Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Cone-beam computed tomography analysis of maxillary premolar canal anatomy: Ahmed’s versus Vertucci’s classifications in a Jordanian cohort
- Raidan Ba-Hattab, Muna M. Shaweesh, Nessrin A. Taha, Elham S. Abu Alhaija
- Restor Dent Endod 2026;51(1):e11. Published online February 26, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2026.51.e11
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
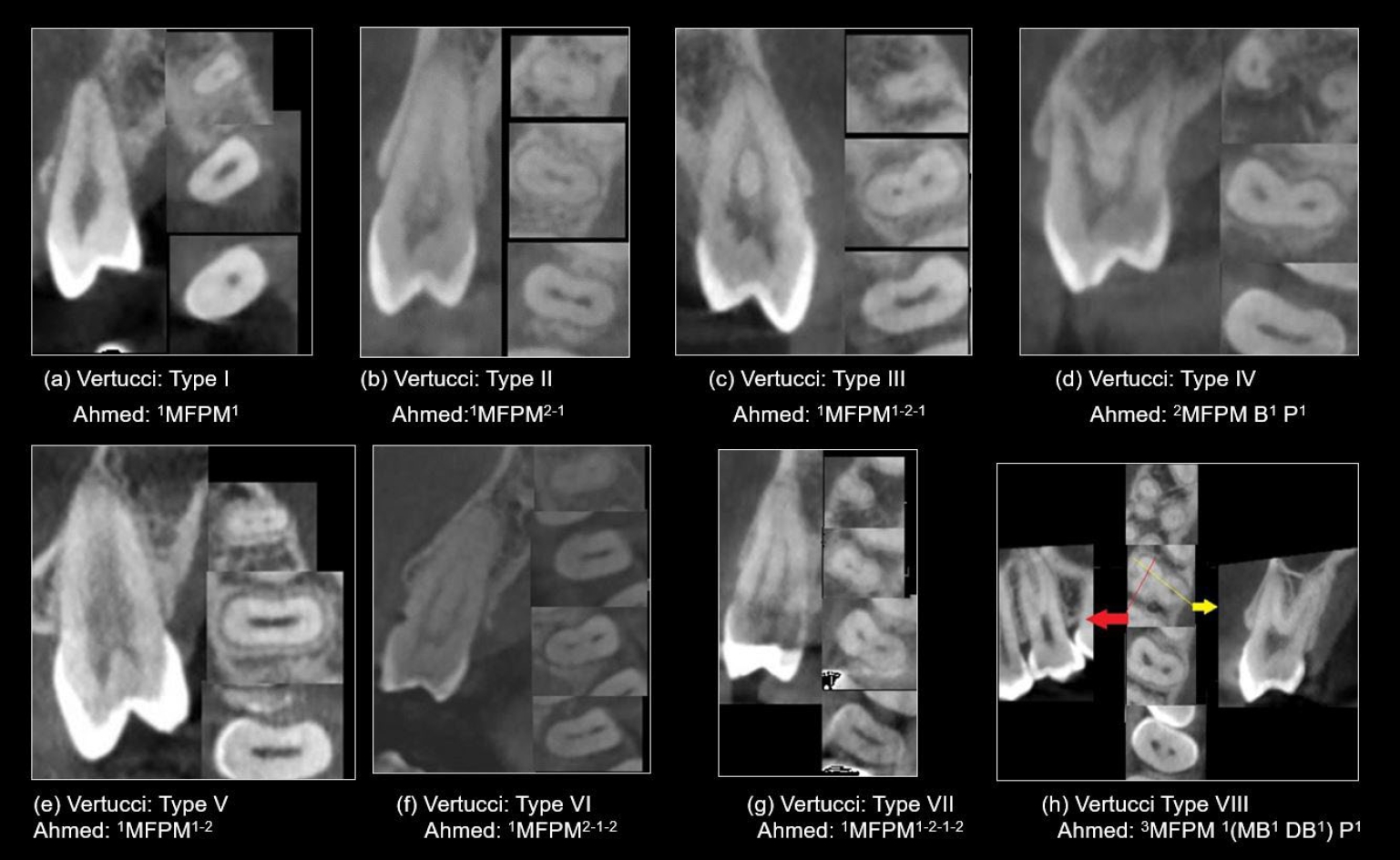
This study analyzed the root and canal configurations of maxillary premolars in a Jordanian subpopulation using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) and classified them based on Vertucci’s and Ahmed’s systems.
Methods
Two hundred CBCT scans of 800 maxillary premolars were retrospectively assessed for root morphology, canal configurations, and root canal divergence and merging. Data was statistically analyzed.
Results
The study included 70 males and 130 females. Most right and left maxillary first premolars (RFPM, LFPM) had two roots (59.0% and 58.5%), with a significant association between sex and root number for RFPM and LFPM (p < 0.05). In contrast, the right and left maxillary second premolars (RSPM, LSPM) mostly had a single root (87.5% and 88.5%), with no association with sex. Vertucci’s classification showed type IV as the predominant configuration in first premolars (RFPM, 65.0% and LFPM, 67.0%) and type I in second premolars (RSPM, 44.0% and LSPM, 49.0%). A significant sex association was found only with RSPM. Ahmed’s classification revealed that maxillary premolar with two separated roots and two separated canals (2MP B1 P1) was mostly found in first premolars (RFPM, 58.0% and LFPM, 56.0%), and maxillary premolar with one root and one canal (1MP1) in second premolars (RSPM, 44.0% and LSPM, 49.0%), with a significant sex association for RSPM and LSPM (p < 0.05). Age had no impact, and symmetry was observed between the right and left sides. Three-rooted premolars were identified in four cases. Almost all of Vertucci’s types and numerous codes from Ahmed’s classification were documented.
Conclusions
CBCT revealed diverse anatomical variations in the Jordanian subpopulation, with Ahmed’s classification providing more detailed canal configurations than Vertucci’s, uncovering previously overlooked variations.
- 210 View
- 18 Download

- Age-dependent root canal instrumentation techniques: a comprehensive narrative review
- Michael Solomonov, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Avi Hadad, Dan Henry Levy, Joe Ben Itzhak, Oleg Levinson, Hadas Azizi
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(2):e21. Published online March 4, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e21
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The aim of this article was to review age-dependent clinical recommendations for appropriate root canal instrumentation techniques. A comprehensive narrative review of canal morphology, the structural characteristics of dentin, and endodontic outcomes at different ages was undertaken instead of a systematic review. An electronic literature search was carried out, including the Medline (Ovid), PubMed, and Web of Science databases. The searches used controlled vocabulary and free-text terms, as follows: ‘age-related root canal treatment,’ ‘age-related instrumentation,’ ‘age-related chemo-mechanical preparation,’ ‘age-related endodontic clinical recommendations,’ ‘root canal instrumentation at different ages,’ ‘geriatric root canal treatment,’ and ‘pediatric root canal treatment.’ Due to the lack of literature with practical age-based clinical recommendations for an appropriate root canal instrumentation technique, a narrative review was conducted to suggest a clinical algorithm for choosing the most appropriate instrumentation technique during root canal treatment. Based on the evidence found through the narrative review, an age-related clinical algorithm for choosing appropriate instrumentation during root canal treatment was proposed. Age affects the morphology of the root canal system and the structural characteristics of dentin. The clinician’s awareness of root canal morphology and dentin characteristics can influence the choice of instruments for root canal treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cross-Sectional Analysis of the Challenges Faced by Undergraduate Dental Students During Root Canal Treatment (RCT) and the Oral Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients After RCT
Mubashir Baig Mirza, Abdullah Bajran Almuteb, Abdulaziz Tariq Alsheddi, Qamar Hashem, Mohammed Ali Abuelqomsan, Ahmed AlMokhatieb, Shahad AlBader, Abdullah AlShehri
Medicina.2025; 61(2): 215. CrossRef - OUTCOMES OF COMBINED ENDODONTIC TREATMENT AND APICAL SURGERY IN MANAGING LARGE PERIAPICAL CYSTS: A CLINICAL STUDY
Sapna Pandey, P Nihar, Amit Kumar, Nitin Bhagat, Vikram Karande, Zameer Pasha, Anukriti Kumari
BULLETIN OF STOMATOLOGY AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY.2025; : 329. CrossRef - El Uso del hipoclorito de sodio en endodoncia: concentración, temperatura y activación
Ábilson Josue Fabiani Ticona, Fernanda Camargo Espejo
Revista de investigación e información en salud.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of Anatomical Dentin Thickness in Mandibular First Molar: An In Vivo Cone‐Beam Computed Tomographic Study
Sahil Choudhari, Kavalipurapu Venkata Teja, Sindhu Ramesh, Jerry Jose, Mariangela Cernera, Parisa Soltani, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva, Gianrico Spagnuolo, Ricardo Danil Guiraldo
International Journal of Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Oral Health Concerns of the ‘Sunset Age’
Pradnya V. Kakodkar, Amandeep Kaur, Shivasakthy Manivasakan, Sounyala Rayannavar, Revati Deshmukh, Smita Athavale
Journal of Medical Evidence.2023; 4(2): 141. CrossRef - Root canal treatment of a six-canal first mandibular molar with extensive periapical lesion: A case report
Xin Li, Shuyu Sun, Tengyi Zheng
Medicine.2023; 102(30): e34336. CrossRef - Endodontic Dentistry: Analysis of Dentinal Stress and Strain Development during Shaping of Curved Root Canals
Laura Iosif, Bogdan Dimitriu, Dan Florin Niţoi, Oana Amza
Healthcare.2023; 11(22): 2918. CrossRef - Mechanisms of age-related changes in the morphology of the pulp system of the first lower molars
N.B. Petrukhina, O.A. Zorina, V.A. Venediktova
Stomatologiya.2022; 101(2): 19. CrossRef
- Cross-Sectional Analysis of the Challenges Faced by Undergraduate Dental Students During Root Canal Treatment (RCT) and the Oral Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients After RCT
- 3,317 View
- 37 Download
- 8 Crossref

- The prevalence of radix molaris in the mandibular first molars of a Saudi subpopulation based on cone-beam computed tomography
- Hassan AL-Alawi, Saad Al-Nazhan, Nassr Al-Maflehi, Mazen A. Aldosimani, Mohammed Nabil Zahid, Ghadeer N. Shihabi
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(1):e1. Published online November 14, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
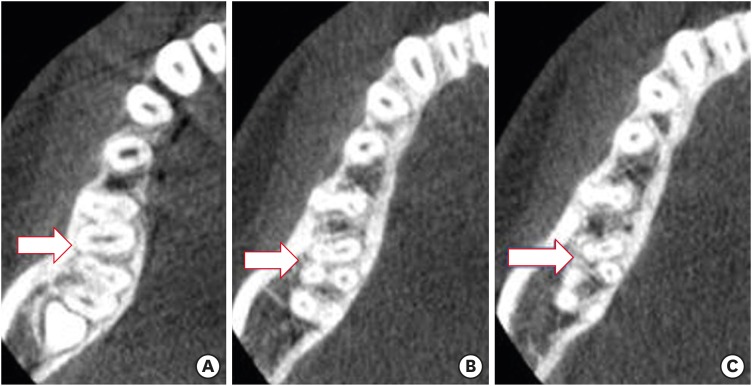
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to determine the incidence of radix molaris (RM) (entomolaris and paramolaris) in the mandibular first permanent molars of a sample Saudi Arabian subpopulation using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT).
Materials and Methods A total of 884 CBCT images of 427 male and 457 female Saudi citizens (age 16 to 70 years) were collected from the radiology department archives of 4 dental centers. A total of 450 CBCT images of 741 mature mandibular first molars that met the inclusion criteria were reviewed. The images were viewed at high resolution by 3 examiners and were analyzed with Planmeca Romexis software (version 5.2).
Results Thirty-three (4.5%) mandibular first permanent molars had RM, mostly on the distal side. The incidence of radix entomolaris (EM) was 4.3%, while that of radix paramolaris was 0.3%. The RM roots had one canal and occurred more unilaterally. No significant difference in root configuration was found between males and females (
p > 0.05). Types I and III EM root canal configurations were most common, while type B was the only RP configuration observed.Conclusions The incidence of RM in the mandibular first molars of this Saudi subpopulation was 4.5%. Identification of the supernumerary root can avoid missing the canal associated with the root during root canal treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of the variations of mandibular molars and the distance from root apex to the inferior alveolar nerve in Saudi Sub-population: Three-dimensional radiographic evaluation
Tariq Mohammed Aqili, Esam Sami Almuzaini, Abdulbari Saleh Aljohani, Ahmed Khaled Al Saeedi, Hassan Abdulmuti Hammudah, Muath Alassaf, Muhannad M. Hakeem, Mohmed Isaqali Karobari
PLOS ONE.2025; 20(2): e0317053. CrossRef - Prevalence of radix molaris in mandibular molars of a subpopulation of Brazil’s Northeast region: a cross-sectional CBCT study
Yasmym Martins Araújo de Oliveira, Maria Clara Mendes Gomes, Maria Fernanda da Silva Nascimento, Ricardo Machado, Danna Mota Moreira, Hermano Camelo Paiva, George Táccio de Miranda Candeiro
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of radix entomolaris and distolingual canals and their association with the incidence of middle mesial canals in mandibular first molars of a Saudi subpopulation
Ahmed A. Madfa, Abdullah F. Alshammari, Eyad Almagadawyi, Afaf Al-Haddad, Ebtsam A. Aledaili
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of the root and canal morphology in the permanent dentition of Saudi Arabian population using cone beam computed and micro-computed tomography – a systematic review
Mohammed Mustafa, Rumesa Batul, Mohmed Isaqali Karobari, Hadi Mohammed Alamri, Abdulaziz Abdulwahed, Ahmed A. Almokhatieb, Qamar Hashem, Abdullah Alsakaker, Mohammad Khursheed Alam, Hany Mohamed Aly Ahmed
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of radix accesoria dentis in a northern Peruvian population evaluated by cone-beam tomography
Karla Renata León-Almanza, Anthony Adrián Jaramillo-Nuñez, Catherin Angélica Ruiz-Cisneros, Paul Martín Herrera-Plasencia
Heliyon.2024; 10(16): e35919. CrossRef - Radix molaris is a hidden truth of mandibular first permanent molars: A descriptive- analytic study using cone beam computed tomography
Mohammed A. Alobaid, Saurabh Chaturvedi, Ebtihal Mobarak S. Alshahrani, Ebtsam M. Alshehri, Amal S. Shaiban, Mohamed Khaled Addas, Giuseppe Minervini
Technology and Health Care.2023; 31(5): 1957. CrossRef - Prevalence of Radix Entomolaris in Mandibular Permanent Molars Analyzed by Cone-Beam CT in the Saudi Population of Ha'il Province
Moazzy I Almansour, Ahmed A Madfa, Adhwaa F Algharbi, Reem Almuslumani, Noeer K Alshammari, Ghufran M Al Hussain
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of radix entomolaris in India and its comparison with the rest of the world
Sumit MOHAN, Jyoti THAKUR
Minerva Dental and Oral Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Radix Paramolaris an Endodontic Challenge: A Case Report
Ashwini B Prasad, Deepak Raisingani, Ridhima Gupta, Rimjhim Jain
Journal of Mahatma Gandhi University of Medical Sciences and Technology.2022; 7(1): 32. CrossRef - Evaluation of Radix Entomolaris and Middle Mesial Canal in Mandibular Permanent First Molars in an Iraqi Subpopulation Using Cone‐Beam Computed Tomography
Ranjdar Mahmood Talabani, Kazhan Omer Abdalrahman, Rawa Jamal Abdul, Dlsoz Omer Babarasul, Sara Hilmi Kazzaz, Heng Bo Jiang
BioMed Research International.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Root Canal Configuration of Maxillary and Mandibular First Molar by CBCT: A Retrospective Cross-Sectional Study
Rakan Rafdan Alhujhuj, Rizwan Jouhar, Muhammad Adeel Ahmed, Abdullatif Abdulrahman Almujhim, Mohammed Tariq Albutayh, Necdet Adanir
Diagnostics.2022; 12(9): 2121. CrossRef - Ethnical Anatomical Differences in Mandibular First Permanent Molars between Indian and Saudi Arabian Subpopulations: A Retrospective Cross-sectional Study
Abdulwahab Alamir, Mohammed Mashyakhy, Apathsakayan Renugalakshmi, Thilla S Vinothkumar, Anandhi S Arthisri, Ahmed Juraybi
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2021; 22(5): 484. CrossRef
- Evaluation of the variations of mandibular molars and the distance from root apex to the inferior alveolar nerve in Saudi Sub-population: Three-dimensional radiographic evaluation
- 2,581 View
- 37 Download
- 12 Crossref

- Endodontic management of a maxillary first molar with three roots and seven root canals with the aid of cone-beam computed tomography
- Gurudutt Nayak, Kamal Krishan Singh, Rhitu Shekhar
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(3):241-248. Published online June 3, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.3.241
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Variation in root canal morphology, especially in maxillary first molar presents a constant challenge for a clinician in their detection and management. This case report describes the successful root canal treatment of a three rooted right maxillary first molar presenting with three canals each in the mesiobuccal and distobuccal roots and one canal in the palatal root. The clinical detection of this morphologic aberration was made using a dental operating microscope, and the canal configuration was established after correlating and computing the clinical, radiographic and cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) scan findings. CBCT images confirmed the configuration of the canals in the mesiobuccal and distobuccal roots to be Al-Qudah and Awawdeh type (3-2) and type (3-2-1), respectively, whereas the palatal root had a Vertucci type I canal pattern. This report reaffirms the importance of careful examination of the floor of the pulp chamber with a dental operating microscope and the use of multiangled preoperative radiographs along with advanced diagnostic aids such as CBCT in identification and successful management of aberrant canal morphologies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Inhibition potential of rhamnolipid biosurfactant against Corynespora cassiicola – a phytopathogen of king chilli
Nilam Sarma, Suresh Deka, Hemen Deka
Studia Biologica.2025; 19(3): 153. CrossRef - Endodontic Management of Maxillary First Molar with Seven Root Canals Diagnosed Using Cone-beam Computed Tomography: A Case Report
Ravindranath Megha, Venkatachalam Prakash
World Journal of Dentistry.2021; 12(1): 89. CrossRef - The MB3 canal in maxillary molars: a micro-CT study
Ronald Ordinola-Zapata, Jorge N. R. Martins, Hugo Plascencia, Marco A. Versiani, Clovis M. Bramante
Clinical Oral Investigations.2020; 24(11): 4109. CrossRef - Maxillary first molar with 7 root canals diagnosed using cone-beam computed tomography
Evaldo Rodrigues, Antônio Henrique Braitt, Bruno Ferraz Galvão, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2017; 42(1): 60. CrossRef - Endodontic management of a maxillary first molar with seven root canal systems evaluated using cone-beam computed tomography scanning
VijayReddy Venumuddala, Sridhar Moturi, SV Satish, BKalyan Chakravarthy, Sudhakar Malapati
Journal of International Society of Preventive and Community Dentistry.2017; 7(5): 297. CrossRef
- Inhibition potential of rhamnolipid biosurfactant against Corynespora cassiicola – a phytopathogen of king chilli
- 2,356 View
- 12 Download
- 5 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


