Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Difficulties experienced by endodontics researchers in conducting studies and writing papers
- Betul Aycan Alim-Uysal, Selin Goker-Kamali, Ricardo Machado
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(2):e20. Published online March 15, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e20

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The study investigated the difficulties experienced by endodontics researchers around the world in conducting studies and writing papers.
Materials and Methods A survey consisting of 18 questions on the difficulties experienced by endodontics researchers in performing studies and writing papers was e-mailed to academics in the field of endodontics working at 202 universities. The independent risk factors were analyzed using binary logistic regression at a significance level of 0.05.
Results A total of 581 individuals (10.7%) agreed to participate in the study. Almost half the participants (48.2%) reported that they had received some type of training in conducting studies and writing papers. In response to the question, “Do you get help from a statistician to perform the statistical analyses of your studies?,” 77.1% answered “yes.” Around 40% of the participants stated that the need to obtain ethical approval negatively affected their desire to conduct studies. The participants’ regions had no effect on the reported difficulties associated with writing papers in English or conducting statistical analyses (
p > 0.05). Most participants (81.8%) reported difficulties in writing the Discussion section, regardless of their region, academic degrees, or years of experience.Conclusions The participants stated they experienced difficulties in many areas, such as conducting statistical analyses, finding new ideas, and writing in English. Engaging in a detailed examination of ethics committee rules, expanding biostatistics education, increasing the number of institutions providing research funding, and increasing the number of endodontics journals can increase the enthusiasm of endodontics researchers to publish papers.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence of radix molaris in mandibular molars of a subpopulation of Brazil’s Northeast region: a cross-sectional CBCT study
Yasmym Martins Araújo de Oliveira, Maria Clara Mendes Gomes, Maria Fernanda da Silva Nascimento, Ricardo Machado, Danna Mota Moreira, Hermano Camelo Paiva, George Táccio de Miranda Candeiro
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Statistical pitfalls in endodontic research
Nandini Suresh
Endodontology.2023; 35(1): 1. CrossRef
- Prevalence of radix molaris in mandibular molars of a subpopulation of Brazil’s Northeast region: a cross-sectional CBCT study
- 2,084 View
- 28 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

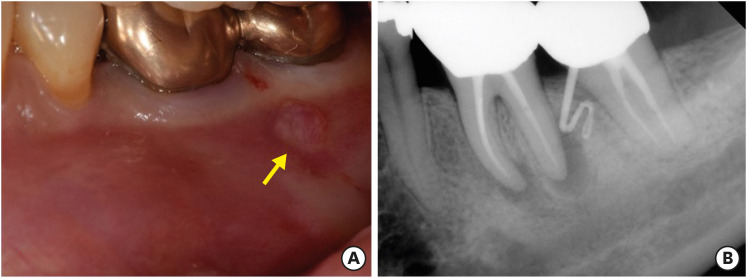
- The application of “bone window technique” using piezoelectric saws and a CAD/CAM-guided surgical stent in endodontic microsurgery on a mandibular molar case
- Ukseong Kim, Sunil Kim, Euiseong Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(3):e27. Published online May 21, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e27
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Apical surgery for a mandibular molar is still challenging for many reasons. This report describes the applications of computer-guided cortical ‘bone-window technique’ using piezoelectric saws that prevented any nerve damage in performing endodontic microsurgery of a mandibular molar. A 49-year-old woman presented with gumboil on tooth #36 (previously endodontically treated tooth) and was diagnosed with chronic apical abscess. Periapical lesions were confirmed using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT). Endodontic microsurgery for the mesial and distal roots of tooth #36 was planned. Following the transfer of data of the CBCT images and the scanned cast to an implant surgical planning program, data from both devices were merged. A surgical stent was designed, on the superimposed three-dimensional model, to guide the preparation of a cortical window on the buccal side of tooth #36. Endodontic microsurgery was performed with a printed surgical template. Minimal osteotomy was required and preservation of the buccal cortical plate rendered this endodontic surgery less traumatic. No postoperative complications such as mental nerve damage were reported. Window technique guided by a computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacture based surgical template can be considerably useful in endodontic microsurgery in complicated cases.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Optimising Outcomes in Endodontic Microsurgery: Evidence, Uncertainties and Future Directions
Ukseong Kim, Euiseong Kim
International Endodontic Journal.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Accuracy of Guided Dual Technique in Esthetic Crown Lengthening: A Prospective Case‐Series Study
Meritxell Enfedaque‐Prat, Albert González‐Barnadas, Adrià Jorba‐García, Javi Vilarrasa, Jorge Toledano‐Serrabona, Rui Figueiredo, Eduard Valmaseda‐Castellón, Octavi Camps‐Font
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2025; 37(6): 1284. CrossRef - Guided endodontics in the application of personalized mini-invasive treatment in clinical cases: a literature review
Shuangshuang Ren, Wanping Wang, Mingyue Cheng, Wenyue Tang, Yue Zhao, Leiying Miao
The Saudi Dental Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Accurately Defining the Location and Dimension of the Bony Lid Under the Guidance of Dynamic Navigation: Report on Three Cases
Kailiang Tang, Xiaole Zhang, Qibao Wang, Xinyu Zhao, Xijiao Yu, Yi Du
Australian Endodontic Journal.2025; 51(3): 785. CrossRef - Minimally Invasive Vertical Incision Subperiosteal Tunnelling Technique for Targeted Endodontic Surgery: Technical Overview and a Case Report
Francesc Abella Sans, Jaime Barragán Montes, Tomasz Zbozen, Nandini Suresh, Lalli Dharmarajan, Paul M. H. Dummer, Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu
International Endodontic Journal.2025; 58(11): 1799. CrossRef - Endodontic Microsurgery of Mandibular Molars with an Autonomous Robotic System
Haiying Zhang, Zi Yang, Mangnan Liu, Yaoxin Wang, Mei Fu, Benxiang Hou, Chen Zhang
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(12): 1830. CrossRef - Endodontic Microsurgery of a Mandibular Molar Using a Dynamic Navigation System (DNS) and Cortical Window Technique: A Case Report
Gustavo Castillo, Silvia Restrepo-Méndez, Oscar Zuluaga, Paola Escobar-Villegas
Journal of Endodontic Microsurgery.2024; 3: 1. CrossRef - The bone lid technique in endodontic microsurgery
Min Zhang, He Liu, Ya Shen
Asian Journal of Surgery.2024; 47(7): 3126. CrossRef - Guided Periradicular Surgery with Er,Cr:YSGG Laser Osteotomy: A Case Report
Julian Torres Celeita, Johanna Hernández la Rotta, Amdie Chirinos Salazar, Jorge Fandiño Rodríguez, Laura López Rincón, Mauren Orduz Solorzano, Diana Parra Galvis, Oscar Jiménez Peña
Journal of Endodontic Microsurgery.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Piezoelectric Endodontic Microsurgery with Modified Cortical Window Technique: A Case Report
Rafael Fernández-Grisales, Wilder Rojas, Carolina Berruecos-Orozco
Journal of Endodontic Microsurgery.2023; 2: 34. CrossRef - The Impact of the Preferred Reporting Items for Case Reports in Endodontics (PRICE) 2020 Guidelines on the Reporting of Endodontic Case Reports
Sofian Youssef, Phillip Tomson, Amir Reza Akbari, Natalie Archer, Fayjel Shah, Jasmeet Heran, Sunmeet Kandhari, Sandeep Pai, Shivakar Mehrotra, Joanna M Batt
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical and radiological outcomes of dynamic navigation in endodontic microsurgery: a prospective study
Chen Chen, Rui Zhang, Wei Zhang, Fangzhe Li, Zan Wang, Li Qin, Yun Chen, Zhuan Bian, Liuyan Meng
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(9): 5317. CrossRef - New-designed 3D printed surgical guide promotes the accuracy of endodontic microsurgery: a study of 14 upper anterior teeth
Dan Zhao, Weige Xie, Tianguo Li, Anqi Wang, Li Wu, Wen Kang, Lu Wang, Shiliang Guo, Xuna Tang, Sijing Xie
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Failure case analysis during each stage of endodontic microsurgery: A retrospective study based on clinical databases
Changwoo Ryu, Sooil Shin, Yong-Bum Cho, Euiseong Kim, Minju Song
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2023; 13(2): 160. CrossRef - Piezoelectric Device and Dynamic Navigation System Integration for Bone Window-Guided Surgery
Frederico C. Martinho, Ina L. Griffin, Patricia A. Tordik
Journal of Endodontics.2023; 49(12): 1698. CrossRef - Bone Window Technique in Endodontic Microsurgery – Report of Two Cases
Spyros Floratos, Vasileios Molonis, Apostolos Tsolakis, Stylianos Kykalos, Konstantinos Kontzoglou
Journal of Endodontic Microsurgery.2022; 2: 24. CrossRef - An Update on Endodontic Microsurgery of Mandibular Molars: A Focused Review
Sun Mi Jang, Euiseong Kim, Kyung-San Min
Medicina.2021; 57(3): 270. CrossRef
- Optimising Outcomes in Endodontic Microsurgery: Evidence, Uncertainties and Future Directions
- 2,271 View
- 41 Download
- 17 Crossref

-
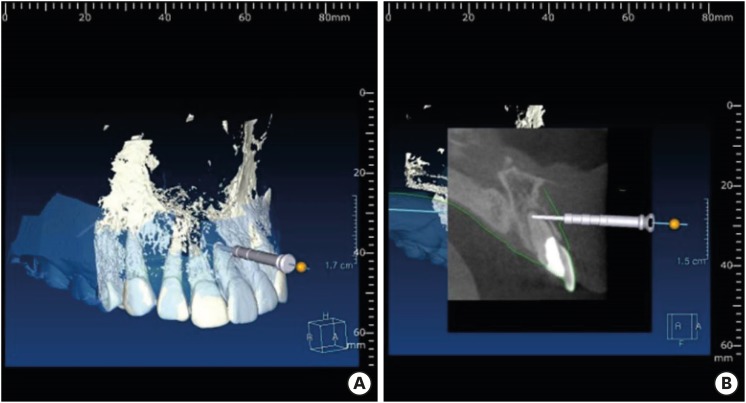
A new minimally invasive guided endodontic microsurgery by cone beam computed tomography and 3-dimensional printing technology

- Jong-Eun Kim, June-Sung Shim, Yooseok Shin
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(3):e29. Published online July 25, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e29
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Endodontic microsurgery is defined as the treatment performed on the root apices of an infected tooth, which was unresolved with conventional root canal therapy. Recently, the advanced technology in 3-dimensional model reconstruction based on computed tomography such as cone beam computed tomography has opened a new avenue in application of personalized, accurate diagnosis and has been increasingly used in the field of dentistry. Nevertheless, direct intra-oral localization of root apex based on the 3-dimensional information is extremely difficult and significant amount of bone removal is inevitable when freehand surgical procedure was employed. Moreover, gingival flap and alveolar bone fenestration are usually required, which leads to prolonged time of surgery, thereby increasing the chance of trauma as well as the risk of infection. The purpose of this case report is to present endodontic microsurgery using the guide template that can accurately target the position of apex for the treatment of an anterior tooth with calcified canal which was untreatable with conventional root canal therapy and unable to track the position of the apex due to the absence of fistula.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A narrative review of papilla preservation techniques in clinical dentistry
Yinghua Fu, Zhixin Zhang, Xiaoping Tang, Jiangling Su
Medicine.2025; 104(3): e41033. CrossRef - Segmentation algorithms of dental CT images: A comprehensive review from classical to deep learning trend
Dianhao Wu, Jingang Jiang, Jinke Wang, Zhuming Bi, Guang Yu
Expert Systems with Applications.2025; 275: 126853. CrossRef - Endodontic Microsurgery of Mandibular Molars with an Autonomous Robotic System
Haiying Zhang, Zi Yang, Mangnan Liu, Yaoxin Wang, Mei Fu, Benxiang Hou, Chen Zhang
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(12): 1830. CrossRef - Removal of Extraradicular Separated Instrument by Targeted Endodontic Microsurgery Using the 3D‐Printed Guide and Trephine: A Case Report
Lin Yang, Liang Chen
Clinical Case Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Augmented Reality-Assisted Micro-Invasive Apicectomy with Markerless Visual–Inertial Odometry: An In Vivo Pilot Study
Marco Farronato, Davide Farronato, Federico Michelini, Giulio Rasperini
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(23): 12588. CrossRef - 3D finite element analysis of stress distribution on the shape of resected root-end or with/without bone graft of a maxillary premolar during endodontic microsurgery
Aein Mon, Mi-El Kim, Kee-Yeon Kum, Ho-Beom Kwon
Journal of Dental Sciences.2024; 19(2): 837. CrossRef - TREATMENT OF YATROGENIC POST-TRAUMATIC NEUROPATHY ASSOCIATED WITH
ENDODONTIC THERAPY USING 3D TECHNOLOGIES
Karen Sevterteryan, Vladislav Tarasenok, Lyudmila Tatintsyan
BULLETIN OF STOMATOLOGY AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY.2024; : 73. CrossRef - Advancements in guided surgical endodontics: A scoping review of case report and case series and research implications
Giusy Rita Maria La Rosa, Matteo Peditto, Andrea Venticinque, Antonia Marcianò, Alberto Bianchi, Eugenio Pedullà
Australian Endodontic Journal.2024; 50(2): 397. CrossRef - Comparison of a Novel Static Computer-aided Surgical and Freehand Techniques for Osteotomy and Root-end Resection
Kyle Westbrook, Corey Rollor, Sara A. Aldahmash, Guadalupe G. Fay, Elias Rivera, Jeffery B. Price, Ina Griffin, Patricia A. Tordik, Frederico C. Martinho
Journal of Endodontics.2023; 49(5): 528. CrossRef - Comparison of the Three-Dimensional Accuracy of Guided Apicoectomy Performed with a Drill or a Trephine: An In Vitro Study
Ramóna Kiscsatári, Eszter Nagy, Máté Szabó, Gábor Braunitzer, József Piffkó, Márk Fráter, Márk Ádám Antal
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(17): 9642. CrossRef - Review of “Outcome of Endodontic Surgery: A Meta- Analysis of the Literature—Part 1: Comparison
of Traditional Root-End Surgery and Endodontic Microsurgery” by Setzer and Colleagues in J Endod 36(11):1757-1765, 2010
Oleksandr Nozhenko
Journal of Endodontic Microsurgery.2023; 2: 41. CrossRef - The Impact of the Preferred Reporting Items for Case Reports in Endodontics (PRICE) 2020 Guidelines on the Reporting of Endodontic Case Reports
Sofian Youssef, Phillip Tomson, Amir Reza Akbari, Natalie Archer, Fayjel Shah, Jasmeet Heran, Sunmeet Kandhari, Sandeep Pai, Shivakar Mehrotra, Joanna M Batt
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - New-designed 3D printed surgical guide promotes the accuracy of endodontic microsurgery: a study of 14 upper anterior teeth
Dan Zhao, Weige Xie, Tianguo Li, Anqi Wang, Li Wu, Wen Kang, Lu Wang, Shiliang Guo, Xuna Tang, Sijing Xie
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - An Exploratory In Vitro Microcomputed Tomographic Investigation of the Efficacy of Semicircular Apicoectomy Performed with Trephine Bur
Eszter Nagy, Brigitta Vőneki, Lívia Vásárhelyi, Imre Szenti, Márk Fráter, Ákos Kukovecz, Márk Ádám Antal
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(16): 9431. CrossRef - The Time Has Come: Journal of Endodontic Microsurgery: A First Peer-Reviewed Open Access Publication Focused on Microsurgery in Endodontics
Ievgen Fesenko
Journal of Endodontic Microsurgery.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Prefabricated Grid-guided Endodontic Microsurgery: A Pilot Study
Cruz Nishanthine, Manali Ramakrishnan Srinivasan, Ravi Devi, Kadhar Begam Farjana, Dasarathan Duraivel
Journal of Operative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022; 6(2): 58. CrossRef - Guided osteotomy
Saini Rashmi, Saini V Kr
Tanta Dental Journal.2022; 19(3): 172. CrossRef - Accuracy of digitally planned, guided apicoectomy with a conventional trephine and a custom-made endodontic trephine: An in vitro comparative study
Eszter Nagy, Gábor Braunitzer, Dániel Gerhard Gryschka, Ibrahim Barrak, Mark Adam Antal
Journal of Stomatology, Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.2022; 123(4): 388. CrossRef - Stress Distribution on Trephine-Resected Root-end in Targeted Endodontic Microsurgery: A Finite Element Analysis
Yeon-Jee Yoo, Hiran Perinpanayagam, Miel Kim, Qiang Zhu, Seung-Ho Baek, Ho-Beom Kwon, Kee-Yeon Kum
Journal of Endodontics.2022; 48(12): 1517. CrossRef - An Update on Endodontic Microsurgery of Mandibular Molars: A Focused Review
Sun Mi Jang, Euiseong Kim, Kyung-San Min
Medicina.2021; 57(3): 270. CrossRef - When to consider the use of CBCT in endodontic treatment planning in adults
Nisha Patel, Andrew Gemmell, David Edwards
Dental Update.2021; 48(11): 932. CrossRef
- A narrative review of papilla preservation techniques in clinical dentistry
- 2,452 View
- 31 Download
- 21 Crossref

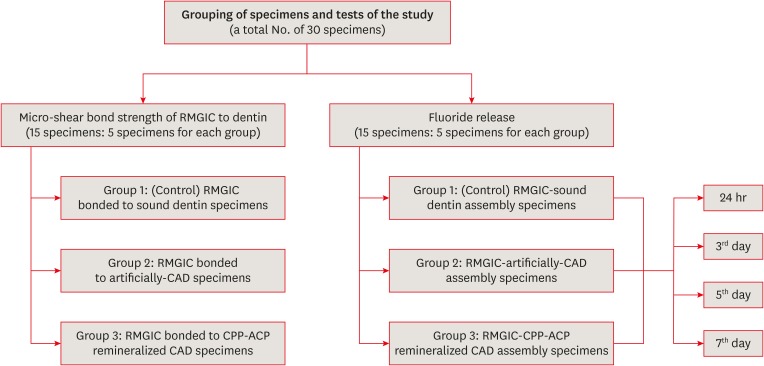
- Effect of casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate on fluoride release and micro-shear bond strength of resin-modified glass ionomer cement in caries-affected dentin
- Jamila Nuwayji Agob, Neven Saad Aref, Essam El Saeid Al-Wakeel
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(4):e45. Published online October 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e45
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study was conducted to evaluate fluoride release and the micro-shear bond strength of resin-modified glass ionomer cement (RMGIC) in casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate (CPP-ACP)-remineralized caries-affected dentin (CAD).
Materials and Methods Exposed dentin surfaces of 30 human third molar teeth were divided into 2 equal groups for evaluating fluoride release and the micro-shear bond strength of RMGIC to CAD. Each group was subdivided into 3 equal subgroups: 1) control (sound dentin); 2) artificially demineralized dentin (CAD); 3) CPP-ACP remineralized dentin (remineralized CAD). To measure fluoride release, 15 disc-shaped specimens of RMGIC (4 mm in diameter and 2 mm in thickness) were bonded on one flat surface of the dentin discs of each group. Fluoride release was tested using ion chromatography at different intervals; 24 hours, 3, 5, 7 days. RMGIC micro-cylinders were built on the flat dentin surface of the 15 discs, which were prepared according to the assigned group. Micro-shear bond strength was measured after 24 hours water storage. Data were analyzed using 1- and 2-way analysis of variance and the
post hoc least significant difference test (α = 0.05).Results Fluoride detected in solutions (at all intervals) and the micro-shear bond strength of RMGIC bonded to CPP-ACP-remineralized dentin were significantly higher than those bonded to artificial CAD (
p < 0.05).Conclusions Demineralized CAD consumes more fluoride released from RMGIC into the solution for remineralization than CPP-ACP mineralized dentin does. CPP-ACP increases the micro-shear bond strength of RMGIC to CAD.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Synergistic effect of nanosilver fluoride with L-arginine on remineralization of early carious lesions
Ahmad S. Albahoth, Mi-Jeong Jeon, Jeong-Won Park
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the bond strength of glass ionomer cement modified with fluoride-loaded chitosan nanoparticles to caries-affected dentin
Hanife Altınışık, Merve Nezir, Hülya Erten Can, Necibe Başaran Mutlu Ağardan, Aysel Berkkan
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Non-collagenous protein analog-induced biomimetic mineralization strategy to restore the dentin interface
Ruhua Chen, Yimeng Xie, Liang Ma, Bing Li, Wei Yao
Biomedical Physics & Engineering Express.2024; 10(6): 062004. CrossRef - A Critical Review on the Factors Affecting the Bond Strength of Direct Restorative Material Alternatives to Amalgam
Zeynep Batu Eken, Nicoleta Ilie
Materials.2024; 17(19): 4853. CrossRef - ÇOCUK DİŞ HEKİMLİĞİNDE GÜMÜŞ DİAMİN FLORÜR KULLANIMI
Zeynep UÇAR, Bahar Melis AKYILDIZ
Selcuk Dental Journal.2022; 9(2): 652. CrossRef - Microshear Bond Strength of Nanoparticle-Incorporated Conventional and Resin-Modified Glass Ionomer to Caries-Affected Dentin
Zahra Fattah, Zahra Jowkar, Safoora Rezaeian, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
International Journal of Dentistry.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef
- Synergistic effect of nanosilver fluoride with L-arginine on remineralization of early carious lesions
- 1,961 View
- 12 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Progression of periapical cystic lesion after incomplete endodontic treatment
- Jong-Ki Huh, Dong-Kyu Yang, Kug-Jin Jeon, Su-Jung Shin
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(2):137-142. Published online February 22, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.2.137
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub We report a case of large radicular cyst progression related to endodontic origin to emphasize proper intervention and follow-up for endodontic pathosis. A 25 yr old man presented with an endodontically treated molar with radiolucency. He denied any intervention because of a lack of discomfort. Five years later, the patient returned. The previous periapical lesion had drastically enlarged and involved two adjacent teeth. Cystic lesion removal and apicoectomy were performed on the tooth. Histopathological analysis revealed that the lesion was an inflammatory radicular cyst. The patient did not report any discomfort except for moderate swelling 3 days after the surgical procedure. Although the patient had been asymptomatic, close follow-ups are critical to determine if any periapical lesions persist after root canal treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prognosis of Vital Teeth Involved in Large Cystic Lesions After a Surgical Intervention: A Longitudinal Ambidirectional Cohort Study
Khalid A. Merdad, Maha Shawky, Khalid A. Aljohani, Rawia Alghamdi, Saja Alzahrani, Omar R. Alkhattab, Abdulaziz Bakhsh
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(2): 83. CrossRef - Assessing the efficacy of apicoectomy without retrograde filling in treating periapical inflammatory cysts
Jeong-Kui Ku, Woo-Young Jeon, Seung-O Ko, Ji-Young Yoon
Journal of the Korean Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons.2024; 50(3): 140. CrossRef - Cystic lesion between a deciduous tooth and the succeeding permanent tooth: a retrospective analysis of 87 cases
Changmo Sohn, Jihye Ryu, Inhye Nam, Sang-Hun Shin, Jae-Yeol Lee
Journal of the Korean Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons.2022; 48(6): 342. CrossRef - The effectiveness of antibacterial treatment of the root canal in chronic apical periodontitis using an erbium-chromium laser
M. A. Postnikov, A. Yu. Rozenbaum, S. E. Chigarina, D. N. Kudryashov, M. B. Khaikin, I. V. Khramova, G. N. Belanov
Endodontics Today.2022; 20(2): 115. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Incomplete Endodontic Care
Carla Y. Falcon, Anthony R. Arena, Rebecca Hublall, Craig S. Hirschberg, Paul A. Falcon
Journal of Endodontics.2021; 47(9): 1398. CrossRef - Tratamento cirúrgico e conservador de cisto periapical de grande proporção: relato de caso
Maraísa Aparecida Pinto Resende, Neuza Maria Souza Picorelli Assis, Augusto César Sette-Dias, Evandro Guimarães de Aguiar, Bruno Salles Sotto-Maior
HU Revista.2018; 43(2): 191. CrossRef
- Prognosis of Vital Teeth Involved in Large Cystic Lesions After a Surgical Intervention: A Longitudinal Ambidirectional Cohort Study
- 2,892 View
- 15 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Accidental injury of the inferior alveolar nerve due to the extrusion of calcium hydroxide in endodontic treatment: a case report
- Yooseok Shin, Byoung-Duck Roh, Yemi Kim, Taehyeon Kim, Hyungjun Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(1):63-67. Published online January 6, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.1.63

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub During clinical endodontic treatment, we often find radiopaque filling material beyond the root apex. Accidental extrusion of calcium hydroxide could cause the injury of inferior alveolar nerve, such as paresthesia or continuous inflammatory response. This case report presents the extrusion of calcium hydroxide and treatment procedures including surgical intervention. A 48 yr old female patient experienced Calcipex II extrusion in to the inferior alveolar canal on left mandibular area during endodontic treatment. After completion of endodontic treatment on left mandibular first molar, surgical intervention was planned under general anesthesia. After cortical bone osteotomy and debridement, neuroma resection and neurorrhaphy was performed, and prognosis was observed. But no improvement in sensory nerve was seen following surgical intervention after 20 mon. A clinician should be aware of extrusion of intracanal medicaments and the possibility of damage on inferior alveolar canal. Injectable type of calcium hydroxide should be applied with care for preventing nerve injury. The alternative delivery method such as lentulo spiral was suggested on the posterior mandibular molar.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nicolau syndrome in endodontics: A narrative review on calcium hydroxide extrusion and its therapeutic risks
Manisha Chaudhary, Akash Kumar Giri, Ashok Ayer
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2026; 16(1): 12. CrossRef - Invasion of Calcium Hydroxide Preparations Leading to Severe Chemical Nerve Injury Treated Through Nerve Repair Using Artificial Nerve Conduit: A Case Report
Akihiro Nishiyama, Andreas Neff, Takahiro Nakada, Takaharu Ariizumi, Akira Iwasaki, Keisuke Sugahara, Akira Katakura, Hannah Wesley
Case Reports in Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Automatic localization of inferior alveolar nerve canal in panoramic dental images
Uma Maheswari Pandyan, Banumathi Arumugam, Ulaganathan Gurunathan, Shahul Hameed Kopuli Ashkar Ali
Signal, Image and Video Processing.2022; 16(5): 1389. CrossRef - Inferior alveolar nerve injury due to the extrusion of calcium hydroxide during endodontic treatment: A case report
Metin Berk Kasapoğlu, Gülce Ecem Doğancalı
Australian Endodontic Journal.2022; 48(2): 342. CrossRef - Inferior alveolar nerve canal segmentation by local features based neural network model
P. Uma Maheswari, A. Banumathi, G. Ulaganathan, R. Yoganandha
IET Image Processing.2022; 16(3): 703. CrossRef - Microsurgical Repair of Inferior Alveolar Nerve Injuries Associated With Endodontic Treatment: Results on Sensory Function and Relief of Pain
Keith A. Sonneveld, Kristopher L. Hasstedt, Roger A. Meyer, Shahrokh C. Bagheri
Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.2021; 79(7): 1434. CrossRef - The significance of diagnosis and treatment planning in periapical lesion overfilled with calcium hydroxide paste
Kyoung-Hwa Jung, Eun-Young Kwon, Youn-Kyung Choi, So-Yeun Kim, Hye-Mi Jeon, Jeong-Kil Park
Journal of Dental Rehabilitation and Applied Science.2021; 37(2): 95. CrossRef - The anatomical relationship between the roots of erupted permanent teeth and the mandibular canal: a systematic review
Michał Puciło, Mariusz Lipski, Magdalena Sroczyk-Jaszczyńska, Aleksandra Puciło, Alicja Nowicka
Surgical and Radiologic Anatomy.2020; 42(5): 529. CrossRef - Massive extrusion of calcium hydroxide paste containing barium sulphate during endodontic treatment
Jéssica Montenegro Fonsêca, Natália Rangel Palmier, Gleyson Kleber Amaral‐Silva, Lady Paola Aristizabal Arboleda, José Flávio Affonso Almeida, Mario Fernando de Goes, Pablo Agustin Vargas, Marcio Ajudarte Lopes, Alan Roger Santos‐Silva
Australian Endodontic Journal.2020; 46(2): 257. CrossRef - The double-edged sword of calcium hydroxide in endodontics
Alan H. Gluskin, Gordon Lai, Christine I. Peters, Ove A. Peters
The Journal of the American Dental Association.2020; 151(5): 317. CrossRef - Endodontic-related inferior alveolar nerve injuries: A review and a therapeutic flow chart
R. Castro, M. Guivarc'h, J.M. Foletti, J.H. Catherine, C. Chossegros, L. Guyot
Journal of Stomatology, Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.2018; 119(5): 412. CrossRef - Relationship between Root Apices and the Mandibular Canal: A Cone-beam Computed Tomographic Comparison of 3 Populations
Alex Lvovsky, Shir Bachrach, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Ajinkya Pawar, Oleg Levinzon, Joe Ben Itzhak, Michael Solomonov
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(4): 555. CrossRef - A case of high density abnormality in x-ray findings of mandible caused by leakage of root canal filling paste
Haruko Kashiwamura, Kyoko Oka, Yoko Tuchihashi, Hanako Yoshioka, Mayumi Kato, Atsuko Baba, Toyohiro Kagawa, Kazuhiko Okamura, Masao Ozaki
Pediatric Dental Journal.2017; 27(3): 162. CrossRef - Oral dysesthesia
Christopher J. Spencer, Gary D. Klasser
The Journal of the American Dental Association.2017; 148(12): 941. CrossRef - Microsurgical Decompression of Inferior Alveolar Nerve After Endodontic Treatment Complications
Bernardo Bianchi, Andrea Ferri, Andrea Varazzani, Michela Bergonzani, Enrico Sesenna
Journal of Craniofacial Surgery.2017; 28(5): 1365. CrossRef
- Nicolau syndrome in endodontics: A narrative review on calcium hydroxide extrusion and its therapeutic risks
- 3,639 View
- 42 Download
- 15 Crossref

- Autotransplantation combined with orthodontic treatment: a case involving the maxillary central incisors with root resorption after traumatic injury
- Manuel Marques Ferreira, Hugo M. Ferreira, Filomena Botelho, Eunice Carrilho
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(3):236-240. Published online May 26, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.3.236
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Traumatic dental injury can result in avulsion of anterior teeth. In young patients, it is a challenge to the dental professional because after replantation, late complications such as ankylosis require tooth extraction. Although prosthetic and orthodontic treatment, and implant placement have been described as the options for intervention, autogenous tooth transplantation could be an effective procedure in growing patients if there is a suitable donor tooth available. This case presents the treatment of a patient who suffered a traumatic injury at 9 years old with avulsion of tooth 21, which had been replanted, and intrusion of tooth 11. Both teeth ankylosed; thus they were removed and autotransplantation of premolars was carried out. After transplantation, the tooth underwent root canal treatment because of pulpal necrosis. Orthodontic treatment began 3 months after transplantation and during 7 years' follow-up the aesthetics and function were maintained without signs of resorption.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Autogenous Transplantation of Teeth Across Clinical Indications: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Martin Baxmann, Karin Christine Huth, Krisztina Kárpáti, Zoltán Baráth
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(14): 5126. CrossRef - Traitement orthodontique des dents permanentes traumatisées
Chantal Naulin-Ifi, Hélène Desnoes, H. Desnoes
Revue d'Orthopédie Dento-Faciale.2023; 57(2): 143. CrossRef - Treatment of an Avulsed and Ankylosed Incisor through Single Tooth Alveolar Osteotomy and Conventional Orthodontic Mechanisms
Georgios Vasoglou, Chrysi Christina Markomanolaki, Michail Vasoglou, Andreas Markomanolakis
Children.2022; 9(5): 732. CrossRef - A conservative approach for an adult patient with a fractured tooth and crowding: Autotransplantation at the fracture site
Chang-Hyen Kim, Byungju Joh, Hee Jin Lim, Jae Hyun Park, Yoon-Ah Kook, Yoonji Kim
American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics.2021; 159(2): 234. CrossRef - Influencing Factors in Autotransplantation of Teeth with Open Apex: A Review of the Literature
María P. Pecci Lloret, Elena Pina Martínez, Francisco J. Rodríguez Lozano, Miguel R. Pecci Lloret, Julia Guerrero Gironés, Francesco Riccitiello, Gianrico Spagnuolo
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(9): 4037. CrossRef - Central incisor ankylosis - A review article
Simona Dianišková, Ivana Moňoková
Stomatológ.2019; 29(1): 40. CrossRef - Prognostic Factors for Clinical Outcomes in Autotransplantation of Teeth with Complete Root Formation: Survival Analysis for up to 12 Years
Youngjune Jang, Yoon Jeong Choi, Seung-Jong Lee, Byoung-Duck Roh, Sang Hyuk Park, Euiseong Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(2): 198. CrossRef
- Autogenous Transplantation of Teeth Across Clinical Indications: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- 1,550 View
- 11 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Current perspectives of bio-ceramic technology in endodontics: calcium enriched mixture cement - review of its composition, properties and applications
- Shivani Utneja, Ruchika Roongta Nawal, Sangeeta Talwar, Mahesh Verma
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(1):1-13. Published online November 3, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Advancements in bio-ceramic technology has revolutionised endodontic material science by enhancing the treatment outcome for patients. This class of dental materials conciliates excellent biocompatibility with high osseoconductivity that render them ideal for endodontic care. Few recently introduced bio-ceramic materials have shown considerable clinical success over their early generations in terms of good handling characteristics. Calcium enriched mixture (CEM) cement, Endosequence sealer, and root repair materials, Biodentine and BioAggregate are the new classes of bio-ceramic materials. The aim of this literature review is to present investigations regarding properties and applications of CEM cement in endodontics. A review of the existing literature was performed by using electronic and hand searching methods for CEM cement from January 2006 to December 2013. CEM cement has a different chemical composition from that of mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) but has similar clinical applications. It combines the biocompatibility of MTA with more efficient characteristics, such as significantly shorter setting time, good handling characteristics, no staining of tooth and effective seal against bacterial leakage.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- CBCT‐Assisted Microsurgical Management of Dual Periapical Lesions Involving Vital and Previously Endodontically Treated Maxillary Molars: A Case Report
Saeed Asgary
Clinical Case Reports.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of calcium-enriched mixture and mineral trioxide aggregate in vital pulp therapy of molars: A systematic review
Aarti Ravishankar Lamb, Sheetal Ghivari, Rishikesh Meshram, Ambar Raut, Maithilee Sapkal, Saniya Rege
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2026; 29(2): 127. CrossRef - Antibacterial Efficacy of Graphene Nanoparticles against Enterococcus faecalis: In Vitro Study
Omer Sheriff Sultan, Preena Sidhu, Kiran Rehman, Thiagrajan Madheswaran, Amalraj Fabian Davamani
European Journal of Dentistry.2025; 19(01): 103. CrossRef - Biomineralization reaction from nanosized calcium silicate: A new method for reducing dentin hypersensitivity
Mi-Jeong Jeon, Yu-Sung Choi, Jeong-Kil Park, Jin-Soo Ahn, Yu-Chih Chiang, Deog-Gyu Seo
Journal of Dental Sciences.2025; 20(1): 428. CrossRef - How to Deal with Pulpitis: An Overview of New Approaches
Jakub Fiegler-Rudol, Wojciech Niemczyk, Katarzyna Janik, Anna Zawilska, Małgorzata Kępa, Marta Tanasiewicz
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(1): 25. CrossRef - Effect of Manipulation Methods and Storage Environments on the Microstructural, Chemical, and Mechanical Properties of Calcium‐Enriched Mixture Cement
Leyla Roghanizadeh, Hassan Torabzadeh, Ardavan Parhizkar, Alireza Akbarzadeh Baghban, Saeed Asgary, Luca Fiorillo
International Journal of Biomaterials.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Advances in 3D Bioprinting of Scaffolds for Dental Tissue Engineering and Regeneration
Senyao Chen, Jianwei Sun, Wenzhi Wu, Zhuo Chen
Advanced Functional Materials.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Vital Pulp Therapy Biomaterials on Tooth Discolouration: A Review of the Literature
Maedeh Gilvari Sarshari, Kiana Shakeri, Ardavan Parhizkar, Naresh Kasoju
International Journal of Biomaterials.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Vital Pulpa Tedavilerinde Biyoseramik Materyallerin Kullanımı: Sistematik Derleme
Duygu Bal, Gül Keskin
Türk Diş Hekimliği Araştırma Dergisi.2025; 4(2): 103. CrossRef - Bioactive Materials in Pediatric Endodontics: Current Applications and Future Directions
Abdulrahman S Alshalan, Fai A Almutiri, Ali H Al-battat, Abdulrahman M Alqahtani, Khalid A Binzamil, Reem M Alabdan, Khalidah K Alrabghi, Asma M Aldohailan, Eman A Alshammari, Abdulrahman S Khurayniq, Mazen T Alshahrani
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative clinical success of direct pulp capping materials: A network meta-regression of randomized clinical trials
Ömer Hatipoğlu, Elif Varlı Tekingür, Fatma Pertek Hatipoğlu
Journal of Dentistry.2025; 162: 106073. CrossRef - Pharmacopée intracanalaire
J. Davril, R. Balthazard, R. Giess, M. Vincent, E. Mortier
EMC - Odontologie.2025; 41(4): 1. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of four different calcium-based medicaments as an indirect pulp capping agent: An in vivo study
Ray Anuja Awadhesh, Nitin Kararia, Deepak Kumar Sharma, Shyam Agrawal, Rachit Mathur, Jyotirmoyee Bhanja
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(10): 1013. CrossRef - Calcium Phosphate Incorporated Polymeric Fibrous Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering: A Comprehensive Review
Parvathy GH, Nidhish Kumar P, Swapna YV, Mathew CT, Jijimon K Thomas
Journal of Macromolecular Science, Part B.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Investigation of the crystal formation from calcium silicate in human dentinal tubules and the effect of phosphate buffer saline concentration
Mi-Jeong Jeon, Jin-Soo Ahn, Jeong-Kil Park, Deog-Gyu Seo
Journal of Dental Sciences.2024; 19(4): 2278. CrossRef - Comprehensive review of composition, properties, clinical applications, and future perspectives of calcium-enriched mixture (CEM) cement: a systematic analysis
Saeed Asgary, Mahtab Aram, Mahta Fazlyab
BioMedical Engineering OnLine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Dentinal tubule penetration following ultrasonic, sonic, and single-cone technique of a biosealer: An ex vivo study
Dina Abdellatif, Massimo Pisano, Renato Gullà, Giuseppe Sangiovanni, Shishir Singh, Francesco Giordano, Alessio Buonavoglia, Alfredo Iandolo
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(3): 331. CrossRef - Physicochemical properties of silicate tricalcium-based cement for use as pulp capping or repair material
Suyane Maria LUNA-CRUZ, Bernardo Almeida AGUIAR, Pierre Basílio Almeida FECHINE, Marco Antônio Húngaro DUARTE, Bruno Carvalho de VASCONCELOS, Juliano Sartori MENDONÇA
Brazilian Oral Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Successful Tampon Pulpotomy in a Molar With an Endodontic Lesion: A Case Report
Saeed Asgary
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative evaluations of shear bond strength of mineral trioxide aggregate, Biodentine, and calcium-enriched mixture to bulk-fill flowable composite using three different adhesive systems: An in vitro study
Asmat Fatima, Huma İftekhar, Sharique Alam, Rajendra Kumar Tewari, Mukhtar Un Nisar Andrabi
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(7): 706. CrossRef - Comparative in vitro analysis of the antifungal activity of different calcium silicate-based endodontic sealers
Luiz Felipe Nunes Moreira, Fernando Peña-Bengoa, Sven Eric Niklander, Carlos Eduardo da Silveira Bueno, Alexandre Sigrist de Martin, Daniel Guimarães Pedro Rocha
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2024; 23: e243355. CrossRef - Enhancing pH Modulation and Calcium Ions Release in External Resorption Artificial Defects
Azadeh Kheradyar, Mamak Adel, Majid Sirati-Sabet, Alireza Kolahdouzan, Sahar Shafagh, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
International Journal of Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of pulpotomy for permanent teeth with carious pulp exposure: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Wenjun Li, Bo Yang, Jing Shi, Carlos Alberto Antunes Viegas
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(7): e0305218. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of cervical pulpotomy and pulpectomy for primary molars with irreversible pulpitis: a multicentre randomised controlled trial
S. Sabbagh, Z. Bahrololoomi, A. Sarraf Shirazi, F. Zarebidoki, S. Salajegheh, F. Fotouhi, A. Akbarzadeh Baghban, S. Asgary
European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry.2024; 25(2): 255. CrossRef - Bioceramic Materials: A Boon in Pediatric Dentistry: A Literature Review
Sheenam Ayub, Sonal Gupta, Menia Gumro
Journal of Primary Care Dentistry and Oral Health.2024; 5(1): 3. CrossRef - Peptide KN-17-Loaded Supramolecular Hydrogel Induces the Regeneration of the Pulp-Dentin Complex
Borui Zhao, Qian Zhang, Houzhi Yang, Shuipeng Yu, Rui Fu, Shurui Shi, Yuanyuan Wang, Wei Zhou, Yange Cui, Qingxiang Guo, Xi Zhang
ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering.2024; 10(4): 2523. CrossRef - Cimentos biocerâmicos na endodontia: atualizações sobre as propriedades regenerativas e antibacterianas
Víctor Lucas Ribeiro Lopes, Even Herlany Pereira Alves, Hélio Mateus Silva Nascimento, Maria de Fátima Leal de Sousa, Daniel Fernando Pereira Vasconcelos, Francisca Meire Soares de Freitas Portela
Cuadernos de Educación y Desarrollo.2024; 16(8): e5259. CrossRef - ZrO2 and ZnO nanoparticles effect on setting time, microhardness, and compressive strength of calcium-enriched-mixture cement
Faezeh Sadat Razavi, Fatemeh Mahmoudi Afsah, Alireza Akbarzadeh Baghban, Hasan Torabzadeh, Saeed Asgary
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2024; 23: e244482. CrossRef - Radiographic Evaluation of Periapical Healing Rates Between Bio-Ceramic Sealer and AH+ Sealer: A Retrospective Study
Dalia Nayil Alharith, Iman T. Mansi, YoumnaElsaid Abdulmotalib, HebaFuad Amous, TagreedSuliman Aljulban, Haifa Mohammed Al Aiban, Sali Mohamad Haffar
Annals of Dental Specialty.2023; 11(2): 124. CrossRef - Bioceramics in endodontics – A review
Chris Cherian Geogi, Ananya Rawat, Sandeep Dubey, Palak Singh
IP Indian Journal of Conservative and Endodontics.2023; 7(4): 163. CrossRef - Exploring the Most Effective Apical Seal for Contemporary Bioceramic and Conventional Endodontic Sealers Using Three Obturation Techniques
Hira Akhtar, Farah Naz, Arshad Hasan, Anum Tanwir, Danish Shahnawaz, Umair Wahid, Fariha Irfan, Muhammad Adeel Ahmed, Khalid H. Almadi, Mazen F. Alkahtany, Tariq Abduljabbar, Fahim Vohra
Medicina.2023; 59(3): 567. CrossRef - Tissue Response to a Heat Resistant Silicate-Based and an Epoxy Resin-Based Endodontic Sealer Implanted in Rat Tibias
Osvaldo Zmener, Cornelis H. Pameijer, Roberto Della Porta, Romina de Lucca
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(18): 10075. CrossRef - Autotransplantation of a Third Molar to Replace an Adjacent Unrestorable Tooth: A Case Report
Saeed Asgary
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Fracture Resistance of Molars With Simulated Strip Perforation Repaired With Different Calcium Silicate-Based Cements
Alaa Kabtoleh, Ossama Aljabban, Yasser Alsayed Tolibah
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Outcomes of Endodontic-Treated Teeth Obturated with Bioceramic Sealers in Combination with Warm Gutta-Percha Obturation Techniques: A Prospective Clinical Study
Denise Irene Karin Pontoriero, Edoardo Ferrari Cagidiaco, Valerio Maccagnola, Daniele Manfredini, Marco Ferrari
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(8): 2867. CrossRef - An in vitro comparative evaluation of the effect of three intracanal medicaments – chlorhexidine gel, triple antibiotic paste, and calcium hydroxide paste on the push-out bond strength of MTA Plus, Biodentine, and calcium-enriched mixture
Gouthami Datta, Ramya Raghu, Ashish Shetty, Gautham P Manjunath, Dishant Patel, Subhashini Rajasekhara
Endodontology.2023; 35(1): 60. CrossRef - Effects of CEM cement and emdogain on proliferation and differentiation of human stem cells from the apical papilla: a comparative in vitro study
Elham Khoshbin, Leila Ghasemi, Rezvan Najafi, Hamed Karkehabadi
Biotechnology Letters.2023; 45(1): 69. CrossRef - Ceramic nanomaterials: Preparation and applications in osteoporosis and bone tissue regeneration
Anish John, Apurva M. Shetty, Kshema Salian, Samantha Neha Sequeria, P. R. Sumukh, Dewi Sukmawati, Gowtham Menon, Shajan Abraham, Jayachandran Venkatesan, V. Anoop Narayanan
Journal of Materials Research.2023; 38(17): 4023. CrossRef - Recent Advances in Endodontic Diagnosis and Modern Treatment Plans
Alfredo Iandolo
Diagnostics.2023; 13(17): 2786. CrossRef - Outcome of pulpotomy in permanent teeth with irreversible pulpitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Amber Ather, Biraj Patel, Jonathan A. L. Gelfond, Nikita B. Ruparel
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Coronal Discoloration Induced by White MTA and CEM Cement
Mamak Adel, Sareh Aflaki, Mohammad Jafar Eghbal, Alireza Darvish, Amanda Mandana Golshiri, Nima Moradi Majd, Rodolfo Reda, Maryam Tofangchiha, Alessio Zanza, Luca Testarelli
Journal of Composites Science.2022; 6(12): 371. CrossRef - Current trends and future perspectives on dental nanomaterials – An overview of nanotechnology strategies in dentistry
Vidhya Rekha Umapathy, Prabhu Manickam Natarajan, C. SumathiJones, Bhuminathan Swamikannu, W.M.S. Johnson, V. Alagarsamy, Ashequr Rahman Milon
Journal of King Saud University - Science.2022; 34(7): 102231. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Sealing Ability and Bond Strength of Two Endodontic Root Canal Sealers: An In Vitro Study
Manuel Marques Ferreira, José Pedro Martinho, Inês Duarte, Diogo Mendonça, Ana Catarina Craveiro, Maria Filomena Botelho, Eunice Carrilho, Carlos Miguel Marto, Ana Coelho, Anabela Paula, Siri Paulo, Nuno Chichorro, Ana Margarida Abrantes
Dentistry Journal.2022; 10(11): 201. CrossRef - Outcomes of root canal therapy or full pulpotomy using two endodontic biomaterials in mature permanent teeth: a randomized controlled trial
Saeed Asgary, Mohammad Jafar Eghbal, Arash Shahravan, Eshaghali Saberi, Alireza Akbarzadeh Baghban, Ardavan Parhizkar
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 26(3): 3287. CrossRef - Trends of calcium silicate biomaterials in medical research and applications: A bibliometric analysis from 1990 to 2020
Hua Yin, Xiaoli Yang, Lisi Peng, Chuanchao Xia, Deyu Zhang, Fang Cui, Haojie Huang, Zhaoshen Li
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Different types of bioceramics as dental pulp capping materials: A systematic review
Sotoudeh Davaie, Tabassom Hooshmand, Sajjad Ansarifard
Ceramics International.2021; 47(15): 20781. CrossRef - Effect of MTA versus CEM apical plugs on fracture resistance of endodontically treated simulated immature teeth restored with cast metal posts: an in-vitro study
Ensieh Grayli, Abbas Dashtban, Leyla Shadan, Naser Behnampour, Elham Afshari
BMC Oral Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of Direct Pulp Capping Bioactive Materials in Dentin Regeneration: A Systematic Review
Ermin Nie, Jiali Yu, Rui Jiang, Xiangzhen Liu, Xiang Li, Rafiqul Islam, Mohammad Khursheed Alam
Materials.2021; 14(22): 6811. CrossRef - Pediatric Endodontic Treatment of Adolescent Patients
Adriana Modesto Vieira, Herbert L. Ray
Dental Clinics of North America.2021; 65(4): 775. CrossRef - Management of primary molars with irreversible pulpitis employing tampon pulpotomy: Report of three cases with 34‐month mean follow‐up
Saeed Asgary, Alireza Sarraf Shirazi, Sedigheh Sabbagh
Clinical Case Reports.2021; 9(4): 2289. CrossRef - Effects of various liquid-to-powder ratios on the compressive strength of calcium enriched mixture: Original research
Mohammad Forough Reyhani, Sheida Hosseinian Ahangarnezhad, Negin Ghasemi, Amin Salem Milani
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2021; 15(2): 129. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Use of Bioceramics in Endodontic Management, Literature Review
Wejdan Ali Alkaabinah, Bashayr Faisal Alanazi, Amlak Munahi Albaqami, Bashayer Mohammed Almutiry, Maram Saleh A Alkhamis, Ali Abdullah Alhejailan, Ibrahim Owaidh M Almutairi, Bassel Hamad Aldahman, Alhanoof Falah Alanazi
Pharmacophore.2021; 12(3): 87. CrossRef - Bioactive Glass Modified Calcium Phosphate Cement with Improved Bioactive Properties: A Potential Material for Dental Pulp-Capping Approaches
Sotoudeh Davaie, Sima Shahabi, Marjan Behroozibakhsh, Sanaz Vali, Farhood Najafi
Journal of Biomimetics, Biomaterials and Biomedical Engineering.2021; 51: 1. CrossRef - Intratubular penetration of endodontic sealers depends on the fluorophore used for CLSM assessment
Taiane Correa Furtado, Igor Abreu de Bem, Lucas Silveira Machado, Jefferson Ricardo Pereira, Marcus Vinícius Reis Só, Ricardo Abreu da Rosa
Microscopy Research and Technique.2021; 84(2): 305. CrossRef - From the Desk of the Editor: The New-Age Bioceramic Root Canal Sealers
Shishir Singh
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2021; 24(5): 413. CrossRef - Influence of Blood Contamination on Push-Out Bond Strength of Three Calcium Silicate-Based Materials to Root Dentin
Cristina Rodrigues Paulo, Joana A. Marques, Diana B. Sequeira, Patrícia Diogo, Rui Paiva, Paulo J. Palma, João Miguel Santos
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(15): 6849. CrossRef - Comparison of the Success Rate of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate, Endosequence Bioceramic Root Repair Material, and Calcium Hydroxide for Apexification of Immature Permanent Teeth: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Izaz Shaik, Bhargavi Dasari, Rashmi Kolichala, Mina Doos, Fida Qadri, Jenefer Loveline Arokiyasamy, Rahul Vinay Chandra Tiwari
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2021; 13(Suppl 1): S43. CrossRef - Local Drug Delivery Systems for Vital Pulp Therapy: A New Hope
Ardavan Parhizkar, Saeed Asgary, Carlo Galli
International Journal of Biomaterials.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Toughening of Bioceramic Composites for Bone Regeneration
Zahid Abbas, Massimiliano Dapporto, Anna Tampieri, Simone Sprio
Journal of Composites Science.2021; 5(10): 259. CrossRef - Performance of Bioceramic-based Root Filling Material with Artifact Reduction Properties in the Detection of Vertical Root Fractures Using Cone-beam Computed Tomography
Ali Bahmani, Hamed Karkehabadi, Abbas Shokri, Maryam Farhadian
The Open Dentistry Journal.2021; 15(1): 170. CrossRef - The effect of partial pulpotomy with iRoot BP Plus in traumatized immature permanent teeth: A randomized prospective controlled trial
YingTing Yang, Bin Xia, Zheng Xu, Guili Dou, Yue Lei, Wei Yong
Dental Traumatology.2020; 36(5): 518. CrossRef - Effect of ultrasonic cleaning on the bond strength of fiber posts in oval canals filled with a premixed bioceramic root canal sealer
Fernando Peña Bengoa, Maria Consuelo Magasich Arze, Cristobal Macchiavello Noguera, Luiz Felipe Nunes Moreira, Augusto Shoji Kato, Carlos Eduardo Da Silveira Bueno
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Silico-Aluminophosphate and Alkali-Aluminosilicate Geopolymers: A Comparative Review
Yan-Shuai Wang, Yazan Alrefaei, Jian-Guo Dai
Frontiers in Materials.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Combination of mineral trioxide aggregate and propolis promotes odontoblastic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells through ERK signaling pathway
Jae-Hwan Kim, Soo-Yung Kim, Su-Mi Woo, Ha-Na Jeong, Ji-Yeon Jung, Seon-Mi Kim, Hae-Soon Lim
Food Science and Biotechnology.2019; 28(6): 1801. CrossRef - Effectiveness of a Novel Calcium-enriched Mixture Root Cement to Decelerate Replacement Resorption in Replanted Teeth: A Case Report
Nasil Sakkir, Tony Francis, Sonal B Joshi
World Journal of Dentistry.2019; 10(6): 457. CrossRef - Which procedures and materials could be applied for full pulpotomy in permanent mature teeth? A systematic review
M. Zanini, M. Hennequin, PY. Cousson
Acta Odontologica Scandinavica.2019; 77(7): 541. CrossRef - Microstructure and chemical analysis of four calcium silicate-based cements in different environmental conditions
K. Ashofteh Yazdi, Sh. Ghabraei, B. Bolhari, M. Kafili, N. Meraji, M. H. Nekoofar, P. M. H. Dummer
Clinical Oral Investigations.2019; 23(1): 43. CrossRef - Treatment Outcomes of 4 Vital Pulp Therapies in Mature Molars
Saeed Asgary, Raheleh Hassanizadeh, Hassan Torabzadeh, Mohammad Jafar Eghbal
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(4): 529. CrossRef - Sectional Fixed Orthodontic Extrusion Technique in Management of Teeth with Complicated Crown-Root Fractures: Report of Two Cases
S. Nagarajan M. P. Sockalingam, Katherine Kong Loh Seu, Halimah Mohamed Noor, Ahmad Shuhud Irfani Zakaria
Case Reports in Dentistry.2018; 2018: 1. CrossRef - Evaluation of Physicochemical Properties of New Calcium Silicate-Based Sealer
Aline Teixeira Mendes, Paula Barcellos da Silva, Bruna Barcelos Só, Lina Naomi Hashizume, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, Ricardo Abreu da Rosa, Marco Antonio Húngaro Duarte, Marcus Vinícius Reis Só
Brazilian Dental Journal.2018; 29(6): 536. CrossRef - Periodontal healing following non-surgical repair of an old perforation with pocket formation and oral communication
Saeed Asgary, Prashant Verma, Ali Nosrat
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Nonsurgical Management and 2-year Follow-up by means of Cone Beam Computed Tomography of an Invasive Cervical Resorption in a Molar
Esam Halboub, Hemant R Chourasia, Rafael A Roges
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2018; 19(9): 1152. CrossRef - Management of merged external/internal root resorption using CEM cement: a case report.
Hesam Mirmohammadi, Saeed Asgary
Journal of Oral Research.2018; 7(8): 318. CrossRef - Maturogenesis of an Immature Dens Evaginatus Nonvital Premolar with an Apically Placed Bioceramic Material (EndoSequence Root Repair Material®): An Unexpected Finding
S. Nagarajan M. P. Sockalingam, Mohd Safwani Affan Alli Awang Talip, Ahmad Shuhud Irfani Zakaria
Case Reports in Dentistry.2018; 2018: 1. CrossRef - The implications and applications of nanotechnology in dentistry: A review
Rawan N. AlKahtani
The Saudi Dental Journal.2018; 30(2): 107. CrossRef - Calcium silicate‐based cements: composition, properties, and clinical applications
Alaa E. Dawood, Peter Parashos, Rebecca H.K. Wong, Eric C. Reynolds, David J. Manton
Journal of Investigative and Clinical Dentistry.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Biocompatibility of three new calcium silicate‐based endodontic sealers on human periodontal ligament stem cells
M. Collado‐González, D. García‐Bernal, R. E. Oñate‐Sánchez, P. S. Ortolani‐Seltenerich, A. Lozano, L. Forner, C. Llena, F. J. Rodríguez‐Lozano
International Endodontic Journal.2017; 50(9): 875. CrossRef - Cytotoxicity and bioactivity of various pulpotomy materials on stem cells from human exfoliated primary teeth
M. Collado‐González, D. García‐Bernal, R. E. Oñate‐Sánchez, P. S. Ortolani‐Seltenerich, T. Álvarez‐Muro, A. Lozano, L. Forner, C. Llena, J. M. Moraleda, F. J. Rodríguez‐Lozano
International Endodontic Journal.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of Three Different Biomaterials on Proliferation and Viability of Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells (In-vitro Study)
Dalia A. Mohamed, Maha I. Abdelfattah, Eman H. A. Aboulezz
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.2017; 5(5): 657. CrossRef - Bioactive-glass in Endodontic Therapy and Associated Microsurgery
Andrea Corrado Profeta, Gian Marco Prucher
The Open Dentistry Journal.2017; 11(1): 164. CrossRef - Comparison of mineral trioxide aggregate and calcium hydroxide for apexification of immature permanent teeth: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Jia-Cheng Lin, Jia-Xuan Lu, Qian Zeng, Wei Zhao, Wen-Qing Li, Jun-Qi Ling
Journal of the Formosan Medical Association.2016; 115(7): 523. CrossRef - Cytotoxic effects of mineral trioxide aggregate, calcium enrichedmixture cement, Biodentine and octacalcium pohosphate onhuman gingival fibroblasts
Eshagh A. Saberi, Narges Farhadmollashahi, Faroogh Ghotbi, Hamed Karkeabadi, Roholla Havaei
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2016; 10(2): 75. CrossRef - Influence of Biodentine® - A Dentine Substitute - On Collagen Type I Synthesis in Pulp Fibroblasts In Vitro
Frangis Nikfarjam, Kim Beyer, Anke König, Matthias Hofmann, Manuel Butting, Eva Valesky, Stefan Kippenberger, Roland Kaufmann, Detlef Heidemann, August Bernd, Nadja Nicole Zöller, Dimitrios Karamichos
PLOS ONE.2016; 11(12): e0167633. CrossRef - Challenges in developing valid techniques for equine endodontic treatment of apically infected cheek teeth
R. M. Baratt
Equine Veterinary Education.2016; 28(11): 609. CrossRef - Regenerative Endodontic Procedure in Korean Children and Adolescents: A Case Report
So-Youn An, Jin-Kyoung Kim, Youn-Soo Shim
Journal of dental hygiene science.2016; 16(4): 317. CrossRef
- CBCT‐Assisted Microsurgical Management of Dual Periapical Lesions Involving Vital and Previously Endodontically Treated Maxillary Molars: A Case Report
- 3,801 View
- 31 Download
- 85 Crossref

- Surgical endodontic management of infected lateral canals of maxillary incisors
- Ji-Hyun Jang, Jung-Min Lee, Jin-Kyu Yi, Sung-Baik Choi, Sang-Hyuk Park
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(1):79-84. Published online October 10, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.1.79
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This case report presents surgical endodontic management outcomes of maxillary incisors that were infected via the lateral canals. Two cases are presented in which endodontically-treated maxillary central incisors had sustained lateral canal infections. A surgical endodontic treatment was performed on both teeth. Flap elevation revealed vertical bone destruction along the root surface and infected lateral canals, and microscopy revealed that the lateral canals were the origin of the lesions. After the infected lateral canals were surgically managed, both teeth were asymptomatic and labial fistulas were resolved. There were no clinical or radiographic signs of surgical endodontic management failure at follow-up visits. This case report highlights the clinical significance and surgical endodontic management of infected lateral canal of maxillary incisor. It is important to be aware of root canal anatomy variability in maxillary incisors. Maxillary central incisors infected via the lateral canal can be successfully managed by surgical endodontic treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Surgical Management of Radicular Cyst with Platelet-rich Fibrin Placement followed by Nonvital Bleaching of a Discolored Maxillary Left Central Incisor (21)
Sagarika Sortey, Gautam Badole, Pratima Shenoi, Rajesh Kubde, Shriya Shahu, Ankita Ramteke, Varsha Uttarwar
Bharati Vidyapeeth Journal of Dentistry and Allied Sciences.2025; 2(1): 31. CrossRef - Apical Surgery of a Maxillary Left Central Tooth Using NeoPutty After Retreatment Failure: A Case Report
Sajedeh Namaei Ghasemi, Zakieh Kheradmand, Siavash Moushekhian, Zeinab Ghasemi
Clinical Case Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Cone Beam Computed Tomography as a Diagnostic Tool in the Diagnosis of an Iatrogenic Root Defect of a Root Canal Treated Maxillary Central Incisor with Periapical Lesion and Its Management by Re-apicectomy
Swathi Aravelli, Uday Kumar, Gunnam Sai Nishitha, K. Mallika Yadav, P. Sivaram, Nimeshika Ramachandruni
Bharati Vidyapeeth Journal of Dentistry and Allied Sciences.2025; 2(4): 155. CrossRef - On the Causes of Persistent Apical Periodontitis. Findings From Endodontic Microsurgery: A Case Report
Mateo José Pesántez-Ibarra, Carolina Berruecos-Orozco, Jeimmy Katherine Molina-Barrera, Néstor Ríos-Osorio, Rafael Fernández-Grisales
Journal of Endodontic Microsurgery.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Expert consensus on difficulty assessment of endodontic therapy
Dingming Huang, Xiaoyan Wang, Jingping Liang, Junqi Ling, Zhuan Bian, Qing Yu, Benxiang Hou, Xinmei Chen, Jiyao Li, Ling Ye, Lei Cheng, Xin Xu, Tao Hu, Hongkun Wu, Bin Guo, Qin Su, Zhi Chen, Lihong Qiu, Wenxia Chen, Xi Wei, Zhengwei Huang, Jinhua Yu, Zhen
International Journal of Oral Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Surgical endodontic treatment of maxillary incisors: Case report
Moazzy I. Almansour
Clinical Case Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Resective and Regenerative Approach for an Unresolved Periapical Lesion: A Surgical Case Report With 24-Month Follow-Up
Anchu R Thomas, Melwin Mathew, Sunil K Nettemu, Anoop Mayya
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - An in vitro endodontic model to quantify the accessory canal filling potential of the vertical and lateral condensation techniques
Thomas Gerhard Wolf, Louisa Willems, Benjamín Briseño‐Marroquín
Australian Endodontic Journal.2021; 47(2): 245. CrossRef - Application of a new system for classifying root and canal anatomy in studies involving micro‐computed tomography and cone beam computed tomography: Explanation and elaboration
H. M. A. Ahmed, N. Ibrahim, N. S. Mohamad, P. Nambiar, R. F. Muhammad, M. Yusoff, P. M. H. Dummer
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(7): 1056. CrossRef - German Dentists’ Preferences for the Treatment of Apical Periodontitis: A Cross-Sectional Survey
Jonas Conrad, Jan Retelsdorf, Sameh Attia, Christof Dörfer, Mohamed Mekhemar
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(20): 7447. CrossRef - Surgical management of an accessory canal in a maxillary premolar: a case report
Hee-Jin Kim, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kwang-Won Lee, Kyung-San Min
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - A new system for classifying accessory canal morphology
H. M. A. Ahmed, P. Neelakantan, P. M. H. Dummer
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(2): 164. CrossRef - Effects of antimicrobial photodynamic therapy and surgical endodontic treatment on the bacterial load reduction and periapical lesion healing. Three years follow up
Aguinaldo S. Garcez, Julio G. Arantes-Neto, Debora P. Sellera, Eduardo Rodrigues Fregnani
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2015; 12(4): 575. CrossRef
- Surgical Management of Radicular Cyst with Platelet-rich Fibrin Placement followed by Nonvital Bleaching of a Discolored Maxillary Left Central Incisor (21)
- 1,962 View
- 14 Download
- 13 Crossref

- An esthetic appliance for the management of crown-root fracture: a case report
- Sang-Min Jeon, Kang-Hee Lee, Bock-Young Jung
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(3):226-229. Published online May 22, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.3.226
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Orthodontic extrusion is usually performed by means of a fixed orthodontic appliance that utilizes arch wire attached to adjacent teeth and transfers the desired force by elastic from the wire to the root. However, clinicians often encounter cases where the bonding required for tooth traction is not possible because the adjacent teeth have been restored with ceramic or veneer. The purpose of this case report is to describe a modified orthodontic extrusion appliance that is useful when conventional orthodontic treatment is not possible. The modified appliance was fabricated using an artificial tooth, clear plastic sheeting, and a braided fiber-reinforced composite strip that covered adjacent teeth without bonding. It satisfied the esthetic and functional needs of the patient and established the optimal biologic width.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Esthetic enhancement of a traumatized anterior tooth with a combination of forced eruption and tooth alignment: a case report
So-Hee Kang, Jung-Hong Ha, Myoung-Uk Jin, Sung-Kyo Kim, Young-Kyung Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(3): 210. CrossRef
- Esthetic enhancement of a traumatized anterior tooth with a combination of forced eruption and tooth alignment: a case report
- 1,268 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Autogenous tooth transplantation for replacing a lost tooth: case reports
- Ji-Youn Kang, Hoon-Sang Chang, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Bin-Na Lee
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(1):48-51. Published online February 26, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.1.48
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The autogenous tooth transplantation is an alternative treatment replacing a missing tooth when a suitable donor tooth is available. It is also a successful treatment option to save significant amount of time and cost comparing implants or conventional prosthetics. These cases, which required single tooth extraction due to deep caries and severe periodontal disease, could have good results by transplanting non-functional but sound donor tooth to the extraction site.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Autogenous tooth transplantation of canines: a prospective clinical study on the influence of extraoral storage time-guided adjunctive antibiotic therapy and patient-related risk factors affecting success, survival, and prognosis after two years of follow
Sebastian Meinzer, Dirk Nolte, Karin Christine Huth
BMC Oral Health.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Autogenous Tooth Transplantation of Canines—A Prospective Clinical Study on the Influence of Adjunctive Antibiosis and Patient-Related Risk Factors During Initial Healing
Sebastian Meinzer, Dirk Nolte, Karin Christine Huth
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(3): 821. CrossRef - 13-year follow-up of autotransplantation using an immature third molar: a case report
Hojin Moon
Journal of Dental Rehabilitation and Applied Science.2025; 41(1): 72. CrossRef - Template-Guided Autogenous Tooth Transplantation Using a CAD/CAM Dental Replica in a Complex Anatomical Scenario: A Case Report
Michael Alfertshofer, Florian Gebhart, Dirk Nolte
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(7): 281. CrossRef - Autogenous Transplantation of Teeth Across Clinical Indications: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Martin Baxmann, Karin Christine Huth, Krisztina Kárpáti, Zoltán Baráth
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(14): 5126. CrossRef - Dental autotransplantation: case report and follow-up
Kassandra García Covarrubias, Erika Etcheverry Doger, Jennifer Antón Sarabia, Mario Alberto Lagunes López
Revista Odontología Pediátrica.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis and evaluation of the effectiveness of autotransplantation of teeth
Filipp V. Dulov, Roman B. Gurkin, Ekaterina S. Derbentsova, Ulia V. Budanova
Russian Journal of Dentistry.2023; 27(3): 193. CrossRef - Pre- and peri-operative factors influence autogenous tooth transplantation healing in insufficient bone sites
Thanapon Suwanapong, Aurasa Waikakul, Kiatanant Boonsiriseth, Nisarat Ruangsawasdi
BMC Oral Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Third molar autotransplantation: An alternative to dental implant - 9 years follow up of a case
Sanjay Kumar, Mansi Jain, Suma Sogi, Prinka Shahi, Saru Dhir, Swati Rana
Annals of Maxillofacial Surgery.2020; 10(2): 529. CrossRef - Prognostic Factors for Clinical Outcomes in Autotransplantation of Teeth with Complete Root Formation: Survival Analysis for up to 12 Years
Youngjune Jang, Yoon Jeong Choi, Seung-Jong Lee, Byoung-Duck Roh, Sang Hyuk Park, Euiseong Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(2): 198. CrossRef - Post-Odontoma autotransplantation of an impacted tooth: A case report
Waikhom Robindro Singh, Kirankumar Aheibam, Anthopia Nameirakpam
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2015; 5(2): 120. CrossRef - Autotransplantation of a Mandibular Third Molar: A Case Report with 5 Years of Follow-up
Mauro Henrique Chagas e Silva, Mariane Floriano Lopes Santos Lacerda, Maria das Gracas Afonso Miranda Chaves, Celso Neiva Campos
Brazilian Dental Journal.2013; 24(3): 289. CrossRef
- Autogenous tooth transplantation of canines: a prospective clinical study on the influence of extraoral storage time-guided adjunctive antibiotic therapy and patient-related risk factors affecting success, survival, and prognosis after two years of follow
- 2,040 View
- 6 Download
- 12 Crossref

- Success and failure of endodontic microsurgery
- Minju Song, Euiseong Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(6):465-476. Published online November 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.6.465
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub In current endodontic practice, introduction of operating microscope, ultrasonic instruments, and microinstruments has induced a big change in the field of surgical retreatment. In this study, we aimed to offer key steps of endodontic microsurgery procedure compared with traditional root-end surgery, and to evaluate factors influencing success and failure based on published articles.
Endodontic microsurgery is a surgical procedure performed with the aid of a microscope, ultrasonic instruments and modern microsurgical instruments. The microscope provides magnification and illumination - essential for identifying minute details of the apical anatomy. Ultrasonic instruments facilitate the precise root-end preparation that is within the anatomical space of the canal. Modern endodontics can therefore be performed with precision and predictability, thus eliminating the disadvantages inherent in traditional periapical surgery such as large osteotomy, beveled apicoectomy, inaccurate root-end preparation and the inability to observe isthmus.
Factors influencing the outcomes of endodontic microsurgery may be diverse, but standardization of procedures can minimize its range. Among patient and tooth-related factors, periodontal status and tooth position are known to be prognostic, but there are only few articles concerning this matter. High-evidence randomized clinical trials or prospective cohort studies are needed to confirm these findings.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Treatment-Related Factors Affecting the Success of Endodontic Microsurgery and the Influence of GTR on Radiographic Healing—A Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Study
Daniel Bieszczad, Jarosław Wichlinski, Tomasz Kaczmarzyk
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(19): 6382. CrossRef - Factors Affecting the Success of Endodontic Microsurgery: A Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Study
Daniel Bieszczad, Jaroslaw Wichlinski, Tomasz Kaczmarzyk
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(14): 3991. CrossRef - Comparison of Clinical Outcomes of Endodontic Microsurgery: 1 Year versus Long-term Follow-up
Minju Song, Taekjin Nam, Su-Jung Shin, Euiseong Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2014; 40(4): 490. CrossRef - The Influence of Bone Tissue Deficiency on the Outcome of Endodontic Microsurgery: A Prospective Study
Minju Song, Sahng Gyoon Kim, Su-Jung Shin, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Euiseong Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2013; 39(11): 1341. CrossRef - Prognostic Factors of Clinical Outcomes in Endodontic Microsurgery: A Prospective Study
Minju Song, Sahng Gyoon Kim, Seung-Jong Lee, Baekil Kim, Euiseong Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2013; 39(12): 1491. CrossRef - Is stopping of anticoagulant therapy really required in a minor dental surgery? - How about in an endodontic microsurgery?
Yong-Wook Cho, Euiseong Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(3): 113. CrossRef
- Treatment-Related Factors Affecting the Success of Endodontic Microsurgery and the Influence of GTR on Radiographic Healing—A Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Study
- 2,437 View
- 34 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Prognostic factors influencing clinical outcome of nonsurgical endodontic treatment
- Seonah Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(6):436-444. Published online November 30, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.6.436
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to assess prospectively the clinical outcome of nonsurgical endodontic treatment and identify patient- and tooth-related factors, rather than treatment-related factors, that were the best predictors of this outcome.
Materials and Methods The inception cohort comprised 441 teeth (320 patients) and 175 teeth (123 patients) were followed up for 1-2 years. Age, gender, presence of medical disease, number of canals, previous endodontic treatment, presence of sensitivity and pain, pulp vitality, swelling or sinus tract of pulpal origin on the gingiva, periapical radiolucency and tendency of unilateral bite on the affected tooth were recorded at treatment start.
Results The outcome was classified on the basis of periapical radiolucency as healed or non healed. The overall healed rate in these cases, including nonsurgical retreatment, was 81.1%. Four tooth-related factors had a negative impact in the bivariate analysis: previous endodontic treatment, necrotic pulp, preoperative gingival swelling or sinus tract of pulpal origin, and preoperative periapical radiolucency. Stepwise logistic regression analysis including patient-, tooth-related factors and level of the root canal filling as a treatment-related factor showed that preoperative gingival lesion (odds ratio [OR]: 4.4;
p = 0.005), preoperative periapical radiolucency (OR: 3.6;p = 0.011), and ≤ 1-2 mm under root filling length (OR: 9.6;p = 0.012) were significant predictors of failure.Conclusions A preoperative gingival lesion of pulpal origin can influence the outcome of nonsurgical endodontic treatment in addition to preoperative periapical radiolucency.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A retrospective study on the prognostic factors and success, survival, and failure outcomes of treated endodontic‐periodontal lesions
Ingar Wong, An Ton, Amiel J. Cassidy, Nicolette Fozzard, Lavanya Ajay Sharma, Robert M. Love, Ajay Sharma
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of gutta-percha removal from the dentinal tubules using different instrumentation techniques with or without solvent: An In vitro study
MukeshKumar Hasija, Babita Meena, Deepti Wadhwa, KulvinderKaur Wadhwani, Virender Yadav
Journal of the International Clinical Dental Research Organization.2020; 12(1): 27. CrossRef - Surgical endodontic management of infected lateral canals of maxillary incisors
Ji-Hyun Jang, Jung-Min Lee, Jin-Kyu Yi, Sung-Baik Choi, Sang-Hyuk Park
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(1): 79. CrossRef - Single visit nonsurgical endodontic therapy for periapical cysts: A clinical study
Ipsita Maity, N. Meena, R. Anitha Kumari
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2014; 5(2): 195. CrossRef
- A retrospective study on the prognostic factors and success, survival, and failure outcomes of treated endodontic‐periodontal lesions
- 4,457 View
- 38 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Treatment of crown-root fracture with a modified crown fragment reattachment technique
- Chang-Won Song, Min-Ju Song, Su-Jung Shin, Jeong-Won Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(5):395-401. Published online September 30, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.5.395
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The development of adhesive dentistry has allowed that the crown fragment reattachment can be another option in the treatment of crown fracture. However, additional crown lengthening procedure or extrusion of the tooth may be necessary in the treatment of crown root fracture because subgingival fracture line in close proximity to the alveolar bone leads to challenges for restorative procedure and the violation of the biologic width. This case report presents a modified crown fragment reattachment technique of crown root fracture with pulp exposure, which was done without additional crown lengthening procedures. After the endodontic treatment, the patient was treated using a post insertion and the fragment reattachment technique, which made it possible to preserve the space for the biologic width and maintain a dry surgical field for adequate adhesion through the modification of the fractured coronal fragment. Since a coronal fracture was occurred and reattached afterward, it was observed that the coronal fragment was well maintained without the additional loss of periodontal attachment through 2-year follow up.
- 1,104 View
- 14 Download

- Pulp response of beagle dog to direct pulp capping materials: Histological study
- Ji-Hyun Bae, Young-Gyun Kim, Pil-Young Yoon, Byeong-Hoon Cho, Yong-Hoon Choi
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(1):5-12. Published online January 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.1.005
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the pulp tissue reaction to direct pulp capping of mechanically exposed beagle dogs'pulp with several capping materials. A total of 36 teeth of 2 healthy beagle dongs were used. The mechanically exposed pulps were capped with one of the followings: (1) Mineral Trioxide Aggregate (MTA: ProRoot® MTA, Dentsply, Tulsa, USA), (2) Clearfil SE Bond (Dentin adhesive system: Kuraray, Osaka, Japan), (3) Ultra-Blend (Photo-polymerized Calcium hydroxide: Ultradent, South Jordan, USA), (4) Dycal (Quick setting Calcium hydroxide: LD Caulk Co., Milford, USA) at 7, 30, and 90 days before sacrificing. The cavities were restored with Z350 flowable composite resin (3M ESPE, St. Paul. MN, USA). After the beagle dogs were sacrificed, the extracted teeth were fixed, decalcified, prepared for histological examination and stained with HE stain. The pulpal tissue responses to direct pulp capping materials were assessed.
In MTA, calcium hydroxide, and photo-polymerized calcium hydroxide groups, initial mild inflammatory cell infiltration, newly formed odontoblast-like cell layer and hard tissue bridge formation were observed. Compared with dentin adhesive system, these materials were biocompatible and good for pulp tissue regeneration.
In dentin adhesive system group, severe inflammatory cell infiltration, pulp tissue degeneration and pulp tissue necrosis were observed. It seemed evident that application of dentin adhesive system in direct pulp capping of beagle dog teeth cannot lead to acceptable repair of the pulp tissue with dentine bridge formation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Experimental Study of Pulp Capping Using Xenogenic Demineralized Dentin Paste
Ji-Young Yun, Yong-Hoon Choi, Young-Kyun Kim, In-Woong Um, Joo-Cheol Park, Ji-Yoon Kim
Journal of Hard Tissue Biology.2016; 25(3): 321. CrossRef - Comparison of gene expression profiles of human dental pulp cells treated with mineral trioxide aggregate and calcium hydroxide
Yong-Beom Kim, Won-Jun Shon, Woocheol Lee, Kee-Yeon Kum, Seung-Ho Baek, Kwang-Shik Bae
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(5): 397. CrossRef - Gene expression profiling in human dental pulp cells treated with mineral trioxide aggregate
Yong-Beom Kim, Won-Jun Shon, WooCheol Lee, Kee-Yeon Kum, Seung-Ho Baek, Kwang-Shik Bae
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(3): 152. CrossRef - Histology of dental pulp healing after tooth replantation in rats
Eun-Jin Go, Han-Seong Jung, Eui-Seong Kim, Il-Young Jung, Seung-Jong Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(4): 273. CrossRef
- Experimental Study of Pulp Capping Using Xenogenic Demineralized Dentin Paste
- 1,321 View
- 11 Download
- 4 Crossref

- The role of Type 2 Diabetes as a predisposing risk factor on the pulpo-periapical pathogenesis: review article
- Jin-Hee Kim, Kwang-shik Bae, Deog-Gyu Seo, Sung-Tae Hong, Yoon Lee, Sam-Pyo Hong, Kee-Yeon Kum
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(3):169-176. Published online May 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.3.169
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Diabetes Mellitus (DM) is a syndrome accompanied with the abnormal secretion or function of insulin, a hormone that plays a vital role in controlling the blood glucose level (BGL). Type 1and 2 DM are most common form and the prevalence of the latter is recently increasing. The aim of this article was to assess whether Type 2 DM could act as a predisposing risk factor on the pulpo-periapical pathogenesis. Previous literature on the pathologic changes of blood vessels in DM was thoroughly reviewed. Furthermore, a histopathologic analysis of artificially-induced periapical specimens obtained from Type 2 diabetic and DM-resistant rats was compared. Histopathologic results demonstrate that the size of periapical bone destruction was larger and the degree of pulpal inflammation was more severe in diabetic rats, indicating that Type 2 DM itself can be a predisposing risk factor that makes the host more susceptible to pulpal infection. The possible reasons may be that in diabetic state the lumen of pulpal blood vessels are thickened by atheromatous deposits, and microcirculation is hindered. The function of polymorphonuclear leukocyte is also impaired and the migration of immune cells is blocked, leading to increased chance of pulpal infection. Also, lack of collateral circulation of pulpal blood vessels makes the pulp more susceptible to infection. These decrease the regeneration capacity of pulpal cells or tissues, delaying the healing process. Therefore, when restorative treatment is needed in Type 2 DM patients, dentists should minimize irritation to the pulpal tissue un der control of BGL.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pulp necrosis following luxated injury to teeth in a patient with uncontrolled type II diabetes mellitus: a case report
Haneol Shin, Seung-Jong Lee, Il-Young Jung, Chan-Young Lee
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(1): 61. CrossRef
- Pulp necrosis following luxated injury to teeth in a patient with uncontrolled type II diabetes mellitus: a case report
- 1,191 View
- 12 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Morphology of the apical root canal system in Korean mandibular first molar
- Hyeon Jeong, Sang-jin Park, Sang-Hyuk Park, Gi-Woon Choi
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(2):137-144. Published online March 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.2.137
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The aim of this study was to investigate the shapes and diameters of the physiological foramen and anatomy of the root canal at 3mm from apex in mandibular first molars.
Sixty mandibular first molars were randomly selected. The apical anatomy of 60 mandibular first molars was investigated by means of a stereomicroscope (60x magnification).
The results were as follows;
1. There was a high percentage of two physiological foramina in mesial (61.67%) and one foramen in distal(71.66%) roots of mandibular first molars.
2.There was a high frequency of accessory foramina in mesial roots with one foramen (26.07%).
3. The diameters of physiological foramen was as follows:
0.329mm in single mesial foramen
0.266mm in mesiobuccal foramen and 0.246mm in mesiolingual foramen
0.375mm in single distal foramen
0.291mm in distobuccal foramen and 0.237mm in distolingual foramen
4. The most common physiological foramen shape was oval (69.93%).
5. The incidence of isthmus in mesial root at 3mm from apex was 55%. The 3mm-sections contained a complete isthmus 31.66% and a partial isthmus 23.34%.
6. 3mm from the apex, the most common canal shape was oval (50.64%).
Knowledge of the apical anatomy of mandibular first molar would be necessary for success of surgical and nonsurgical endodontic treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Variations in Canal Morphology, Shapes, and Positions of Major Foramen in Maxillary and Mandibular Teeth
B. Swathika, Md. Kalim Ullah, S. Ganesan, Prabu Muthusamy, Prasanna Vuyyuru, Kongkana Kalita, C. Swarnalatha, Suresh J. Babu, Abhishek Singh Nayyar
Journal of Microscopy and Ultrastructure.2021; 9(4): 190. CrossRef - Assessment of Root and Root Canal Morphology of Human Primary Molars using CBCT
Yoomin Choi, Seonmi Kim, Namki Choi
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2020; 47(1): 25. CrossRef - An evaluation of canal curvature at the apical one third in type II mesial canals of mandibular molars
Hye-Rim Yun, Dong-Kyun Lee, Ho-Keel Hwang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(2): 104. CrossRef
- Variations in Canal Morphology, Shapes, and Positions of Major Foramen in Maxillary and Mandibular Teeth
- 1,219 View
- 1 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Slumping tendency and rheological property of flowable composites
- In-Bog Lee, Sun-Hong Min, Sun-Young Kim, Byung-Hoon Cho, Seung-Ho Back
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(2):130-136. Published online March 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.2.130
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The aim of this study was to develop a method for measuring the slumping resistance of flowable resin composites and to evaluate the efficacy using rheological methodology.
Five commercial flowable composites (Aelitefil flow:AF, Filtek flow:FF, DenFil flow:DF, Tetric flow:TF and Revolution:RV) were used. Same volume of composites in a syringe was extruded on a glass slide using a custom-made loading device. The resin composites were allowed to slump for 10 seconds at 25℃ and light cured. The aspect ratio (height/diameter) of cone or dome shaped specimen was measured for estimating the slumping tendency of composites. The complex viscosity of each composite was measured by a dynamic oscillatory shear test as a function of angular frequency using a rheometer. To compare the slumping tendency of composites, one way-ANOVA and Turkey's post hoc test was performed for the aspect ratio at 95% confidence level. Regression analysis was performed to investigate the relationship between the complex viscosity and the aspect ratio. The results were as follows.
1. Slumping tendency based on the aspect ratio varied among the five materials (AF < FF < DF < TF < RV).
2. Flowable composites exhibited pseudoplasticity in which the complex viscosity decreased with increasing frequency (shear rate). AF was the most significant, RV the least.
3. The slumping tendency was strongly related with the complex viscosity. Slumping resistance increased with increasing the complex viscosity.
The slumping tendency could be quantified by measuring the aspect ratio of slumped flowable composites. This method may be applicable to evaluate the clinical handling characteristics of flowable composites.
- 897 View
- 2 Download

- Histological evaluation of direct pulp capping with DSP-derived synthetic peptide in beagle dog
- Jae-Hoon Kim, Jun-Bae Hong, Bum-Soon Lim, Byeong-Hoon Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(2):120-129. Published online January 14, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.2.120
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Abstract The purpose of this study was to investigate the pulpal response to direct pulp capping with dentin sialo-protein (DSP) -derived synthetic peptide in teeth of dogs, and to compare its efficacy to capping substances Ca(OH)2 and white mineral trioxide aggregate (WMTA). A total of 72 teeth of 6 healthy male beagle dogs were used. The mechanically exposed pulps were capped with one of the following: (1) DSP-derived synthetic peptide (PEP group); (2) Ca(OH)2 (CH group); (3) a mixture paste of peptide and Ca(OH)2 (PEP+CH group); or (4) white MTA (WMTA group). The access cavity was restored with a reinforced glass ionomer cement. Two dogs were sacrificed at each pre-determined intervals (2 weeks, 1 month, and 3 months). After the specimens were prepared for standard histological processing, sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Under a light microscope, inflammatory response and hard tissue formation were evaluated in a blind manner by 2 observers. In the PEP group, only 3 of 17 specimens showed hard tissue formation, indication that the DSP-derived synthetic peptide did not induce proper healing of the pulp. Compared with the CH group, the PEP group demonstrated an increased inflammatory response and poor hard tissue formation. The CH and WMTA groups showed similar results for direct pulp capping in mechanically exposed teeth of dogs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Tubular Dentin Regeneration Using a CPNE7-Derived Functional Peptide
Yoon Lee, Yeoung-Hyun Park, Dong-Seol Lee, You-Mi Seo, Ji-Hyun Lee, Joo-Hwang Park, Han-Wool Choung, So-Hyun Park, Won Shon, Joo-Cheol Park
Materials.2020; 13(20): 4618. CrossRef - Pulp response of beagle dog to direct pulp capping materials: Histological study
Ji-Hyun Bae, Young-Gyun Kim, Pil-Young Yoon, Byeong-Hoon Cho, Yong-Hoon Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(1): 5. CrossRef
- Tubular Dentin Regeneration Using a CPNE7-Derived Functional Peptide
- 1,568 View
- 7 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Effects of one or two applications of all-in-one adhesive on microtensile bond strength to unground enamel
- Chang-Yong Son, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Bock Hur, Jeong-Kil Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(6):445-451. Published online November 30, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.6.445
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purposes of this study were to compare the effects of one or two applications of all-in-one adhesives on microtensile bond strengths (µTBS) to unground enamel and to investigate the morphological changes in enamel surfaces treated with these adhesives using a scanning electron microscopy (SEM).
Twenty-five noncarious, unrestored human mandibular molars were used. The unground enamel surfaces were cleansed with pumice. The following adhesives were applied to lingual, mid-coronal surfaces according to manufacture's directions; Clearfil SE bond in SE group, Adper Prompt L-Pop™1 coat in LP1 group, 2 coats in LP2 group, Xeno® III 1 coat in XN1 group, and 2 coats in XN2 group. After application of the adhesives, a hybrid light-activated resin composite was built up on the unground enamel. Each tooth was sectioned to make a cross-sectional area of approximately 1.0 mm2 for each stick. The microtensile bond strength was determined. Each specimen was observed under SEM to examine the morphological changes. Data were analyzed with one-way ANOVA.
The results of this study were as follows;
1. The microtensile bond strength values were; SE (19.77±2.44 MPa), LP1 (13.88±3.67 MPa), LP2 (14.50±2.52 MPa), XN1 (14.42±2.51 MPa) and XN2 (15.28±2.79 MPa). SE was significantly higher than the other groups in bond strength (p < 0.05). All groups except SE were not significantly different in bond strength (p < 0.05).
2. All groups were characterized as shallow and irregular etching patterns.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of various bonding systems on the microtensile bond strength of immediate and delayed dentin sealing
Jin-hee Ha, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Bock Hur, Jeong-Kil Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2008; 33(6): 526. CrossRef
- The effect of various bonding systems on the microtensile bond strength of immediate and delayed dentin sealing
- 1,361 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Study on the interface between light-cured glass ionomer base and indirect composite resin inlay and dentin
- Song-Hee Lee, Dong-Jun Kim, Yun-Chan Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, In-Nam Hwang
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(3):158-169. Published online May 31, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.3.158
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study was done to evaluate the shear bond strength between light-cured glass ionomer cement (GIC) base and resin cement for luting indirect resin inlay and to observe bonding aspects which is produced at the interface between them by SEM.
Two types of light cured GIC (Fuji II LC Improved, GC Co. Tokyo, Japan and Vitrebond™, 3M, Paul, Minnesota, U.S.A) were used in this study. For shear bond test, GIC specimens were made and immersed in 37℃ distilled water for 1 hour, 24 hours, 1 week and 2 weeks. Eighty resin inlays were prepared with Artglass® (Heraeus Kultzer, Germany) and luted with Variolink® II (Ivoclar Vivadent, Liechtenstein).
Shear bond strength of each specimen was measured and fractured surface were examined. Statistical analysis was done with one-way ANOVA.
Twenty four extracted human third molars were selected and Class II cavities were prepared and GIC based at axiopulpal lineangle. The specimens were immersed in 37℃ distilled water for 1 hour, 24 hours, 1 week and 2 weeks. And then the resin inlays were luted to prepared teeth. The specimens were sectioned vertically with low speed saw. The bonding aspect of the specimens were observed by SEM (JSM-5400®, Jeol, Tokyo, Japan). There was no significant difference between the shear bond strength according to storage periods of light cured GIC base. And cohesive failure was mostly appeared in GIC. On scanning electron micrograph, about 30 - 120 µm of the gaps were observed on the interface between GIC base and dentin. No gaps were observed on the interface between GIC and resin inlay.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative analysis of strain according to two wavelengths of light source and constant temperature bath deposition in ultraviolet-curing resin for dental three-dimensional printing
Dong-Yeon Kim, Gwang-Young Lee, Hoo-Won Kang, Cheon-Seung Yang
Journal of Korean Acedemy of Dental Technology.2020; 42(3): 208. CrossRef
- Comparative analysis of strain according to two wavelengths of light source and constant temperature bath deposition in ultraviolet-curing resin for dental three-dimensional printing
- 1,128 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- A NEW POST REMOVAL TECHNIQUE USING ATD TUGGING DEVICE
- Yun-Woo Park, Se-Hee Park, Hye-Jin Shin, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(3):215-220. Published online January 14, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.3.215
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub ABSTRACT It is common for clinicians to encounter endodontically treated teeth that contain posts within their roots. If endodontic treatment is failed, these posts must be removed to facilitate successful nonsurgical retreatment.
There have been many techniques such as ultrasonic instrument, Ruddle post removal system, Eggler post remover and Masserann kit developed to facilitate removal of posts from the root canal space. But these methods may be disadvantageous because long length of time required for post removal and fracture of post or teeth. In now days new post removal technique using ATD automatic bridge remover was introduced. Advantages of this method are simple and short time consuming compare to others.
This article served as a successful case report of post removal using ATD automatic bridge remover.
- 996 View
- 5 Download

- Morphological patterns of self-etching primers and self-etching adhesive bonded to tooth structure
- Young-Gon Cho, Seok-Jong Lee, Jin-Ho Jeong, Young-Gon Lee, Soo-Mee Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2003;28(1):23-33. Published online January 31, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.1.023
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare in vitro interfacial relationship of restorations bonded with three self-etching primer adhesives and one self-etching adhesive.
Class I cavity preparations were prepared on twenty extracted human molars. Prepared teeth were divided into four groups and restored with four adhesives and composites: Clearfil SE Bond/Clearfil™ AP-X (SE), UniFil Bond/UniFil® F (UF), FL Bond/Filtek™ Z 250 (FL) and Prompt L-Pop/Filtek™ Z 250 (LP)
After storing in distilled water of room temperature for 24 hours, the specimens were vertically sectioned and decalcified. Morphological patterns between the enamel/dentin and adhesives were observed under SEM.
The results of this study were as follows;
1. They showed close adaptation between enamel and SE, UF and FL except for LP.
2. The hybrid layer in dentin was 2 µm thick in SE, 1.5 µm thick in UF, and 0.4 µm in both FL and LP. So, the hybrid layers of SE and UF were slightly thicker than that of FL and LP.
3. The lengths and diameters of resin tags in UF and FL were similar, but those of LP were slightly shorter and slenderer than those of SE.
4. The resin tags were long rod shape in SE, and funnel shape in other groups.
Within the limitations of this study, it was concluded that self-etching primer adhesives showed close adaptation on enamel. In addition, the thickness of hybrid layer ranged from 0.4-1.5 µm between adhesives and dentin. The resin tags were long rod or funnel shape, and dimension of them was similar or different among adhesives.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of appication time of self-etching primers on dentinal microtensile bond strength
Young-Gon Cho, Young-Gon Lee, Jong-Uk Kim, Byung-Cheul Park, Jong-Jin Kim, Hee-Young Choi, Cheul-Hee Jin, Sang-Hoon Yoo
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2004; 29(5): 430. CrossRef
- Influence of appication time of self-etching primers on dentinal microtensile bond strength
- 1,099 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- ANTICARIOGENCI EFFECT OF COMPOMER AND RMGIC
- Sung-Ho Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2002;27(1):12-15. Published online January 14, 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2002.27.1.012
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub ABSTRACT The first purpose of present study was to compare the anticariogenic effect of compomer, resin modified glass ionomer cement and composite (RMGIC).
The second purpose was to evaluate the recently introduced methods, which use confocal scanning microscope, in detecting initial caries around restoration.
2×4×1.5mm cavities were prepared from the recently extracted 50 human teeth on the buccal or lingual surface. The prepared teeth were randomly devided into 5 groups and restored with each filling material. Group 1: Dyract AP, Group 2: compoglass F, Group 3: F2000, Group 4: Z100, Group 5:Fuji Ⅱ LC. The teeth were stored for 30 days in the distilled water, then stored in the buffer solution for artificial caries development; pH 4.3, lactic acid 100 mM, calcium 16 mM, phosphate 8mM, sodium azide 3mM. Then, the samples were sectioned longitudinally and examined with confical scanning microscope. The results showed that the use of compomer and resin modified glass ionomer cement showed caries inhibition zone whereas the composite did not. There was no difference in the width of caries inhibition zone between compomers and RMGIC. The confocal scanning microscope was useful in detecting initial caries around restoration.
- 1,121 View
- 2 Download


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


