-
Endodontic characteristics of mandibular premolar with dens evaginatus: a retrospective study
-
Minjin Kim, Sujin Jeon, Min-Seock Seo
-
Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(3):e28. Published online July 11, 2024
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e28
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
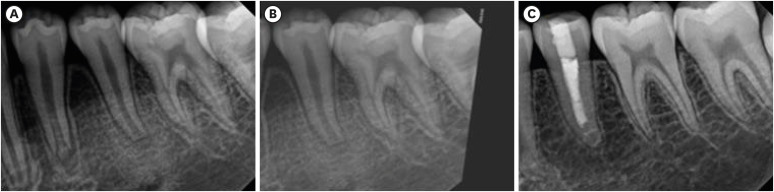
This study aimed to investigate the endodontic characteristics of mandibular premolars with dens evaginatus (DE) that require endodontic treatment. Materials and MethodsPatients who underwent endodontic treatment were enrolled. The inclusion criteria were patients who underwent root canal treatment in the lower permanent teeth with DE and were followed up for at least 1 year. Preoperative clinical and radiographic variables were obtained. The frequency distribution of the preoperative variables was compared using the χ2 or Fisher’s exact tests. The significance of the change in periapical health index (PAI) and root development stages before and after treatment was examined using the Wilcoxon signed-rank test. ResultsA total of 150 teeth of 134 patients with an average age of 15.3 years were included. The percentage distribution comparison of the preoperative variables and obturation techniques revealed significant differences in pulpal and periapical diagnosis, and percussion, and especially regarding age, root development stage, and PAI. Age was the only statistically significant preoperative variable associated with root growth (p < 0.05). ConclusionsApproximately, 60% of DEs requiring endodontic treatment had immature roots. Age being the most significant predisposing factor, early treatment provides the greatest opportunity for full root development.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - A tooth with multiple supernumerary cusps and taurodontism concurrently accompanied with other taurodont teeth: a rare case report
Zihui Tang, Hongchen Zhang, Rongrong Dang, Qiushi Zhang, Yan Huang, Yanwei Yang
Surgical and Radiologic Anatomy.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
-
3,455
View
-
106
Download
-
1
Web of Science
-
1
Crossref
-
The effect of different confluence confirmation strategies on the obturation of Vertucci type II canal: micro-CT analysis
-
Seungjae Do, Min-Seock Seo
-
Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(1):e12. Published online January 26, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e12
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
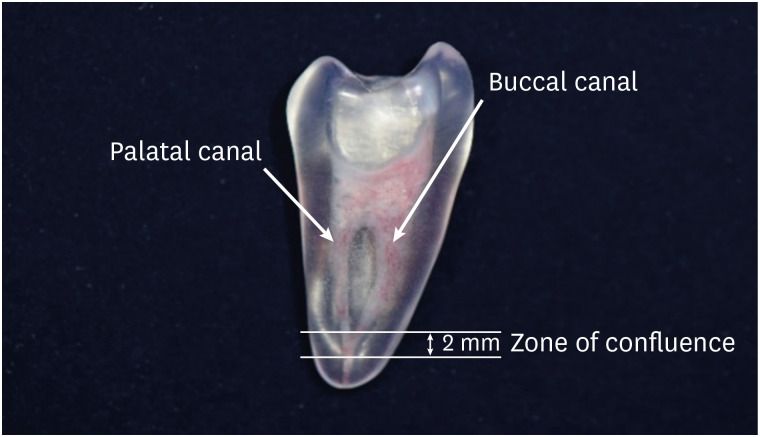
The present study aims to compare the obturation quality of 2 confluence confirmation techniques in artificial maxillary first premolars showing Vertucci type II root canal configuration. Materials and MethodsThirty artificial maxillary premolars having Vertucci type II root canal configuration were made. They were divided into 3 groups according to the confluence confirmation technique as follows. Gutta-percha indentation (GPI) group (confluence confirmation using a gutta-percha cone and a K file); electronic apex locator (EAL) group (confluence confirmation using K files and EAL); and no confluence detection (NCD) group. In the GPI group and the EAL group, shaping and obturation were performed with the modified working length (WL). In the NCD group, shaping was performed without WL adjustment and obturation was carried out with an adjusted master cone. Micro-computed tomography was used before preparation and after obturation to calculate the percentage of gutta-percha occupied volume (%GPv) and the volume increase in the apical 4 mm. Data were analyzed using 1-way analysis of variance and post hoc Tukey's test. ResultsStatistically significant difference was not found in terms of the %GPv from the apex to apical 4 mm. However, the NCD group showed a statistically significant volume increase compared with the EAL group (p < 0.05). ConclusionsIn terms of gutta-percha occupied volume, no significant difference was observed among the 3 groups. Confluence confirmation using an EAL in teeth with Vertucci type II configuration showed less volume increase during canal shaping compared with no confluence confirmation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - ANALISE TOMOGRÁFICA DAS TERMINAÇÕES APICAIS DOS CONDUTOS MV1 e MV2 EM MOLARES SUPERIORES
Milena Matos Borges, Giulio César Moreira Manzi, Michel Sena Fernandes Faria Lima, Izabella Lucas de Abreu Lima, Diogo de Azevedo Miranda, Flávio Ricardo Manzi
ARACÊ .2026; 8(1): e11921. CrossRef - Root and root canal morphology of mandibular first and second molars in a Jordanian subpopulation: a cross-sectional cone-beam computed tomography study
Rawan Abu Zaghlan, Laith Abu Qdais, Farouq Mansour, Faisal Mansour, Faleh Sawair
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Can the addition of surfactants to NaOCl irrigation impact on the percentage of voids of root canal filling?
Laise Pena Braga Monteiro, Marcella Yasmin Reis Guerreiro, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Carolina Oliveira de Lima, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva, Juliana Melo da Silva Brandão
Australian Endodontic Journal.2024; 50(2): 260. CrossRef
-
2,234
View
-
46
Download
-
2
Web of Science
-
3
Crossref
-
Root canal volume change and transportation by Vortex Blue, ProTaper Next, and ProTaper Universal in curved root canals
-
Hyun-Jin Park, Min-Seock Seo, Young-Mi Moon
-
Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(1):e3. Published online December 24, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e3
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
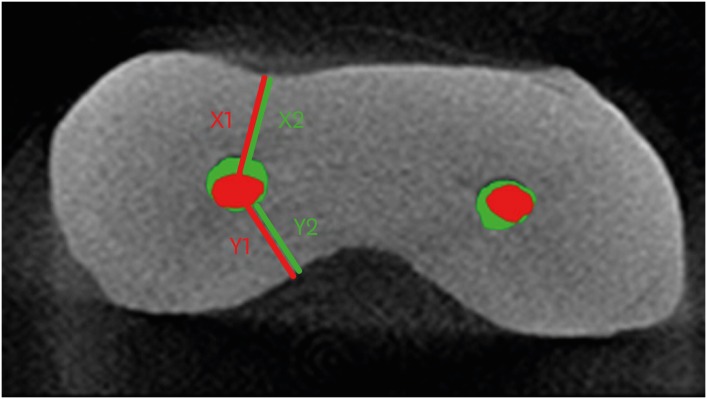
The aim of this study was to compare root canal volume change and canal transportation by Vortex Blue (VB; Dentsply Tulsa Dental Specialties), ProTaper Next (PTN; Dentsply Maillefer), and ProTaper Universal (PTU; Dentsply Maillefer) nickel-titanium rotary files in curved root canals. Materials and MethodsThirty canals with 20°–45° of curvature from extracted human molars were used. Root canal instrumentation was performed with VB, PTN, and PTU files up to #30.06, X3, and F3, respectively. Changes in root canal volume before and after the instrumentation, and the amount and direction of canal transportation at 1, 3, and 5 mm from the root apex were measured by using micro-computed tomography. Data of canal volume change were statistically analyzed using one-way analysis of variance and Tukey test, while data of amount and direction of transportation were analyzed using Kruskal-Wallis and Mann-Whitney U test. ResultsThere were no significant differences among 3 groups in terms of canal volume change (p > 0.05). For the amount of transportation, PTN showed significantly less transportation than PTU at 3 mm level (p = 0.005). VB files showed no significant difference in canal transportation at all 3 levels with either PTN or PTU files. Also, VB files showed unique inward transportation tendency in the apical area. ConclusionsOther than PTN produced less amount of transportation than PTU at 3 mm level, all 3 file systems showed similar level of canal volume change and transportation, and VB file system could prepare the curved canals without significant shaping errors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - The effect of nickel-titanium rotary systems on the biomechanical behaviour of mandibular first molars with curved and straight mesial roots: a finite element analysis study
Yaprak Cesur, Sevinc Askerbeyli Örs, Ahmet Serper, Mert Ocak
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Micro-Computed Tomographic Evaluation of the Shaping Ability of Vortex Blue and TruNatomyTM Ni-Ti Rotary Systems
Batool Alghamdi, Mey Al-Habib, Mona Alsulaiman, Lina Bahanan, Ali Alrahlah, Leonel S. J. Bautista, Sarah Bukhari, Mohammed Howait, Loai Alsofi
Crystals.2024; 14(11): 980. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Centering Ability and Canal Transportation of Rotary File Systems in Different Kinematics Using CBCT
Nupur R Vasava, Shreya H Modi, Chintan Joshi, Mona C Somani, Sweety J Thumar, Aashray A Patel, Anisha D Parmar, Kruti M Jadawala
World Journal of Dentistry.2024; 14(11): 983. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of nickel titanium rotary instruments on canal transportation and centering ability in curved canals by using cone beam computed tomography: An in vitro study
Krishnaveni Krishnaveni, Nikitha Kalla, Nagalakshmi Reddy, Sharvanan Udayar
Journal of Dental Specialities.2023; 11(2): 105. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Root Canal Centering Ability of Two Heat-treated Single-shaping NiTi Rotary Instruments in Simulated Curved Canals: An In Vitro Study
Preethi Varadan, Chakravarthy Arumugam, Athira Shaji, R R Mathan
World Journal of Dentistry.2023; 14(6): 535. CrossRef - A Comparison of Canal Width Changes in Simulated Curved Canals prepared with Profile and Protaper Rotary Systems
Aisha Faisal, Huma Farid, Robia Ghafoor
Pakistan Journal of Health Sciences.2022; : 55. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Respect of the Root Canal Trajectory by Rotary Niti Instruments (Protaper®Universal): Retrospective Radiographic Study
Salma El Abbassi, Sanaa Chala, Majid Sakout, Faïza Abdallaoui
Integrative Journal of Medical Sciences.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
-
1,821
View
-
12
Download
-
7
Crossref
-
Quantification of the tug-back by measuring the pulling force and micro computed tomographic evaluation
-
Su-Jin Jeon, Young-Mi Moon, Min-Seock Seo
-
Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(4):273-281. Published online September 4, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.4.273
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
The aims of this study were to quantify tug-back by measuring the pulling force and investigate the correlation of clinical tug-back pulling force with in vitro gutta-percha (GP) cone adaptation score using micro-computed tomography (µCT). Materials and MethodsTwenty-eight roots from human single-rooted teeth were divided into 2 groups. In the ProTaper Next (PTN) group, root canals were prepared with PTN, and in the ProFile (PF) group, root canals were prepared using PF (n = 14). The degree of tug-back was scored after selecting taper-matched GP cones. A novel method using a spring balance was designed to quantify the tug-back by measuring the pulling force. The correlation between tug-back scores, pulling force, and percentage of the gutta-percha occupied area (pGPOA) within apical 3 mm was investigated using µCT. The data were analyzed using Pearson's correlation analysis, one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Tukey's test. ResultsSpecimens with a strong tug-back had a mean pulling force of 1.24 N (range, 0.15–1.70 N). This study showed a positive correlation between tug-back score, pulling force, and pGPOA. However, there was no significant difference in these factors between the PTN and PF groups. Regardless of the groups, pGPOA and pulling force were significantly higher in the specimens with a higher tug-back score (p < 0.05). ConclusionsThe degree of subjective tug-back was a definitive determinant for master cone adaptation in the root canal. The use of the tug-back scoring system and pulling force allows the interpretation of subjective tug-back in a more objective and quantitative manner.
-
Healing outcomes of root canal treatment for C-shaped mandibular second molars: a retrospective analysis
-
Hye-Ra Ahn, Young-Mi Moon, Sung-Ok Hong, Min-Seock Seo
-
Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(4):262-270. Published online August 29, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.4.262
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
This study aimed to evaluate the healing rate of non-surgical endodontic treatment between C-shaped and non-C-shaped mandibular second molars. Materials and MethodsClinical records and radiological images of patients who had undergone endodontic treatment on mandibular second molars between 2007 and 2014 were screened. The periapical index scoring system was applied to compare healing outcomes. Information about preoperative and postoperative factors as well as the demographic data of the patients was acquired and evaluated using chi-square and multinomial logistic regression tests. ResultsThe total healing rate was 68.4%. Healing rates for the mandibular second molar were 70.9% in C-shaped canals (n = 79) and 66.6% in non-C-shaped ones (n = 117). The difference was not statistically significant. ConclusionsThe presence of a C-shaped canal in the mandibular second molar did not have a significantly negative effect on healing after treatment. Instead, proper pulpal diagnosis and final restoration were indicated as having significantly greater influence on the healing outcomes of C-shaped and non-C-shaped canals, respectively.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Predicting early endodontic treatment failure following primary root canal treatment
Young-Eun Jang, Yemi Kim, Sin-Young Kim, Bom Sahn Kim
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Influencing Non-Surgical Root Canal Treatment Outcomes in Mandibular Second Molars: A Retrospective Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Analysis
Da-Min Park, Woo-Hyun Seok, Ji-Young Yoon
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(10): 2931. CrossRef - Retrospective Assessment of Healing Outcome of Endodontic Treatment for Mandibular Molars with C-shaped Root Canal
Kishore Kumar Majety, Basanta Kumar Choudhury, Anika Bansal, Achla Sethi, Jaina Panjabi
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2017; 18(7): 591. CrossRef
-
1,977
View
-
21
Download
-
3
Crossref
-
Analysis of gene expression during odontogenic differentiation of cultured human dental pulp cells
-
Min-Seock Seo, Kyung-Gyun Hwang, Hyongbum Kim, Seung-Ho Baek
-
Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(3):142-148. Published online August 29, 2012
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.3.142
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
We analyzed gene-expression profiles after 14 day odontogenic induction of human dental pulp cells (DPCs) using a DNA microarray and sought candidate genes possibly associated with mineralization. Materials and MethodsInduced human dental pulp cells were obtained by culturing DPCs in odontogenic induction medium (OM) for 14 day. Cells exposed to normal culture medium were used as controls. Total RNA was extracted from cells and analyzed by microarray analysis and the key results were confirmed selectively by reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). We also performed a gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) of the microarray data. ResultsSix hundred and five genes among the 47,320 probes on the BeadChip differed by a factor of more than two-fold in the induced cells. Of these, 217 genes were upregulated, and 388 were down-regulated. GSEA revealed that in the induced cells, genes implicated in Apoptosis and Signaling by wingless MMTV integration (Wnt) were significantly upregulated. ConclusionsGenes implicated in Apoptosis and Signaling by Wnt are highly connected to the differentiation of dental pulp cells into odontoblast.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - iPSC-derived cranial neural crest-like cells can replicate dental pulp tissue with the aid of angiogenic hydrogel
Yoshifumi Kobayashi, Julie Nouet, Erdenechimeg Baljinnyam, Zain Siddiqui, Daniel H. Fine, Diego Fraidenraich, Vivek A. Kumar, Emi Shimizu
Bioactive Materials.2022; 14: 290. CrossRef - The role of sclerostin and dickkopf-1 in oral tissues – A review from the perspective of the dental disciplines
Mohammad Samiei, Klara Janjić, Barbara Cvikl, Andreas Moritz, Hermann Agis
F1000Research.2019; 8: 128. CrossRef - The Influence of Pro-Inflammatory Factors on Sclerostin and Dickkopf-1 Production in Human Dental Pulp Cells Under Hypoxic Conditions
Klara Janjić, Mohammad Samiei, Andreas Moritz, Hermann Agis
Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Do hypoxia and L-mimosine modulate sclerostin and dickkopf-1 production in human dental pulp-derived cells? Insights from monolayer, spheroid and tooth slice cultures
Klara Janjić, Barbara Cvikl, Christoph Kurzmann, Andreas Moritz, Hermann Agis
BMC Oral Health.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - The effects of dexamethasone on the apoptosis and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament cells
Sung-Mi Kim, Yong-Gun Kim, Jin-Woo Park, Jae-Mok Lee, Jo-Young Suh
Journal of Periodontal & Implant Science.2013; 43(4): 168. CrossRef
-
1,783
View
-
3
Download
-
5
Crossref
-
Evaluation of apical canal shapes produced sequentially during instrumentation with stainless steel hand and Ni-Ti rotary instruments using Micro-computed tomography
-
Woo-Jin Lee, Jeong-Ho Lee, Kyung-A Chun, Min-Seock Seo, Yeon-Jee Yoo, Seung-Ho Baek
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(3):231-237. Published online May 31, 2011
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.3.231
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
-
Objectives
The purpose of this study was to determine the optimal master apical file size with minimal transportation and optimal efficiency in removing infected dentin. We evaluated the transportation of the canal center and the change in untouched areas after sequential preparation with a #25 to #40 file using 3 different instruments: stainless steel K-type (SS K-file) hand file, ProFile and LightSpeed using microcomputed tomography (MCT).
Materials and Methods
Thirty extracted human mandibular molars with separated orifices and apical foramens on mesial canals were used. Teeth were randomly divided into three groups: SS K-file, Profile, LightSpeed and the root canals were instrumented using corresponding instruments from #20 to #40. All teeth were scanned with MCT before and after instrumentation. Cross section images were used to evaluate canal transportation and untouched area at 1- , 2- , 3- , and 5- mm level from the apex. Data were statistically analyzed according to' repeated nested design'and Mann-Whitney test (p = 0.05).
Results
In SS K-file group, canal transportation was significantly increased over #30 instrument. In the ProFile group, canal transportation was significantly increased after preparation with the #40 instrument at the 1- and 2- mm levels. LightSpeed group showed better centering ability than ProFile group after preparation with the #40 instrument at the 1 and 2 mm levels.
Conclusions
SS K-file, Profile, and LightSpeed showed differences in the degree of apical transportation depending on the size of the master apical file.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Comparison of the shaping abilities of three nickel–titanium instrumentation systems using micro-computed tomography
Jin Yi Baek, Hyun Mi Yoo, Dong Sung Park, Tae Seok Oh, Kee Yeon Kum, Seung Yun Shin, Seok Woo Chang
Journal of Dental Sciences.2014; 9(2): 111. CrossRef
-
1,102
View
-
5
Download
-
1
Crossref
|