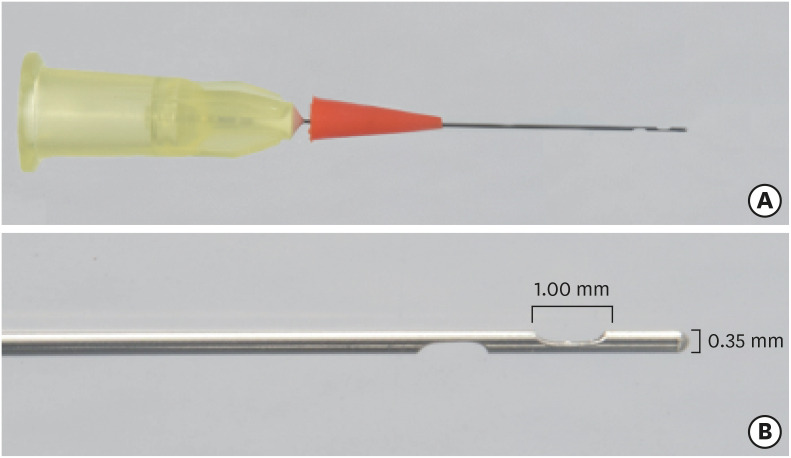
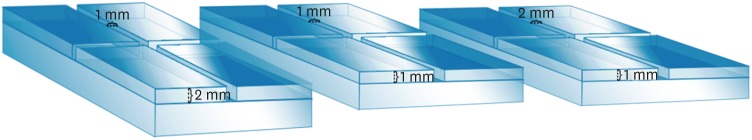
-
How do imaging protocols affect the assessment of root-end fillings?
-
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Reinhilde Jacobs, Mostafa EzEldeen, Karla de Faria-Vasconcelos, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Bernardo Camargo dos Santos, Mário Tanomaru-Filho
-
Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(1):e2. Published online December 15, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e2
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
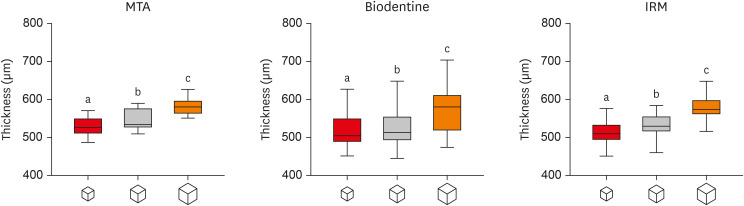
This study investigated the impact of micro-computed tomography (micro-CT)-based voxel size on the analysis of material/dentin interface voids and thickness of different endodontic cements. Materials and MethodsFollowing root-end resection and apical preparation, maxillary premolars were filled with mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA), Biodentine, and intermediate restorative material (IRM) (n = 24). The samples were scanned using micro-CT (SkyScan 1272; Bruker) and the cement/dentin interface and thickness of materials were evaluated at voxel sizes of 5, 10, and 20 µm. Analysis of variance and the Tukey test were conducted, and the degree of agreement between different voxel sizes was evaluated using the Bland and Altman method (p < 0.05). ResultsAll materials showed an increase in thickness from 5 to 10 and 20 µm (p < 0.05). When evaluating the interface voids, materials were similar at 5 µm (p > 0.05), while at 10 and 20 µm Biodentine showed the lowest percentage of voids (p < 0.05). A decrease in the interface voids was observed for MTA and IRM at 20 µm, while Biodentine showed differences among all voxel sizes (p < 0.05). The Bland-Altman plots for comparisons among voxel sizes showed the largest deviations when comparing images between 5 and 20 µm. ConclusionsVoxel size had an impact on the micro-CT evaluation of thickness and interface voids of endodontic materials. All cements exhibited an increase in thickness and a decrease in the void percentage as the voxel size increased, especially when evaluating images at 20 µm.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effect of ultrasonic activation of endodontic sealers on root canal filling quality during the single-cone obturation procedure: a systematic review and meta-analysis of laboratory-based studies
Shuting Feng, Weiqing Zhou, Xiaojun Chu, Shuaimei Xu, Xiongqun Zeng
Odontology.2025; 113(4): 1380. CrossRef - Marginal Adaptation and Porosity of a Novel MTA Brand Applied as Root-End Filling Material: A Micro-CT Study
Yaneta Kouzmanova, Ivanka Dimitrova
Applied Sciences.2024; 14(7): 2758. CrossRef - Supplementary methods for filling material removal: A systematic review and meta-analysis of micro-CT imaging studies
Bruna Venzke Fischer, Taynara Santos Goulart, Filipe Colombo Vitali, Diego Leonardo de Souza, Cleonice da Silveira Teixeira, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
Journal of Dentistry.2024; 151: 105445. CrossRef
-
1,690
View
-
18
Download
-
3
Web of Science
-
3
Crossref
-
Combination of a new ultrasonic tip with rotary systems for the preparation of flattened root canals
-
Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Jáder Camilo Pinto, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
-
Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(4):e56. Published online October 27, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e56
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
This study evaluated 2 nickel-titanium rotary systems and a complementary protocol with an ultrasonic tip and a small-diameter instrument in flattened root canals. Materials and MethodsThirty-two human maxillary second premolars with flattened canals (buccolingual diameter ≥4 times larger than the mesiodistal diameter) at 9 mm from the radiographic apex were selected. The root canals were prepared by ProDesign Logic (PDL) 30/0.01 and 30/0.05 or Hyflex EDM (HEDM) 10/0.05 and 25/0.08 (n = 16), followed by application of the Flatsonic ultrasonic tip in the cervical and middle thirds and a PDL 25/0.03 file in the apical third (FPDL). The teeth were scanned using micro-computed tomography before and after the procedures. The percentage of volume increase, debris, and uninstrumented surface area were analyzed using the Kruskal-Wallis, Dunn, Wilcoxon, analysis of variance/Tukey, and paired and unpaired t-tests (α = 0.05). ResultsNo significant difference was found in the volume increase and uninstrumented surface area between PDL and HEDM (p > 0.05). PDL had a higher percentage of debris than HEDM in the middle and apical thirds (p < 0.05). The FPDL protocol resulted in less debris and uninstrumented surface area for PDL and HEDM (p < 0.05). This protocol, with HEDM, reduced debris in the middle and apical thirds and uninstrumented surface area in the apical third (p < 0.05). ConclusionsHigh percentages of debris and uninstrumented surface area were observed after preparation of flattened root canals. The HEDM, Flatsonic tip, and 25/0.03 instrument protocol enhanced cleaning in flattened root canals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Kök Kanal Tedavisi Yenilemelerinde Ultrasonik Uç Kullanımı
Ayşenur Kızıltaş Gül, Turan Mert Hisar, Seniha Miçooğulları
Selcuk Dental Journal.2025; 12(1): 157. CrossRef - Flatsonic Ultrasonic Tip Optimizes the Removal of Remaining Filling Material in Flattened Root Canals: A Micro–computed Tomographic Analysis
Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Jáder Camilo Pinto, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mário Tanomaru-Filho
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(5): 612. CrossRef - The Effect of Combined Ultrasonic Tip and Mechanized Instrumentation on the Reduction of the Percentage of Non-Instrumented Surfaces in Oval/Flat Root Canals: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Marcella Dewes Cassal, Pedro Cardoso Soares, Marcelo dos Santos
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Heat-treated NiTi instruments and final irrigation protocols for biomechanical preparation of flattened canals
Kleber Kildare Teodoro CARVALHO, Igor Bassi Ferreira PETEAN, Alice Corrêa SILVA-SOUSA, Rafael Verardino CAMARGO, Jardel Francisco MAZZI-CHAVES, Yara Terezinha Corrêa SILVA-SOUSA, Manoel Damião SOUSA-NETO
Brazilian Oral Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
-
1,452
View
-
25
Download
-
3
Web of Science
-
4
Crossref
-
A micro-computed tomographic study using a novel test model to assess the filling ability and volumetric changes of bioceramic root repair materials
-
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Jader Camilo Pinto, Gabriella Oliveira Figueira, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
-
Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(1):e2. Published online December 8, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e2
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
New premixed bioceramic root repair materials require moisture for setting. Using micro-computed tomography (micro-CT), this study evaluated the filling ability and volumetric changes of calcium silicate-based repair materials (mineral trioxide aggregate repair high-plasticity [MTA HP] and Bio-C Repair, Angelus), in comparison with a zinc oxide and eugenol-based material (intermediate restorative material [IRM]; Dentsply DeTrey). Materials and MethodsGypsum models with cavities 3 mm deep and 1 mm in diameter were manufactured and scanned using micro-CT (SkyScan 1272. Bruker). The cavities were filled with the cements and scanned again to evaluate their filling capacity. Another scan was performed after immersing the samples in distilled water for 7 days to assess the volumetric changes of the cements. The statistical significance of differences in the data was evaluated using analysis of variance and the Tukey test with a 5% significance level. ResultsBio-C Repair had a greater filling ability than MTA HP (p < 0.05). IRM was similar to Bio-C and MTA HP (p > 0.05). MTA HP presented the largest volumetric change (p < 0.05), showing more volume loss than Bio-C and IRM, which were similar (p > 0.05). ConclusionsBio-C Repair is a new endodontic material with excellent filling capacity and low volumetric change. The gypsum model proposed for evaluating filling ability and volumetric changes by micro-CT had appropriate and reproducible results. This model may enhance the physicochemical evaluation of premixed bioceramic materials, which need moisture for setting.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Comparative evaluation of sealing potential of mineral trioxide aggregate, biodentine, and bio-C repair in furcation perforations: A glucose penetration study
Ashwija Shetty, Hajira Anjum Sultana, A. Srirekha, C. Champa, Suditi Pal, V. Sahithi
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(2): 144. CrossRef - Evaluation of volumetric and surface stability of calcium silicate-based repair cements at different pHs
Ana Cristina Padilha Janini, Débora Leticia Bittencourt Leite Alves, Victor Augusto Benedicto dos Santos, Brenda Fornazaro Moraes, Nilvan Alves da Silva, Matheus Barros-Costa, Luciano Augusto Cano Martins, Francisco Haiter Neto, Marina Angélica Marciano
Clinical Oral Investigations.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Bioceramics in Endodontics: Limitations and Future Innovations—A Review
Peramune Arachchilage Amila Saman Prasad Kumara, Paul Roy Cooper, Peter Cathro, Maree Gould, George Dias, Jithendra Ratnayake
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(4): 157. CrossRef - Physicochemical properties and periodontal ligament stem cell response to NeoMTA 2
Danilo Cassiano Ferraz, Jáder Camilo Pinto, Ariadne Letra, Renato Menezes Silva, Letícia Chaves de Souza, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Clinical Oral Investigations.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Ultrasonic Condensation Time on Void Formation and Microhardness of Well-RootTM PT Apical Plugs in 3D-Printed Immature Teeth
Krasimir Hristov, Ralitsa Bogovska-Gigova
Materials.2025; 18(21): 4835. CrossRef - Effect of pH on the solubility and volumetric change of ready-to-use Bio-C Repair bioceramic material
Luana Raphael da SILVA, Jader Camilo PINTO, Juliane Maria GUERREIRO-TANOMARU, Mário TANOMARU-FILHO
Brazilian Oral Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of blood and artificial saliva contamination on marginal adaptation and sealing ability of different retrograde filling materials: A comparative analysis
Yantrapragada Lakshmi Sunanda, Krishna Prasad Parvathaneni, T. B. V. G. Raju, Abitha Seshadri, Gowtam Dev Dondapati
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(7): 743. CrossRef - Marginal Adaptation and Porosity of a Novel MTA Brand Applied as Root-End Filling Material: A Micro-CT Study
Yaneta Kouzmanova, Ivanka Dimitrova
Applied Sciences.2024; 14(7): 2758. CrossRef - Volumetric change of calcium silicate-based repair materials in a simulated inflammatory environment: A micro-computed tomography study
Giovanna da Cunha Mendonça, Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Jáder Camilo Pinto, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mário Tanomaru-Filho
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(8): 817. CrossRef - Biocompatibility, bioactivity, porosity, and sealer/dentin interface of bioceramic ready-to-use sealers using a dentin-tube model
Rafaela Nanami Handa Inada, Evelin Carine Alves Silva, Camila Soares Lopes, Marcela Borsatto Queiroz, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Guilherme Ferreira da Silva, Paulo Sérgio Cerri, Juliane Maria Guerreiro–Tanomaru, Mário Tanomaru-Filho
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Healing the Open Apex: A Case Report on Innovative Apexogenesis of a Maxillary Molar Using Bio-C Repair
Ashwija Shetty, Hajira A Sultana, Keerthan B V, Nithin S Reddy
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation the Marginal Adaptation for the Bio C Repair and Other Root end Filling Material by Using Scanning Electron Microscope (A Comparative In Vitro Study)
Fatimah HAMADHİ, Zainab M.
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2023; 26(3): 261. CrossRef - Biocompatibility, bioactive potential, porosity, and interface analysis calcium silicate repair cements in a dentin tube model
Rafaela Nanami Handa Inada, Marcela Borsatto Queiroz, Camila Soares Lopes, Evelin Carine Alves Silva, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Guilherme Ferreira da Silva, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Paulo Sérgio Cerri, Mário Tanomaru-Filho
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(7): 3839. CrossRef - A new proposal for evaluating of the solubility of bioceramic materials in dentin tubes after immersion in PBS: a laboratory investigation
Giovanna da Cunha MENDONÇA, Karina Ines Medina Carita TAVARES, Airton Oliveira SANTOS-JUNIOR, Jáder Camilo PINTO, Juliane Maria GUERREIRO-TANOMARU, Mário TANOMARU-FILHO
Revista de Odontologia da UNESP.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
-
1,898
View
-
25
Download
-
10
Web of Science
-
14
Crossref
-
Biocompatibility and bioactive potential of the NeoMTA Plus endodontic bioceramic-based sealer
-
Roberto Alameda Hoshino, Mateus Machado Delfino, Guilherme Ferreira da Silva, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mário Tanomaru-Filho, Estela Sasso-Cerri, Paulo Sérgio Cerri
-
Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(1):e4. Published online December 17, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e4
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
This study evaluated the biocompatibility and bioactive potential of NeoMTA Plus mixed as a root canal sealer in comparison with MTA Fillapex. Materials and MethodsPolyethylene tubes filled with NeoMTA Plus (n = 20), MTA Fillapex (n = 20), or nothing (control group, CG; n = 20) were inserted into the connective tissue in the dorsal subcutaneous layer of rats. After 7, 15, 30 and 60 days, the specimens were processed for paraffin embedding. The capsule thickness, collagen content, and number of inflammatory cells (ICs) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) immunolabeled cells were measured. von Kossa-positive structures were evaluated and unstained sections were analyzed under polarized light. Two-way analysis of variance was performed, followed by the post hoc Tukey test (p ≤ 0.05). ResultsAt 7 days, the capsules around NeoMTA Plus and MTA Fillapex had more ICs and IL-6-immunostained cells than the CG. However, at 60 days, there was no significant difference in the IC number between NeoMTA Plus and the CG (p = 0.1137) or the MTA Fillapex group (p = 0.4062), although a greater number of IL-6-immunostained cells was observed in the MTA Fillapex group (p = 0.0353). From 7 to 60 days, the capsule thickness of the NeoMTA Plus and MTA Fillapex specimens significantly decreased, concomitantly with an increase in the collagen content. The capsules around root canal sealers showed positivity to the von Kossa stain and birefringent structures. ConclusionsThe NeoMTA Plus root canal sealer is biocompatible and exhibits bioactive potential.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Retrievability of NeoMTA 2 vs AH Plus Sealer from Retreated Mesial Canals of Mandibular First Molars: A Microcomputed Tomography Ex Vivo Study
Mey A Al-Habib, Mona Alsulaiman
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2025; 26(5): 493. CrossRef - Effect of calcium silicate-based repair sealers on bone healing in rat skull defects: histological and histomorphometric study
J. M. Sauer, C. E. S. Bueno, R. A. Pelegrine, C. E. Fontana, E. F. Martinez, P. G. Montagner, W. M. Nascimento, A. G. S. Limoeiro, D. G. P. Rocha, M. F. V. Marceliano-Alves, M. P. W. Galhardi, M. Klymus, A. S. Martin
Endodontics Today.2025; 23(3): 433. CrossRef - Biocompatibility and bioactivity of bioceramic endodontic sealer: NeoSealer Flo
Evelin Carine Alves SILVA, Jéssica Arielli PRADELLI, Guilherme Ferreira da SILVA, Paulo Sérgio CERRI, Mario TANOMARU-FILHO, Juliane Maria GUERREIRO-TANOMARU
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The osteoinductive potential of different root-end filling materials in a rat femur model
Seçkin Aksu, Ebru Delikan, Ayşe Özcan Küçük, Zehra Demiray Asoğlu, Şakir Necat Yılmaz
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical outcomes of nonsurgical root canal treatment using NeoSealer Flo and Endosequence BC Sealer: A retrospective analysis with short-term follow-up
Christian Lepure, Ryan M. Walsh, Sayeed Attar, Casey L. Turner, Joshua Crawford, Poorya Jalali
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Biocompatibility and bioactive potential of NeoPUTTY calcium silicate‐based cement: An in vivo study in rats
Evelin Carine Alves Silva, Jéssica Arielli Pradelli, Guilherme Ferreira da Silva, Paulo Sérgio Cerri, Mario Tanomaru‐Filho, Juliane Maria Guerreiro‐Tanomaru
International Endodontic Journal.2024; 57(6): 713. CrossRef - Carbon Nanotubes Induce Mineralization of Human Cementoblasts
Ting-Hsuan Wang, Kiyoko Watanabe, Koichiro Muromachi, Nobushiro Hamada, Nobuyuki Tani-Ishii
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(8): 1117. CrossRef - Tissue repair capacity of bioceramic endodontic sealers in rat subcutaneous tissue
George Sampaio Bonates dos Santos, Ceci Nunes Carvalho, Rudys Rodolfo de Jesus Tavares, Paulo Goberlânio de Barros Silva, George Táccio de Miranda Candeiro, Etevaldo Matos Maia Filho
Brazilian Dental Journal.2023; 34(3): 25. CrossRef - Participation of fibroblast growth factor‐1 and interleukin‐10 in connective tissue repair following subcutaneous implantation of bioceramic materials in rats
Mateus Machado Delfino, José Leandro de Abreu Jampani, Camila Soares Lopes, Juliane Maria Guerreiro‐Tanomaru, Mário Tanomaru‐Filho, Estela Sasso‐Cerri, Paulo Sérgio Cerri
International Endodontic Journal.2023; 56(3): 385. CrossRef - Biocompatibility and bioactive potential of an experimental tricalcium silicate‐based cement in comparison with Bio‐C repair and MTA Repair HP materials
Marcela Borsatto Queiroz, Rafaela N. H. Inada, José Leandro de Abreu Jampani, Juliane Maria Guerreiro‐Tanomaru, Estela Sasso‐Cerri, Mário Tanomaru‐Filho, Paulo Sérgio Cerri
International Endodontic Journal.2023; 56(2): 259. CrossRef - Calcium Silicate-Based Sealer Dentinal Tubule Penetration—A Systematic Review of In Vitro Studies
Israa Ashkar, José Luis Sanz, Leopoldo Forner, María Melo
Materials.2023; 16(7): 2734. CrossRef - Bioactivity Potential of Bioceramic-Based Root Canal Sealers: A Scoping Review
Mauro Schmitz Estivalet, Lucas Peixoto de Araújo, Felipe Immich, Adriana Fernandes da Silva, Nadia de Souza Ferreira, Wellington Luiz de Oliveira da Rosa, Evandro Piva
Life.2022; 12(11): 1853. CrossRef - Tricalcium silicate cement sealers
Anita Aminoshariae, Carolyn Primus, James C. Kulild
The Journal of the American Dental Association.2022; 153(8): 750. CrossRef - Bioactive potential of Bio‐C Pulpo is evidenced by presence of birefringent calcite and osteocalcin immunoexpression in the rat subcutaneous tissue
Marcela Borsatto Queiroz, Rafaela Nanami Handa Inada, Camila Soares Lopes, Juliane Maria Guerreiro‐Tanomaru, Estela Sasso‐Cerri, Mário Tanomaru‐Filho, Paulo Sérgio Cerri
Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials.2022; 110(10): 2369. CrossRef - An Updated Review on Properties and Indications of Calcium Silicate‐Based Cements in Endodontic Therapy
Fateme Eskandari, Alireza Razavian, Rozhina Hamidi, Khadije Yousefi, Susan Borzou, Zohaib Khurshid
International Journal of Dentistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
-
2,107
View
-
31
Download
-
11
Web of Science
-
15
Crossref
-
Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of a new system for root canal filling using calcium silicate-based root canal sealers
-
Mario Tanomaru-Filho, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Jader Camilo Pinto, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru
-
Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(3):e34. Published online June 9, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e34
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
This study evaluated by using micro-computed tomography (micro-CT) the filling ability and sealer apical extrusion promoted by a new Sealer Injection System (SIS; Angelus) with side openings needle, in comparison with the conventional injection system, associated with a new ready-to-use calcium silicate-based sealer (Bio-C Sealer). Materials and MethodsAcrylic resin models containing a main curved artificial canal and 3 simulated lateral canals in apical, middle and cervical thirds were used. The main root canals were prepared using a rotary system up to size 35.05. The canals were filled with Bio-C sealer by using a single cone technique and the conventional delivery system or SIS. Samples were scanned in micro-CT. The percentage of voids throughout the entire extension of the main root canal and in each third of the lateral canals, besides the apical extrusion of the sealer was calculated. Data were submitted to t-test (p < 0.05). ResultsThere was no difference between both systems in the main root canals filling. Although the volume percentage of voids was similar in the apical and middle thirds of lateral canals, SIS had the greatest filling ability of the cervical third lateral canal. Moreover, the conventional system showed the highest apical extrusion of the sealer. ConclusionsThe conventional and SIS obturation systems had an appropriate filling ability of the main root canal. SIS had the best filling of the cervical third of the lateral canals, besides lower sealer apical extrusion, suggesting its clinical indication.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Remineralizing capacity of zinc oxide eugenol sealer following the addition of nanohydroxyapatite-tyrosine amino acid: An in vivo animal study
Rasha M. Al-Shamaa, Raghad A. Al-Askary
Journal of Oral Biosciences.2025; 67(1): 100567. CrossRef - Advanced analytical tests and acellular bioactivity of zinc oxide eugenol sealer following the addition of nanohydroxyapatite-tyrosine amino acid: An in vitro study
Rasha M. Al-Shamaa, Raghad A. Al-Askary
Endodontology.2025; 37(2): 149. CrossRef - Tissues response and bone-forming capacity of zinc oxide–eugenol sealer following the addition of nanohydroxyapatite-tyrosine amino acid: An in vivo animal study
Rasha M. Al-Shamaa, Raghad A. Al-Askary
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2024; 14(3): 322. CrossRef - Filling ability of ready-to-use or powder-liquid calcium silicate-based sealers after ultrasonic agitation
Mário Tanomaru-Filho, Maíra Bonassi Lucchesi, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Jáder Camilo Pinto, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru
Brazilian Dental Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment the bioactivity of zinc oxid eugenol sealer after the addition of different concentrations of nano hydroxyapatite-tyrosine amino acid
Rasha M. Al-Shamaa, Raghad A. Al-Askary
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2024; 23: e243733. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of dentinal tubule penetration and push-out bond strength of new injectable hydraulic calcium disilicate based root canal sealer: A single blinded in vitro study
Aman Verma, Anshul Arora, Sonali Taneja
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2024; 14(2): 143. CrossRef - A critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study root canal fillings
Gustavo De‐Deus, Erick Miranda Souza, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Marco Simões‐Carvalho, Daniele Moreira Cavalcante, Marco Aurélio Versiani
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S2): 384. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomography in preventive and restorative dental research: A review
Mehrsima Ghavami-Lahiji, Reza Tayefeh Davalloo, Gelareh Tajziehchi, Paria Shams
Imaging Science in Dentistry.2021; 51(4): 341. CrossRef - Contribution of XP‐Endo files to the root canal filling removal: A systematic review and meta‐analysis ofin vitrostudies
Emel Uzunoglu‐Özyürek, Selen Küçükkaya Eren, Sevilay Karahan
Australian Endodontic Journal.2021; 47(3): 703. CrossRef - Micro‐CT evaluation of filling of flattened root canals using a new premixed ready‐to‐use calcium silicate sealer by single‐cone technique
Karina I. M. C. Tavares, Jáder C. Pinto, Airton O. Santos‐Junior, Fernanda F. E. Torres, Juliane M. Guerreiro‐Tanomaru, Mário Tanomaru‐Filho
Microscopy Research and Technique.2021; 84(5): 976. CrossRef - Development of A Nano-Apatite Based Composite Sealer for Endodontic Root Canal Filling
Angelica Bertacci, Daniele Moro, Gianfranco Ulian, Giovanni Valdrè
Journal of Composites Science.2021; 5(1): 30. CrossRef
-
1,487
View
-
15
Download
-
11
Crossref
-
Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of the flow and filling ability of endodontic materials using different test models
-
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Gisselle Moraima Chavez-Andrade, Jader Camilo Pinto, Fábio Luiz Camargo Villela Berbert, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
-
Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(2):e11. Published online January 8, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e11
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
This study compared the flow and filling of several retrograde filling materials using new different test models. Materials and MethodsGlass plates were manufactured with a central cavity and 4 grooves in the horizontal and vertical directions. Grooves with the dimensions used in the previous study (1 × 1 × 2 mm; length, width, and height respectively) were compared with grooves measuring 1 × 1 × 1 and 1 × 2 × 1 mm. Biodentine, intermediate restorative material (IRM), and mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) were evaluated. Each material was placed in the central cavity, and then another glass plate and a metal weight were placed over the cement. The glass plate/material set was scanned using micro-computed tomography. Flow was calculated by linear measurements in the grooves. Central filling was calculated in the central cavity (mm3) and lateral filling was measured up to 2 mm from the central cavity. ResultsBiodentine presented the least flow and better filling than IRM when evaluated in the 1 × 1 × 2 model. In a comparison of the test models, MTA had the most flow in the 1 × 1 × 2 model. All materials had lower lateral filling when the 1 × 1 × 2 model was used. ConclusionsFlow and filling were affected by the size of the test models. Higher grooves and materials with greater flow resulted in lower filling capacity. The test model measuring 1 × 1 × 2 mm showed a better ability to differentiate among the materials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Physical, chemical and biological properties of MTA Angelus and novel AGM MTA: an in vitro analysis
Sara Nashibi, Parisa Amdjadi, SeyedehSana Ahmadi, Sara Hekmatian, Maryam Torshabi
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Bioceramics in Endodontics: Limitations and Future Innovations—A Review
Peramune Arachchilage Amila Saman Prasad Kumara, Paul Roy Cooper, Peter Cathro, Maree Gould, George Dias, Jithendra Ratnayake
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(4): 157. CrossRef - Marginal Adaptation and Porosity of a Novel MTA Brand Applied as Root-End Filling Material: A Micro-CT Study
Yaneta Kouzmanova, Ivanka Dimitrova
Applied Sciences.2024; 14(7): 2758. CrossRef - Evaluation of the physical properties of bromelain-modified biodentine for direct pulp capping
Paridhi Agrawal, Manoj Chandak, Aditya Patel, Jay Bhopatkar
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - How do imaging protocols affect the assessment of root-end fillings?
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Reinhilde Jacobs, Mostafa EzEldeen, Karla de Faria-Vasconcelos, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Bernardo Camargo dos Santos, Mário Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A micro-computed tomographic study using a novel test model to assess the filling ability and volumetric changes of bioceramic root repair materials
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Jader Camilo Pinto, Gabriella Oliveira Figueira, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Micro-computed tomography in preventive and restorative dental research: A review
Mehrsima Ghavami-Lahiji, Reza Tayefeh Davalloo, Gelareh Tajziehchi, Paria Shams
Imaging Science in Dentistry.2021; 51(4): 341. CrossRef
-
1,283
View
-
11
Download
-
7
Crossref
|