Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Morphological characteristics of the mesiobuccal root in the presence of a second mesiobuccal canal: a micro-CT study
- Lucas P. Lopes Rosado, Matheus Lima Oliveira, Karla Rovaris, Deborah Queiroz Freitas, Frederico Sampaio Neves
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(1):e6. Published online January 18, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e6
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
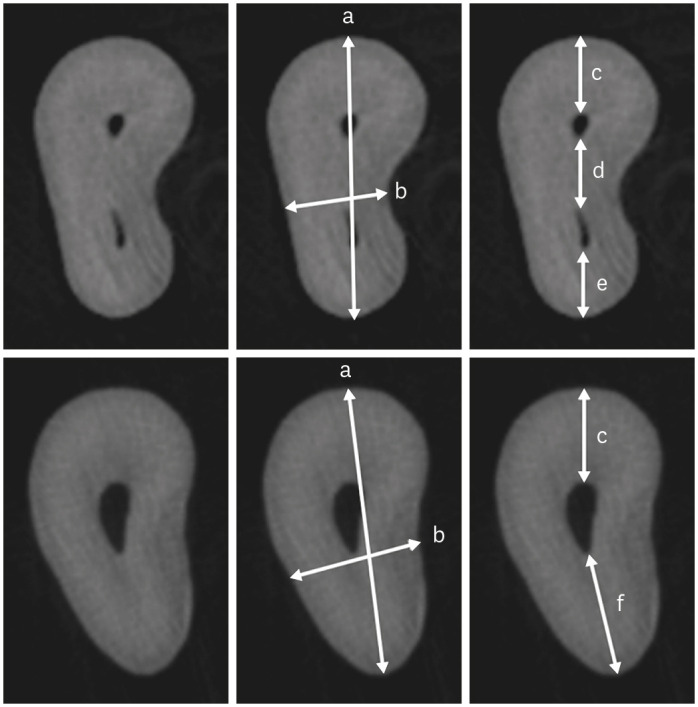
ePub Objectives This study investigated the internal morphology of mesiobuccal (MB) roots of maxillary molars with a second mesiobuccal (MB2) canal.
Materials and Methods Forty-seven maxillary first or second molars from Brazilians were scanned using micro-computed tomography. The following measurements were obtained from the MB roots: root thickness, root width, and dentin thickness of the buccal aspect of the first mesiobuccal (MB1) canal, between the MB1 and MB2 canals, and the palatal aspect of the MB2 and MB1 canals at 3 mm from the root apex and in the furcation region. For statistical analysis, the Student’s
t -test and analysis of variance with thepost-hoc Tukey test were used (α = 0.05).Results In maxillary molars with an MB2 canal, MB roots were significantly thicker (
p = 0.0014) and narrower (p = 0.0016) than in maxillary molars without an MB2 canal. The dentin thickness of the palatal aspect of the MB1 canal was also significantly greater than that of MB roots without an MB2 canal at 3 mm from the root apex (p = 0.0007) and in the furcation region (p < 0.0001). In the furcation region of maxillary molars with an MB2 canal, the dentin thickness between the MB1 and MB2 canals was significantly smaller than that in the buccal and palatal aspects (p < 0.0001).Conclusions The internal morphology of MB roots of maxillary molars with an MB2 canal revealed differences in dentin thickness, root diameter, and distance between the canals when compared with maxillary molars without an MB2 canal.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness and safety of three NiTi systems in endodontic retreatment of MB1 and MB2 root canals: a micro-CT and CBCT combined analysis
Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Rocharles Cavalcante Fontenele, Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Jáder Camilo Pinto, Pedro Luis Busto Rosim, Andréa Gonçalves, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru
Clinical Oral Investigations.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Cone-beam computed tomography evaluation of root and canal morphology of maxillary molars in a Chinese kazakh population
Shuchun Yang, Chenye Li, Hui Shi, Ming Liu, Xu Wang
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Can maxillary molar dimensions predict the presence of the second mesiobuccal canal?
Lucas P. Lopes Rosado, Deborah Queiroz Freitas, Karla Rovaris, Matheus L. Oliveira, Frederico Sampaio Neves
Oral Radiology.2023; 39(3): 482. CrossRef - Can the detection of second mesiobuccal canals be enhanced based on the volume of adjacent canals?
Lucas P. Lopes Rosado, Deborah Q. Freitas, Karla Rovaris, Matheus L. Oliveira, Frederico S. Neves
Archives of Oral Biology.2023; 146: 105604. CrossRef - Assessment of the coronal root canal morphology of permanent maxillary first molars using digital 3D-reconstruction technology based on micro-computed tomography data
Mudan Wang, Yuxuan Gao, Qi Deng, Yuan Gao, Dongzhe Song, Dingming Huang
Journal of Dental Sciences.2023; 18(2): 586. CrossRef
- Effectiveness and safety of three NiTi systems in endodontic retreatment of MB1 and MB2 root canals: a micro-CT and CBCT combined analysis
- 1,805 View
- 36 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- A cone-beam computed tomography study of the prevalence and location of the second mesiobuccal root canal in maxillary molars
- Seong-Ju Lee, Eun-Hye Lee, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(4):e46. Published online September 3, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e46
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
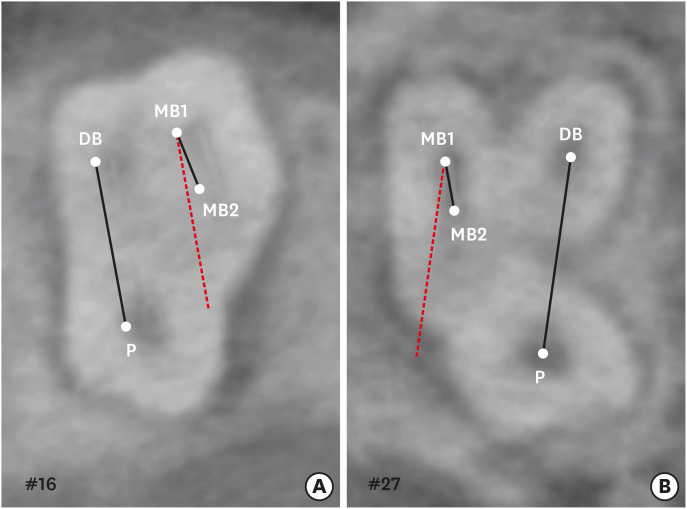
ePub Objectives This study aimed to investigate the incidence and location of the second mesiobuccal root (MB2) canal in maxillary molars with the aid of various measuring points and lines using cone-beam computed tomography (CT).
Materials and Methods A total of 205 images of patients who underwent cone-beam CT examinations between 2011 and 2015 as part of their dental diagnosis and treatment were included. There were 76 images of the maxillary first molar and 135 images of the maxillary second molar. Canal orifices were detected at −1 mm from the top of the pulpal floor on cone-beam CT images. Image assessment was performed by 2 observers in reformatted image planes using software. Assessments included measurement of the distance between the MB1 and MB2 canals, and the angles between the lines connecting the MB1-MB2 and distobuccal (DB)-palatal (P) canals. The data were analyzed using the student's
t -test.Results The prevalence of the MB2 canal was 86.8% in the first molar and 28.9% in the second molar. The angle between the lines connecting the MB1-MB2 and DB-P canals was 2.3° ± 5.7° in the first molar and −3.95° ± 7.73° in the second molar. The distance between the MB1 and MB2 canals was 2.1 ± 0.44 mm in the first molar and 1.98 ± 0.42 mm in the second molar.
Conclusions The angles between the lines connecting the MB1-MB2 and DB-P canals was almost parallel. These findings may aid in the prediction of the location of the MB2 canal orifice.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Position of Second Mesiobuccal Canal Relative to Distobuccal and Palatal Canals of Maxillary Molars in an Iranian Population
Sina Mosadeghian, Azadeh Torkzadeh, Parisa Ranjbarian, Roya Asaadi
Journal of Research in Dental and Maxillofacial Sciences.2025; 10(1): 34. CrossRef - Machine Learning Models in the Detection of MB2 Canal Orifice in CBCT Images
Shishir Shetty, Meliz Yuvali, Ilker Ozsahin, Saad Al-Bayatti, Sangeetha Narasimhan, Mohammed Alsaegh, Hiba Al-Daghestani, Raghavendra Shetty, Renita Castelino, Leena R David, Dilber Uzun Ozsahin
International Dental Journal.2025; 75(3): 1640. CrossRef - EVALUATION OF THE PREVALENCE AND LOCATION OF SECOND MESIOBUCCAL CANALS IN 2100 UPPER FIRST AND SECOND MOLAR TEETH: A CONE BEAM COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY STUDY
Bahar Kaplan, Özkan Adıgüzel, Ayşe Gül Öner Talmaç, Elif Meltem Aslan
İnönü Üniversitesi Sağlık Hizmetleri Meslek Yüksek Okulu Dergisi.2025; 13(3): 752. CrossRef - A novel method for the precise second mesiobuccal canal orifice location: A combined strategy for enhanced clinical practice
Yuhan Wang, Lingyun Li, Lu Zhang, Xiaoyan Wang
Journal of Dental Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Study on the Geometric Location Method of the Danger Zone in the Mesial Roots of Mandibular First Molars
Jinjie Yan, Yuanling Peng, Jing Yang, Jie Liu, Linxian Wang, Tingyuan Zhao, Jian Zhang, Kehua Que
Journal of Endodontics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Correlation between Intraorifice Distance and the Anatomical Characteristics of the Second Mesiobuccal Canal of Maxillary Molars: A CBCT Study
Isabella Perondi, Silvio Taschieri, Martino Baruffaldi, Roberto Fornara, Luca Francetti, Stefano Corbella, Deepa Gurunathan
International Journal of Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Endodontic management of type I maxillary first molar with two palatal roots using cone-beam computed tomography
Nuha Alghamdi
Dental Journal.2024; 57(1): 1. CrossRef - 3D geometric analysis of second mesiobuccal canal in permanent maxillary first molar tooth
Indrani Khadilkar, Divya Nangia, Amrita Chawla, Sidhartha Sharma, Vijay Kumar, Shalini Gupta, Ajay Logani
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(1): 140. CrossRef - Prevalence of mesiobuccal-2 canals in maxillary first and second molars among the Bruneian population—CBCT analysis
Hui Yi Onn, Malissa Siao Yun Abdullah Sikun, Hanif Abdul Rahman, Jagjit Singh Dhaliwal
BDJ Open.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Location angle of second mesio-buccal canal in maxillary molars of an Indian population: an in vivo retrospective CBCT evaluation and proposal of a new classification
Kishor Vhorkate, Kulvinder Banga, Ajinkya M. Pawar, Shugufta Mir, Suraj Arora, Dian Agustin Wahjuningrum, Anuj Bhardwaj, Alexander Maniangat Luke
PeerJ.2022; 10: e14234. CrossRef - Maxillary molar root and canal morphology of Neolithic and modern Chinese
H.Y. Ren, K.Y. Kum, Y.S. Zhao, Y.J. Yoo, J.S. Jeong, Hiran Perinpanayagam, X.Y. Wang, G.J. Li, F. Wang, H. Fang, Y. Gu
Archives of Oral Biology.2021; 131: 105272. CrossRef
- Position of Second Mesiobuccal Canal Relative to Distobuccal and Palatal Canals of Maxillary Molars in an Iranian Population
- 4,086 View
- 45 Download
- 11 Crossref

- Dilemmas pertaining to three canals in the mesiobuccal root of a maxillary second molar: a case report
- Ankit Arora, Shashi Rashmi Acharya, Muliya Vidya Saraswathi, Padmaja Sharma, Amber Ather
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(3):172-177. Published online August 23, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.3.172
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The mesiobuccal root of the maxillary molars is well known to pose a hindrance during endodontic therapy. Presented here is a case of a maxillary left second molar where three canals were located in its mesiobuccal root with the use of visual and diagnostic aids. Difficulties encountered during the process of unveiling the tooth's internal anatomy were discussed. The dilemmas encountered pertained to the root canal configuration, the nomenclature of the extra canals, and the justification for the presence of a third canal. The root canal configuration of 3-2-1 was confirmed for the mesiobuccal root using information gained from clinical, radiographic, and multi-detector computed tomography (MDCT) scan findings. This case demonstrates the need for efforts to locate extra canals in the mesiobuccal root of the maxillary molars as their internal anatomy remains a mystery.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical Significance of Mesiobuccal and Distobuccal Canal Variations in Maxillary Molars: A Case Series and a Mini Review
Mohsen Aminsobhani, Somayeh Majidi, Vlaho Brailo
Case Reports in Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A case report on endodontic management of the rarest Vertucci's Type VIII configuration in maxillary second molar with three mesiobuccal canals
ShrustiAjay Govil, Geeta Asthana, Shikha Kanodia, Abhishek Parmar
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2021; 24(4): 404. CrossRef - The MB3 canal in maxillary molars: a micro-CT study
Ronald Ordinola-Zapata, Jorge N. R. Martins, Hugo Plascencia, Marco A. Versiani, Clovis M. Bramante
Clinical Oral Investigations.2020; 24(11): 4109. CrossRef - Three Root Canals in the Mesiobuccal Root of Maxillary Molars: Case Reports and Literature Review
Ibrahim Ali Ahmad, Anas Al-Jadaa
Journal of Endodontics.2014; 40(12): 2087. CrossRef
- Clinical Significance of Mesiobuccal and Distobuccal Canal Variations in Maxillary Molars: A Case Series and a Mini Review
- 1,694 View
- 8 Download
- 4 Crossref

- In-depth morphological study of mesiobuccal root canal systems in maxillary first molars: review
- Seok-Woo Chang, Jong-Ki Lee, Yoon Lee, Kee-Yeon Kum
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(1):2-10. Published online February 26, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.1.2
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub A common failure in endodontic treatment of the permanent maxillary first molars is likely to be caused by an inability to locate, clean, and obturate the second mesiobuccal (MB) canals. Because of the importance of knowledge on these additional canals, there have been numerous studies which investigated the maxillary first molar MB root canal morphology using
in vivo and laboratory methods. In this article, the protocols, advantages and disadvantages of various methodologies for in-depth study of maxillary first molar MB root canal morphology were discussed. Furthermore, newly identified configuration types for the establishment of new classification system were suggested based on two image reformatting techniques of micro-computed tomography, which can be useful as a further 'Gold Standard' method for in-depth morphological study of complex root canal systems.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An epidemiological study of extracted mandibular premolars from adolescent patients in Damascus using two classification system analyzed with CBCT and digital periapical radiographs
Yasser Alsayed Tolibah, Mohammed N. Al-Shiekh, Mohammad Tamer Abbara, Marwan Alhaji, Osama Aljabban, Nada Bshara
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Cone beam computed tomography analysis of the root and canal morphology of the maxillary second molars in a Hail province of the Saudi population
Ahmed A. Madfa, Moazzy I. Almansour, Saad M. Al-Zubaidi, Albandari H. Alghurayes, Safanah D. AlDAkhayel, Fatemah I. Alzoori, Taif F. Alshammari, Abrar M. Aldakhil
Heliyon.2023; 9(9): e19477. CrossRef - Signs of a missed root canal
M. Yu. Pokrovsky, O. A. Aleshina, T. P. Goryacheva, A. M. Pokrovskiy
Endodontics Today.2023; 21(3): 205. CrossRef - Root Canal Morphology of Maxillary First and Second Molars in a Qatari Population: A Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Study
Maryam Mohammed Al-Obaid, Fatima Abdullah Al-Sheeb
European Dental Research and Biomaterials Journal.2021; 2(01): 34. CrossRef - A Study Comparing the Characteristics of Zinc Oxide Eugenol-Based and Mineral Trioxide Aggregate-Based Root Canal Sealers
Seok-Eun Lee, Ja-Won Cho, Hyun-Jun Yoo, Myung-Gu Lee, Yeol-Mae Jeon, Da-Hui Kim, Hye-Won Park
International Journal of Clinical Preventive Dentistry.2021; 17(3): 117. CrossRef - Root Canal Configuration of Burmese (Myanmar) Maxillary First Molar: A Micro-Computed Tomography Study
M. M. Kyaw Moe, H. J. Jo, J. H. Ha, S. K. Kim, Antonino Lo Giudice
International Journal of Dentistry.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Three-Dimensional Analysis of Root Anatomy and Root Canal Curvature in Mandibular Incisors Using Micro-Computed Tomography with Novel Software
JongKi Lee, Shin-Hoon Lee, Jong-Rak Hong, Kee-Yeon Kum, Soram Oh, Adel Saeed Al-Ghamdi, Fawzi Ali Al-Ghamdi, Ayman Omar Mandorah, Ji-Hyun Jang, Seok Woo Chang
Applied Sciences.2020; 10(12): 4385. CrossRef - An investigation into dose optimisation for imaging root canal anatomy using cone beam CT
Margarete B McGuigan, Christie Theodorakou, Henry F Duncan, Jonathan Davies, Anita Sengupta, Keith Horner
Dentomaxillofacial Radiology.2020; 49(7): 20200072. CrossRef - Analysis of Root Canal Anatomy and Variation in Morphology of Maxillary First Molar Using Various Methods: An In Vitro Study
Youssef A Algarni
World Journal of Dentistry.2019; 10(4): 291. CrossRef - Root Canal Morphology of Mandibular Primary Molars: A Micro-CT Study
Meryem ZİYA, Burcu Nihan YÜKSEL, Şaziye SARI
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2019; 22(4): 382. CrossRef - Comparison of the implementation of extra root canal treatment before and after fee schedule change in the Taiwan National Health Insurance System
Nien-Chieh Lee, Yen-Hsiang Chang, Hui-Tzu Tu, Chang-Fu Kuo, Kuang-Hui Yu, Lai-Chu See
Journal of Dental Sciences.2018; 13(2): 145. CrossRef - Influence of environment on testing of hydraulic sealers
Mira Kebudi Benezra, Pierre Schembri Wismayer, Josette Camilleri
Scientific Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - CBCT uses in clinical endodontics: the effect of CBCT on the ability to locate MB2 canals in maxillary molars
J. Parker, A. Mol, E. M. Rivera, P. Tawil
International Endodontic Journal.2017; 50(12): 1109. CrossRef - Comparison of Alternative Image Reformatting Techniques in Micro–Computed Tomography and Tooth Clearing for Detailed Canal Morphology
Ki-Wook Lee, Yeun Kim, Hiran Perinpanayagam, Jong-Ki Lee, Yeon-Jee Yoo, Sang-Min Lim, Seok Woo Chang, Byung-Hyun Ha, Qiang Zhu, Kee-Yeon Kum
Journal of Endodontics.2014; 40(3): 417. CrossRef - In Vitro Biocompatibility, Inflammatory Response, and Osteogenic Potential of 4 Root Canal Sealers: Sealapex, Sankin Apatite Root Sealer, MTA Fillapex, and iRoot SP Root Canal Sealer
Seok-Woo Chang, So-Youn Lee, Soo-Kyung Kang, Kee-Yeon Kum, Eun-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2014; 40(10): 1642. CrossRef - Análise do preparo de canais radiculares utilizando-se a diafanização
Georje de Martin, Rogério Albuquerque Azeredo
Revista de Odontologia da UNESP.2014; 43(2): 111. CrossRef
- An epidemiological study of extracted mandibular premolars from adolescent patients in Damascus using two classification system analyzed with CBCT and digital periapical radiographs
- 2,216 View
- 14 Download
- 16 Crossref

- The canal system in the mesiobuccal root of the maxillary first molar
- Dong-Hyun Cho, Ho-Young Choi, Sang-Hyuk Park, Gi-Woon Choi
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2003;28(3):232-240. Published online May 31, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.3.232
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study is to investigate the canal system in the mesiobuccal root of the maxillry first molar.
61 maxillary first molars were randomly selected. Serial transverse sections were made perpendicular to the long axis of the mesiobuccal root. Each section was placed in 3% sodium hypochlorite for 24 hours and rinsed in water and dried. The resected surface was stained with 2% methylene blue dye and examined with stereomicroscope.
Canal configuration analysis showed that 36.1% of the specimen classified as type I, 16.4% as type II, 37.7% as type III and 9.8% as type IV.
Type II canal was merged in one canal within 1 to 4mm of the apex. 40% of type II canal converged at 2mm of the apex.
Type IV canal was divided into two canal within 2 to 4mm of the apex. 66.6% of type IV canal branched off at 2mm of the apex.
None of the sections had more than two main root canal.
48.4% of the sections in 3mm with two canals contained an isthmusand more than 70% with two canals has isthmus at 4 to 5mm sections.
63.9% of the mesiobuccal root of maxillary first molar had two canaland 76.5% of sections with two canals in 5 MM had an isthmus. Because of this complexity the clinician should always search for extra canal carefullyand root canal system, including an isthmus, should be cleaned and shaped completelyand obturated three dimensionally for successful endodontic treatment.
- 1,075 View
- 4 Download


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


