Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Difference in light transmittance and depth of cure of flowable composite depending on tooth thickness: an in vitro experimental study
- Seong-Pyo Bae, Myung-Jin Lee, Kyung-San Min, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kwang-Won Lee
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(4):e39. Published online November 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e39
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study aimed to quantify light attenuation through varying tooth thicknesses and its impact on the depth of cure of composite resin.
Methods
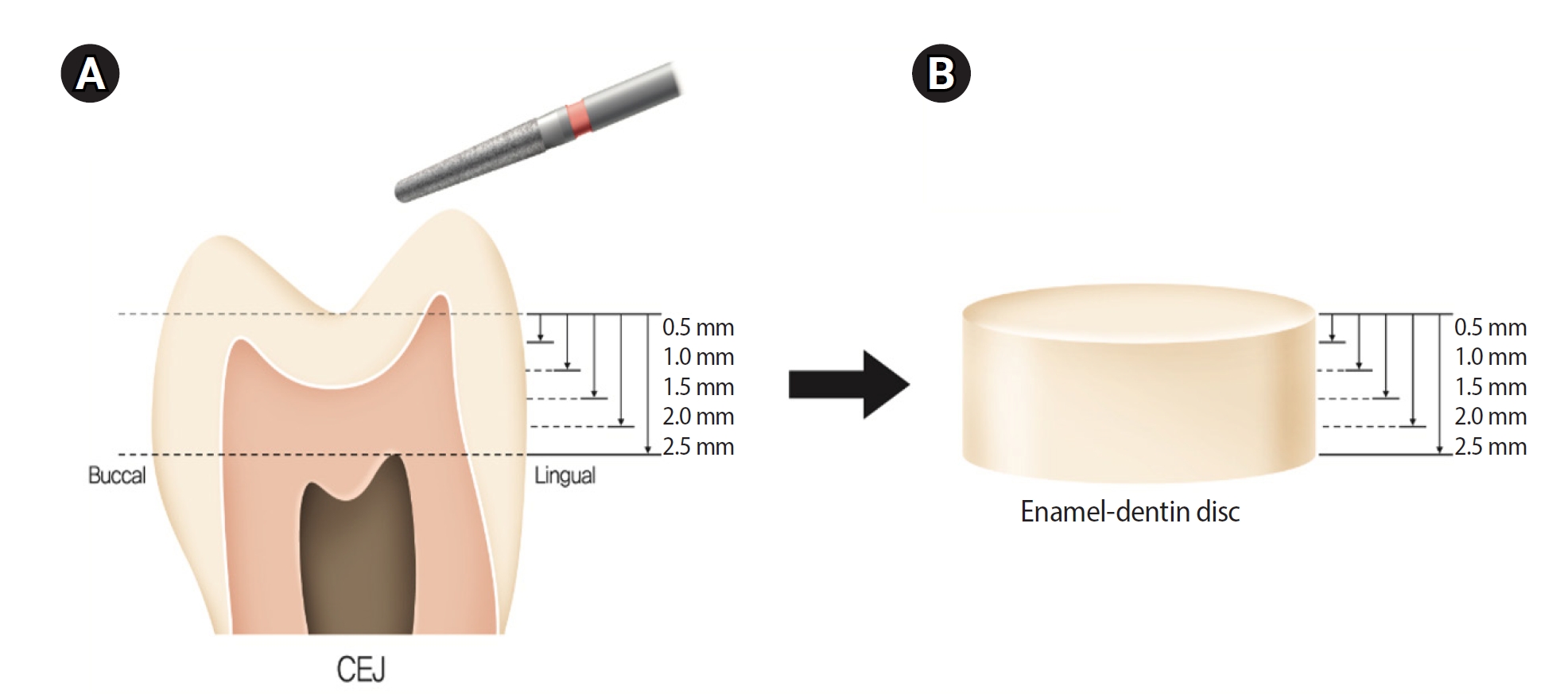
Twenty extracted premolars were used to create enamel-dentin discs that were sanded progressively in 0.5 mm increments from 2.5 mm to 0.5 mm. Light irradiance was measured with and without tooth specimens to evaluate light transmittance. Resin was cured beneath different thicknesses, and the depth of cure was assessed using the Vickers hardness test.
Results
The results demonstrated that light transmittance significantly decreased as tooth thickness increased (p < 0.01), leading to reduced resin polymerization. In the 2.0-mm and 2.5-mm tooth thickness groups, the depth of cure was significantly lower than in the control group without tooth specimens (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
Ultimately, for tooth structures exceeding 2 mm, self-cure or dual-cure resin polymerization is thought to be more efficient than light polymerization.
- 1,231 View
- 118 Download

- Effect of different storage media on elemental analysis and microhardness of cervical cavity margins restored with a bioactive material
- Hoda Saleh Ismail, Brian Ray Morrow, Ashraf Ibrahim Ali, Rabab Elsayed Elaraby Mehesen, Salah Hasab Mahmoud, Franklin Garcia-Godoy
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(1):e6. Published online January 17, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e6
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to investigate the elemental analysis and microhardness of a bioactive material (Activa) and marginal tooth structure after storage in different media.
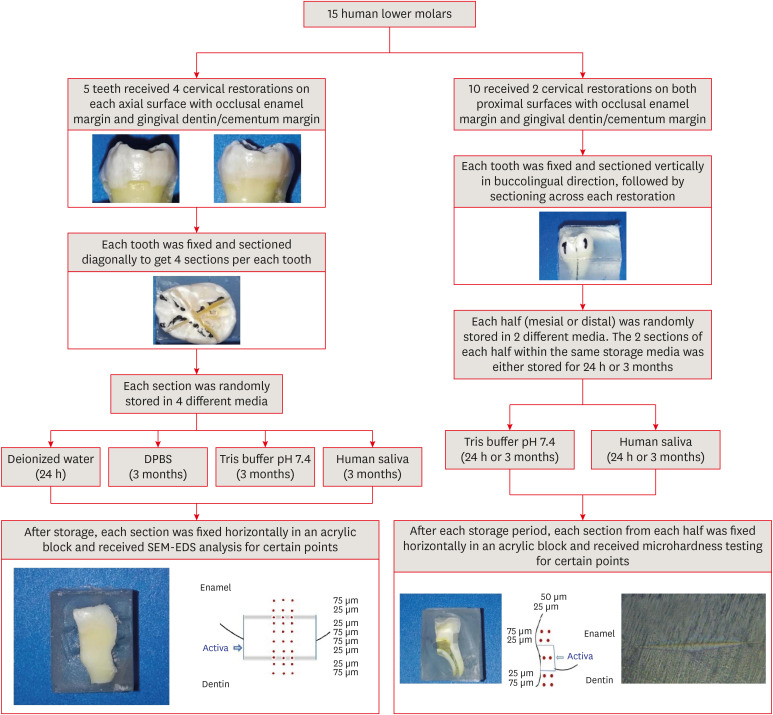
Materials and Methods Fifteen teeth received cervical restorations with occlusal enamel and gingival dentin margins using the tested material bonded with a universal adhesive, 5 of them on the 4 axial surfaces and the other 10 on only the 2 proximal surfaces. The first 5 teeth were sectioned into 4 restorations each, then stored in 4 different media; deionized water, Dulbecco's phosphate buffered saline (DPBS), Tris buffer, and saliva. The storage period for deionized water was 24 hours while it was 3 months for the other media. Each part was analyzed by scanning electron microscopy-energy dispersive spectroscopy (SEM-EDS) analysis for different substrates/distances and the wt% of calcium, phosphorus, silica, and fluoride were calculated. The other 10 teeth were sectioned across the restoration, stored in either Tris buffer or saliva for 24 hours or 3 months, and were evaluated for microhardness of different substrates/areas. Data were analyzed using analysis of variance and Tukey’s
post hoc test.Results Enamel and dentin interfaces in the DPBS group exhibited a significant increase in calcium and phosphorus wt%. Both silica and fluoride significantly increased in tooth structure up to a distance of 75 μm in the 3-month-media groups than the immediate group. Storage media did not affect the microhardness values.
Conclusions SEM-EDS analysis suggests an ion movement between Activa and tooth structure through a universal adhesive while stored in DPBS.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Elemental and micromorphological analysis of ion releasing restoration/carious dentin interface
Alaa Esmat Abdelsalam, Hoda Saleh Ismail, Hamdi Hosni Hamama
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of curing mode and aging on the bonding performance of universal adhesives in coronal and root dentin
Hoda Saleh Ismail, Ashraf Ibrahim Ali, Mohamed Elshirbeny Elawsya
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Elemental and micromorphological analysis of ion releasing restoration/carious dentin interface
- 2,166 View
- 100 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Effects of 3 different light-curing units on the physico-mechanical properties of bleach-shade resin composites
- Azin Farzad, Shahin Kasraei, Sahebeh Haghi, Mahboubeh Masoumbeigi, Hassan Torabzadeh, Narges Panahandeh
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(1):e9. Published online February 7, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e9
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study investigated the microhardness, flexural strength, and color stability of bleach-shade resin composites cured with 3 different light-curing units.
Materials and Methods In this
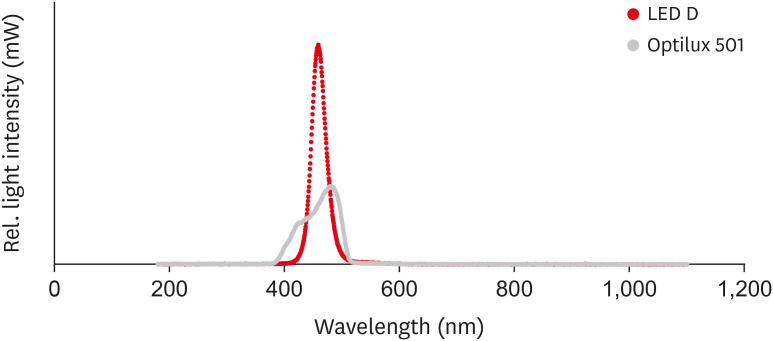
in vitro experimental study, 270 samples were fabricated of bleach and A2 shades of 3 commercial resin composites (Point 4, G-aenial Anterior, and Estelite Sigma Quick). Samples (n = 5 for each trial) were cured with Bluephase N, Woodpecker LED.D, and Optilux 501 units and underwent Vickers microhardness and flexural strength tests. The samples were tested after 24 hours of storage in distilled water. Color was assessed using a spectrophotometer immediately after preparation and 24 hours after curing. Data were analyzed using 3-way analysis of variance and the Tukey test (p ≤ 0.001).Results Samples cured with Optilux exhibited the highest and those cured with LED.D exhibited the lowest microhardness (
p = 0.023). The bleach shade of Point 4 composite cured with Optilux displayed the highest flexural strength, while the same composite and shade cured with Sigma Quick exhibited the lowest (p ≤ 0.001). The color change after 24 hours was greatest for the bleach shade of G-aenial cured with Bluephase N and least for the A2 shade of Sigma Quick cured with Optilux (p ≤ 0.001).Conclusions Light curing with polywave light-emitting diode (LED) yielded results between or statistically similar to those of quartz-tungsten-halogen and monowave LED in the microhardness and flexural strength of both A2 and bleach shades of resin composites. However, the brands of light-curing devices showed significant differences in color stability.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mechanical Behaviour of Novel Nanohybrid Resin Composite Using Two Light Cure Systems
Ghada H. Naguib, Jumana Mazhar, Abeer Alnowaiser, Abdulghani Mira, Hisham Mously, Rabab Aljawi, Samar H. Abuzinadah, Mohamed T. Hamed
International Dental Journal.2025; 75(2): 1136. CrossRef - Repair Bond Strength of Aged Composite: Effect of Thermocycling and Surface Treatment
Sina Yarmoradian, Ladan Ranjbar Omrani, Elham Ahmadi, Niyousha Rafeie, Mahdi Abbasi, Nastaran Dabiri Shahabi
Journal of Research in Dental and Maxillofacial Sciences.2025; 10(3): 228. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Depth of Cure by Microhardness of Bulk-Fill Composites with Monowave and Polywave LED Light-Curing Units
Socratis Thomaidis, Dimitris Kampouropoulos, Maria Antoniadou, Afrodite Kakaboura
Applied Sciences.2024; 14(24): 11532. CrossRef - Effect of hard segment chemistry and structure on the self‐healing properties of UV‐curable coatings based on the urethane acrylates with built‐in Diels–Alder adduct
Paulina Bednarczyk, Karolina Mozelewska, Małgorzata Nowak, Joanna Klebeko, Joanna Rokicka, Paula Ossowicz‐Rupniewska
Journal of Applied Polymer Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Dental Bleaching Agents on the Surface Roughness of Dental Restoration Materials
Alexandru Dan Popescu, Mihaela Jana Tuculina, Oana Andreea Diaconu, Lelia Mihaela Gheorghiță, Claudiu Nicolicescu, Cristian Niky Cumpătă, Cristiana Petcu, Jaqueline Abdul-Razzak, Ana Maria Rîcă, Ruxandra Voinea-Georgescu
Medicina.2023; 59(6): 1067. CrossRef - Effect of Polywave and Monowave Light Curing Units on Color Change of Composites Containing Trime-thylbenzoyl-Diphenyl-Phosphine Before and After Aging
Negar Madihi, Maryam Hoorizad ganjkar, Negin Nasoohi, Ali Kaboudanian Ardestani
Journal of Research in Dental and Maxillofacial Sciences.2023; 8(4): 249. CrossRef
- Mechanical Behaviour of Novel Nanohybrid Resin Composite Using Two Light Cure Systems
- 2,208 View
- 35 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Influence of modeling agents on the surface properties of an esthetic nano-hybrid composite
- Zeynep Bilge Kutuk, Ecem Erden, Damla Lara Aksahin, Zeynep Elif Durak, Alp Can Dulda
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(2):e13. Published online January 29, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e13
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objective The aim of this study was to evaluate the influence of different modeling agents on the surface microhardness (Vickers hardness number; VHN), roughness (Ra), and color change (ΔE) of a nano-hybrid composite with or without exposure to discoloration by coffee.
Materials and Methods Sixty-four cylinder-shaped nano-hybrid composite specimens were prepared using a Teflon mold. The specimens' surfaces were prepared according to the following groups: group 1, no modeling agent; group 2, Modeling Liquid; group 3, a universal adhesive (G-Premio Bond); and group 4, the first step of a 2-step self-adhesive system (OptiBond XTR). Specimens were randomly allocated into 2 groups (
n = 8) according to the storage medium (distilled water or coffee). VHN, Ra, and ΔE were measured at 24 hours, 1 week, and 6 weeks. The Kruskal-Wallis test followed by the Bonferroni correction for pairwise comparisons was used for statistical analysis (α = 0.05).Results Storage time did not influence the VHN of the nano-hybrid composite in any group (
p > 0.05). OptiBond XTR Primer application affected the VHN negatively in all investigated storage medium and time conditions (p < 0.05). Modeling Liquid application yielded improved Ra values for the specimens stored in coffee at each time point (p < 0.05). Modeling Liquid application was associated with the lowest ΔE values in all investigated storage medium and time conditions (p < 0.05).Conclusion Different types of modeling agents could affect the surface properties and discoloration of nano-hybrid composites.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Do modeling liquid and glycerin gel compromise the color stability of one-shade composites
Ezgi Erden Kayalidere, Merve Sahin
Odontology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Placement Techniques on Marginal Integrity, Wear Behavior, and Clinical Efficiency of a Bulk-Fill Resin Composite
Kerem Can Işık, Handan Yıldırım-Işık, Uğur Tuna Sazlıkoğlu, Mediha Büyükgöze-Dindar
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2026; 17(3): 108. CrossRef - The Impact of Modeling Liquids on Surface Roughness and Color Properties of Bulkfill Resin Composites After Simulated Tooth Brushing: An in Vitro Study. Part I
Camila Falconí‐Páez, Claudia González‐Vaca, Juliana Guarneri, Newton Fahl, Paulina Aliaga‐Sancho, Maria Lujan Mendez‐Bauer, Cesar Augusto Galvão Arrais, Andrés Dávila‐Sánchez
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2025; 37(2): 514. CrossRef - Coating Agents for Resin Composites: Effect on Color Stability, Roughness, and Surface Micromorphology Subjected to Brushing Wear
FR Hojo, TC Martins, WF Vieira-Junior, FMG França, CP Turssi, RT Basting
Operative Dentistry.2025; 50(1): 101. CrossRef - Effect of modeling liquid application on color stability and surface roughness of single-shade composites
Melek Güven Bekdaş, Ihsan Hubbezoglu
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of modeling liquids on the color adaptation and optical properties of single and simply shade resin composites
Bengü Doğu Kaya, Mehmet Buldur, Burcu Gözetici-Çil
Odontology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of modeling liquids on Vickers microhardness, flexural strength and color stability of resin-based composites
Ahmed Alshawi, Benin Dikmen, Sevda Ozel Yildiz, Ugur Erdemir
Materials Research Express.2025; 12(11): 115402. CrossRef - Does composite repair time affect repair protocol, immediate or delayed?
Murat Can Ersen, Nevin Cobanoglu
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of combining dental composite brushes with modeling resins on the color stability and topographic features of composites
Abdulrahman A Balhaddad, Faisal Alharamlah, Alhanoof Aldossary, Wejdan Almutairi, Turki Alshehri, Mary Anne S Melo, Afnan O Al-Zain, Eman H Ismail
Journal of Applied Biomaterials & Functional Materials.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Investigation of the Degree of Monomer Conversion in Dental Composites through Various Methods: An In Vitro Study
Musa Kazim Ucuncu, Ozge Celiksoz, Emine Sen, Yasemin Yucel Yucel, Bircan Dinc
Applied Sciences.2024; 14(11): 4406. CrossRef - EFEITO DOS LÍQUIDOS MODELADORES NA SUPERFÍCIE DA RESINA COMPOSTA – UMA REVISÃO DE LITERATURA
Samuel Silva Dias, Matheus Fernando Lopes, Jeffison Teles Dias, Caio Junji Tanaka, Jose Augusto Rodrigues
RECIMA21 - Revista Científica Multidisciplinar - ISSN 2675-6218.2024; 5(2): e524899. CrossRef - Effect of Instrument Lubricant on Mechanical Properties of Restorative Composite
G Pippin, D Tantbirojn, M Wolfgang, JS Nordin, A Versluis
Operative Dentistry.2024; 49(4): 475. CrossRef - Full analysis of the effects of modeler liquids on the properties of direct resin-based composites: a meta-analysis review of in vitro studies
Eduardo Trota Chaves, Lisia Lorea Valente, Eliseu Aldrighi Münchow
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(7): 3289. CrossRef - Influence of Modeling Liquids and Universal Adhesives Used as Lubricants on Color Stability and Translucency of Resin-Based Composites
Gaetano Paolone, Claudia Mazzitelli, Giacomo Zechini, Salvatore Scolavino, Cecilia Goracci, Nicola Scotti, Giuseppe Cantatore, Enrico Gherlone, Alessandro Vichi
Coatings.2023; 13(1): 143. CrossRef - Influence of Instrument Lubrication on Properties of Dental Composites
Juliusz Kosewski, Przemysław Kosewski, Agnieszka Mielczarek
European Journal of Dentistry.2022; 16(04): 719. CrossRef - Effect of Modelıng Liquid Use on Color and Whiteness Index Change of Composite Resins
Numan AYDIN, Serpil KARAOĞLANOĞLU, Bilge ERSÖZ
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2022; 25(Supplement): 119. CrossRef - Effects of Immediate Coating on Unset Composite with Different Bonding Agents to Surface Hardness
Nantawan Krajangta, Supissara Ninbanjong, Sunisa Khosook, Kanjana Chaitontuak, Awiruth Klaisiri
European Journal of Dentistry.2022; 16(04): 828. CrossRef - Modeling Liquids and Resin-Based Dental Composite Materials—A Scoping Review
Gaetano Paolone, Claudia Mazzitelli, Uros Josic, Nicola Scotti, Enrico Gherlone, Giuseppe Cantatore, Lorenzo Breschi
Materials.2022; 15(11): 3759. CrossRef - Shear Bond Strength of Composite Diluted with Composite-Handling Agents on Dentin and Enamel
Mijoo Kim, Deuk-Won Jo, Shahed Al Khalifah, Bo Yu, Marc Hayashi, Reuben H. Kim
Polymers.2022; 14(13): 2665. CrossRef - Effect of Modeling Resins on Microhardness of Resin Composites
Ezgi T. Bayraktar, Pinar Y. Atali, Bora Korkut, Ezgi G. Kesimli, Bilge Tarcin, Cafer Turkmen
European Journal of Dentistry.2021; 15(03): 481. CrossRef
- Do modeling liquid and glycerin gel compromise the color stability of one-shade composites
- 2,199 View
- 35 Download
- 20 Crossref

- The effect of preheating resin composites on surface hardness: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Ali A. Elkaffas, Radwa I. Eltoukhy, Salwa A. Elnegoly, Salah H. Mahmoud
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(4):e41. Published online October 29, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e41
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This paper presents a systematic review and meta-analysis of the effect of preheating on the hardness of nanofilled, nanoceramic, nanohybrid, and microhybrid resin composites.
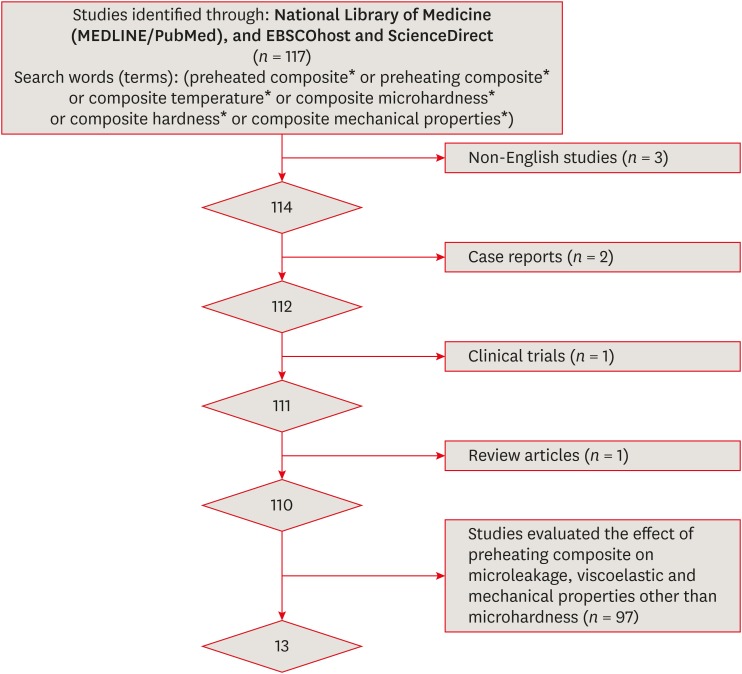
Materials and Methods An electronic search of papers on MEDLINE/PubMed, ScienceDirect, and EBSCOhost was performed. Only
in vitro studies were included. Non-English studies, case reports, clinical trials, and review articles were excluded. A meta-analysis of the reviewed studies was conducted to quantify differences in the microhardness of the Z250 microhybrid resin composite using the Comprehensive Meta-Analysis software.Results Only 13 studies met the inclusion criteria for this systematic review. The meta-analysis showed that there were significant differences between the non-preheated and preheated modes for both the top and bottom surfaces of the specimens (
p < 0.05). The microhardness of the Z250 resin composite on the top surface in the preheated mode (78.1 ± 2.9) was higher than in the non-preheated mode (67.4 ± 4.0;p < 0.001). Moreover, the microhardness of the Z250 resin composite on the bottom surface in the preheated mode (71.8 ± 3.8) was higher than in the non-preheated mode (57.5 ± 5.7,p < 0.001).Conclusions Although the results reported in the reviewed studies showed great variability, sufficient scientific evidence was found to support the hypothesis that preheating can improve the hardness of resin composites.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of preheating and water storage on the color, whiteness, and translucency of modern resin‐based composites
Corina Mirela Prodan, Cristina Gasparik, Javier Ruiz‐López, Diana Dudea
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2025; 37(2): 533. CrossRef - Effects of pre-heating on physical–mechanical–chemical properties of contemporary resin composites
Thamires Bueno, Nivien Masoud, Anna Akkus, Italo Silva, Karen McPherson, Adilson Yoshio Furuse, Fabio Rizzante
Odontology.2025; 113(1): 135. CrossRef - The effects of a carbonated beverage on the optical properties and microhardness of preheated bulk-fill composite resin restorations
Nancy Soliman Farghal, Ayya Abu Shamleh, Osamah Al Hurmuzi, Okba Mahmoud
Frontiers in Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Degree of Conversion, Flexural Strength, and Microhardness of a Novel Flowable Resin Composite
Bengü Doğu Kaya, Selinsu Öztürk, Nazlı Zeynep Kuzu, Ayşe Aslı Şenol, Erkut Kahramanoğlu, Pınar Yılmaz Atalı, Bilge Tarçın
Selcuk Dental Journal.2025; 12(2): 202. CrossRef - Clinical performance of different bulk‐fill composite resin systems in classIIcavities: A 2‐year randomized clinical trial
Badria Goda, Kareem Hamdi, Radwa I. Eltoukhy, Ashraf I. Ali, Salah Hasab Mahmoud
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2024; 36(8): 1122. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of microleakage in Class II cavities restored with snowplow technique using flowable or preheated packable bulk-fill composite resin as gingival increment by dye extraction method: An in vitro study
M. A. Ranjini, V. Geetha, B. Vedavathi, H. K. Ashok, Akshata J. Airsang, S. Swathi
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(11): 1158. CrossRef - Influence of Light‐Curing Time and Increment Thickness on the Properties of Bulk Fill Composite Resins With Distinct Application Systems
Carlos Rocha Gomes Torres, Taiana Paola Prado, Daniele Mara da Silva Ávila, Cesar Rogério Pucci, Alessandra Bühler Borges, Heng Bo Jiang
International Journal of Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Last Generation Bis-GMA Free Composite For Indirect Posterior Restorations: A Case Report
M. Delgado
Endodontics Today.2024; 21(4): 305. CrossRef - The clinical performance of dental resin composite repeatedly preheated: A randomized controlled clinical trial
Mahmoud Elkady, Safaa Abdelhakim, Mona Riad
Journal of Dentistry.2024; 144: 104940. CrossRef - Preheating effect on microhardness and depth of cure of three bulk-fill composite resins: An in vitro study
Aashna Sunil Sahetia, Divya Rupesh Jain, Padmaja Panditrao Sirsat, Meenal N. Gulve, Swapnil J. Kolhe, Surbhi P. Patel
Endodontology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Shear Bond Strength of Lithium Disilicate Veneers Using Pre-heated Resin Composite With Two Conventional Resin Cements: An In Vitro Study
Ghalia Akyle, Hassan Achour
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Glass Fiber Reinforcement on Marginal Microleakage in Class II Composite Restorations: An In Vitro Pilot Study
Csaba Dudás, Emánuel Kardos, Melinda Székely, Lea Ádám, Zsuzsanna Bardocz-Veres, Evelyn Szőllősi, Kinga Mária Jánosi, Bernadette Kerekes-Máthé
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(12): 410. CrossRef - Effect of preheating on the physicochemical properties and bond strength of composite resins utilized as dental cements: An in vitro study
Carolina Carramilo Raposo, Luanna Marinho Sereno Nery, Edilausson Moreno Carvalho, Paulo Vitor Campos Ferreira, Diego Machado Ardenghi, José Bauer, Darlon Martins Lima
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2023; 129(1): 229.e1. CrossRef - Examining the Impact of Preheating on the Fracture Toughness and Microhardness of Composite Resin: A Systematic Review
Jay Bhopatkar, Anuja Ikhar, Manoj Chandak, Aditya Patel, Paridhi Agrawal
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - In Vitro Effect of Mouthrinses on the Microhardness of Three Different Nanohybrid Composite Resins
Jhonn Luis Bernaldo-Faustino, Julissa Amparo Dulanto-Vargas, Kilder Maynor Carranza-Samanez, Carlos A. Munoz-Viveros
International Journal of Dentistry.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Efecto del precalentamiento en la microdureza superficial de seis resinas compuestas
Gloria Cristina Moreno Abello, Kavhas Castro, Paula Alejandra Ovalle Barrera, Paula Bernal, Laura Catalina Lara Hernández
Universitas Odontologica.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Wear and Color Stability of Preheated Bulk-fill and Conventional Resin Composites
AA Abdulmajeed, AA Suliman, BJ Selivany, A Altitinchi, TA Sulaiman
Operative Dentistry.2022; 47(5): 585. CrossRef - Comparison of Mechanical Properties of a Self-Adhesive Composite Cement and a Heated Composite Material
Anastazja Skapska, Zenon Komorek, Mariusz Cierech, Elzbieta Mierzwinska-Nastalska
Polymers.2022; 14(13): 2686. CrossRef - Effects of ionizing radiation on surface properties of current restorative dental materials
Débora Michelle Gonçalves de Amorim, Aretha Heitor Veríssimo, Anne Kaline Claudino Ribeiro, Rodrigo Othávio de Assunção e Souza, Isauremi Vieira de Assunção, Marilia Regalado Galvão Rabelo Caldas, Boniek Castillo Dutra Borges
Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Quality assessment tools used in systematic reviews of in vitro studies: A systematic review
Linh Tran, Dao Ngoc Hien Tam, Abdelrahman Elshafay, Thao Dang, Kenji Hirayama, Nguyen Tien Huy
BMC Medical Research Methodology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Preheated composite: Innovative approach for aesthetic restoration
Reema N Asani, Vandana J Gade, Kalyani G Umale, Rachana Gawande, Rohit R Amburle, Raksha R Kusumbe, Purva P Kale, Priya R Kosare
Archives of Dental Research.2021; 11(2): 103. CrossRef
- Influence of preheating and water storage on the color, whiteness, and translucency of modern resin‐based composites
- 2,808 View
- 29 Download
- 21 Crossref

- Analysis of the shelf life of chitosan stored in different types of packaging, using colorimetry and dentin microhardness
- Antonio Miranda da Cruz-Filho, Angelo Rafael de Vito Bordin, Luis Eduardo Souza-Flamini, Débora Fernandes da Costa Guedes, Paulo César Saquy, Ricardo Gariba Silva, Jesus Djalma Pécora
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(2):87-94. Published online March 27, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.2.87
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Chitosan has been widely investigated and used. However, the literature does not refer to the shelf life of this solution. This study evaluated, through the colorimetric titration technique and an analysis of dentin micro-hardness, the shelf life of 0.2% chitosan solution.
Materials and Methods Thirty human canines were sectioned, and specimens were obtained from the second and third slices, from cemento-enamel junction to the apex. A 0.2% chitosan solution was prepared and distributed in 3 identical glass bottles (v1, v2, and v3) and 3 plastic bottles (p1, p2, and p3). At 0, 7, 15, 30, 45, 60, 90, 120, 150, and 180 days, the specimens were immersed in each solution for 5 minutes (
n = 3 each). The chelating effect of the solution was assessed by micro-hardness and colorimetric analysis of the dentin specimens. 17% EDTA and distilled water were used as controls. Data were analyzed statistically by two-way and Tukey-Kramer multiple comparison (α = 0.05).Results There was no statistically significant difference among the solutions with respect to the study time (
p = 0.113) and micro-hardness/time interaction (p = 0.329). Chitosan solutions and EDTA reduced the micro-hardness in a similar manner and differed significantly from the control group (p < 0.001). Chitosan solutions chelated calcium ions throughout the entire experiment.Conclusions Regardless of the storage form, chitosan demonstrates a chelating property for a minimum period of 6 months.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Chitosan’s Ability to Remove the Smear Layer—A Systematic Review of Ex Vivo Studies
Ana Ferreira-Reguera, Inês Ferreira, Irene Pina-Vaz, Benjamín Martín-Biedma, José Martín-Cruces
Medicina.2025; 61(1): 114. CrossRef - The Utilization of Chitosan and Arduino Interface in Making a Microplastic Filter
Kate Cyrene P. Pineda, Maeven Uriel A. Dela Cruz, Quirsten Daniel R. Repalda, Aldrin Jeynard A. Gonzales, DL Chaturika C. Douglas, Alina Siara D. Hajan, Julie Ann B. Real
International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology.2025; : 2742. CrossRef - Antimicrobial evaluation of root canal irrigants of natural sources with and without gamma radiation activation - An in vitro study
Hoda Raafat Yousri, Abeer Hashem Mahran, Ahmed Abdel Rahman Hashem, Amal A. El-Batouti
Endodontology.2024; 36(4): 383. CrossRef - Influence of Chitosan 0.2% in Various Final Cleaning Methods on the Bond Strength of Fiberglass Post to Intrarradicular Dentin
Naira Geovana Camilo, Alex da Rocha Gonçalves, Larissa Pinzan Flauzino, Cristiane Martins Rodrigues Bernardes, Andreza Maria Fábio Aranha, Priscilla Cardoso Lazari-Carvalho, Marco Aurélio de Carvalho, Helder Fernandes de Oliveira
Polymers.2023; 15(22): 4409. CrossRef - Evaluation and comparison of anti-inflammatory properties of ibuprofen using two drug delivery systems after third molar surgery: using chitosan microspheres as a carrier for local drug delivery in to the third molar socket and through the oral route
Karthik KP, Balamurugan R
British Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.2021; 59(2): 191. CrossRef - Optimization of chitosan nanoparticle synthesis and its potential application as germination elicitor of Oryza sativa L.
K. Divya, Smitha Vijayan, Sreekumar Janardanan Nair, M.S. Jisha
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.2019; 124: 1053. CrossRef - Crosstalk between chitosan and cell signaling pathways
Behrouz Farhadihosseinabadi, Amir Zarebkohan, Mohamad Eftekhary, Mohammad Heiat, Mehrdad Moosazadeh Moghaddam, Mazaher Gholipourmalekabadi
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences.2019; 76(14): 2697. CrossRef
- Chitosan’s Ability to Remove the Smear Layer—A Systematic Review of Ex Vivo Studies
- 1,499 View
- 8 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Carbohydrate-electrolyte drinks exhibit risks for human enamel surface loss
- Mary Anne Sampaio de Melo, Vanara Florêncio Passos, Juliana Paiva Marques Lima, Sérgio Lima Santiago, Lidiany Karla Azevedo Rodrigues
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(4):246-254. Published online August 16, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.4.246
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this investigation was to give insights into the impact of carbohydrate-electrolyte drinks on the likely capacity of enamel surface dissolution and the influence of human saliva exposure as a biological protective factor.
Materials and Methods The pH, titratable acidity (TA) to pH 7.0, and buffer capacity (β) of common beverages ingested by patients under physical activity were analyzed. Then, we randomly distributed 50 specimens of human enamel into 5 groups. Processed and natural coconut water served as controls for testing three carbohydrate-electrolyte drinks. In all specimens, we measured surface microhardness (Knoop hardness numbers) and enamel loss (profilometry, µm) for baseline and after simulated intake cycling exposure model. We also prepared areas of specimens to be exposed to human saliva overnight prior to the simulated intake cycling exposure. The cycles were performed by alternated immersions in beverages and artificial saliva. ANOVA two-way and Tukey HDS tests were used.
Results The range of pH, TA, and β were 2.85 - 4.81, 8.33 - 46.66 mM/L and 3.48 - 10.25 mM/L × pH, respectively. The highest capacity of enamel surface dissolution was found for commercially available sports drinks for all variables. Single time human saliva exposure failed to significantly promote protective effect for the acidic attack of beverages.
Conclusions In this study, carbohydrate-electrolyte drinks usually consumed during endurance training may have a greater capacity of dissolution of enamel surface depending on their physicochemical proprieties associated with pH and titratable acidity.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of developmentally hypomineralised enamel after surface pretreatment with Papacarie Duo gel and different etching modes: an in vitro SEM and AFM study
Y.-L. Lee, K. C. Li, C. K. Y. Yiu, D. H. Boyd, M. Ekambaram
European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry.2022; 23(1): 117. CrossRef - Is the consumption of beverages and food associated to dental erosion? A cross-sectional study in Portuguese athletes
M.-R.G. Silva, M.-A. Chetti, H. Neves, M.-C. Manso
Science & Sports.2021; 36(6): 477.e1. CrossRef - Assessment of surface roughness changes on orthodontic acrylic resin by all-in-one spray disinfectant solutions
Kuei-ling Hsu, Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad, Isadora Martini Garcia, Fabricio Mezzomo Collares, Louis DePaola, Mary Anne Melo
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2020; 14(2): 77. CrossRef - Nitrate-rich beetroot juice offsets salivary acidity following carbohydrate ingestion before and after endurance exercise in healthy male runners
Mia C. Burleigh, Nicholas Sculthorpe, Fiona L. Henriquez, Chris Easton, Yi-Hung Liao
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(12): e0243755. CrossRef - Dental erosion’ prevalence and its relation to isotonic drinks in athletes: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Pedro Henrique Pereira de Queiroz Gonçalves, Ludmila Silva Guimarães, Fellipe Navarro Azevedo de Azeredo, Letícia Maira Wambier, Lívia Azeredo A. Antunes, Leonardo Santos Antunes
Sport Sciences for Health.2020; 16(2): 207. CrossRef - Atomic force microscopy analysis of enamel nanotopography after interproximal reduction
Shadi Mohebi, Nazila Ameli
American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics.2017; 152(3): 295. CrossRef
- Evaluation of developmentally hypomineralised enamel after surface pretreatment with Papacarie Duo gel and different etching modes: an in vitro SEM and AFM study
- 2,126 View
- 17 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Effect of acidic solutions on the microhardness of dentin and set OrthoMTA and their cytotoxicity on murine macrophage
- Soram Oh, Hiran Perinpanayagam, Yoon Lee, Jae-Won Kum, Yeon-Jee Yoo, Sang-Min Lim, Seok Woo Chang, Won-Jun Shon, Woocheol Lee, Seung-Ho Baek, Kee-Yeon Kum
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(1):12-21. Published online December 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.1.12

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives To evaluate the effects of three acids on the microhardness of set mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) and root dentin, and cytotoxicity on murine macrophage.
Materials and Methods OrthoMTA (BioMTA) was mixed and packed into the human root dentin blocks of 1.5 mm diameter and 5 mm height. Four groups, each of ten roots, were exposed to 10% citric acid (CA), 5% glycolic acid (GA), 17% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), and saline for five minutes after setting of the OrthoMTA. Vickers surface microhardness of set MTA and dentin was measured before and after exposure to solutions, and compared between groups using one-way ANOVA with Tukey test. The microhardness value of each group was analyzed using student
t test. Acid-treated OrthoMTA and dentin was examined by scanning electron microscope (SEM). Cell viability of tested solutions was assessed using WST-8 assay and murine macrophage.Results Three test solutions reduced microhardness of dentin. 17% EDTA demonstrated severe dentinal erosion, significantly reduced the dentinal microhardness compared to 10% CA (
p = 0.034) or 5% GA (p = 0.006). 10% CA or 5% GA significantly reduced the surface microhardness of set MTA compared to 17% EDTA and saline (p < 0.001). Acid-treated OrthoMTA demonstrated microporous structure with destruction of globular crystal. EDTA exhibited significantly more cellular toxicity than the other acidic solutions at diluted concentrations (0.2, 0.5, 1.0%).Conclusions Tested acidic solutions reduced microhardness of root dentin. Five minute's application of 10% CA and 5% GA significantly reduced the microhardness of set OrthoMTA with lower cellular cytotoxicity compared to 17% EDTA.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Removal Efficiency of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate: A narrative Review of Retrieval Techniques
Mohammed A. Hussein, Rasha H. Jehad
Journal of Medical and Oral Biosciences.2025; : 36. CrossRef - Impact of calcium hydroxide and 2-hydroxyisocaproic acid on the microhardness of root dentine: an in vitro study
Nandini T. Niranjan, Protim Ghosh Dastidar, Raghavendra Penukonda, Galvin Sim Siang Lin, Roopa Babannavar, Arun Jaysheel, Harshada Pattar
Odontology.2024; 112(3): 711. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Effect of Chitosan-Based Irrigation Solutions on the Bond Strength of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate to Bulk-Fill Composite
Arzu Şahin Mantı, Bağdagül Helvacıoğlu Kıvanç
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2024; 15(12): 370. CrossRef - Effect of Various Acid Solutions as an Aid in Removing the OrthoMTA-Based Root Canal Filling
Naveen Chhabra, Abhishek Parolia
Materials.2023; 16(13): 4535. CrossRef - Effect of Glycolic Acid, Maleic Acid, and EDTA in the Removal of Smear Layer from Root Canal Dentin
Tarini Mullick, Nidambur Vasudev Ballal
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A comparative evaluation of the effect of various chelating agents on the microhardness of root canal dentin: An in vitro study
Mineet Kaul, Zinnie Nanda, Kranthikumar Reddy, Rahul Deore, Divya Mandlecha, Esha Jaiswal
Endodontology.2023; 35(3): 234. CrossRef - Calcium hydroxide and niobium pentoxide treatment effects before MTA placement
Kolli Sankeerthana, Kittappa Karthikeyan, Sekar Mahalaxmi
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(1): 48. CrossRef - Calcium silicate and calcium aluminate cements for dentistry reviewed
Carolyn Primus, James L. Gutmann, Franklin R. Tay, Anna B. Fuks
Journal of the American Ceramic Society.2022; 105(3): 1841. CrossRef - Influence of Acidic Environmental Conditions on Push‐Out Bonding Strength of Four Calcium Silicate‐Based Materials to Root Dentin
Beliz Özel, Raif Erişen, Boonlert Kukiattrakoon
International Journal of Dentistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The effects of sodium hypochlorite and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid on the microhardness of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate and TotalFill Bioceramic Putty
Jacklyn H.R. Chu, Kalie Y. Chia, Alexander L. Qui, Alex Moule, William N. Ha
Australian Endodontic Journal.2020; 46(1): 33. CrossRef - Pre-application of dentin bonding agent prevents discoloration caused by mineral trioxide aggregate
Yoo-Lim Choi, Young-Eun Jang, Bom Sahn Kim, Jin-Woo Kim, Yemi Kim
BMC Oral Health.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Glycolic acid as the final irrigant in endodontics: Mechanical and cytotoxic effects
Yuri Dal Bello, Hisadora Fracaro Porsch, Ana Paula Farina, Matheus Albino Souza, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Ana Karina Bedran-Russo, Doglas Cecchin
Materials Science and Engineering: C.2019; 100: 323. CrossRef - Carbohydrate-electrolyte drinks exhibit risks for human enamel surface loss
Mary Anne Sampaio de Melo, Vanara Florêncio Passos, Juliana Paiva Marques Lima, Sérgio Lima Santiago, Lidiany Karla Azevedo Rodrigues
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(4): 246. CrossRef
- Removal Efficiency of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate: A narrative Review of Retrieval Techniques
- 2,641 View
- 17 Download
- 13 Crossref

- Effect of organic acids in dental biofilm on microhardness of a silorane-based composite
- Sedighe Sadat Hashemikamangar, Seyed Jalal Pourhashemi, Mohammad Talebi, Nazanin Kiomarsi, Mohammad Javad Kharazifard
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(3):188-194. Published online June 2, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.3.188
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the effect of lactic acid and acetic acid on the microhardness of a silorane-based composite compared to two methacrylate-based composite resins.
Materials and Methods Thirty disc-shaped specimens each were fabricated of Filtek P90, Filtek Z250 and Filtek Z350XT. After measuring of Vickers microhardness, they were randomly divided into 3 subgroups (
n = 10) and immersed in lactic acid, acetic acid or distilled water. Microhardness was measured after 48 hr and 7 day of immersion. Data were analyzed using repeated measures ANOVA (p < 0.05). The surfaces of two additional specimens were evaluated using a scanning electron microscope (SEM) before and after immersion.Results All groups showed a reduction in microhardness after 7 day of immersion (
p < 0.001). At baseline and 7 day, the microhardness of Z250 was the greatest, followed by Z350 and P90 (p < 0.001). At 48 hr, the microhardness values of Z250 and Z350 were greater than P90 (p < 0.001 for both), but those of Z250 and Z350 were not significantly different (p = 0.095). Also, the effect of storage media on microhardness was not significant at baseline, but significant at 48 hr and after 7 day (p = 0.001 andp < 0.001, respectively). Lactic acid had the greatest effect.Conclusions The microhardness of composites decreased after 7 day of immersion. The microhardness of P90 was lower than that of other composites. Lactic acid caused a greater reduction in microhardness compared to other solutions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of hydroelectrolytic beverages on the roughness and microhardness of bulk fill resin composites
Renata Siqueira Scatolin, Caio Castro Grigoletto, Laura Nobre Ferraz, Rafael Pino Vitti
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2025; 24: e254003. CrossRef - Investigating the effect of three carbonated drinks on tooth enamel roughness and microhybrid composite
Sara Akbari Fard, Saeed Nemati Anaraki, Haleh Kazemi -Yazdi, Mahsa Qenaat
journal of research in dental sciences.2024; 21(3): 174. CrossRef - Evaluating the effect of natural, industrial juices and beverage on orthodontic bonding composite (in-vitro study)
Rusal S Ahmed, Alan I Saleem
Journal of Baghdad College of Dentistry.2023; 35(3): 10. CrossRef - Stoichiometric models of sucrose and glucose fermentation by oral streptococci: Implications for free acid formation and enamel demineralization
Marzieh Mansouri, Evan P. O'Brien, Karabi Mondal, Chien-Chia Chen, James L. Drummond, Luke Hanley, Karl J. Rockne
Dental Materials.2023; 39(4): 351. CrossRef - Effect of mouthwashes on the microhardness of aesthetic composite restorative materials
Noura Abdulaziz Alessa
Anales del Sistema Sanitario de Navarra.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the Effect of Natural and Industrial Orange Juices and Beverage on Surface Roughness of Orthodontic Bonding Composite
Rusal Saad Ahmed, Alan Issa Saleem
Dental Hypotheses.2022; 13(3): 107. CrossRef - Effects of particle distribution and calculation method on results of nano-indentation technique in heterogeneous nanocomposites-experimental and numerical approaches
M. Heidari, A. Karimzadeh, M.R. Ayatollahi, M.Y. Yahya
International Journal of Solids and Structures.2021; 225: 111054. CrossRef - New Resin-Based Bulk-Fill Composites: in vitro Evaluation of Micro-Hardness and Depth of Cure as Infection Risk Indexes
Marco Colombo, Simone Gallo, Claudio Poggio, Vittorio Ricaldone, Carla Renata Arciola, Andrea Scribante
Materials.2020; 13(6): 1308. CrossRef - Tribological Behavior of Restorative Dental Microcomposites After Exposure to Mouth Acids
A. C. Branco, J. Brito, M. Codorniz, M. Steinhausen, F. Martins, J. Reis, P. Maurício, R. Colaço, A. P. Serro
Tribology Letters.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Vickers Micro-Hardness of New Restorative CAD/CAM Dental Materials: Evaluation and Comparison after Exposure to Acidic Drink
Marco Colombo, Claudio Poggio, Alessandro Lasagna, Marco Chiesa, Andrea Scribante
Materials.2019; 12(8): 1246. CrossRef - 30 Months Clinical Evaluation of Posterior Composite Resin Restorations
Serdar Akarsu, Hüseyin Özgür Özdemir
The Journal of Dentists.2018; 6: 6. CrossRef - Survival and Associated Risk Factors of Selective Caries Removal Treatments in Primary Teeth: A Retrospective Study in a High Caries Risk Population
Ximena C. Melgar, Niek J.M. Opdam, Marcos Britto Correa, Renata Franzon, Flávio Fernando Demarco, Fernando B. Araujo, Luciano Casagrande
Caries Research.2017; 51(5): 466. CrossRef
- Effect of hydroelectrolytic beverages on the roughness and microhardness of bulk fill resin composites
- 1,598 View
- 6 Download
- 12 Crossref

- Effect of resin thickness on the microhardness and optical properties of bulk-fill resin composites
- Eun-Ha Kim, Kyoung-Hwa Jung, Sung-Ae Son, Bock Hur, Yong-Hoon Kwon, Jeong-Kil Park
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(2):128-135. Published online January 13, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.2.128
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the effects of the resin thickness on the microhardness and optical properties of bulk-fill resin composites.
Methods Four bulk-fill (Venus Bulk Fill, Heraeus Kulzer; SDR, Dentsply Caulk; Tetric N-Ceram Bulk Fill, Ivoclar vivadent; SonicFill, Kerr) and two regular resin composites (Charisma flow, Heraeus Kulzer; Tetric N-Ceram, Ivoclar vivadent) were used. Sixty acrylic cylindrical molds were prepared for each thickness (2, 3 and 4 mm). The molds were divided into six groups for resin composites. The microhardness was measured on the top and bottom surfaces, and the colors were measured using Commission Internationale d'Eclairage (CIE)
L *a *b * system. Color differences according to the thickness and translucency parameters and the correlations between the microhardness and translucency parameter were analyzed. The microhardness and color differences were analyzed by ANOVA and Scheffe'spost hoc test, and a studentt -test, respectively. The level of significance was set to α = 0.05.Results The microhardness decreased with increasing resin thickness. The bulk-fill resin composites showed a bottom/top hardness ratio of almost 80% or more in 4 mm thick specimens. The highest translucency parameter was observed in Venus Bulk Fill. All resin composites used in this study except for Venus Bulk Fill showed linear correlations between the microhardness and translucency parameter according to the thickness.
Conclusions Within the limitations of this study, the bulk-fill resin composites used in this study can be placed and cured properly in the 4 mm bulk.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of Bonding Strategies on the Fracture Resistance and Failure Mode of CAD/CAM Resin Composite Overlays Following Simulated Aging: An In Vitro Comparison
Ali A. Elkaffas, Abdullah Alshehri, Ali R. Alqahtani, Yara Ibrahim, Mohamed Atef Elkholy, Patricia Pereira, Saleh Alhindi
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Fracture resistance of five intra-orifice barriers in endodontically treated mandibular premolars: An in vitro study
İrfan Yüksekkaya, Uğur Aydın, Oğuz Çetinkaya, Emre Çulha
Vojnosanitetski pregled.2026; 83(1): 49. CrossRef - Experimental study of polishing systems on surface roughness and color stability of novel bulk-fill composite resins
Seda Nur Karakaş, Sevde Gül Batmaz, Volkan Çiftçi, Cihan Küden
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Color Change in Commercial Resin Composites with Different Photoinitiators
Feng Gao, David W. Berzins
Bioengineering.2025; 12(10): 1047. CrossRef - Fracture resistance of milled and 3D printed ultra-thin occlusal veneers made of CAD/CAM resin-based ceramics cemented by variable luting approaches
Ali A. Elkaffas, Abdullah Alshehri, Abdullah Ali Alqahtani, Abdulellah F. Almudahi, Khalid K. Alanazi, Feras Abdulqader Alhalabi, Mohammed Ali Abuelqomsan, Ali R. Alqahtani
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - COLOUR STABILITY OF COMPOSITE RESINS IN THE PRESENCE OF HERBAL TEAS: A SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC STUDY
GOWRISH S., VANDANA SADANANDA, MURTAZA HATIM ZAKIYUDDIN
International Journal of Applied Pharmaceutics.2025; : 308. CrossRef - Comparison of Color Stability Between Single-Layer Bulk-Fill Composites and Bilayer Conventional and Bulk-Fill Composites
Hyunduk Kim, Hyuntae Kim, Ji-Soo Song, Mohammad AlQarni, Mohammad Alkeshan, Teo Jeon Shin, Young-Jae Kim, Jung-Wook Kim, Ki-Taeg Jang, Hong-Keun Hyun
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2025; 52(3): 266. CrossRef - Surface roughness of flowable bulk fill composite resin by different polishing protocols
Youn-Su Choi, Youngmin Kwon, Jin-Woo Kim, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho
Journal of Dental Rehabilitation and Applied Science.2025; 41(3): 188. CrossRef - The effect of polishing pastes on the surface roughness, microhardness, gloss, and color change of resin composites
Murat Büyükpolat, Numan Aydın, Bilge Eryılmaz, Serpil Karaoğlanoğlu, Bilge Ersöz
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictors of procedural errors in class II resin composite restorations using bitewing radiographs
Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad, Nawaf AlGhamdi, Mohammed Alqahtani, Osama A. Alsulaiman, Ali Alshammari, Malik J. Farraj, Ahmed A. Alsulaiman
The Saudi Dental Journal.2024; 36(4): 638. CrossRef - Evaluation of Surface Roughness and Microhardness of Bulk-fill and Nanohybrid Composite after Exposure to Different Beverages at Various Time Intervals – An In vitro Study
Sachin Bengal, Gautam P. Badole, Pratima R. Shenoi, Rajesh Kubde, Shriya Shahu
Annals of African Medicine.2024; 23(3): 466. CrossRef - Influence of Light‐Curing Time and Increment Thickness on the Properties of Bulk Fill Composite Resins With Distinct Application Systems
Carlos Rocha Gomes Torres, Taiana Paola Prado, Daniele Mara da Silva Ávila, Cesar Rogério Pucci, Alessandra Bühler Borges, Heng Bo Jiang
International Journal of Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Preheating effect on microhardness and depth of cure of three bulk-fill composite resins: An in vitro study
Aashna Sunil Sahetia, Divya Rupesh Jain, Padmaja Panditrao Sirsat, Meenal N. Gulve, Swapnil J. Kolhe, Surbhi P. Patel
Endodontology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical Longevity of Sonicated and Unsonicated Composite Resin Restorations in Posterior Permanent Teeth: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Lorrane Salvador de Mello, Fabiola Fontes Galdino, Jayzon Stephan Brooks, Tatiana Kelly da Silva Fidalgo, Kátia Rodrigues Reis
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Translucency of bulk‐fill composite materials: A systematic review
Gaetano Paolone, Sofia Baldani, Niccolò De Masi, Mauro Mandurino, Giacomo Collivasone, Nicola Scotti, Enrico Gherlone, Giuseppe Cantatore
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2024; 36(7): 995. CrossRef - Assessment of Microhardness of Bulk-Fill Class II Resin Composite Restorations Performed by Preclinical Students: An In Vitro Study
Ali Abdel-Halim Abdel-Azim Hassan, Abdulelah Sameer Sindi, Abeer Mohamed Atout, Mohamed SM Morsy, Khurshid A. Mattoo, Vishnu Teja Obulareddy, Ankita Mathur, Vini Mehta
European Journal of General Dentistry.2024; 13(02): 158. CrossRef - Effect of Indenter Load on Vickers Microhardness and Indentation Depth of One Resin Composite
Richard B. Price, Braden Sullivan
Materials.2024; 17(24): 6156. CrossRef - The Effect of Layer Thickness and Light Intensity on the Degree of Conversion, Microhardness and Cytotoxicity of Bulk Fill Composite Resins
Sevde Gül BATMAZ, Ayşe DÜNDAR, Çağatay BARUTÇUGİL
Clinical and Experimental Health Sciences.2023; 13(4): 795. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of the Color Stability and Clinical performance of bulk-filled composites: A Split-mouth Randomized Controlled Trial
Karuna YM, Srikant N, Kundabala M, Anupama Nayak P, Ashwin Rao, Maimoona TM
Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology.2023; : 5091. CrossRef - Effect of Using Manufacturer-recommended Exposure Times to Photo-activate Bulk-fill and Conventional Resin-based Composites
LM Barcelos, SSL Braga, RAS Pereira, RB Price, CJ Soares
Operative Dentistry.2023; 48(3): 304. CrossRef - Effect of Different Polymerization Times on Color Change, Translucency Parameter, and Surface Hardness of Bulk-Fill Resin Composites
HY Gonder, M Fidan
Nigerian Journal of Clinical Practice.2022; 25(10): 1751. CrossRef - The effect of contemporary finishing and polishing systems on the surface roughness of bulk fill resin composite and nanocomposites
Seda Gömleksiz, Oğuzhan Gömleksiz
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2022; 34(6): 915. CrossRef - Evaluation of the microleakage in class II cavities restored with composite resin by using different placement techniques and light cure units– An in vitro study
Swathi Miskin, Chandrasekhar Manduru, Nagalakshmi Reddy Sampathi, Upendranatha Reddy Nagireddy, Sujayeendranatha Reddy E, Sushma Chandra
International Dental Journal of Student's Research.2022; 10(2): 53. CrossRef - Comparison of mechanical and optical properties of a newly marketed universal composite resin with contemporary universal composite resins: An in vitro study
Sevil Gurgan, Uzay Koc Vural, Ivana Miletic
Microscopy Research and Technique.2022; 85(3): 1171. CrossRef - Effect of Additional Light Curing on Colour Stability of Composite Resins
Kubra Alan Unsal, Emel Karaman
International Dental Journal.2022; 72(3): 346. CrossRef - Evaluation of Glass-Ionomer versus Bulk-Fill Resin Composite: A Two-Year Randomized Clinical Study
İlhan Uzel, Arzu Aykut-Yetkiner, Nazan Ersin, Fahinur Ertuğrul, Elif Atila, Mutlu Özcan
Materials.2022; 15(20): 7271. CrossRef - Awareness and Utilization of Bulk-Fill Composites among Dental Practitioners in Saudi Arabia
Hani M. Nassar, Ensanya A. Abou Neel
The Open Dentistry Journal.2021; 15(1): 160. CrossRef - Dental Bulk-Fill Resin Composites Polymerization Efficiency: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Reem Ajaj, Nada Farsi, Lama Alzain, Nour Nuwaylati, Raneem Ghurab, Hani Nassar
Journal of Composites Science.2021; 5(6): 149. CrossRef - Handling and Mechanical Properties of Low-viscosity Bulk-fill Resin Composites
E Hirokane, T Takamizawa, T Tamura, S Shibasaki, A Tsujimoto, WW Barkmeier, MA Latta, M Miyazaki
Operative Dentistry.2021; 46(5): E185. CrossRef - Utilizing Light Cure Units: A Concise Narrative Review
Fatin A. Hasanain, Hani M. Nassar
Polymers.2021; 13(10): 1596. CrossRef - The Effect of Different Dietary and Therapeutic Solutions on the Color Stability of Resin-Matrix Composites Used in Dentistry: An In Vitro Study
Lígia Lopes-Rocha, José Manuel Mendes, Joana Garcez, Ana Góis Sá, Teresa Pinho, Júlio C. M. Souza, Orlanda Torres
Materials.2021; 14(21): 6267. CrossRef - Fracture resistance of endodontically treated premolars restored with bulk-fill composite resins
Fereshteh Shafiei, Paria Dehghanian, Nasibeh Ghaderi, Maryam Doozandeh
Dental Research Journal.2021; 18(1): 60. CrossRef - Mechanical properties of low and regular viscosity bulk fill composites in a 3D dentin cavity model
Rodolfo Xavier Sousa-Lima, Ana Margarida dos Santos Melo, Lílian Karine Cardoso Guimarães, Rodrigo Othávio de Assunção e Souza, Marília Regalado Galvão Rabelo Caldas, Isauremi Vieira de Assunção, Boniek Castillo Dutra Borges
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2021; 35(3): 325. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of the strength characteristics of light polymerization polymers for dental restoration using the acoustic emission method. Fractographic studies of the surface and fractures of the samples: part two
V. Kukhta, V. Makeev, O. Kyrmanov, V. Skalsky, O. Stankevich
SUCHASNA STOMATOLOHIYA.2021; 109(5): 23. CrossRef - Impact of light-cure protocols on the porosity and shrinkage of commercial bulk fill dental resin composites with different flowability
Daina Dayana Arenas Buelvas, João Felipe Besegato, Bruno Luiz Santana Vicentin, Eduardo Inocente Jussiani, Márcio Grama Hoeppner, Avacir Casanova Andrello, Eduardo Di Mauro
Journal of Polymer Research.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of time on the post-irradiation curing of six resin-based composites
Christina Kaiser, Richard Bengt Price
Dental Materials.2020; 36(8): 1019. CrossRef The Effects of Irradiance on Translucency and Surface Gloss of Different Bulk-Fill Composite Resins: An in vitro Study
Abrar N Bin Nooh, Hend Al Nahedh, Mohammad AlRefeai, Fahad AlKhudhairy
Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dentistry.2020; Volume 12: 571. CrossRef- Color Stability and Micro-Hardness of Bulk-Fill Composite Materials after Exposure to Common Beverages
Nora Bahbishi, Waad Mzain, Bayan Badeeb, Hani M. Nassar
Materials.2020; 13(3): 787. CrossRef - Polymerization Stress and Gap Formation of Self-adhesive, Bulk-fill and Flowable Composite Resins
EL Nakano, ASC de Souza, LCC Boaro, LH Catalani, RR Braga, F Gonçalves
Operative Dentistry.2020; 45(6): E308. CrossRef - Varying the Polishing Protocol Influences the Color Stability and Surface Roughness of Bulk-Fill Resin-Based Composites
Filipa Freitas, Teresa Pinheiro de Melo, António HS Delgado, Paulo Monteiro, João Rua, Luís Proença, Jorge Caldeira, Ana Mano Azul, José João Mendes
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2020; 12(1): 1. CrossRef - Characterization and Comparative Analysis of Voids in Class II Composite Resin Restorations by Optical Coherence Tomography
CA Pardo Díaz, CAK Shimokawa, CS Sampaio, AZ Freitas, ML Turbino
Operative Dentistry.2020; 45(1): 71. CrossRef - Clinical performance and chemical-physical properties of bulk fill composites resin —a systematic review and meta-analysis
Leticia Cristina Cidreira Boaro, Diana Pereira Lopes, Andréia Santos Caetano de Souza, Ellea Lie Nakano, Mirko Dennys Ayala Perez, Carmem Silvia Pfeifer, Flávia Gonçalves
Dental Materials.2019; 35(10): e249. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Polymerization Depth of Bulk Fill Resin Composites Polymerized by Different Procedures: An In-Vitro Study
Esra ÖZYURT, Aysegul KURT, Handan YILDIRIM
Clinical and Experimental Health Sciences.2019; 9(4): 304. CrossRef - Internal adaptation of composite restorations with or without an intermediate layer: Effect of polymerization shrinkage parameters of the layer material
Seung-Hoon Han, Alireza Sadr, Yasushi Shimada, Junji Tagami, Sung-Ho Park
Journal of Dentistry.2019; 80: 41. CrossRef - Color Stability of Bulk-Fill Resin Composites after Immersion in Different Media
Sungkyoon Kang, Jihyun Song
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2019; 46(4): 353. CrossRef - Degree of Conversion and Polymerization Shrinkage of Low Shrinkage Bulk-Fill Resin Composites
Haidy N. Salem, Sherif M. Hefnawy, Shaymaa M. Nagi
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2019; 10(3): 465. CrossRef - Bulk-Fill Composites: Effectiveness of Cure With Poly- and Monowave Curing Lights and Modes
JK Gan, AU Yap, JW Cheong, N Arista, CBK Tan
Operative Dentistry.2018; 43(2): 136. CrossRef - Depth of cure of bulk fill resin composites: A systematic review
Renally Bezerra Wanderley Lima, Cristhian Camilo Madrid Troconis, Marina Barrêto Pereira Moreno, Fabián Murillo‐Gómez, Mario Fernando De Goes
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2018; 30(6): 492. CrossRef - Influence of Bulk Thickness, Curing Time, and Curing Unit Type on the Microhardness of Different-Viscosity Bulk-Fill Composites
M. Saipullaev, U. Erdemir, E. Yildiz
Mechanics of Composite Materials.2018; 54(5): 675. CrossRef - Color of bulk‐fill composite resin restorative materials
Çağatay Barutcigil, Kubilay Barutcigil, Mehmet Mustafa Özarslan, Ayşe Dündar, Burak Yilmaz
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Incremental and Bulk-fill Techniques With Bulk-fill Resin Composite in Different Cavity Configurations
S-H Han, S-H Park
Operative Dentistry.2018; 43(6): 631. CrossRef - Surface changes of various bulk‐fill resin‐based composites after exposure to different food‐simulating liquid and beverages
Saijai Tanthanuch, Boonlert Kukiattrakoon, Kasidit Eiam‐O‐Pas, Kan Pokawattana, Nicha Pamanee, Wichachon Thongkamkaew, Asok Kochatung
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2018; 30(2): 126. CrossRef - Impact of 35% Hydrogen Peroxide on Color and Translucency Changes in Enamel and Dentin
Rebeca Pereira de Menezes, Paula Damasceno Silva, Pollyana Caldeira Leal, André Luis Faria-e-Silva
Brazilian Dental Journal.2018; 29(1): 88. CrossRef - A comparative study of bulk-fill composites: degree of conversion, post-gel shrinkage and cytotoxicity
Flávia Gonçalves, Luiza Mello de Paiva Campos, Ezequias Costa Rodrigues-Júnior, Fabrícia Viana Costa, Pamela Adeline Marques, Carlos Eduardo Francci, Roberto Ruggiero Braga, Letícia Cristina Cidreira Boaro
Brazilian Oral Research.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of cytotoxicity test models for evaluating resin-based composites
SM Lim, AUJ Yap, CSL Loo, J Ng, CY Goh, CHL Hong, WS Toh
Human & Experimental Toxicology.2017; 36(4): 339. CrossRef - Comparison of Internal Adaptation in Class II Bulk-fill Composite Restorations Using Micro-CT
SH Han, SH Park
Operative Dentistry.2017; 42(2): 203. CrossRef - Color stability of bulk-fill and incremental-fill resin-based composites polished with aluminum-oxide impregnated disks
Uzay Koc-Vural, Ismail Baltacioglu, Pinar Altinci
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2017; 42(2): 118. CrossRef - Evaluation of bulk-fill resin composite on the shear bond strength of metal brackets
Mi-Gyoung Park
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2017; 44(2): 95. CrossRef - Effect of water storage on flexural strength of silorane and methacrylate-based composite resins
Narges Panahandeh, Hassan Torabzadeh, Hani Naderi, Seyedeh Mahsa Sheikh-Al-Eslamian
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2017; 42(4): 309. CrossRef - Shear bond strength of different dentin substitute restorative materials to dentin of primary teeth
Faika ABDELMEGID, Fouad SALAMA, Nawaf ALBOGAMI, Muhannad ALBABTAIN, Abdulkareem ALQAHTANI
Dental Materials Journal.2016; 35(5): 782. CrossRef - Internal adaptation of resin composites at two configurations: Influence of polymerization shrinkage and stress
Seung-Hoon Han, Alireza Sadr, Junji Tagami, Sung-Ho Park
Dental Materials.2016; 32(9): 1085. CrossRef - Effect of a broad-spectrum LED curing light on the Knoop microhardness of four posterior resin based composites at 2, 4 and 6-mm depths
Maan M. ALShaafi, Thomas Haenel, Braden Sullivan, Daniel Labrie, Mohammed Q. Alqahtani, Richard B. Price
Journal of Dentistry.2016; 45: 14. CrossRef - Influence of increment thickness on light transmission, degree of conversion and micro hardness of bulk fill composites
Sufyan Garoushi, Pekka Vallittu, Akikazu Shinya, Lippo Lassila
Odontology.2016; 104(3): 291. CrossRef - Criteria for clinical translucency evaluation of direct esthetic restorative materials
Yong-Keun Lee
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(3): 159. CrossRef - The effect of different drinks on the color stability of different restorative materials after one month
Neslihan Tekçe, Safa Tuncer, Mustafa Demirci, Merve Efe Serim, Canan Baydemir
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(4): 255. CrossRef
- Influence of Bonding Strategies on the Fracture Resistance and Failure Mode of CAD/CAM Resin Composite Overlays Following Simulated Aging: An In Vitro Comparison
- 2,302 View
- 21 Download
- 65 Crossref

- Effect of intracanal medicaments used in endodontic regeneration procedures on microhardness and chemical structure of dentin
- Ghaeth Hamdon Yassen, George Joseph Eckert, Jeffrey Allen Platt
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(2):104-112. Published online December 24, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.2.104
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study was performed to investigate the effects of different intracanal medicaments on chemical structure and microhardness of dentin.
Materials and Methods Fifty human dentin discs were obtained from intact third molars and randomly assigned into two control groups and three treatment groups. The first control group received no treatment. The second control group (no medicament group) was irrigated with sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl), stored in humid environment for four weeks and then irrigated with ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA). The three treatment groups were irrigated with NaOCl, treated for four weeks with either 1 g/mL triple antibiotic paste (TAP), 1 mg/mL methylcellulose-based triple antibiotic paste (DTAP), or calcium hydroxide [Ca(OH)2] and finally irrigated with EDTA. After treatment, one half of each dentin disc was subjected to Vickers microhardness (
n = 10 per group) and the other half was used to evaluate the chemical structure (phosphate/amide I ratio) of treated dentin utilizing attenuated total reflection Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (n = 5 per group). One-way ANOVA followed by Fisher's least significant difference were used for statistical analyses.Results Dentin discs treated with different intracanal medicaments and those treated with NaOCl + EDTA showed significant reduction in microhardness (
p < 0.0001) and phosphate/amide I ratio (p < 0.05) compared to no treatment control dentin. Furthermore, dentin discs treated with TAP had significantly lower microhardness (p < 0.0001) and phosphate/amide I ratio (p < 0.0001) compared to all other groups.Conclusions The use of DTAP or Ca(OH)2 medicaments during endodontic regeneration may cause significantly less microhardness reduction and superficial demineralization of dentin compared to the use of TAP.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effects of Sodium Dichloroisocyanurate and Calcium Hydroxide as Intracanal Medicaments on Microhardness and Fracture Resistance of Dentin: An In Vitro Study
Fereshte Sobhnamayan, Alireza Adl, Negin Firouzi, Saeed Moravej, Samina Gavahianjahromi
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of allicin-incorporated graphene oxide hydrogel on dentin microhardness
Rathna Piriyanga, Manish Ranjan, Anand Sherwood, Mohammad Fareed, Mohmed Isaqali Karobari
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Recent Advances in Injectable Hydrogel Biotherapeutics for Regenerative Dental Medicine
Renan Dal‐Fabbro, Arwa Daghrery, Caroline Anselmi, Igor Paulino M. Soares, Alexandre Henrique dos Reis‐Prado, Pedro Henrique Chaves de Oliveira, Marco C. Bottino
Macromolecular Bioscience.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Ex vivo analysis of clindamycin’s impact on dentin microhardness and surface chemistry
Mandana Naseri, Farshid Gholami, Kamyar Khosravi, Mohammadreza Vatankhah, Mohammad Atai, Omid Dianat
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(10): 982. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of effect of modified triple antibiotic paste and calcium hydroxide as intracanal medicament on microhardness of root dentin: An in vitro study
Aparna Palekar, Piyush Mantri, Minal Awinashe, Basawaraj Biradar, Mukund Singh
Endodontology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Use of Nanofibers in Regenerative Endodontic Therapy—A Systematic Review
Sebastian Candrea, Alexandrina Muntean, Anida-Maria Băbțan, Antonia Boca, Claudia Nicoleta Feurdean, Ioana Roxana Bordea, Adina Bianca Boșca, Aranka Ilea
Fibers.2024; 12(5): 42. CrossRef - Effect of sodium hypochlorite and ethylenediaminotetraacetic acid activated by laser and ultrasonic energy on surface morphology and chemical composition of intracanal dentin
Adriana Katunarić, Sandra Flinčec Grgac, Dragana Gabrić, Božidar Pavelić, Ivona Bago
Microscopy Research and Technique.2024; 87(4): 818. CrossRef - Development of a Thermoresponsive Core–Shell Hydrogel for Sequential Delivery of Antibiotics and Growth Factors in Regenerative Endodontics
Sayna Shamszadeh, Saeed Asgary, Mohammad Akrami, Fatemeh Mashhadiabbas, Alireza Akbarzadeh Baghban, Forough Shams
Frontiers in Bioscience-Elite.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Intracanal medicaments and coronal sealing materials influence on root fracture resistance and coronal discoloration: An in vitro study
Rasoul Sahebalam, Marzie Boskabady, Maryam Naghavi, Samira Dehghanitafti
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2024; 14(2): 199. CrossRef - Final irrigation with bioglass solution in regenerative endodontic procedure induces tissue formation inside the root canals, collagen maturation, proliferation cell and presence of osteocalcin
Kiani dos Santos de Paula, Alexandre Henrique dos Reis‐Prado, Witalo Pereira de Jesus, Juliana Goto, Lara Cancella de Arantes, Marina Verçosa, Luciano Tavares Angelo Cintra, Edilson Ervolino, Raphael Escorsim Szawka, Murilo Camuri Crovace, Ricardo Alves d
International Endodontic Journal.2024; 57(5): 586. CrossRef - In vitro analysis of compressive strength of root dentin on application of intracanal medicaments for different time periods
Kushal Kumar Ghosh, Sayantan Mukherjee, Paromita Mazumdar, Sahil Ali, Lovely Das
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(12): 1289. CrossRef - Effects of endodontic root canal irrigants on tooth dentin revealed by infrared spectroscopy: a systematic literature review
Hamza Elfarraj, Franco Lizzi, Kerstin Bitter, Paul Zaslansky
Dental Materials.2024; 40(8): 1138. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of antimicrobial efficacy of triple antibiotic paste and propolis extract using three different vehicles as intracanal medicament: An in vitro study
Gunde Veronica, B. V Thimma Reddy, Uday K. Chowdary Birapu, Raghavendra K. Jadadoddi, R Hemanth Kumar, Kanamarlapudi V. Saikiran
Journal of Dr. NTR University of Health Sciences.2024; 13(4): 323. CrossRef - Outcome of Regenerative Endodontic Procedures in Nonvital Immature Permanent Teeth Using 2 Intracanal Medications: A Prospective Randomized Clinical Study
Aladdin Al-Qudah, Mohammad Almomani, Layla Hassoneh, Lama Awawdeh
Journal of Endodontics.2023; 49(7): 776. CrossRef - The Effect of Calcium Hydroxide, Triple Antibiotic Paste and Chlorhexidine on Pain in Teeth with Symptomatic Apical Periodontitis: A Randomised Controlled Trial
Asma Munir Khan, Irfana Khursheed Ahmed Gangoo, Naila Amir Ali, Mansoor Khan, Muhammad Qasim Javed, Mustafa Hussein AlAttas, Ayman M. Abulhamael, Hammam Ahmed Bahammam, Loai Alsofi, Rayan Suliman Al Yahya
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(4): 3091. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of the depth of penetration and postoperative pain associated with the use of continuous chelation using HEBP and standard irrigation protocol in the endodontic treatment of adult permanent nonvital teeth: A randomized controlled tr
Janhvi Samir Parekh, Mrunalini J. Vaidya, Vibha R. Hegde
Endodontology.2023; 35(4): 344. CrossRef - Regenerative Endodontics and Minimally Invasive Dentistry: Intertwining Paths Crossing Over Into Clinical Translation
Hisham Elnawam, Menatallah Abdelmougod, Ahmed Mobarak, Mai Hussein, Hamdy Aboualmakarem, Michael Girgis, Rania El Backly
Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of calcium hydroxide on fracture resistance and microhardness of dentin in human teeth
Simar Sethi, Alpa Gupta, Ansy Hanna Kurian, Dax Abraham, Parul Chauhan, Kritika Aneja, Sucheta Jala, Arundeep Singh
Endodontology.2022; 34(4): 223. CrossRef - Evaluation of Effects of Various Irrigating Solutions on Chemical Structure of Root Canal Dentin Using FTIR, SEM, and EDS: An In Vitro Study
Indu Padmakumar, Dharam Hinduja, Abdul Mujeeb, Raghu Kachenahalli Narasimhaiah, Ashwini Kumar Saraswathi, Mubashir Baig Mirza, Ali Robaian, Syed Nahid Basheer, Mohmed Isaqali Karobari, Giuseppe Alessandro Scardina
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2022; 13(4): 197. CrossRef - The Effects of Double Antibiotic Paste and Amoxicillin-clavulanate Paste Used in Endodontic Regeneration on Microhardness of Radicular Dentine: An In vitro Study
Meenu Madhukumar, Praveena Geetha, K. Radhakrishnan Nair, Manu Unnikrishnan
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2021; 13(Suppl 1): S510. CrossRef - The effect of intracanal medication variations on microhardness of simulated immature root dentin
Pınar Serdar Eymirli, Ayhan Eymirli, Emel Uzunoğlu Özyürek
Australian Endodontic Journal.2021; 47(3): 616. CrossRef - Antibacterial Effect and Bioactivity of Innovative and Currently Used Intracanal Medicaments in Regenerative Endodontics
Sarah Alfadda, Theeb Alquria, Eda Karaismailoglu, Hacer Aksel, Adham A. Azim
Journal of Endodontics.2021; 47(8): 1294. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Effect of Nitrofurantoin Paste as an Intracanal Medicament on the Chemical Structure of Radicular Dentine
Mewan Abdulrahman, Bestoon Faraj, Kawa Dizaye
Sulaimani Dental Journal.2021; 8(2): 8. CrossRef - Effect of hydrogel-based antibiotic intracanal medicaments on crown discoloration
Rayan B. Yaghmoor, Jeffrey A. Platt, Kenneth J. Spolnik, Tien Min Gabriel Chu, Ghaeth H. Yassen
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Microhardness and Fracture Resistance of Radicular Dentin Treated with Different Concentrations of Calcium Hydroxide in Endodontic Regeneration Procedures
Sara N. Hashem, Maha Adel Elhousiny
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.2021; 9(D): 324. CrossRef - Effect of medicaments used in endodontic regeneration on the morphological characteristics of bovine radicular dentin: Experimental immature tooth model
Maira C. Conte, Cleonice da Silveira Teixeira, Eduardo A. Bortoluzzi, Wilson T. Felippe, Luciane G. P. dos Santos, Mariana T. Pandolfo, Patrícia da Agostim Cancelier, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
Microscopy Research and Technique.2020; 83(4): 354. CrossRef - Effect of intracanal medicaments on radicular dentine: An attenuated total reflection-Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy analysis
Promila Verma, Afsana Ansari, Aseem Prakash Tikku, Anil Chandra, Rakesh Kumar Yadav, Ramesh Bharti, Rhythm Bains
Asian Journal of Oral Health and Allied Sciences.2020; 10: 3. CrossRef - Effect of Hydrogel-Based Antibiotic Intracanal Medicaments on Push-Out Bond Strength
Rayan B. Yaghmoor, Jeffrey A. Platt, Kenneth J. Spolnik, Tien Min Gabriel Chu, Ghaeth H. Yassen
European Journal of Dentistry.2020; 14(04): 575. CrossRef - Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Enterococcus faecalis Isolated From Root Canal: An In Vitro Study
Nazanin Zargar, Mohammad J Nasiri, Hengameh Ashraf, Bahareh Hajikhani, Shirin Etminani Esfahani, Maryam Etminani Esfahani
Avicenna Journal of Pharmaceutical Research.2020; 1(2): 60. CrossRef - The Effect of Calcium Hydroxide and Nano–calcium Hydroxide on Microhardness and Superficial Chemical Structure of Root Canal Dentin: An Ex Vivo Study
Mandana Naseri, Leila Eftekhar, Farshid Gholami, Mohammad Atai, Omid Dianat
Journal of Endodontics.2019; 45(9): 1148. CrossRef - Antimicrobial efficacy of clindamycin and triple antibiotic paste as root canal medicaments on tubular infection: An in vitro study
Nazanin Zargar, Motahare Rayat Hosein Abadi, Mohammad Sabeti, Zahra Yadegari, Alireza Akbarzadeh Baghban, Omid Dianat
Australian Endodontic Journal.2019; 45(1): 86. CrossRef - Influence of silver nanoparticle solution on the mechanical properties of resin cements and intrarradicular dentin
Thaís Yumi Umeda Suzuki, Juno Gallego, Wirley Gonçalves Assunção, André Luiz Fraga Briso, Paulo Henrique dos Santos, Chun-Pin Lin
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(6): e0217750. CrossRef - Triple antibiotic paste: momentous roles and applications in endodontics: a review
Ardavan Parhizkar, Hanieh Nojehdehian, Saeed Asgary
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Retention of BioAggregate and MTA as coronal plugs after intracanal medication for regenerative endodontic procedures: an ex vivo study
Suzan Abdul Wanees Amin, Shaimaa Ismail Gawdat
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) application chemical characterization of enamel, dentin and bone
Camila de Carvalho Almança Lopes, Pedro Henrique Justino Oliveira Limirio, Veridiana Resende Novais, Paula Dechichi
Applied Spectroscopy Reviews.2018; 53(9): 747. CrossRef - Chlorhexidine Prevents Root Dentine Mineral Loss and Fracture Caused by Calcium Hydroxide over Time
Michael Ranniery Garcia Ribeiro, Érika Bárbara Abreu Fonseca Thomaz, Darlon Martins Lima, Tarcísio Jorge Leitão, José Bauer, Soraia De Fátima Carvalho Souza
International Journal of Dentistry.2017; 2017: 1. CrossRef - Attachment and proliferation of dental pulp stem cells on dentine treated with different regenerative endodontic protocols
M. A. Alghilan, L. J. Windsor, J. Palasuk, G. H. Yassen
International Endodontic Journal.2017; 50(7): 667. CrossRef - Second-generation Platelet Concentrate (Platelet-rich Fibrin) as a Scaffold in Regenerative Endodontics: A Case Series
Hengameh Bakhtiar, Shahram Esmaeili, Setareh Fakhr Tabatabayi, Mohammad Reza Ellini, Mohammad Hossein Nekoofar, Paul M.H. Dummer
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(3): 401. CrossRef - Antibacterial Effects of Antimicrobials Used in Regenerative Endodontics against Biofilm Bacteria Obtained from Mature and Immature Teeth with Necrotic Pulps
Jordon C. Jacobs, Alex Troxel, Ygal Ehrlich, Kenneth Spolnik, Josef S. Bringas, Richard L. Gregory, Ghaeth H. Yassen
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(4): 575. CrossRef - Triple Antibiotic Polymer Nanofibers for Intracanal Drug Delivery: Effects on Dual Species Biofilm and Cell Function
Divya Pankajakshan, Maria T.P. Albuquerque, Joshua D. Evans, Malgorzata M. Kamocka, Richard L. Gregory, Marco C. Bottino
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(10): 1490. CrossRef - Inhibitory effect of gels loaded with a low concentration of antibiotics against biofilm formation by Enterococcus faecalis and Porphyromonas gingivalis
Amnah A. Algarni, Ghaeth H. Yassen, Richard L. Gregory
Journal of Oral Science.2015; 57(3): 213. CrossRef
- The Effects of Sodium Dichloroisocyanurate and Calcium Hydroxide as Intracanal Medicaments on Microhardness and Fracture Resistance of Dentin: An In Vitro Study
- 2,451 View
- 26 Download
- 41 Crossref

- Surface microhardness of three thicknesses of mineral trioxide aggregate in different setting conditions
- Noushin Shokouhinejad, Leila Jafargholizadeh, Mehrfam Khoshkhounejad, Mohammad Hossein Nekoofar, Maryam Raoof
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(4):253-257. Published online August 20, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.4.253
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to compare the surface microhardness of mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) samples having different thicknesses and exposed to human blood from one side and with or without a moist cotton pellet on the other side.
Materials and Methods Ninety cylindrical molds with three heights of 2, 4, and 6 mm were fabricated. In group 1 (dry condition), molds with heights of 2, 4, and 6 mm (10 molds of each) were filled with ProRoot MTA (Dentsply Tulsa Dental), and the upper surface of the material was not exposed to any additional moisture. In groups 2 and 3, a distilled water- or phosphate-buffered saline (PBS)-moistened cotton pellet was placed on the upper side of MTA, respectively. The lower side of the molds in all the groups was in contact with human blood-wetted foams. After 4 day, the Vickers microhardness of the upper surface of MTA was measured.
Results In the dry condition, the 4 and 6 mm-thick MTA samples showed significantly lower microhardness than the 2 mm-thick samples (
p = 0.003 andp = 0.001, respectively). However, when a distilled water- or PBS-moistened cotton pellet was placed over the MTA, no significant difference was found between the surface microhardness of samples having the abovementioned three thicknesses of the material (p = 0.210 andp = 0.112, respectively).Conclusions It could be concluded that a moist cotton pellet must be placed over the 4 to 6 mm-thick MTA for better hydration of the material. However, this might not be necessary when 2 mm-thick MTA is used.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of the Effects of Different Irrigation Solutions on MTA and Dentin Microhardness
Gokay Buyukcolpan, İdil Özden, Hesna Sazak Öveçoğlu
Clinical and Experimental Health Sciences.2025; 15(3): 524. CrossRef - Retrograde Versus Orthograde Obturation in Relation to Root Resection: Evaluation of Microhardness of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate In Vitro
Lukas Stundžia, Rita Vėberienė, Indrė Graunaitė, Aurelijus Domeika, Neringa Skučaitė, Cesar Rogério Pucci
International Journal of Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - MTA as modulator of periapical tissue healing in rat molar: A histological study
Christian Khoswanto, Ira Kusuma Dewi
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2024; 14(2): 201. CrossRef - An Update on Endodontic Microsurgery of Mandibular Molars: A Focused Review
Sun Mi Jang, Euiseong Kim, Kyung-San Min
Medicina.2021; 57(3): 270. CrossRef - Assessment of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate Setting in Simulated Root Canal with Different Root Canal Wall Thickness: In Vitro Study
Radovan Žižka, Radim Čtvrtlík, Jan Tomáštík, Kamila Fačevicová, Ondřej Vencálek, Jiří Šedý, David Marinčák
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(4): 1727. CrossRef - Evaluation of the bioactivity of fluoride‐enriched mineral trioxide aggregate on osteoblasts
S. Proksch, J. Brossart, K. Vach, E. Hellwig, M. J. Altenburger, L. Karygianni
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(8): 912. CrossRef - Antimicrobial and antibiofilm activities of MTA supplemented with bismuth lipophilic nanoparticles
Rene HERNANDEZ-DELGADILLO, Casiano DEL ANGEL-MOSQUEDA, Juan Manuel SOLÍS-SOTO, Silvia MUNGUIA-MORENO, Nayely PINEDA-AGUILAR, Rosa Isela SÁNCHEZ-NÁJERA, Shankararaman CHELLAM, Claudio CABRAL-ROMERO
Dental Materials Journal.2017; 36(4): 503. CrossRef - Carbohydrate-electrolyte drinks exhibit risks for human enamel surface loss
Mary Anne Sampaio de Melo, Vanara Florêncio Passos, Juliana Paiva Marques Lima, Sérgio Lima Santiago, Lidiany Karla Azevedo Rodrigues
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(4): 246. CrossRef
- Evaluation of the Effects of Different Irrigation Solutions on MTA and Dentin Microhardness
- 1,455 View
- 9 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Color and hardness changes in artificial white spot lesions after resin infiltration
- Ji-Hoon Kim, Ho-Hyun Son, Juhea Chang
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(2):90-95. Published online May 18, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.2.90
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to determine the effect of resin infiltration technique on color and surface hardness of white spot lesion (WSL) with various degrees of demineralization.
Materials and Methods Ten human upper premolars were cut and divided into quarters with a 3 × 4 mm window on the enamel surface. Each specimens were separated into four groups (
n = 10) and immersed in demineralization solution to create WSL: control, no treatment (baseline); 12 h, 12 hr demineralization; 24 h, 24 hr demineralization; 48 h, 48 hr demineralization. Resin infiltration was performed to the specimens using Icon (DMG). CIEL *a *b * color parameters of the enamel-dentin complex were determined using a spectroradiometer at baseline, after caries formation and after resin infiltration. Surface hardness was measured by Vickers Micro Hardness Tester (Shimadzu, HMV-2). The differences in color and hardness among the groups were analyzed with ANOVA followed by Tukey test.Results Resin infiltration induced color changes and increased the hardness of demineralized enamel. After resin infiltration, there was no difference in color change (Δ
E *) or microhardness among the groups (p < 0.05).Conclusion There was no difference in the effect of resin infiltration on color and hardness among groups with different extents of demineralization.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- In Vitro Evaluation of the Effect of Microabrasion and Resin Infiltration Materials on Enamel Microhardness and Penetration Depth
Elif Ercan Devrimci, İdil Gönüllü, Hande Kemaloğlu, Murat Türkün, Ayşegül Demirbaş
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2026; 17(2): 67. CrossRef - Resin infiltration revolution in minimal invasive treatment – A review
Akancha Kumari, Sonal Gupta, Ashima Varshney, Neha Lal
Journal of Global Oral Health.2025; 8: 124. CrossRef - Effect of CPP-ACPF, resin infiltration, and colloidal silica infiltration on surface microhardness of artificial white spot lesions in primary teeth: An in vitro study
ArantaAvinash Chindane, AnilT Patil, B Sandhyarani
Dental Research Journal.2022; 19(1): 52. CrossRef - IMMEDIATE RESULT OF ICON INFILTRATION IN WHITE SPOT LESIONS CAUSED BY FLUOROSIS: A CASE REPORT
Al-Sadi Abdulaziz Nasser Zain, P.M. Skrypnykov, V.I. Shynkevych, O.A. Pysarenko
Ukrainian Dental Almanac.2022; (2): 34. CrossRef - A comparative evaluation of penetration depth and surface microhardness of Resin Infiltrant, CPP-ACPF and Novamin on enamel demineralization after banding: an in vitro study
Nishita Rana, Namita Singh, Shaila, Abi. M. Thomas, Rajan Jairath
Biomaterial Investigations in Dentistry.2021; 8(1): 64. CrossRef - Spectrophotometric Evaluation of Color Change in Tooth Enamel Defects Using Resin Infiltrate: An In Vivo Study
Anil Gupta, Shikha Dogra, Sakshi Joshi, Vimanyu Kataria, Jyotika Saini, Monika Nagpal, Payal Narula
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2020; 13(2): 150. CrossRef - Effect of Casein Phosphopeptide–amorphous Calcium Phosphate and Calcium Sodium Phosphosilicate on Artificial Carious Lesions: Anin vitroStudy
Iqra Chaudhary, Abhay M Tripathi
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2017; 10(3): 261. CrossRef - Effect of Resin Infiltration on Artificial Caries: Anin vitroEvaluation of Resin Penetration and Microhardness
Deepesh Prajapati, Rashmi Nayak, Deepika Pai, Nagraj Upadhya, Vipin K Bhaskar, Pujan Kamath
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2017; 10(3): 250. CrossRef - Application of quantitative light-induced fluorescence to determine the depth of demineralization of dental fluorosis in enamel microabrasion: a case report
Tae-Young Park, Han-Sol Choi, Hee-Won Ku, Hyun-Su Kim, Yoo-Jin Lee, Jeong-Bum Min
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(3): 225. CrossRef
- In Vitro Evaluation of the Effect of Microabrasion and Resin Infiltration Materials on Enamel Microhardness and Penetration Depth
- 1,531 View
- 12 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Effect of the difference in spectral outputs of the single and dual-peak LEDs on the microhardness and the color stability of resin composites
- Hye-Jung Park, Sung-Ae Son, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Yong-Hoon Kwon, Jeong-Kil Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(2):108-113. Published online March 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.2.108
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives To determine the effect of the spectral output of single and dual-peak light emitting diode (LED) curing lights on the microhardness and color stability of commercial resin composites formulated with camphorquinone and alternative photoinitiators in combination.
Materials and Methods Three light-polymerized resin composites (Z100 (3M ESPE), Tetric Ceram (Ivoclar Vivadent) and Aelite LS Posterior (Bisco)) with different photoinitiator systems were used. The resin composites were packed into a Teflon mold (8 mm diameter and 2 mm thickness) on a cover glass. After packing the composites, they were light cured with single-peak and dual-peak LEDs. The Knoop microhardness (KHN) and color difference (ΔE) for 30 days were measured. The data was analyzed statistically using a student's
t -test (p < 0.05).Results All resin composites showed improved microhardness when a third-generation dual-peak LED light was used. The color stability was also higher for all resin composites with dual-peak LEDs. However, there was a significant difference only for Aelite LS Posterior.
Conclusions The dual-peak LEDs have a beneficial effect on the microhardness and color stability of resin composites formulated with a combination of camphorquinone and alternative photoinitiators.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of irradiance from curing units on the microhardness of composite - a systematic review
Neenu Francis, Rakesh R. Rajan, Vijay Kumar, Anju Varughese, Vineetha Karuveetil, C. M. Sapna
Evidence-Based Dentistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Micro-computed tomography evaluation of volumetric polymerization shrinkage and degree of conversion of composites cured by various light power outputs
Pablo J. ATRIA, Camila S. SAMPAIO, Eduardo CÁCERES, Jessica FERNÁNDEZ, Andre F. REIS, Marcelo GIANNINI, Paulo G. COELHO, Ronaldo HIRATA
Dental Materials Journal.2018; 37(1): 33. CrossRef - Effect of the irradiance distribution from light curing units on the local micro-hardness of the surface of dental resins
Thomas Haenel, Berenika Hausnerová, Johannes Steinhaus, Richard B.T. Price, Braden Sullivan, Bernhard Moeginger
Dental Materials.2015; 31(2): 93. CrossRef - 1,3-Butadiene as an Adhesion Promoter Between Composite Resin and Dental Ceramic in a Dielectric Barrier Discharge Jet
Geum-Jun Han, Sung-No Chung, Bae-Hyeock Chun, Chang-Keun Kim, Kyu Hwan Oh, Byeong-Hoon Cho
Plasma Chemistry and Plasma Processing.2013; 33(2): 539. CrossRef - Optimal combination of 3-component photoinitiation system to increase the degree of conversion of resin monomers
Chang-Gyu Kim, Ho-Jin Moon, Dong-Hoon Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(4): 313. CrossRef
- Effect of irradiance from curing units on the microhardness of composite - a systematic review
- 1,319 View
- 3 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Effect of pre-heating on some physical properties of composite resin
- Myoung Uk Jin, Sung Kyo Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(1):30-37. Published online January 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.1.030
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of pre-heating on some physical properties of composite resin.
Eighty extracted, noncarious human molars were used in the present study. Four different temperatures of composite resin were used: 4℃, 17℃, 48℃, and 56℃. The 4℃ and 17℃ values represented the refrigerator storage temperature and room temperature respectively. For 48℃ and 56℃, composite resin was heated to the temperatures. As physical properties of composite resin, shear bond strength, microhardness, and degree of conversion were measured. The data for each group were subjected to one-way ANOVAs followed by the Tukey's HSD test at 95% confidence level.
Both in enamel and dentin, among composite resin of 4℃, 17℃, 48℃, and 56℃, the pre-heated composite resin up to 56℃ revealed the highest shear bond strength, and pre-heated composite resin to the higher temperature revealed higher shear bond strength.
Microhardness value was also higher with composite resin of higher temperature.
Degree of conversion was also higher with composite resin of the higher temperature.
In this study, it seems that pre-heating composite resin up to the higher temperature may show higher shear bond strength, higher microhardness value, and higher degree of conversion. Therefore, when using composite resin in the clinic, preheating the composite resin could be recommended to have enhanced physical properties of it.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Thermocycling on the Microhardness of Pre-Heated and Non-Heated Zirconium Composite Resin
P. Saloni, Kavitha Sankaran, S. Balaji Ganesh, S. Jayalakshmi, V. Vishnu Priya, R. Gayathri
Journal of International Oral Health.2025; 17(4): 304. CrossRef - Evaluation of Shear Bond Strength of Lithium Disilicate Veneers Using Pre-heated Resin Composite With Two Conventional Resin Cements: An In Vitro Study
Ghalia Akyle, Hassan Achour
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The different effects of preheating and heat treatment on the surface microhardness of nanohybrid resin composite
Brelian Elok Septyarini, Irfan Dwiandhono, Dian N. Agus Imam
Dental Journal.2020; 53(1): 6. CrossRef
- Effect of Thermocycling on the Microhardness of Pre-Heated and Non-Heated Zirconium Composite Resin
- 2,316 View
- 11 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Polymerization of dual cured composites by different thickness
- Yun Ju Kim, Myoung Uk Jin, Sung Kyo Kim, Tae-Yub Kwon, Young Kyung Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(3):169-176. Published online May 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.3.169
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of thickness, filling methods and curing methods on the polymerization of dual cured core materials by means of microhardness test.
Two dual cured core materials, MultiCore Flow (Ivoclar Vivadent AG, Schaan, Liechtenstein) and Bis-Core (Bisco Inc., Schaumburg, IL, USA) were used in this study. 2 mm (bulky filled), 4 mm (bulky filled), 6 mm (bulky and incrementally filled) and 8 mm (bulky and incrementally filled)-thickness specimens were prepared with light cure or self cure mode. After storage at 37℃ for 24 hours, the Knoop hardness values (KHN) of top and bottom surfaces were measured and the microhardness ratio of top and bottom surfaces was calculated. The data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA and Scheffe multiple comparison test, with α = 0.05.
The effect of thickness on the polymerization of dual cured composites showed material specific results. In 2, 4 and 6 mm groups, the KHN of two materials were not affected by thickness. However, in 8 mm group of MultiCore Flow, the KHN of the bottom surface was lower than those of other groups (
p < 0.05). The effect of filling methods on the polymerization of dual cured composites was different by their thickness or materials. In 6 mm thickness, there was no significant difference between bulk and incremental filling groups. In 8 mm thickness, Bis-Core showed no significant difference between groups. However, in MultiCore Flow, the microhardness ratio of bulk filling group was lower than that of incremental filling group (p < 0.05). The effect of curing methods on the polymerization of dual cured composites showed material specific results. In Bis-Core, the KHN of dual cured group were higher than those of self cured group at both surfaces (p < 0.05). However, in MultiCore Flow, the results were not similar at both surfaces. At the top surface, dual cured group showed higher KHN than that of self cured group (p < 0.05). However, in the bottom surface, dual cured group showed lower value than that of self cured group (p < 0.05).-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of polymerization behaviors, microhardness and compressive strength between bulk-fill resin and dual-cured core resin
Hye Jeong Kim, Jiyoung Kwon, Hyun-Jung Kim, Reuben H. Kim, Duck-Su Kim, Ji-Hyun Jang
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of curing modes on micro-hardness of dual-cure resin cements
Ki-Deok Lee, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(2): 132. CrossRef
- Comparison of polymerization behaviors, microhardness and compressive strength between bulk-fill resin and dual-cured core resin
- 2,067 View
- 5 Download
- 2 Crossref

-
The effects of tooth bleaching agents on microhardness of enamel
in situ - Yoon-Woo Park, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(6):470-476. Published online November 30, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.6.470
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The objective of this
in situ study was to evaluate the effects of whitening strip (Claren, LG Household & Health Care Ltd, 2.6% hydrogen peroxide) and gel (Opalescence, Ultradent, 10% carbamide peroxide) on microhardness of enamel in comparison with untreated control. Extracted twenty human upper incisors were disinfected, cleaned, and labial side of each incisor sectioned into 3 fragments by 2 × 2 mm size. After sectioning, labial sides of fragments were flattened and fixed to orthodontic bracket using flowable composite resin. Specimens prepared from each tooth were attached to the labial side of upper incisors of twenty volunteers one by one and treated by three different methods: (1) untreated control (2) treated with whitening strip for 14 days (3) treated with whitening gel for 14 days.Microhardness (Microhardness tester, Zwick) of each specimen was measured at the baseline of pre-treatment, immediate after bleaching treatment, 14 days after bleaching treatment and Knoop Hardness Number was determined. Microhardness changes of experimental groups were compared.
The results show that tooth whitening strip and gel used in this study does not effect the micro-hardness of enamel during bleaching procedure.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Surface Damage and Bleaching Effect according to the Application Type of Home Tooth Bleaching Applicants
Na-Yeoun Tak, Do-Seon Lim, Hee-Jung Lim, Im-Hee Jung
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2020; 20(4): 252. CrossRef - Effect of the bleaching light on whitening efficacy
Jong-Hyun Park, Hye-Jin Shin, Deok-Young Park, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(2): 95. CrossRef
- Surface Damage and Bleaching Effect according to the Application Type of Home Tooth Bleaching Applicants
- 2,976 View
- 14 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Influence of thickness on the degree of cure of composite resin core material
- Pyoung-Cheol Kwon, Jeong-Won Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(5):352-358. Published online September 30, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.5.352
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to investigate the influence of thickness on the degree of cure of dual-cured composite core.
2, 4, 6, 8 mm thickness Luxacore Dual and Luxacore Self (DMG Inc, Hamburg, Germany) core composites were cured by bulk or incremental filling with halogen curing unit or self-cure mode. The specimens were stored at 37℃ for 24 hours and the Knoop's hardness of top and bottom surfaces were measured.
The statistical analysis was performed using ANOVA and Tukey's test at p = 0.05 significance level.
In self cure mode, polymerization is not affected by the thickness. In Luxacore dual, polymerization of the bottom surface was effective in 2, 4 and 6 (incremental) mm specimens. However the 6 (bulk) and 8 (bulk, incremental) mm filling groups showed lower bottom/top hardness ratio (p < 0.05). Within the limitation of this experiment, incremental filling is better than bulk filling in case of over 4 mm depth, and bulk filling should be avoided.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Strategies for enhancing the shear bond strength using highly acidic universal adhesive and dual-cured composite resin
Sumin Choi, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho, Se-Hee Park, Yoon Lee
Journal of Dental Rehabilitation and Applied Science.2025; 41(1): 11. CrossRef - A Study of Composite Surface Hardness When Cured Using Special Accessories with a Curing Light
Samir Koheil
Dental Research and Management.2020; : 11. CrossRef - Effect of curing modes on micro-hardness of dual-cure resin cements
Ki-Deok Lee, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(2): 132. CrossRef
- Strategies for enhancing the shear bond strength using highly acidic universal adhesive and dual-cured composite resin
- 1,338 View
- 3 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Effect of each light curing units on the microhardness and microleakage of composite resin
- Eu-Jin Jung, Hee-Joo Lee, Bock Hur
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(1):58-65. Published online January 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.1.058
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The objectives of this study was to evaluate current visible light curing units regarding microhardness and microleakage. Fourty samples of composite resin(Z-250, 3M) were cured by different light curing units(Flipo, LOKKI; Credi II, 3M; XL 3000, 3M; Optilux 500,Demetron) in acrylic blocks. Microhardness was measured using a calibrated Vickers indenter on both top and bottom surfaces after 24 hours of storage in air at room temperature. Class V cavities were prepared on buccal and lingual surfaces of fourty extracted human molars. Each margin was on enamel and dentin/cementum. Composite resin(Z-250, 3M) was filled in cavities and cured by four different light curing units(Flipo, LOKKI; Credi II, 3M; XL 3000, 3M; Optilux 500, Demetron).
The results of this syudy were as follows:
Microhardness
1. Flipo showed low microhardness compared to Optilux 500, Credi II significantly in upper surface. Flipo didn't show a significant difference compared to XL 3000.
2. The microhardness resulting from curing with Flipo was lower than that of others on lower surfaces.
Microleakage
1. Dentin margin showed significantly high dye penetration rate than enamel margin in all groups(p<0.05).
2. No significant differences were found on both enamel and dentin margin regarding curing units.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of Surface Microhardness of the Flowable Bulk-Fill Resin and the Packable Bulk-Fill Resin according to Light Curing Time and Distance
Hyung-Min Kim, Moon-Jin Jeong, Hee-Jung Lim, Do-Seon Lim
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2023; 23(2): 123. CrossRef
- Comparison of Surface Microhardness of the Flowable Bulk-Fill Resin and the Packable Bulk-Fill Resin according to Light Curing Time and Distance
- 1,137 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Influence of microhardness and fluoride content of tooth structure by fluoride-containing restorative materials
- Su-Jong Lee, Young-Gon Cho, Jong-Uk Kim, Byung-Cheul Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(1):36-43. Published online January 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.1.036
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare the microhardness and the fluoride content of enamel and dentin around fluoride- or non fluoride-containing restorations. Forty extracted human teeth were used and prepared cervical cavities on proximal surface. Experimental teeth were divided into five groups. Group 1 : Prime & Bond NT and Z100, Group 2 : Prime & Bond NT and F2000, Group 3 : Scotchbond Multi-Purpose and Z100, Group 4 : Scothcbond Multi-purpose and F2000, Group 5 : Fuji II LC. The cavities were filled with dentin adhesives and restorative materials. After each tooth was bisected, one half was tested microhardness and the other half was analyzed the fluoride at the enamel and dentin by an EPMA-WDX device. The results were as follows:
1. There was no statistical difference among the microhardness of enamel surface in all group.
2. The microhardness at dentin of 100 µm point in Group 2 and 20 µm point in Group 4 was lower than that of normal dentin (p>0.05).
3. There was no statistical difference among the fluoride content of enamel surface in all group.
4. The fluoride content at the dentin of 30 µm point in Group 2 and 5 were higher than those at 100 µm and 200 µm point in Group 2 and normal dentin (p<0.05).
5. At the dentin of 30 µm point, Group 2 showed higher fluoride content than Group 1 and 3, and Group 5 showed higher fluoride content than other groups.
- 863 View
- 1 Download

- Polymerization ability of several light curing sources on composite resin
- Hye-Jin Shin, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2003;28(2):156-161. Published online March 31, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.2.156
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study is to evaluate the polymerization ability of three different light sources by microhardness test. Stainless steel molds of 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 mm in thickness of 7 mm in diameter were prepared. The hybrid composite Z100 was packed into the hole of the mold and curing light was activated for designated time. Three different light sources, conventional halogen, light emitting diode, and plasma arc, were used for curing of composite. Two different curing times applied; one is to follow the manufacturer's recommendation and the other is to extend the curing time of LED and plasma arc for balancing the light energy with halogen. Immediately after curing, the Vickers hardness was measured at the bottom of specimen.
The results were as follows.
The composite cured with LED showed equal to higher microhardnesss than halogen.
The composite was cured with plasma arc by manufacturer's recommendation showed lowest microhardness at all thickness. However, when curing time was extended, microhardness was higher than the others.
In conclusion, this study suggested that plasma arc needs properly extended curing time.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Power density of light curing units through resin inlays fabricated with direct and indirect composites
Hoon-Sang Chang, Young-Jun Lim, Jeong-Mi Kim, Sung-Ok Hong
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(5): 353. CrossRef
- Power density of light curing units through resin inlays fabricated with direct and indirect composites
- 1,162 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Mechanical properties and microleakage of composite resin materials cured by variable light intensities
- Seung-Ryul Han, Kyung-San Min, Dong-Hoon Shin
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2003;28(2):134-145. Published online March 31, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.2.134
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Mechanical properties and microleakage of two composites [conventional hybrid type DenFil (VERICOM Co., Anyang, Korea) / micro matrix hybrid type Esthet X (Dentsply Caulk, Milford, DE, U.S.A.)] were evaluated to assess whether variable light intensity curing is better than conventional curing technique.
Curing was done for 40 seconds in two ways of 2 step soft-start technique and 5 step ramping technique. Three kinds of light intensities of 50, 100, 200 mW/cm2 were initially used for 10, 20, 30 seconds each and the maximum intensity of 600 mW/cm2 was used for the rest of curing time in a soft-start curing technique. In a ramping technique, curing was done with the same initial intensities and the light intensity was increased 5 times with the same rate to the maximum intensity of 600 mW/cm2.
After determining conditions that showed no different mechanical properties with conventional technique, Esthet X composite was filled in a class V cavity, which dimension was 4×3×1.5 mm and cured under those conditions.
Microleakage was evaluated in two ways of dye penetration and maximum gap estimation through SEM observation. ANOVA and Spearman's rho test were used to confirm any statistical significance among groups.
The results were as follows:
Several curing conditions of variable light intensities resulted in the similar mechanical properties with a conventional continuous curing technique, except conditions that start curing with an initial light intensity of 50 mW/cm2,
Conventional and ramping techniques were better than soft-start technique in mechanical properties of microhardness and compressive strength.
Soft-start group that started curing with an initial light intensity of 100 mW/cm2 for 10 seconds showed the least dye penetration. Soft-start group that started curing with an initial light intensity of 200 mW/cm2 for 10 seconds showed the smallest marginal gap, if there was no difference among groups.
Soft-start technique resulted in better dye-proof margin than conventional technique (p=0.014) and ramping technique(p=0.002).
There was a very low relationship(p=0.157) between the methods of dye penetration and marginal gap determination through SEM evaluation.
From the results of this study, it was revealed that ramping technique would be better than conventional technique in mechanical properties, however, soft-start technique might be better than conventional one in microleakage.
It was concluded that much endeavor should be made to find out the curing conditions, which have advantages of both aspects or to solve these kinds of problems through a novel idea of polymerization.
- 885 View
- 2 Download

- MICROHARDNESS AND MICROLEAKAGE OF COMPOSITE RESIN CURED BY VISIBLE LIGHT WITH VARIOUS BAND OF WAVELENGTH
- Soo-Man Park, Jae-Yong Lee, Seung-Ryul Han, Sang-Yoon Ha, Dong-Hoon Shin
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2002;27(4):403-410. Published online January 14, 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2002.27.4.403
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub ABSTRACT Several ways of curing are being tried to improve material’s properties and reduce marginal gap. However, all are considering about the pattern of light intensity. It was noted from the preliminary study the change of light wavelength from filter changing may give an impact on material’s property and microleakage.
The object of this study was to verify the effect of filters with various wavelength width on the microhardness and microleakage of composite resin; hybrid type of DenFil and submicron hybrid type of Esthet X. Composite resins were cured using 3 kinds of filter; narrow-banded(465-475 nm), mid-banded(430-470 nm), wide-banded(400-500 nm). After the estimation of microhardness, degree of dye penetration and the maximum gap from SEM evaluation were done between 4 groups that showed no difference in microhardness value of the lower surface.
The results were as follows:
Adequate microhardness could not be gained with a narrow-banded filter irrespective of curing time. At the upper surface, DenFil should be polymerized with middle or wide-banded filter for 20 seconds at least, while Esthet X be cured with middle or wide-banded filter for 30 seconds at least to get similar hardness value to control group.
There was little dye penetration in enamel margin, but all dentin margins showed much more dye penetration irrespective of curing conditions. Although there was no statistical difference, groups cured with mid-banded filter for 40 seconds and with wide-width filter for 20 seconds showed relatively less dye penetration.
It was revealed from the SEM examination that group cured with wide-banded filter had the smallest gap without statistical significance. Spearman’s rho test showed that the correlation between the results of dye penetration and SEM examination was very low.
From these results, it could be concluded that curing with wide-width filter would be better than the other techniques, even though the curing technique using mid-width filter seems to have its own unique advantage.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of Two Different Light-Curing Units and Curing Times on Bulk-Fill Restorative Materials
Gokcen Deniz Bayrak, Elif Yaman-Dosdogru, Senem Selvi-Kuvvetli
Polymers.2022; 14(9): 1885. CrossRef
- The Effect of Two Different Light-Curing Units and Curing Times on Bulk-Fill Restorative Materials
- 1,114 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


