Previous issues
- Page Path
- HOME > Browse articles > Previous issues
- Statistical notes for clinical researchers: covariance and correlation
- Hae-Young Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(1):e4. Published online January 5, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e4
-
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of Depression, Anxiety, and Stress on Mental Health Among Peruvian Healthcare Professionals
Diego Ismael Valencia-Pecho, Silvana Varela-Guevara, Miguel Basauri-Delgado, Jacksaint Saintila
Healthcare.2026; 14(4): 490. CrossRef - Occupational Lead Exposure Among Civilian Indoor Shooting Range Workers in Korea: A Report of Blood Lead Levels and Airborne Lead
Sungjin Park, Jaeyoung Park, Bumjoon Lee, Yi-Ryoung Lee, Jiho Kim, Younmo Cho, Hyeongyeong Choi, Kyeongyeon Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationship of incidence of radix entomolaris and C‐shaped canal in mandibular molars using CBCT: A multi‐centre study
Sobrina Mohamed Khazin, Siti Hajar Omar, Marlena Kamaruzaman, Huwaina Abd Ghani, Mandava Deepthi, Diyana Kamarudin, Safura Anita Baharin, Vinayak Pishipati Kalyan Chakravarthy
Australian Endodontic Journal.2025; 51(1): 26. CrossRef - Advancing building façade design: digital fabrication of an optimized non-conventional roster brick prototype
Dalhar Susanto, Raisa Putri Alifa, Stefanie Aylien, Miktha Farid Alkadri
Journal of Asian Architecture and Building Engineering.2025; : 1. CrossRef - A Study on Gender Differences in the Maximum Attractiveness Values for Cephalometric Measures
Xiaofan Feng, Xin Chen, Hongyu Ren
Journal of Craniofacial Surgery.2025; 36(7): e1080. CrossRef - Feasibility study of microwave‐induced thermoacoustic/ultrasound dual‐modality imaging for the assessment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Jieni Song, Wenwu Ling, Wanting Peng, Ling Song, Zeqi Yang, Lian Feng, Lin Huang, Yan Luo
Medical Physics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Estimator Campuran Spline Truncated dan Deret Fourier dalam Regresi Nonparametrik Untuk Data Kategori
Kadek Adi Surya Negara, I Nyoman Budiantara, Vita Ratnasari
Jurnal Gaussian.2025; 14(2): 588. CrossRef - Improving the forecast accuracy of wind power by leveraging multiple hierarchical structure
Lucas English, Mahdi Abolghasemi
Sustainable Energy, Grids and Networks.2024; 40: 101517. CrossRef - Simplified Methods for Modelling Dependent Parameters in Health Economic Evaluations: A Tutorial
Xuanqian Xie, Alexis K. Schaink, Sichen Liu, Myra Wang, Juan David Rios, Andrei Volodin
Applied Health Economics and Health Policy.2024; 22(3): 331. CrossRef - Numerical modeling of ocean currents and suspended sediment distribution in Benoa Bay, Bali
Siti Sulistiana, I Wayan Nurjaya, Mochamad Tri Hartanto, H.M. Manik, N.P. Zamani, J. Lumban Gaol, A.S. Atmadipoera, O. Meng Chuan, T. Osawa
BIO Web of Conferences.2024; 106: 03005. CrossRef - The effectiveness of the TRACE online nutrition intervention in improving dietary intake, sleep quality and physical activity levels for Australian adults with food addiction: a randomised controlled trial
Mark Leary, Janelle A. Skinner, Kirrilly M. Pursey, Antonio Verdejo‐Garcia, Rebecca Collins, Clare Collins, Phillipa Hay, Tracy L. Burrows
Journal of Human Nutrition and Dietetics.2024; 37(4): 978. CrossRef - Influence of the radius of Monson’s sphere and excursive occlusal contacts on masticatory function of dentate subjects
Dominique Ellen Carneiro, Luiz Ricardo Marafigo Zander, Carolina Ruppel, Giancarlo De La Torre Canales, Rubén Auccaise-Estrada, Alfonso Sánchez-Ayala
Archives of Oral Biology.2024; 159: 105879. CrossRef - Analytical Performance Specifications for Input Variables: Investigation of the Model of End-Stage Liver Disease
Eline S Andersen, Richard Röttger, Claus L Brasen, Ivan Brandslund
Clinical Chemistry.2024; 70(4): 653. CrossRef - A prototype variable corresponding to the proportion of ischemia for the comparison between robotic and open partial nephrectomy: a meta-analysis accompanied by sensitivity analysis
Sotirios Artsitas, Dimitrios Artsitas, Irene Koronaki, Konstantinos G. Toutouzas, George C. Zografos
Beni-Suef University Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Cephalometric determinants of facial attractiveness: A quadratic correlation study
Joana Godinho, Diana Fernandes, Patrícia Pires, Luis Jardim
American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics.2023; 163(3): 398. CrossRef - Sympathovagal Balance Is a Strong Predictor of Post High-Volume Endurance Exercise Cardiac Arrhythmia
Daniel W. T. Wundersitz, Bradley J. Wright, Brett A. Gordon, Stephanie Pompei, Carl J. Lavie, Voltaire Nadurata, Kimberly Nolan, Michael I. C. Kingsley
Frontiers in Physiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Performance investigation of the natural draft wet cooling tower at different wet-bulb temperatures
Gaurav Raj, Prakash Chandra, Piyush Kumar Pathak
International Journal of Ambient Energy.2022; 43(1): 5864. CrossRef - Statistical notes for clinical researchers: simple linear regression 1 – basic concepts
Hae-Young Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef
- Impact of Depression, Anxiety, and Stress on Mental Health Among Peruvian Healthcare Professionals
- 3,151 View
- 56 Download
- 18 Crossref

-
Appreciations to peer reviewers in 2017: contributions to the journal,
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics - Byeong-Hoon Cho, Su-Jung Shin
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(1):e6. Published online January 12, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e6
- 720 View
- 3 Download

- Corrigendum: Corrections to the funding. Quantification of the tug-back by measuring the pulling force and micro computed tomographic evaluation
- Su-Jin Jeon, Young-Mi Moon, Min-Seock Seo
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(1):e8. Published online January 24, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e8
- 742 View
- 7 Download

-
Root canal irrigants influence the hydrophobicity and adherence of
Staphylococcus epidermidis to root canal dentin: anin vitro study - Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Omer Sheriff Sultan, Sreedharan Kannathasan, Amir Shahreza Patel, Ebenezer Chitra, Prasanna Neelakantan, Fabian Davamani
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(1):e1. Published online December 7, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives To determine the effect of root canal irrigants on the hydrophobicity and adherence of
Staphylococcus epidermidis (S. epidermidis ) to root canal dentinin vitro .Materials and Methods Root dentin blocks (
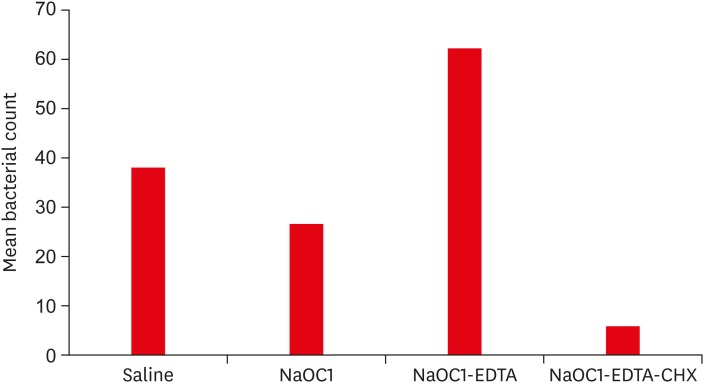
n = 60) were randomly divided into 4 groups based on the irrigation regimen: group 1, saline; group 2, 5.25% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl); group 3, 5.25% NaOCl followed by 17% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA); group 4, same as group 3 followed by 2% chlorhexidine (CHX). The hydrophobicity ofS. epidermidis to root dentin was calculated by cell surface hydrophobicity while the adherence was observed by fluorescence microscopy, and bacteria were quantified using ImageJ software (National Institutes of Health). Statistical analysis of the data was done using Kruskal-Wallis test and Mann-WhitneyU test (p = 0.05).Results The hydrophobicity and adherence of
S. epidermidis to dentin were significantly increased after irrigating with group 3 (NaOCl-EDTA) (p < 0.05), whereas in group 4 (NaOCl-EDTA-CHX) both hydrophobicity and adherence were significantly reduced (p < 0.05).Conclusions The adherence of
S. epidermidis to dentin was influenced differently by root canal irrigants. Final irrigation with CHX reduces the bacterial adherence and may impact biofilm formation.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Quaternary ammonium silane (k21) based intracanal medicament triggers biofilm destruction
Esther Sook Kuan Kok, Xian Jin Lim, Soo Xiong Chew, Shu Fen Ong, Lok Yin See, Siao Hua Lim, Ling Ang Wong, Fabian Davamani, Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Amr Fawzy, Umer Daood
BMC Oral Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Quaternary ammonium silane (k21) based intracanal medicament triggers biofilm destruction
- 1,434 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Influence of size and insertion depth of irrigation needle on debris extrusion and sealer penetration
- Emel Uzunoglu-Özyürek, Hakan Karaaslan, Sevinç Aktemur Türker, Bahar Özçelik
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(1):e2. Published online December 22, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e2
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
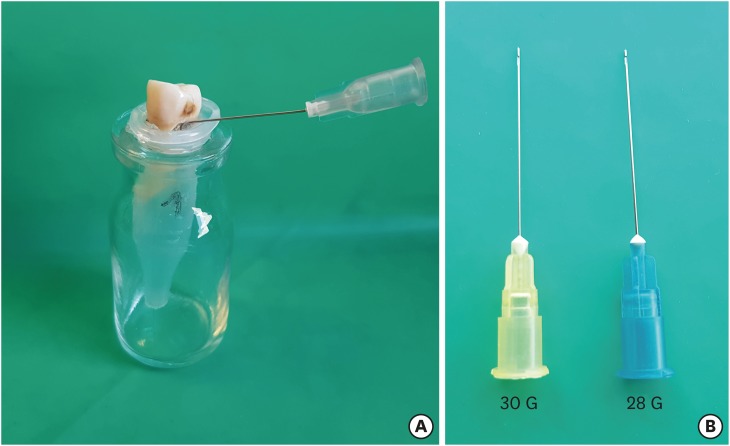
ePub Objectives To determine the effect of size and insertion depth of irrigation needle on the amount of apical extruded debris and the amount of penetration depth of sealer using a confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM).
Materials and Methods Twenty maxillary premolars were assigned to 2 groups (
n = 10), according to the size of needle tip, 28 G or 30 G. Buccal roots of samples were irrigated with respective needle type inserted 1 mm short of the working length (WL), while palatal roots were irrigated with respective needle type inserted 3 mm short of the WL. Prepared teeth were removed from the pre-weighed Eppendorf tubes. Canals were filled with F3 gutta-percha cone and rhodamine B dye-labeled AH 26 sealer. Teeth were transversally sectioned at 1 and 3 mm levels from the apex and observed under a CLSM. Eppendorf tubes were incubated to evaporate the irrigant and were weighed again. The difference between pre- and post-weights was calculated, and statistical evaluation was performed.Results Inserting needles closer to the apex and using needles with wider diameters were associated with significantly more debris extrusion (
p < 0.05). The position of needles and level of sections had statistically significant effects on sealer penetration depth (p < 0.05 for both).Conclusions Following preparation, inserting narrower needles compatible with the final apical diameter of the prepared root canal at 3 mm short of WL during final irrigation might prevent debris extrusion and improve sealer penetration in the apical third.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of laser-induced pulpal anesthesia of single-rooted teeth with irreversible pulpitis treated by single-visit root canal therapy - A randomized clinical trial
Geeta Asthana, Dhwani Morakhia, Ravina Parmar, Rajashree Tamuli
Endodontology.2025; 37(3): 244. CrossRef - Efficacy of different irrigation needles used in endodontics: an in silico and an in vitro investigation
Maulee Sheth, Ankit Arora, Sonali Kapoor, Balraj Shukla
Biomaterial Investigations in Dentistry.2025; 12: 264. CrossRef - Preliminary insights: exploring irrigation practices during endodontic treatment among general dental practitioners in Malaysia
Kai Qi Chiew, Xin Ni Lim, Shekhar Bhatia, Naveen Chhabra
British Dental Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficiency of diode laser in control of post-endodontic pain: a randomized controlled trial
Hend H. Ismail, Maram Obeid, Ehab Hassanien
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(6): 2797. CrossRef - Endodontic management of an aberrant germinated composite odontome: A case report
Ankit Arora, Kavina Desai, Sonali Kapoor, Seema Gajera
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(3): 684. CrossRef - Potentials of 3D-Modeling in the Preclinical Stage of Root Needle Research
Aleksandr V. Kuligin, Larisa N. Kazakova, Oksana S. Tereshchuk, Vadim V. Bokov
I.P. Pavlov Russian Medical Biological Herald.2022; 30(1): 95. CrossRef - Effect of root canal geometry and needle type on apical extrusion of irrigant: an ex vivo study
Büşra SERÇE FİKİRLİ, Bülent ALTUNKAYNAK, Güven KAYAOĞLU
Acta Odontologica Turcica.2022; 39(3): 58. CrossRef - An in vitro radiological evaluation of irrigant penetration in the root canals using three different irrigation systems: Waterpik WP-100 device, passive irrigation, and manual dynamic irrigation systems
Suragani Hemalatha, Archana Srinivasan, A Srirekha, Lekha Santhosh, C Champa, Ashwija Shetty
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2022; 25(4): 403. CrossRef - Preparation Ability of ProTaper Next and XP-endo Shaper Instruments in Isthmus-containing Root Canal System
Mustafa Sarıkahya, Tayfun Alaçam
Conservative Dentistry and Endodontic Journal.2021; 5(2): 28. CrossRef - Penetration depth of irrigants into root dentine after sonic, ultrasonic and photoacoustic activation
K. M. Galler, V. Grubmüller, R. Schlichting, M. Widbiller, A. Eidt, C. Schuller, M. Wölflick, K.‐A. Hiller, W. Buchalla
International Endodontic Journal.2019; 52(8): 1210. CrossRef
- Effect of laser-induced pulpal anesthesia of single-rooted teeth with irreversible pulpitis treated by single-visit root canal therapy - A randomized clinical trial
- 1,782 View
- 18 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Root canal volume change and transportation by Vortex Blue, ProTaper Next, and ProTaper Universal in curved root canals
- Hyun-Jin Park, Min-Seock Seo, Young-Mi Moon
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(1):e3. Published online December 24, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e3
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
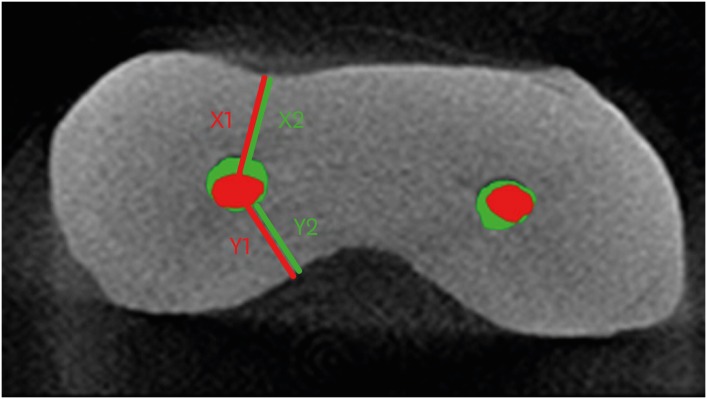
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to compare root canal volume change and canal transportation by Vortex Blue (VB; Dentsply Tulsa Dental Specialties), ProTaper Next (PTN; Dentsply Maillefer), and ProTaper Universal (PTU; Dentsply Maillefer) nickel-titanium rotary files in curved root canals.
Materials and Methods Thirty canals with 20°–45° of curvature from extracted human molars were used. Root canal instrumentation was performed with VB, PTN, and PTU files up to #30.06, X3, and F3, respectively. Changes in root canal volume before and after the instrumentation, and the amount and direction of canal transportation at 1, 3, and 5 mm from the root apex were measured by using micro-computed tomography. Data of canal volume change were statistically analyzed using one-way analysis of variance and Tukey test, while data of amount and direction of transportation were analyzed using Kruskal-Wallis and Mann-Whitney
U test.Results There were no significant differences among 3 groups in terms of canal volume change (
p > 0.05). For the amount of transportation, PTN showed significantly less transportation than PTU at 3 mm level (p = 0.005). VB files showed no significant difference in canal transportation at all 3 levels with either PTN or PTU files. Also, VB files showed unique inward transportation tendency in the apical area.Conclusions Other than PTN produced less amount of transportation than PTU at 3 mm level, all 3 file systems showed similar level of canal volume change and transportation, and VB file system could prepare the curved canals without significant shaping errors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of nickel-titanium rotary systems on the biomechanical behaviour of mandibular first molars with curved and straight mesial roots: a finite element analysis study
Yaprak Cesur, Sevinc Askerbeyli Örs, Ahmet Serper, Mert Ocak
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Micro-Computed Tomographic Evaluation of the Shaping Ability of Vortex Blue and TruNatomyTM Ni-Ti Rotary Systems
Batool Alghamdi, Mey Al-Habib, Mona Alsulaiman, Lina Bahanan, Ali Alrahlah, Leonel S. J. Bautista, Sarah Bukhari, Mohammed Howait, Loai Alsofi
Crystals.2024; 14(11): 980. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Centering Ability and Canal Transportation of Rotary File Systems in Different Kinematics Using CBCT
Nupur R Vasava, Shreya H Modi, Chintan Joshi, Mona C Somani, Sweety J Thumar, Aashray A Patel, Anisha D Parmar, Kruti M Jadawala
World Journal of Dentistry.2024; 14(11): 983. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of nickel titanium rotary instruments on canal transportation and centering ability in curved canals by using cone beam computed tomography: An in vitro study
Krishnaveni Krishnaveni, Nikitha Kalla, Nagalakshmi Reddy, Sharvanan Udayar
Journal of Dental Specialities.2023; 11(2): 105. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Root Canal Centering Ability of Two Heat-treated Single-shaping NiTi Rotary Instruments in Simulated Curved Canals: An In Vitro Study
Preethi Varadan, Chakravarthy Arumugam, Athira Shaji, R R Mathan
World Journal of Dentistry.2023; 14(6): 535. CrossRef - A Comparison of Canal Width Changes in Simulated Curved Canals prepared with Profile and Protaper Rotary Systems
Aisha Faisal, Huma Farid, Robia Ghafoor
Pakistan Journal of Health Sciences.2022; : 55. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Respect of the Root Canal Trajectory by Rotary Niti Instruments (Protaper®Universal): Retrospective Radiographic Study
Salma El Abbassi, Sanaa Chala, Majid Sakout, Faïza Abdallaoui
Integrative Journal of Medical Sciences.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- The effect of nickel-titanium rotary systems on the biomechanical behaviour of mandibular first molars with curved and straight mesial roots: a finite element analysis study
- 1,787 View
- 12 Download
- 7 Crossref

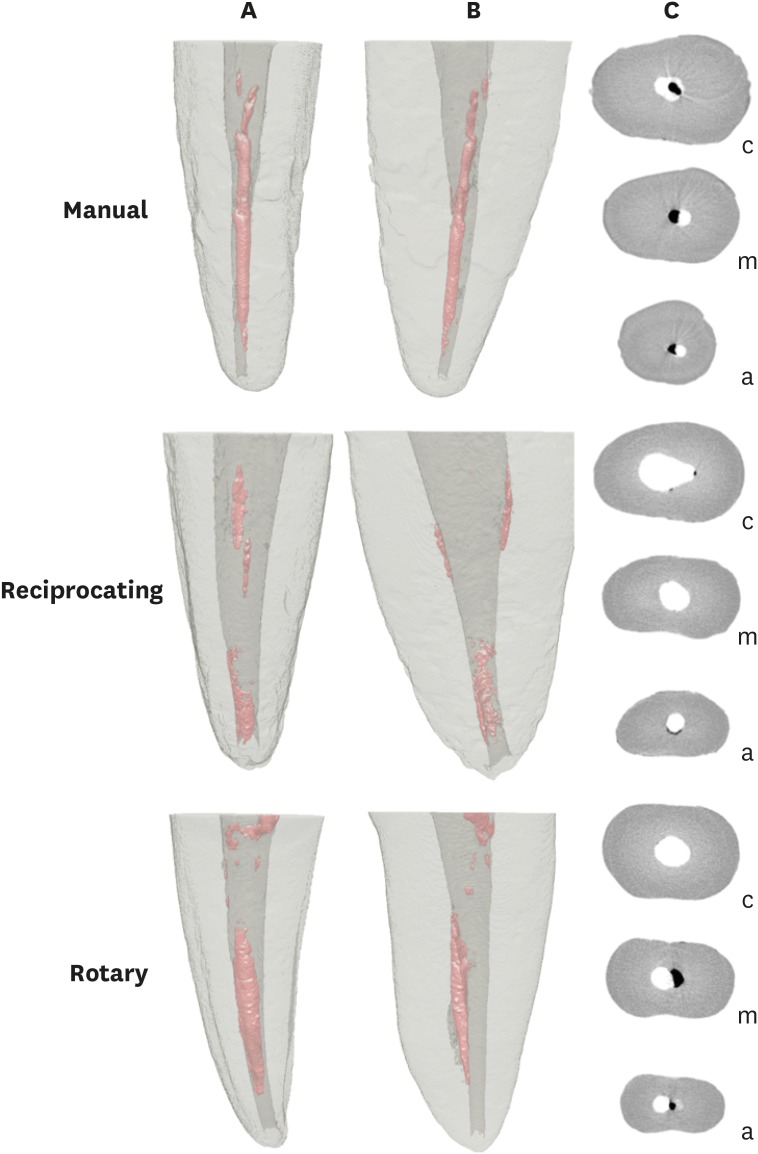
- Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of canal retreatments performed by undergraduate students using different techniques
- Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Marianna Fernandes Carapiá, Brenda Leite Muniz, Mariana Santoro Rocha, Edson Jorge Lima Moreira
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(1):e5. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e5
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the amount of remaining root canal filling materials after retreatment procedures performed by undergraduate students using manual, rotary, and reciprocating techniques through micro-computed tomographic analysis. The incidence of instrument fracture and the instrumentation time were also evaluated.
Materials and Methods Thirty maxillary single rooted teeth were prepared with Reciproc R25 files and filled with gutta-percha and AH Plus sealer by the continuous wave of condensation technique. Then, the specimens were assigned to 3 groups (
n = 10), according to the retreatment technique used: manual, rotary, and reciprocating groups, which used K-file, Mtwo retreatment file, and Reciproc file, respectively. Retreatments were performed by undergraduate students. The sample was scanned after root canal filling and retreatment procedures, and the images of the canals were examined to quantify the amount of remaining filling material. The incidence of instrument fracture and the instrumentation time were recorded.Results Remaining filling material was observed in all specimens regardless of the technique used. The mean volume of remaining material was significantly lower in the Reciproc group than in the manual K-file and Mtwo retreatment groups (
p < 0.05). The time required to achieve a satisfactory removal of canal filling material and refinement was significantly lower in the Mtwo retreatment and Reciproc groups (p < 0.05) when compared to the manual K-file group. No instrument fracture was observed in any of the groups.Conclusions Reciproc was the most effective instrument in the removal of canal fillings after retreatments performed by undergraduate students.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Assessment of isthmus filling using two obturation techniques performed by students with different levels of clinical experience
Yang Yu, Chong-Yang Yuan, Xing-Zhe Yin, Xiao-Yan Wang
Journal of Dental Sciences.2024; 19(1): 169. CrossRef - Optical microscopy evaluation of root canal filling removal by beginner operators in posterior teeth
Bogdan Dimitriu, Ioana Suciu, Oana Elena Amza, Mihai Ciocârdel, Dana Bodnar, Ana Maria Cristina Țâncu, Mihaela Tanase, Maria Sabina Branescu, Mihaela Chirilă
Journal of Medicine and Life.2024; 17(6): 555. CrossRef - Micro-CT Study on the Supplementary Effect of XP-Endo Finisher R after Endodontic Retreatment with Mtwo-R
I Tsenova-Ilieva, V Dogandzhiyska, M Raykovska, E Karova
Nigerian Journal of Clinical Practice.2023; 26(12): 1844. CrossRef - Critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study removal of root filling materials
Mahdi A. Ajina, Pratik K. Shah, Bun San Chong
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S1): 119. CrossRef - Efficiency of Supplementary Contemporary Single-file Systems in Removing Filling Remnants from Oval-shaped Canals: An In Vitro Study
Neveen A Shaheen, Dalia A Sherif, Nahla G Elhelbawy
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2021; 22(9): 1055. CrossRef - Efficacy of an arrow‐shaped ultrasonic tip for the removal of residual root canal filling materials
Emmanuel J.N.L. Silva, Carolina O. de Lima, Ana F.A. Barbosa, Cláudio M. Ferreira, Bruno M. Crozeta, Ricardo T. Lopes
Australian Endodontic Journal.2021; 47(3): 467. CrossRef - XP‐endo Finisher R instrument optimizes the removal of root filling remnants in oval‐shaped canals
G. De‐Deus, F. G. Belladonna, A. S. Zuolo, D. M. Cavalcante, J. C. A. Carvalhal, M. Simões‐Carvalho, E. M. Souza, R. T. Lopes, E. J. N. L. Silva
International Endodontic Journal.2019; 52(6): 899. CrossRef
- Assessment of isthmus filling using two obturation techniques performed by students with different levels of clinical experience
- 1,425 View
- 12 Download
- 7 Crossref

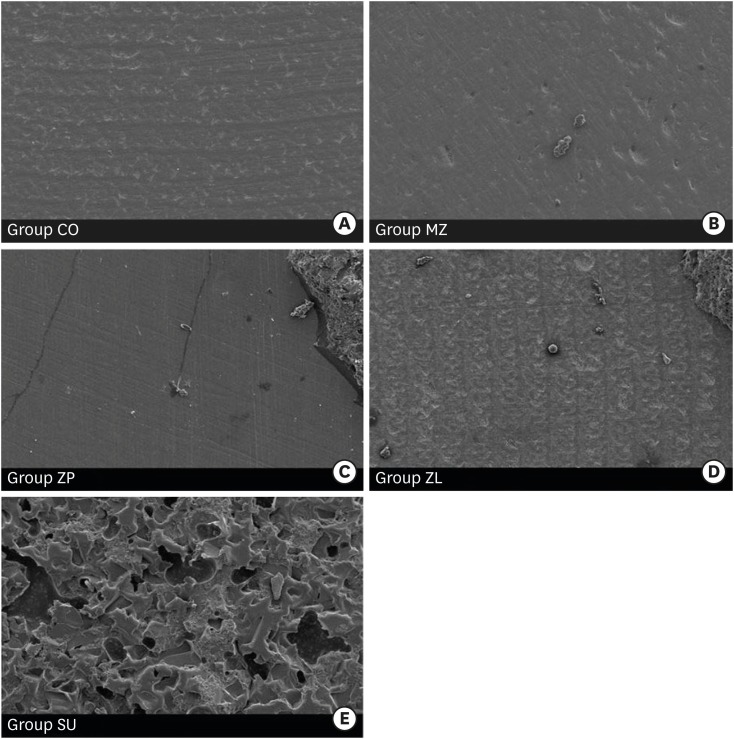
- Comparison of bond strengths of ceramic brackets bonded to zirconia surfaces using different zirconia primers and a universal adhesive
- Ji-Yeon Lee, Jaechan Ahn, Sang In An, Jeong-won Park
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(1):e7. Published online January 22, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e7
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study is to compare the shear bond strengths of ceramic brackets bonded to zirconia surfaces using different zirconia primers and universal adhesive.
Materials and Methods Fifty zirconia blocks (15 × 15 × 10 mm, Zpex, Tosoh Corporation) were polished with 1,000 grit sand paper and air-abraded with 50 µm Al2O3 for 10 seconds (40 psi). They were divided into 5 groups: control (CO), Metal/Zirconia primer (MZ, Ivoclar Vivadent), Z-PRIME Plus (ZP, Bisco), Zirconia Liner (ZL, Sun Medical), and Scotchbond Universal adhesive (SU, 3M ESPE). Transbond XT Primer (used for CO, MZ, ZP, and ZL) and Transbond XT Paste was used for bracket bonding (Gemini clear ceramic brackets, 3M Unitek). After 24 hours at 37°C storage, specimens underwent 2,000 thermocycles, and then, shear bond strengths were measured (1 mm/min). An adhesive remnant index (ARI) score was calculated. The data were analyzed using one-way analysis of variance and the Bonferroni test (
p = 0.05).Results Surface treatment with primers resulted in increased shear bond strength. The SU group showed the highest shear bond strength followed by the ZP, ZL, MZ, and CO groups, in that order. The median ARI scores were as follows: CO = 0, MZ = 0, ZP = 0, ZL = 0, and SU = 3 (
p < 0.05).Conclusions Within this experiment, zirconia primer can increase the shear bond strength of bracket bonding. The highest shear bond strength is observed in SU group, even when no primer is used.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of universal adhesives for orthodontic bonding to enamel and restorative materials: A systematic review
Claire-Adeline Dantagnan, Maureen Boudrot, Julia Bosco, Gauthier Dot, Ali Nassif, Philippe François, Jean-Pierre Attal
International Orthodontics.2026; 24(2): 101089. CrossRef - State-of-the-Art Zirconia and Glass–Ceramic Materials in Restorative Dentistry: Properties, Clinical Applications, Challenges, and Future Perspectives
Sorin Gheorghe Mihali, Adela Hiller
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(23): 12841. CrossRef - Shear bond strength and ARI scores of metal brackets to glazed glass ceramics and zirconia: an in vitro study investigating surface treatment protocols
Claire Pédemay, Philippe François, Vincent Fouquet, Sarah Abdel-Gawad, Jean-Pierre Attal, Claire-Adeline Dantagnan
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of different pretreatments and attachment materials on shear bond strength of indirectly bonded brackets using CAD/CAM transfer trays to monolithic zirconia
Rebecca Jungbauer, Christian M. Hammer, Daniel Edelhoff, Peter Proff, Bogna Stawarczyk
Dental Materials.2023; 39(2): 170. CrossRef - Mechanical and chemical surface treatment enhances bond strength between zirconia and orthodontic brackets: an in vitro study
Nareudee Limpuangthip, Atikom Surintanasarn, Ploylada Vitavaspan
BDJ Open.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Different Surface Treatments and Orthodontic Bracket Type on Shear Bond Strength of High‐Translucent Zirconia: An In Vitro Study
Yasamin Babaee Hemmati, Hamid Neshandar Asli, Mehran Falahchai, Sina Safary, Sandrine Bittencourt Berger
International Journal of Dentistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Does Surface Treatment With Different Primers Increase The Shear Bond Strength Between Metallic Bracket and Monolithic Zirconia?
Emine Begüm BÜYÜKERKMEN, Ayşe Selenge AKBULUT, Murat KEÇECİ
Selcuk Dental Journal.2022; 9(2): 451. CrossRef - Effect of Different Surface Treatments on the Surface Roughness and Orthodontic Bond Strength of Partially-stabilized Zirconia
Mustafa Borga Dönmez, Betül Ballı Demirel, Münir Demirel, Yasemin Gündoğdu, Hamdi Şükür Kılıç
Meandros Medical and Dental Journal.2022; 23(3): 335. CrossRef - Shear Bond Strength of Polypropylene Fiber in Orthodontic Adhesive on Glazed Monolithic Zirconia
Dhanabhol Riowruangsanggoon, Apiwat Riddhabhaya, Nattisa Niyomtham, Irin Sirisoontorn
Polymers.2022; 14(21): 4627. CrossRef - Effects of Three Novel Bracket Luting Agents Containing Zirconia Primer on Shear Bond Strength of Metal Orthodontic Brackets Attached to Monolithic Zirconia Crowns: A Preliminary In Vitro Study
Milad Shamohammadi Heidari, Mehrnaz Moradinejad, Hamed Tabatabaei, Vahid Rakhshan, Dinesh Rokaya
International Journal of Dentistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of different pretreatments and attachment materials on shear bond strength between monolithic zirconia restorations and metal brackets
Rebecca Jungbauer, Peter Proff, Daniel Edelhoff, Bogna Stawarczyk
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Bracket Bonding to All-Ceramic Materials with Universal Adhesives
Cecilia Goracci, Giuseppe Di Bello, Lorenzo Franchi, Chris Louca, Jelena Juloski, Jovana Juloski, Alessandro Vichi
Materials.2022; 15(3): 1245. CrossRef - Effect of enamel-surface modifications on shear bond strength using different adhesive materials
Bo-wen Zheng, Shan Cao, Majedh Abdo Ali Al-Somairi, Jia He, Yi Liu
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of various mechanical and chemical surface conditioning on the bonding of orthodontic brackets to all ceramic materials
Dalia A. Abuelenain, Amal I. Linjawi, Ahmed S. Alghamdi, Fahad M. Alsadi
Journal of Dental Sciences.2021; 16(1): 370. CrossRef - The Performance of Universal Adhesives on Orthodontic Bracket Bonding
Muhittin Ugurlu, Muhammed Hilmi Buyukcavus
European Journal of General Dentistry.2021; 10(01): 019. CrossRef - A comparison of shear bond strength of brackets bonded to zirconia
Hannah Knott, Xiaoming Xu, Edwin Kee, Qingzhao Yu, Paul Armbruster, Richard Ballard
Australasian Orthodontic Journal.2021; 37(1): 62. CrossRef - Influence of Surface Treatment and Resin Cements on the Bond Strength between the Y-TZP Zirconia and Composite Resin Interface
Lucas Campagnaro Maciel, Amanda Pádua Proeza, Hélyda Coelho Guimarães Balbino, Marcela Moráo Corteletti, Ricardo Huver De Jesus, Laís Regiane da Silva Concílio
Journal of Health Sciences.2019; 21(5): 477. CrossRef - Effect of Simplified Bonding on Shear Bond Strength between Ceramic Brackets and Dental Zirconia
Ga-Youn Ju, Soram Oh, Bum-Soon Lim, Hyun-Seung Lee, Shin Hye Chung
Materials.2019; 12(10): 1640. CrossRef
- Effectiveness of universal adhesives for orthodontic bonding to enamel and restorative materials: A systematic review
- 2,534 View
- 18 Download
- 18 Crossref

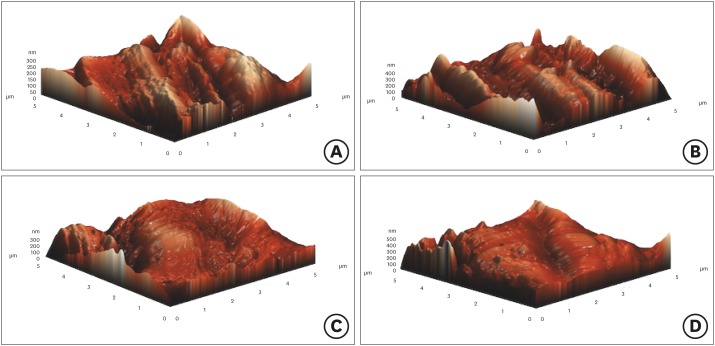
- The effect of root canal preparation on the surface roughness of WaveOne and WaveOne Gold files: atomic force microscopy study
- Taha Özyürek, Koray Yılmaz, Gülşah Uslu, Gianluca Plotino
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(1):e10. Published online February 2, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e10
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives To examine the surface topography of intact WaveOne (WO; Dentsply Sirona Endodontics) and WaveOne Gold (WOG; Dentsply Sirona Endodontics) nickel-titanium rotary files and to evaluate the presence of alterations to the surface topography after root canal preparations of severely curved root canals in molar teeth.
Materials and Methods Forty-eight severely curved canals of extracted molar teeth were divided into 2 groups (
n = 24/each group). In group 1, the canals were prepared using WO and in group 2, the canals were prepared using WOG files. After the preparation of 3 root canals, instruments were subjected to atomic force microscopy analysis. Average roughness and root mean square values were chosen to investigate the surface features of endodontic files. The data was analyzed using one-way analysis of variance andpost hoc Tamhane's tests at 5% significant level.Results The surface roughness values of WO and WOG files significantly changed after use in root canals (
p < 0.05). The used WOG files exhibited higher surface roughness change when compared with the used WO files (p < 0.05).Conclusions Using WO and WOG Primary files in 3 root canals affected the surface topography of the files. After being used in root canals, the WOG files showed a higher level of surface porosity value than the WO files.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative Analysis of Surface Roughness and Plastic Deformation of Reciprocating Instruments after Clinical Use
Ángel Herrera, Magdalena Azabal, Jesús R. Jimenez-Octavio, Juan C. del Real-Romero, Sara López de Armentia, Juan M. Asensio-Gil, Ana Arias
Materials.2024; 17(16): 3978. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Surface Roughness of Different Rotary Nickel-Titanium (NiTi) Files After Autoclaving: An Atomic Force Microscopic Study
Angela Alex, Ranjith Kumar Sivarajan, Vijay Venkatesh
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of endodontic irrigants on surface roughness of various nickel-titanium rotary endodontic instruments
Tamer M. Hamdy, Yasmine Mohsen Alkabani, Amira Galal Ismail, Manar M. Galal
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Metallurgical Tests in Endodontics: A Narrative Review
Alessio Zanza, Marco Seracchiani, Rodolfo Reda, Gabriele Miccoli, Luca Testarelli, Dario Di Nardo
Bioengineering.2022; 9(1): 30. CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue Resistance and Surface Roughness of Rotary NiTi Instruments after Simulated Clinical Use in Curved Root Canals – An Atomic Force Microscopy Study
Raksha Bhat, Arjun Kini, Preethesh Shetty, Payalben Kansara, Bapanaiah Penugonda
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - In Vitro Study of Irrigation solution of Chitosan Nanoparticles to Inhibit the Adhesion and Biofilm Formation of Enterococcus faecalis in the Root Canal
Imelda Darmawi, Trimurni Abidin, Harry Agusnar, Basri A. Gani
Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology.2022; : 2691. CrossRef - Alteration in surface roughness of reciprocating endodontic instruments
Khoa Van Pham
F1000Research.2021; 10: 875. CrossRef - Surface profile of different heat-treated nickel-titanium files before and after root canal preparation
Iandara de Lima Scardini, Denise Maria Zezell, Juliana Lisboa Couto Marques, Laila Gonzales Freire, Marcelo dos Santos
Brazilian Dental Journal.2021; 32(6): 8. CrossRef - Impact of Endodontic Instrumentation on Surface Roughness of Various Nickel-Titanium Rotary Files
Muhammad Sohail Zafar
European Journal of Dentistry.2021; 15(02): 273. CrossRef - A new method for assessment of nickel-titanium endodontic instrument surface roughness using field emission scanning electronic microscope
Khoa Van Pham, Canh Quang Vo
BMC Oral Health.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Surface Alterations Induced on Endodontic Instruments by Sterilization Processes, Analyzed with Atomic Force Microscopy: A Systematic Review
Mario Dioguardi, Vito Crincoli, Luigi Laino, Mario Alovisi, Enrica Laneve, Diego Sovereto, Bruna Raddato, Khrystyna Zhurakivska, Filiberto Mastrangelo, Domenico Ciavarella, Lucio Lo Russo, Lorenzo Lo Muzio
Applied Sciences.2019; 9(22): 4948. CrossRef - Atomic force microscopy and energy dispersive X‐ray spectrophotometry analysis of reciprocating and continuous rotary nickel‐titanium instruments following root canal retreatment
Bulem Üreyen Kaya, Cevat Emre Erik, Gülsen Kiraz
Microscopy Research and Technique.2019; 82(7): 1157. CrossRef - Influence of heat treatment on torsional resistance and surface roughness of nickel‐titanium instruments
E. J. N. L. Silva, J. F. N. Giraldes, C. O. de Lima, V. T. L. Vieira, C. N. Elias, H. S. Antunes
International Endodontic Journal.2019; 52(11): 1645. CrossRef
- Comparative Analysis of Surface Roughness and Plastic Deformation of Reciprocating Instruments after Clinical Use
- 1,734 View
- 12 Download
- 13 Crossref

- Mineral content analysis of root canal dentin using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy
- Selen Küçükkaya Eren, Emel Uzunoğlu, Banu Sezer, Zeliha Yılmaz, İsmail Hakkı Boyacı
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(1):e11. Published online February 4, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e11
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to introduce the use of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) for evaluation of the mineral content of root canal dentin, and to assess whether a correlation exists between LIBS and scanning electron microscopy/energy dispersive spectroscopy (SEM/EDS) methods by comparing the effects of irrigation solutions on the mineral content change of root canal dentin.
Materials and Methods Forty teeth with a single root canal were decoronated and longitudinally sectioned to expose the canals. The root halves were divided into 4 groups (
n = 10) according to the solution applied: group NaOCl, 5.25% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) for 1 hour; group EDTA, 17% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) for 2 minutes; group NaOCl+EDTA, 5.25% NaOCl for 1 hour and 17% EDTA for 2 minutes; a control group. Each root half belonging to the same root was evaluated for mineral content with either LIBS or SEM/EDS methods. The data were analyzed statistically.Results In groups NaOCl and NaOCl+EDTA, the calcium (Ca)/phosphorus (P) ratio decreased while the sodium (Na) level increased compared with the other groups (
p < 0.05). The magnesium (Mg) level changes were not significant among the groups. A significant positive correlation was found between the results of LIBS and SEM/EDS analyses (r = 0.84,p < 0.001).Conclusions Treatment with NaOCl for 1 hour altered the mineral content of dentin, while EDTA application for 2 minutes had no effect on the elemental composition. The LIBS method proved to be reliable while providing data for the elemental composition of root canal dentin.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- In vitro evaluation of antimicrobial photodynamic therapy with photosensitizers and calcium hydroxide on bond strength, chemical composition, and sealing of glass-fiber posts to root dentin
Thalya Fernanda Horsth Maltarollo, Paulo Henrique dos Santos, Henrique Augusto Banci, Mariana de Oliveira Bachega, Beatriz Melare de Oliveira, Marco Hungaro Antonio Duarte, Índia Olinta de Azevedo Queiroz, Rodrigo Rodrigues Amaral, Luciano Angelo Tavares
Lasers in Medical Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Using 5% Apple Vinegar Irrigation Solution Adjunct to Diode Laser on Smear Layer Removal and Calcium/Phosphorus Ion Ratio during Root Canal Treatment
Tarek AA Salam, Haythem SA Kader, Elsayed E Abdallah
CODS - Journal of Dentistry.2024; 15(1): 3. CrossRef - Evaluation of chemical composition of root canal dentin between two age groups using different irrigating solutions: An in vitro sem-eds study
Naresh Kumar K, Abhijith Kallu, Surender L.R, Sravani Nirmala, Narender Reddy
International Dental Journal of Student's Research.2024; 12(1): 18. CrossRef - Minimally invasive management of vital teeth requiring root canal therapy
E. Karatas, M. Hadis, W. M. Palin, M. R. Milward, S. A. Kuehne, J. Camilleri
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effects of a Novel Nanohydroxyapatite Gel and Er: YAG Laser Treatment on Dentin Hypersensitivity
Demet Sahin, Ceren Deger, Burcu Oglakci, Metehan Demirkol, Bedri Onur Kucukyildirim, Mehtikar Gursel, Evrim Eliguzeloglu Dalkilic
Materials.2023; 16(19): 6522. CrossRef - Chitosan Homogenizing Coffee Ring Effect for Soil Available Potassium Determination Using Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy
Xiaolong Li, Rongqin Chen, Zhengkai You, Tiantian Pan, Rui Yang, Jing Huang, Hui Fang, Wenwen Kong, Jiyu Peng, Fei Liu
Chemosensors.2022; 10(9): 374. CrossRef - Quantitative analysis of cadmium in rice roots based on LIBS and chemometrics methods
Wei Wang, Wenwen Kong, Tingting Shen, Zun Man, Wenjing Zhu, Yong He, Fei Liu
Environmental Sciences Europe.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- In vitro evaluation of antimicrobial photodynamic therapy with photosensitizers and calcium hydroxide on bond strength, chemical composition, and sealing of glass-fiber posts to root dentin
- 1,776 View
- 11 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Plugger temperature of cordless heat carriers according to the time elapsed
- Hoon-Sang Chang, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(1):e12. Published online February 7, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e12
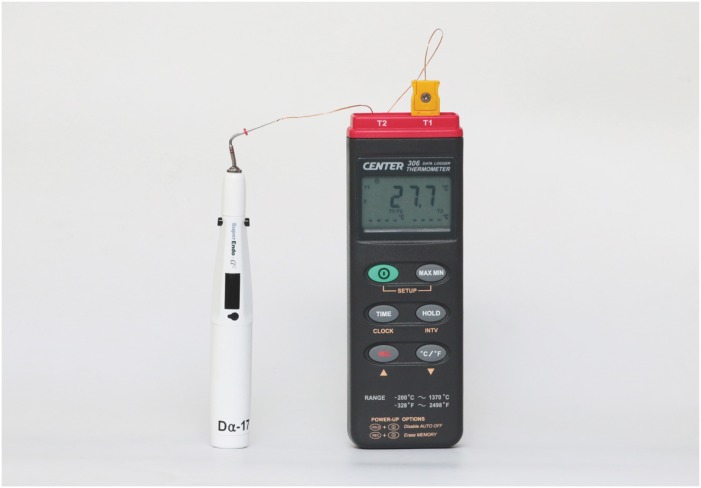

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objective The purpose of this study was to measure the temperature of the plugger tip of 3 cordless heat carriers set at 200°C.
Materials and Methods Pluggers of the same taper (0.06, 0.08, 0.10) and similar tip sizes (sizes of 50 and 55) from 3 cordless heat carriers, namely SuperEndo-α2 (B & L Biotech), Friendo (DXM), and Dia-Pen (Diadent), were used and an electric heat carrier, System B (SybronEndo), was used as the control. The plugger tips were covered with customized copper sleeves, heated for 10 seconds, and the temperature was recorded with a computerized measurement system attached to a K-type thermometer at room temperature (
n = 10). The data were analyzed with 2-way analysis of variance at a 5% level of significance.Results The peak temperature of the plugger tips was significantly affected by the plugger taper and by the heat carrier brand (
p < 0.05). The peak temperature of the plugger tips was between 177°C and 325°C. The temperature peaked at 207°C–231°C for the 0.06 taper pluggers, 195°C–313°C for the 0.08 taper pluggers, and 177°C–325°C for the 0.10 taper pluggers. Only 5 of the 12 plugger tips showed a temperature of 200°C ± 10°C. The time required to reach the highest temperature or 200°C ± 10°C was at least 4 seconds.Conclusion When using cordless heat carriers, clinicians should pay attention to the temperature setting and to the activation time needed to reach the intended temperature of the pluggers.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative Analysis of Temperature Variation with Three Continuous Wave Obturation Systems in Endodontics: An In Vitro Study
Jesús Mena-Álvarez, Maria Ruiz-Barrio, Norberto Quispe-López, Ana de Pedro-Muñoz, Cristina Rico-Romano
Applied Sciences.2022; 12(12): 6229. CrossRef - Effect of Heat Softening versus Ultrasonic Removal of Root-End Gutta-Percha on the Quality of Root-End Preparation for Endodontic Microsurgery
Zhiting Ling, Ziting Zheng, Yuting Zeng, Lifang Jiang, Yuan Wu, Buling Wu, Wenjuan Yan, Lavinia C. Ardelean
Scanning.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef
- Comparative Analysis of Temperature Variation with Three Continuous Wave Obturation Systems in Endodontics: An In Vitro Study
- 1,292 View
- 8 Download
- 2 Crossref

- A simple technique for impression taking of teeth and functionally generated paths
- Takatsugu Yamamoto, Yohei Sato, Hidehiko Watanabe, Amit Punj, Minoru Abe, Yasuko Momoi, Chikahiro Ohkubo
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(1):e9. Published online February 3, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e9
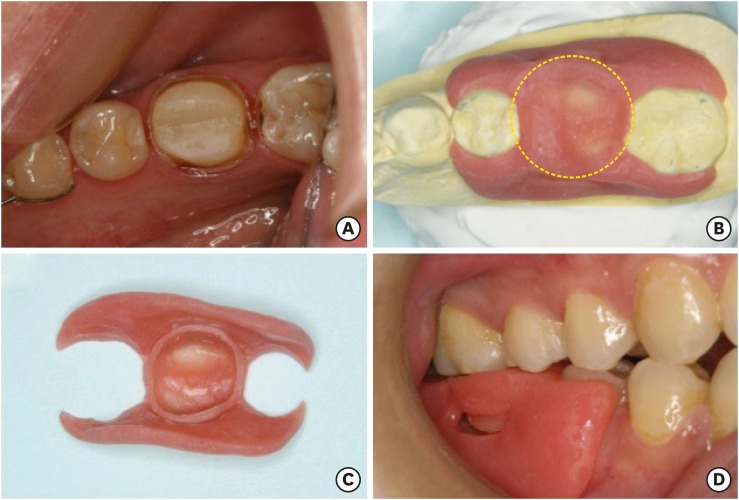
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The objective of this case report is to introduce a simple technique for simultaneously taking a closed-mouth impression and functionally generated path (FGP) for a full coverage crown restoration. A monolithic zirconia crown was the restoration of choice. An alginate impression of the abutment tooth was taken to fabricate a custom-made closed-mouth impression tray covering the abutment tooth and the adjacent teeth. The tray had an FGP table and an abutment tray in cameo and intaglio surfaces, respectively. The impression was taken with silicone impression material after adjusting the abutment tray and inscribing the FGP using self-curing acrylic resins. Plaster casts were made from the impression, and a zirconia crown was fabricated. The crown was cemented to the abutment tooth with minimal adjustments. This simple technique resulted in a well-fitting crown that accounted for mandibular movements. Using the custom closed-mouth impression tray incorporating an FGP table simultaneously aids in fabricating an accurately fitting restoration that incorporates harmonious mandibular movements using a single impression capture.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication of fixed prosthesis by employing functionally generated path technique and dual scan technique in a tardive dyskinesia patient: a case report
Shilpa, Du-Hyeong Lee
The Journal of Korean Academy of Prosthodontics.2023; 61(3): 227. CrossRef - Morphological design of occlusal wear facets for the mandibular first molar crown using different bite registration methods
Hu Chen, Xu Yang, Linlin Li, Yong Wang, Yuchun Sun
Journal of Prosthodontics.2023; 32(5): 439. CrossRef
- Fabrication of fixed prosthesis by employing functionally generated path technique and dual scan technique in a tardive dyskinesia patient: a case report
- 1,956 View
- 20 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Management of dental erosion induced by gastro-esophageal reflux disorder with direct composite veneering aided by a flexible splint matrix
- Sherin Jose Chockattu, Byathnal Suryakant Deepak, Anubhav Sood, Nandini T. Niranjan, Arun Jayasheel, Mallikarjun K. Goud
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(1):e13. Published online February 6, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e13
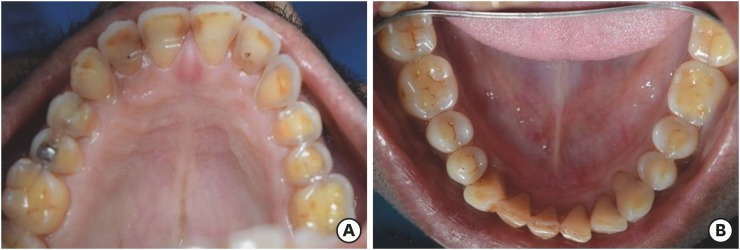
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Dental erosion is frequently overlooked in clinical practice. The management of erosion-induced damage to the dentition is often delayed, such that extensive occlusal rehabilitation is required. These cases can be diagnosed by a careful clinical examination and a thorough review of the patient's medical history and/or lifestyle habits. This case report presents the diagnosis, categorization, and management of a case of gastro-esophageal reflux disease-induced palatal erosion of the maxillary teeth. The early management of such cases is of utmost importance to delay or prevent the progression of damage both to the dentition and to occlusal stability. Non-invasive adhesively bonded restorations aid in achieving this goal.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Acidic Media on Surface Topography and Color Stability of Two Different Glass Ceramics
Fatma Makkeyah, Nesrine A. Elsahn, Mahmoud M. Bakr, Mahmoud Al Ankily
European Journal of Dentistry.2025; 19(01): 173. CrossRef - Mechanical Performance and Surface Roughness of Lithium Disilicate and Zirconia-Reinforced Lithium Silicate Ceramics Before and After Exposure to Acidic Challenge
Ahmed Elsherbini, Salma M. Fathy, Walid Al-Zordk, Mutlu Özcan, Amal A. Sakrana
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(3): 117. CrossRef - Biomechanical reinforcement by CAD-CAM materials affects stress distributions of posterior composite bridges: 3D finite element analysis.
Alaaeldin Elraggal, Islam M. Abdelraheem, David C. Watts, Sandipan Roy, Vamsi Krishna Dommeti, Abdulrahman Alshabib, Khaled Abid Althaqafi, Rania R. Afifi
Dental Materials.2024; 40(5): 869. CrossRef - Surface Properties and Wear Resistance of Injectable and Computer-Aided Design/Computer Aided Manufacturing–Milled Resin Composite Thin Occlusal Veneers
Nesrine A. Elsahn, Hatem M. El-Damanhoury, Zainab Shirazi, Abdul Rahman M. Saleh
European Journal of Dentistry.2023; 17(03): 663. CrossRef - Effect of acidic media on flexural strength and fatigue of CAD-CAM dental materials
Alaaeldin Elraggal, Rania. R Afifi, Rasha A. Alamoush, Islam Abdel Raheem, David C. Watts
Dental Materials.2023; 39(1): 57. CrossRef - Three-year Follow-up of Conservative Direct Composite Veneers on Eroded Teeth
RQ Ramos, NF Coelho, GC Lopes
Operative Dentistry.2022; 47(2): 131. CrossRef - The effects of intrinsic and extrinsic acids on nanofilled and bulk fill resin composites: Roughness, surface hardness, and scanning electron microscopy analysis
Milena F. Alencar, Mirella T. Pereira, Maria D. R. De‐Moraes, Sérgio L. Santiago, Vanara F. Passos
Microscopy Research and Technique.2020; 83(2): 202. CrossRef
- Effect of Acidic Media on Surface Topography and Color Stability of Two Different Glass Ceramics
- 2,287 View
- 20 Download
- 7 Crossref


 KACD
KACD



 First
First Prev
Prev


