Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Restor Dent Endod > Volume 34(2); 2009 > Article
- Original Article Morphology of the apical root canal system in Korean mandibular first molar
- Hyeon Jeong, Sang-jin Park, Sang-Hyuk Park, Gi-Woon Choi
-
2009;34(2):-144.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.2.137
Published online: March 31, 2009
Department of Conservative Dentistry, Division of Dentistry, Graduate of Kyung Hee University, Korea.
- Corresponding Author: Gi-Woon Choi. Professor of Division of Dentistry, Graduate school of KyungHee University, 1, Hoegi Dong, Dongdaemun Gu, Seoul, Korea, 130-702. Tel: 82-2-958-9336, gwchoi@khu.ac.kr
Copyright © 2009 The Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry
- 1,209 Views
- 1 Download
- 3 Crossref
Abstract
-
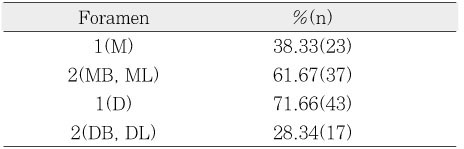
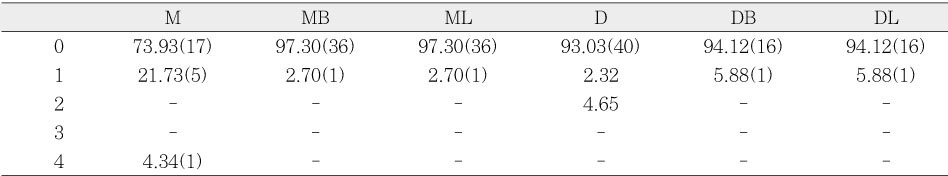
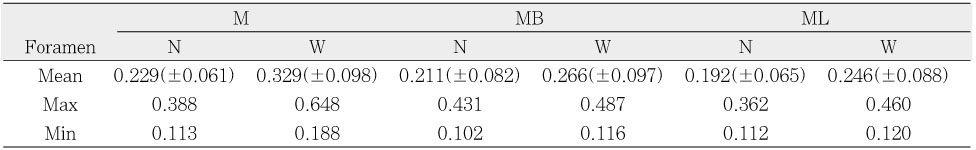
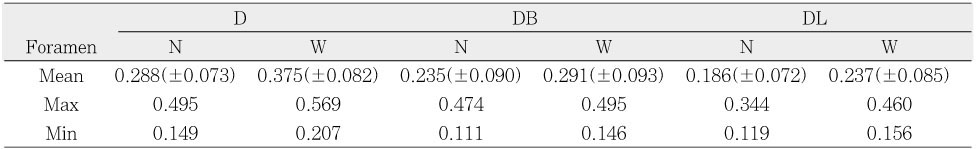
The aim of this study was to investigate the shapes and diameters of the physiological foramen and anatomy of the root canal at 3mm from apex in mandibular first molars.Sixty mandibular first molars were randomly selected. The apical anatomy of 60 mandibular first molars was investigated by means of a stereomicroscope (60x magnification).The results were as follows;1. There was a high percentage of two physiological foramina in mesial (61.67%) and one foramen in distal(71.66%) roots of mandibular first molars.2.There was a high frequency of accessory foramina in mesial roots with one foramen (26.07%).3. The diameters of physiological foramen was as follows:4. The most common physiological foramen shape was oval (69.93%).5. The incidence of isthmus in mesial root at 3mm from apex was 55%. The 3mm-sections contained a complete isthmus 31.66% and a partial isthmus 23.34%.6. 3mm from the apex, the most common canal shape was oval (50.64%).Knowledge of the apical anatomy of mandibular first molar would be necessary for success of surgical and nonsurgical endodontic treatment.
- 1. Schilder H. Filling root canals in three dimensions. J Endod. 2006;32(4):281-290.ArticlePubMed
- 2. Jou YT, Karabucak B, Levin J. Endodontic working width: current concepts and techniques. Dent Clin North Am. 2004;48(1):323-335.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Simon JHS. The apex: how critical is it? Gen Dent. 1994;42(4):330-334.PubMed
- 4. Baugh D, Wallace J. The role of apical instrumentation in root canal treatment: a review of the literature. J Endod. 2005;31(5):333-340.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Weine F. Endodontic therapy. 1982;3rd ed. St. Louis: C. V. Mosby; 282-283.
- 6. Walton RE. Histologic evaluation of different methods of enlarging the pulp canal space. J Endod. 1976;2(10):304-311.ArticlePubMed
- 7. Wu MK, Barkis DRA, Wesseling P. Does the first file to bind correspond to the diameter of the canal in the apical region? Int Endod J. 2002;35(3):264-267.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Lumley PJ, Walmsley AD, Walton RE, Rippin JW. Cleaning of oval canals using ultrasonic or sonic instrumentation. J Endod. 1993;19(9):453-457.ArticlePubMed
- 9. Wu MK, Wesselink PR. A primary observation on the preparation and obturation in oval canals. Int Endod J. 2001;34(2):137-141.PubMed
- 10. Marroquin BB, Al-sayed MAA, Willershausen-Zonnchen B. Morphology of the physiological foramen: 1. Maxillary and mandibular molars. J Endod. 2004;30(5):321-328.PubMed
- 11. Wu MK, R'oris A, Barkis D, Paul R, Wesselink PR. Prevalance and extent of long oval canals in the apical third. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2000;89(6):739-743.PubMed
- 12. Weller NR, Niemczyk SP, Kim S. Incidence and position of the canal isthmus. Part 1. Mesiobuccal root of the maxillary first molar. J Endod. 1995;21(7):380-383.ArticlePubMed
- 13. Mannocci F, Peru M, Sherriff M, Pitt Ford TR, Cook R. a micro-computed tomographic study. Int Endod J. 2005;38(8):558-563.PubMed
- 14. Hsu YY, Kim S. The resected root surface. The issue of canal isthmuses. Dent Clin North Am. 1997;41(3):529-540.PubMed
- 15. von Arx T. Frequency and type of canal isthmuses in first molars detected by endoscopic inspection during periradicular surgery. Int Endod J. 2005;38(3):160-168.ArticlePubMed
- 16. von Arx T, Walker W. Microsurgical instruments for root-end cavity preparation following apicoectomy. Endod Dent Traumatol. 2000;16(2):47-62.PubMed
- 17. Rubinstein RA, Kim S. Short-term observation of the results of endodontic surgery with the use of a surgical operation microscope and super-EBA as root-end filling material. J Endod. 1999;25(1):43-48.Article
- 18. Kim S, Pecora G, Rubinstein RA. Color atlas of microsurgery in endodontics. 2001;Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders Company; 89-92.
- 19. Morfis A, Sylaras SN, Georgopoulou M, Kernani M, Prountzos F. Study of the apices of human permanent teeth with the use of a scanning electron microscope. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1994;77(2):172-176.ArticlePubMed
- 20. Peak JD, Hayes SJ, Bryant ST, Dummer PM. The outcome of root canal treatment. A retrospective study within the armed forces. Br Dent J. 2001;190(3):140-144.ArticlePubMed
- 21. Harty FJ, Parkins BJ, Wengraf AM. Success rate in root canal therapy. A retrospective study of conventional cases. Br Dent J. 1970;128(2):65-70.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 22. Cohen S, Burns RC, Herbranson EJ. Pathways of the pulp. 2002;8th ed. St. Louis: Mosby; 710-713.
- 23. Blaskovic-Subat V, Smojver B, Maricic B, Sutalo J. A computerized method for the evaluation of root canal morphology. Int Endod J. 1995;28(6):290-296.ArticlePubMed
- 24. Peters OA, Laib B, Ruegsegger P, Barbakow F. Three-dimensional analysis of root canal geometry by high-resolution computed tomography. J Dent Res. 2000;79(6):1405-1409.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 25. Kuttler Y. Microscopic investigation of root apexes. J Am Dent Assoc. 1955;50(5):544-552.ArticlePubMed
- 26. Burch JG, Hulen S. The relationship of the apical foramen to the anatomical apex of the tooth root. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1972;34(2):262-268.PubMed
- 27. Ponce EH, Vilar Fernandez J. The cemento-dentino-canal junction, the apical foramen, and the apical constriction: evaluation by optical microscopy. J Endod. 2003;29(3):214-219.ArticlePubMed
- 28. Buchanan Ls. The standardized-taper root canal preparation: part 1. concept for variably tapered shaping instruments. Int Endod J. 2000;33(6):516-529.PubMed
- 29. Teixeira FB, Sano CL, Gomes BPFA, Zaia AA, Ferraz CCR, Souza Filho FJ. A preliminary in vitro study of the incidence and position of the root canal isthmus in maxillary and mandibular first molars. Int Endod J. 2003;36(4):276-280.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 30. Pineda F. Roentgenographic investigation of the mesiobuccal root of the maxillary first molar. Oral Surg. 1973;36(2):253-260.ArticlePubMed
- 31. Yang SF, Rivera EM, Baumgardener KR, Walton RE, Stanford C. Anaerobic tissue-dissolving abilities of calcium hydroxide and sodium hypochlorite. J Endod. 1995;21(12):613-616.ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
M : single mesial, MB : mesiobuccal, ML : mesiolingual
D : single distal, DB : distobuccal, DL : distolingual
M : single mesial, MB : mesiobuccal, ML : mesiolingua
D : single distal, DB : distobuccal, DL : distolingual
Tables & Figures
REFERENCES
Citations

- Variations in Canal Morphology, Shapes, and Positions of Major Foramen in Maxillary and Mandibular Teeth
B. Swathika, Md. Kalim Ullah, S. Ganesan, Prabu Muthusamy, Prasanna Vuyyuru, Kongkana Kalita, C. Swarnalatha, Suresh J. Babu, Abhishek Singh Nayyar
Journal of Microscopy and Ultrastructure.2021; 9(4): 190. CrossRef - Assessment of Root and Root Canal Morphology of Human Primary Molars using CBCT
Yoomin Choi, Seonmi Kim, Namki Choi
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2020; 47(1): 25. CrossRef - An evaluation of canal curvature at the apical one third in type II mesial canals of mandibular molars
Hye-Rim Yun, Dong-Kyun Lee, Ho-Keel Hwang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(2): 104. CrossRef
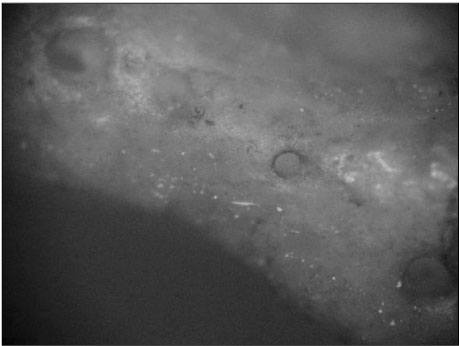
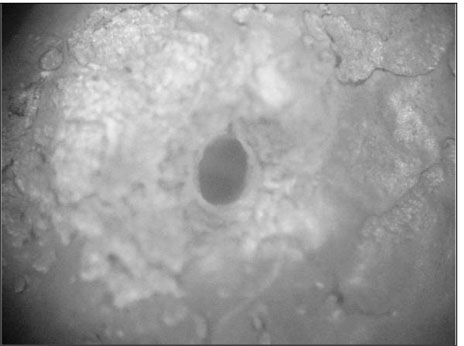
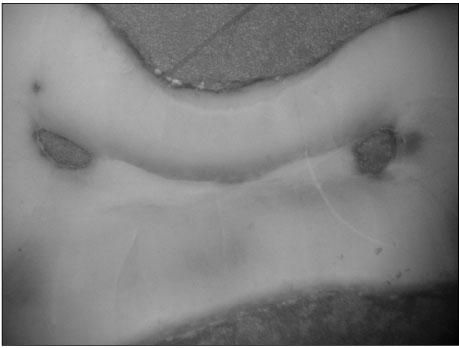
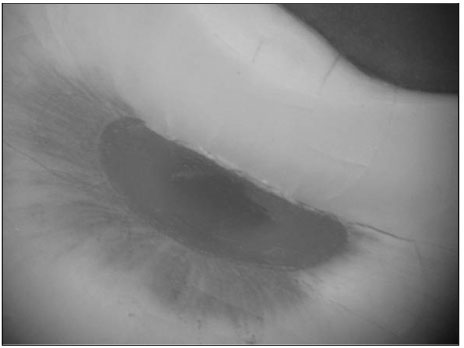
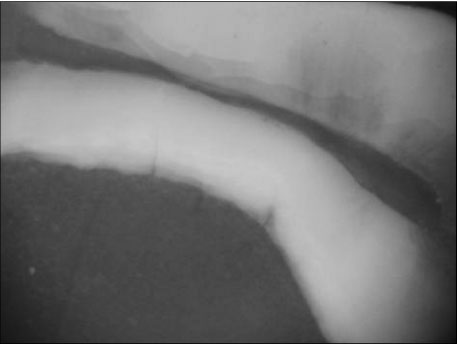
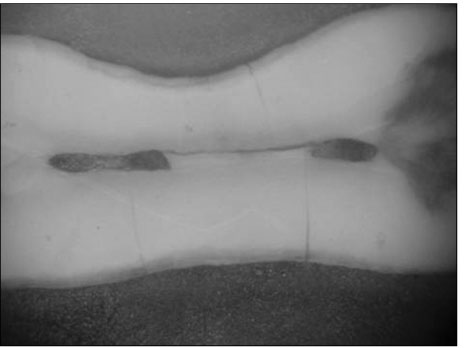
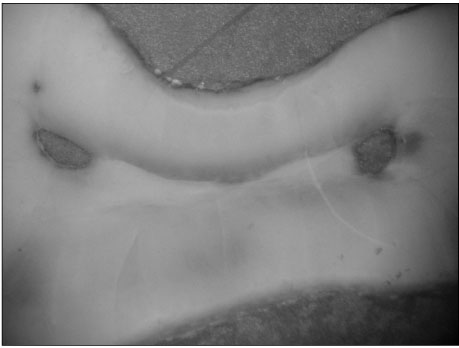
Figure 1
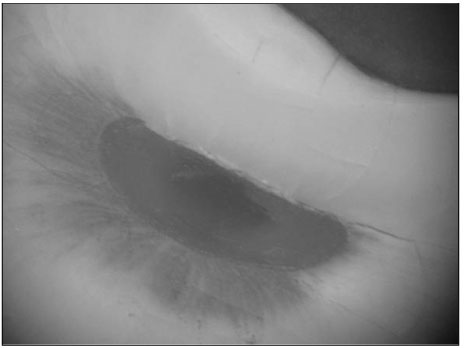
Figure 2
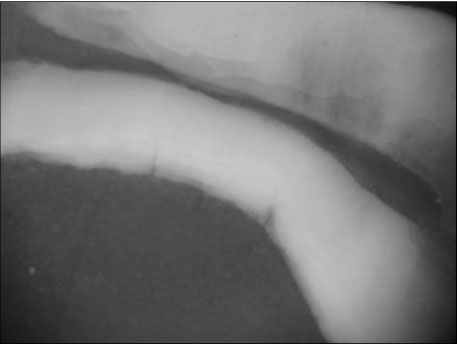
Figure 3
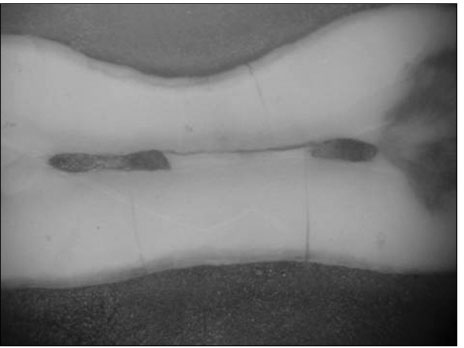
Figure 4
Figure 5
Figure 6
Number of physiological foramen and accessory foramen frequency in mesial and distal roots of mandibular first molars (%, n)
M : single mesial, MB : mesiobuccal, ML : mesiolingual
D : single distal, DB : distobuccal, DL : distolingual
Frequency of accessory foramen (<0.10mm) in mandibular first molars (%, n)
M : single mesial, MB : mesiobuccal, ML : mesiolingua
D : single distal, DB : distobuccal, DL : distolingual
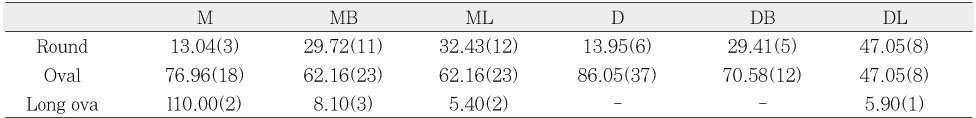
Narrow and wide diameters of the mesial physiological foramina of mandibular first molars (mm)
M : single mesial, MB : mesiobuccal, ML : mesiolingual
N : narrow diameter, W : wide diameter
Narrow and wide diameters of the distal physiological foramina of mandibular first molars (mm)
D : single distal, DB : distobuccal, DL : distolingual
N : narrow diameter, W : wide diameter
Shape of the mesial and distal physiological foramina of mandibular first molar (%, n)
M : single mesial, MB : mesiobuccal, ML : mesiolingual
D : single distal, DB : distobuccal, DL : distolingual
Incidence of isthmus in the mesial roots of mandibular first molars(%, n)
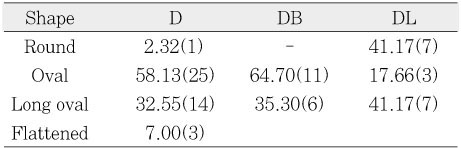
Shape of the distal canals at 3mm level (%, n)
D : single distal, DB : distobuccal,
DL : distolingual
M : single mesial, MB : mesiobuccal, ML : mesiolingual D : single distal, DB : distobuccal, DL : distolingual
M : single mesial, MB : mesiobuccal, ML : mesiolingua D : single distal, DB : distobuccal, DL : distolingual
M : single mesial, MB : mesiobuccal, ML : mesiolingual N : narrow diameter, W : wide diameter
D : single distal, DB : distobuccal, DL : distolingual N : narrow diameter, W : wide diameter
M : single mesial, MB : mesiobuccal, ML : mesiolingual D : single distal, DB : distobuccal, DL : distolingual
D : single distal, DB : distobuccal, DL : distolingual

 KACD
KACD
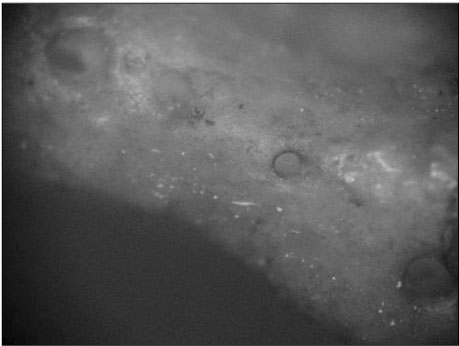
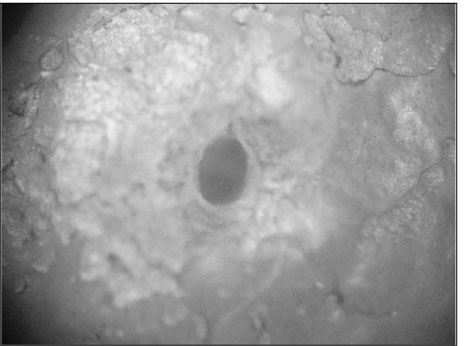

 ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite

