-
Push-out bond strength and intratubular biomineralization of a hydraulic root-end filling material premixed with dimethyl sulfoxide as a vehicle
-
Ju-Ha Park, Hee-Jin Kim, Kwang-Won Lee, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kyung-San Min
-
Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(1):e8. Published online January 20, 2023
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e8
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
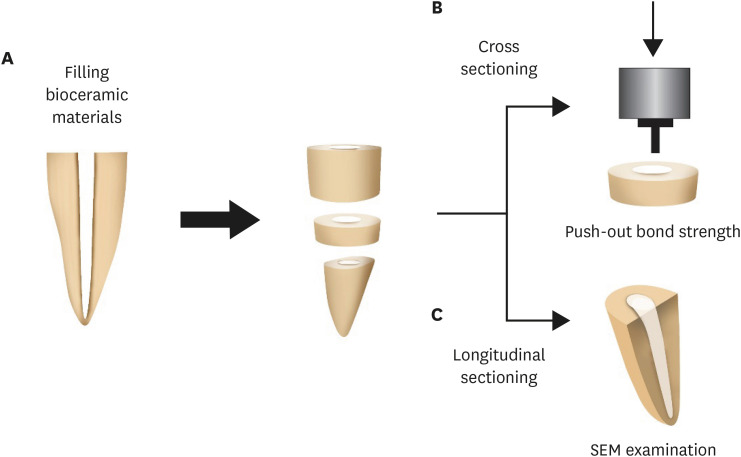
This study was designed to evaluate the parameters of bonding performance to root dentin, including push-out bond strength and dentinal tubular biomineralization, of a hydraulic bioceramic root-end filling material premixed with dimethyl sulfoxide (Endocem MTA Premixed) in comparison to a conventional powder-liquid–type cement (ProRoot MTA). Materials and MethodsThe root canal of a single-rooted premolar was filled with either ProRoot MTA or Endocem MTA Premixed (n = 15). A slice of dentin was obtained from each root. Using the sliced specimen, the push-out bond strength was measured, and the failure pattern was observed under a stereomicroscope. The apical segment was divided into halves; the split surface was observed under a scanning electron microscope, and intratubular biomineralization was examined by observing the precipitates formed in the dentinal tubule. Then, the chemical characteristics of the precipitates were evaluated with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopic (EDS) analysis. The data were analyzed using the Student’s t-test followed by the Mann-Whitney U test (p < 0.05). ResultsNo significant difference was found between the 2 tested groups in push-out bond strength, and cohesive failure was the predominant failure type. In both groups, flake-shaped precipitates were observed along dentinal tubules. The EDS analysis indicated that the mass percentage of calcium and phosphorus in the precipitate was similar to that found in hydroxyapatite. ConclusionsRegarding bonding to root dentin, Endocem MTA Premixed may have potential for use as an acceptable root-end filling material.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effectiveness of Sectioning Method and Filling Materials on Roughness and Cell Attachments in Root Resection Procedure
Tarek Ashi, Naji Kharouf, Olivier Etienne, Bérangère Cournault, Pierre Klienkoff, Varvara Gribova, Youssef Haikel
European Journal of Dentistry.2025; 19(01): 240. CrossRef - Bond Strength and Adhesive Interface Quality of New Pre‐Mixed Bioceramic Root Canal Sealer
Gustavo Creazzo, Bruna Monteiro de Barros Ciribelli Alves, Helena Cristina de Assis, Karen Gisselle Garay Villamayor, Manoel Damião de Sousa‐Neto, Jardel Francisco Mazzi‐Chaves, Fabiane Carneiro Lopes‐Olhê
Microscopy Research and Technique.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the root dentin bond strength and intratubular biomineralization of a premixed calcium aluminate-based hydraulic bioceramic endodontic sealer
Yu-Na Lee, Min-Kyeong Kim, Hee-Jin Kim, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kwang-Won Lee, Kyung-San Min
Journal of Oral Science.2024; 66(2): 96. CrossRef - Removal efficiency of a fast setting pozzalan-based bioactive cement: a micro CT study
Feyza Çetinkaya, Ahter Şanal Çıkman, Ali Keleş, Banu Arıcıoğlu
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Antibacterial Activity and Sustained Effectiveness of Calcium Silicate-Based Cement as a Root-End Filling Material against Enterococcus faecalis
Seong-Hee Moon, Seong-Jin Shin, Seunghan Oh, Ji-Myung Bae
Materials.2023; 16(18): 6124. CrossRef
-
452
View
-
35
Download
-
6
Web of Science
-
5
Crossref
-
Surgical management of an accessory canal in a maxillary premolar: a case report
-
Hee-Jin Kim, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kwang-Won Lee, Kyung-San Min
-
Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(3):e30. Published online July 29, 2019
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e30
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
We report the surgical endodontic treatment of a maxillary first premolar with a lateral lesion that originated from an accessory canal. Although lesions originating from accessory canals frequently heal with simple conventional endodontic therapy, some lesions may need additional and different treatment. In the present case, conventional root canal retreatment led to incomplete healing with the need for further treatment (i.e., surgery). Surgical endodontic management with a fast-setting calcium silicate cement was performed on the accessory canal using a dental operating microscope. At the patient's 9-month recall visit, the lesion was resolved upon radiography. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - The Impact of the Preferred Reporting Items for Case Reports in Endodontics (PRICE) 2020 Guidelines on the Reporting of Endodontic Case Reports
Sofian Youssef, Phillip Tomson, Amir Reza Akbari, Natalie Archer, Fayjel Shah, Jasmeet Heran, Sunmeet Kandhari, Sandeep Pai, Shivakar Mehrotra, Joanna M Batt
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Main and Accessory Canal Filling Quality of a Premixed Calcium Silicate Endodontic Sealer According to Different Obturation Techniques
Su-Yeon Ko, Hae Won Choi, E-Deun Jeong, Vinicius Rosa, Yun-Chan Hwang, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kyung-San Min
Materials.2020; 13(19): 4389. CrossRef
-
187
View
-
3
Download
-
2
Crossref
-
Recognition and management of palatogingival groove for tooth survival: a literature review
-
Hee-Jin Kim, Yoorina Choi, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kwang-Won Lee, Kyung-San Min
-
Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(2):77-86. Published online April 12, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.2.77
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
Palatogingival groove (PGG) is an anomaly in the maxillary anterior teeth, often accompanied by the area of bony destruction adjacent to the teeth with no carious or traumatic history. The hidden trap in the tooth can harbor plaque and bacteria, resulting in periodontal destruction with or without pulpal pathologic change. Related diseases can involve periodontal destruction, combined endodontic-periodontal lesions, or separate endodontic and periodontal lesions. Disease severity and prognosis related to PGG depend on several factors, including location, range, depth, and type of the groove. Several materials have been used and recommended for cases of extensive periodontal destruction from PGG to remove and block the inflammatory source and recover the health of surrounding periodontal tissues. Even in cases of severe periodontal destruction, several studies have reported favorable treatment outcomes with proper management. With new options in diagnosis and treatment, clinicians need a detailed understanding of the characteristics, treatment, and prognosis of PGG to successfully manage the condition. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Three-year follow-up case report: root canal treatment combined with intentional replantation for treating type III palatogingival groove in a maxillary lateral incisor
Jixu Jia, Miao Cheng, Sumeng Shi, Yanchun Qiao
Frontiers in Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of palatogingival groove and its association with periapical lesions and periodontal bone loss: a cone beam computed tomography study
Dilan Pelin Yildirim, Selin Goker Kamali
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Cone-beam computed tomographic evaluation to estimate the prevalence of palatogingival groove in the maxillary anterior teeth and its radiographic characteristics: An institutional retrospective study
Mousumi Biswas, Dibyendu Mazumdar, Binayak Saha, Siddhi Agarwala, Kallol Kumar Saha, Kuntal Chowdhury
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(3): 233. CrossRef - A Three-Dimensional Assessment of a Type I Shallow Palatogingival Groove by Cone Beam Computed Tomography: A Case Report
Ramachandra Reddy Gowda Venkatesha, Karthik Rajaram Mohan, Saramma Mathew Fenn, Sabitha Gokulraj, Kumar Appusamy
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnostic Approaches of Palatogingival Groove: A Systematic Review
Greta Venskutė
Journal of Dental Health and Oral Research.2024; : 1. CrossRef - Palatal groove associated with periodontal lesions: a systematic review illustrated by a decisional tree for management
Yvan Gaudex, Vianney Gandillot, Isabelle Fontanille, Philippe Bouchard, Stephane Kerner, Maria Clotilde Carra
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Palatogingival Groove: The Known–unknown Devourer
Sandeep Tandon, Rinku Mathur, Ambika S Rathore, Tripti S Rai, Kanchan Kumari Dhaker, Sumedha Gupta
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2024; 17(S1): S95. CrossRef - Nomogram to predict radicular grooves in maxillary lateral incisors in preoperative orthodontic population
Xiuneng Zhou, Jie Deng, Nianke Liu, Chunhui Yang, Shiyu Li, Yaling Song
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Management of Palatogingival Groove in Maxillary Lateral Incisor: A Report of a Rare Case With a Brief Review of Literature
Irfan Ansari, Sanjay Miglani, Vijay Yadav, Shamimul Hasan
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of palatogingival groove affecting maxillary anterior teeth in Saudi subpopulation: A cone-beam computed tomographic study with literature review
Ali Ibrahim Aljuailan, Roqayah Aljuailan, Rahul N. Gaikwad, Shaul Hameed Kolarkodi, Nasser Rufaydan Alamri
The Saudi Dental Journal.2023; 35(8): 1039. CrossRef - Bioceramics in Endodontics: Updates and Future Perspectives
Xu Dong, Xin Xu
Bioengineering.2023; 10(3): 354. CrossRef - Interdisciplinary approach for diagnosis and management of the tooth with type III palatogingival groove
Harakh Chand Baranwal, Jyoti Yadav
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2023; 13(2): 211. CrossRef - Progress in Diagnosis and Treatment of Palatogingival Groove
倩 郑
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2022; 12(04): 2723. CrossRef - Palatogingival grooves associated with periodontal bone Loss of maxillary incisors in a Chinese population
Rui Zhang, Jie Xiong, Markus Haapasalo, Ya Shen, Liuyan Meng
Australian Endodontic Journal.2022; 48(2): 313. CrossRef - Surgical management of lateral lesions with intentional replantation in single-rooted mandibular first premolars with radicular groove
Ya-Hsin Yu, Minje Kim, Samuel Kratchman, Bekir Karabucak
The Journal of the American Dental Association.2022; 153(4): 371. CrossRef - Management of the palato-radicular groove with a periodontal regenerative procedure and prosthodontic treatment: A case report
Dan-Hua Ling, Wei-Ping Shi, Yan-Hong Wang, Dan-Ping Lai, Yan-Zhen Zhang
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2022; 10(17): 5732. CrossRef - Combined Periodontal and Endodontic Management of Palatal Radicular Groove with Platelet-Rich Fibrin and Biodentine®
Arjun Hari Rijal, Bhageshwar Dhami, Pratistha Ghimire, Konstantinos Michalakis
Case Reports in Dentistry.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Intentional replantation combined root resection therapy for the treatment of type III radicular groove with two roots: A case report
Dan Tan, Shi-Ting Li, Hao Feng, Zhong-Chao Wang, Cai Wen, Min-Hai Nie
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2022; 10(20): 6991. CrossRef - DENTAL DEFECTS WITH SUBGINGIVAL EXTENSION: A RESTORATIVE CONUNDRUM
Seema Yadav
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH.2021; : 20. CrossRef - Misdiagnosis or Missed Diagnosis? Cone-Beam Computed Tomography-Aided Multidisciplinary Management of Maxillary Central Incisor with Palatogingival Groove
R. Kurinji Amalavathy, K.M. Vidya, Sonali Nabil Sarooshi, Hrudi Sundar Sahoo
Indian Journal of Dental Sciences.2021; 13(1): 46. CrossRef - Root and Root Canal Morphology: Study Methods and Classifications
Duaa M Shihab , Anas F Mahdee
Journal of Baghdad College of Dentistry.2021; 33(4): 11. CrossRef - Prevalence and radiological characteristics of palatogingival groove: A retrospective cone-beam computed tomography study in an Indian cohort
MS Lekshmi, Sheetal Sharma, ShaliniR Gupta, Sidhartha Sharma, Vijay Kumar, Amrita Chawla, Ajay Logani
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2021; 24(4): 359. CrossRef - Successful Multidisciplinary Management of an Endodontic‐Periodontal Lesion Associated With a Palato‐Radicular Groove: A Case Report
Diksha Katwal, Jennifer K. Fiorica, Jane Bleuel, Stephen J. Clark
Clinical Advances in Periodontics.2020; 10(2): 88. CrossRef - Anatomical, microbiological, and genetic considerations in treatment of Chinese periodontal patients
Edwin X. J. Goh, Marianne M. A. Ong
Journal of Investigative and Clinical Dentistry.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - A new system for classifying tooth, root and canal anomalies
H. M. A. Ahmed, P. M. H. Dummer
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(4): 389. CrossRef
-
841
View
-
18
Download
-
25
Crossref
-
Effects of proanthocyanidin, a crosslinking agent, on physical and biological properties of collagen hydrogel scaffold
-
Yoorina Choi, Hee-Jin Kim, Kyung-San Min
-
Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(4):296-303. Published online October 4, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.4.296
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
The purpose of the present study was to evaluate the effects of proanthocyanidin (PAC), a crosslinking agent, on the physical properties of a collagen hydrogel and the behavior of human periodontal ligament cells (hPDLCs) cultured in the scaffold. Materials and MethodsViability of hPDLCs treated with PAC was measured using the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. The physical properties of PAC treated collagen hydrogel scaffold were evaluated by the measurement of setting time, surface roughness, and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). The behavior of the hPDLCs in the collagen scaffold was evaluated by cell morphology observation and cell numbers counting. ResultsThe setting time of the collagen scaffold was shortened in the presence of PAC (p < 0.05). The surface roughness of the PAC-treated collagen was higher compared to the untreated control group (p < 0.05). The thermogram of the crosslinked collagen exhibited a higher endothermic peak compared to the uncrosslinked one. Cells in the PAC-treated collagen were observed to attach in closer proximity to one another with more cytoplasmic extensions compared to cells in the untreated control group. The number of cells cultured in the PAC-treated collagen scaffolds was significantly increased compared to the untreated control (p < 0.05). ConclusionsOur results showed that PAC enhanced the physical properties of the collagen scaffold. Furthermore, the proliferation of hPDLCs cultured in the collagen scaffold crosslinked with PAC was facilitated. Conclusively, the application of PAC to the collagen scaffold may be beneficial for engineering-based periodontal ligament regeneration in delayed replantation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - A highly biocompatible CE-crosslinked collagen implant with exceptional anti-calcification and collagen regeneration capabilities for aging skin rejuvenation
Qi Wang, Huiyu Yan, Linyan Yao, Wenhua Li, Jianxi Xiao
Journal of Materials Chemistry B.2024; 12(18): 4467. CrossRef - Dexamethasone release from hyaluronic acid microparticle and proanthocyanidin-gelatin hydrogel in sciatic tissue regeneration
Kazem Javanmardi, Hamideh Shahbazi, Ava Soltani Hekmat, Mehdi Khanmohammadi, Arash Goodarzi
Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - New Materials Based on Collagen and Taxifolin Derivatives: Production and Properties
Yu. V. Shatalin, M. I. Kobyakova, V. S. Shubina
Биологические мембраны Журнал мембранной и клеточной биологии.2024; 41(1): 82. CrossRef - Modulation of Adhesion and Migration of NIH/3T3 Cells in Collagen Materials by Taxifolin Derivatives
Yu. V. Shatalin, M. I. Kobyakova, V. S. Shubina
Biochemistry (Moscow), Supplement Series A: Membrane and Cell Biology.2023; 17(S1): S85. CrossRef - Development and characterization of crosslinked k-carrageenan/sericin blend with covalent agents or thermal crosslink for indomethacin extended release
Wedja Timóteo Vieira, Meuris Gurgel Carlos da Silva, Laura de Oliveira Nascimento, Melissa Gurgel Adeodato Vieira
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.2023; 246: 125558. CrossRef - New Challenges and Prospective Applications of Three-Dimensional Bioactive Polymeric Hydrogels in Oral and Craniofacial Tissue Engineering: A Narrative Review
Gamal Abdel Nasser Atia, Hany K. Shalaby, Naema Goda Ali, Shaimaa Mohammed Morsy, Mohamed Mohamady Ghobashy, Hager Abdel Nasser Attia, Paritosh Barai, Norhan Nady, Ahmad S. Kodous, Hasi Rani Barai
Pharmaceuticals.2023; 16(5): 702. CrossRef - Polyphenols: Bioavailability, Microbiome Interactions and Cellular Effects on Health in Humans and Animals
Michael B. Scott, Amy K. Styring, James S. O. McCullagh
Pathogens.2022; 11(7): 770. CrossRef - Advances of Hydrogel Therapy in Periodontal Regeneration—A Materials Perspective Review
Maoxue Li, Jiaxi Lv, Yi Yang, Guoping Cheng, Shujuan Guo, Chengcheng Liu, Yi Ding
Gels.2022; 8(10): 624. CrossRef - Collagen stabilization by natural cross-linkers: A qualitative and quantitative FTIR study on ultra-thin dentin collagen model
Rong WANG, Tyler STANLEY, Xiaomei YAO, Hang LIU, Yong WANG
Dental Materials Journal.2022; 41(3): 440. CrossRef - Cross-Linking Agents for Electrospinning-Based Bone Tissue Engineering
Dong-Jin Lim
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(10): 5444. CrossRef - Dense lamellar scaffold, biomimetically inspired, for reverse cardiac remodeling: Effect of proanthocyanidins and glutaraldehyde
Thais Alves, Juliana Ferreira Souza, Venancio Alves Amaral, Alessandra Candida Rios, Tais Costa, Kessi Crescencio, Fernando Batain, Denise Grotto, Renata Lima, Lindemberg Silveira Filho, Jose Oliveira Junior, Patricia Severino, Norberto Aranha, Marco Chau
Journal of Dispersion Science and Technology.2021; 42(2): 248. CrossRef - The effect of the cross-linker ratio used in gellan gum biomaterial synthesis on biomineralization
Serbülent TÜRK, Burak ÜNLÜ, Mahmut ÖZACAR
Bulletin of Biotechnology.2021; 2(2): 27. CrossRef - The recent advances in scaffolds for integrated periodontal regeneration
Hyun Nyun Woo, Young Joon Cho, Solaiman Tarafder, Chang H. Lee
Bioactive Materials.2021; 6(10): 3328. CrossRef - Plant based cross-linkers for tissue engineering applications
Abhishek Indurkar, Ashish Pandit, Ratnesh Jain, Prajakta Dandekar
Journal of Biomaterials Applications.2021; 36(1): 76. CrossRef - Plant-based biomaterials in tissue engineering
Abhishek Indurkar, Ashish Pandit, Ratnesh Jain, Prajakta Dandekar
Bioprinting.2021; 21: e00127. CrossRef - Traditional Chinese Medicine and orthopedic biomaterials: Host of opportunities from herbal extracts
Huijuan Tang, Andrell Hosein, Monica Mattioli-Belmonte
Materials Science and Engineering: C.2021; 120: 111760. CrossRef - Adsorption of Gold Ions onto Sericin and Alginate Particles Chemically Crosslinked by Proanthocyanidins: a Complete Fixed-Bed Column Study
Nilza Tatiane das Graças Santos, Richard Landers, Meuris Gurgel Carlos da Silva, Melissa Gurgel Adeodato Vieira
Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research.2020; 59(1): 318. CrossRef - Proanthocyanidin as a crosslinking agent for fibrin, collagen hydrogels and their composites with decellularized Wharton’s-jelly-extract for tissue engineering applications
Elham Hasanzadeh, Narges Mahmoodi, Arefeh Basiri, Faezeh Esmaeili Ranjbar, Zahra Hassannejad, Somayeh Ebrahimi-Barough, Mahmoud Azami, Jafar Ai, Vafa Rahimi-Movaghar
Journal of Bioactive and Compatible Polymers.2020; 35(6): 554. CrossRef - Hydrogels for the Delivery of Plant-Derived (Poly)Phenols
Nicola Micale, Andrea Citarella, Maria Sofia Molonia, Antonio Speciale, Francesco Cimino, Antonella Saija, Mariateresa Cristani
Molecules.2020; 25(14): 3254. CrossRef - Natural biopolymer‐based hydrogels for use in food and agriculture
Miri Klein, Elena Poverenov
Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture.2020; 100(6): 2337. CrossRef - Grape Seed-Inspired Smart Hydrogel Scaffolds for Melanoma Therapy and Wound Healing
Hongshi Ma, Quan Zhou, Jiang Chang, Chengtie Wu
ACS Nano.2019; 13(4): 4302. CrossRef - Improvement of the Physical Properties of Guided Bone Regeneration Membrane from Porcine Pericardium by Polyphenols-Rich Pomace Extract
Nazario Russo, Clara Cassinelli, Elisa Torre, Marco Morra, Giorgio Iviglia
Materials.2019; 12(16): 2564. CrossRef - Novel Biomedical Applications of Crosslinked Collagen
Lisha Gu, Tiantian Shan, Yu-xuan Ma, Franklin R. Tay, Lina Niu
Trends in Biotechnology.2019; 37(5): 464. CrossRef - The prospects of collagen as a basis for curable and activated osteoplastic materials
N. L. Fatkhudinova, A. V. Vasilyev, T. B. Bukharova, E. O. Osidak, N. V. Starikova, S. P. Domogatsky, D. V. Goldshtein, A. A. Kulakov
Stomatologiya.2018; 97(6): 78. CrossRef
-
225
View
-
6
Download
-
24
Crossref
-
Non-destructive management of white spot lesions by using tooth jewelry
-
Hee-Jin Kim, Lorena Karanxha, Su-Jung Park
-
Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(4):236-239. Published online November 21, 2012
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.4.236
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
Although several methods including composite resin restoration and microabrasion have been used for management of white spot lesion, tooth jewelry can be considered as another noninvasive option. This case report describes the management of white spot lesions by using tooth jewelry. This report also highlights the patients' preference for tooth jewelry as an esthetic concern. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Putting the mouth back in the body – the neglected area of dental and oral travel health
Irmgard L Bauer
Tropical Diseases, Travel Medicine and Vaccines.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Tooth adornments, gems, and grills
Harpuneet Kaur
International Journal of Oral Health Sciences.2022; 12(2): 50. CrossRef - Gold Enamel Choumps – A Case report
Sargam D. Kotecha, Y. Deepa Hedge, Kalpna Chaudhry, Ramakrishna Yeluri, Updesh Masih, Chanchal Singh
Egyptian Journal of Forensic Sciences.2016; 6(3): 303. CrossRef - Application of quantitative light-induced fluorescence to determine the depth of demineralization of dental fluorosis in enamel microabrasion: a case report
Tae-Young Park, Han-Sol Choi, Hee-Won Ku, Hyun-Su Kim, Yoo-Jin Lee, Jeong-Bum Min
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(3): 225. CrossRef
-
216
View
-
3
Download
-
4
Crossref
-
Endodontic management of a C-shaped maxillary first molar with three independent buccal root canals by using cone-beam computed tomography
-
Lorena Karanxha, Hee-Jin Kim, Sung-Ok Hong, Wan Lee, Pyung-Sik Kim, Kyung-San Min
-
Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(3):175-179. Published online August 29, 2012
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.3.175
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The aim of this study was to present a method for endodontic management of a maxillary first molar with unusual C-shaped morphology of the buccal root verified by cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) images. This rare anatomical variation was confirmed using CBCT, and nonsurgical endodontic treatment was performed by meticulous evaluation of the pulpal floor. Posttreatment image revealed 3 independent canals in the buccal root obturated efficiently to the accepted lengths in all 3 canals. Our study describes a unique C-shaped variation of the root canal system in a maxillary first molar, involving the 3 buccal canals. In addition, our study highlights the usefulness of CBCT imaging for accurate diagnosis and management of this unusual canal morphology. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Nonsurgical endodontic retreatment of C-shaped maxillary molars: case reports and review of literature
Ming Liu, Yanling Huang, Yixuan Wu, Yi Zhang, Zhisheng Zhang, Qianju Wu
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of Fused Rooted Maxillary First and Second Molars with Merged and C-shaped Canal Configurations: Prevalence, Characteristics, and Correlations in a Saudi Arabian Population
Mohammed Mashyakhy, Hemant Ramesh Chourasia, Ahmad Jabali, Abdulmajeed Almutairi, Gianluca Gambarini
Journal of Endodontics.2019; 45(10): 1209. CrossRef - C-shaped root canals of mandibular second molars in a Korean population: a CBCT analysis
Hee-Sun Kim, Daun Jung, Ho Lee, Yoon-Sic Han, Sohee Oh, Hye-Young Sim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence and Characteristics of the Maxillary C-shaped Molar
Jorge N.R. Martins, António Mata, Duarte Marques, Craig Anderson, João Caramês
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(3): 383. CrossRef - Use of cone-beam computed tomography and three-dimensional modeling for assessment of anomalous pulp canal configuration: a case report
Alper Sinanoglu, Dilek Helvacioglu-Yigit, Ibrahim Mutlu
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(2): 161. CrossRef - Endodontic management of a mandibular second molar with radix entomolaris: a case report
Rosaline Hannah, Deivanayagam Kandaswamy, Nachimuthu Jayaprakash
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(2): 132. CrossRef
-
163
View
-
2
Download
-
6
Crossref
-
Coronal microleakage of four temporary restorative materials in Class II-type endodontic access preparations
-
Sang-Mi Yun, Lorena Karanxha, Hee-Jin Kim, Sung-Ho Jung, Su-Jung Park, Kyung-San Min
-
Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(1):29-33. Published online March 2, 2012
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.1.29
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
-
Objectives
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the microleakage of 4 temporary materials in teeth with Class II-type endodontic access preparations by using a glucose penetration model.
Materials and Methods
Glucose reaction test was performed to rule out the presence of any reaction between glucose and temporary material. Class II-type endodontic access preparations were made in extracted human premolars with a single root (n = 10). Each experimental group was restored with Caviton (GC), Spacer (Vericom), IRM (Dentsply-Caulk), or Fuji II(GC). Microleakage of four materials used as temporary restorative materials was evaluated by using a glucose penetration model. Data were analyzed by the one-way analysis of variance followed by a multiple-comparison Tukey test. The interface between materials and tooth were examined under a scanning electron microscope (SEM).
Results
There was no significant reaction between glucose and temporary materials used in this study. Microleakage was significantly lower for Caviton and Spacer than for Fuji II and IRM. SEM observation showed more intimate adaptation of tooth-restoration interfaces in Caviton and Spacer than in IRM and Fuji II.
Conclusions
Compared to IRM and Fuji II, Caviton and Spacer can be considered better temporary sealing materials in Class II-type endodontic access cavities.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Comparative Evaluation of Sealing Ability, Water Absorption, and Solubility of Three Temporary Restorative Materials: An in vitro Study
AR Prabhakar, N Shantha Rani
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2017; 10(2): 136. CrossRef - Sealing Ability of Three Different Materials Used as Retrograde Filling
Ji-Hoon Park, Seung-Bok Kang, Yong-Hoon Choi, Ji-Hyun Bae
Journal of Korean Dental Science.2012; 5(2): 60. CrossRef
-
202
View
-
1
Download
-
2
Crossref
|