-
Isolating design variables by assessing the impact of cross-section geometry on the mechanical performance of nickel-titanium rotary instruments: a comparative in vitro study
-
Anne Rafaella Tenório Vieira, Guilherme Ferreira da Silva, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, João Vitor Oliveira de Amorim, Thaine Oliveira Lima, Raimundo Sales de Oliveira Neto, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Murilo Priori Alcalde
-
Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(3):e28. Published online July 24, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e28
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
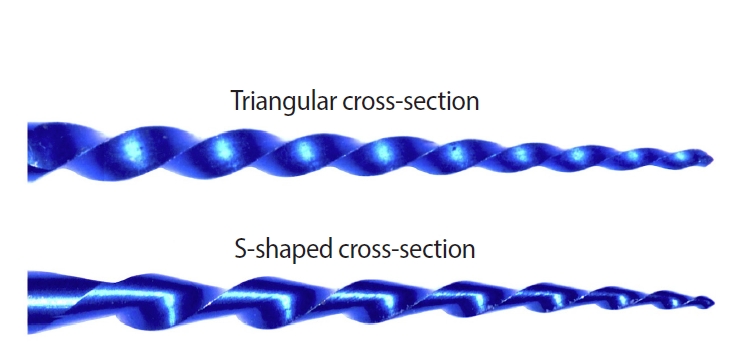
This study aimed to assess the effect of cross-section geometry on the mechanical properties of nickel-titanium (NiTi) instruments by comparing two instruments with identical tip size, taper, and thermal treatment but differing in cross-section design.
Methods
One hundred four NiTi rotary instruments, being S-shaped and triangular cross-section, manufactured with Blueish thermal treatment, were tested (n = 52 per group). Differential scanning calorimetry was employed, and the metal mass volume and cross-section area were assessed. The cyclic fatigue, torsional, and bending resistance tests were assessed. Data were analyzed using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov and Student t tests, and the level of significance was set at 5%.
Results
The instruments exhibited similar start and finish temperatures of phase transformation. The S-shaped instruments had significantly lower metal mass volume and cross-sectional area (p < 0.05). S-shaped instruments demonstrated superior cyclic fatigue resistance, greater angular deflection, and lower bending stiffness (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
Cross-section geometry significantly influences the mechanical properties of NiTi rotary instruments.
-
Impact of the use of high-power 810-nm diode laser as monotherapy on the clinical and tomographic success of the treatment of teeth with periapical lesions: an observational clinical study
-
Fabricio Hinojosa Pedraza, Abel Victor Isidro Teves-Cordova, Murilo Priori Alcalde, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte
-
Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(2):e15. Published online May 15, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e15
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
The aim of this study was to demonstrate the impact of a high-power 810-nm diode laser as monotherapy on the clinical and tomographic success of treating teeth with periapical lesions, through a series of 31 cases.
Methods
Teeth with apical lesions underwent endodontic treatment in which a high-power 810-nm diode laser with saline solution was used as monotherapy for disinfection. This type of therapy aimed to replace the traditional irrigation protocol with sodium hypochlorite. This research is the first to assess the clinical success of this alternative treatment, along with tomographic evaluations conducted over periods ranging from 2 to 7 years, analyzed using the periapical index based on cone-beam computed tomography (CBCTPAI). All cases were performed by a single clinician following the same laser protocol, which involved using 1 W of continuous power and four cycles of 20 seconds of laser activation.
Results
All teeth showed no clinical symptoms upon follow-up examination. However, the tomographic evaluation revealed that the success rates for teeth receiving primary treatment were 60% and 80% according to strict and loose criteria, respectively. For teeth requiring retreatment, the success rates were 12.5% and 37.5% using strict and loose criteria, respectively.
Conclusions
The teeth with apical lesions that underwent primary treatment did not present clinical symptoms, but they showed a moderate success rate on tomographic evaluation. However, despite lacking clinical symptoms, teeth with apical lesions that required retreatment had a very low success rate on tomographic evaluation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Diode Laser-Guided Protocol for Endo-Perio Lesions: Toward a Multi-Stage Therapeutic Strategy—A Case Series and Brief Literature Review
Ioana-Roxana Munteanu, George-Dumitru Constantin, Ruxandra-Elena Luca, Ioana Veja, Mariana-Ioana Miron
Medicina.2025; 61(12): 2157. CrossRef
-
3,712
View
-
180
Download
-
1
Web of Science
-
1
Crossref
-
Bibliometric analysis of the GentleWave system: trends, collaborations, and research gaps
-
Raimundo Sales de Oliveira Neto, Thais de Moraes Souza, João Vitor Oliveira de Amorim, Thaine Oliveira Lima, Guilherme Ferreira da Silva, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, Murilo Priori Alcalde, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte
-
Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(2):e17. Published online May 12, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e17
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
The study aimed to conduct a bibliometric analysis of the GentleWave system (Sonendo, Inc.).
Methods
An electronic search was conducted in June 2024 using the Web of Science Collection database. Two reviewers independently screened publications, extracting data on authorship, publication details, study design, and citation metrics. Statistical analyses were performed in R to assess variable correlations, while the VOSviewer (Visualization of Similarities Viewer) software was used to map author and keyword networks.
Results
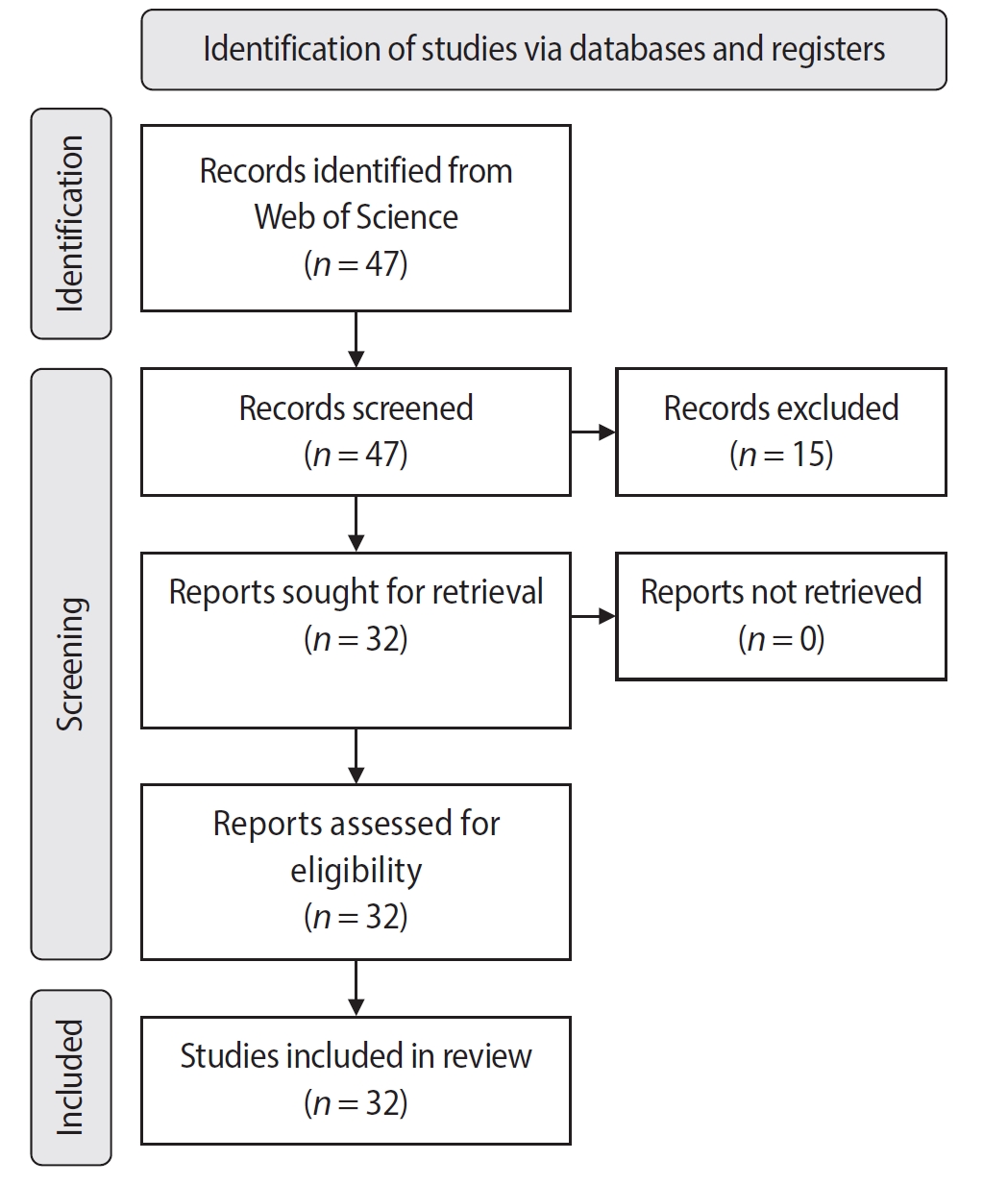
The search yielded 47 records, with 32 studies included. Publications spanned 2014 to 2024. The Journal of Endodontics published the highest number of studies (n = 15), and the International Endodontic Journal had the highest impact factor (5.4). The University of British Columbia and Sonendo, Inc. were the most frequent affiliations. Among the 32 articles, 28 were in vitro studies, primarily focusing on microbiology (n = 9). A total of 95 authors were identified, with Haapasalo and Shen being the most cited (n = 229). The articles accumulated 495 citations, demonstrating a strong positive correlation between the number of studies and citation counts (r = 0.98).
Conclusions
The analysis highlights a predominance of in vitro studies. Geographic concentration in the United States and Canada limits diversity, while the strong correlation between study numbers and citations suggests that increased publication volume enhances visibility.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Three-year Outcomes of Conventional Versus Minimally Invasive Endodontic Treatment Protocols: A Retrospective Study
Kiavash Hossini, He Liu, Ya Shen, Jolanta Aleksejuniene, Fahda Algahtani, Ahmed Hieawy
Journal of Endodontics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
-
3,273
View
-
79
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
Shaping ability and cyclic fatigue resistance between Genius ProFlex, ZenFlex, and TruNatomy rotary systems: an experimental study
-
Raimundo Sales de Oliveira Neto, Murilo Priori Alcalde, Pedro Cesar Gomes Titato, Pedro Henrique Souza Calefi, Carlos Alberto Spironelli Ramos, Guilherme Ferreira da Silva, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte
-
Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(1):e9. Published online February 13, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e9
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
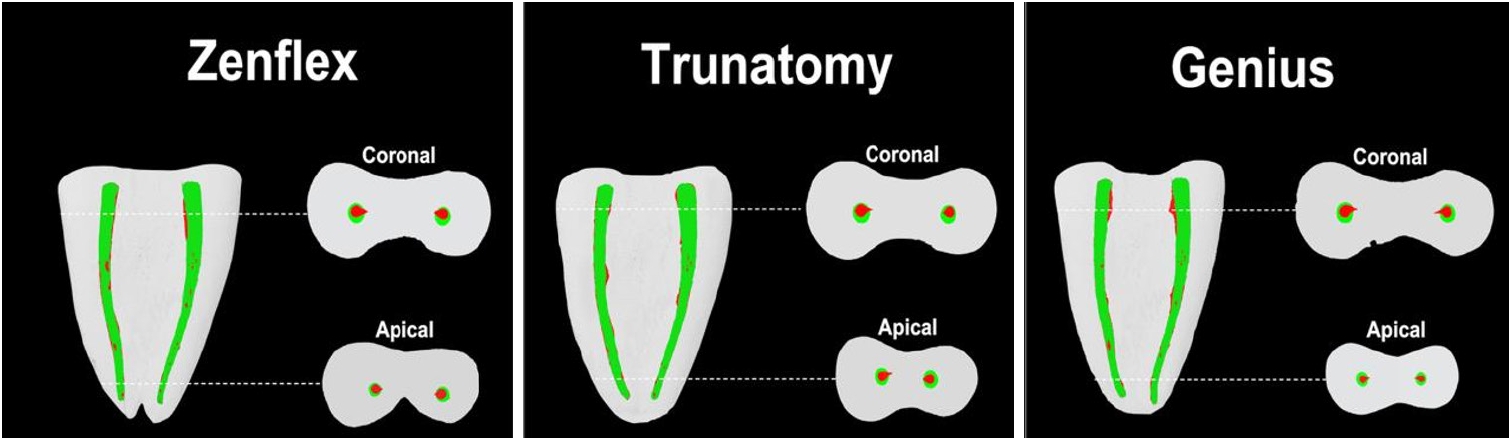
The aim of this study was to investigate the efficacy of three newly introduced rotary endodontic systems: Genius ProFlex (Medidenta), TruNatomy (Dentsply Maillefer), and ZenFlex (Kerr).
Methods
Forty-five mandibular molars with root canal curvatures <5° were utilized. Micro-computed tomography scans were performed pre- and post-preparation to assess apical transportation, centralization, percentage of dentin wear, and canal volume alterations. Eight instruments of each diameter underwent cyclic fatigue testing.
Results
The percentage of dentin wear on mesial and distal walls showed no significant differences among ZenFlex, TruNatomy, and Genius ProFlex at 1, 2, 3, and 4 mm from the apical foramen and root canal orifice (p > 0.05). Centering ability varied in the mesiolingual canal (p < 0.05). No notable differences were observed in transportation (p > 0.05). Genius ProFlex demonstrated lower volumetric changes (p < 0.05). There were significant differences in cyclic fatigue, with higher values for Genius ProFlex and lower values for TruNatomy (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
The three nickel-titanium rotary instruments are safe and efficient for root canal preparation, with Genius ProFlex exhibiting superior cyclic fatigue resistance.
-
Impact of different agitation methods on smear layer cleaning of mesial canals with accentuated curvature
-
Abel Teves Cordova, Murilo Priori Alcalde, Michel Espinosa Klymus, Leonardo Rigoldi Bonjardim, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte
-
Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(2):e12. Published online March 4, 2024
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e12
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
This study evaluated the impact of different methods of irrigant agitation on smear layer removal in the apical third of curved mesial canals of 3 dimensionally (D) printed mandibular molars. Materials and MethodsSixty 3D-printed mandibular second molars were used, presenting a 70° curvature and a Vertucci type II configuration in the mesial root. A round cavity was cut 2 mm from the apex using a trephine of 2 mm in diameter, 60 bovine dentin disks were made, and a smear layer was formed. The dentin disks had the adaptation checked in the apical third of the teeth with wax. The dentin disks were evaluated in environmental scanning electron microscope before and after the following irrigant agitation methods: G1(PIK Ultrasonic Tip), G2 (Passive Ultrasonic Irrigation with Irrisonic– PUI), G3 (Easy Clean), G4 (HBW Ultrasonic Tip), G5 (Ultramint X Ultrasonic tip), and G6 (conventional irrigation-CI) (n = 10). All groups were irrigated with 2.5% sodium hypochlorite and 17% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid. ResultsAll dentin disks were 100% covered by the smear layer before treatment, and all groups significantly reduced the percentage of the smear layer after treatment. After the irrigation protocols, the Ultra-X group showed the lowest coverage percentage, statistically differing from the conventional, PIK, and HBW groups (p < 0.05). There was no significant difference among Ultramint X, PUI-Irrisonic, and Easy Clean (p > 0.05). None of the agitation methods could remove the smear layer altogether. ConclusionsUltramint X resulted in the most significant number of completely clean specimens.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - A new cleaning protocol in minimally invasive endodontic surgery: RUA (“retro irrigant activation”)
Dina Abdellatif, Davide Mancino, Massimo Pisano, Sara De Fontaine, Alfredo Iandolo
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(3): 297. CrossRef - Impact of the use of high-power 810-nm diode laser as monotherapy on the clinical and tomographic success of the treatment of teeth with periapical lesions: an observational clinical study
Fabricio Hinojosa Pedraza, Abel Victor Isidro Teves-Cordova, Murilo Priori Alcalde, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2025; 50(2): e15. CrossRef - Smear layer removal comparing conventional irrigation, passive ultrasonic irrigation, EndoActivator System, and a new sonic device (Perfect Clean System) by scanning electron microscopy: An ex vivo study
Bruna Fernanda Alionço Gonçalves, Divya Reddy, Ricardo Machado, Paulo César Soares Júunior, Sérgio Aparecido Ignácio, Douglas Augusto Fernandes Couto, Karine Santos Frasquetti, Vânia Portela Ditzel Westphalen, Everdan Carneiro, Ulisses Xavier da Silva Net
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(12): e0314940. CrossRef
-
2,283
View
-
126
Download
-
2
Web of Science
-
3
Crossref
-
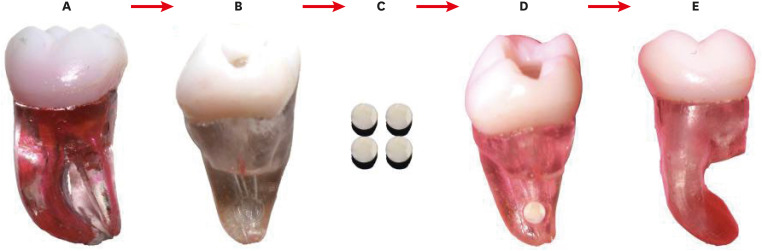
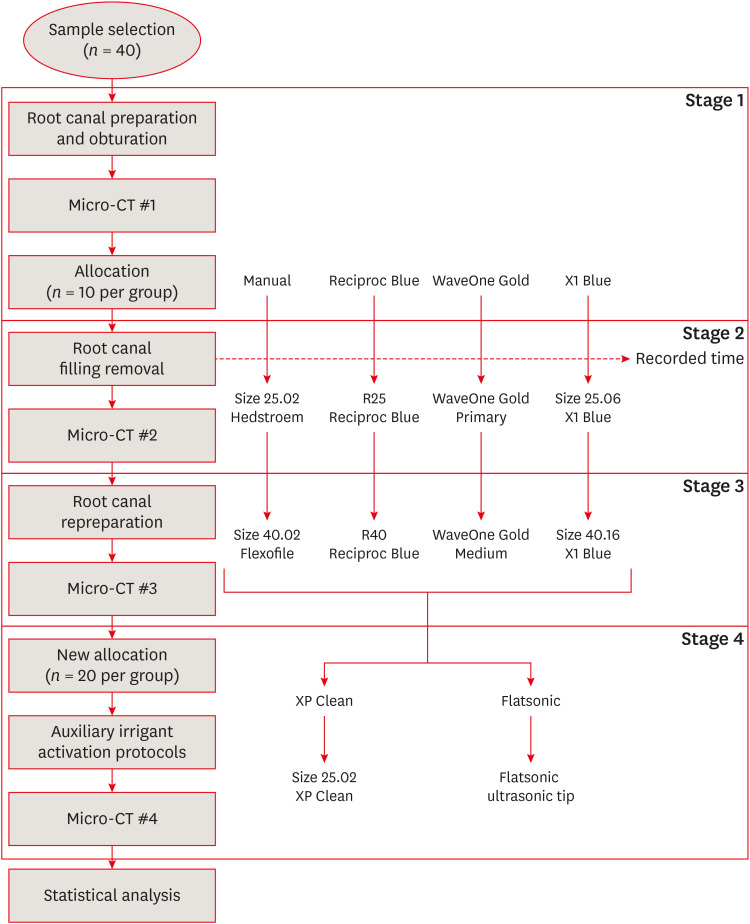
Efficacy of reciprocating instruments and final irrigant activation protocols on retreatment of mesiobuccal roots of maxillary molars: a micro-CT analysis
-
Lilian Tietz, Renan Diego Furlan, Ricardo Abreu da Rosa, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Murilo Priori Alcalde, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, Theodoro Weissheimer, Marcus Vinicius Reis Só
-
Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(1):e13. Published online February 15, 2022
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e13
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
This study evaluated the efficacy of 3 reciprocating systems and the effects of 2 instruments for irrigant activation on filling material removal. Materials and MethodsForty mesiobuccal roots of maxillary molars were prepared up to size 25.06 and obturated. Micro-computed tomography (micro-CT) examination #1 was performed. Teeth were then divided into 4 groups (n = 10), according to the retreatment protocol: (1) manual, (2) Reciproc Blue, (3) WaveOne Gold, and (4) X1 Blue. Micro-CT examinations #2 and #3 were performed after filling removal and repreparation, respectively. Next, all teeth were divided into 2 new groups (n = 20) according to the irrigant activation protocol: XP Clean (XP Clean size 25.02) and Flatsonic (Flatsonic ultrasonic tip). Micro-CT examination #4 was performed after irrigant activation. Statistical analysis was performed with a significance level set at 5%. ResultsWaveOne Gold removed a significantly greater amount of filling material than the manual group (p < 0.05). The time to reach the WL was similar for all reciprocating systems (p > 0.05). X1 Blue was faster than the manual group (p < 0.05). Only manual group improved the filling material removal after the repreparation stage (p < 0.05). Both activation protocols significantly improved the filling material removal (p < 0.05), without differences between them (p > 0.05). ConclusionsNone of the tested instruments completely removed the filling material. X1 Blue size 25.06 reached the working length in the shortest time. XP Clean and Flatsonic improved the filling material removal.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Supplementary instrumentation did not enhance the removal of residual gutta-percha: a micro-computed tomography study
Selin Nur Ayaz, Meltem Kucuk, Deniz Yanık Nalbantoğlu, Ali Keles, Amine Yigit, Fugen Dagli Comert Tasman, Bekir Karabucak
Odontology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Supplementary methods for filling material removal: A systematic review and meta-analysis of micro-CT imaging studies
Bruna Venzke Fischer, Taynara Santos Goulart, Filipe Colombo Vitali, Diego Leonardo de Souza, Cleonice da Silveira Teixeira, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
Journal of Dentistry.2024; 151: 105445. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Ability of 3 Reciprocating Instruments to Remove Obturation Material: A Micro–Computed Tomography Study
Fábio Luiz Cecagno, Alexandre Sigrist De Martin, Carlos Eduardo Fontana, Bruno Cavalini Cavenago, Wayne Martins Nascimento, Ana Grasiela da Silva Limoeiro, Carlos Eduardo da Silveira Bueno
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(3): 376. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of cleaning efficiency of single file NiTi rotary system during root canal treatment procedure - A scanning electron microscope study
Ruchi Vashisht, Umesh Kumar, Swaty Jhamb, Ruchi Singla
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2023; 26(3): 316. CrossRef - Influence of rotary and reciprocating kinematics on the accuracy of an integrated apex locator
Verônica de Almeida Gardelin, Júlia Itzel Acosta Moreno Vinholes, Renata Grazziotin‐Soares, Fernanda Geraldo Pappen, Fernando Branco Barletta
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(S1): 202. CrossRef
-
2,259
View
-
34
Download
-
4
Web of Science
-
5
Crossref
-
Effect of ultrasonic agitation on push-out bond strength and adaptation of root-end filling materials
-
Murilo Priori Alcalde, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, Marina Angélica Marciano, Jussaro Alves Duque, Samuel Lucas Fernandes, Mariana Bailo Rosseto, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte
-
Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(2):e23. Published online April 27, 2018
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e23
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
This study evaluated the effect of ultrasonic agitation of mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA), calcium silicate-based cement (CSC), and Sealer 26 (S26) on adaptation at the cement/dentin interface and push-out bond strength. Materials and MethodsSixty maxillary canines were divided into 6 groups (n = 10): MTA, S26, and CSC, with or without ultrasonic activation (US). After obturation, the apical portions of the teeth were sectioned, and retrograde cavities were prepared and filled with cement by hand condensation. In the US groups, the cement was activated for 60 seconds: 30 seconds in the mesio-distal direction and 30 seconds in the buccal-lingual direction, using a mini Irrisonic insert coupled with the ultrasound transducer. After the materials set, 1.5-mm thick sections were obtained from the apexes. The presence of gaps and the bond between cement and dentin were analyzed using low-vacuum scanning electron microscopy. Push-out bond strength was measured using a universal testing machine. ResultsUltrasonic agitation increased the interfacial adaptation of the cements. The S26 US group showed a higher adaptation value than MTA (p < 0.05). US improved the push-out bond strength for all the cements (p < 0.05). ConclusionsThe US of retrograde filling cements enhanced the bond to the dentin wall of the root-end filling materials tested.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effect of ultrasonic activation on setting time, pH and calcium ion release, solubility, and chemical structure of calcium silicate sealers
Simone Argenta Scalabrin, Lina Naomi Hashizume, Theodoro Weissheimer, Gabriel Barcelos Só, Jefferson Ricardo Pereira, Milton Carlos Kuga, Ricardo Abreu da Rosa, Marcus Vinicius Reis Só
Brazilian Dental Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of different disinfection protocols on the bond strength of NeoMTA 2 bioceramic sealer used as a root canal apical plug (in vitro study)
Nada Omar, Nihal Refaat Kabel, Muhammad Abbass Masoud, Tamer M. Hamdy
BDJ Open.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Endo-Z bur or Bladesonic ultrasonic tip on the adaptation of filling material. A micro-CT study
Pedro Henrique Fiorin de Souza, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Jáder Camilo Pinto, Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mário Tanomaru-Filho
Brazilian Dental Journal.2023; 34(5): 29. CrossRef - Effect of Different Mixing Methods on Physicochemical Properties of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate: A Systematic Review
Amin Salem Milani, Faraz Radmand, Behrad Rahbani, Mahdi Hadilou, Farnaz Haji Abbas Oghli, Fatemeh Salehnia, Milad Baseri, Stefano Pagano
International Journal of Dentistry.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Micro-CT comparative evaluation of porosity and dentin adaptation of root end filling materials applied with incremental, bulk, and ultrasonic activation techniques
Berkan Celikten, Aysenur Oncu, Mehrdad Koohnavard, Mert Ocak, Kaan Orhan
Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part H: Journal of Engineering in Medicine.2022; 236(8): 1209. CrossRef - Effect of ultrasonic activation of the adhesive system on dentin tubule penetration and the pushout bond strength of fiber posts
Isabel Verdum, Igor Abreu de Bem, Pedro Henrique Marks Duarte, Lucas Silveira Machado, Jefferson Ricardo Pereira, Marcus Vinícius Reis Só, Ricardo Abreu da Rosa
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2022; 127(2): 295. CrossRef - Influence of Ultrasonic Activation on the Physicochemical Properties of Calcium Silicate-Based Cements
Fredson Márcio Acris De Carvalho, Yara Teresinha Corrêa Silva-Sousa, Carlos Eduardo Saraiva Miranda, Paulo Henrique Miller Calderon, Ana Flávia Simões Barbosa, Luciana Martins Domingues De Macedo, Fuad Jacob Abi Rached-Junior, Boonlert Kukiattrakoon
International Journal of Dentistry.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of the flow and filling ability of endodontic materials using different test models
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Gisselle Moraima Chavez-Andrade, Jader Camilo Pinto, Fábio Luiz Camargo Villela Berbert, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Dental discoloration caused by Grey-MTAFlow cement: analysis of its physicochemical, biological and antimicrobial properties
Lauter Eston PELEPENKO, Flávia SAAVEDRA, Gabriela Fernanda BOMBARDA, Brenda Paula Figueiredo de Almeida GOMES, Adriana DE-JESUS-SOARES, Alexandre Augusto ZAIA, Marco Antonio Hungaro DUARTE, Mario TANOMARU-FILHO, Marina Angélica MARCIANO
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Ultrasonic Activation of Endodontic Sealers on Intratubular Penetration and Bond Strength to Root Dentin
Igor Abreu De Bem, Renata Aqel de Oliveira, Theodoro Weissheimer, Carlos Alexandre Souza Bier, Marcus Vinícius Reis Só, Ricardo Abreu da Rosa
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(9): 1302. CrossRef
-
1,534
View
-
9
Download
-
10
Crossref
|