Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Success rate of direct pulp capping on permanent teeth using bioactive materials: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials
- Karem Paula Pinto, Gabriela Ribeiro da Silva, Cláudio Malizia Alves Ferreira, Luciana Moura Sassone, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(4):e34. Published online September 6, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e34
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to evaluate the success rate of direct pulp capping (DPC) on permanent teeth, comparing the use of MTA with calcium hydroxide and calcium silicate-based cements. A systematic search was carried out in 4 databases until July 2023. The selection was based on PICOS criteria and only randomized clinical trials were included. The risk of bias was assessed using RoB-2 tool, and meta-analyses were performed using RevMan 5.3 software. The overall quality of evidence was determined using the GRADE tool. Thirteen studies were included. Meta-analyses indicated significantly higher success rate for DPC using MTA compared to calcium hydroxide, while no significant difference was observed between MTA and Biodentine, showing a success rate from 80% to 100% even after 3 years of follow-up. Five studies were classified as having high risk of bias and the GRADE assessment revealed low certainty of evidence. DPC is highly effective for permanent teeth when using MTA or Biodentine. There is a need for future well-designed randomized clinical trials to evaluate the efficacy of DPC using newer bioceramic materials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Physicochemical effects of nano type-B bone substitute on pulp protective cement formulations
Njwan Fadhel SHEHAB
Dental Materials Journal.2026; 45(1): 92. CrossRef - Photobiomodulation-assisted pulp capping using nano-hydroxyapatite and mineral trioxide aggregate: Report of two cases
Priya Pal, Rhythm Bains, Promila Verma, Vivek Kumar Bains
Journal of Healthcare Research and Education.2026; 2: 2. CrossRef - Histological Tissue Response to Calcium Silicate-Based Cements Assessed in Human Tooth Culture Models: A Systematic Review
Alberto Cabrera-Fernández, Hebertt Gonzaga dos Santos Chaves, Aránzazu Díaz-Cuenca, Juan J. Segura-Egea, Jenifer Martín-González, João Peça, Diana B. Sequeira, João Miguel Marques dos Santos
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2026; 17(2): 78. CrossRef - Indian Association of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics consensus statement on deep caries management
Deepak Kumar Sharma, R. S. Mohan Kumar, Shishir Singh, Suparna Ganguly Saha, Meenal Nithin Gulve, Dipali Y. Shah, Sathish Abraham, Shruthi Nagaraja, Raksha Bhat
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(8): 714. CrossRef
- Physicochemical effects of nano type-B bone substitute on pulp protective cement formulations
- 19,177 View
- 569 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Nanoleakage of apical sealing using a calcium silicate-based sealer according to canal drying methods
- Yoon-Joo Lee, Kyung-Mo Cho, Se-Hee Park, Yoon Lee, Jin-Woo Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(2):e20. Published online April 19, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e20

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study investigated the nanoleakage of root canal obturations using calcium silicate-based sealer according to different drying methods.
Materials and Methods Fifty-two extracted mandibular premolars with a single root canal and straight root were selected for this study. After canal preparation with a nickel-titanium rotary file system, the specimens were randomly divided into 4 groups according to canal drying methods (1: complete drying, 2: blot drying/distilled water, 3: blot drying/NaOCl, 4: aspiration only). The root canals were obturated using a single-cone filling technique with a calcium silicate–based sealer. Nanoleakage was evaluated using a nanoflow device after 24 hours, 1 week, and 1 month. Data were collected twice per second at the nanoscale and measured in nanoliters per second. Data were statistically analyzed using the Kruskal-Wallis and Mann–Whitney
U -tests (p < 0.05).Results The mean flow rate measured after 24 hours showed the highest value among the time periods in all groups. However, the difference in the flow rate between 1 week and 1 month was not significant. The mean flow rate of the complete drying group was the highest at all time points. After 1 month, the mean flow rate in the blot drying group and the aspiration group was not significantly different.
Conclusions Within the limitations of this study, the canal drying method had a significant effect on leakage and sealing ability in root canal obturations using a calcium silicate-based sealer. Thus, a proper drying procedure is critical in endodontic treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of interactions between sealers and irrigants on the physicochemical and surface characteristics of endodontic sealers
Hye-In Kim, Yeon-Ju You, Yemi Kim, Jin-Woo Kim, Young-Eun Jang
Clinical Oral Investigations.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
- Effects of interactions between sealers and irrigants on the physicochemical and surface characteristics of endodontic sealers
- 2,511 View
- 110 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- The status of clinical trials regarding root canal sealers
- Ahmad AL Malak, Yasmina EL Masri, Mira Al Ziab, Nancy Zrara, Tarek Baroud, Pascale Salameh
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(1):e5. Published online January 15, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e5
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
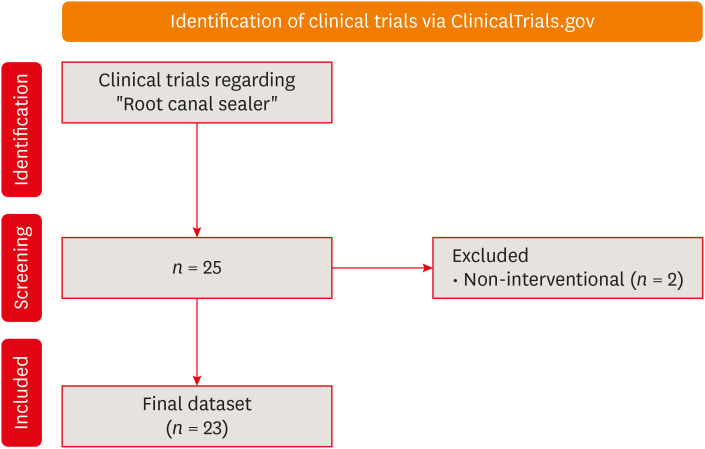
ePub Objectives This study aimed to present the results and analyses of clinical trials, including updates on the different functions of root canal sealers.
Materials and Methods In June 2023, we performed a comprehensive search of ClinicalTrials.gov to identify interventional clinical trials pertaining to root canal sealers. In total, 23 clinical trials conducted up to June 2023 were included in this study.
Results Approximately half of the trials (11 out of 23) were completed, while none were terminated or withdrawn. Each included trial had a minimum of 10 participants, with 11 trials having more than 100 participants. None of the assessed trials provided outcomes, and the majority (17 out of 23) lacked associated publications. In terms of geographic distribution, the USA and Canada did not contribute to any root canal sealer trials.
Conclusions This study highlights the lack of diversity in trial locations, the absence of reported results, and a scarcity of clinical trials examining the physicochemical properties of different sealers. Most published trials primarily focused on assessing the post-operative pain effect of these sealers, but no significant difference was found regarding post-operative pain control.
- 3,930 View
- 55 Download

- Push-out bond strength and intratubular biomineralization of a hydraulic root-end filling material premixed with dimethyl sulfoxide as a vehicle
- Ju-Ha Park, Hee-Jin Kim, Kwang-Won Lee, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kyung-San Min
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(1):e8. Published online January 20, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e8
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
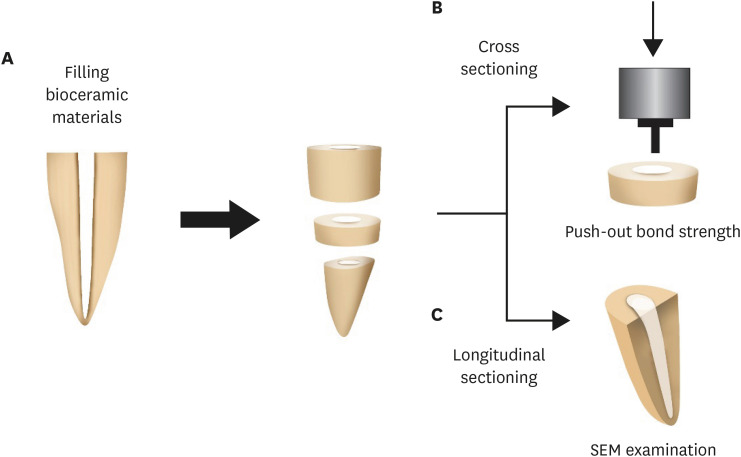
ePub Objectives This study was designed to evaluate the parameters of bonding performance to root dentin, including push-out bond strength and dentinal tubular biomineralization, of a hydraulic bioceramic root-end filling material premixed with dimethyl sulfoxide (Endocem MTA Premixed) in comparison to a conventional powder-liquid–type cement (ProRoot MTA).
Materials and Methods The root canal of a single-rooted premolar was filled with either ProRoot MTA or Endocem MTA Premixed (
n = 15). A slice of dentin was obtained from each root. Using the sliced specimen, the push-out bond strength was measured, and the failure pattern was observed under a stereomicroscope. The apical segment was divided into halves; the split surface was observed under a scanning electron microscope, and intratubular biomineralization was examined by observing the precipitates formed in the dentinal tubule. Then, the chemical characteristics of the precipitates were evaluated with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopic (EDS) analysis. The data were analyzed using the Student’st -test followed by the Mann-WhitneyU test (p < 0.05).Results No significant difference was found between the 2 tested groups in push-out bond strength, and cohesive failure was the predominant failure type. In both groups, flake-shaped precipitates were observed along dentinal tubules. The EDS analysis indicated that the mass percentage of calcium and phosphorus in the precipitate was similar to that found in hydroxyapatite.
Conclusions Regarding bonding to root dentin, Endocem MTA Premixed may have potential for use as an acceptable root-end filling material.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of intratubular biomineralization between in vivo and in vitro conditions
Sieun Nam, Yeon-Jee Yoo, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kyung-San Min
Journal of Oral Science.2026; 68(1): 30. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Sectioning Method and Filling Materials on Roughness and Cell Attachments in Root Resection Procedure
Tarek Ashi, Naji Kharouf, Olivier Etienne, Bérangère Cournault, Pierre Klienkoff, Varvara Gribova, Youssef Haikel
European Journal of Dentistry.2025; 19(01): 240. CrossRef - Bond Strength and Adhesive Interface Quality of New Pre‐Mixed Bioceramic Root Canal Sealer
Gustavo Creazzo, Bruna Monteiro de Barros Ciribelli Alves, Helena Cristina de Assis, Karen Gisselle Garay Villamayor, Manoel Damião de Sousa‐Neto, Jardel Francisco Mazzi‐Chaves, Fabiane Carneiro Lopes‐Olhê
Microscopy Research and Technique.2025; 88(7): 1989. CrossRef - Evaluation of clinical and radiographic outcome of premixed injectable mineral trioxide aggregate and conventional mineral trioxide aggregate as pulpotomy medicaments in primary molars – A split-mouth randomized control trial
U. S. Aiswarya, Sharan S. Sargod, Sundeep K. Hegde, H. T. Ajay Rao, Nanditha Hegde
Journal of Indian Society of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry.2025; 43(4): 559. CrossRef - Evaluation of the root dentin bond strength and intratubular biomineralization of a premixed calcium aluminate-based hydraulic bioceramic endodontic sealer
Yu-Na Lee, Min-Kyeong Kim, Hee-Jin Kim, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kwang-Won Lee, Kyung-San Min
Journal of Oral Science.2024; 66(2): 96. CrossRef - Removal efficiency of a fast setting pozzalan-based bioactive cement: a micro CT study
Feyza Çetinkaya, Ahter Şanal Çıkman, Ali Keleş, Banu Arıcıoğlu
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Antibacterial Activity and Sustained Effectiveness of Calcium Silicate-Based Cement as a Root-End Filling Material against Enterococcus faecalis
Seong-Hee Moon, Seong-Jin Shin, Seunghan Oh, Ji-Myung Bae
Materials.2023; 16(18): 6124. CrossRef
- Comparison of intratubular biomineralization between in vivo and in vitro conditions
- 3,370 View
- 94 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref

- Effects of calcium silicate cements on neuronal conductivity
- Derya Deniz-Sungur, Mehmet Ali Onur, Esin Akbay, Gamze Tan, Fügen Daglı-Comert, Taner Cem Sayın
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(2):e18. Published online March 7, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e18
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
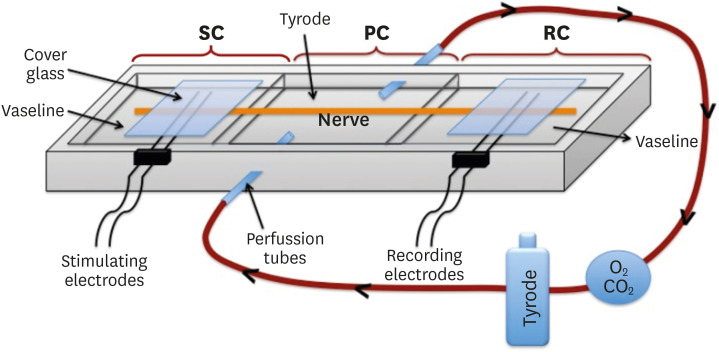
ePub Objectives This study evaluated alterations in neuronal conductivity related to calcium silicate cements (CSCs) by investigating compound action potentials (cAPs) in rat sciatic nerves.
Materials and Methods Sciatic nerves were placed in a Tyrode bath and cAPs were recorded before, during, and after the application of test materials for 60-minute control, application, and recovery measurements, respectively. Freshly prepared ProRoot MTA, MTA Angelus, Biodentine, Endosequence RRM-Putty, BioAggregate, and RetroMTA were directly applied onto the nerves. Biopac LabPro version 3.7 was used to record and analyze cAPs. The data were statistically analyzed.
Results None of the CSCs totally blocked cAPs. RetroMTA, Biodentine, and MTA Angelus caused no significant alteration in cAPs (
p > 0.05). Significantly lower cAPs were observed in recovery measurements for BioAggregate than in the control condition (p < 0.05). ProRoot MTA significantly but transiently reduced cAPs in the application period compared to the control period (p < 0.05). Endosequence RRM-Putty significantly reduced cAPs.Conclusions Various CSCs may alter cAPs to some extent, but none of the CSCs irreversibly blocked them. The usage of fast-setting CSCs during apexification or regeneration of immature teeth seems safer than slow-setting CSCs due to their more favorable neuronal effects.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Endodontic Sealers and Innovations to Enhance Their Properties: A Current Review
Anna Błaszczyk-Pośpiech, Natalia Struzik, Maria Szymonowicz, Przemysław Sareło, Maria Wiśniewska-Wrona, Kamila Wiśniewska, Maciej Dobrzyński, Magdalena Wawrzyńska
Materials.2025; 18(18): 4259. CrossRef
- Endodontic Sealers and Innovations to Enhance Their Properties: A Current Review
- 1,598 View
- 21 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Effect of irrigants on the color stability, solubility, and surface characteristics of calcium-silicate based cements
- Selen Küçükkaya Eren, Sevinc Askerbeyli Örs, Hacer Aksel, Şenay Canay, Duygu Karasan
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(1):e10. Published online February 10, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e10

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to investigate the color stability, solubility, and surface characteristics of 3 calcium silicate-based cements (CSCs) after immersion in different solutions.
Materials and Methods ProRoot white mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA), Biodentine, and Endosequence Root Repair Material (ERRM) were placed in cylindrical molds and stored at 37°C for 24 hours. Each specimen was immersed in distilled water, 5% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl), 2% chlorhexidine, or 0.1% octenidine hydrochloride (OCT) for 24 hours. Color changes were measured with a spectrophotometer. Solubility was determined using an analytical balance with 10−5 g accuracy. The surface characteristics were analyzed using scanning electron microscopy and energy-dispersive spectroscopy. Data were analyzed using 2-way analysis of variance, the Tukey test, and the paired
t -test.Results MTA exhibited significant discoloration in contact with NaOCl (
p < 0.05). White precipitation occurred on the surfaces of Biodentine and ERRM after contact with the solutions, and none of the materials presented dark brown discoloration. All materials showed significant solubility after immersion in the solutions (p < 0.05), irrespective of the solution type (p > 0.05). The surface topography and elemental composition of the samples showed different patterns of crystal formation and precipitation depending on the solution type.Conclusions All materials presented some amount of solubility and showed crystal precipitation after contact with the solutions. Biodentine and ERRM are suitable alternatives to ProRoot MTA as they do not exhibit discoloration. The use of OCT can be considered safe for CSCs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Time-dependent Tooth Color Changes Following Conventional, Silver-based, and Photodynamic Root Canal Irrigants: An In Vitro Study
Laila Mohamed Mohamed Kenawi, Mohamed Fattouh, Khaled Abid Althaqafi, Abla Arafa
The Open Dentistry Journal.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of interactions between sealers and irrigants on the physicochemical and surface characteristics of endodontic sealers
Hye-In Kim, Yeon-Ju You, Yemi Kim, Jin-Woo Kim, Young-Eun Jang
Clinical Oral Investigations.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Chemical and in vivo analyses of calcium silicate‐based materials in bone and connective tissues
Ana Cristina Padilha Janini, Lauter Eston Pelepenko, Brenda Fornazaro Moraes, Victor Augusto Benedicto dos Santos, Matheus Barros‐Costa, Isabela Alvarenga Maciel dos Santos, Fábio Roberto de Souza Batista, Juliana de Aguiar Silveira Meira, Mariza Akemi Ma
International Endodontic Journal.2025; 58(3): 484. CrossRef - Topic: Perspectives on Success and Failure of Endodontic Treatments
Ilma Robo, Manola Kelmendi, Eva Habazaj, Kleves Elezi, Rialda Xhizdari, Nevila Alliu
SN Comprehensive Clinical Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Bismuth release from endodontic materials: Proposed mechanisms for systemic circulation and organ accumulation
Lauter Eston Pelepenko, Benjamin Hewitt, Rodrigo Bueno de Oliveira, Brenda Fornazaro Moraes, Débora C. Coraça-Huber, Ana Cristina Padilha Janini, Marina Angélica Marciano
Journal of Hazardous Materials.2025; 494: 138580. CrossRef - Effect of Vital Pulp Therapy Biomaterials on Tooth Discolouration: A Review of the Literature
Maedeh Gilvari Sarshari, Kiana Shakeri, Ardavan Parhizkar, Naresh Kasoju
International Journal of Biomaterials.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Data about application of chlorhexidine as a periodontal irrigant –
Systematic Review.
Ilma Robo, Manola Kelmendi , Eva Habazaj , Kristi Sulanjaku , Nevila Alliu
Acta Stomatologica Marisiensis Journal.2025; 8(1): 6. CrossRef - Biocompatibility of Hydraulic Calcium Silicate-Based Cement MTA FlowTM on Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells In Vitro
Paulius Tušas, Josette Camilleri, Milda Alksnė, Egidijus Šimoliūnas, Saulius Drukteinis, Eglė Marija Urbonė, Virginija Bukelskienė, Vygandas Rutkūnas, Vytautė Pečiulienė
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2025; 16(7): 252. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Effects of Different Irrigation Solutions on MTA and Dentin Microhardness
Gokay Buyukcolpan, İdil Özden, Hesna Sazak Öveçoğlu
Clinical and Experimental Health Sciences.2025; 15(3): 524. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of the Intratubular Penetration Ability of Two Retrograde Obturation Techniques in Micro-Endodontic Surgical Procedure: An In Vitro Study with Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy
Alberto Casino Alegre, Michell Ramírez López, Manuel Monterde Hernández, Susana Aranda Verdú, Jorge Rubio Climent, Antonio Pallarés Sabater
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(11): 509. CrossRef - The outcome of combined use of iRoot BP Plus and iRoot SP for root-end filling in endodontic microsurgery: a randomized controlled trial
Xu Dong, Qin Su, Wen Li, Jinbo Yang, Dongzhe Song, Jing Yang, Xin Xu
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - How Does Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid Irrigation Affect Biodentine? A Multimethod Ex Vivo Study
Katarzyna Dąbrowska, Aleksandra Palatyńska-Ulatowska, Leszek Klimek
Materials.2024; 17(6): 1230. CrossRef - Color stability and solubility of Biodentine and NeoPutty in contact with different irrigation solutions
Sıla Nur Usta, Cangül Keskin
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The impact of various irrigation solutions on the color stabilities of five calcium silicate cement: an in-vitro study
Aslı Soğukpınar Onsuren, Onur Kesici, Elif Uğurbekler Hündü
Selcuk Dental Journal.2024; 11(3): 313. CrossRef - Bioceramics in Endodontics: Updates and Future Perspectives
Xu Dong, Xin Xu
Bioengineering.2023; 10(3): 354. CrossRef - Effect of calcium silicate-based endodontic sealers on tooth color: A 3-year in vitro experimental study
Carmen Llena, Ana Herrero, Sandra Lloret, Martha Barraza, Jose Luis Sanz
Heliyon.2023; 9(2): e13237. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Shear Bond Strength of Four Bioceramic Materials with Different Restorative Materials and Timings
Abeer S. Alqahtani, Ayman M. Sulimany, Abdullah S. Alayad, Abdulaziz S. Alqahtani, Omar A. Bawazir
Materials.2022; 15(13): 4668. CrossRef
- Time-dependent Tooth Color Changes Following Conventional, Silver-based, and Photodynamic Root Canal Irrigants: An In Vitro Study
- 2,164 View
- 37 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 17 Crossref

- Comparison of the sealing ability of various bioceramic materials for endodontic surgery
- Benjamin Rencher, Ana M. Chang, Hanson Fong, James D. Johnson, Avina Paranjpe
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(3):e35. Published online June 8, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e35
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
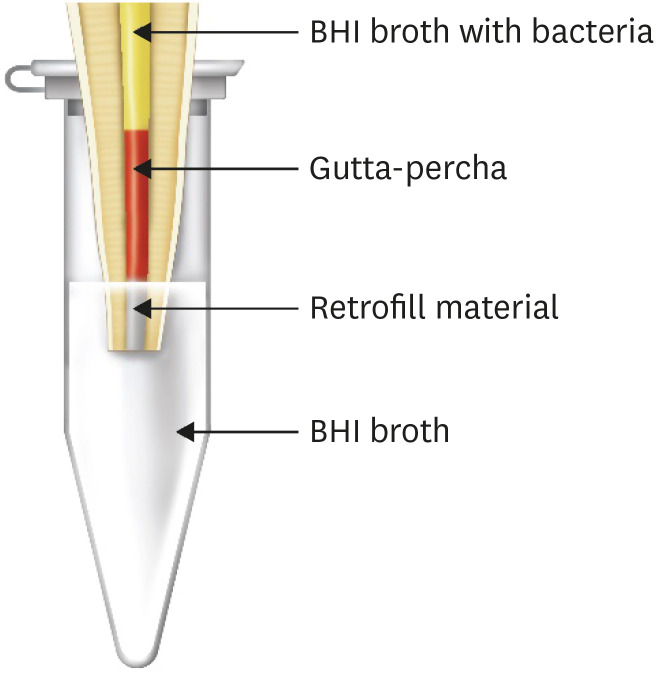
ePub Objectives Endosequence Bioceramic Root Repair Material (BC-RRM) is used in endodontic microsurgery. It is available as a paste and a putty. However, no studies to date have examined the sealing ability of these forms alone or in combination as root-end filling materials. Hence, this study aimed to compare the sealing properties of these 2 forms of BC-RRM.
Materials and Methods Forty-two extracted upper anterior teeth were divided into 3 experimental groups, a positive and negative control. After the root canal treatment, the root ends were resected, retroprepared and retrofilled with either putty, paste + putty or mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA). The teeth were mounted in tubes so the apical 3 mm was submerged in Brain Heart Infusion (BHI) broth. The coronal portions of the canals were inoculated with
Enterococcus faecalis and BHI broth and incubated for 30 days. The broth in the tubes was analyzed for colony forming units to check for leakage of bacteria from the canal. The teeth from the groups were sectioned and analyzed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The Kruskal-Wallis test and analysis of variance were used to analyze the data with a significance levelp < 0.05.Results The BC-RRM and MTA groups showed similar sealing ability. The positive control showed leakage in all samples. The SEM imaging showed the presence of bacteria in all experimental groups at the material-tooth interface.
Conclusions No significant differences were noted in the experimental groups, providing sufficient evidence that any combination could be effectively used during endodontic microsurgery.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sealing ability and marginal adaptation of premixed versus manually mixed bioceramic root-end filling materials: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Ayham Hattab, Mouhammad Al-Tayyan, Osama Hajeer
BMC Oral Health.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - An Ex-vivo Evaluation of Sealability of Three Bioceramic Physical Variants in Coronal and Apical Thirds of Root Canals
Murali H Rao, Rajkumar Krishnan, Pavithra Gopal, Elizabeth Thomas
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2025; 25(11): 1022. CrossRef - Clinical applications and classification of calcium silicate-based cements based on their history and evolution: a narrative review
Kenta Tsuchiya, Salvatore Sauro, Hidehiko Sano, Jukka P. Matinlinna, Monica Yamauti, Shuhei Hoshika, Yu Toida, Rafiqul Islam, Atsushi Tomokiyo
Clinical Oral Investigations.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Strontium- and bioactive glass-enriched dentin repair cement: Mechanical performance and physicochemical characteristics
Nathalia Cristina Tavella-Silva, Larissa Moreira Spinola Castro Raucci, Victor Miguel Polizeli, Carlos Eduardo Saraiva Miranda, Ivone Regina de Oliveira, Walter Raucci Neto
Ceramics International.2025; 51(22): 35947. CrossRef - Conventional vs. Ready‐To‐Use Bioceramic Cements: In Vitro Bond Strength Performance in Blood‐Contaminated Dentine
Gabriela Kato Bego, Graziela Bianchi Leoni, Elias Daniel Covas Rodrigues, Larissa Moreira Spinola de Castro Raucci, Walter Raucci Neto
Australian Endodontic Journal.2025; 51(2): 466. CrossRef - Effect of calcium silicate-based repair sealers on bone healing in rat skull defects: histological and histomorphometric study
J. M. Sauer, C. E. S. Bueno, R. A. Pelegrine, C. E. Fontana, E. F. Martinez, P. G. Montagner, W. M. Nascimento, A. G. S. Limoeiro, D. G. P. Rocha, M. F. V. Marceliano-Alves, M. P. W. Galhardi, M. Klymus, A. S. Martin
Endodontics Today.2025; 23(3): 433. CrossRef - Randomized Trial of Bioceramic Apical Barrier Methods in Necrotic Immature Incisors: Effects on Pain, Extrusion, and Procedure Duration
Yasser Alsayed Tolibah, Nada Bshara, Osama Aljabban, Mohammad Tamer Abbara, Marwan Alhaji, Imad-Addin Almasri, Ziad D. Baghdadi
Children.2025; 12(10): 1423. CrossRef - Sealing ability of mineral trioxide aggregate: A scoping review of laboratory assessment methods
Kenta Tsuchiya, Salvatore Sauro, Jukka P. Matinlinna, Hidehiko Sano, Monica Yamauti, Deepak Mehta, Kyung‐San Min, Atsushi Tomokiyo
European Journal of Oral Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Root Development Following Bioceramic Material Application in Immature Permanent Teeth: A Case Series With 24‐Month Follow‐Up
Yasser Alsayed Tolibah, Nada Bshara, Mohammad Tamer Abbara, Marwan Alhaji, Osama Aljabban, Ibrahim Ali Ahmad, Ziad D. Baghdadi, Hannah Wesley
Case Reports in Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Laboratory study of the sealing ability of materials used in retrograde root filling
L.A. Nadzharyan, A.V. Vasilyev, V.A. Badalyan, A.S. Galkin, A.V. Mironov, F.F. Losev
Stomatology.2025; 104(6): 5. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Marginal Adaptation of Two Hydraulic Calcium Silicate Cements Used in Apical Plugs: An In Vitro Study
Sara Filipe, José Pedro Martinho, Siri Paulo, Catarina Carvalho, Ana Coelho, Inês Amaro, Eunice Carrilho, Anabela Paula, Carlos Miguel Marto, Henrique Girão, Mónica Zuzarte, Ana S. Pires, Manuel Marques Ferreira
Applied Sciences.2024; 14(2): 480. CrossRef - A Study on Nanoleakage of Apical Retrograde Filling of Premixed Calcium Silicate-Based Cement Using a Lid Technique
Nyamsuren Enkhbileg, Jin Woo Kim, Seok Woo Chang, Se-Hee Park, Kyung Mo Cho, Yoon Lee
Materials.2024; 17(10): 2366. CrossRef - The outcome of combined use of iRoot BP Plus and iRoot SP for root-end filling in endodontic microsurgery: a randomized controlled trial
Xu Dong, Qin Su, Wen Li, Jinbo Yang, Dongzhe Song, Jing Yang, Xin Xu
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Bacterial sealing ability of calcium silicate-based sealer for endodontic surgery: an in-vitro study
Mai M. Mansour, Sybel M. Moussa, Marwa A. Meheissen, Mahmoud R. Aboelseoud
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Marginal Adaptation of Three Biomaterials as Apical Barrier in Experimental Apexification Model
Nagehan Aktaş, Didem Sakaryalı Uyar, Didem Atabek
ADO Klinik Bilimler Dergisi.2024; 13(3): 409. CrossRef - In vitro evaluation of the sealing ability of combined use of iRoot BP Plus and iRoot SP for root-end filling
Xu Dong, Qian Xie, Xin Xu
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(6): 2969. CrossRef - Outcomes of endodontic microsurgery using different calcium silicate–based retrograde filling materials: a cohort retrospective cone-beam computed tomographic analysis
Rawan F. Eskandar, Mey A. Al-Habib, Mohammed A. Barayan, Hadeel Y. Edrees
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Bioceramics in Endodontics: Updates and Future Perspectives
Xu Dong, Xin Xu
Bioengineering.2023; 10(3): 354. CrossRef - Biological properties of Ceraputty as a retrograde filling material: an in vitro study on hPDLSCs
Sergio López-García, Francisco J. Rodríguez-Lozano, José Luis Sanz, Leopoldo Forner, María Pilar Pecci-Lloret, Adrián Lozano, Laura Murcia, Sonia Sánchez-Bautista, Ricardo E. Oñate-Sánchez
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(8): 4233. CrossRef - Bone Window Technique in Endodontic Microsurgery – Report of Two Cases
Spyros Floratos, Vasileios Molonis, Apostolos Tsolakis, Stylianos Kykalos, Konstantinos Kontzoglou
Journal of Endodontic Microsurgery.2022; 2: 24. CrossRef
- Sealing ability and marginal adaptation of premixed versus manually mixed bioceramic root-end filling materials: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- 5,867 View
- 99 Download
- 16 Web of Science
- 20 Crossref

- Flow characteristics and alkalinity of novel bioceramic root canal sealers
- Anastasios Katakidis, Konstantinos Sidiropoulos, Elisabeth Koulaouzidou, Christos Gogos, Nikolaos Economides
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(4):e42. Published online August 18, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e42
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
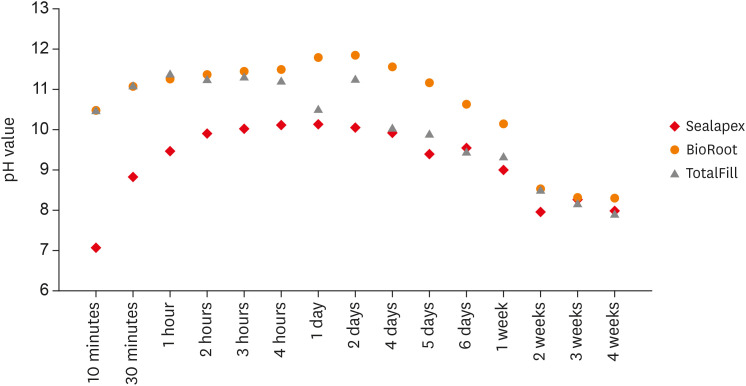
ePub Objective This study aimed to examine the physical properties (pH and flow) of 2 novel bioceramic sealers.
Materials and Methods The tested sealers were a calcium hydroxide sealer (Sealapex) and 2 bioceramic sealers (BioRoot RCS and TotalFill BC Sealer). Flow measurements were conducted according to ISO 6876/2012, with a press method of 0.05 mL of sealer. The pH of fresh samples was tested immediately after manipulation, while set samples were stored for 3 times the recommended setting time. The predetermined time intervals ranged from 3 minutes to 24 hours for fresh samples and from 10 minutes to 7 days and 4 weeks for the set samples. Analysis of variance was performed, with
p = 0.05 considered indicating significance.Results The mean flow values were 26.99 mm for BioRoot, 28.19 for Sealapex, and 30.8 mm for TotalFill BC Sealer, satisfying the ISO standard. In the set samples, BioRoot RCS had higher pH values at 24 hours to 1 week after immersion in distilled water. At 2 weeks, both bioceramic sealers had similar pH values, greater than that of Sealapex. In the fresh samples, the bioceramic sealers had significantly higher initial pH values than Sealapex (
p < 0.05). At 24 hours post-immersion, all sealers showed an alkaline pH, with the highest pH observed for TotalFill.Conclusions The TotalFill BC Sealer demonstrated the highest flow. The bioceramic sealers initially presented higher alkaline activity than the polymeric calcium hydroxide sealer. However, at 3 and 4 weeks post-immersion, all sealers had similar pH values.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- In vitro comparative evaluation of physicochemical and mechanical properties, cytocompatibility, and antimicrobial efficacy of various bioceramic root canal sealers
Fushi Wang, Jiaxing Li, Jingjing Wan, Siyuan Li, Shijia Tang, Li Wang, Liuyan Meng
Ceramics International.2026; 52(7): 9561. CrossRef - Comparative analysis between resin-based root canal sealer and recent bioceramic-based root canal sealers using MicroCT, film thickness, and solubility
Amira Galal Ismail, Manar M. Galal, Tamer M. Hamdy
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2026; 16(2): 101400. CrossRef - Functional and Bioactive Performance of Premixed Bioceramic Sealers with Warm Obturation: A Scoping Review
Patryk Wiśniewski, Stanisław Krokosz, Małgorzata Pietruska, Anna Zalewska
Gels.2025; 11(11): 932. CrossRef - Physicochemical properties of AH plus bioceramic sealer, Bio-C Sealer, and ADseal root canal sealer
Tamer M. Hamdy, Manar M. Galal, Amira Galal Ismail, Shehabeldin Saber
Head & Face Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Characterization and Assessment of Physical Properties of 3 Single Syringe Hydraulic Cement–based Sealers
Veksina Raman, Josette Camilleri
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(3): 381. CrossRef - The Impact of Silver Nanoparticles on Dentinal Tubule Penetration of Endodontic Bioceramic Sealer
Sundus Bukhary, Sarah Alkahtany, Amal Almohaimede, Nourah Alkhayatt, Shahad Alsulaiman, Salma Alohali
Applied Sciences.2024; 14(24): 11639. CrossRef - Influence of root canal moisture on the penetration of TotalFill bioceramic sealer into the dentinal tubules: A confocal laser scanning microscopy study
Archika M Singh, Tarek M Elsewify, Walid S El-Sayed, Husam H Nuawafleh, Ranya F Elemam, Bassem M Eid
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2024; 14(2): 187. CrossRef - Unusual Canal Morphology in Mandibular Premolars With Two Distal and One Mesial Canal: A Case Series
Jinesh A, Sanjana Jayakumar Nair, Saurabh Gupta, Harsh Chansoria, Gaurav Rawat
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A scientometric, bibliometric, and thematic map analysis of hydraulic calcium silicate root canal sealers
Anastasios Katakidis, Konstantinos Kodonas, Anastasia Fardi, Christos Gogos
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Thermal, chemical and physical analysis of VDW.1Seal, Fill Root ST, and ADseal root canal sealers
Shehabeldin Saber, Manar M. Galal, Amira Galal Ismail, Tamer M. Hamdy
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - α-tricalcium phosphate/fluorapatite-based cement - promising dental root canal filling material
Abdul Kazuz, Zeljko Radovanovic, Djordje Veljovic, Vesna Kojic, Dimitar Jakimov, Tamara Vlajic-Tovilovic, Vesna Miletic, Rada Petrovic, Djordje Janackovic
Processing and Application of Ceramics.2022; 16(1): 22. CrossRef
- In vitro comparative evaluation of physicochemical and mechanical properties, cytocompatibility, and antimicrobial efficacy of various bioceramic root canal sealers
- 2,964 View
- 28 Download
- 11 Crossref

- A micro-computed tomographic study of remaining filling materials of two bioceramic sealers and epoxy resin sealer after retreatment
- KyungJae Kim, Da Vin Kim, Sin-Young Kim, SungEun Yang
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(2):e18. Published online April 26, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e18
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objective This study evaluated the presence of residual root canal filling material after retreatment using micro-computed tomography (micro-CT).
Materials and Methods Extracted human teeth (single- and double-rooted,
n = 21/each; C-shaped,n = 15) were prepared with ProFile and randomly assigned to three subgroups for obturation with gutta-percha and three different sealers (EndoSeal MTA, EndoSequence BC sealer, and AH Plus). After 10 days, the filling material was removed and the root canals were instrumented one size up from the previous master apical file size. The teeth were scanned using micro-CT before and after retreatment. The percentage of remaining filling material after retreatment was calculated at the coronal, middle, and apical thirds. Data were analyzed using the Kruskal-Wallis test and Mann-WhitneyU test with Bonferronipost hoc correction.Results The tested sealers showed no significant differences in the percentage of remaining filling material in single- and double-rooted teeth, although EndoSeal MTA showed the highest value in C-shaped roots (
p < 0.05). The percentage of remaining filling material of AH Plus and EndoSeal MTA was significantly higher in C-shaped roots than in single- or double-roots (p < 0.05), while that of BC sealer was similar across all root types. EndoSeal MTA showed the highest values at the apical thirds of single- and double-roots (p < 0.05); otherwise, no significant differences were observed among the coronal, middle, and apical thirds.Conclusions Within the limitations of this study, a large amount of EndoSeal MTA remained after retreatment, especially in C-shaped root canals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of a deep neural network and empirical model for predicting local gas holdup profiles in bubble columns
Sebastián Uribe, Ahmed Alalou, Mario E. Cordero, Muthanna Al‐Dahhan
The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering.2025; 103(6): 2918. CrossRef - An In Vitro Comparison of Epoxy Resin Sealer Removal During Endodontic Retreatment
Prashant A Bondarde, Aditi S Patkar, Aishwarya R Pawar, Rukmini Pande, Akshata Deshpande, Rachana S Agrawal, Seema Gupta
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Calcium silicate-based sealers remnants in isthmuses of mesial roots of mandibular molars: an in vitro evaluation
David Saldanha de Brito Alencar, Ana Cristina Padilha Janini, Lauter Eston Pelepenko, Brenda Fornazaro Moraes, Francisco Haiter Neto, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Marina Angélica Marciano
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2025; 50(3): e25. CrossRef - Push-out bond strength of two endodontic sealers in retreated canals using different solvents
Sara Gamal Ghanem, Walaa M. Ghoneim, Ahmed H. Labib
Tanta Dental Journal.2025; 22(3): 504. CrossRef - Assessing Volume of Two Sealers’ Remnants after Reinstrumentation Using 3D Imaging Technology: An In Vitro Comparative Study
Khalel Mutaz Dawod, Raghad Abdulrazzaq Al-Hashimi
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2025; 26(8): 743. CrossRef - Removal efficacy of two different root canal sealers in retrograde cavities: a micro-CT study
Özge Başar, Ahter Şanal Çıkman, Cangül Keskin
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the retreatability of bioceramic root canal sealers with various formulations in simulated grooves
Meltem Sümbüllü, Afzal Ali, Abdulaziz Bakhsh, Hakan Arslan
PeerJ.2025; 13: e20398. CrossRef - Correlation of Bond Strength and Dentinal Tubule Penetration Evaluation of Four Different Endodontic Sealers: AH Plus, MTA Fillapex, Endoseal MTA, and Endoseal TCS (Maruchi): An In Vitro Study
Arezoo Mirzaei Sadeghloo, Seyedali Seyedmajidi, Akam Saeidi, Elham Mahmoudi, Murilo Baena Lopes
International Journal of Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Root canal cleanliness and debris extrusion following retreatment of thermoplastic injection technique and bioceramic-based root canal sealer
Deniz Bender, Mert Ocak, Emel Uzunoğlu Özyürek
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of Different Obturation Techniques Using Different Root Canal Sealers on the Residual Filling Material After Retreatment Procedures
M Sarı, K Yılmaz
Nigerian Journal of Clinical Practice.2024; 27(2): 174. CrossRef - Effect of Different Obturation Techniques on the Amount of Debris Extrusion During Endodontic Retreatment Using XP Endo Retreatment Set Files (In vitro Study)
Pawan Mohamad Amin, Hawzhen Mohammed Saeed
Sulaimani Dental Journal.2023; 10: 49. CrossRef - The efficiency of different irrigation activation techniques in the removal of calcium silicate‐based endodontic sealer from artificially created groove
Meltem Sümbüllü, Afzal Ali, Mine Büker, Hakan Arslan
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(S1): 238. CrossRef - Efficiency of diode laser and ultrasonic‐activated irrigation in retreatment of gutta percha and bioceramic sealer: An in vitro study
Rahaf A. Almohareb, Reem M. Barakat, Noor Aljarallah, Halah Mudhish, Amjaad Almutairi, Fahda N. Algahtani
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(2): 318. CrossRef - Efficiency of the new reciprocating and rotary systems with or without ultrasonics in removing root-canals filling with calcium silicate-based sealer (MTA)
Ahmad A. Madarati, Aya M. N. Sammani, Ahmad A. Alnazzawi, Ali Alrahlah
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Retreatability of calcium silicate‐based root canal sealer using reciprocating instrumentation with different irrigation activation techniques in single‐rooted canals
Daniele Angerame, Matteo De Biasi, Davide Porrelli, Lorenzo Bevilacqua, Riccardo Zanin, Matteo Olivi, Vassilios Kaitsas, Giovanni Olivi
Australian Endodontic Journal.2022; 48(3): 415. CrossRef - Critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study removal of root filling materials
Mahdi A. Ajina, Pratik K. Shah, Bun San Chong
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S1): 119. CrossRef - An Updated Review on Properties and Indications of Calcium Silicate‐Based Cements in Endodontic Therapy
Fateme Eskandari, Alireza Razavian, Rozhina Hamidi, Khadije Yousefi, Susan Borzou, Zohaib Khurshid
International Journal of Dentistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - How do imaging protocols affect the assessment of root-end fillings?
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Reinhilde Jacobs, Mostafa EzEldeen, Karla de Faria-Vasconcelos, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Bernardo Camargo dos Santos, Mário Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Efficacy of Er:YAG Laser-Activated Shock Wave-Enhanced Emission Photoacoustic Streaming Compared to Ultrasonically Activated Irrigation and Needle Irrigation in the Removal of Bioceramic Filling Remnants from Oval Root Canals—An Ex Vivo Study
Gabrijela Kapetanović Petričević, Marko Katić, Valentina Brzović Rajić, Ivica Anić, Ivona Bago
Bioengineering.2022; 9(12): 820. CrossRef - An in vitro comparative evaluation of retreatability of a bioceramic and resin sealer using cone-beam computed tomography analysis
Sumit Sharma, Ramya Raghu, Ashish Shetty, Subhashini Rajasekhara, Harika Lakshmisetty, G. Bharath
Endodontology.2022; 34(3): 173. CrossRef - Positive and negative properties of four endodontic sealant groups: a systematic review
E. V. Chestnyh, I. O. Larichkin, M. V. Iusufova, D. I. Oreshkina, E. I. Oreshkina, V. S. Minakova, S. V. Plekhanova
Kuban Scientific Medical Bulletin.2021; 28(3): 130. CrossRef - Retrievability of bioceramic-based sealers in comparison with epoxy resin-based sealer assessed using microcomputed tomography: A systematic review of laboratory-based studies
Buvaneshwari Arul, Aswathi Varghese, Anisha Mishra, Subashini Elango, Sairathna Padmanaban, Velmurugan Natanasabapathy
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2021; 24(5): 421. CrossRef - Micro CT pilot evaluation of removability of two endodontic sealers
David Colmenar, Tenzin Tamula, Qiang Zhu, Chul Ahn, Carolyn Primus, Takashi Komabayashi
Journal of Oral Science.2021; 63(4): 306. CrossRef - Comparison of Obturation Quality between Calcium Silicate-Based Sealers and Resin-Based Sealers for Endodontic Re-treatment
Hye-Ryeon Jin, Young-Eun Jang, Yemi Kim
Materials.2021; 15(1): 72. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of a new system for root canal filling using calcium silicate-based root canal sealers
Mario Tanomaru-Filho, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Jader Camilo Pinto, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of the flow and filling ability of endodontic materials using different test models
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Gisselle Moraima Chavez-Andrade, Jader Camilo Pinto, Fábio Luiz Camargo Villela Berbert, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Retreatment efficacy of hydraulic calcium silicate sealers used in single cone obturation
M. Garrib, J. Camilleri
Journal of Dentistry.2020; 98: 103370. CrossRef
- Development of a deep neural network and empirical model for predicting local gas holdup profiles in bubble columns
- 2,406 View
- 31 Download
- 27 Crossref

- Bacterial leakage and micro-computed tomography evaluation in round-shaped canals obturated with bioceramic cone and sealer using matched single cone technique
- Kallaya Yanpiset, Danuchit Banomyong, Kanet Chotvorrarak, Ratchapin Laovanitch Srisatjaluk
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(3):e30. Published online July 5, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e30
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
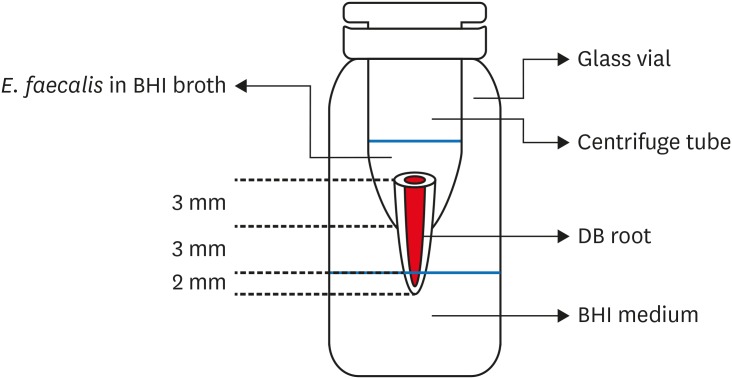
ePub Objectives To evaluate sealing ability of root canals obturated with bioceramic-impregnated gutta percha cone (BCC) or gutta percha (GP), with bioceramic sealer (BCS) or AH Plus (AH; Dentsply-Maillefer), in roundly-prepared canals using matched single-cone technique, based on bacterial leakage test, and to analyze obturation quality using micro-computed tomography (CT) analysis.
Materials and Methods Ninety-two distobuccal roots of maxillary molars were prepared using nickel-titanium files to apical size 40/0.06. The roots were divided into 4 groups (
n = 20) that were obturated with a master cone and sealer: GP/AH, BCC/AH, GP/BCS, and BCC/BCS. Bacterial leakage model usingEnterococcus faecalis was used to evaluate sealing ability for 60-day period. Obturated samples from each group (n = 4) were analyzed using micro-CT.Results All groups showed bacterial leakage at 20%–45% of samples with mean leakage times of 42–52 days. There were no significant differences in bacterial leakage among the groups. Micro-CT showed minimal gaps and voids in all groups at less than 1%.
Conclusions In roundly-prepared canals, the single cone obturation with BCC/BCS was comparable to GP/AH for bacterial leakage at 60 days.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Time-Dependent Volumetric and Porosity Changes of Bioceramic, Silicone Bioactive Glass-Based, and Epoxy Resin-Based Root Canal Sealers: A Micro-CT Analysis
Thanh Quang Nguyen, Chantida Pawaputanon Na Mahasarakham, Pinpana Thaweesit, Kanet Chotvorrarak, Angsana Jainaen
European Journal of Dentistry.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Root Dentin Moisture on the Apical Sealing Ability of Root Canal Sealers: In vitro Study
Zahraa Khalil Alani, Manal Hussain Abd-alla
Al-Rafidain Journal of Medical Sciences ( ISSN 2789-3219 ).2025; 8(2): 122. CrossRef - Synthesis, physical properties, and root canal sealing of experimental MTA- and salicylate-based root canal sealers
Rafael Pino Vitti, Kusai Baroudi, Tarun Walia, Raghavandra M. Shetty, Flávia Goulart da Rosa Cardoso, Flávia de Moura Pereira, Evandro Piva, Cesar Henrique Zanchi, Gabriel Flores Abuna, Carolina Oliveira de Lima, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Flávio
PLOS One.2025; 20(7): e0329476. CrossRef - Impact of cone system compatibility on single cone bioceramic obturation in canals prepared with variable taper NiTi rotary files
Reem M. Barakat, Rahaf A. Almohareb, Njoom Aleid, Hoor Almowais, Aljawhara Alharbi, Meshal Al-Sharafa, Ali Alrahlah
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Estudio de la obturación con selladores biocerámicos de conductos radiculares de premolares inferiores
Alicia Beatriz Bonafé, Cecilia Inés Rourera, Carla Pedraza, Yamila Victoria Zanoni, Soledad Salduna, Cecilia Noemi De Caso, Gabriela Martín
Methodo Investigación Aplicada a las Ciencias Biológicas.2025; 10(3): 31. CrossRef - Sealing ability of mineral trioxide aggregate: A scoping review of laboratory assessment methods
Kenta Tsuchiya, Salvatore Sauro, Jukka P. Matinlinna, Hidehiko Sano, Monica Yamauti, Deepak Mehta, Kyung‐San Min, Atsushi Tomokiyo
European Journal of Oral Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Bacterial Leakage Testing in Dentistry: A Comprehensive Review on Methods, Models, and Clinical Relevance
Niher Tabassum Snigdha, Mohmed Isaqali Karobari, Sukhamoy Gorai
Scientifica.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - In vitro comparative evaluation of apical leakage using a bioceramic sealer with three different obturating techniques: A glucose leakage model
Tanvi S Agrawal, Shishir Singh, Rajesh S Podar, Gaurav Kulkarni, Anuprita Gadkari, Navin Agarwal
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(1): 76. CrossRef - In Vitro Microscopical and Microbiological Assessment of the Sealing Ability of Calcium Silicate-Based Root Canal Sealers
Karin Christine Huth, Sabina Noreen Wuersching, Leander Benz, Stefan Kist, Maximilian Kollmuss
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2024; 15(11): 341. CrossRef - Comparison between AH plus sealer and total fill bioceramic sealer performance in previously untreated and retreatment cases of maxillary incisors with large-sized periapical lesion: a randomized controlled trial
Eisa Wahbi, Hassan Achour, Yasser Alsayed Tolibah
BDJ Open.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Bacterial sealing ability of calcium silicate-based sealer for endodontic surgery: an in-vitro study
Mai M. Mansour, Sybel M. Moussa, Marwa A. Meheissen, Mahmoud R. Aboelseoud
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment the bioactivity of zinc oxid eugenol sealer after the addition of different concentrations of nano hydroxyapatite-tyrosine amino acid
Rasha M. Al-Shamaa, Raghad A. Al-Askary
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2024; 23: e243733. CrossRef - Assessment of Bacterial Sealing Ability of Two Different Bio-Ceramic Sealers in Single-Rooted Teeth Using Single Cone Obturation Technique: An In Vitro Study
Doaa M. AlEraky, Ahmed M. Rahoma, Hatem M. Abuohashish, Abdullh AlQasser, Abbas AlHamali, Hussain M. AlHussain, Hussain M. AlShoalah, Zakrya AlSaghah, Abdulrahman Khattar, Shimaa Rifaat
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(5): 2906. CrossRef - How do imaging protocols affect the assessment of root-end fillings?
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Reinhilde Jacobs, Mostafa EzEldeen, Karla de Faria-Vasconcelos, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Bernardo Camargo dos Santos, Mário Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The impact of Morse taper implant design on microleakage at implant-healing abutment interface
Soyeon KIM, Joo Won LEE, Jae-Heon KIM, Van Mai TRUONG, Young-Seok PARK
Dental Materials Journal.2022; 41(5): 767. CrossRef - A critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study root canal fillings
Gustavo De‐Deus, Erick Miranda Souza, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Marco Simões‐Carvalho, Daniele Moreira Cavalcante, Marco Aurélio Versiani
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S2): 384. CrossRef - Micro‐CT assessment of gap‐containing areas along the gutta‐percha‐sealer interface in oval‐shaped canals
Gustavo De‐Deus, Gustavo O. Santos, Iara Zamboni Monteiro, Daniele M. Cavalcante, Marco Simões‐Carvalho, Felipe G. Belladonna, Emmanuel J. N. L. Silva, Erick M. Souza, Raphael Licha, Carla Zogheib, Marco A. Versiani
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(7): 795. CrossRef - Comparison of Sealing Ability of Bioceramic Sealer, AH Plus, and GuttaFlow in Conservatively Prepared Curved Root Canals Obturated with Single-Cone Technique: An In vitro Study
Shalan Kaul, Ajay Kumar, Bhumika Kamal Badiyani, Laxmi Sukhtankar, M. Madhumitha, Amit Kumar
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2021; 13(Suppl 1): S857. CrossRef - Micro-CT Evaluation of Four Root Canal Obturation Techniques
Mahmood Reza Kalantar Motamedi, Amin Mortaheb, Maryam Zare Jahromi, Brett E. Gilbert, Marilena Vivona
Scanning.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Effects of Both Fiber Post/Core Resin Construction System and Root Canal Sealer on the Material Interface in Deep Areas of Root Canal
Hiroki Miura, Shinji Yoshii, Masataka Fujimoto, Ayako Washio, Takahiko Morotomi, Hiroshi Ikeda, Chiaki Kitamura
Materials.2021; 14(4): 982. CrossRef - Sealing ability and microbial leakage of root-end filling materials: MTA versus epoxy resin: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Mario Dioguardi, Mario Alovisi, Diego Sovereto, Giuseppe Troiano, Giancarlo Malagnino, Michele Di Cosola, Angela Pia Cazzolla, Luigi Laino, Lorenzo Lo Muzio
Heliyon.2021; 7(7): e07494. CrossRef - Development of A Nano-Apatite Based Composite Sealer for Endodontic Root Canal Filling
Angelica Bertacci, Daniele Moro, Gianfranco Ulian, Giovanni Valdrè
Journal of Composites Science.2021; 5(1): 30. CrossRef - BIOCERAMIC-BASED ROOT CANAL SEALERS
L Somolová, Z Zapletalová, M Rosa, B Novotná, I Voborná, Y Morozova
Česká stomatologie a praktické zubní lékařství.2021; 121(4): 116. CrossRef - Calcium Silicate-Based Root Canal Sealers: A Narrative Review and Clinical Perspectives
Germain Sfeir, Carla Zogheib, Shanon Patel, Thomas Giraud, Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Frédéric Bukiet
Materials.2021; 14(14): 3965. CrossRef - Physico-Chemical Properties of Calcium-Silicate vs. Resin Based Sealers—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Laboratory-Based Studies
Viresh Chopra, Graham Davis, Aylin Baysan
Materials.2021; 15(1): 229. CrossRef - Comparison of apical sealing ability of bioceramic sealer and epoxy resin-based sealer using the fluid filtration technique and scanning electron microscopy
Widcha Asawaworarit, Thitapa Pinyosopon, Kanittha Kijsamanmith
Journal of Dental Sciences.2020; 15(2): 186. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of a new system for root canal filling using calcium silicate-based root canal sealers
Mario Tanomaru-Filho, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Jader Camilo Pinto, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - A micro-computed tomographic evaluation of root canal filling with a single gutta-percha cone and calcium silicate sealer
Jong Cheon Kim, Maung Maung Kyaw Moe, Sung Kyo Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of sealing ability of gutta percha and resilon as root canal filling materials- a systematic review
Pragya Pandey, Himanshi Aggarwal, A.P. Tikku, Arpit Singh, Rhythm Bains, Shambhavi Mishra
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2020; 10(2): 220. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of the flow and filling ability of endodontic materials using different test models
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Gisselle Moraima Chavez-Andrade, Jader Camilo Pinto, Fábio Luiz Camargo Villela Berbert, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Root fillings with a matched-taper single cone and two calcium silicate–based sealers: an analysis of voids using micro-computed tomography
Eugenio Pedullà, Roula S. Abiad, Gianluca Conte, Giusy R. M. La Rosa, Ernesto Rapisarda, Prasanna Neelakantan
Clinical Oral Investigations.2020; 24(12): 4487. CrossRef - Influence of different disinfection protocols on gutta-percha cones surface roughness assessed by two different methods
A.M. Nunes, J.P. Gouvea, L. da Silva
Journal of Materials Research and Technology.2019; 8(6): 5464. CrossRef - Endodontic sealers based on calcium silicates: a systematic review
David Donnermeyer, Sebastian Bürklein, Till Dammaschke, Edgar Schäfer
Odontology.2019; 107(4): 421. CrossRef
- Time-Dependent Volumetric and Porosity Changes of Bioceramic, Silicone Bioactive Glass-Based, and Epoxy Resin-Based Root Canal Sealers: A Micro-CT Analysis
- 2,801 View
- 36 Download
- 33 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


