Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Cytocompatibility and cell proliferation evaluation of calcium phosphate-based root canal sealers
- Letícia Boldrin Mestieri, Ivana Maria Zaccara, Lucas Siqueira Pinheiro, Fernando Branco Barletta, Patrícia Maria Polli Kopper, Fabiana Soares Grecca
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(1):e2. Published online November 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e2
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
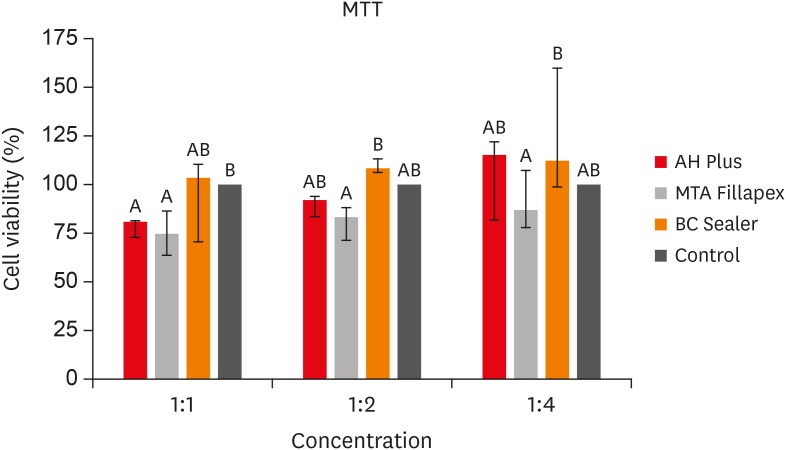
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the cell viability and migration of Endosequence Bioceramic Root Canal Sealer (BC Sealer) compared to MTA Fillapex and AH Plus.
Materials and Methods BC Sealer, MTA Fillapex, and AH Plus were placed in contact with culture medium to obtain sealers extracts in dilution 1:1, 1:2 and 1:4. 3T3 cells were plated and exposed to the extracts. Cell viability and migration were assessed by 3-(4,5-dimethyl-thiazoyl)-2,5-diphenyl-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) and Scratch assay, respectively. Data were analyzed by Kruskal-Wallis and Dunn's test (
p < 0.05).Results The MTT assay revealed greater cytotoxicity for AH Plus and MTA Fillapex at 1:1 dilution when compared to control (
p < 0.05). At 1:2 and 1:4 dilutions, all sealers were similar to control (p > 0.05) and MTA Fillapex was more cytotoxic than BC Sealer (p < 0.05). Scratch assay demonstrated the continuous closure of the wound according to time. At 30 hours, the control group presented closure of the wound (p < 0.05). At 36 hours, only BC Sealer presented the closure when compared to AH Plus and MTA Fillapex (p < 0.05). At 42 hours, AH Plus and MTA Fillapex showed a wound healing (p > 0.05).Conclusions All tested sealers demonstrated cell viability highlighting BC Sealer, which showed increased cell migration capacity suggesting that this sealer may achieve better tissue repair when compared to other tested sealers.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Oxidative Stress, Pro-Inflammatory Response, Cytotoxicity and Apoptosis Induced by Contemporary Endodontic Sealers in Human Periodontal Ligament Fibroblasts
Stanisław Krokosz, Virginia Ewa Lis, Sara Zięba, Mateusz Maciejczyk, Ewa Zalewska, Maria Obrycka, Edyta Gołaś, Małgorzata Żendzian-Piotrowska, Jerzy Ładny, Anna Skutnik-Radziszewska, Karol Dąbrowski, Julia Kuźmiuk, Anna Zalewska
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2026; 17(2): 105. CrossRef - Effect of Nano-Silica on Mechanical Properties and Cytotoxicity of Calcium-Silicate-Based Root Canal Filling Materials
Hao He, Bolang Hao, Xiang Xiong, Yi Cheng, Jia Lou, Zheyu He, Dongyang Li, Zhihuan Wang, Jian Qin
Crystals.2025; 15(1): 55. CrossRef - Premixed calcium silicate-based root canal sealers have better biological properties than AH Plus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of in vivo animal studies and in vitro laboratory studies
Cristiana Pereira Malta, Samantha Simoni Santi, Raquel Cristine Silva Barcelos, Fabrício Batistin Zanatta, Carlos Alexandre Souza Bier, Renata Dornelles Morgental
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(4): 345. CrossRef - Biological Properties of Bioceramic Sealers on Osteoblastic Cells: A Comparative Study
Angelita Piovezana Guerra, Danielle Gregorio, Gean Carlos Yamamoto, Nathalia Thalitha Bernardes dos Santos, Regina Celia Poli-Frederico, Luciana Prado Maia
Brazilian Dental Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Premixed calcium silicate‐based ceramic sealers promote osteogenic/cementogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells: A microscopy study
Sergio López‐García, Sonia Sánchez‐Bautista, David García‐Bernal, Adrián Lozano, Leopoldo Forner, José L. Sanz, Laura Murcia, Francisco J. Rodríguez‐Lozano, Ricardo E. Oñate‐Sánchez
Microscopy Research and Technique.2024; 87(7): 1584. CrossRef - Cytotoxicity Comparison of Sure-seal root and Adseal Sealers on mouse fibroblast Cells:Invitro study
Azam haddadikohsar, Mohammad shokrzade, Marjan Fallah, Fatemeh Shakeri
journal of research in dental sciences.2024; 21(1): 46. CrossRef - Cytotoxicity and cell migration evaluation of a strontium silicate-based root canal sealer on stem cells from rat apical papilla: an in vitro study
Guanglei Zhou, Yu Zhao, Liangjing Cai, Liwei Liu, Xu Li, Lu Sun, Jiayin Deng
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A comparative study of biological properties of three root canal sealers
Yujia Yan, Yanyao Li, Yaqi Chi, Mengzhen Ji, Ya Shen, Ling Zou
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Biomineralization potential and biological properties of a new tantalum oxide (Ta2O5)–containing calcium silicate cement
F. J. Rodríguez-Lozano, A. Lozano, S. López-García, D. García-Bernal, J. L. Sanz, J. Guerrero-Gironés, C. Llena, L. Forner, M. Melo
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 26(2): 1427. CrossRef - Cytotoxicity and Genotoxicity of Epoxy Resin-Based Root Canal Sealers before and after Setting Procedures
Mijoo Kim, Marc Hayashi, Bo Yu, Thomas K. Lee, Reuben H. Kim, Deuk-won Jo
Life.2022; 12(6): 847. CrossRef - Characterization, Antimicrobial Effects, and Cytocompatibility of a Root Canal Sealer Produced by Pozzolan Reaction between Calcium Hydroxide and Silica
Mi-Ah Kim, Vinicius Rosa, Prasanna Neelakantan, Yun-Chan Hwang, Kyung-San Min
Materials.2021; 14(11): 2863. CrossRef - Bone repair in defects filled with AH Plus sealer and different concentrations of MTA: a study in rat tibiae
Jessica Emanuella Rocha Paz, Priscila Oliveira Costa, Albert Alexandre Costa Souza, Ingrid Macedo de Oliveira, Lucas Fernandes Falcão, Carlos Alberto Monteiro Falcão, Maria Ângela Area Leão Ferraz, Lucielma Salmito Soares Pinto
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Incorporation of amoxicillin-loaded microspheres in mineral trioxide aggregate cement: an in vitro study
Fábio Rocha Bohns, Vicente Castelo Branco Leitune, Isadora Martini Garcia, Bruna Genari, Nélio Bairros Dornelles, Silvia Stanisçuaski Guterres, Fabrício Aulo Ogliari, Mary Anne Sampaio de Melo, Fabrício Mezzomo Collares
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Oxidative Stress, Pro-Inflammatory Response, Cytotoxicity and Apoptosis Induced by Contemporary Endodontic Sealers in Human Periodontal Ligament Fibroblasts
- 1,624 View
- 10 Download
- 13 Crossref

- Effects of four novel root-end filling materials on the viability of periodontal ligament fibroblasts
- Makbule Bilge Akbulut, Pembegul Uyar Arpaci, Ayce Unverdi Eldeniz
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(3):e24. Published online May 25, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e24
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this
in vitro study was to evaluate the biocompatibility of newly proposed root-end filling materials, Biodentine, Micro-Mega mineral trioxide aggregate (MM-MTA), polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) bone cement, and Smart Dentin Replacement (SDR), in comparison with contemporary root-end filling materials, intermediate restorative material (IRM), Dyract compomer, ProRoot MTA (PMTA), and Vitrebond, using human periodontal ligament (hPDL) fibroblasts.Materials and Methods Ten discs from each material were fabricated in sterile Teflon molds and 24-hour eluates were obtained from each root-end filling material in cell culture media after 1- or 3-day setting. hPDL fibroblasts were plated at a density of 5 × 103/well, and were incubated for 24 hours with 1:1, 1:2, 1:4, and 1:8 dilutions of eluates. Cell viability was evaluated by XTT assay. Data was statistically analysed. Apoptotic/necrotic activity of PDL cells exposed to material eluates was established by flow cytometry.
Results The Vitrebond and IRM were significantly more cytotoxic than the other root-end filling materials (
p < 0.05). Those cells exposed to the Biodentine and Dyract compomer eluates showed the highest survival rates (p < 0.05), while the PMTA, MM-MTA, SDR, and PMMA groups exhibited similar cell viabilities. Three-day samples were more cytotoxic than 1-day samples (p < 0.05). Eluates from the cements at 1:1 dilution were significantly more cytotoxic (p < 0.05). Vitrebond induced cell necrosis as indicated by flow cytometry.Conclusions This
in vitro study demonstrated that Biodentine and Compomer were more biocompatible than the other root-end filling materials. Vitrebond eluate caused necrotic cell death.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- In Vitro Biocompatibility of Calcium Silicate-Based Materials for Retrograde Endodontic Treatment Under Different Setting Conditions
Kremena Markova, Neshka Manchorova-Veleva, Veselina Todorova, Lyubomir Vangelov, Desislava Petkova
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2026; 17(3): 124. CrossRef - Effects of Three Retrograde Filling Materials on Production of Inflammatory Cytokines and Resorbing Mediators
Samaneh Arab, Marjan Bahraminasab, Masoumeh Motamedi, Jamshid Hadjati, Alaviye Vahid
Journal of Microbiota.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Apoptotic effects of biodentine, calcium-enriched mixture (CEM) cement, ferric sulfate, and mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) on human mesenchymal stem cells isolated from the human pulp of exfoliated deciduous teeth
Bahareh NAZEMI SALMAN, Mahshid MOHEBBI RAD, Ehsan SABURI
Minerva Dental and Oral Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of Mechanical/Chemical Properties and Cytotoxicity of Resin-Modified Glass Ionomer Cements Containing Sr/F-Bioactive Glass Nanoparticles and Methacrylate Functionalized Polyacids
Wisitsin Potiprapanpong, Parichart Naruphontjirakul, Chutikarn Khamsuk, Somruethai Channasanon, Arnit Toneluck, Siriporn Tanodekaew, Naruporn Monmaturapoj, Anne M. Young, Piyaphong Panpisut
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(12): 10231. CrossRef - Comparative biological properties of resin-free and resin-based calcium silicate-based endodontic repair materials on human periodontal ligament stem cells
Shehabeldin M. Saber, Shaimaa M. Gomaa, Mohamed M. Elashiry, Ahmed El-Banna, Edgar Schäfer
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(11): 6757. CrossRef - Comparison of root end sealing ability of three retrograde filling materials in teeth with root apices resected at 900 using dye penetration method under fluorescent microscope
Dr. Payal Chaudhari, Manoj Chandak, Dr. Aditya Patel
F1000Research.2023; 12: 1049. CrossRef - The Effects of Tricalcium-Silicate-Nanoparticle-Containing Cement: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies
Naho Ezawa, Yoshihiko Akashi, Kei Nakajima, Katsutoshi Kokubun, Masahiro Furusawa, Kenichi Matsuzaka
Materials.2023; 16(12): 4451. CrossRef - Evaluation of the cytotoxic effects of a new Harvard MTA compared to MTA Flow and ProRoot MTA on human gingival fibroblasts
Abdel-Rahman Youssef, Samia Elsherief
The Saudi Dental Journal.2021; 33(7): 679. CrossRef - Cytotoxicity and Bioactivity of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate and Bioactive Endodontic Type Cements: A Systematic Review
Uma Dixit, Rucha Shivajirao Bhise Patil, Rupanshi Parekh
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2021; 14(1): 30. CrossRef - MTT versus other cell viability assays to evaluate the biocompatibility of root canal filling materials: a systematic review
A. V. B. Pintor, L. D. Queiroz, R. Barcelos, L. S. G. Primo, L. C. Maia, G. G. Alves
International Endodontic Journal.2020; 53(10): 1348. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of the flow and filling ability of endodontic materials using different test models
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Gisselle Moraima Chavez-Andrade, Jader Camilo Pinto, Fábio Luiz Camargo Villela Berbert, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Long-term Follow-up for Apical Microsurgery of Teeth with Core and Post Restorations
Astrid Truschnegg, Petra Rugani, Barbara Kirnbauer, Lumnije Kqiku, Norbert Jakse, Robert Kirmeier
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(2): 178. CrossRef - Comparison of Cytotoxic Effects of Calcium Silicate-based Materials on Human Pulp Fibroblasts
Mehmet Adıgüzel, Fuat Ahmetoğlu, Ayçe Ünverdi Eldeniz, Mehmet Gökhan Tekin, Bülent Göğebakan
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2019; 13(4): 241. CrossRef
- In Vitro Biocompatibility of Calcium Silicate-Based Materials for Retrograde Endodontic Treatment Under Different Setting Conditions
- 1,876 View
- 5 Download
- 13 Crossref

- White mineral trioxide aggregate mixed with calcium chloride dihydrate: chemical analysis and biological properties
- Hany Mohamed Aly Ahmed, Norhayati Luddin, Thirumulu Ponnuraj Kannan, Khairani Idah Mokhtar, Azlina Ahmad
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(3):176-187. Published online April 17, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.3.176
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the chemical and biological properties of fast-set white mineral trioxide aggregate (FS WMTA), which was WMTA combined with calcium chloride dihydrate (CaCl2·2H2O), compared to that of WMTA.
Materials and Methods Surface morphology, elemental, and phase analysis were examined using scanning electron microscope (SEM), energy dispersive X-ray microanalysis (EDX), and X-ray diffraction (XRD), respectively. The cytotoxicity and cell attachment properties were evaluated on human periodontal ligament fibroblasts (HPLFs) using methyl-thiazol-diphenyltetrazolium (MTT) assay and under SEM after 24 and 72 hours, respectively.
Results Results showed that the addition of CaCl2·2H2O to WMTA affected the surface morphology and chemical composition. Although FS WMTA exhibited a non-cytotoxic profile, the cell viability values of this combination were lesser than WMTA, and the difference was significant in 7 out of 10 concentrations at the 2 time intervals (
p < 0.05). HPLFs adhered over the surface of WMTA and at the interface, after 24 hours of incubation. After 72 hours, there were increased numbers of HPLFs with prominent cytoplasmic processes. Similar findings were observed with FS WMTA, but the cells were not as confluent as with WMTA.Conclusions The addition of CaCl2·2H2O to WMTA affected its chemical properties. The favorable biological profile of FS WMTA towards HPLFs may have a potential impact on its clinical application for repair of perforation defects.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of three additives on properties of mineral trioxide aggregate cements: a systematic review and meta-analysis of in vitro studies
Behnam Bolhari, Faranak Noori, Hadi Assadian, Amir Raee, Sholeh Ghabraei, Ahmad-Reza Shamshiri, Artak Heboyan
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of sorption and solubility of materials based on calcium aluminate
Renata Josipovic, Violeta Petrovic, Marijana Popovic-Bajic, Irena Kuzmanovic-Radman, Mirjana Umicevic-Davidovic, Aleksandra Djeri, Slavoljub Zivkovic
Stomatoloski glasnik Srbije.2023; 70(1): 26. CrossRef - Chitosan-Based Accelerated Portland Cement Promotes Dentinogenic/Osteogenic Differentiation and Mineralization Activity of SHED
Hasan Subhi, Adam Husein, Dasmawati Mohamad, Nik Rozainah Nik Abdul Ghani, Asma-Abdullah Nurul
Polymers.2021; 13(19): 3358. CrossRef - Chemical modification of MTA and CEM cement to decrease setting time and improve bioactivity properties by adding alkaline salts
Faeze Jamali Zavare, Hanieh Nojehdehian, Maryam Moezizadeh, Mehdi Daneshpooya
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2020; 14(1): 1. CrossRef - Biological effects of acid-eroded MTA Repair HP and ProRoot MTA on human periodontal ligament stem cells
Mar Collado-González, Sergio López-García, David García-Bernal, Ricardo E. Oñate-Sánchez, Christopher J. Tomás-Catalá, Jose M. Moraleda, Adrián Lozano, Leopoldo Forner, Francisco J. Rodríguez-Lozano
Clinical Oral Investigations.2019; 23(10): 3915. CrossRef - Comparative Cytocompatibility and Mineralization Potential of Bio-C Sealer and TotalFill BC Sealer
Sergio López-García, Miguel R. Pecci-Lloret, Julia Guerrero-Gironés, María P. Pecci-Lloret, Adrián Lozano, Carmen Llena, Francisco Javier Rodríguez-Lozano, Leopoldo Forner
Materials.2019; 12(19): 3087. CrossRef - Evaluation of changes in ion release and biological properties of NeoMTA‐Plus and Endocem‐MTA exposed to an acidic environment
F. J. Rodríguez‐Lozano, M. Collado‐González, S. López‐García, D. García‐Bernal, J. M. Moraleda, A. Lozano, L. Forner, L. Murcia, R. E. Oñate‐Sánchez
International Endodontic Journal.2019; 52(8): 1196. CrossRef
- The effect of three additives on properties of mineral trioxide aggregate cements: a systematic review and meta-analysis of in vitro studies
- 1,708 View
- 9 Download
- 7 Crossref

- The effect of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α to induce matrix metalloproteinase (MMPs) from the human dental pulp, gingival, and periodontal ligament cells
- Eun-Mi Rhim, Sang-Hyuk Park, Duck-Su Kim, Sun-Young Kim, Kyoung-Kyu Choi, Gi-Woon Choi
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(1):26-36. Published online January 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.1.26
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives In the present study, three kinds of tissues cells (pulp, gingiva, and periodontal ligament) were investigated if those cells express MMP and TIMP when they were stimulated with neuropeptides (substance P, CGRP) or proinflammatory cytokine, TNF-α.
Materials and Methods The cells cultured from human dental pulp (PF), gingiva (GF) and periodontal ligament were (PDLF) stimulated with Mock, SP, TNF-α, and CGRP for 24 hrs and 48 hrs. for an RNase protection assay and Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay.
Cells (PF, GF and PDLF) seeded in 100 mm culture dish were stimulated with SP (10-5, 10-8 M) or only with medium (Mock stimulation) for 4hrs and for 24 hrs for RNase Protection Assay, and they were stimulated with CGRP (10-5 M) and TNF-α (2 ng/mL) for 24 hrs and with various concentraion of TNF-α (2, 10, and 100 ng/mL) for Rnase Protection Assay with a human MMP-1 probe set including MMP 1, 2, 8, 7, 8, 9, 12, and TIMP 2, 3.
In addition, cells (PF, GF and PDLF) were stimulated with Mock and various concentraion of TNF-α (2, 10, and 100 ng/mL) for 24 hrs and with TNF-α (10 ng/mL) for 48 hrs, and the supernatents from the cells were collected for Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) for MMP-1 and MMP-13.
Results The expression of MMPs in PF, GF, PDLF after stimulation with SP and CGRP were not changed compared with Mock stimulation for 4 hrs and 24 hrs. The expression of MMP-1, -12, -13 24 hrs after stimulation with TNF-α were upregulated, however the expression of TIMP-3 in PF, GF, PDLF after stimulation with TNF-α were downregulated. TNF-α (2 ng/mL, 10 ng/mL, 100 ng/mL) increased MMP-1 and MMP-12 expression in PF dose dependently for 24 hrs.
Conclusions TNF-α in the area of inflammation may play an important role in regulating the remodeling of dentin, cementum, and alveolar bone.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Decoding the Ultimate Effects of Dipeptidyl Peptidase‐4 Inhibitors on Angiogenesis: An Updated Comprehensive Review of the Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms
Andrew Z. Zaka, Safwat A. Mangoura, Marwa A. Ahmed, Beshoy Allam
ChemistrySelect.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Anti‐Inflammatory Effects of Melatonin and 5‐Methoxytryptophol on Lipopolysaccharide‐Induced Acute Pulpitis in Rats
Fatma Kermeoğlu, Umut Aksoy, Abdullah Sebai, Gökçe Savtekin, Hanife Özkayalar, Serkan Sayıner, Ahmet Özer Şehirli, Shuai CHEN
BioMed Research International.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Cross-Talk between Ciliary Epithelium and Trabecular Meshwork Cells In-Vitro: A New Insight into Glaucoma
Natalie Lerner, Elie Beit-Yannai, Wayne Iwan Lee Davies
PLoS ONE.2014; 9(11): e112259. CrossRef
- Decoding the Ultimate Effects of Dipeptidyl Peptidase‐4 Inhibitors on Angiogenesis: An Updated Comprehensive Review of the Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms
- 1,571 View
- 5 Download
- 3 Crossref

- The effect of neuropeptides on secretion of Interleukin-8 (IL-8)
- Kyung-Jun Kim, Sang-Hyuk Park, Kyoung-Kyu Choi, Sang-Jin Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(3):153-160. Published online May 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.3.153
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub We investigated the secretion of Interleukin-8 (IL-8) from ginviva and periodontal ligament stimulated with Substance P (SP) and Calcitonin Gene-related Peptide (CGRP). Gingiva (GF), periodontal ligament (PDLF) and pulp (PF) tissues were collected from extracted intact 3rd molars.
Cultured cells were stimulated with different concentrations of SP for 4 hrs, and stimulated with SP, CGRP and Tumor Necrosis Factor-α (TNF-α) for 8 hrs. Then RNase Protection Assay was carried out. ELISA was performed using supernatants of stimulated cells for quantitative analysis of IL-8. Results were assessed using student t-test with significance of P < 0.05.
According to this study, the results were as follows:
IL-8 mRNA was detected in all type of cells studied (PF, GF and PDLF).
IL-8 mRNA expression was not increased after stimulating 4 hrs with SP (10-5M) and SP (10-8M) compared with Mock stimulation in all type of cells studied.
IL-8 mRNA expression was not increased after stimulating 8 hrs with SP (10-4M) and CGRP (10-6M) compared with Mock stimulation in all type of cells studied.
TNF-α(2 ng/ml) increased the expression of IL-8 mRNA in all kind of cells studied.
The secretion of IL-8 from GF was increased 8 hrs after the stimulation with CGRP (10-6M) (p < 0.05).
The secretion of IL-8 from PDLF was increased 8 hrs after the stimulation with SP (10-4M) (p < 0.05).
Calcitonin Gene-related Peptide (CGRP) increased Interleukin-8 (IL-8) which plays an important role in chemotaxis of neutrophil in Calcitonin Gene-related Peptide (CGRP) gingival tissue, whereas Substance P increased the secretion of IL-8 from periodontal ligament.
- 1,382 View
- 1 Download

-
MMP and TIMP production in periodontal ligament fibroblasts stimulated by
Prevotella nigrescens lipopolysaccharide - Won-Kyung Yang, WooCheol Lee, Mi-Ri Kim, Ho-Hyun Son
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(5):372-384. Published online September 30, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.5.372
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to monitor the secretion of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase (TIMP) by human periodontal ligament (PDL) fibroblasts stimulated with
Prevotella nigrescens lipopolysaccharide (LPS), and to examine the effect of calcium hydroxide treatment onP. nigrescens LPS.LPS was extracted and purified from anaerobically cultured P. nigrescens. PDL fibroblasts were stimulated by the LPS (0, 0.1, 1, 10
ug/ml ) or LPS (10ug/ml ) pretreated with 12.5 mg/ml of Ca(OH)2 for 3 days, for various periods of time (12, 24, 48 h). Immunoprecipitation were performed for protein level analysis of MMP-1, MMP-2 and TIMP-1. Total RNA was isolated and real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was performed for quantification of MMP-1 mRNA.According to this study, the results were as follows:
1. The production of MMP-1 by stimulation with
P. nigrescens LPS increased in time-dependent manner, and showed maximum value at 48 h in both protein and mRNA level. But there was no dose-dependent increase.2. MMP-2 production time-dependently increased when stimulated with 1 and 10
ug/ml LPS, but there was no dose-dependent increase.3. TIMP-1 production increased to 24 h, but decreased at 48 h. It increased when stimulated with 0.1 and 1
ug/ml LPS, but suppressed at 10ug/ml .4.
P. nigrescens LPS pretreated with Ca(OH)2 markedly downregulated MMP-1 gene expression.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- MMPs at Work: Deciphering Their Role in the Cellular Mechanisms of Orthodontic Tooth Movement
Mariana Ramos Patrão, Pedro Mariano Pereira, Jorge Caldeira, Madalena Salema-Oom
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2026; 27(1): 542. CrossRef - Anti-inflammatory effects of PPARγ on human dental pulp cells
Jeong-Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2006; 31(3): 203. CrossRef
- MMPs at Work: Deciphering Their Role in the Cellular Mechanisms of Orthodontic Tooth Movement
- 1,614 View
- 5 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Tissue engineering of dental pulp on type I collagen
- Gwang-Hee Lee, Sung-Yoon Huh, Sang-Hyuk Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(4):370-377. Published online July 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.4.370
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to regenerate human dental pulp tissues similar to native pulp tissues. Using the mixture of type I collagen solution, primary cells collected from the different tissues (pulp, gingiva, and skin) and NIH 3T3 (1 × 105 cells/ml/well) were cultured at 12-well plate at 37℃ for 14 days. Standardized photographs were taken with digital camera during 14 days and the diameter of the contracted collagen gel matrix was measured and statistically analyzed with student t-test. As one of the pulp tissue engineering, normal human dental pulp tissue and collagen gel matrix cultured with dental pulp cells for 14 days were fixed and stained with Hematoxyline & Eosin.
According to this study, the results were as follows:
1. The contraction of collagen gel matrix cultured with pulp cells for 14 days was significantly higher than other fibroblasts (gingiva, skin) (p < 0.05).
2. The diameter of collagen gel matrix cultured with pulp cells was reduced to 70.4% after 7 days, and 57.1% after 14 days.
3. The collagen gel without any cells did not contract, whereas the collagen gel cultured with gingiva and skin showed mild contraction after 14 days (88.1% and 87.6% respectively).
4. The contraction of the collagen gel cultured with NIH 3T3 cells after 14 days was higher than those cultured with gingival and skin fibroblasts, but it was not statistically significant (72.1%, p > 0.05).
5. The collagen gel matrix cultured with pulp cells for 14 days showed similar shape with native pulp tissue without blood vessels.
This approach may provide a means of engineering a variety of other oral tissue as well and these cell behaviors may provide information needed to establish pulp tissue engineering protocols.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Human amniotic membrane extracellular matrix scaffold for dental pulp regeneration in vitro and in vivo
Hengameh Bakhtiar, Azin Ashoori, Sarah Rajabi, Mohamad Pezeshki‐Modaress, Alireza Ayati, Mohammad Reza Mousavi, Mohammad Reza Ellini, Amir Kamali, Amir Azarpazhooh, Anil Kishen
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(4): 374. CrossRef
- Human amniotic membrane extracellular matrix scaffold for dental pulp regeneration in vitro and in vivo
- 1,622 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


