clockwise rotation until fracture was conducted using a customized device. To evaluate cyclic fatigue resistance, files were rotated in an artificial curved canal until fracture in a dynamic mode (n = 15/group). The torsional data were analyzed using 1-way analysis of variance and the Tukeypost-hoc comparison test, while the cyclic fatigue data were analyzed using the Mann-WhitneyU test at a significance level of 95%.Results PTU showed significantly greater toughness, followed by DPT and G6 (
p < 0.05). G6 showed the lowest resistance in ultimate torsional strength, while it showed a higher fracture angle than the other files (p < 0.05). In the cyclic fatigue test, DPT showed a significantly higher number of cycles to failure than PTU or G6 (p < 0.05).Conclusions Within the limitations of this study, it can be concluded that the torsional resistance of NiTi files was affected by the cross-sectional area, while the cyclic fatigue resistance of NiTi files was influenced by the surface treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- FARKLI YAPISAL ÖZELLİKTEKİ NİKEL-TİTANYUM KÖK KANAL EĞELERİNİN SODYUM HİPOKLORİT VE SERUM FİZYOLOJİK ÇÖZELTİLERİNDEKİ DÖNGÜSEL YORGUNLUK DİRENÇLERİNİN KARŞILAŞTİRİLMASI
Abdulkadir ÖZŞAHİN, Meltem DARTAR ÖZTAN, Emine ODABAŞI TEZER
Atatürk Üniversitesi Diş Hekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi.2021; : 1. CrossRef - Heat Treatment and Surface Treatment of Nickel–Titanium Endodontic Instruments
Sang Won Kwak, Ya Shen, He Liu, Zhejun Wang, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Markus Haapasalo
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Torsional Resistance of Two New Heat Treated Nickel Titanium Rotary Instruments: An in Vitro Evaluation
Gianluca Gambarini, Gabriele Miccoli, Dario Di Nardo, Andrea Del Giudice, Alessandro Mazzoni, Marco Seracchiani, Luca Testarelli
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- FARKLI YAPISAL ÖZELLİKTEKİ NİKEL-TİTANYUM KÖK KANAL EĞELERİNİN SODYUM HİPOKLORİT VE SERUM FİZYOLOJİK ÇÖZELTİLERİNDEKİ DÖNGÜSEL YORGUNLUK DİRENÇLERİNİN KARŞILAŞTİRİLMASI
- 1,341 View
- 6 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Effect of adaptive motion on cyclic fatigue resistance of a nickel titanium instrument designed for retreatment
- Taha Özyürek, Koray Yılmaz, Gülşah Uslu
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(1):34-38. Published online December 19, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.1.34

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to evaluate the cyclic fatigue resistance of the ProTaper Universal D1 file (Dentsply Maillefer) under continuous and adaptive motion.
Materials and Methods Forty ProTaper Universal D1 files were included in this study. The cyclic fatigue tests were performed using a dynamic cyclic fatigue testing device, which had an artificial stainless steel canal with a 60° angle of curvature and a 5 mm radius of curvature. The files were randomly divided into two groups (Group 1, Rotary motion; Group 2, Adaptive motion). The time to failure of the files were recorded in seconds. The number of cycles to failure (NCF) was calculated for each group. The data were statistically analyzed using Student's
t -test. The statistical significant level was set atp < 0.05.Results The cyclic fatigue resistance of the adaptive motion group was significantly higher than the rotary motion group (
p < 0.05).Conclusion Within the limitations of the present study, the ‘Adaptive motion’ significantly increased the resistance of the ProTaper Universal D1 file to cyclic facture.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of Different Separated File Retrieval Strategies on the Biomechanical Behavior of a Mandibular Molar: A Finite Element Analysis Study
Anas Sira, Nawar Naguib Nawar, Shehabeldin Mohamed Saber, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(1): 64. CrossRef - Surface Alterations of Ni‐Ti Files After Retreatment of Root Canals Filled With Different Sealers: AFM and SEM Study
Duygu Aksoy, Sibel Koçak, Mustafa Murat Koçak, Baran Can Sağlam
Microscopy Research and Technique.2025; 88(10): 2704. CrossRef - Evaluatation of two nickle-titanium systems’ (Neolix and X Pro Gold) resistance to fracture after immersion in sodium hypochlorite.
Solmaz Araghi, Abbas Delvarani, Faeze dehghan, Parisa Kaghazloo
journal of research in dental sciences.2024; 21(1): 17. CrossRef - Assessment the impact of operator experience on cyclic fatigue resistance in reciprocating and rotary NiTi files: a comparative study between dental students and pediatric dentistry specialists
Hande Özyürek, Mesut Elbay, Taha Özyürek
Frontiers in Materials.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of gutta-percha removal from the dentinal tubules using different instrumentation techniques with or without solvent: An In vitro study
MukeshKumar Hasija, Babita Meena, Deepti Wadhwa, KulvinderKaur Wadhwani, Virender Yadav
Journal of the International Clinical Dental Research Organization.2020; 12(1): 27. CrossRef - Influences of Continuous Rotation and TF adaptive Motion on the Resistance of Different Retreatment File Systems to Deformation and Fracture: An In Vitro study
Divya Meena, Ramyadharshini LNU, V Nivedha, Anand Sherwood
Journal of Operative Dentistry & Endodontics.2018; 3(2): 71. CrossRef - Comparison of cyclic fatigue life of nickel-titanium files: an examination using high-speed camera
Taha Özyürek, Neslihan Büşra Keskin, Fatma Furuncuoğlu, Uğur İnan
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2017; 42(3): 224. CrossRef
- The Effect of Different Separated File Retrieval Strategies on the Biomechanical Behavior of a Mandibular Molar: A Finite Element Analysis Study
- 1,624 View
- 6 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Screw-in forces during instrumentation by various file systems
- Jung-Hong Ha, Sang Won Kwak, Sung-Kyo Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(4):304-309. Published online November 8, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.4.304
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to compare the maximum screw-in forces generated during the movement of various Nickel-Titanium (NiTi) file systems.
Materials and Methods Forty simulated canals in resin blocks were randomly divided into 4 groups for the following instruments: Mtwo size 25/0.07 (MTW, VDW GmbH), Reciproc R25 (RPR, VDW GmbH), ProTaper Universal F2 (PTU, Dentsply Maillefer), and ProTaper Next X2 (PTN, Dentsply Maillefer,
n = 10). All the artificial canals were prepared to obtain a standardized lumen by using ProTaper Universal F1. Screw-in forces were measured using a custom-made experimental device (AEndoS-k , DMJ system) during instrumentation with each NiTi file system using the designated movement. The rotation speed was set at 350 rpm with an automatic 4 mm pecking motion at a speed of 1 mm/sec. The pecking depth was increased by 1 mm for each pecking motion until the file reach the working length. Forces were recorded during file movement, and the maximum force was extracted from the data. Maximum screw-in forces were analyzed by one-way ANOVA and Tukey'spost hoc comparison at a significance level of 95%.Results Reciproc and ProTaper Universal files generated the highest maximum screw-in forces among all the instruments while M-two and ProTaper Next showed the lowest (
p < 0.05).Conclusions Geometrical differences rather than shaping motion and alloys may affect the screw-in force during canal instrumentation. To reduce screw-in forces, the use of NiTi files with smaller cross-sectional area for higher flexibility is recommended.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Restoration of teeth lacking complete ferrules using cast precious metal alloy post-and-cores and knife-edged crowns: A retrospective clinical study
Fangyue Xiang, Keying Shi, Haoyang Hua, Jing Zhao, Yuanna Zheng
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2025; 134(5): 1729. CrossRef - Comparison of mechanical properties and shaping performance of ProGlider and ProTaper ultimate slider
Jeyi Song, Ji-Hyun Jang, Seok Woo Chang, Shin Hye Chung, Soram Oh
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Thermal Treatment Prevents Effects of Downward Loads on the Screw-In Force Generation and Canal-Centering Ability of Nickel–Titanium Rotary Instruments
Keiichiro Maki, Arata Ebihara, Yanshan Luo, Yuka Kasuga, Hayate Unno, Satoshi Omori, Shunsuke Kimura, Takashi Okiji
Materials.2025; 18(15): 3610. CrossRef - Radial Lands and Alternating Cutting Edges Contribute to Reduced Screw-in and Torque in Curved Root Canals - An In Vitro Study
Greta Heimberg, Sebastian Bürklein, Edgar Schäfer, Thomas Gerhard Wolf, David Donnermeyer
Journal of Endodontics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of rotation and insertion speeds of rotary Ni-Ti file on the vertical force and torque during root canal preparation: by a new automatic root canal shaping simulation method
Hyungwoo Lee, In-Bog Lee
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2025; 52(4): 221. CrossRef - Screw-in force, torque generation, and performance of glide-path files with three rotation kinetics
Jee-Yeon Woo, Ji-Hyun Jang, Seok Woo Chang, Soram Oh
Odontology.2024; 112(3): 761. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of stress distribution against the root canal wall at three different levels using novel NiTi rotary files – A finite element analysis
Rimjhim Singh, Sandeep Dubey, Palak Singh, Praveen Singh Samant, Suparna Ganguly Saha
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(1): 62. CrossRef - Effect of Periodic Changes in Rotation Speed on Torsional Stress and Screw-in Force by Alternative Rotation Technique
Jung-Hong Ha, Hyo-Jin Jo, Sang Won Kwak, Asgeir Sigurdsson, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2023; 49(1): 77. CrossRef - A Comparative Evaluation of the Apically Extruded Debris from Root Canals Prepared by R-Motion NiTi File System
Farah B. Al-Saffar, Hikmet A. Al-Gharrawi, Luca Testarelli
International Journal of Dentistry.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Effect of Rotational Modes on Torque/Force Generation and Canal Centering Ability during Rotary Root Canal Instrumentation with Differently Heat-Treated Nickel–Titanium Instruments
Satoshi Omori, Arata Ebihara, Keiko Hirano, Yuka Kasuga, Hayate Unno, Taro Nakatsukasa, Shunsuke Kimura, Keiichiro Maki, Takao Hanawa, Takashi Okiji
Materials.2022; 15(19): 6850. CrossRef - Effect of Core Mass and Alloy on Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Different Nickel-Titanium Endodontic Instruments in Matching Artificial Canals
Sebastian Bürklein, Lennart Zupanc, David Donnermeyer, Karsten Tegtmeyer, Edgar Schäfer
Materials.2021; 14(19): 5734. CrossRef - Comparison of Torque, Screw-in Force, and Shaping Ability of Glide Path Instruments in Continuous Rotation and Optimum Glide Path Motion
Pyae Hein Htun, Arata Ebihara, Keiichiro Maki, Shunsuke Kimura, Miki Nishijo, Moe Sandar Kyaw, Takashi Okiji
Journal of Endodontics.2021; 47(1): 94. CrossRef - Analysis of Torque and Force Induced by Rotary Nickel-Titanium Instruments during Root Canal Preparation: A Systematic Review
Myint Thu, Arata Ebihara, Sherif Adel, Takashi Okiji
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(7): 3079. CrossRef - Influence of rotational speed on torque/force generation and shaping ability during root canal instrumentation of extracted teeth with continuous rotation and optimum torque reverse motion
M. S. Kyaw, A. Ebihara, Y. Kasuga, K. Maki, S. Kimura, P. H. Htun, T. Nakatsukasa, T. Okiji
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(9): 1614. CrossRef - Effect of Optimum Torque Reverse Motion on Torque and Force Generation during Root Canal Instrumentation with Crown-down and Single-length Techniques
Shunsuke Kimura, Arata Ebihara, Keiichiro Maki, Miki Nishijo, Daisuke Tokita, Takashi Okiji
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(2): 232. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of torque and apical force to assess the cutting behaviour of ProTaper Next and ProTaper Universal endodontic instruments
Gustavo de Cristofaro Almeida, Diego Pinheiro Aun, Pedro Damas Resende, Isabella Faria da Cunha Peixoto, Ana Cecília Diniz Viana, Vicente Tadeu Lopes Buono, Maria Guiomar de Azevedo Bahia
Australian Endodontic Journal.2020; 46(1): 52. CrossRef - Enhanced root canal-centering ability and reduced screw-in force generation of reciprocating nickel-titanium instruments with a post-machining thermal treatment
Keiichiro MAKI, Arata EBIHARA, Shunsuke KIMURA, Miki NISHIJO, Daisuke TOKITA, Kana MIYARA, Takashi OKIJI
Dental Materials Journal.2020; 39(2): 251. CrossRef - Ex-Vivo Comparison of Torsional Stress on Nickel–Titanium Instruments Activated by Continuous Rotation or Adaptive Motion
Joo Yeong Lee, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Materials.2020; 13(8): 1900. CrossRef - Evaluation of stress distribution in nickel-titanium rotary instruments with different geometrical designs subjected to bending and torsional load: a finite element study
Manar Galal, Tamer M. Hamdy
Bulletin of the National Research Centre.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of mechanical properties of WaveOne Gold Primary reciprocating instruments
Tong FANGLI, Keiichiro MAKI, Shunsuke KIMURA, Miki NISHIJO, Daisuke TOKITA, Arata EBIHARA, Takashi OKIJI
Dental Materials Journal.2019; 38(3): 490. CrossRef - Comparison of Screw-In Forces during Movement of Endodontic Files with Different Geometries, Alloys, and Kinetics
Sang Won Kwak, Chan-Joo Lee, Sung Kyo Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Jung-Hong Ha
Materials.2019; 12(9): 1506. CrossRef - Gripping the Gripped: Removal of Foreign Bodies from Root Canal System
Shweta Jain, Sachin Jain, Shikha Jain, Sophia Thakur
Dental Research and Management.2019; : 13. CrossRef - Mechanical Properties of Orifice Preflaring Nickel-titanium Rotary Instrument Heat Treated Using T-Wire Technology
Maamoun Ataya, Jung-Hong Ha, Sang Won Kwak, Ibrahim H. Abu-Tahun, Rashid El Abed, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(12): 1867. CrossRef - How biomechanics can affect the endodontic treated teeth and their restorative procedures?
Carlos José Soares, Monise de Paula Rodrigues, André Luis Faria-e-Silva, Paulo Cesar Freitas Santos-Filho, Crisnicaw Veríssimo, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Antheunis Versluis
Brazilian Oral Research.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of selected mechanical properties of NiTi rotary glide path files manufactured from controlled memory wires
Miki NISHIJO, Arata EBIHARA, Daisuke TOKITA, Hisashi DOI, Takao HANAWA, Takashi OKIJI
Dental Materials Journal.2018; 37(4): 549. CrossRef - Nickel–titanium instruments in endodontics: a concise review of the state of the art
Giulio Gavini, Marcelo dos Santos, Celso Luis Caldeira, Manoel Eduardo de Lima Machado, Laila Gonzales Freire, Elaine Faga Iglecias, Ove Andrea Peters, George Táccio de Miranda Candeiro
Brazilian Oral Research.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Dynamic Torque and Vertical Force Analysis during Nickel-titanium Rotary Root Canal Preparation with Different Modes of Reciprocal Rotation
Daisuke Tokita, Arata Ebihara, Miki Nishijo, Kana Miyara, Takashi Okiji
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(10): 1706. CrossRef
- Restoration of teeth lacking complete ferrules using cast precious metal alloy post-and-cores and knife-edged crowns: A retrospective clinical study
- 1,602 View
- 11 Download
- 27 Crossref

- Preference of undergraduate students after first experience on nickel-titanium endodontic instruments
- Sang Won Kwak, Gary Shun-Pan Cheung, Jung-Hong Ha, Sung Kyo Kim, Hyojin Lee, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(3):176-181. Published online June 23, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.3.176
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to compare two nickel-titanium systems (rotary
vs . reciprocating) for their acceptance by undergraduate students who experienced nickel-titanium (NiTi) instruments for the first time.Materials and Methods Eighty-one sophomore dental students were first taught on manual root canal preparation with stainless-steel files. After that, they were instructed on the use of ProTaper Universal system (PTU, Dentsply Maillefer), then the WaveOne (WO, Dentsply Maillefer). They practiced with each system on 2 extracted molars, before using those files to shape the buccal or mesial canals of additional first molars. A questionnaire was completed after using each file system, seeking students' perception about 'Ease of use', 'Flexibility', 'Cutting-efficiency', 'Screwing-effect', 'Feeling-safety', and 'Instrumentation-time' of the NiTi files, relative to stainless-steel instrumentation, on a 5-point Likert-type scale. They were also requested to indicate their preference between the two systems. Data was compared between groups using
t -test, and with Chi-square test for correlation of each perception value with the preferred choice (p = 0.05).Results Among the 81 students, 55 indicated their preferred file system as WO and 22 as PTU. All scores were greater than 4 (better) for both systems, compared with stainless-steel files, except for 'Screwing-effect' for PTU. The scores for WO in the categories of 'Flexibility', 'Screwing-effect', and 'Feeling-safety' were significantly higher scores than those of PTU. A significant association between the 'Screwing-effect' and students' preference for WO was observed.
Conclusions Novice operators preferred nickel-titanium instruments to stainless-steel, and majority of them opted for reciprocating file instead of continuous rotating system.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors influencing the agreement between teachers and students in the assessment of preclinical endodontics using a rubric
B. Baracco, N. Escribano, D. Da Silva, V. Belliard, L. Ceballos, V. Fuentes
BMC Medical Education.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Technical Quality and Students' Perception of Endodontic Preclinical Training Using Natural or LikeReal Artificial Teeth
Gabriela Biagioni, Fernanda Comodo, Marcelo Santos Coelho
European Journal of Dental Education.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Endodontic Procedural Errors and Associated Factors among Undergraduate Dental Students: A Cross-sectional Study
Vivek Padmanabhan, Md Sofiqul Islam, Mohamed A Elsayed, Duaa R Saleh, Amal M Alnahdi
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2024; 24(12): 998. CrossRef - Clinicians’ perspectives, inducements, preferences, and clinical experiences regarding the use of electronic apex locator and apex locator integrated engine-driven instrumentation: a cross-sectional study
Sena Kaşıkçı, Sena Kolunsağ Özbek, Ebru Şirinoğlu, Olcay Özdemir
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation and Comparison of Manual and Mechanical Endodontic Instrumentation Completed by Undergraduate Dental Students on Endodontic Blocks
António Ginjeira, Abayomi O. Baruwa, Karla Baumotte
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(11): 363. CrossRef - The first experiences of preclinical dentistry students with rotary instruments: A pilot study
Işıl Kaya Büyükbayram, Gizem Çolakoğlu, Sana Mahroos Al-Shammari, Katia Stoicefidis
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2024; 14(2): 205. CrossRef - Comparative Efficacy of Manual vs. Rotary/Reciprocating NiTi Instrumentation by Novice Dental Students on Simulated Root Canals
Ethan Smith, Olivia Davis
International Journal of Dental Research and Allied Sciences.2024; 4(2): 82. CrossRef - First Experience of an Undergraduate Dental Student with a Reciprocating System in Simulated Root Canals—A Pilot Study
Ana Rita Arede, Inês Ferreira, Ana Cristina Braga, Irene Pina-Vaz
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(8): 4848. CrossRef - Effect on undergraduate student self-confidence in using 3D printed primary molars for root canal treatment simulation training
C. Delfosse, T. Marquillier, S. Ndoye, P.-Y. Cousson, M. Hennequin, C. Catteau
European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry.2023; 24(1): 105. CrossRef - Influence of operator expertise on glide path and root canal preparation of curved root canals with rotary and reciprocating motions
Ana Belén Dablanca‐Blanco, Ana Arias, María José Ginzo‐Villamayor, María Consuelo Pérez, Pablo Castelo‐Baz, Benjamín Martín‐Biedma
Australian Endodontic Journal.2022; 48(1): 37. CrossRef - Quality of root canal treatment performed by undergraduate students using nickel‐titanium reciprocating versus hand instruments
Seniha Miçooğulları Kurt, Gözde Kandemir Demirci, Burcu Serefoglu, Mehmet Emin Kaval, Pelin Güneri, Mehmet Kemal Çalışkan
Journal of Dental Education.2022; 86(12): 1662. CrossRef - Radiographic assessment of endodontic mishaps in an undergraduate student clinic: a 2-year retrospective study
Manal Matoug-Elwerfelli, Ahmed Abdou, Wejdan Almutairi, Malak Alhuthayli, Shaikhah Aloyaynaa, Rahaf Almohareb
PeerJ.2022; 10: e13858. CrossRef - Ex vivo shaping ability of reciprocating instruments operated by new users: Reciproc versus WaveOne
Mary S. H. Lam, Jeffrey W. W. Chang, Gary S. P. Cheung
Clinical Oral Investigations.2021; 25(5): 2791. CrossRef - Body temperature fatigue behaviour of reciprocating and rotary glide path instruments in sodium hypochlorite solutions alone or combined with etidronate
Dario Perez‐Villalba, José C. Macorra, Juan J. Perez‐Higueras, Ove A. Peters, Ana Arias
Australian Endodontic Journal.2021; 47(3): 450. CrossRef - Undergraduate Students’ Acceptance of a Reciprocating One-File System for Endodontic Treatment
Benjamin Mahmoodi, Adriano Azaripour, Kawe Sagheb, Keyvan Sagheb, Brita Willershausen, Jens Weusmann
European Journal of Dentistry.2020; 14(03): 393. CrossRef - Fracture of endodontic instruments - Part 1: Literature review on factors that influence instrument breakage
Maheshan Pillay, Martin Vorster, Peet J Van der Vyver
South African Dental Journal.2020; 75(10): 553. CrossRef - A comparative study of root canal shaping using protaper universal and protaper next rotary files in preclinical dental education
Gül Çelik, Feyza Özdemir Kısacık, Emir Faruk Yılmaz, Arife Mersinlioğlu, İhsan Furkan Ertuğrul, Hikmet Orhan
PeerJ.2019; 7: e7419. CrossRef - Undergraduate dentistry students’ perception of difficulties regarding endodontic treatment
Lorrane G. Tavares, Stella M. F. Lima, Miriane G. Lima, Marcos P. Arruda, Thiago C. Menegazzi, Taia M. B. Rezende
Australian Endodontic Journal.2019; 45(1): 98. CrossRef - First Experience of Rotary Nickel Titanium Root Canal Instrumentation Performed by Undergraduate Students and General Dentists
marwa sharaan, Noreen Kamel, Dimitrios Tziafas
Journal of Dentistry and Oral Care.2017; 3(2): 1. CrossRef
- Factors influencing the agreement between teachers and students in the assessment of preclinical endodontics using a rubric
- 1,622 View
- 10 Download
- 19 Crossref

- Effect of repetitive pecking at working length for glide path preparation using G-file
- Jung-Hong Ha, Hyo-Jin Jeon, Rashid El Abed, Seok-Woo Chang, Sung-Kyo Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(2):123-127. Published online January 7, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.2.123
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Glide path preparation is recommended to reduce torsional failure of nickel-titanium (NiTi) rotary instruments and to prevent root canal transportation. This study evaluated whether the repetitive insertions of G-files to the working length maintain the apical size as well as provide sufficient lumen as a glide path for subsequent instrumentation.
Materials and Methods The G-file system (Micro-Mega) composed of G1 and G2 files for glide path preparation was used with the J-shaped, simulated resin canals. After inserting a G1 file twice, a G2 file was inserted to the working length 1, 4, 7, or 10 times for four each experimental group, respectively (
n = 10). Then the canals were cleaned by copious irrigation, and lubricated with a separating gel medium. Canal replicas were made using silicone impression material, and the diameter of the replicas was measured at working length (D0) and 1 mm level (D1) under a scanning electron microscope. Data was analysed by one-way ANOVA andpost-hoc tests (p = 0.05).Results The diameter at D0 level did not show any significant difference between the 1, 2, 4, and 10 times of repetitive pecking insertions of G2 files at working length. However, 10 times of pecking motion with G2 file resulted in significantly larger canal diameter at D1 (
p < 0.05).Conclusions Under the limitations of this study, the repetitive insertion of a G2 file up to 10 times at working length created an adequate lumen for subsequent apical shaping with other rotary files bigger than International Organization for Standardization (ISO) size 20, without apical transportation at D0 level.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Glide Path – An Ineluctable Route for Successful Endodontic Mechanics: A Literature Review
Mahima Bharat Mehta, Anupam Sharma, Aniket Jadhav, Aishwarya Handa, Abhijit Bajirao Jadhav, Ashwini A. Narayanan
Journal of the International Clinical Dental Research Organization.2024; 16(2): 101. CrossRef - Effect of repetitive up-and-down movements on torque/force generation, surface defects and shaping ability of nickel-titanium rotary instruments: an ex vivo study
Moe Sandar Kyaw, Arata Ebihara, Yoshiko Iino, Myint Thu, Keiichiro Maki, Shunsuke Kimura, Pyae Hein Htun, Takashi Okiji
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of the Number of Pecking Motions at Working Length on the Shaping Ability of Single-file Systems in Long Oval-shaped Curved Canals
Lixiao Wang, Ruitian Lin, Hui Chen, Zihan Li, Franklin R. Tay, Lisha Gu
Journal of Endodontics.2022; 48(4): 548. CrossRef - Influence of pecking frequency at working length on the volume of apically extruded debris: A micro-computed tomography analysis
Li-Xiao Wang, Hui Chen, Rui-Tian Lin, Li-Sha Gu
Journal of Dental Sciences.2022; 17(3): 1274. CrossRef - Comparison of the effects from coronal pre‐flaring and glide‐path preparation on torque generation during root canal shaping procedure
Sang Won Kwak, Jung‐Hong Ha, Ya Shen, Markus Haapasalo, Hyeon‐Cheol Kim
Australian Endodontic Journal.2022; 48(1): 131. CrossRef - Effective Establishment of Glide-Path to Reduce Torsional Stress during Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instrumentation
Ibrahim H. Abu-Tahun, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Asgeir Sigurdsson, Mehmet Baybora Kayahan, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Materials.2019; 12(3): 493. CrossRef - Stress Generation during Pecking Motion of Rotary Nickel-titanium Instruments with Different Pecking Depth
Jung-Hong Ha, Sang Won Kwak, Asgeir Sigurdsson, Seok Woo Chang, Sung Kyo Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(10): 1688. CrossRef - Debris extrusion by glide-path establishing endodontic instruments with different geometries
Jung-Hong Ha, Sung Kyo Kim, Sang Won Kwak, Rashid El Abed, Yong Chul Bae, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Dental Sciences.2016; 11(2): 136. CrossRef - Effects of Pitch Length and Heat Treatment on the Mechanical Properties of the Glide Path Preparation Instruments
Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Chan-Joo Lee, Rashid El Abed, Ibrahim H. Abu-Tahun, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(5): 788. CrossRef
- Glide Path – An Ineluctable Route for Successful Endodontic Mechanics: A Literature Review
- 1,533 View
- 7 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Buckling resistance, bending stiffness, and torsional resistance of various instruments for canal exploration and glide path preparation
- Sang-Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, WooCheol Lee, Sung-Kyo Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(4):270-275. Published online July 16, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.4.270
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study compared the mechanical properties of various instruments for canal exploration and glide-path preparations.
Materials and Methods The buckling resistance, bending stiffness, ultimate torsional strength, and fracture angle under torsional load were compared for C+ file (CP, Dentsply Maillefer), M access K-file (MA, Dentsply Maillefer), Mani K-file (MN, Mani), and NiTiFlex K-file (NT, Dentsply Maillefer). The files of ISO size #15 and a shaft length of 25 mm were selected. For measuring buckling resistance (
n = 10), the files were loaded in the axial direction of the shaft, and the maximum load was measured during the files' deflection. The files (n = 10) were fixed at 3-mm from the tip and then bent 45° with respect to their long axis, while the bending force was recorded by a load cell. For measuring the torsional properties, the files (n = 10) were also fixed at 3-mm, and clockwise rotations (2-rpm) were applied to the files in a straight state. The torsional load and the distortion angle were recorded until the files succumbed to the torque.Results The CP was shown to require the highest load to buckle and bend the files, and the NT showed the least. While MA and MN showed similar buckling resistances, MN showed higher bending stiffness than MA. The NT had the lowest bending stiffness and ultimate torsional strength (
p < 0.05).Conclusions The tested instruments showed different mechanical properties depending on the evaluated parameters. CP and NT files were revealed to be the stiffest and the most flexible instruments, respectively.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Buckling resistance of various pathfinding endodontic instruments: An in vitro study
Ujjwal Das, Rajesh Kumar Das, Kallol Kumar Saha, Lugu Buru Murmu, Srimanta Banerjee, Rishila Nag
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(4): 384. CrossRef - Comparison of torsional, bending, and buckling resistances of different nickel-titanium glide path files
Feyyaz Çeliker, İrem Çetinkaya
Matéria (Rio de Janeiro).2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Analysis of Endodontic 0.15 Stainless-Steel K-Files: Exploring Design, Composition, and Mechanical Performance
Abayomi Omokeji Baruwa, Filipa Chasqueira, Sofia Arantes-Oliveira, João Caramês, Duarte Marques, Jaime Portugal, Jorge N. R. Martins
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(2): 29. CrossRef - Comparative Analysis of Endodontic ISO Size 06, 08, and 10 Stainless Steel K-Files Used for Glide Path Procedures
Abayomi Omokeji Baruwa, Filipa Chasqueira, Sofia Arantes-Oliveira, João Caramês, Duarte Marques, Jaime Portugal, Jorge N. R. Martins
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(4): 98. CrossRef - Glide Path in Endodontics: A Literature Review of Current Knowledge
Vlad Mircea Lup, Giulia Malvicini, Carlo Gaeta, Simone Grandini, Gabriela Ciavoi
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(8): 257. CrossRef - Shaping Ability and Buckling Resistance of TruNatomy, WaveOne gold, and XP-Endo Shaper Single-File Systems
Neveen Ali Shaheen, Nahla Gamal Eldin Elhelbawy
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2022; 13(3): 261. CrossRef - A comparison of different hand and rotary endodontic glide path files for buckling resistance
Ruchika Gupta, Pramod Mohite, Suvarna Patil, Nandita Bansal
Endodontology.2021; 33(2): 102. CrossRef - Buckling Resistance of Various Nickel-Titanium Glide Path Preparation Instruments in Dynamic or Static Mode
Jung-Hong Ha, Sang Won Kwak, Antheunis Versluis, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(8): 1125. CrossRef - Influence of heat treatment on color and flexibility of nickel-titanium endodontic instruments
Bernardo Corrêa de ALMEIDA, Carlos Nelson ELIAS
RGO - Revista Gaúcha de Odontologia.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Negotiation, Glide Path, and Preflaring Procedures on Root Canal Shaping—Terminology, Basic Concepts, and a Systematic Review
Gianluca Plotino, Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Frederic Bukiet, Nicola M. Grande, Sajesh K. Veettil, Gustavo De-Deus, Hany Mohamed Aly Ahmed
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(6): 707. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of buckling resistance of Proglider and One-G file: An in vitro study
Priyanka Himmatrao Patil, Meenal Nitin Gulve, Swapnil Janardan Kolhe
Endodontology.2018; 30(1): 21. CrossRef - Mechanical Properties of Various Heat-treated Nickel-titanium Rotary Instruments
Hye-Jin Goo, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Eugenio Pedullà, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(11): 1872. CrossRef - Debris extrusion by glide-path establishing endodontic instruments with different geometries
Jung-Hong Ha, Sung Kyo Kim, Sang Won Kwak, Rashid El Abed, Yong Chul Bae, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Dental Sciences.2016; 11(2): 136. CrossRef
- Buckling resistance of various pathfinding endodontic instruments: An in vitro study
- 2,556 View
- 46 Download
- 13 Crossref

- Cyclic fatigue resistance tests of Nickel-Titanium rotary files using simulated canal and weight loading conditions
- Ok-In Cho, Antheunis Versluis, Gary SP Cheung, Jung-Hong Ha, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(1):31-35. Published online February 26, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.1.31
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study compared the cyclic fatigue resistance of nickel-titanium (NiTi) files obtained in a conventional test using a simulated canal with a newly developed method that allows the application of constant fatigue load conditions.
Materials and Methods ProFile and K3 files of #25/.06, #30/.06, and #40/.04 were selected. Two types of testing devices were built to test their fatigue performance. The first (conventional) device prescribed curvature inside a simulated canal (C-test), the second new device exerted a constant load (L-test) whilst allowing any resulting curvature. Ten new instruments of each size and brand were tested with each device. The files were rotated until fracture and the number of cycles to failure (NCF) was determined. The NCF were subjected to one-way ANOVA and Duncan's
post-hoc test for each method. Spearman's rank correlation coefficient was computed to examine any association between methods.Results Spearman's rank correlation coefficient (ρ = -0.905) showed a significant negative correlation between methods. Groups with significant difference after the L-test divided into 4 clusters, whilst the C-test gave just 2 clusters. From the L-test, considering the negative correlation of NCF, K3 gave a significantly lower fatigue resistance than ProFile as in the C-test. K3 #30/.06 showed a lower fatigue resistance than K3 #25/.06, which was not found by the C-test. Variation in fatigue test methodology resulted in different cyclic fatigue resistance rankings for various NiTi files.
Conclusions The new methodology standardized the load during fatigue testing, allowing determination fatigue behavior under constant load conditions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fracture Resistance of Heat-treated NiTi Instruments by the Load of Mechanical Preparation According to Tooth Type and Canal Number
Badria AlAli, Amre Atmeh, Mohamed Jamal, Fatemeh Ahmad, Amar H. Khamis, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Rashid El Abed
Journal of Endodontics.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - File-Specific Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of NiTi Instruments After Repeated Use in Simulated Canals: Patterns Compatible with Potential Stress-Induced Martensite Transformation Effects
Hyeonu Jo, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Asgeir Sigurdsson, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Materials.2026; 19(5): 866. CrossRef - Effect of autoclave sterilization on the cyclic fatigue resistance of EdgeFile X7, 2Shape, and F-one nickel–titanium endodontic instruments
ArkanH Al-Amidi, HikmetAbdul-Rahim Al-Gharrawi
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2023; 26(1): 26. CrossRef - Investigation of cyclic fatigue of rotary endodontic instruments
Z. S. Khabadze, F. R. Ismailov
Endodontics Today.2022; 20(1): 28. CrossRef - Torsional Resistance of Heat-Treated Nickel-Titanium Instruments under Different Temperature Conditions
Hyo Jin Jo, Sang Won Kwak, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Sung Kyo Kim, Jung-Hong Ha
Materials.2021; 14(18): 5295. CrossRef - Effect of surface treatment on the mechanical properties of nickel-titanium files with a similar cross-section
Sang Won Kwak, Joo Yeong Lee, Hye-Jin Goo, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2017; 42(3): 216. CrossRef - Effect from Rotational Speed on Torsional Resistance of the Nickel-titanium Instruments
Jung-Hong Ha, Sang Won Kwak, Sung Kyo Kim, Asgeir Sigurdsson, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(3): 443. CrossRef - Mechanical Properties of Various Heat-treated Nickel-titanium Rotary Instruments
Hye-Jin Goo, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Eugenio Pedullà, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(11): 1872. CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue Resistance and Force Generated by OneShape Instruments during Curved Canal Preparation
Zhuyu Wang, Wen Zhang, Xiaolei Zhang, Luigi F. Rodella
PLOS ONE.2016; 11(8): e0160815. CrossRef - Conditioning of root canal anatomy on static and dynamics of nickel-titanium rotary instruments
Italo Di Giuseppe, Davide Di Giuseppe, Vito Antonio Malagnino, Enrico Paolo Silla, Francesco Somma
Giornale Italiano di Endodonzia.2015; 29(2): 58. CrossRef - Effect from surface treatment of nickel‐titanium rotary files on the fracture resistance
Bo Hoon Kim, Jung‐Hong Ha, Woo Cheol Lee, Sang‐Won Kwak, Hyeon‐Cheol Kim
Scanning.2015; 37(1): 82. CrossRef - Effect of alloy type on the life‐time of torsion‐preloaded nickel‐titanium endodontic instruments
Jung‐Hong Ha, Sung Kyo Kim, Gary Shun‐Pan Cheung, Seong Hwa Jeong, Yong Chul Bae, Hyeon‐Cheol Kim
Scanning.2015; 37(3): 172. CrossRef - ‘Screw‐in’ tendency of rotary nickel–titanium files due to design geometry
J. H. Ha, G. S. P. Cheung, A. Versluis, C. J. Lee, S. W. Kwak, H. C. Kim
International Endodontic Journal.2015; 48(7): 666. CrossRef - Elastic Limits in Torsion of Reciprocating Nickel-Titanium Instruments
Jung-Hong Ha, Seo-Ryeong Kim, Antheunis Versluis, Gary Shun-Pan Cheung, Jin-Woon Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(5): 715. CrossRef - Buckling resistance, bending stiffness, and torsional resistance of various instruments for canal exploration and glide path preparation
Sang-Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, WooCheol Lee, Sung-Kyo Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(4): 270. CrossRef - Safety of the Factory Preset Rotation Angle of Reciprocating Instruments
Jin-Woon Kim, Jung-Hong Ha, Gary Shun-Pan Cheung, Antheunis Versluis, Sang-Won Kwak, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2014; 40(10): 1671. CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Rotary NiTi Instruments after Simulated Clinical Use in Curved Root Canals
Oscar Faciola Pessoa, Juliana Melo da Silva, Giulio Gavini
Brazilian Dental Journal.2013; 24(2): 117. CrossRef - Methods and models to study nickel–titanium instruments
Ya Shen, Gary S.P. Cheung
Endodontic Topics.2013; 29(1): 18. CrossRef - An overview of the mechanical properties of nickel–titanium endodontic instruments
Huimin Zhou, Bin Peng, Yu‐Feng Zheng
Endodontic Topics.2013; 29(1): 42. CrossRef
- Fracture Resistance of Heat-treated NiTi Instruments by the Load of Mechanical Preparation According to Tooth Type and Canal Number
- 1,646 View
- 5 Download
- 19 Crossref

- Comparison of the centering ability of Wave·One and Reciproc nickel-titanium instruments in simulated curved canals
- Young-Jun Lim, Su-Jung Park, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Kyung-San Min
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(1):21-25. Published online February 26, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.1.21
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to evaluate the shaping ability of newly marketed single-file instruments, Wave·One (Dentsply-Maillefer) and Reciproc (VDW GmbH), in terms of maintaining the original root canal configuration and curvature, with or without a glide-path.
Materials and Methods According to the instruments used, the blocks were divided into 4 groups (
n = 10): Group 1, no glide-path / Wave·One; Group 2, no glide-path / Reciproc; Group 3, #15 K-file / Wave·One; Group 4, #15 K-file / Reciproc. Pre- and post-instrumented images were scanned and the canal deviation was assessed. The cyclic fatigue stress was loaded to examine the cross-sectional shape of the fractured surface. The broken fragments were evaluated under the scanning electron microscope (SEM) for topographic features of the cross-section. Statistically analysis of the data was performed using one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey's test (α = 0.05).Results The ability of instruments to remain centered in prepared canals at 1 and 2 mm levels was significantly lower in Group 1 (
p < 0.05). The centering ratio at 3, 5, and 7 mm level were not significantly different.Conclusions The Wave·One file should be used following establishment of a glide-path larger than #15.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Centering Ability and Canal Transportation of Nickel-Titanium (NiTi) Single-File Systems With and Without Glide Path in Extracted Natural Teeth: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Indumathi Manoharan, Deblina Basu, Mathan Rajan
Cureus.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the Centering Ability and Canal Transportation of Rotary File Systems in Different Kinematics Using CBCT
Nupur R Vasava, Shreya H Modi, Chintan Joshi, Mona C Somani, Sweety J Thumar, Aashray A Patel, Anisha D Parmar, Kruti M Jadawala
World Journal of Dentistry.2024; 14(11): 983. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Root Canal Centering Ability of ProTaper, Mtwo, WaveOne, and Reciproc Using Cone-beam Computed Tomography: In Vitro Study
M Remya, Asha Joseph, Prabath Singh, Anju Varughese, Pallavi Chandran, Deepthy Subramanian, S Vijay Kumar
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2022; 23(6): 589. CrossRef - Shaping ability of ProTaper Gold and WaveOne Gold nickel-titanium rotary instruments in simulated S-shaped root canals
Lu Shi, Junling Zhou, Jie Wan, Yunfei Yang
Journal of Dental Sciences.2022; 17(1): 430. CrossRef - Comparison of canal transportation and centering ability of manual K-files and reciprocating files in glide path preparation: a micro-computed tomography study of constricted canals
Jing-Yi Liu, Zhi-Xiong Zhou, Wei-Ju Tseng, Bekir Karabucak
BMC Oral Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Canal transportation and centering ability of root canals prepared using rotary and reciprocating systems with and without PathFiles in cone-beam computed tomography-based three-dimensional molar prototypes
MSruthi Sunildath, Josey Mathew, Liza George, RV Vineet, Priya Thomas, Dhanya John
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2021; 24(3): 246. CrossRef - Shaping Ability of Reciproc R25 File and Mtwo System Used in Continuous and Reciprocating Motion
Vincenzo Campanella, Leonardo Gianni, Antonio Libonati, Gianni Gallusi
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2020; 21(2): 171. CrossRef - Canal shaping with a reciprocating system is easy to learn
E. Muñoz, L. Forner, S. Garcet, F. J. Rodríguez‐Lozano, C. Llena
International Endodontic Journal.2019; 52(8): 1244. CrossRef - Shaping Ability of HyFlex EDM and ProTaper Next Rotary Instruments in Curved Root Canals: A Micro-CT Study
Ahmed K Turkistani, Madiha M Gomaa, Lubna A Shafei, Loai Alsofi, Abdul Majeed, Emad AlShwaimi
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2019; 20(6): 680. CrossRef - Root canal volume change and transportation by Vortex Blue, ProTaper Next, and ProTaper Universal in curved root canals
Hyun-Jin Park, Min-Seock Seo, Young-Mi Moon
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of shaping ability of ProTaper Next and 2Shape nickel–titanium files in simulated severe curved canals
Simone Staffoli, Taha Özyürek, Avi Hadad, Alex Lvovsky, Michael Solomonov, Hadas Azizi, Joe Ben Itzhak, Maurizo Bossù, Nicola M. Grande, Gianluca Plotino, Antonella Polimeni
Giornale Italiano di Endodonzia.2018; 32(2): 52. CrossRef - Comparing the Centering Ability of Different Pathfinding Systems and Their Effect on Final Instrumentation by Hyflex CM
Lu Shi, Shova Wagle
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(11): 1868. CrossRef - Rotary endodontics in primary teeth – A review
Sageena George, S. Anandaraj, Jyoti S. Issac, Sheen A. John, Anoop Harris
The Saudi Dental Journal.2016; 28(1): 12. CrossRef - Performance of Three Single Instrument Systems in the Preparation of Long Oval Canals
Beatriz Serrato Coelho, Rodrigo Otavio Jatahy Ferreira do Amaral, Denise Piotto Leonardi, Bruno Marques-da-Silva, Yara Teresinha Corrêa Silva-Sousa, Fredson Marcio Acris de Carvalho, Flares Baratto-Filho
Brazilian Dental Journal.2016; 27(2): 217. CrossRef - Quantitative transportation assessment in curved canals prepared with an off-centered rectangular design system
Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal SILVA, Vania Cristina Gomes VIEIRA, Michele Dias Nunes TAMEIRÃO, Felipe Gonçalves BELLADONNA, Aline de Almeida NEVES, Erick Miranda SOUZA, Gustavo DE-DEUS
Brazilian Oral Research.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Cervical and Apical Enlargement Associated with the WaveOne System on the Transportation and Centralization of Endodontic Preparations
Rodrigo Otavio Jatahy Ferreira do Amaral, Denise Piotto Leonardi, Marilisa Carneiro Leão Gabardo, Beatriz Serrato Coelho, Kauhanna Vianna de Oliveira, Flares Baratto Filho
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(4): 626. CrossRef - Comparison of canal transportation in simulated curved canals prepared with ProTaper Universal and ProTaper Gold systems
Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Brenda Leite Muniz, Frederico Pires, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Aline Almeida Neves, Erick Miranda Souza, Gustavo De-Deus
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(1): 1. CrossRef - The Influence of Brushing Motion on the Cutting Behavior of 3 Reciprocating Files in Oval-shaped Canals
Shereen Alattar, Walid Nehme, Franck Diemer, Alfred Naaman
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(5): 703. CrossRef - Cyclic fatigue of instruments for endodontic glide path
Gianluca Gambarini, Gianluca Plotino, GianPaolo Sannino, Nicola Maria Grande, Alessio Giansiracusa, Lucila Piasecki, Ulisses Xavier da Silva Neto, Dina Al-Sudani, Luca Testarelli
Odontology.2015; 103(1): 56. CrossRef - Influence of the glide path on various parameters of root canal prepared with WaveOne reciprocating file using cone beam computed tomography
Anil Dhingra, Nidhi Nagar, Vipul Sapra
Dental Research Journal.2015; 12(6): 534. CrossRef - Apical Transportation, Centering Ability, and Cleaning Effectiveness of Reciprocating Single-file System Associated with Different Glide Path Techniques
Guilherme Moreira de Carvalho, Emílio Carlos Sponchiado Junior, Angela Delfina Bittencourt Garrido, Raphael Carlos Comelli Lia, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia, André Augusto Franco Marques
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(12): 2045. CrossRef - Influence of cervical preflaring on apical transportation in curved root canals instrumented by reciprocating file systems
Neisiana Barbieri, Denise Piotto Leonardi, Marina Samara Baechtold, Gisele Maria Correr, Marilisa Carneiro Leão Gabardo, João César Zielak, Flares Baratto-Filho
BMC Oral Health.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Current Assessment of Reciprocation in Endodontic Preparation: A Comprehensive Review—Part II: Properties and Effectiveness
Gianluca Plotino, Hany Mohamed Aly Ahmed, Nicola Maria Grande, Stephen Cohen, Frédéric Bukiet
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(12): 1939. CrossRef - Influence of flexion angle of files on the decentralization of oval canals during instrumentation
Maria Antonieta Veloso Carvalho de OLIVEIRA, Letícia Duarte ALVES, Analice Giovani PEREIRA, Luís Henrique Araújo RAPOSO, João Carlos Gabrielli BIFFI
Brazilian Oral Research.2015; 29(1): 1. CrossRef - Quantitative Transportation Assessment in Simulated Curved Canals Prepared with an Adaptive Movement System
Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Michele Dias Nunes Tameirão, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Aline Almeida Neves, Erick Miranda Souza, Gustavo De-Deus
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(7): 1125. CrossRef - Efficacy of reciprocating and rotary systems for removing root filling material: A micro-computed tomography study
D. Helvacioglu-Yigit, A. Yilmaz, G. Kiziltas-Sendur, O. S. Aslan, P. V. Abbott
Scanning.2014; 36(6): 576. CrossRef - Effect of passive ultrasonic agitation during final irrigation on cleaning capacity of hybrid instrumentation
Marcilene Coelho Vinhorte, Eduardo Hideki Suzuki, Maíra Sousa de Carvalho, André Augusto Franco Marques, Emílio Carlos Sponchiado Júnior, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(2): 104. CrossRef - Performance of RaCe Instrumentation System in Curved Root Canals: A Comprehensive Analysis by Three Study Methods
Denise Piotto Leonardi, Gilson Blitzkow Sydney, Mario Tanomaru Filho, Flares Baratto-Filho, Samantha Schaffer Pugsley Baratto, Paulo Sergio Cerri
Brazilian Dental Journal.2013; 24(3): 230. CrossRef - Endodontic treatment of mandibular molar with root dilaceration using Reciproc single-file system
Daniely Amorin Meireles, Mariana Mena Barreto Bastos, André Augusto Franco Marques, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia, Emílio Carlos Sponchiado
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(3): 167. CrossRef
- Centering Ability and Canal Transportation of Nickel-Titanium (NiTi) Single-File Systems With and Without Glide Path in Extracted Natural Teeth: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- 1,662 View
- 8 Download
- 29 Crossref

- Influence of glide path on the screw-in effect and torque of nickel-titanium rotary files in simulated resin root canals
- Jung-Hong Ha, Sang-Shin Park
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(4):215-219. Published online November 21, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.4.215
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to investigate the screw-in effect and torque generation depending on the size of glide path during root canal preparation.
Materials and Methods Forty Endo-Training Blocks (REF A 0177, Dentsply Maillefer) were used. They were divided into 4 groups. For groups 1, 2, 3, and 4, the glide path was established with ISO #13 Path File (Dentsply Maillefer), #15 NiTi K-file NITIFLEX (Dentsply Maillefer), modified #16 Path File (equivalent to #18), and #20 NiTi K-file NITIFLEX, respectively. The screw-in force and resultant torque were measured using a custom-made experimental apparatus while canals were instrumented with ProTaper S1 (Dentsply Maillefer) at a constant speed of 300 rpm with an automated pecking motion. A statistical analysis was performed using one-way analysis of variance and the Duncan
post hoc comparison test.Results Group 4 showed lowest screw-in effect (2.796 ± 0.134) among the groups (
p < 0.05). Torque was inversely proportional to the glide path of each group. In #20 glide path group, the screw-in effect and torque decreased at the last 1 mm from the apical terminus. However, in the other groups, the decrease of the screw-in effect and torque did not occur in the last 1 mm from the apical terminus.Conclusions The establishment of a larger glide path before NiTi rotary instrumentation appears to be appropriate for safely shaping the canal. It is recommended to establish #20 glide path with NiTi file when using ProTaper NiTi rotary instruments system safely.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of Debris Extrusion and Preparation Time by Traverse, R‐Motion Glider C, and Other Glide Path Systems in Severely Curved Canals
Taher Al Omari, Layla Hassouneh, Khawlah Albashaireh, Alaa Dkmak, Rami Albanna, Ali Al-Mohammed, Ahmed Jamleh, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
International Journal of Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Radial Lands and Alternating Cutting Edges Contribute to Reduced Screw-in and Torque in Curved Root Canals - An In Vitro Study
Greta Heimberg, Sebastian Bürklein, Edgar Schäfer, Thomas Gerhard Wolf, David Donnermeyer
Journal of Endodontics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Three-Dimensional Printed Teeth in Endodontics: A New Protocol for Microcomputed Tomography Studies
Tiago Reis, Cláudia Barbosa, Margarida Franco, Ruben Silva, Nuno Alves, Pablo Castelo-Baz, Jose Martín-Cruces, Benjamín Martín-Biedma
Materials.2024; 17(8): 1899. CrossRef - Evaluation of Pain Following the Use of Different Single-file Glide Path Systems: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Zeliha Danaci, Kübra Yeşildal Yeter
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(2): 120. CrossRef - Cone-beam computed tomographic evaluation and fracture resistance of endodontically retreated teeth using hyflex remover, Mtwo, and ProTaper retreatment file systems: An in vitro study
Isha Singh, Dakshita Joy Sinha, Pallavi Sharma, Kunal Bedi, Priyanka Rani, Swapnil Vats
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2024; 14(1): 56. CrossRef - Screw-in force, torque generation, and performance of glide-path files with three rotation kinetics
Jee-Yeon Woo, Ji-Hyun Jang, Seok Woo Chang, Soram Oh
Odontology.2024; 112(3): 761. CrossRef - Morphological and structural variations of Nickel-Titanium endodontic instruments subjected to instrumentation loads: in vitro study
Yenny Marcela Orozco-Ocampo, César Augusto Álvarez-Vargas, Francy Nelly Jiménez-García, Daniel Escobar-Rincón, Paola Ximena Jaramillo-Gil
Revista UIS Ingenierías.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Nickel ion release and surface analyses on instrument fragments fractured beyond the apex: a laboratory investigation
Sıdıka Mine Toker, Ekim Onur Orhan, Arzu Beklen
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the Efficiency to Remove the Infected Dentin via Enterococcus faecalis Bacterial Count and to Adequately Shape the Canal Using Hand Kedo-SH Files, Rotary Kedo-SG (Blue) and Pro AF Baby Gold Files in Primary Molars: An In Vitro Study
Shruthi B Patil, Kaavya Shanker
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2023; 16(S2): S142. CrossRef - Buckling resistance, torque, and force generation during retreatment with D-RaCe, HyFlex Remover, and Mtwo retreatment files
Yoojin Kim, Seok Woo Chang, Soram Oh
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Cyclic and torsional fatigue resistance of a new rotary file on a rotary and reciprocating motion
Gabriel Barcelos Só, Giovana Siocheta, Pedro Calefi, Murilo Alcalde, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, Marco Antônio H. Duarte, Marcus Vinicius Reis Só, Ricardo Abreu da Rosa
Microscopy Research and Technique.2023; 86(12): 1635. CrossRef - Influence of different kinematics on stationary and dynamic torsional behavior of JIZAI nickel-titanium rotary instruments: An in vitro study
Myint Thu, Arata Ebihara, Moe Sandar Kyaw, Satoshi Omori, Keiichiro Maki, Shunsuke Kimura, Hayate Unno, Takashi Okiji
Journal of Dental Sciences.2023; 18(3): 1170. CrossRef - Dynamic torque and screw-in force of four different glide path instruments assessed in simulated single- and double-curved canals: An in vitro study
Myint Thu, Arata Ebihara, Keiichiro Maki, Shunsuke Kimura, Moe-Sandar Kyaw, Yuka Kasuga, Miki Nishijo, Takashi Okiji
Journal of Dental Sciences.2023; 18(4): 1598. CrossRef - Effect of Periodic Changes in Rotation Speed on Torsional Stress and Screw-in Force by Alternative Rotation Technique
Jung-Hong Ha, Hyo-Jin Jo, Sang Won Kwak, Asgeir Sigurdsson, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2023; 49(1): 77. CrossRef - Effect of Rotational Modes on Torque/Force Generation and Canal Centering Ability during Rotary Root Canal Instrumentation with Differently Heat-Treated Nickel–Titanium Instruments
Satoshi Omori, Arata Ebihara, Keiko Hirano, Yuka Kasuga, Hayate Unno, Taro Nakatsukasa, Shunsuke Kimura, Keiichiro Maki, Takao Hanawa, Takashi Okiji
Materials.2022; 15(19): 6850. CrossRef - Shaping ability of rotary and reciprocating single-file systems in combination with and without different glide path techniques in simulated curved canals
Lu Shi, Yunfei Yang, Jie Wan, Wen Xie, Ruiming Yang, Ying Yao
Journal of Dental Sciences.2022; 17(4): 1520. CrossRef - Evolution and development: engine-driven endodontic rotary nickel-titanium instruments
Yuhong Liang, Lin Yue
International Journal of Oral Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of the effects from coronal pre‐flaring and glide‐path preparation on torque generation during root canal shaping procedure
Sang Won Kwak, Jung‐Hong Ha, Ya Shen, Markus Haapasalo, Hyeon‐Cheol Kim
Australian Endodontic Journal.2022; 48(1): 131. CrossRef - Shaping ability of ProTaper Gold and WaveOne Gold nickel-titanium rotary instruments in simulated S-shaped root canals
Lu Shi, Junling Zhou, Jie Wan, Yunfei Yang
Journal of Dental Sciences.2022; 17(1): 430. CrossRef - Endodontic Rotary Files, What Should an Endodontist Know?
Ana-Belén Dablanca-Blanco, Pablo Castelo-Baz, Ramón Miguéns-Vila, Pablo Álvarez-Novoa, Benjamín Martín-Biedma
Medicina.2022; 58(6): 719. CrossRef - Present status and future directions: Canal shaping
Ana Arias, Ove A. Peters
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S3): 637. CrossRef - Comparison of Torque, Screw-in Force, and Shaping Ability of Glide Path Instruments in Continuous Rotation and Optimum Glide Path Motion
Pyae Hein Htun, Arata Ebihara, Keiichiro Maki, Shunsuke Kimura, Miki Nishijo, Moe Sandar Kyaw, Takashi Okiji
Journal of Endodontics.2021; 47(1): 94. CrossRef - Analysis of Torque and Force Induced by Rotary Nickel-Titanium Instruments during Root Canal Preparation: A Systematic Review
Myint Thu, Arata Ebihara, Sherif Adel, Takashi Okiji
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(7): 3079. CrossRef - Comparison of canal transportation and centering ability of manual K-files and reciprocating files in glide path preparation: a micro-computed tomography study of constricted canals
Jing-Yi Liu, Zhi-Xiong Zhou, Wei-Ju Tseng, Bekir Karabucak
BMC Oral Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of rotational speed on torque/force generation and shaping ability during root canal instrumentation of extracted teeth with continuous rotation and optimum torque reverse motion
M. S. Kyaw, A. Ebihara, Y. Kasuga, K. Maki, S. Kimura, P. H. Htun, T. Nakatsukasa, T. Okiji
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(9): 1614. CrossRef - Shot peening increases resistance to cyclic fatigue fracture of endodontic files
Javier Nino-Barrera, Jose Sanchez-Aleman, Manuel Acosta-Humanez, Luis Gamboa-Martinez, Carlos Cortes-Rodriguez
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Optimum glide path motion is safer than continuous rotation of files in glide path preparation
Giulio Gavini, Eduardo Akisue, Dirce Akemi Sacaguti Kawakami, Celso Luiz Caldeira, George Táccio de Miranda Candeiro, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, Pedro Henrique Souza Calefi, Murilo Priori Alcalde, Marco Antonio Húngaro Duarte
Australian Endodontic Journal.2021; 47(3): 544. CrossRef - Root canals shaped by nickel-titanium instrumentation with automated computerized numerical control systems
Liming Wang, Wenxiang Li, Yeon-Jee Yoo, Shin Hye Chung, Soram Oh, Hiran Perinpanayagam, Kee-Yeon Kum, Yu Gu
BMC Oral Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - An Update on Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instruments in Endodontics: Mechanical Characteristics, Testing and Future Perspective—An Overview
Alessio Zanza, Maurilio D’Angelo, Rodolfo Reda, Gianluca Gambarini, Luca Testarelli, Dario Di Nardo
Bioengineering.2021; 8(12): 218. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Cleaning Efficiency and Apical Extrusion of Debris Using Two Pediatric Rotary Endodontic Files: An In Vitro Study
Nilima Thosar, Sudhindra Baliga, Faraz Ahmed, Nilesh Rathi, Shreyans A Jain, Jayati Mehta
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2021; 14(2): 196. CrossRef - Body temperature fatigue behaviour of reciprocating and rotary glide path instruments in sodium hypochlorite solutions alone or combined with etidronate
Dario Perez‐Villalba, José C. Macorra, Juan J. Perez‐Higueras, Ove A. Peters, Ana Arias
Australian Endodontic Journal.2021; 47(3): 450. CrossRef - Effect of Optimum Torque Reverse Motion on Torque and Force Generation during Root Canal Instrumentation with Crown-down and Single-length Techniques
Shunsuke Kimura, Arata Ebihara, Keiichiro Maki, Miki Nishijo, Daisuke Tokita, Takashi Okiji
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(2): 232. CrossRef - Ex-Vivo Comparison of Torsional Stress on Nickel–Titanium Instruments Activated by Continuous Rotation or Adaptive Motion
Joo Yeong Lee, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Materials.2020; 13(8): 1900. CrossRef - Influence of glide path size and operating kinetics on time to reach working length and fracture resistance of Twisted File adaptive and Endostar E3 nickel-titanium file systems
Tamilkumaran Ramyadharshini, Inbaraj Anand Sherwood, V Shanmugham Vigneshwar, Prakasam Ernest Prince, Murugadoss Vaanjay
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Buckling Resistance of Various Nickel-Titanium Glide Path Preparation Instruments in Dynamic or Static Mode
Jung-Hong Ha, Sang Won Kwak, Antheunis Versluis, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(8): 1125. CrossRef - Comparison of torque, force generation and canal shaping ability between manual and nickel-titanium glide path instruments in rotary and optimum glide path motion
Pyae Hein Htun, Arata Ebihara, Keiichiro Maki, Shunsuke Kimura, Miki Nishijo, Daisuke Tokita, Takashi Okiji
Odontology.2020; 108(2): 188. CrossRef - THE INFLUENCE OF DIFFERENT TORQUE SETTINGS ON THE AMOUNT OF APICALLY EXTRUDED DEBRIS DURING ROTARY INSTRUMENTATION
Demet ALTUNBAŞ, Mustafa TOYOĞLU
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2020; 23(3): 160. CrossRef - Glide Path: “Path to the successful root canal instrumentation”- Review
Anjali Mairal Oak
Journal of Indian Dental Association.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Torsional fatigue strength of reciprocating and rotary pathfinding instruments manufactured from different NiTi alloys
Rodrigo Ricci VIVAN, Murilo Priori ALCALDE, George CANDEIRO, Giulio GAVINI, Celso Luis CALDEIRA, Marco Antonio Hungaro DUARTE
Brazilian Oral Research.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Screw-In Forces during Movement of Endodontic Files with Different Geometries, Alloys, and Kinetics
Sang Won Kwak, Chan-Joo Lee, Sung Kyo Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Jung-Hong Ha
Materials.2019; 12(9): 1506. CrossRef - Effect of glide path preparation with PathFile and ProGlider on the cyclic fatigue resistance of WaveOne nickel-titanium files
Gülşah Uslu, Uğur İnan
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Force and vibration generated in apical direction by three endodontic files of different kinematics during simulated canal preparation: An in vitro analytical study
Ankit Nayak, PK Kankar, Prashant K Jain, Niharika Jain
Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part H: Journal of Engineering in Medicine.2019; 233(8): 839. CrossRef - Effective Establishment of Glide-Path to Reduce Torsional Stress during Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instrumentation
Ibrahim H. Abu-Tahun, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Asgeir Sigurdsson, Mehmet Baybora Kayahan, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Materials.2019; 12(3): 493. CrossRef - Real‐time dynamic torque values and axial forces during preparation of straight root canals using three different endodontic motors and hand preparation
S. Bürklein, J. P. Stüber, E. Schäfer
International Endodontic Journal.2019; 52(1): 94. CrossRef - Comparison of glide paths created with K-files, PathFiles, and the ProGlider file, and their effects on subsequent WaveOne preparation in curved canals
Linxia Zheng, Xiongfei Ji, Chengxi Li, Lulu Zuo, Xin Wei
BMC Oral Health.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of cyclic fatigue resistance and bending properties of two reciprocating nickel‐titanium glide path files
T. Özyürek, G. Uslu, M. Gündoğar, K. Yılmaz, N. M. Grande, G. Plotino
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(9): 1047. CrossRef - Root Canal Shaping Effect of Instruments with Offset Mass of Rotation in the Mandibular First Molar: A Micro–computed Tomographic Study
Maung Maung Kyaw Moe, Jung Hong Ha, Myoung Uk Jin, Young Kyung Kim, Sung Kyo Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(5): 822. CrossRef - Evaluation of selected mechanical properties of NiTi rotary glide path files manufactured from controlled memory wires
Miki NISHIJO, Arata EBIHARA, Daisuke TOKITA, Hisashi DOI, Takao HANAWA, Takashi OKIJI
Dental Materials Journal.2018; 37(4): 549. CrossRef - Effect of the Glide Path Establishment on the Torque Generation to the Files during Instrumentation: An In Vitro Measurement
Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Gary Shun-Pan Cheung, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Sung Kyo Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(3): 496. CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Novel Glide Path Instruments with Different Alloy Properties and Kinematics
Burcu Serefoglu, Mehmet Emin Kaval, Seniha Micoogullari Kurt, Mehmet Kemal Çalişkan
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(9): 1422. CrossRef - Cyclic fatigue resistance of R‐Pilot, HyFlex EDM and PathFile nickel‐titanium glide path files in artificial canals with double (S‐shaped) curvature
G. Uslu, T. Özyürek, K. Yılmaz, M. Gündoğar
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(5): 584. CrossRef - A Comparison of the Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Used and New Glide Path Files
Taha Özyürek, Gülşah Uslu, Uğur İnan
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(3): 477. CrossRef - Comparison of apical extrusion of intracanal bacteria by various glide-path establishing systems: an in vitro study
Alberto Dagna, Rashid El Abed, Sameeha Hussain, Ibrahim H Abu-Tahun, Livia Visai, Federico Bertoglio, Floriana Bosco, Riccardo Beltrami, Claudio Poggio, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2017; 42(4): 316. CrossRef - Comparing the Centering Ability of Different Pathfinding Systems and Their Effect on Final Instrumentation by Hyflex CM
Lu Shi, Shova Wagle
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(11): 1868. CrossRef - Torsional Performance of ProTaper Gold Rotary Instruments during Shaping of Small Root Canals after 2 Different Glide Path Preparations
Ana Arias, Rafaela Andrade de Vasconcelos, Alexis Hernández, Ove A. Peters
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(3): 447. CrossRef - Dynamic Torque and Vertical Force Analysis during Nickel-titanium Rotary Root Canal Preparation with Different Modes of Reciprocal Rotation
Daisuke Tokita, Arata Ebihara, Miki Nishijo, Kana Miyara, Takashi Okiji
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(10): 1706. CrossRef - Stress Generation during Pecking Motion of Rotary Nickel-titanium Instruments with Different Pecking Depth
Jung-Hong Ha, Sang Won Kwak, Asgeir Sigurdsson, Seok Woo Chang, Sung Kyo Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(10): 1688. CrossRef -
In vitro comparison of the cyclic fatigue resistance of HyFlex EDM, One G, and ProGlider nickel titanium glide path instruments in single and double curvature canals
Koray Yılmaz, Gülşah Uslu, Taha Özyürek
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2017; 42(4): 282. CrossRef - Debris extrusion by glide-path establishing endodontic instruments with different geometries
Jung-Hong Ha, Sung Kyo Kim, Sang Won Kwak, Rashid El Abed, Yong Chul Bae, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Dental Sciences.2016; 11(2): 136. CrossRef - Effects of Pitch Length and Heat Treatment on the Mechanical Properties of the Glide Path Preparation Instruments
Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Chan-Joo Lee, Rashid El Abed, Ibrahim H. Abu-Tahun, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(5): 788. CrossRef - Screw-in forces during instrumentation by various file systems
Jung-Hong Ha, Sang Won Kwak, Sung-Kyo Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(4): 304. CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue Resistance and Force Generated by OneShape Instruments during Curved Canal Preparation
Zhuyu Wang, Wen Zhang, Xiaolei Zhang, Luigi F. Rodella
PLOS ONE.2016; 11(8): e0160815. CrossRef - Differences in torsional performance of single- and multiple-instrument rotary systems for glide path preparation
Ana Arias, Rupinderpal Singh, Ove A. Peters
Odontology.2016; 104(2): 192. CrossRef - Effect of glide path and apical preparation size on the incidence of apical crack during the canal preparation using Reciproc, WaveOne, and ProTaper Next systems in curved root canals: A stereomicroscope study
Hüseyin Sinan Topçuoğlu, Salih Düzgün, Firdevs Akpek, Gamze Topçuoğlu
Scanning.2016; 38(6): 585. CrossRef - Geometric Optimization for Development of Glide Path Preparation Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instrument
Jung-Hong Ha, Chan-Joo Lee, Sang-Won Kwak, Rashid El Abed, Dongseok Ha, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(6): 916. CrossRef - Glide Path Management with Single- and Multiple-instrument Rotary Systems in Curved Canals: A Micro–Computed Tomographic Study
Alison Luís Kirchhoff, Rene Chu, Isabel Mello, Andres Dario Plazas Garzon, Marcelo dos Santos, Rodrigo Sanches Cunha
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(11): 1880. CrossRef - Safe root canal preparation using reciprocating nickel-titanium instruments
Jung-Hong Ha
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(3): 253. CrossRef - Effect of repetitive pecking at working length for glide path preparation using G-file
Jung-Hong Ha, Hyo-Jin Jeon, Rashid El Abed, Seok-Woo Chang, Sung-Kyo Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(2): 123. CrossRef - Influence of a glide path on the dentinal crack formation of ProTaper Next system
Sevinç Aktemur Türker, Emel Uzunoğlu
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(4): 286. CrossRef - ‘Screw‐in’ tendency of rotary nickel–titanium files due to design geometry
J. H. Ha, G. S. P. Cheung, A. Versluis, C. J. Lee, S. W. Kwak, H. C. Kim
International Endodontic Journal.2015; 48(7): 666. CrossRef - Comparison of the Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of 5 Different Rotary Pathfinding Instruments Made of Conventional Nickel-Titanium Wire, M-wire, and Controlled Memory Wire
Ismail Davut Capar, Mehmet Emin Kaval, Hüseyin Ertas, Bilge Hakan Sen
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(4): 535. CrossRef - Comparision of two different preparation protocol of Ni-Ti Rotary PathFile-ProTaper instruments in simulated s-shaped canals
Elıf Delve Başer Can, Müzeyyen Gerek, Mehmet Baybora Kayahan, Kambız Mohsenı, Hakki Sunay, Gündüz Bayirli
Acta Odontologica Scandinavica.2014; 72(1): 76. CrossRef - Torsional and cyclic fatigue resistances of glide path preparation instruments: G‐file and PathFile
Sang Yup Sung, Jung‐Hong Ha, Sang‐Won Kwak, Rashid El Abed, Kyeongmin Byeon, Hyeon‐Cheol Kim
Scanning.2014; 36(5): 500. CrossRef - Buckling resistance, bending stiffness, and torsional resistance of various instruments for canal exploration and glide path preparation
Sang-Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, WooCheol Lee, Sung-Kyo Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(4): 270. CrossRef - Shaping Ability of Different Nickel-Titanium Systems in Simulated S-shaped Canals with and without Glide Path
Sebastian Bürklein, Thomas Poschmann, Edgar Schäfer
Journal of Endodontics.2014; 40(8): 1231. CrossRef - Stress Generation during Self-Adjusting File Movement: Minimally Invasive Instrumentation
Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Sang Yup Sung, Jung-Hong Ha, Michael Solomonov, Jung-Min Lee, Chan-Joo Lee, Byung-Min Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2013; 39(12): 1572. CrossRef
- Comparison of Debris Extrusion and Preparation Time by Traverse, R‐Motion Glider C, and Other Glide Path Systems in Severely Curved Canals
- 2,499 View
- 13 Download
- 76 Crossref

- A survey of experience-based preference of Nickel-Titanium rotary files and incidence of fracture among general dentists
- WooCheol Lee, Minju Song, Euiseong Kim, Hyojin Lee, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(4):201-206. Published online November 21, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.4.201
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose was to investigate the preference and usage technique of NiTi rotary instruments and to retrieve data on the frequency of re-use and the estimated incidence of file separation in the clinical practice among general dentists.
Materials and Methods A survey was disseminated via e-mail and on-site to 673 general dentists. The correlation between the operator's experience or preferred technique and frequency of re-use or incidence of file fracture was assessed.
Results A total of 348 dentists (51.7%) responded. The most frequently used NiTi instruments was ProFile (39.8%) followed by ProTaper. The most preferred preparation technique was crown-down (44.6%). 54.3% of the respondents re-used NiTi files more than 10 times. There was a significant correlation between experience with NiTi files and the number of reuses (
p = 0.0025). 54.6% of the respondents estimated experiencing file separation less than 5 times per year. The frequency of separation was significantly correlated with the instrumentation technique (p = 0.0003).Conclusions A large number of general dentists in Korea prefer to re-use NiTi rotary files. As their experience with NiTi files increased, the number of re-uses increased, while the frequency of breakage decreased. Operators who adopt the hybrid technique showed less tendency of separation even with the increased number of re-use.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Migration of a Separated Endodontic File Into the Mandibular Canal: An 8-Year Follow-up Case Report
Chiaki Akiba Katz, Misaki Fujimoto, Hidetaka Kuroda, Koichiro Muromachi
Journal of Endodontics.2026; 52(2): 321. CrossRef - Adoption of rotary instrumentation among general practitioners in Qassim region, Saudi Arabia: A cross-sectional survey
Badi B. Alotaibi
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2024; 14(2): 181. CrossRef - Undergraduate Endodontic Training and Its Relation to Contemporary Practice: Multicenter Cross-Sectional Study in Saudi Arabia
Fahda N. Algahtani, Reem M. Barakat, Lujain M. Alqarni, Alanoud F. Alqabbani, Manal F. Alkadi, Rahaf A. Almohareb, André Luiz Ferreira Costa
International Journal of Clinical Practice.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Fracture Incidence of Kedo-S Square Pediatric Rotary Files: A Prospective Clinical Study
Lakshimi Lakshmanan, Ganesh Jeevanandan, Prabhadevi C Maganur, Satish Vishwanathaiah
European Journal of Dentistry.2022; 16(03): 594. CrossRef - Prevention and management of fractured instruments in endodontic treatment
Wei-Rong Tang
World Journal of Surgical Procedures.2015; 5(1): 82. CrossRef - Influence of operator's experience level on lifespan of the WaveOne Primary file in extracted teeth
Abdulrahman Mohammed Saleh, Saeid Tavanafar, Pouyan Vakili-Gilani, Noor Jamal Al Sammerraie, Faahim Rashid
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 222. CrossRef
- Migration of a Separated Endodontic File Into the Mandibular Canal: An 8-Year Follow-up Case Report
- 2,063 View
- 11 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Influence of taper on the screw-in effect of nickel-titanium rotary files in simulated resin root canal
- Hye-Jin Sung, Jung-Hong Ha, Sung-Kyo Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(5):380-386. Published online September 30, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.5.380
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The introduction of nickel-titanium alloy endodontic instruments has greatly simplified shaping the root canal systems. However, these new instruments have several unexpected disadvantages. One of these is tendency to screw into the canal. In this study, the influence of taper on the screw-in effect of the Ni-Ti rotary instrument were evaluated.
Materials and Methods A total of 20 simulated root canals with an S-shaped curvature in clear resin blocks were divided into two groups. ProFile .02, .04, .06 (Dentsply-Maillefer) and GT rotary files .08, .10, .12 (Dentsply) were used in Profile group, and K3 .04, .06, .08, .10, and .12 (SybronEndo, Glendora) were used in K3 group. Files were used with a single pecking motion at a constant speed of 300 rpm. A special device was made to measure the force of screw-in effect. A dynamometer of the device recorded the screw-in force during simulated canal preparation and the recorded data was stored in computer with designed software. The data were subjected to one-way ANOVA and Tukey's multiple range test for post-hoc test.
p value of less than 0.05 was regarded significant.Results The more tapered instruments generated more screw-in forces in Profile group (
p < 0.05). In K3 group, 0.08, 0.10. and 0.12 tapered instruments showed more screw-in force than 0.04 tapered one, and 0.08 and 0.12 tapered instruments showed more screw-in force than 0.06 tapered one (p < 0.05).Conclusions The more tapered instruments seems to produce more screw-in force. To avoid this screw-in force during instrumentation, more attention may be needed when using more tapered instruments.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Radial Lands and Alternating Cutting Edges Contribute to Reduced Screw-in and Torque in Curved Root Canals - An In Vitro Study
Greta Heimberg, Sebastian Bürklein, Edgar Schäfer, Thomas Gerhard Wolf, David Donnermeyer
Journal of Endodontics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of Torque and Force Induced by Rotary Nickel-Titanium Instruments during Root Canal Preparation: A Systematic Review
Myint Thu, Arata Ebihara, Sherif Adel, Takashi Okiji
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(7): 3079. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of mechanical properties of differently tapered nickeltitanium endodontic rotary instruments
Yohei FUKUMORI, Miki NISHIJYO, Daisuke TOKITA, Kana MIYARA, Arata EBIHARA, Takashi OKIJI
Dental Materials Journal.2018; 37(4): 667. CrossRef - Influence of glide path on the screw-in effect and torque of nickel-titanium rotary files in simulated resin root canals
Jung-Hong Ha, Sang-Shin Park
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(4): 215. CrossRef - Mechanical and geometric features of endodontic instruments and its clinical effect
Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(1): 1. CrossRef
- Radial Lands and Alternating Cutting Edges Contribute to Reduced Screw-in and Torque in Curved Root Canals - An In Vitro Study
- 2,369 View
- 21 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Influence of root canal curvature on the screw-in effect of nickel-titanium rotary files in simulated resin root canal
- Ji-Young Son, Jung-Hong Ha, Young-Kyung Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(5):374-379. Published online September 30, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.5.374
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Nickel-titanium (Ni-Ti) rotary instruments have some unexpected disadvantages including the tendency to screw-in to the canal. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the influence of root canal curvatures on the screw-in effect of Ni-Ti rotary files.
Materials and Methods A total of 80 simulated root canals in clear resin blocks were used in the study. Canals with curvature of 0, 10, 20 and 30 degrees were instrumented with ProTaper instruments SX, S1, S2 and a ProFile of #25/0.06 to 1.0-2.0 mm beyond the initial point of root curvature. The screw-in force was measured with a specially designed device while canal was instrumented with a ProFile of #30/0.06 at a constant speed of 300 rpm. The data were subjected to one-way ANOVA and Scheffe multiple range test for post-hoc test.
Results Larger degree of canal curvature generated significantly lesser screw-in forces in all groups (
p < 0.001).Conclusions More attention needs to be paid when using rotary instruments in canals with less curvature than canals with more curvatures to prevent or reduce any accidental overinstrumentation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of different kinematics on stationary and dynamic torsional behavior of JIZAI nickel-titanium rotary instruments: An in vitro study
Myint Thu, Arata Ebihara, Moe Sandar Kyaw, Satoshi Omori, Keiichiro Maki, Shunsuke Kimura, Hayate Unno, Takashi Okiji
Journal of Dental Sciences.2023; 18(3): 1170. CrossRef - Analysis of Torque and Force Induced by Rotary Nickel-Titanium Instruments during Root Canal Preparation: A Systematic Review
Myint Thu, Arata Ebihara, Sherif Adel, Takashi Okiji
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(7): 3079. CrossRef - Mechanical and geometric features of endodontic instruments and its clinical effect
Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(1): 1. CrossRef
- Influence of different kinematics on stationary and dynamic torsional behavior of JIZAI nickel-titanium rotary instruments: An in vitro study
- 1,421 View
- 4 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Comparison of screw-in effect for several nickel-titanium rotary instruments in simulated resin root canal
- Jung-Hong Ha, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young-Kyung Kim, Sung-Kyo Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(4):267-272. Published online July 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.4.267
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Screw-in effect is one of the unintended phenomena that occurs during the root canal preparation with nickel-titanium rotary files. The aim of this study was to compare the screw-in effect among various nickel-titanium rotary file systems.
Six different nickel-titanium rotary instruments (ISO 20/.06 taper) were used: K3™ (SybronEndo, Glendora, CA, USA), Mtwo (VDW GmbH, München, Germany), NRT with safe-tip and with active tip (Mani Inc., Shioya-gun, Japan), ProFile® (Dentsply-Maillefer, Ballaigues, Switzerland) and ProTaper® (Dentsply-Maillefer, Ballaigues, Switzerland). For ProTaper®, S2 was selected because it has size 20. Root canal instrumentations were done in sixty simulated single-curved resin root canals with a rotational speed of 300 rpm and single pecking motion. A special device was designed to measure the force of screw-in effect. A dynamometer of the device recorded the screw-in force during simulated canal preparation and the recorded data was stored in a computer with designed software (LCV-USE-VS, Lorenz Messtechnik GmbH, Alfdorf, Germany). The data were subjected to one-way ANOVA and Tukey's multiple range test for post-hoc test. P value of less than 0.05 was regarded significant.
ProTaper® produced significantly more screw-in effects than any other instruments in the study (p < 0.001). K3™ produced significantly more screw-in effects than Mtwo, and ProFile® (p < 0.001). There was no significant difference among Mtwo, NRT, and ProFile® (p > 0.05), and between NRT with active tip and NRT with safe one neither (p > 0.05).
From the result of the present study, it was concluded, therefore, that there seems significant differences of screw-in effect among the tested nickel-titanium rotary instruments. The radial lands and rake angle of nickel-titanium rotary instrument might be the cause of the difference.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of Radial Lands on the Reduction of Torque/Force Generation of a Heat-Treated Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instrument
Taro Nakatsukasa, Arata Ebihara, Moe Sandar Kyaw, Satoshi Omori, Hayate Unno, Shunsuke Kimura, Keiichiro Maki, Takashi Okiji
Applied Sciences.2022; 12(5): 2620. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of mechanical properties and shaping performance of heat-treated nickel titanium rotary instruments used in the single-length technique
Taro NAKATSUKASA, Arata EBIHARA, Shunsuke KIMURA, Keiichiro MAKI, Miki NISHIJO, Daisuke TOKITA, Takashi OKIJI
Dental Materials Journal.2021; 40(3): 743. CrossRef - Analysis of Torque and Force Induced by Rotary Nickel-Titanium Instruments during Root Canal Preparation: A Systematic Review
Myint Thu, Arata Ebihara, Sherif Adel, Takashi Okiji
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(7): 3079. CrossRef - Influence of rotational speed on torque/force generation and shaping ability during root canal instrumentation of extracted teeth with continuous rotation and optimum torque reverse motion
M. S. Kyaw, A. Ebihara, Y. Kasuga, K. Maki, S. Kimura, P. H. Htun, T. Nakatsukasa, T. Okiji
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(9): 1614. CrossRef - Influence of glide path on the screw-in effect and torque of nickel-titanium rotary files in simulated resin root canals
Jung-Hong Ha, Sang-Shin Park
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(4): 215. CrossRef - Influence of root canal curvature on the screw-in effect of nickel-titanium rotary files in simulated resin root canal
Ji-Young Son, Jung-Hong Ha, Young-Kyung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(5): 374. CrossRef - Influence of taper on the screw-in effect of nickel-titanium rotary files in simulated resin root canal
Hye-Jin Sung, Jung-Hong Ha, Sung-Kyo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(5): 380. CrossRef
- Impact of Radial Lands on the Reduction of Torque/Force Generation of a Heat-Treated Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instrument
- 1,898 View
- 6 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Effects of anticurvature filing on danger zone width in curved root canals
- Eui Seong Kim, Hyun Jung Kim, Deog Gyu Seo, Byoung Duck Roh
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(3):232-239. Published online May 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.3.232
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The aim of this study was to compare the effects of anticurvature filing with stainless steel k-file versus nickel-titanium ProFile in the shaping of mesial root canals of extracted mandibular molars.
A total of 60 canals from 30 mesial roots of mandibular molar teeth were randomly assigned to three groups with n=20 each. They were prepared with different instruments and methods: The first group with stainless steel k-file and circumferential filing, the second with precurved stainless steel k-file and anticurvature filing and the third with ProFile (.06 taper) and anticurvature filing. Using a micro-computed tomography system (skyscan-1076, SKYSCAN, Antwerpen, Belgium), pre-and post-operative specimens were scanned. Subsequently, canal images were superimposed and changes in root dentin thickness were measured at distal side (danger zone) of the canal. The data was analyzed using a one-way ANOVA and the comparison of means was conducted using a post hoc multiple comparison Tukey test.
There were significant differences in the change of root dentin thickness at the 7.5~8.5mm level between group 1 and 2, 3.5~6mm level between group 1 and 3 and 3.5~6mm level between group 2 and 3(n=20, P<0.05).
- 1,086 View
- 15 Download

- Stress distribution for NiTi files of triangular based and rectangular based cross-sections using 3-dimensional finite element analysis
- Hyun-Ju Kim, Chan-Joo Lee, Byung-Min Kim, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(1):1-7. Published online January 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.1.001
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare the stress distributions of NiTi rotary instruments based on their cross-sectional geometries of triangular shape-based cross-sectional design, S-shaped cross-sectional design and modified rectangular shape-based one using 3D FE models.
NiTi rotary files of S-shaped and modified rectangular design of cross-section such as Mtwo or NRT showed larger stress change while file rotation during simulated shaping.
The stress of files with rectangular cross-section design such as Mtwo, NRT was distributed as an intermittent pattern along the long axis of file. On the other hand, the stress of files with triangular cross-section design was distributed continuously.
When the residual stresses which could increase the risk of file fatigue fracture were analyzed after their withdrawal, the NRT and Mtwo model also presented higher residual stresses.
From this result, it can be inferred that S-shaped and modified rectangular shape-based files were more susceptible to file fracture than the files having triangular shape-based one.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Ex-Vivo Comparison of Torsional Stress on Nickel–Titanium Instruments Activated by Continuous Rotation or Adaptive Motion
Joo Yeong Lee, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Materials.2020; 13(8): 1900. CrossRef - Autogenous teeth used for bone grafting: a comparison with traditional grafting materials
Young-Kyun Kim, Su-Gwan Kim, Pil-Young Yun, In-Sung Yeo, Seung-Chan Jin, Ji-Su Oh, Heung-Joong Kim, Sun-Kyoung Yu, Sook-Young Lee, Jae-Sung Kim, In-Woong Um, Mi-Ae Jeong, Gyung-Wook Kim
Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology and Oral Radiology.2014; 117(1): e39. CrossRef - Analysis of crystalline structure of autogenous tooth bone graft material: X-Ray diffraction analysis
Gyung-Wook Kim, In-Sung Yeo, Su-Gwan Kim, In-Woong Um, Young-Kyun Kim
Journal of the Korean Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons.2011; 37(3): 225. CrossRef
- Ex-Vivo Comparison of Torsional Stress on Nickel–Titanium Instruments Activated by Continuous Rotation or Adaptive Motion
- 1,466 View
- 6 Download
- 3 Crossref

- The instrument-centering ability of four Nickel-Titanium instruments in simulated curved root canals
- Jae-Hoon Ku, Hoon-Sang Chang, Seok-Woo Chang, Hwan-Hee Cho, Ji-Myung Bae, Kyung-San Min
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(2):113-118. Published online March 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.2.113
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The aim of this study was to evaluate the ability of newly marketed NRT instruments to maintain the original root canal configuration and curvature during preparation in comparison with the three existing instruments in simulated root canals.
Simulated canals in resin blocks were prepared with ProFile, K3, ProTaper, and NRT instrument (n = 10 canals in each case). Pre- and post-operative images were recorded, and assessment of canal shape was completed with a computer image analysis program. The data were analyzed statistically using the One-way ANOVA followed by Duncan's test.
The ability of instruments to remain centered in prepared canals at 1-, 2-mm levels was significantly better in ProFile groups than in other groups (
p < 0.05). The change of centering ratio in NRT groups at 5-mm level was significantly greater than ProFile group and at 6- and 7-mm level than all other groups (p < 0.05).Although the NRT system was comparable to other systems in regards to its ability to maintain the canal configuration of apical portion, this system was more influenced by the mid-root curvature due to its stainless-steel files for coronal preflaring.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A comparison of the shaping ability of reciprocating NiTi instruments in simulated curved canals
Young-Sil Yoo, Yong-Bum Cho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(4): 220. CrossRef - Effect of cross-sectional area of 6 nickel-titanium rotary instruments on the fatigue fracture under cyclic flexural stress: A fractographic analysis
Soo-Youn Hwang, So-Ram Oh, Yoon Lee, Sang-Min Lim, Kee-Yeon Kum
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(5): 424. CrossRef
- A comparison of the shaping ability of reciprocating NiTi instruments in simulated curved canals
- 1,262 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- SHAPING ABILITY OF NICKEL-TITANIUMROTARY FILES
- Wan-Ky Park, Hee-Joo Lee, Bock Hur
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(1):44-50. Published online January 14, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.1.044
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub ABSTRACT This study compared the shaping ability of nickel-titanium rotary files with different rake angle and radial land.
The nickel-titanium files used in this study were Profile(Dentsply, Maillefer, Ballaigues, Switzerland), Hero 642(Micromega, Besancon, France), and K3(SybronEndo, Glendora, Ca, USA) file. Resin blocks substituted for root canals. 36 resin blocks were divided into 3 groups with 12 canals each. The time for canal preparation was recorded. The images of pre- and postoperative resin canal were scanned and those were superimposed. Amounts of canal deviation, total canal widths, inner canal widths, and outer canal widths were measured at apical 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7mm levels.
The amount of canal deviation was the smallest in Profile group, and the time for canal preparation was the shortest in Hero 642 group. K3 group resulted in competent characteristics in both measurements. Positive rake angle seemed to result in fast shaping of root canal and radial land guide the instrument in center of the canals and around curvatures. Radial land also tended to reduce the sense of screwing into the root canal.
The proper selection of the nickel-titanium file based on the knowledge about file design is needed for the safer, simpler and faster root canal therapy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of screw-in effect for several nickel-titanium rotary instruments in simulated resin root canal
Jung-Hong Ha, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young-Kyung Kim, Sung-Kyo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(4): 267. CrossRef - Influence of root canal curvature on the screw-in effect of nickel-titanium rotary files in simulated resin root canal
Ji-Young Son, Jung-Hong Ha, Young-Kyung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(5): 374. CrossRef - Comparison of shaping ability using various Nickel-Titanium rotary files and hybrid technique
Jung-Won Kim, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2007; 32(6): 530. CrossRef - Comparison of shaping ability of rotary Ni-Ti file systems used by undergraduates
Mun-Seong Kang, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Bock Hur, Jeong-Kil Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2006; 31(1): 1. CrossRef - Comparative study on morphology of cross-section and cyclic fatigue test with different rotary NiTi files and handling methods
Jae-Gwan Kim, Kee-Yeon Kum, Eui-Seong Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2006; 31(2): 96. CrossRef - Comparison of shaping ability between various hybrid instrumentation methods with ProTaper
Eun-Sook Hong, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2006; 31(1): 11. CrossRef
- Comparison of screw-in effect for several nickel-titanium rotary instruments in simulated resin root canal
- 1,126 View
- 5 Download
- 6 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


