-
Calcium silicate-based root canal sealers: a literature review
-
Miyoung Lim, Chanyong Jung, Dong-Hoon Shin, Yong-bum Cho, Minju Song
-
Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(3):e35. Published online June 9, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e35
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
Epoxy resin-based sealers are currently widely used, and several studies have considered AH Plus to be the gold-standard sealer. However, it still has limitations, including possible mutagenicity, cytotoxicity, inflammatory response, and hydrophobicity. Drawing upon the advantages of mineral trioxide aggregate, calcium silicate-based sealers were introduced with high levels of biocompatibility and hydrophilicity. Because of the hydrophilic environment in root canals, water resorption and solubility of root canal sealers are important factors contributing to their stability. Sealers displaying lower microleakage and stronger push-out bond strength are also needed to endure the dynamic tooth environment. Although the physical properties of calcium silicate-based sealers meet International Organization for Standardization recommendations, and they have consistently reported to be biocompatible, they have not overcome conventional resin-based sealers in actual practice. Therefore, further studies aiming to improve the physical properties of calcium silicate-based sealers are needed. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Does the Use of a Bioceramic Sealer Reduce Postoperative Pain Compared With an Epoxy Resin‐Based Sealer After Primary Root Canal Treatment and Retreatment?—An Umbrella Review
Lokhasudhan Govindaraju, Rajeswari Kalaiselvam, Mathan Rajan Rajendran, Aleksandar Jakovljevic, Jelena Jacimovic, Henry F. Duncan, Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu
International Endodontic Journal.2026; 59(3): 341. CrossRef - Evidence synthesis of postoperative pain with bioceramic vs. epoxy resin sealers: umbrella review of randomized trials within existing systematic reviews
Mrunali Dahikar, Ashish Mandwe, Kulvinder Singh Banga, Alexander Maniangat Luke, Suraj Arora, Unmesh Khanvilkar, Ajinkya M. Pawar
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of interactions between sealers and irrigants on the physicochemical and surface characteristics of endodontic sealers
Hye-In Kim, Yeon-Ju You, Yemi Kim, Jin-Woo Kim, Young-Eun Jang
Clinical Oral Investigations.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Physical and mechanical properties of a strontium silicate-based sealer
Shannon Wong, Xiaofei Zhu, Tun-Yi Hsu, Sami Chogle, Russell A. Giordano, Yuwei Fan
Odontology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of Release of Calcium Ions from Apical Plugs of Different Bioceramic Sealers in Regenerative Endodontics for Immature Permanent Teeth
Alok Dubey, Nischitha Naik, Bhavana Sujanamulk, Mushir Mulla, Munaz Mulla, Alkananda Sahoo, Mohamed T Salama, Murali Patla S Bhat
World Journal of Dentistry.2026; 17(1): 69. CrossRef - Push-out bond strength of bioceramic-based sealers following different irrigation activation techniques
Fatma Begüm Peker, Hümeyra Çapkın, Ahsen Narbay
Journal of Applied Biomaterials & Functional Materials.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Different Tapered Gutta-Percha Points on Push-Out Bond Strength of Two Root Canal Sealers
Warattama Suksaphar, Pakit Tungsawat, Ninnita Wongwatanasanti, Siripat Lertnantapanya, Prattana Yodmanothum
European Journal of General Dentistry.2025; 14(03): 285. CrossRef - Effect of Electrical Heat Carrier Temperature on Bacterial Leakage of Endodontically Treated Teeth Using a Bioceramic Sealer
Mir Ahmad Nabavi, Mahmood Reza Kalantar Motamedi, Pedram Fattahi, Saber Khazaei
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Nanoparticles modified bioceramic sealers on solubility, antimicrobial efficacy, pushout bond strength and marginal adaptation at apical-third of canal dentin
Basil Almutairi, Fahad Alkhudhairy
PeerJ.2025; 13: e18840. CrossRef - Assessing the antimicrobial properties of bioceramic sealers enhanced with herbal extracts against E. faecalis
KS Sachin, K Shibani Shetty, KB Jeyalakshmi, S Harishma, S Harshini
Folia Medica.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Estudio comparativo de la solubilidad de dos selladores endodónticos biocerámicos y un sellador a base de resinas
//Comparative study of the solubility of two bioceramic endodontic sealers and one epoxi-resin based sealer
Alejandro Leonhardt, Nicolás Paduli, Osvaldo Zmener, Miguel Chantiri
Revista de la Asociación Odontológica Argentina.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Enhancing root canal sealing: Exploring the sealing potential of epoxy and calcium silicate-based sealers with chitosan nanoparticle enhancement
S. Harishma, Srilekha Jayakumar, K Shibani Shetty, Barkavi Panchatcharam, Jwaalaa Rajkumar, S. Harshini
Endodontology.2025; 37(3): 306. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Genotoxicity and Cytotoxicity of Bioceramic Endodontic Sealers in HepG2 and V79 Cell Lines: An In Vitro Study Using the Comet and Micronucleus Assays
Antonija Tadin, Marija Badrov, Danijela Juric Kacunic, Nada Galic, Matea Macan, Ivan Kovacic, Davor Zeljezic
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2025; 16(5): 169. CrossRef - In Vitro Apatite-Forming Ability of Different Root Canal Sealers (A Comparative Study)
Raghad A Al-Askary, Wiaam M. O. Al-Ashou, Sawsan H. Al-Jubori
Journal of International Society of Preventive and Community Dentistry.2025; 15(2): 173. CrossRef - Microstructural and elemental characterization of novel bioactive glass bioceramic sealer using Fourier transform infrared and X-ray diffraction analysis
Poulomi Guha, Pradeep Solete, Delphine Antony, Nishitha Arun, Mohmed Isaqali Karobari, Surendar Ramamoorthi
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(5): 412. CrossRef - Microstructural and Elemental Characterization of Calcium Silicate-Based Sealers
Mateusz Radwanski, Ireneusz Piwonski, Tomasz Szmechtyk, Salvatore Sauro, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska
Nanomaterials.2025; 15(10): 756. CrossRef - Apical negative pressure-enhanced sealer infiltration for obturating long oval-shaped root canals with the single-cone technique
Yaxu Feng, Brian E. Bergeron, Shijin Zhang, Danyang Sun, Kole Fisher, Franklin R. Tay, Bing Fan
Journal of Dentistry.2025; 160: 105909. CrossRef - Effects of different apical preparation sizes and root canal sealers on the fracture resistance of roots aged for 12 months in endodontically retreated mandibular premolars
Dilek Hancerliogullari, Sevda Durust Baris, Ali Turkyilmaz, Ali Erdemir
British Dental Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of different endodontic treatment protocols on tooth survival: A retrospective cohort study with multistate analysis and group balancing
Ahmed Elmaasarawi, Mohamed Mekhemar, Andreas Bartols
International Endodontic Journal.2025; 58(10): 1529. CrossRef - Evaluation of 2,6-xylidine precipitate on sealer penetration of calcium silicate-based sealer and resin-based sealer: An in vitro study
M. B. Kalpana, Divya Shetty, Rajaram Naik
Endodontology.2025; 37(2): 183. CrossRef - Translational Advances in Regenerative Dentistry: Functional Biomaterials and Emerging Technologies
Seher Yaylacı, Hacer Eberliköse, Hakan Ceylan
Current Oral Health Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Marginal adaptation of heat and non-heat compatible bioceramic sealers in warm obturation: an in vitro SEM study
Thanomsuk Jearanaiphaisarn, Thanida Leelayuttakarn, Panisara Amatamahuthana, Pinmanus Chenpairojsakul, Keskanya Subbalekha, Pavena Chivatxaranukul
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of irrigating solutions on the hydration of calcium silicate-based dental biomaterials: An in vitro study
Pradeep M. Divya, Amit Jena, Saumyakanta Mohanty, Govind Shashirekha, Rashmi Rekha Mallick, Priyanka Sarangi
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(8): 758. CrossRef - Multispecies Biofilms Treated With Endodontic Sealers or Calcium Hydroxide: Antimicrobial Activity and Changes in Community Composition
Steven K. Uttech, Ronald Ordinola‐Zapata, W. Craig Noblett, Maria Martell, Bruno Lima, Christopher Staley
International Endodontic Journal.2025; 58(11): 1764. CrossRef - A comparative analysis of adhesion abilities between AH Plus® Bioceramic, Ceraseal® and AH Plus® on root canal dentine surfaces
Ike Dwi Maharti, Indira Larasputri, Nendar Herdianto, Anggraini Margono, Riesma Tasomara, Romilda Rosseti
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(9): 881. CrossRef - Clinical and radiographic success of single-cone bioceramic obturation versus traditional techniques: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Firas Elmsmari, Yousef Elsayed, Abdelrahman Aboubakr, Mahdi Kaafarani, Osama Nour, Ajinkya M. Pawar
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2025; 15(6): 1422. CrossRef - The Effect of Irrigation Solutions on the Setting Time, Solubility, and pH of Three Types of Premixed Bioceramic‐Based Root Canal Sealers
Kitichai Singharat, Ninnita Wongwatanasanti, Warattama Suksaphar, Pakit Tungsawat, Zhengrui Li
International Journal of Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Endodontie – State of the Art von A bis Z
Will Qian, Andreas Bartols
Zahnmedizin up2date.2025; 19(04): 281. CrossRef - Assessing Volume of Two Sealers’ Remnants after Reinstrumentation Using 3D Imaging Technology: An In Vitro Comparative Study
Khalel Mutaz Dawod, Raghad Abdulrazzaq Al-Hashimi
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2025; 26(8): 743. CrossRef - Functional and Bioactive Performance of Premixed Bioceramic Sealers with Warm Obturation: A Scoping Review
Patryk Wiśniewski, Stanisław Krokosz, Małgorzata Pietruska, Anna Zalewska
Gels.2025; 11(11): 932. CrossRef - Correlation of Bond Strength and Dentinal Tubule Penetration Evaluation of Four Different Endodontic Sealers: AH Plus, MTA Fillapex, Endoseal MTA, and Endoseal TCS (Maruchi): An In Vitro Study
Arezoo Mirzaei Sadeghloo, Seyedali Seyedmajidi, Akam Saeidi, Elham Mahmoudi, Murilo Baena Lopes
International Journal of Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Osteogenic Potential of Various Premixed Hydraulic Calcium Silicate-Based Sealers on Human Bone Marrow Stem Cells
Na-Hyun You, Donghee Lee, Yemi Kim, Sieun Nam, Sin-Young Kim
Materials.2025; 18(23): 5326. CrossRef - Polydopamine‐Functionalized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles as a Root Canal Sealer: Characterization, Biological, and Physicochemical Properties
Arul Nayagi Raj, Aditya Shetty, Lakshmi Nidhi Rao, Giuseppe Ciccarella
Bioinorganic Chemistry and Applications.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Management of rarely seen internal tunnelling root resorption associated with a maxillary permanent incisor
Kirsty A. Carney, Thibault N. E. Colloc, Julie K. Kilgariff
British Dental Journal.2024; 236(12): 955. CrossRef - Top tips for treatment planning: tooth-by-tooth prognosis - Part 3: endodontic prognosis
Prashanti Eachempati, Andrew Harris, Guy Lambourn, Tony Francis, Ewen McColl
British Dental Journal.2024; 237(9): 686. CrossRef - Retreatability of calcium silicate-based sealers based on micro-computed tomographic evaluation − A systematic review
Sundus Mohammed Bukhary
The Saudi Dental Journal.2024; 36(10): 1278. CrossRef - Evaluation of Setting Time, Flowability, Film Thickness, and Radiopacity of Experimental Monocalcium Silicate‐Based Root Canal Sealers
Sukanya Juntha, Pakit Tungsawat, Ninnita Wongwatanasanti, Warattama Suksaphar, Siripat Lertnantapanya, Carlos M. Ardila
International Journal of Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Root Canal Treatment and Demand for Continuing Education among Thai Dental Practitioners
Ninnita Wongwatanasanti, Pakit Tungsawat, Warattama Suksaphar, Siripat Lertnantapanya, Prattana Yodmanotham
The Open Dentistry Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical outcome of non-surgical root canal treatment using different sealers and techniques of obturation in 237 patients: A retrospective study
Mateusz Radwanski, Krystyna Pietrzycka, Tan Fırat Eyüboğlu, Mutlu Özcan, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Endodontic sealers after exposure to chlorhexidine digluconate: An assessment of physicochemical properties
Vasileios Kapralos, Josette Camilleri, Andreas Koutroulis, Håkon Valen, Dag Ørstavik, Pia Titterud Sunde
Dental Materials.2024; 40(3): 420. CrossRef - Assessment the bioactivity of zinc oxid eugenol sealer after the addition of different concentrations of nano hydroxyapatite-tyrosine amino acid
Rasha M. Al-Shamaa, Raghad A. Al-Askary
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2024; 23: e243733. CrossRef - Interfacial adaptation of newly prepared nano-tricalcium silicate-58s bioactive glass-based endodontic sealer
Nawal A. Al-Sabawi, Sawsan Hameed Al-Jubori
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2024; 18(2): 115. CrossRef - Marginal adaptation of customized gutta percha cone with calcium silicate based sealer versus MTA and biodentine apical plugs in simulated immature permanent teeth (an in vitro study)
Mary M. Mina, Sybel M. Moussa, Mahmoud R. Aboelseoud
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Solubility of Endoseal and AH26 Root Canal Sealers
Nooshin Fakhari, Ali Reza Mirjani, Abbas Bagheri, Jalil Modaresi
Journal of Research in Dental and Maxillofacial Sciences.2024; 9(1): 1. CrossRef - Novel bioactive nanospheres show effective antibacterial effect against multiple endodontic pathogens
Jin Liu, Haoze Wu, Jun Qiu, Sirui Yang, Doudou Xiang, Xinhua Zhang, Jinxin Kuang, Min Xiao, Qing Yu, Xiaogang Cheng
Heliyon.2024; 10(7): e28266. CrossRef - Evaluation of canal patency and cleanliness following retreatment of bioceramic sealer‐obturated root canals using three different irrigant activation protocols
Daiasharailang Lyngdoh, Sharique Alam, Huma Iftekhar, Surendra Kumar Mishra
Australian Endodontic Journal.2024; 50(3): 475. CrossRef - Antibiofilm Efficacy of Calcium Silicate-Based Endodontic Sealers
Matilde Ruiz-Linares, Vsevolod Fedoseev, Carmen Solana, Cecilia Muñoz-Sandoval, Carmen María Ferrer-Luque
Materials.2024; 17(16): 3937. CrossRef - Enhancing the Biological Properties of Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Calcium Silicate Cements: An In Vitro Study
Minji Choi, Jiyoung Kwon, Ji-Hyun Jang, Duck-Su Kim, Hyun-Jung Kim
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2024; 15(11): 337. CrossRef - Cytotoxicity and cell migration evaluation of a strontium silicate-based root canal sealer on stem cells from rat apical papilla: an in vitro study
Guanglei Zhou, Yu Zhao, Liangjing Cai, Liwei Liu, Xu Li, Lu Sun, Jiayin Deng
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - An In Vitro Comparative Analysis of Physico–Mechanical Properties of Commercial and Experimental Bioactive Endodontic Sealers
Abdulmajeed Kashaf, Faisal Alonaizan, Khalid S. Almulhim, Dana Almohazey, Deemah Abdullah Alotaibi, Sultan Akhtar, Ashwin C. Shetty, Abdul Samad Khan
Bioengineering.2024; 11(11): 1079. CrossRef - Chemical, Antibacterial, and Cytotoxic Properties of Four Different Endodontic Sealer Leachates Over Time
Jo-Hsun Chen, Veksina Raman, Sarah A. Kuehne, Josette Camilleri, Josefine Hirschfeld
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(11): 1612. CrossRef - Comparative Analysis of Fracture Resistance of Endodontic Sealer Types and Filling Methods
Yun Song, Kee-Deog Kim, Bock-Young Jung, Wonse Park, Nan-Sim Pang
Materials.2024; 18(1): 40. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Removal of Bioceramic Sealers Using Rotary Retreatment Files Supplemented with Passive Ultrasonic Activation: An In Vitro Study
Anuradha B Patil, Amrut Bambawale, Pooja R Barghare, Sumanthini V Margasahayam, Divya Naik, Jayeeta S Verma
World Journal of Dentistry.2024; 15(4): 292. CrossRef - Nonsurgical Endodontic Management of Nonperforating Internal Root Resorption in a Maxillary Central Incisor: A Case Report with a 4-Year Follow-Up
Paras M. Gehlot, Divya S. Rajkumar, Annapoorna B. Mariswamy, Upendra Natha N. Reddy, Chaitanya Chappidi
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2024; 16(Suppl 3): S3005. CrossRef - Evaluating the Sealing Performance of Endodontic Sealers: Insights Into Achieving Complete Sealing
Ajay Chhabra, Ramya K P., Saravana Prathap, Priyanka Yadav, Himani Mehra, Sona J Parvathy
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of vehicles on the physical properties and biocompatibility of premixed calcium silicate cements
Gitae SON, Gyeung Mi SEON, Sang Hoon CHOI, Hyeong-Cheol YANG
Dental Materials Journal.2024; 43(2): 276. CrossRef - Comparative cytotoxicity study of putty- and powder-type calcium silicate cements
Sora Park, Dohyun Cho, Ji Hyeon Yoon, Yeonjoo Kang, Quang Canh Vo, Gitae Son, Hongjoo Park, Hyeong-Cheol Yang
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2024; 51(4): 259. CrossRef - Physical-chemical properties and acellular bioactivity of newly prepared nano-tricalcium silicate-58s bioactive glass-based endodontic sealer
Nawal A. Al-Sabawi, Sawsan Hameed Al-Jubori
Journal of Oral Biosciences.2023; 65(4): 305. CrossRef - Dentinal Tubule Penetrability and Bond Strength of Two Novel Calcium Silicate-Based Root Canal Sealers
Karissa Shieh, Jack Yang, Elsa Heng Zhu, Ove Andreas Peters, Sepanta Hosseinpour
Materials.2023; 16(9): 3309. CrossRef - Cytotoxicity and Mineralization Activity of Calcium Silicate-Based Root Canal Sealers Compared to Conventional Resin-Based Sealer in Human Gingival Fibroblast Cells
Mohammad Shokrzadeh, Farzaneh Sadat Motafeghi, Anahita Lotfizadeh, Mohammad Ghorbani, Azam Haddadi Kohsar, Cesar Rogério Pucci
International Journal of Dentistry.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Effect of three different photosensitizers in photodynamic therapy on bond strength of a calcium silicate‐based sealer to radicular dentin
Cihan Küden, Seda Nur Karakaş
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(S1): 265. CrossRef - Effect of endodontic sealer on postoperative pain: a network meta-analysis
Cynthia Maria Chaves Monteiro, Ana Cristina Rodrigues Martins, Alessandra Reis, Juliana Larocca de Geus
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Antimicrobial Activity of Five Calcium Silicate Based Root Canal Sealers against a Multispecies Engineered Biofilm: An In Vitro Study
Carla Zogheib, Issam Khalil, Wajih Hage, Dolla Karam Sarkis, Mireille Kallasy, Germain Sfeir, May Mallah, Roula El Hachem
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2023; 24(9): 707. CrossRef - Calcium silicate sealers in endodontics
Archana Chavan, Nidambur Ballal
Acta stomatologica Naissi.2023; 39(87): 2624. CrossRef - Assessing the Sealing Performance and Clinical Outcomes of Endodontic Treatment in Patients with Chronic Apical Periodontitis Using Epoxy Resin and Calcium Salicylate Seals
Razvan Mihai Horhat, Bogdan Andrei Bumbu, Laura Orel, Oana Velea-Barta, Laura Cirligeriu, Gratiana Nicoleta Chicin, Marius Pricop, Mircea Rivis, Stefania Dinu, Delia Ioana Horhat, Felix Bratosin, Roxana Manuela Fericean, Rodica Anamaria Negrean, Luminita
Medicina.2023; 59(6): 1137. CrossRef -
In Vitro Cytotoxicity and Mineralization Potential of an Endodontic Bioceramic Material
Soumya Sheela, Mohannad Nassar, Fatma M. AlGhalban, Mehmet O. Gorduysus
European Journal of Dentistry.2023; 17(02): 548. CrossRef - Dislodgment Resistance, Adhesive Pattern, and Dentinal Tubule Penetration of a Novel Experimental Algin Biopolymer-Incorporated Bioceramic-Based Root Canal Sealer
Galvin Sim Siang Lin, Norhayati Luddin, Huwaina Abd Ghani, Josephine Chang Hui Lai, Tahir Yusuf Noorani
Polymers.2023; 15(5): 1317. CrossRef - Impact of Final Irrigation Protocol on the Push-Out Bond Strength of Two Types of Endodontic Sealers
Germain Sfeir, Frédéric Bukiet, Wajih Hage, Roula El Hachem, Carla Zogheib
Materials.2023; 16(5): 1761. CrossRef - Clinical Approaches to the Three-Dimensional Endodontic Obturation Protocol for Teeth with Periapical Bone Lesions
Angela Gusiyska, Elena Dyulgerova
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(17): 9755. CrossRef - Evaluating the bioactivity of endodontic sealers with respect to their thermo-nanomechanical properties
Andreea Marica, Luminita Fritea, Florin Banica, Iosif Hulka, Gerlinde Rusu, Cosmin Sinescu, Traian Octavian Costea, Simona Cavalu
Materials Science-Poland.2023; 41(3): 126. CrossRef - Advances and challenges in regenerative dentistry: A systematic review of calcium phosphate and silicate-based materials on human dental pulp stem cells
B. Christie, N. Musri, N. Djustiana, V. Takarini, N. Tuygunov, M.N. Zakaria, A. Cahyanto
Materials Today Bio.2023; 23: 100815. CrossRef - Radiographic Evaluation of Periapical Healing Rates Between Bio-Ceramic Sealer and AH+ Sealer: A Retrospective Study
Dalia Nayil Alharith, Iman T. Mansi, YoumnaElsaid Abdulmotalib, HebaFuad Amous, TagreedSuliman Aljulban, Haifa Mohammed Al Aiban, Sali Mohamad Haffar
Annals of Dental Specialty.2023; 11(2): 124. CrossRef - Obturation canalaire
N. Linas, M.-L. Munoz-Sanchez, N. Decerle, P.-Y. Cousson
EMC - Médecine buccale.2023; 16(5): 1. CrossRef - Biodentine Inhibits the Initial Microbial Adhesion of Oral Microbiota In Vivo
Ali Al-Ahmad, Michael Haendel, Markus Altenburger, Lamprini Karygianni, Elmar Hellwig, Karl Wrbas, Kirstin Vach, Christian Tennert
Antibiotics.2022; 12(1): 4. CrossRef - Pilot Evaluation of Sealer-Based Root Canal Obturation Using Epoxy-Resin-Based and Calcium-Silicate-Based Sealers: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Minju Song, Min-Gyu Park, Sang-Won Kwak, Ruben H. Kim, Jung-Hong Ha, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Materials.2022; 15(15): 5146. CrossRef - The antibacterial activity of mineral trioxide aggregate containing calcium fluoride
Miyoung Lim, Seunghoon Yoo
Journal of Dental Sciences.2022; 17(2): 836. CrossRef - Physicochemical and Mechanical Properties of Premixed Calcium Silicate and Resin Sealers
Naji Kharouf, Salvatore Sauro, Ammar Eid, Jihed Zghal, Hamdi Jmal, Anta Seck, Valentina Macaluso, Frédéric Addiego, Francesco Inchingolo, Christine Affolter-Zbaraszczuk, Florent Meyer, Youssef Haikel, Davide Mancino
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2022; 14(1): 9. CrossRef - Comparison of Fracture Resistance between Single-cone and Warm Vertical Compaction Technique Using Bio-C Sealer® in Mandibular Incisors: An In Vitro Study
Raphael Lichaa, George Deeb, Rami Mhanna, Carla Zogheib
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2022; 23(2): 143. CrossRef - In vitro physicochemical characterization of five root canal sealers and their influence on an ex vivo oral multi‐species biofilm community
Flavia M. Saavedra, Lauter E. Pelepenko, William S. Boyle, Anqi Zhang, Christopher Staley, Mark C. Herzberg, Marina A. Marciano, Bruno P. Lima
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(7): 772. CrossRef - Premixed Calcium Silicate-Based Root Canal Sealer Reinforced with Bioactive Glass Nanoparticles to Improve Biological Properties
Min-Kyung Jung, So-Chung Park, Yu-Jin Kim, Jong-Tae Park, Jonathan C. Knowles, Jeong-Hui Park, Khandmaa Dashnyam, Soo-Kyung Jun, Hae-Hyoung Lee, Jung-Hwan Lee
Pharmaceutics.2022; 14(9): 1903. CrossRef - A critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study root canal fillings
Gustavo De‐Deus, Erick Miranda Souza, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Marco Simões‐Carvalho, Daniele Moreira Cavalcante, Marco Aurélio Versiani
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S2): 384. CrossRef - Bioactivity Potential of Bioceramic-Based Root Canal Sealers: A Scoping Review
Mauro Schmitz Estivalet, Lucas Peixoto de Araújo, Felipe Immich, Adriana Fernandes da Silva, Nadia de Souza Ferreira, Wellington Luiz de Oliveira da Rosa, Evandro Piva
Life.2022; 12(11): 1853. CrossRef - The influence of humidity on bond strength of AH Plus, BioRoot RCS, and Nanoseal-S sealers
Sunanda Laxman Gaddalay, Damini Vilas Patil, Ramchandra Kabir
Endodontology.2022; 34(3): 202. CrossRef - The Effect of Bioceramic HiFlow and EndoSequence Bioceramic Sealers on Increasing the Fracture Resistance of Endodontically Treated Teeth: An In Vitro Study
Mohamad Khir Abdulsamad Alskaf, Hassan Achour, Hasan Alzoubi
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Unravelling the effects of ibuprofen-acetaminophen infused copper-bioglass towards the creation of root canal sealant
Chitra S, Riju Chandran, Ramya R, Durgalakshmi D, Balakumar S
Biomedical Materials.2022; 17(3): 035001. CrossRef - A Micro-CT Analysis of Initial and Long-Term Pores Volume and Porosity of Bioactive Endodontic Sealers
Mateusz Radwanski, Michal Leski, Adam K. Puszkarz, Jerzy Sokolowski, Louis Hardan, Rim Bourgi, Salvatore Sauro, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska
Biomedicines.2022; 10(10): 2403. CrossRef - A comprehensive in vitro comparison of the biological and physicochemical properties of bioactive root canal sealers
Sabina Noreen Wuersching, Christian Diegritz, Reinhard Hickel, Karin Christine Huth, Maximilian Kollmuss
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 26(10): 6209. CrossRef - Stability and solubility test of endodontic materials
Ivan Matovic, Jelena Vucetic
Stomatoloski glasnik Srbije.2022; 69(4): 169. CrossRef - Antimicrobial effectiveness of root canal sealers againstEnterococcus faecalis
Paola Castillo-Villagomez, Elizabeth Madla-Cruz, Fanny Lopez-Martinez, Idalia Rodriguez-Delgado, Jorge Jaime Flores-Treviño, Guadalupe Ismael Malagon-Santiago, Myriam Angelica de La Garza-Ramos
Biomaterial Investigations in Dentistry.2022; 9(1): 47. CrossRef - Tricalcium silicate cement sealers
Anita Aminoshariae, Carolyn Primus, James C. Kulild
The Journal of the American Dental Association.2022; 153(8): 750. CrossRef - Influence of variations in the environmental pH on the solubility and water sorption of a calcium silicate‐based root canal sealer
E. J. N. L. Silva, C. M. Ferreira, K. P. Pinto, A. F. A. Barbosa, M. V. Colaço, L. M. Sassone
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(8): 1394. CrossRef - Calcium Silicate-Based Root Canal Sealers: A Narrative Review and Clinical Perspectives
Germain Sfeir, Carla Zogheib, Shanon Patel, Thomas Giraud, Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Frédéric Bukiet
Materials.2021; 14(14): 3965. CrossRef - Development of A Nano-Apatite Based Composite Sealer for Endodontic Root Canal Filling
Angelica Bertacci, Daniele Moro, Gianfranco Ulian, Giovanni Valdrè
Journal of Composites Science.2021; 5(1): 30. CrossRef - Bone repair in defects filled with AH Plus sealer and different concentrations of MTA: a study in rat tibiae
Jessica Emanuella Rocha Paz, Priscila Oliveira Costa, Albert Alexandre Costa Souza, Ingrid Macedo de Oliveira, Lucas Fernandes Falcão, Carlos Alberto Monteiro Falcão, Maria Ângela Area Leão Ferraz, Lucielma Salmito Soares Pinto
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Characterization, Antimicrobial Effects, and Cytocompatibility of a Root Canal Sealer Produced by Pozzolan Reaction between Calcium Hydroxide and Silica
Mi-Ah Kim, Vinicius Rosa, Prasanna Neelakantan, Yun-Chan Hwang, Kyung-San Min
Materials.2021; 14(11): 2863. CrossRef - Synthesis and Characterization of Novel Calcium-Silicate Nanobioceramics with Magnesium: Effect of Heat Treatment on Biological, Physical and Chemical Properties
Konstantina Kazeli, Ioannis Tsamesidis, Anna Theocharidou, Lamprini Malletzidou, Jonathan Rhoades, Georgia K. Pouroutzidou, Eleni Likotrafiti, Konstantinos Chrissafis, Theodoros Lialiaris, Lambrini Papadopoulou, Eleana Kontonasaki, Evgenia Lymperaki
Ceramics.2021; 4(4): 628. CrossRef - Calcium Silicate Cements vs. Epoxy Resin Based Cements: Narrative Review
Mario Dioguardi, Cristian Quarta, Diego Sovereto, Giuseppe Troiano, Khrystyna Zhurakivska, Maria Bizzoca, Lorenzo Lo Muzio, Lucio Lo Russo
Oral.2021; 1(1): 23. CrossRef - In Vitro Microleakage Evaluation of Bioceramic and Zinc-Eugenol Sealers with Two Obturation Techniques
Francesco De Angelis, Camillo D’Arcangelo, Matteo Buonvivere, Rachele Argentino, Mirco Vadini
Coatings.2021; 11(6): 727. CrossRef - Efficacy Of Calcium Silicate-Based Sealers In Root Canal Treatment: A Systematic Review
Hattan Mohammed Omar Baismail, Mohammed Ghazi Moiser Albalawi, Alaa Mofareh Thoilek Alanazi, Muhannad Atallah Saleem Alatawi, Badr Soliman Alhussain
Annals of Dental Specialty.2021; 9(1): 87. CrossRef - Apical Sealing Ability of Two Calcium Silicate-Based Sealers Using a Radioactive Isotope Method: An In Vitro Apexification Model
Inês Raquel Pereira, Catarina Carvalho, Siri Paulo, José Pedro Martinho, Ana Sofia Coelho, Anabela Baptista Paula, Carlos Miguel Marto, Eunice Carrilho, Maria Filomena Botelho, Ana Margarida Abrantes, Manuel Marques Ferreira
Materials.2021; 14(21): 6456. CrossRef
-
13,928
View
-
254
Download
-
100
Crossref
-
Dental care for patients taking antiresorptive drugs: a literature review
-
Minju Song
-
Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(4):e42. Published online November 1, 2019
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e42
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
Antiresorptive drugs (ARDs), such as bisphosphonates or denosumab, that prevent bone resorption are widely used in patients with osteoporosis or with cancer that has metastasized to the bones. Although osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ) is a well-documented complication of ARD use, the benefits ARDs outweigh the complication. Thus, research has focused on finding ways to prevent or reduce the risk of developing ONJ. Dentists, as part of a multi-professional team, have a critical role in preventing ONJ. However, many dentists tend to hesitate to provide dental care to patients with ONJ, or tend to think that it is a problem to be dealt with by oral surgeons. This review gives an overview of ARD-related ONJ and provides the guidelines for dental care in patients taking ARDs to lower the risk of developing ONJ. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Successful prevention of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw after dental extractions by socket preservation with alloplast plus tetracycline in patients taking antiresorptive drugs
Liang-Ho Lin, Chun-Hsiang Wang, Shin-Yu Lu
Journal of Dental Sciences.2026; 21(1): 468. CrossRef - Dynamic Navigation in Endodontics: Scope, Benefits, and Challenges - A Systematic Review
Ankita Kapoor, Ragavi Alagarsamy, Babu Lal, Amal Singh Rana, Amandeep Kaur, Sidhartha Sharma, Ajay Logani
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(7): 879. CrossRef - Biosimilars in osteoporosis treatment: focus on denosumab
Matti Aapro, Peyman Hadji, Daniele Santini, Ralf Schmidmaier, Richard Eastell
Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy.2025; 25(8): 887. CrossRef - Assessment of the occurrence of apical periodontitis and endodontically treated/non-treated teeth in a Lower Austrian patient population treated for osteoporosis: a cohort study
Pascal Grün, Marius Meier, Johannes Dittrich, Arb Gjergjindreaj, Dragan Ströbele, Florian Pfaffeneder-Mantai, Sepideh Hatamikia, Margrit-Ann Geibel, Dritan Turhani
Annals of Medicine & Surgery.2024; 86(9): 5049. CrossRef - Endodontic and periapical status of patients with osteoporosis
Selin Goker Kamalı, Dilek Turkaydın
The Journal of the American Dental Association.2024; 155(12): 1022. CrossRef - Postoperative pain in oncological patients subjected to nonsurgical root canal treatment: a prospective case-control study
Kaline Romeiro, Luciana F. Gominho, Isabela N. Rôças, José F. Siqueira Jr
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Periodontal ligament‐associated protein‐1 promotes osteoclastogenesis in mice by modulating TGF‐β1/Smad1 pathway
Shuang Liu, Xijiao Yu, Qiushuang Guo, Shuaiqi Zhao, Kaixian Yan, Meng Hou, Fuxiang Bai, Shu Li
Journal of Periodontology.2024; 95(2): 146. CrossRef - What Is the Appropriate Antibiotic Administration During Tooth Extractions in Patients Receiving High-Dose Denosumab?
Eiji Iwata, Takumi Hasegawa, Hiroaki Ohori, Toshiya Oko, Tsutomu Minamikawa, Daisuke Miyai, Masaki Kobayashi, Naoki Takata, Shungo Furudoi, Junichiro Takeuchi, Kosuke Matsumoto, Akira Tachibana, Masaya Akashi
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Perfil Odontológico dos Pacientes em Uso de Bisfosfonatos em um Hospital Oncológico
Jade Fontenele Tagliabue, Lísia Daltro Borges Alves, Héliton Spíndola Antunes
Revista Brasileira de Cancerologia.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of the Degree of Information of Dental Surgeons about Antiresorptive Drugs According to the Time Since Graduation in Dentistry
Flávia Godinho Costa Wanderley Rocha, Roberto Paulo Correia de Araújo
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Osteonecrosis of the Jaw and Antiresorptive Agents in Benign and Malignant Diseases: A Critical Review Organized by the ECTS
Athanasios D Anastasilakis, Jessica Pepe, Nicola Napoli, Andrea Palermo, Christos Magopoulos, Aliya A Khan, M Carola Zillikens, Jean-Jacques Body
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 107(5): 1441. CrossRef - Accuracy of Dynamic Navigation for Non-Surgical Endodontic Treatment: A Systematic Review
Egle Marija Jonaityte, Goda Bilvinaite, Saulius Drukteinis, Andres Torres
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(12): 3441. CrossRef - Periapical status in patients affected by osteoporosis: A retrospective clinical study
Erika Cadoni, Francesca Ideo, Giuseppe Marongiu, Silvia Mezzena, Luca Frigau, Quirico Mela, Antonio Capone, Henry F. Duncan, Elisabetta Cotti
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2022; 8(5): 1068. CrossRef - LONG-TERM USE OF DENOSUMAB IN GIANT CELL TUMORS AND VERTEBRAL ANEURYSMAL BONE CYSTS
Pedro Luis Bazán, Micaela Cinalli, Felipe Lanari Zabiaur, Roberto Castelli, Claudio Silveri, José Luis Monayer, Enrique Gustavo Gobbi, Alejandro Maria Steverlynck
Coluna/Columna.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A 5-year retrospective cohort study of denosumab induced medication related osteonecrosis of the jaw in osteoporosis patients
Seoyeon Jung, Jaeyeon Kim, Jin Hoo Park, Ki-Yeol Kim, Hyung Jun Kim, Wonse Park
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Management of Patients under Treatment with Monoclonal Antibodies and New Biological Therapies
Marta Amigo-Basilio, Covadonga Álvarez-González, Carlos Cobo-Vázquez, Isabel Leco-Berrocal, Luis Miguel Sáez-Alcaide, Cristina Méniz-García
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(11): 4865. CrossRef - Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw, a Hidden Enemy. An Integrative Review
Odel Chediak-Barbur
Universitas Odontologica.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - A Retrospective Observational Study of Risk Factors for Denosumab-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw in Patients with Bone Metastases from Solid Cancers
Satoe Okuma, Yuhei Matsuda, Yoshiki Nariai, Masaaki Karino, Ritsuro Suzuki, Takahiro Kanno
Cancers.2020; 12(5): 1209. CrossRef
-
4,507
View
-
52
Download
-
18
Crossref
-
Effects of the cathepsin K inhibitor with mineral trioxide aggregate cements on osteoclastic activity
-
Hee-Sun Kim, Soojung Kim, Hyunjung Ko, Minju Song, Miri Kim
-
Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(2):e17. Published online April 23, 2019
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e17
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
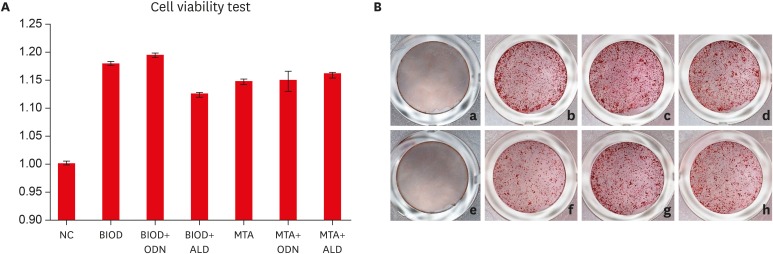
- Objectives
Root resorption is an unexpected complication after replantation procedures. Combining anti-osteoclastic medicaments with retrograde root filling materials may avert this resorptive activity. The purpose of this study was to assess effects of a cathepsin K inhibitor with calcium silicate-based cements on osteoclastic activity. MethodsMC3T3-E1 cells were cultured for biocompatibility analyses. RAW 264.7 cells were cultured in the presence of the receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B and lipopolysaccharide, followed by treatment with Biodentine (BIOD) or ProRoot MTA with or without medicaments (Odanacatib [ODN], a cathepsin inhibitor and alendronate, a bisphosphonate). After drug treatment, the cell counting kit-8 assay and Alizarin red staining were performed to evaluate biocompatibility in MC3T3-E1 cells. Reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction, tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) staining and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays were performed in RAW 264.7 cells to determine the expression levels of inflammatory cytokines, interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2). Data were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance and Tukey's post hoc test (p < 0.05). ResultsBiocompatibility results showed that there were no significant differences among any of the groups. RAW 264.7 cells treated with BIOD and ODN showed the lowest levels of TNF-α and PGE2. Treatments with BIOD + ODN were more potent suppressors of inflammatory cytokine expression (p < 0.05). ConclusionThe cathepsin K inhibitor with calcium silicate-based cement inhibits osteoclastic activity. This may have clinical application in preventing inflammatory root resorption in replanted teeth.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Root-filling materials for endodontic surgery: biological and clinical aspects
Andreas Koutroulis, Vasileios Kapralos, Dag Ørstavik, Pia Titterud Sunde
Biomaterial Investigations in Dentistry.2024; 11: 115. CrossRef - Effect of intra‐alveolar delivery of Frondoside A on inflammatory response of delayed tooth replantation
Lan Herr, Ju Ri Ye, Sang Wook Kang, Sang Tae Ro, Yong Kwon Chae, Ko Eun Lee, Mi Sun Kim, Myeong Kwan Jih, Chunui Lee, Sung Chul Choi, Ok Hyung Nam
Dental Traumatology.2024; 40(2): 178. CrossRef - Bone-targeting PLGA derived lipid drug delivery system ameliorates bone loss in osteoporotic ovariectomized rats
Youyun Zeng, Yiding Shen, Shuyi Wu, Lei Cai, Zhen Wang, Kexin Cai, Jiating Shen, Kendrick Hii Ru Yie, Hualin Zhang, Lihua Xu, Jinsong Liu
Materials & Design.2022; 221: 110967. CrossRef
-
1,576
View
-
8
Download
-
3
Crossref
-
A study on the compatibility between one-bottle dentin adhesives and composite resins using micro-shear bond strength
-
Minju Song, Yooseok Shin, Jeong-Won Park, Byoung-Duck Roh
-
Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(1):30-36. Published online September 26, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.1.30
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
This study was performed to determine whether the combined use of one-bottle self-etch adhesives and composite resins from same manufacturers have better bond strengths than combinations of adhesive and resins from different manufacturers. Materials and Methods25 experimental micro-shear bond test groups were made from combinations of five dentin adhesives and five composite resins with extracted human molars stored in saline for 24 hr. Testing was performed using the wire-loop method and a universal testing machine. Bond strength data was statistically analyzed using two way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Tukey's post hoc test. ResultsTwo way ANOVA revealed significant differences for the factors of dentin adhesives and composite resins, and significant interaction effect (p < 0.001). All combinations with Xeno V (Dentsply De Trey) and Clearfil S3 Bond (Kuraray Dental) adhesives showed no significant differences in micro-shear bond strength, but other adhesives showed significant differences depending on the composite resin (p < 0.05). Contrary to the other adhesives, Xeno V and BondForce (Tokuyama Dental) had higher bond strengths with the same manufacturer's composite resin than other manufacturer's composite resin. ConclusionsNot all combinations of adhesive and composite resin by same manufacturers failed to show significantly higher bond strengths than mixed manufacturer combinations.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Influence of etching mode and composite resin type on bond strength to dentin using universal adhesive system
Stefan Dačić, Milan Miljković, Aleksandar Mitić, Goran Radenković, Marija Anđelković‐Apostolović, Milica Jovanović
Microscopy Research and Technique.2021; 84(6): 1212. CrossRef - Is the presence of 10-MDP associated to higher bonding performance for self-etching adhesive systems? A meta-analysis of in vitro studies
Julia Fehrenbach, Cristina Pereira Isolan, Eliseu Aldrighi Münchow
Dental Materials.2021; 37(10): 1463. CrossRef - Dentin bond strengths of all-in-one adhesives combined with different manufacturers’ flowable resin composites
Koichi SHINKAI, Daiki YOSHII, Akira KOIDE, Masaya SUZUKI, Shiro SUZUKI
Dental Materials Journal.2021; 40(5): 1094. CrossRef - DİŞ HEKİMLİĞİNDE ADEZİV SİSTEMLER
Elmas TÜRKER, Buket AYNA
Atatürk Üniversitesi Diş Hekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of EDC on Dentin-Resin Shear Bond Strength and Demineralized Dentin Thermal Properties
Lin Tang, Yi Zhang, Yuhua Liu, Yongsheng Zhou
Materials.2016; 9(11): 920. CrossRef
-
1,473
View
-
7
Download
-
5
Crossref
-
Cytotoxicity of newly developed pozzolan cement and other root-end filling materials on human periodontal ligament cell
-
Minju Song, Tae-Sun Yoon, Sue-Youn Kim, Euiseong Kim
-
Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(1):39-44. Published online January 20, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.1.39
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
The purpose of this study was to evaluate in vitro cytotoxicity of the pozzolan cement and other root-end filling materials using human periodontal ligament cell. Materials and MethodsEndocem (Maruchi), white ProRoot MTA (Dentsply), white Angelus MTA (Angelus), and Super EBA (Bosworth Co.) were tested after set completely in an incubator at 37℃ for 7 days, Endocem was tested in two ways: 1) immediately after mixing (fresh specimens) and 2) after setting completely like other experimental materials. The methods for assessment included light microscopic examination, cell counting and WST-1 assay on human periodontal ligament cell. ResultsIn the results of microscopic examination and cell counting, Super EBA showed significantly lower viable cell than any other groups (p < 0.05). As the results of WST-1 assay, compared with untreated control group, there was no significant cell viability of the Endocem group. However, the fresh mixed Endocem group had significantly less cell viability. The cells exposed to ProRoot MTA and Angelus MTA showed the highest viability, whereas the cells exposed to Super EBA displayed the lowest viability (p < 0.05). ConclusionsThe cytotoxicity of the pozzolan cement (Endocem) was comparable with ProRoot MTA and Angelus MTA. Considering the difficult manipulation and long setting time of ProRoot MTA and Angelus MTA, Endocem can be used as the alternative of retrofilling material.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - In Vitro Biocompatibility of Calcium Silicate-Based Materials for Retrograde Endodontic Treatment Under Different Setting Conditions
Kremena Markova, Neshka Manchorova-Veleva, Veselina Todorova, Lyubomir Vangelov, Desislava Petkova
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2026; 17(3): 124. CrossRef - Effects of Three Retrograde Filling Materials on Production of Inflammatory Cytokines and Resorbing Mediators
Samaneh Arab, Marjan Bahraminasab, Masoumeh Motamedi, Jamshid Hadjati, Alaviye Vahid
Journal of Microbiota.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Physicochemical Properties, Cytocompatibility, and Biocompatibility of a Bioactive Glass Based Retrograde Filling Material
Kazumasa Murata, Ayako Washio, Takahiko Morotomi, Thira Rojasawasthien, Shoichiro Kokabu, Chiaki Kitamura
Nanomaterials.2021; 11(7): 1828. CrossRef - Cell migration and osteo/odontogenesis stimulation of iRoot FS as a potential apical barrier material in apexification
Y. Liu, X. M. Liu, J. Bi, S. Yu, N. Yang, B. Song, X. Chen
International Endodontic Journal.2020; 53(4): 467. CrossRef - Biocompatibility of Biodentine™ ® with Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells: In Vitro Study
Duaa Abuarqoub, Nazneen Aslam, Hanan Jafar, Zakariya Abu Harfil, Abdalla Awidi
Dentistry Journal.2020; 8(1): 17. CrossRef - A micro-computed tomographic study of remaining filling materials of two bioceramic sealers and epoxy resin sealer after retreatment
KyungJae Kim, Da Vin Kim, Sin-Young Kim, SungEun Yang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Gap Volume after Retrofilling Using 4 Different Filling Materials: Evaluation by Micro–computed Tomography
Sue Youn Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Su-Jung Shin, Euiseong Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(4): 635. CrossRef - Anti-inflammatory and Mineralization Effects of ProRoot MTA and Endocem MTA in Studies of Human and Rat Dental Pulps In Vitro and In Vivo
Do-Hee Kim, Ji-Hyun Jang, Bin-Na Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Sun-Hun Kim, Kyung-San Min, Jeong-Tae Koh, Yun-Chan Hwang
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(10): 1534. CrossRef - Effects of Three Calcium Silicate Cements on Inflammatory Response and Mineralization-Inducing Potentials in a Dog Pulpotomy Model
Chung-Min Kang, Jiwon Hwang, Je Seon Song, Jae-Ho Lee, Hyung-Jun Choi, Yooseok Shin
Materials.2018; 11(6): 899. CrossRef - Cytocompatibility of Biodentine and iRoot FS with human periodontal ligament cells: an in vitro study
T. Luo, J. Liu, Y. Sun, Y. Shen, L. Zou
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(7): 779. CrossRef - Biological response of commercially available different tricalcium silicate‐based cements and pozzolan cement
Serhat Köseoğlu, Tuğba Pekbağr?yan?k, Ebru Kucukyilmaz, Mehmet Sağlam, Sukru Enhos, Ayşe Akgün
Microscopy Research and Technique.2017; 80(9): 994. CrossRef - Biological efficacy of two mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA)-based materials in a canine model of pulpotomy
Myeongyeon LEE, Chung-Min KANG, Je Seon SONG, Yooseok SHIN, Seunghye KIM, Seong-Oh KIM, Hyung-Jun CHOI
Dental Materials Journal.2017; 36(1): 41. CrossRef - Cytotoxicities and genotoxicities of cements based on calcium silicate and of dental formocresol
Hyunjung Ko, Youngdan Jeong, Miri Kim
Mutation Research/Genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis.2017; 815: 28. CrossRef - Bioactive-glass in Endodontic Therapy and Associated Microsurgery
Andrea Corrado Profeta, Gian Marco Prucher
The Open Dentistry Journal.2017; 11(1): 164. CrossRef - A Randomized Controlled Study of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate and Super Ethoxybenzoic Acid as Root-end Filling Materials in Endodontic Microsurgery: Long-term Outcomes
Sunil Kim, Minju Song, Su-Jung Shin, Euiseong Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(7): 997. CrossRef - Effects of two fast-setting calcium-silicate cements on cell viability and angiogenic factor release in human pulp-derived cells
Chooryung J. Chung, Euiseong Kim, Minju Song, Jeong-Won Park, Su-Jung Shin
Odontology.2016; 104(2): 143. CrossRef - Cytotoxicity and Initial Biocompatibility of Endodontic Biomaterials (MTA and Biodentine™) Used as Root-End Filling Materials
Diana María Escobar-García, Eva Aguirre-López, Verónica Méndez-González, Amaury Pozos-Guillén
BioMed Research International.2016; 2016: 1. CrossRef - In Vitro Cytotoxicity Evaluation of Three Root-End Filling Materials in Human Periodontal Ligament Fibroblasts
Hernán Coaguila-Llerena, Abraham Vaisberg, Zulema Velásquez-Huamán
Brazilian Dental Journal.2016; 27(2): 187. CrossRef - Dynamic intratubular biomineralization following root canal obturation with pozzolan‐based mineral trioxide aggregate sealer cement
Yeon‐Jee Yoo, Seung‐Ho Baek, Kee‐Yeon Kum, Won‐Jun Shon, Kyung‐Mi Woo, WooCheol Lee
Scanning.2016; 38(1): 50. CrossRef - A Randomized Controlled Study of the Use of ProRoot Mineral Trioxide Aggregate and Endocem as Direct Pulp Capping Materials
Minju Song, Minji Kang, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Euiseong Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(1): 11. CrossRef - Comparative Analysis of Selected Physicochemical Properties of Pozzolan Portland and MTA-Based Cements
Maura Cristiane Gonçales Orçati Dorileo, Ricardo Dalla Villa, Orlando Aguirre Guedes, Andreza Maria Fábio Aranha, Alex Semenoff-Segundo, Matheus Coelho Bandeca, Alvaro Henrique Borges
International Scholarly Research Notices.2014; 2014: 1. CrossRef - Surgical endodontics: past, present, and future
James L. Gutmann
Endodontic Topics.2014; 30(1): 29. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of physicochemical properties of root perforation sealer materials
Maura Cristiane Gonçales Orçati Dorileo, Fábio Luis Miranda Pedro, Matheus Coelho Bandeca, Orlando Aguirre Guedes, Ricardo Dalla Villa, Alvaro Henrique Borges
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(3): 201. CrossRef
-
1,662
View
-
1
Download
-
23
Crossref
-
Inhibition of Streptococcus mutans biofilm formation on composite resins containing ursolic acid
-
Soohyeon Kim, Minju Song, Byoung-Duck Roh, Sung-Ho Park, Jeong-Won Park
-
Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(2):65-72. Published online May 28, 2013
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.2.65
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
To evaluate the inhibitory effect of ursolic acid (UA)-containing composites on Streptococcus mutans (S. mutans) biofilm. Materials and MethodsComposite resins with five different concentrations (0.04, 0.1, 0.2, 0.5, and 1.0 wt%) of UA (U6753, Sigma Aldrich) were prepared, and their flexural strengths were measured according to ISO 4049. To evaluate the effect of carbohydrate source on biofilm formation, either glucose or sucrose was used as a nutrient source, and to investigate the effect of saliva treatment, the specimen were treated with either unstimulated whole saliva or phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). For biofilm assay, composite disks were transferred to S. mutans suspension and incubated for 24 hr. Afterwards, the specimens were rinsed with PBS and sonicated. The colony forming units (CFU) of the disrupted biofilm cultures were enumerated. For growth inhibition test, the composites were placed on a polystyrene well cluster, and S. mutans suspension was inoculated. The optical density at 600 nm (OD600) was recorded by Infinite F200 pro apparatus (TECAN). One-way ANOVA and two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni correction were used for the data analyses. ResultsThe flexural strength values did not show significant difference at any concentration (p > 0.01). In biofilm assay, the CFU score decreased as the concentration of UA increased. The influence of saliva pretreatment was conflicting. The sucrose groups exhibited higher CFU score than glucose group (p < 0.05). In bacterial growth inhibition test, all experimental groups containing UA resulted in complete inhibition. ConclusionsWithin the limitations of the experiments, UA included in the composite showed inhibitory effect on S. mutans biofilm formation and growth.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Environmental Stress Induces Altered Composition of Streptococcus mutans Membrane Vesicles: pH‐Driven Changes in Membrane Vesicle Production and Composition
Taylor C. Boone, Swetha K. Shankar, Melodie L. Weller
Molecular Oral Microbiology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Anti-cariogenic effect of experimental resin cement containing ursolic acid using dental microcosm biofilm
Jonghyun Jo, Mi-Jeong Jeon, Sun Kyu Park, Su-Jung Shin, Baek-il Kim, Jeong-Won Park
Journal of Dentistry.2024; 151: 105447. CrossRef - Rapid specific detection of oral bacteria using Cas13-based SHERLOCK
Jett Liu, Camden Carmichael, Hatice Hasturk, Wenyuan Shi, Batbileg Bor
Journal of Oral Microbiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Novel Bioactive Nanocomposites Containing Calcium Fluoride and Calcium Phosphate with Antibacterial and Low-Shrinkage-Stress Capabilities to Inhibit Dental Caries
Abdullah Alhussein, Rashed Alsahafi, Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad, Lamia Mokeem, Abraham Schneider, Mary-Ann Jabra-Rizk, Radi Masri, Gary D. Hack, Thomas W. Oates, Jirun Sun, Michael D. Weir, Hockin H. K. Xu
Bioengineering.2023; 10(9): 991. CrossRef - Quorum sensing inhibition and antibiofilm action of triterpenoids: An updated insight
Sudipta Paul Bhattacharya, Snigdha Karmakar, Kusumita Acharya, Arijit Bhattacharya
Fitoterapia.2023; 167: 105508. CrossRef - The Application of Small Molecules to the Control of Typical Species Associated With Oral Infectious Diseases
Sirui Yang, Xiaoying Lyu, Jin Zhang, Yusen Shui, Ran Yang, Xin Xu
Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Anti-Planktonic and Anti-Biofilm Properties of Pentacyclic Triterpenes—Asiatic Acid and Ursolic Acid as Promising Antibacterial Future Pharmaceuticals
Zuzanna Sycz, Dorota Tichaczek-Goska, Dorota Wojnicz
Biomolecules.2022; 12(1): 98. CrossRef - Development and Physicochemical Characterization of Eugenia brejoensis Essential Oil-Doped Dental Adhesives with Antimicrobial Action towards Streptococcus mutans
Maury Luz Pereira, Danyelle Cristina Pereira Santos, Carlos Alberto Mendes Soares Júnior, Tamyris Alicely Xavier Nogueira Bazan, Clovis Macêdo Bezerra Filho, Márcia Vanusa da Silva, Maria Tereza dos Santos Correia, Andres Felipe Millan Cardenas, Fabiana S
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2022; 13(3): 149. CrossRef - Does Secondary Plant Metabolite Ursolic Acid Exhibit Antibacterial Activity against Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Living in Single- and Multispecies Biofilms?
Zuzanna Sycz, Dorota Wojnicz, Dorota Tichaczek-Goska
Pharmaceutics.2022; 14(8): 1691. CrossRef - Prolonged Inhibition of Streptococcus mutans Growth and Biofilm Formation by Sustained Release of Chlorhexidine from Varnish Coated Dental Abutments: An in Vitro Study
Mark Feldman, Walid Shaaban Moustafa Elsayed, Michael Friedman, Irith Gati, Doron Steinberg, Hesham Marei, Paolo Francesco Manicone
International Journal of Dentistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Interkingdom Signaling Interference: The Effect of Plant-Derived Small Molecules on Quorum Sensing in Plant-Pathogenic Bacteria
Janak Raj Joshi, Netaly Khazanov, Amy Charkowski, Adi Faigenboim, Hanoch Senderowitz, Iris Yedidia
Annual Review of Phytopathology.2021; 59(1): 153. CrossRef - Small Molecule Compounds, A Novel Strategy against Streptococcus mutans
Sirui Yang, Jin Zhang, Ran Yang, Xin Xu
Pathogens.2021; 10(12): 1540. CrossRef - Titanium dioxide nanotubes added to glass ionomer cements affect S. mutans viability and mechanisms of virulence
Isaac Jordão de Souza ARAÚJO, Mariana Gallante RICARDO, Orisson Ponce GOMES, Priscila Alves GIOVANI, Júlia PUPPIN-RONTANI, Vanessa Arias PECORARI, Elizabeth Ferreira MARTINEZ, Marcelo Henrique NAPIMOGA, Francisco Humberto NOCITI JUNIOR, Regina Maria PUPPI
Brazilian Oral Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Ursolic and Oleanolic Acids on Lipid Membranes: Studies on MRSA and Models of Membranes
Sandrine Verstraeten, Lucy Catteau, Laila Boukricha, Joelle Quetin-Leclercq, Marie-Paule Mingeot-Leclercq
Antibiotics.2021; 10(11): 1381. CrossRef - Ursolic acid inhibits multi-species biofilms developed by Streptococcus mutans, Streptococcus sanguinis, and Streptococcus gordonii
Xiaoying Lyu, Liang Wang, Yusen Shui, Qingsong Jiang, Lan Chen, Wen Yang, Xiaoya He, Jumei Zeng, Yuqing Li
Archives of Oral Biology.2021; 125: 105107. CrossRef - The physical properties and anticariogenic effect of experimental resin cement containing ursolic acid
Hyunkyung Yoo, So Youn Kim, Su-Jung Shin, Jeong-Won Park
Odontology.2021; 109(3): 641. CrossRef - Ursolic acid: A systematic review of its pharmacology, toxicity and rethink on its pharmacokinetics based on PK-PD model
Qiang Sun, Man He, Meng Zhang, Sha Zeng, Li Chen, Lijuan Zhou, Haibo Xu
Fitoterapia.2020; 147: 104735. CrossRef - Effects of UVB and UVC irradiation on cariogenic bacteria in vitro
Shigeki Uchinuma, Yasushi Shimada, Khairul Matin, Keiichi Hosaka, Masahiro Yoshiyama, Yasunori Sumi, Junji Tagami
Lasers in Medical Science.2019; 34(5): 981. CrossRef - Ursolic acid (UA): A metabolite with promising therapeutic potential
Dharambir Kashyap, Hardeep Singh Tuli, Anil K. Sharma
Life Sciences.2016; 146: 201. CrossRef - Protective Effects on Gastric Lesion of Ursolic acid
Sun Whoe Kim, In Young Hwang, Sun Yi Lee, Choon Sik Jeong
Journal of Food Hygiene and Safety.2016; 31(4): 286. CrossRef - Ursolic Acid—A Pentacyclic Triterpenoid with a Wide Spectrum of Pharmacological Activities
Łukasz Woźniak, Sylwia Skąpska, Krystian Marszałek
Molecules.2015; 20(11): 20614. CrossRef - Antibacterial effect of self-etching adhesive systems onStreptococcus mutans
Seung-Ryong Kim, Dong-Hoon Shin
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(1): 32. CrossRef - Dental materials with antibiofilm properties
Zhejun Wang, Ya Shen, Markus Haapasalo
Dental Materials.2014; 30(2): e1. CrossRef - Antibacterial properties of composite resins incorporating silver and zinc oxide nanoparticles onStreptococcus mutansandLactobacillus
Shahin Kasraei, Lida Sami, Sareh Hendi, Mohammad-Yousef AliKhani, Loghman Rezaei-Soufi, Zahra Khamverdi
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(2): 109. CrossRef - Synergistic effect of xylitol and ursolic acid combination on oral biofilms
Yunyun Zou, Yoon Lee, Jinyoung Huh, Jeong-Won Park
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(4): 288. CrossRef - The virulence of Streptococcus mutans and the ability to form biofilms
W. Krzyściak, A. Jurczak, D. Kościelniak, B. Bystrowska, A. Skalniak
European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases.2014; 33(4): 499. CrossRef
-
1,948
View
-
5
Download
-
26
Crossref
-
A survey of experience-based preference of Nickel-Titanium rotary files and incidence of fracture among general dentists
-
WooCheol Lee, Minju Song, Euiseong Kim, Hyojin Lee, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
-
Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(4):201-206. Published online November 21, 2012
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.4.201
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
The purpose was to investigate the preference and usage technique of NiTi rotary instruments and to retrieve data on the frequency of re-use and the estimated incidence of file separation in the clinical practice among general dentists. Materials and MethodsA survey was disseminated via e-mail and on-site to 673 general dentists. The correlation between the operator's experience or preferred technique and frequency of re-use or incidence of file fracture was assessed. ResultsA total of 348 dentists (51.7%) responded. The most frequently used NiTi instruments was ProFile (39.8%) followed by ProTaper. The most preferred preparation technique was crown-down (44.6%). 54.3% of the respondents re-used NiTi files more than 10 times. There was a significant correlation between experience with NiTi files and the number of reuses (p = 0.0025). 54.6% of the respondents estimated experiencing file separation less than 5 times per year. The frequency of separation was significantly correlated with the instrumentation technique (p = 0.0003). ConclusionsA large number of general dentists in Korea prefer to re-use NiTi rotary files. As their experience with NiTi files increased, the number of re-uses increased, while the frequency of breakage decreased. Operators who adopt the hybrid technique showed less tendency of separation even with the increased number of re-use.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Migration of a Separated Endodontic File Into the Mandibular Canal: An 8-Year Follow-up Case Report
Chiaki Akiba Katz, Misaki Fujimoto, Hidetaka Kuroda, Koichiro Muromachi
Journal of Endodontics.2026; 52(2): 321. CrossRef - Adoption of rotary instrumentation among general practitioners in Qassim region, Saudi Arabia: A cross-sectional survey
Badi B. Alotaibi
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2024; 14(2): 181. CrossRef - Undergraduate Endodontic Training and Its Relation to Contemporary Practice: Multicenter Cross-Sectional Study in Saudi Arabia
Fahda N. Algahtani, Reem M. Barakat, Lujain M. Alqarni, Alanoud F. Alqabbani, Manal F. Alkadi, Rahaf A. Almohareb, André Luiz Ferreira Costa
International Journal of Clinical Practice.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Fracture Incidence of Kedo-S Square Pediatric Rotary Files: A Prospective Clinical Study
Lakshimi Lakshmanan, Ganesh Jeevanandan, Prabhadevi C Maganur, Satish Vishwanathaiah
European Journal of Dentistry.2022; 16(03): 594. CrossRef - Prevention and management of fractured instruments in endodontic treatment
Wei-Rong Tang
World Journal of Surgical Procedures.2015; 5(1): 82. CrossRef - Influence of operator's experience level on lifespan of the WaveOne Primary file in extracted teeth
Abdulrahman Mohammed Saleh, Saeid Tavanafar, Pouyan Vakili-Gilani, Noor Jamal Al Sammerraie, Faahim Rashid
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 222. CrossRef
-
2,062
View
-
11
Download
-
6
Crossref
-
Success and failure of endodontic microsurgery
-
Minju Song, Euiseong Kim
-
Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(1):66-66. Published online February 4, 2012
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.1.66
-
-
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
-
Success and failure of endodontic microsurgery
-
Minju Song, Euiseong Kim
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(6):465-476. Published online November 30, 2011
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.6.465
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
In current endodontic practice, introduction of operating microscope, ultrasonic instruments, and microinstruments has induced a big change in the field of surgical retreatment. In this study, we aimed to offer key steps of endodontic microsurgery procedure compared with traditional root-end surgery, and to evaluate factors influencing success and failure based on published articles.
Endodontic microsurgery is a surgical procedure performed with the aid of a microscope, ultrasonic instruments and modern microsurgical instruments. The microscope provides magnification and illumination - essential for identifying minute details of the apical anatomy. Ultrasonic instruments facilitate the precise root-end preparation that is within the anatomical space of the canal. Modern endodontics can therefore be performed with precision and predictability, thus eliminating the disadvantages inherent in traditional periapical surgery such as large osteotomy, beveled apicoectomy, inaccurate root-end preparation and the inability to observe isthmus.
Factors influencing the outcomes of endodontic microsurgery may be diverse, but standardization of procedures can minimize its range. Among patient and tooth-related factors, periodontal status and tooth position are known to be prognostic, but there are only few articles concerning this matter. High-evidence randomized clinical trials or prospective cohort studies are needed to confirm these findings. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Treatment-Related Factors Affecting the Success of Endodontic Microsurgery and the Influence of GTR on Radiographic Healing—A Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Study
Daniel Bieszczad, Jarosław Wichlinski, Tomasz Kaczmarzyk
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(19): 6382. CrossRef - Factors Affecting the Success of Endodontic Microsurgery: A Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Study
Daniel Bieszczad, Jaroslaw Wichlinski, Tomasz Kaczmarzyk
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(14): 3991. CrossRef - Comparison of Clinical Outcomes of Endodontic Microsurgery: 1 Year versus Long-term Follow-up
Minju Song, Taekjin Nam, Su-Jung Shin, Euiseong Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2014; 40(4): 490. CrossRef - The Influence of Bone Tissue Deficiency on the Outcome of Endodontic Microsurgery: A Prospective Study
Minju Song, Sahng Gyoon Kim, Su-Jung Shin, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Euiseong Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2013; 39(11): 1341. CrossRef - Prognostic Factors of Clinical Outcomes in Endodontic Microsurgery: A Prospective Study
Minju Song, Sahng Gyoon Kim, Seung-Jong Lee, Baekil Kim, Euiseong Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2013; 39(12): 1491. CrossRef - Is stopping of anticoagulant therapy really required in a minor dental surgery? - How about in an endodontic microsurgery?
Yong-Wook Cho, Euiseong Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(3): 113. CrossRef
-
2,460
View
-
35
Download
-
6
Crossref
-
Evaluation of canal preparation for apical sealing with various Ni-Ti rotary instruments
-
Yooseok Shin, Su-Jung Shin, Minju Song, Euiseong Kim
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(4):300-305. Published online July 31, 2011
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.4.300
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
-
Objectives
The aim of this study was to evaluate the various NiTi rotary instruments regarding their ability to provide a circular apical preparation.
Materials and Methods
50 single canal roots were selected, cut at the cementodentinal junction and the coronal 1/3 of the canals was flared using Gates Glidden burs. Samples were randomly divided into 5 experimental groups of 10 each. In group I, GT files, Profile 04 and Quantec #9 and #10 files were used. In Group II Lightspeed was used instead of Quantec. In Group III, Orifice shaper, Profile .06 series and Lightspeed were used. In Group IV, Quantec #9 and #10 files were used instead of Lightspeed. In Group V, the GT file and the Profile .04 series were used to prepare the entire canal length. All tooth samples were cut at 1 mm, 3 mm and 5 mm from the apex and were examined under the microscope.
Results
Groups II and III (Lightspeed) showed a more circular preparation in the apical 1mm samples than the groups that used Quantec (Group I & IV) or GT files and Profile .04 series.(Group V)(p < 0.05) There was no significant difference statistically among the apical 3, 5 mm samples. In 5 mm samples, most of the samples showed complete circularity and none of them showed irregular shape.
Conclusions
Lightspeed showed circular preparation at apical 1 mm more frequently than other instruments used in this study. However only 35% of samples showed circularity even in the Lightspeed Group which were enlarged 3 ISO size from the initial apical binding file (IAF) size. So it must be considered that enlarging 3 ISO size isn't enough to make round preparation.
|