Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Restor Dent Endod > Volume 28(3); 2003 > Article
- Original Article The canal system in the mesiobuccal root of the maxillary first molar
- Dong-Hyun Cho, Ho-Young Choi, Sang-Hyuk Park, Gi-Woon Choi
-
2003;28(3):-240.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.3.232
Published online: May 31, 2003
Department of Conservative Dentistry, College of Dentistry, Kyunghee University, Korea.
- Corresponding author (gwchoi@khu.ac.kr)
Copyright © 2003 Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry
- 1,074 Views
- 4 Download
Abstract
-
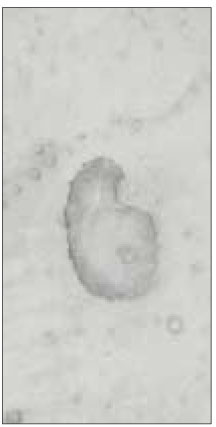
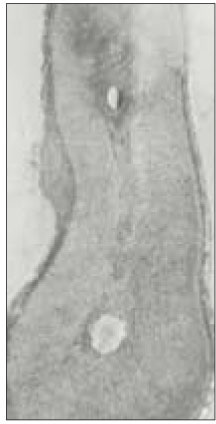
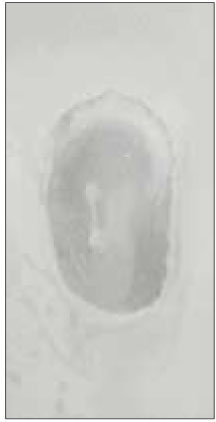
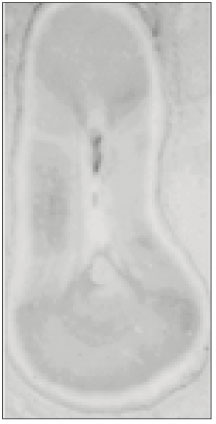
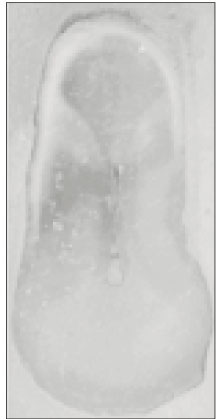
This study is to investigate the canal system in the mesiobuccal root of the maxillry first molar.61 maxillary first molars were randomly selected. Serial transverse sections were made perpendicular to the long axis of the mesiobuccal root. Each section was placed in 3% sodium hypochlorite for 24 hours and rinsed in water and dried. The resected surface was stained with 2% methylene blue dye and examined with stereomicroscope.
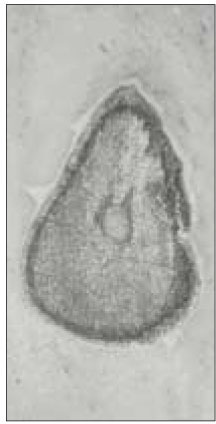
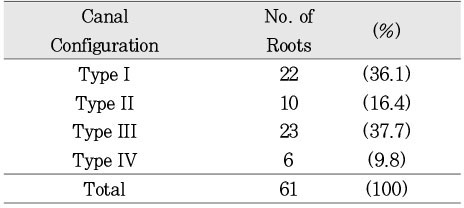
Canal configuration analysis showed that 36.1% of the specimen classified as type I, 16.4% as type II, 37.7% as type III and 9.8% as type IV.
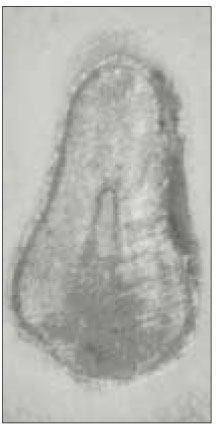
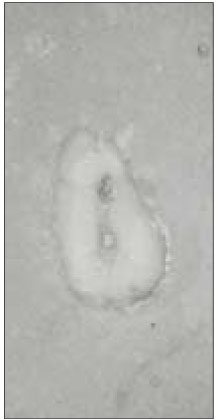
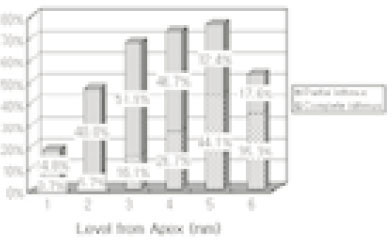
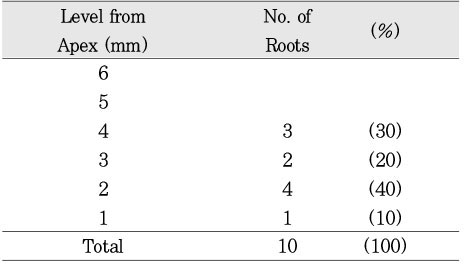
Type II canal was merged in one canal within 1 to 4mm of the apex. 40% of type II canal converged at 2mm of the apex.
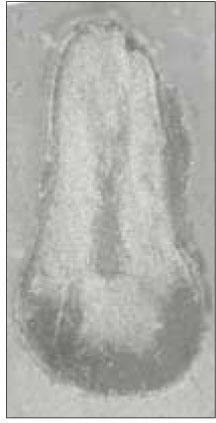
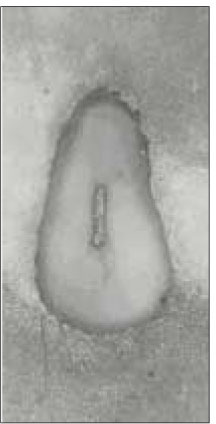
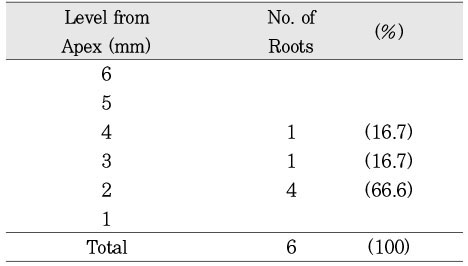
Type IV canal was divided into two canal within 2 to 4mm of the apex. 66.6% of type IV canal branched off at 2mm of the apex.
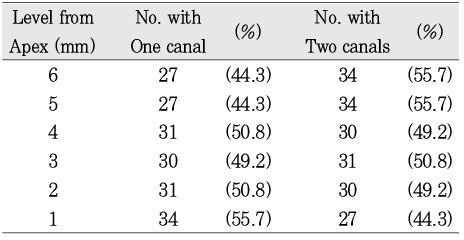
None of the sections had more than two main root canal.
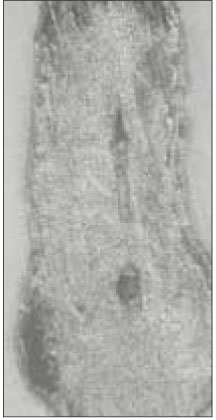
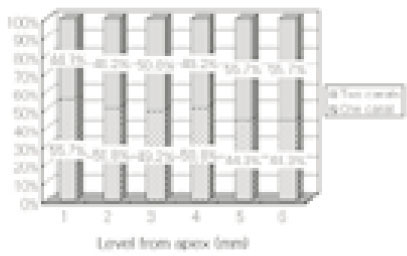
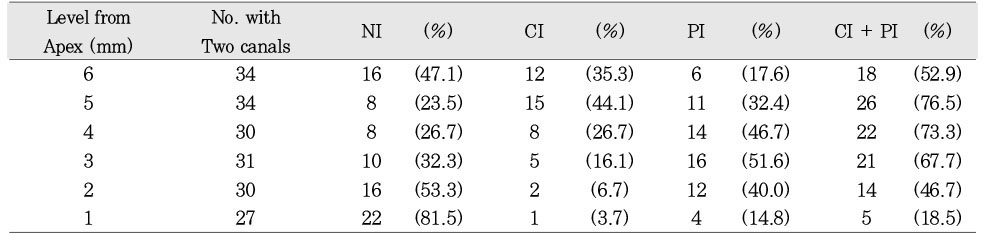
48.4% of the sections in 3mm with two canals contained an isthmusand more than 70% with two canals has isthmus at 4 to 5mm sections.
63.9% of the mesiobuccal root of maxillary first molar had two canaland 76.5% of sections with two canals in 5 MM had an isthmus. Because of this complexity the clinician should always search for extra canal carefullyand root canal system, including an isthmus, should be cleaned and shaped completelyand obturated three dimensionally for successful endodontic treatment.
- 1. Schilder H. Filling root canals in three dimensions. Dent Clin North Am. 1967;723-744.ArticlePubMed
- 2. Beer R, Baumann MA, Kim S. Endodontology. 2000;1st ed. New York: Thieme; 47-50.
- 3. Ingle JI, Barkland LK. Endodontics. 1994;4th ed. Malvern: Williams & Wilkins; 95-96.
- 4. Cohen S, Burns RC, Herbranson EJ. Pathways of the pulp. 2002;8th ed. St. Louis: Mosby; 196-197.
- 5. Weine FS. Endodontic therapy. 1996;5th ed. St. Louis: Mosby; 266-278.
- 6. Hess W. The anatomy of the root canals of the teeth of permanent dentition. 1925;John Bale, Sons & Danielsson Ltd.
- 7. Okumura T. Anatomy of the root canals. J Am Dent Assoc. 1927;14: 632-636.Article
- 8. Weine FS, Healey HJ, Gerstein H, Evanson L. Canal configuration in the mesiobuccal root of the maxillary first molar and its endodontic significance. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1969;28(3):419-425.ArticlePubMed
- 9. Seidberg BH. Frequency of two mesiobuccal root canals in maxillary permanent first molars. J Am Dent Assoc. 1973;87(4):852-856.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Hartwell G, Bellizzi R. Clinical investigation of in vivo endodontically treated mandibular and maxillary molars. J Endod. 1982;8(12):555-557.ArticlePubMed
- 11. Neaverth EJ, Kotler LM, Kaltenbach RF. Clinical investigation (in vivo) of endodontically treated maxillary first molars. J Endod. 1987;13(10):506-512.ArticlePubMed
- 12. Weller RN, Niemczyk SP, Kim S. Incidence and position of the canal isthmus. Part 1. Mesiobuccal root of the maxillary first molar. J Endod. 1995;21(7):380-383.ArticlePubMed
- 13. Pineda F. Roentgenographic investigation of the mesiobuccal root of the maxillary first molar. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1973;36(2):253-260.ArticlePubMed
- 14. Green D. Double canals in single roots. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1973;35(5):689-696.PubMed
- 15. Wheeler RC. A Textbook of dental anatomy and physiology. 1965;4th ed. 228-245.
- 16. Vertucci FJ. Root canal anatomy of human permanent teeth. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1984;58(5):589-599.PubMed
- 17. Weine FS. Endodontic therapy. 1996;5th ed. St. Louis: Mosby; 242-246.
- 18. Cohen S, Burns RC, Herbranson EJ. Pathways of the pulp. 2002;8th ed. St. Louis: Mosby; 710-711.
- 19. Peak JD, Hayes SJ, Bryant ST, Dummer PM. The outcome of root canal treatment. A retrospective study within the armed forces (Royal Air Force). Br Dent J. 2001;190(3):140-144.ArticlePubMed
- 20. Harty FJ, Parkins BJ, Wengraf AM. Success rate in root canal therapy. A retrospective study of conventional cases. Br Dent J. 1970;128(2):65-70.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 21. Nordenram A, Svardstrom G. Results of apiocoectomy. Sven Tandlak Tidskr. 1970;63(9):593-604.PubMed
- 22. Hession RW. Endodontic Morphology II - A radiographic analysis. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1977;44(4):610-620.PubMed
- 23. Horiuchi H. Determining the internal morphology of root canal. Int Endod J. 1993;26(1):12-13.PubMed
- 24. Robertson D, Leeb J, McKee M, Brewer E. A clearing technique for the study of root canal system. J Endod. 1980;6(1):421-424.PubMed
- 25. Wolcott J, Ishley D, Kennedy W, Johnson S, Minnich S. Clinical investigation of second mesiobuccal canals in endodontically treated and retreated maxillary molars. J Endod. 2002;28(6):477-479.ArticlePubMed
- 26. Alavi AM, Opasanon A, Ng YL, Gulabivala K. Root and canal morphology of Thai maxillary molars. Int Endod J. 2002;35(5):478-485.PubMed
- 27. Tam A, Yu DC. Location of canal isthmus and accessory canals in the mesiobuccal root of maxillary first permanent molars. J Can Dent Assoc. 2002;68(1):28-33.PubMed
- 28. al Shalabi RM, Omer OE, Glennon J, Jennings M, Claffey NM. Root canal anatomy of maxillary first and second permanent molars. Int Endod J. 2000;33(5):405-414.ArticlePubMed
- 29. Kulild JC, Peters DD. Incidence and configuration of canal systems in the mesiobuccal root of maxillary first and second molars. J Endod. 1990;16(7):311-317.PubMed
- 30. Hsu YY, Kim S. The resected root surface: The issue of canal isthmus. Dent Clin North Am. 1997;41(3):529-540.PubMed
- 31. Yang SF, Rivera EM, Baumgardner KR, Walton RE, Stanford C. Anaerobic tissue-dissolving abilities of calcium hydroxide and sodium hypochlorite. J Endod. 1995;21(12):613-616.ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
Tables & Figures
REFERENCES
Citations

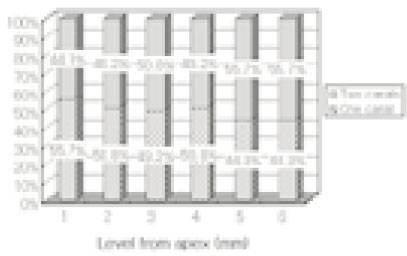
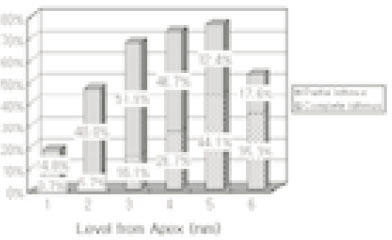
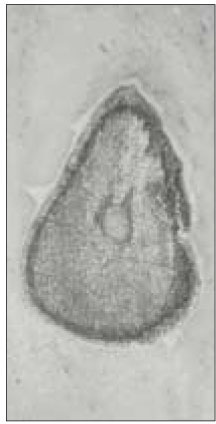
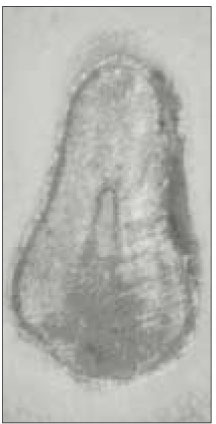
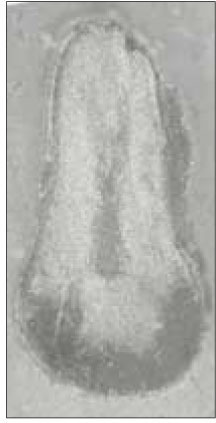
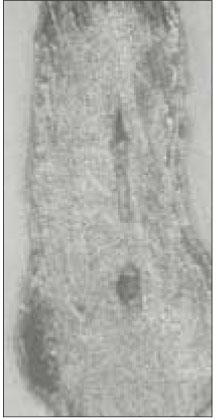
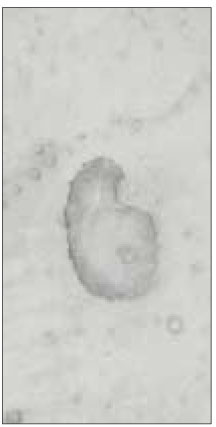
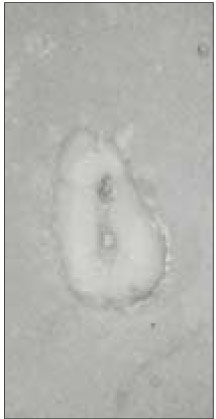
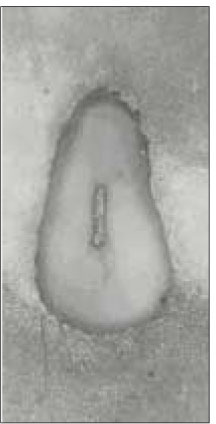
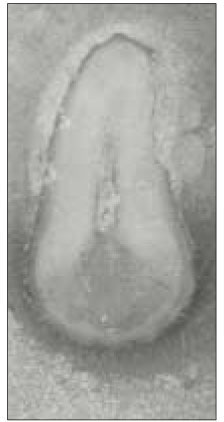
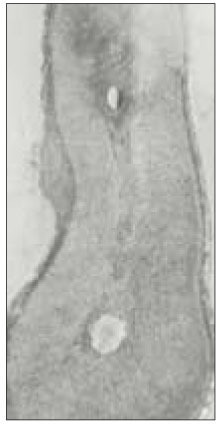
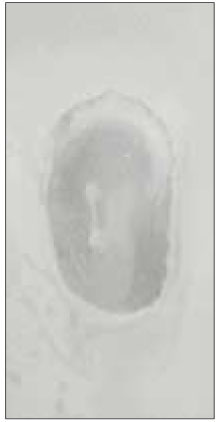
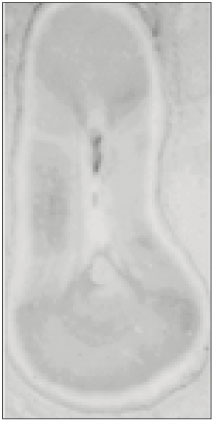
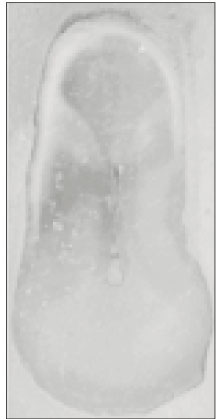
Fig. 1
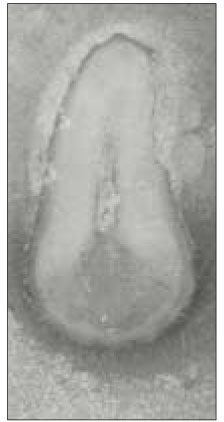
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
Fig. 4
Fig. 5
Fig. 6
Fig. 7
Fig. 8
Fig. 9
Fig. 10
Fig. 11
Fig. 12
Fig. 13
Fig. 14
Canal configurations in the mesiobuccal root of maxillary first molars.(n=61)
Level of convergence of type II canals. (n=10)
Level of divergence of type IV canals. (n=6)
Number of canals at each level(1~6mm). (n=61)
Incidence of an isthmus at each level in sections with two canals (1~6mm).
NI, no isthmus; CI, complete isthmus; PI, partial isthmus
NI, no isthmus; CI, complete isthmus; PI, partial isthmus

 KACD
KACD
 ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite

