-
Physical-mechanical, chemical and biological properties of graphene-reinforced glass ionomer cements
-
Tatiane Ramos dos Santos Jordão, Laura Soares Viana Fernandes, Karla Lorene de França Leite, Adílis Alexandria, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Lucianne Cople Maia, Tatiana Kelly da Silva Fidalgo
-
Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(4):e37. Published online October 10, 2024
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e37
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
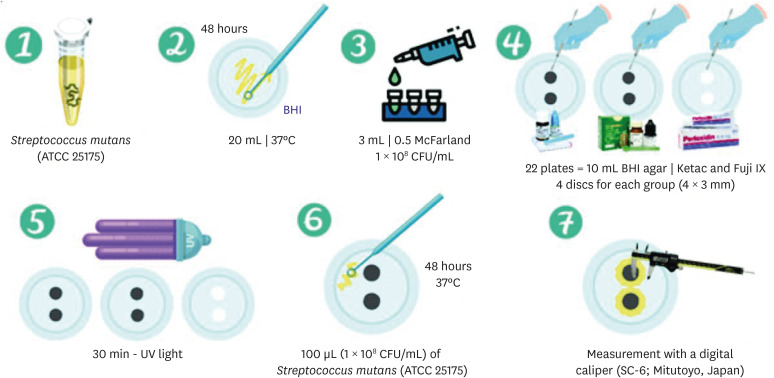
This study aimed to evaluate the physical-mechanical, chemical, and biological properties of graphene-reinforced glass ionomer cements (GICs). Materials and MethodsDifferent proportions of graphene powder were incorporated into 2 high-viscosity self-curing GIC, Ketac Molar (GKetac) and Fuji IX (GFuji), in 4 different concentrations: 0.5%, 1%, 2%, and 5%. The control groups included the GICs without graphene. Experiments were performed to analyze linear (Ra) and volumetric roughness (Sa), antimicrobial activity, radiopacity, fluoride release, microhardness, solubility, and water sorption. Data were analyzed using Kruskal-Wallis, Mann-Whitney, Wilcoxon, analysis of variance, and Tukey’s test (p ≤ 0.05). ResultsThe GKetac 0% and GFuji0% groups presented higher Ra (4.05 and 2.72) and Sa (4.76 and 5.16), respectively. No inhibition zone was observed, and the incorporation of graphene reduced radiopacity. Moreover, there was no influence on the solubility and water sorption after 21 days. A greater fluoride release was observed in the period of 7 days for most of the groups. After 21 days, GKetac 5%, 2%, and 1% presented higher releasing than 0% and 0.5% (p ≤ 0.05). ConclusionsThe graphene incorporation improved the microhardness of GICs in lower concentrations. Graphene incorporation to GICs modified some physical-mechanical, and chemical, but not affected biological properties.
-
Does minimally invasive canal preparation provide higher fracture resistance of endodontically treated teeth? A systematic review of in vitro studies
-
Sıla Nur Usta, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Seda Falakaloğlu, Mustafa Gündoğar
-
Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(4):e34. Published online October 17, 2023
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e34
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
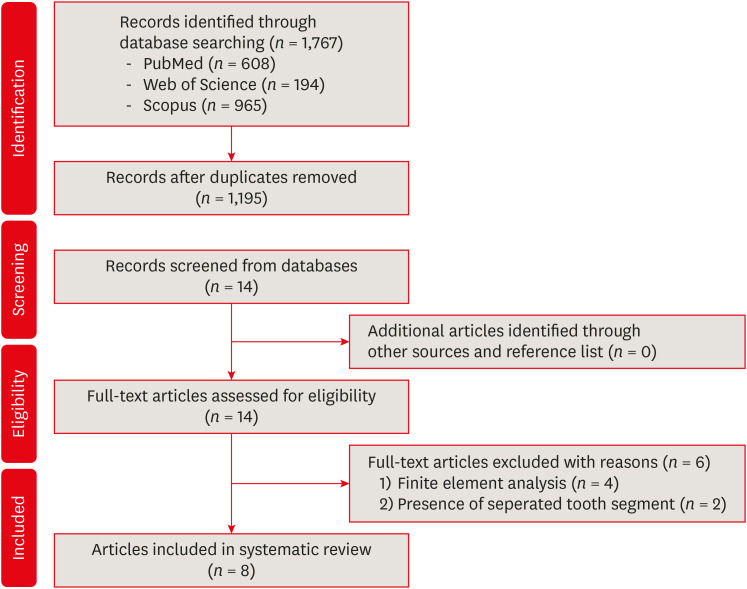
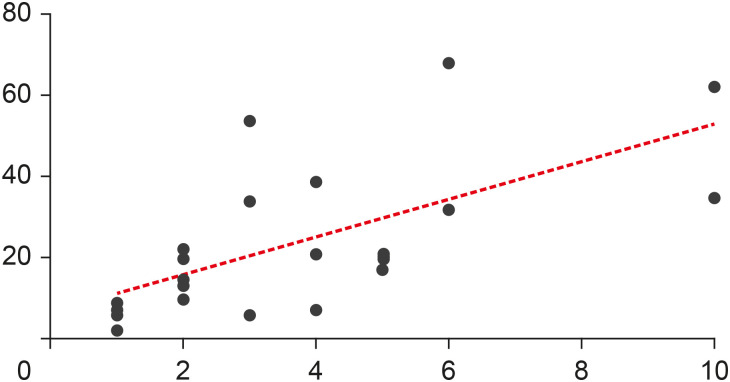
This systematic review aimed to investigate whether minimally invasive root canal preparation ensures higher fracture resistance compared to conventional root canal preparation in endodontically treated teeth (ETT). A comprehensive search strategy was conducted on the “PubMed, Web of Science, and Scopus” databases, alongside reference and hand searches, with language restrictions applied. Two independent reviews selected pertinent laboratory studies that explored the effect of minimally invasive root canal preparation on fracture resistance, in comparison to larger preparation counterparts. The quality of the studies was assessed, and the risk of bias was categorized as low, moderate, or high. The electronic search yielded a total of 1,767 articles. After applying eligibility criteria, 8 studies were included. Given the low methodological quality of these studies and the large variability of fracture resistance values, the impact of reduced apical size and/or taper on the fracture resistance of the ETT can be considered uncertain. This systematic review could not reveal sufficient evidence regarding the effect of minimally invasive preparation on increasing fracture resistance of ETT, primarily due to the inherent limitations of the studies and the moderate risk of bias. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Impact of conservative versus conventional instrumentation on the release of inflammatory mediators and post‐operative pain in mandibular molars with asymptomatic irreversible pulpitis: A randomized clinical trial
Sıla Nur Usta, Ana Arias, Emre Avcı, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva
International Endodontic Journal.2025; 58(6): 862. CrossRef - Mapping risk of bias criteria in systematic reviews of in vitro endodontic studies: an umbrella review
Rafaella Rodrigues da Gama, Lucas Peixoto de Araújo, Evandro Piva, Leandro Perello Duro, Adriana Fernandes da Silva, Wellington Luiz de Oliveira da Rosa
Evidence-Based Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Micro‐computed tomography evaluation of minimally invasive root canal preparation in 3D‐printed C‐shaped canal
Nutcha Supavititpattana, Siriwan Suebnukarn, Panupat Phumpatrakom, Kamon Budsaba
Australian Endodontic Journal.2024; 50(3): 621. CrossRef - Ex vivo investigation on the effect of minimally invasive endodontic treatment on vertical root fracture resistance and crack formation
Andreas Rathke, Henry Frehse, Maria Bechtold
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
-
3,838
View
-
112
Download
-
4
Web of Science
-
4
Crossref
-
Influence of access cavity design on calcium hydroxide removal using different cleaning protocols: a confocal laser scanning microscopy study
-
Seda Falakaloğlu, Merve Yeniçeri Özata, Betül Güneş, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Mustafa Gündoğar, Burcu Güçyetmez Topal
-
Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(3):e25. Published online July 24, 2023
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e25
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the influence of endodontic access cavities design on the removal of calcium hydroxide medication of the apical third of mandibular incisor root canal walls and dentinal tubules with different cleaning protocols: EDDY sonic activation, Er,Cr:YSGG laser-activated irrigation, or conventional irrigation with IrriFlex. Materials and MethodsSeventy-eight extracted human mandibular incisors were assigned to 6 experimental groups (n = 13) according to the endodontic access cavity and cleaning protocol for calcium hydroxide removal: traditional access cavity (TradAC)/EDDY; ultraconservative access cavity performed in the incisal edge (UltraAC.Inc)/EDDY; TradAC/Er,Cr:YSGG; UltraAC.Inc/Er,Cr:YSGG; TradAC/IrriFlex; or UltraAC.Inc/IrriFlex. Confocal laser scanning microscopy images were used to measure the non-penetration percentage, maximum residual calcium hydroxide penetration depth, and penetration area at 2 and 4 mm from the apex. Data were statistically analyzed using Shapiro-Wilk and WRS2 package for 2-way comparison of non-normally distributed parameters (depth of penetration, area of penetration, and percentage of non-penetration) according to cavity and cleaning protocol with the significance level set at 5%. ResultsThe effect of cavity and cleaning protocol interactions on penetration depth, penetration area and non-penetration percentage was not found statistically significant at 2 and 4 mm levels (p > 0.05). ConclusionsThe present study demonstrated that TradAC or UltraAC.Inc preparations with different cleaning protocols in extracted mandibular incisors did not influence the remaining calcium hydroxide at 2 and 4 mm from the apex.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effect of Apical Preparation Size and Preparation Taper on Smear Layer Removal Using Two Different Irrigation Needles: A Scanning Electron Microscopy Study
Rania Lebbos, Naji Kharouf, Deepak Mehta, Jamal Jabr, Cynthia Kamel, Roula El Hachem, Youssef Haikel, Marc Krikor Kaloustian
European Journal of Dentistry.2025; 19(03): 678. CrossRef - Combination of Chitosan Nanoparticles, EDTA, and Irrigation Activation Enhances TGF-β1 Release from Dentin: A Laboratory Study
Sıla Nur Usta, Emre Avcı, Ayşe Nur Oktay, Cangül Keskin
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(8): 1081. CrossRef
-
2,425
View
-
67
Download
-
2
Web of Science
-
2
Crossref
-
Fracture incidence of Reciproc instruments during root canal retreatment performed by postgraduate students: a cross-sectional retrospective clinical study
-
Liliana Machado Ruivo, Marcos de Azevedo Rios, Alexandre Mascarenhas Villela, Alexandre Sigrist de Martin, Augusto Shoji Kato, Rina Andrea Pelegrine, Ana Flávia Almeida Barbosa, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Carlos Eduardo da Silveira Bueno
-
Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(4):e49. Published online September 9, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e49
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
To evaluate the fracture incidence of Reciproc R25 instruments (VDW) used during non-surgical root canal retreatments performed by students in a postgraduate endodontic program. Materials and MethodsFrom the analysis of clinical record cards and periapical radiographs of root canal retreatments performed by postgraduate students using the Reciproc R25, a total of 1,016 teeth (2,544 root canals) were selected. The instruments were discarded after a single use. The general incidence of instrument fractures and its frequency was analyzed considering the group of teeth and the root thirds where the fractures occurred. Statistical analysis was performed using the χ2 test (p < 0.01). ResultsSeven instruments were separated during the procedures. The percentage of fracture in relation to the number of instrumented canals was 0.27% and 0.68% in relation to the number of instrumented teeth. Four fractures occurred in maxillary molars, 1 in a mandibular molar, 1 in a mandibular premolar and 1 in a maxillary incisor. A greater number of fractures was observed in molars when compared with the number of fractures observed in the other dental groups (p < 0.01). Considering all of the instrument fractures, 71.43% were located in the apical third and 28.57% in the middle third (p < 0.01). One instrument fragment was removed, one bypassed, while in 5 cases, the instrument fragment remained inside the root canal. ConclusionsThe use of Reciproc R25 instruments in root canal retreatments carried out by postgraduate students was associated with a low incidence of fractures.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Reciprocating Torsional Fatigue and Mechanical Tests of Thermal-Treated Nickel Titanium Instruments
Victor Talarico Leal Vieira, Alejandro Jaime, Carlos Garcia Puente, Giuliana Soimu, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Carlos Nelson Elias, Gustavo de Deus
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(3): 359. CrossRef - Neodymium-Doped Yttrium Aluminum Perovskite (Nd:YAP) Laser in the Elimination of Endodontic Nickel-Titanium Files Fractured in Rooted Canals (Part 2: Teeth With Significant Root Curvature)
Amaury Namour, Marwan El Mobadder, Clément Cerfontaine, Patrick Matamba, Lucia Misoaga, Delphine Magnin , Praveen Arany, Samir Nammour
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Temperature-Dependent Effects on Cyclic Fatigue Resistance in Three Reciprocating Endodontic Systems: An In Vitro Study
Marcela Salamanca Ramos, José Aranguren, Giulia Malvicini, Cesar De Gregorio, Carmen Bonilla, Alejandro R. Perez
Materials.2025; 18(5): 952. CrossRef - The Cost of Instrument Retrieval on the Root Integrity
Marco A. Versiani, Hugo Sousa Dias, Emmanuel J. N. L. Silva, Felipe G. Belladonna, Jorge N. R. Martins, Gustavo De‐Deus
International Endodontic Journal.2025; 58(12): 1948. CrossRef - Multimethod analysis of large‐ and low‐tapered single file reciprocating instruments: Design, metallurgy, mechanical performance, and irrigation flow
Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Fernando Peña‐Bengoa, Natasha C. Ajuz, Victor T. L. Vieira, Jorge N. R. Martins, Duarte Marques, Ricardo Pinto, Mario Rito Pereira, Francisco Manuel Braz‐Fernandes, Marco A. Versiani
International Endodontic Journal.2024; 57(5): 601. CrossRef - Nd: YAP Laser in the Elimination of Endodontic Nickel-Titanium Files Fractured in Rooted Canals (Part 1: Teeth With Minimal Root Curvature)
Amaury Namour, Marwan El Mobadder, Patrick Matamba, Lucia Misoaga, Delphine Magnin , Praveen Arany, Samir Nammour
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue of Different Reciprocating Endodontic Instruments Using Matching Artificial Root Canals at Body Temperature In Vitro
Sebastian Bürklein, Paul Maßmann, Edgar Schäfer, David Donnermeyer
Materials.2024; 17(4): 827. CrossRef - Endodontic Orthograde Retreatments: Challenges and Solutions
Alessio Zanza, Rodolfo Reda, Luca Testarelli
Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dentistry.2023; Volume 15: 245. CrossRef - Design, metallurgy, mechanical properties, and shaping ability of 3 heat-treated reciprocating systems: a multimethod investigation
Emmanuel J. N. L. Silva, Jorge N. R. Martins, Natasha C. Ajuz, Henrique dos Santos Antunes, Victor Talarico Leal Vieira, Francisco Manuel Braz-Fernandes, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Marco Aurélio Versiani
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(5): 2427. CrossRef - Noncontact 3D evaluation of surface topography of reciprocating instruments after retreatment procedures
Miriam Fatima Zaccaro-Scelza, Renato Lenoir Cardoso Henrique Martinez, Sandro Oliveira Tavares, Fabiano Palmeira Gonçalves, Marcelo Montagnana, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva, Pantaleo Scelza
Brazilian Dental Journal.2022; 33(3): 38. CrossRef
-
2,140
View
-
18
Download
-
7
Web of Science
-
10
Crossref
-
Ten years of minimally invasive access cavities in Endodontics: a bibliometric analysis of the 25 most-cited studies
-
Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Karem Paula Pinto, Natasha C. Ajuz, Luciana Moura Sassone
-
Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(3):e42. Published online July 21, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e42
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
This study aimed to analyze the main features of the 25 most-cited articles in minimally invasive access cavities. Materials and MethodsAn electronic search was conducted on the Clarivate Analytics' Web of Science ‘All Databases’ to identify the most-cited articles related to this topic. Citation counts were cross-matched with data from Elsevier's Scopus and Google Scholar. Information about authors, contributing institutions and countries, year and journal of publication, study design and topic, access cavity, and keywords were analyzed. ResultsThe top 25 most-cited articles received a total of 572 (Web of Science), 1,160 (Google Scholar) and 631 (Scopus) citations. It was observed a positive significant association between the number of citations and age of publication (r = 0.6907, p < 0.0001); however, there was no significant association regarding citation density and age of publication (r = −0.2631, p = 0.2038). The Journal of Endodontics made the highest contribution (n = 15, 60%). The United States had the largest number of publications (n = 7) followed by Brazil (n = 4), with the most contributions from the University of Tennessee and Grande Rio University (n = 3), respectively. The highest number of most-cited articles were ex vivo studies (n = 16), and ‘fracture resistance’ was the major topic studied (n = 10). ConclusionsThis study revealed a growing interest for researchers in the field of minimally invasive access cavities. Future trends are focused on the expansion of collaborative networks and the conduction of laboratory studies on under-investigated parameters.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Research Trends in Internal Root Resorption from 1947 to 2022: A Bibliometric Analysis of the 50 Most-cited Articles
Laise Pena Braga Monteiro, Larissa Pillar Gomes Martel, Roberta Fonseca de Castro, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva, Juliana Melo da Silva Brandão
Journal of Advanced Oral Research.2025; 16(2): 196. CrossRef - Bibliometric analysis of the publications that list the most-cited articles in endodontics
Oscar Alejandro Gutiérrez-Alvarez, Luis Alberto Pantoja-Villa, Benigno Miguel Calderón-Rojas
Endodontology.2025; 37(2): 128. CrossRef - Sixty Years of Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid Use in Endodontics: A Comprehensive Bibliometric Study
Camila Segatto Hartmann, Luiz Fernando Monteiro Czornobay, Julia Menezes Savaris, Aurélio de Oliveira Rocha, Lucas Menezes dos Anjos, Bruno Alexandre Pacheco de Castro Henriques, Mariane Cardoso, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia, Cleonice da Silveira Teixe
Journal of Endodontics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the forces applied by rubber dam clamps on mandibular first molar teeth with different endodontic access cavities: a 3D FEA study
Mehmet Eskibağlar, Serkan Erdem, Büşra Karaağaç Eskibağlar, Mete Onur Kaman
PeerJ.2024; 12: e17921. CrossRef - A Global Overview of Guided Endodontics: A Bibliometric Analysis
Thaine Oliveira Lima, Aurélio de Oliveira Rocha, Lucas Menezes dos Anjos, Nailson Silva Meneses Júnior, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Murilo Priori Alcalde, Mariane Cardoso, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(1): 10. CrossRef - Novel method for augmented reality guided endodontics: An in vitro study
Marco Farronato, Andres Torres, Mariano S. Pedano, Reinhilde Jacobs
Journal of Dentistry.2023; 132: 104476. CrossRef - Contribution of Türkiye to the Field of Endodontology: A Visualized Bibliometric Analysis Based on Web of Science
Olcay ÖZDEMİR, Yağız ÖZBAY, Neslihan YILMAZ ÇIRAKOĞLU
Medical Records.2023; 5(1): 91. CrossRef - Effect of access cavities on the biomechanics of mandibular molars: a finite element analysis
Xiao Wang, Dan Wang, Yi-rong Wang, Xiao-gang Cheng, Long-xing Ni, Wei Wang, Yu Tian
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Contemporary research trends on nanoparticles in endodontics: a bibliometric and scientometric analysis of the top 100 most-cited articles
Sıla Nur Usta, Zeliha Uğur-Aydın, Kadriye Demirkaya, Cumhur Aydın
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Evolving trend of systematic reviews and meta-analyses in endodontics: A bibliometric study
GalvinSim Siang Lin, JiaZheng Leong, WenXin Chong, MikoChong Kha Chee, ChinSheng Lee, Manahil Maqbool, TahirYusuf Noorani
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2022; 12(3): 236. CrossRef - Global research trends on photodynamic therapy in endodontics: A bibliometric analysis
Lucas Peixoto de Araújo, Wellington Luiz de Oliveira da Rosa, Leandro Bueno Gobbo, Tamares Andrade da Silva, José Flávio Affonso de Almeida, Caio Cezar Randi Ferraz
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2022; 40: 103039. CrossRef - Minimal Invasive Endodontics: A Comprehensive Narrative Review
Jaydip Marvaniya, Kishan Agarwal, Dhaval N Mehta, Nirav Parmar, Ritwik Shyamal , Jenee Patel
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
-
2,559
View
-
25
Download
-
8
Web of Science
-
12
Crossref
-
Influence of autoclave sterilization procedures on the cyclic fatigue resistance of heat-treated nickel-titanium instruments: a systematic review
-
Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Mayara Zanon, Fernanda Hecksher, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Rafaela Andrade de Vasconcelos, Tatiana Kelly da Silva Fidalgo
-
Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(2):e25. Published online March 31, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e25
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
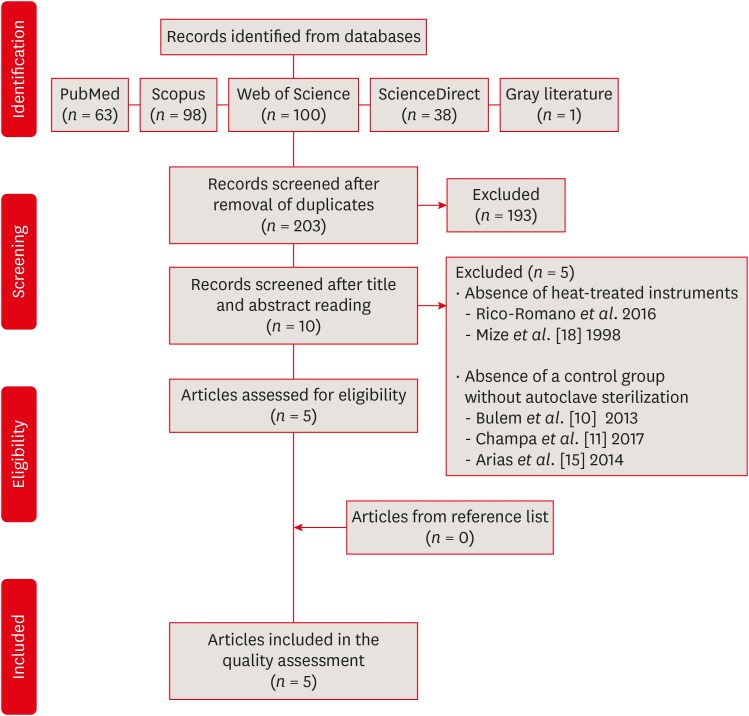
This systematic review evaluated the influence of autoclave sterilization procedures on the cyclic fatigue resistance of heat-treated nickel-titanium (NiTi) instruments. Materials and MethodsA systematic search without restrictions was conducted in the following electronic databases: PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, ScienceDirect, Cochrane, and Open Grey. The hand search was also performed in the main endodontic journals. The eligible studies were submitted to the methodological assessment and data extraction. ResultsFrom 203 abstracts, a total of 10 articles matched the eligible criteria. After reading the full articles, 2 were excluded because of the absence of the heat-treated instruments in the experimental design and 3 due to the lack of a control group using heat-treated instruments without autoclave sterilization. From the 5 included studies, 1 presented a low risk of bias, 3 presented moderate and 1 high risk. It was observed heterogeneous findings in the included studies, with autoclave sterilization cycles increasing, decreasing or not affecting the cyclic fatigue life of heat-treated NiTi instruments. However, the retrieved studies evaluating the cyclic fatigue resistance of endodontic instruments presented different protocols and assessing outcomes, this variability makes the findings less comparable within and also between groups and preclude the establishment of an unbiased scientific evidence base. ConclusionsConsidering the little scientific evidence and considerable risk of bias, it is still possible to conclude that autoclave sterilization procedures appear to influence the cyclic fatigue resistance of heat-treated NiTi instruments.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Impact of Repeated Use on Cyclic and Torsional Fatigue of 3 Rotary Files: Implications for Clinical Safety
Raimundo Sales de Oliveira Neto, Rafael da Rocha Tavares Duarte, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Guilherme Ferreira da Silva, Murilo Priori Alcalde, Leonardo Rigoldi Bonjardim
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(7): 954. CrossRef - Effect of simulated clinical use and sterilization on the cyclic fatigue resistance of nickel titanium files
Mohammad Alajemi, Ammar AbuMostafa
PeerJ.2024; 12: e17418. CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue of Different Ni-Ti Endodontic Rotary File Alloys: A Comprehensive Review
Dina Abdellatif, Alfredo Iandolo, Michela Scorziello, Giuseppe Sangiovanni, Massimo Pisano
Bioengineering.2024; 11(5): 499. CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Rotary versus Reciprocating Endodontic Files: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Ana De Pedro-Muñoz, Cristina Rico-Romano, Patricia Sánchez-Llobet, José María Montiel-Company, Jesús Mena-Álvarez
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(3): 882. CrossRef - Influence of sodium hypochlorite on cyclic fatigue resistance of nickel–titanium instruments: A systematic review and meta-analysis of in vitro studies
Alexandre Henrique dos Reis-Prado, Lucas Guimarães Abreu, Lara Cancella de Arantes, Kiani dos Santos de Paula, Sabrina de Castro Oliveira, Juliana Goto, Ana Cecília Diniz Viana, Francine Benetti
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(11): 6291. CrossRef - Cyclic fatigue resistance of EdgeTaper Platinum, Protaper Gold, and TruNatomy Prime rotary files before and after autoclave sterilization
Rahaf A. Almohareb, Reem M. Barakat, Fahda N. Algahtani, Manal F. Alkadi
PeerJ.2023; 11: e14656. CrossRef - Effect of calcium hydroxide on fracture resistance and microhardness of dentin in human teeth
Simar Sethi, Alpa Gupta, Ansy Hanna Kurian, Dax Abraham, Parul Chauhan, Kritika Aneja, Sucheta Jala, Arundeep Singh
Endodontology.2022; 34(4): 223. CrossRef - Effect of body temperature on the cyclic fatigue resistance of the nickel”titanium endodontic instruments: A systematic review and meta-analysis of in vitro studies
Selventhra Savitha, Sidhartha Sharma, Vijay Kumar, Amrita Chawla, Perumal Vanamail, Ajay Logani
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2022; 25(4): 338. CrossRef - Fracture Resistance of Heat-Treated Nickel-Titanium Rotary Files After Usage and Autoclave Sterilization: An In Vitro Study
Rashid El Abed, Aisha Alshehhi, Yoo Jung Kang, Dana Al Raeesi, Amar H. Khamis, Mohamed Jamal, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2022; 48(11): 1428. CrossRef - Effect of Autoclaving Cycles on the Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Race and Race Evo Nickel-Titanium Endodontic Rotary Files: An In Vitro Study
Rahaf A. Almohareb, Reem Barakat, Aroob Albakri, Manal Altamimi
Metals.2021; 11(12): 1947. CrossRef - Effect of number of uses and sterilization on the instrumented area and resistance of reciprocating instruments
Victor de Ornelas Peraça, Samantha Rodrigues Xavier, Fabio de Almeida Gomes, Luciane Geanini Pena dos Santos, Erick Miranda Souza, Fernanda Geraldo Pappen
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of sterilization procedures on the physical and mechanical properties of rotating endodontic instruments: a systematic review and network meta-analysis
Mario Dioguardi, Claudia Arena, Diego Sovereto, Riccardo Aiuto, Luigi Laino, Gaetano Illuzzi, Enrica Laneve, Bruna Raddato, Vito Carlo Alberto Caponio, Antonio Dioguardi, Khrystyna Zhurakivska, Giuseppe Troiano, Lorenzo Lo
Muzio
Frontiers in Bioscience-Landmark.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
-
2,254
View
-
41
Download
-
12
Crossref
-
Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of canal retreatments performed by undergraduate students using different techniques
-
Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Marianna Fernandes Carapiá, Brenda Leite Muniz, Mariana Santoro Rocha, Edson Jorge Lima Moreira
-
Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(1):e5. Published online January 15, 2018
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e5
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
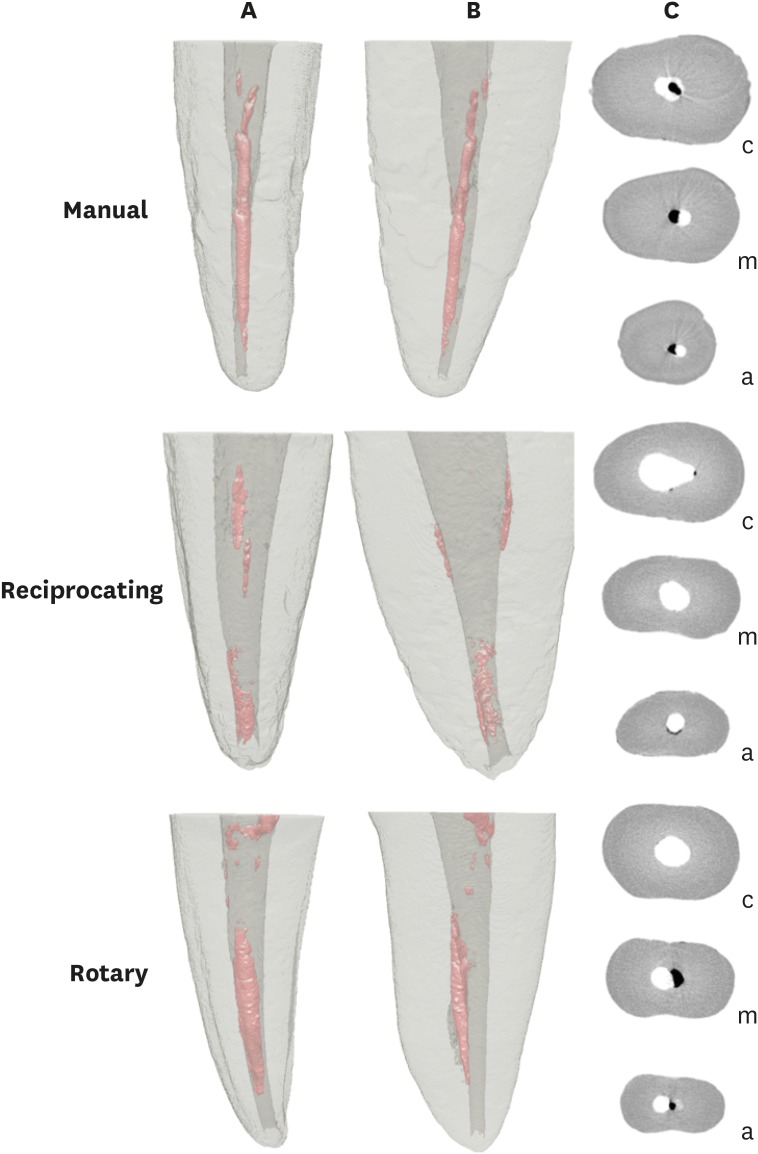
This study evaluated the amount of remaining root canal filling materials after retreatment procedures performed by undergraduate students using manual, rotary, and reciprocating techniques through micro-computed tomographic analysis. The incidence of instrument fracture and the instrumentation time were also evaluated. Materials and MethodsThirty maxillary single rooted teeth were prepared with Reciproc R25 files and filled with gutta-percha and AH Plus sealer by the continuous wave of condensation technique. Then, the specimens were assigned to 3 groups (n = 10), according to the retreatment technique used: manual, rotary, and reciprocating groups, which used K-file, Mtwo retreatment file, and Reciproc file, respectively. Retreatments were performed by undergraduate students. The sample was scanned after root canal filling and retreatment procedures, and the images of the canals were examined to quantify the amount of remaining filling material. The incidence of instrument fracture and the instrumentation time were recorded. ResultsRemaining filling material was observed in all specimens regardless of the technique used. The mean volume of remaining material was significantly lower in the Reciproc group than in the manual K-file and Mtwo retreatment groups (p < 0.05). The time required to achieve a satisfactory removal of canal filling material and refinement was significantly lower in the Mtwo retreatment and Reciproc groups (p < 0.05) when compared to the manual K-file group. No instrument fracture was observed in any of the groups. ConclusionsReciproc was the most effective instrument in the removal of canal fillings after retreatments performed by undergraduate students.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Assessment of isthmus filling using two obturation techniques performed by students with different levels of clinical experience
Yang Yu, Chong-Yang Yuan, Xing-Zhe Yin, Xiao-Yan Wang
Journal of Dental Sciences.2024; 19(1): 169. CrossRef - Optical microscopy evaluation of root canal filling removal by beginner operators in posterior teeth
Bogdan Dimitriu, Ioana Suciu, Oana Elena Amza, Mihai Ciocârdel, Dana Bodnar, Ana Maria Cristina Țâncu, Mihaela Tanase, Maria Sabina Branescu, Mihaela Chirilă
Journal of Medicine and Life.2024; 17(6): 555. CrossRef - Micro-CT Study on the Supplementary Effect of XP-Endo Finisher R after Endodontic Retreatment with Mtwo-R
I Tsenova-Ilieva, V Dogandzhiyska, M Raykovska, E Karova
Nigerian Journal of Clinical Practice.2023; 26(12): 1844. CrossRef - Critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study removal of root filling materials
Mahdi A. Ajina, Pratik K. Shah, Bun San Chong
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S1): 119. CrossRef - Efficiency of Supplementary Contemporary Single-file Systems in Removing Filling Remnants from Oval-shaped Canals: An In Vitro Study
Neveen A Shaheen, Dalia A Sherif, Nahla G Elhelbawy
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2021; 22(9): 1055. CrossRef - Efficacy of an arrow‐shaped ultrasonic tip for the removal of residual root canal filling materials
Emmanuel J.N.L. Silva, Carolina O. de Lima, Ana F.A. Barbosa, Cláudio M. Ferreira, Bruno M. Crozeta, Ricardo T. Lopes
Australian Endodontic Journal.2021; 47(3): 467. CrossRef - XP‐endo Finisher R instrument optimizes the removal of root filling remnants in oval‐shaped canals
G. De‐Deus, F. G. Belladonna, A. S. Zuolo, D. M. Cavalcante, J. C. A. Carvalhal, M. Simões‐Carvalho, E. M. Souza, R. T. Lopes, E. J. N. L. Silva
International Endodontic Journal.2019; 52(6): 899. CrossRef
-
1,160
View
-
12
Download
-
7
Crossref
-
Intraoperative discomfort associated with the use of a rotary or reciprocating system: a prospective randomized clinical trial
-
Aline Cristine Gomes, Adriana Jesus Soares, Erick M Souza, Alexandre Augusto Zaia, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva
-
Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(2):140-145. Published online April 20, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.2.140
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
The aim of this randomized, controlled, prospective clinical study was to evaluate patients' intraoperative discomfort during root canal preparations in which either multi-file rotary (Mtwo) or single-file reciprocating (Reciproc) systems were used. Materials and MethodsFifty-five adult patients, aged between 25 and 69 years old, with irreversible pulpitis or pulp necrosis participated in this study. Either the mesiobuccal or the distobuccal canals for maxillary molars and either the mesiobuccal or the mesiolingual canals for mandibular molars were randomly chosen to be instrumented with Mtwo multi-file rotary or Reciproc single-file reciprocating systems. Immediately after each canal instrumentation under anesthesia, patient discomfort was assessed using a 1 - 10 visual analog scale (VAS), ranging from ‘least possible discomfort’ (1) to ‘greatest possible discomfort’ (10). The Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used to determine significant differences at p< 0.05. ResultsLittle intraoperative discomfort was found in all cases. No statistically significant differences in intraoperative discomfort between the 2 systems were found (p = 0.660). ConclusionsRoot canal preparation with multi-file rotary or single-file reciprocating systems had similar and minimal effects on patients' intraoperative discomfort.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Post-Operative Pain in Reciprocating Versus Rotary Kinematics Post-Endodontic Treatment: A Systematic Review
Youssef Algarni
Archives of Pharmacy Practice.2024; 15(2): 53. CrossRef - Postoperative pain perception and associated risk factors in children after continuous rotation versus reciprocating kinematics: A randomised prospective clinical trial
Ahmad Abdel Hamid Elheeny, Dania Ibrahem Sermani, Mahmoud Ahmed Abdelmotelb
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(S1): 345. CrossRef - Patient discomfort levels during instrumentation procedure using nickel‐titanium files with different kinetic movements
So‐Ra Park, Se‐Hee Park, Kyung‐Mo Cho, Jin‐Woo Kim, Hyeon‐Cheol Kim
Australian Endodontic Journal.2022; 48(3): 372. CrossRef - Effect of XP‐endo Shaper versus conventional rotary files on postoperative pain and bacterial reduction in oval canals with necrotic pulps: a randomized clinical study
R. S. Emara, S. I. Gawdat, H. M. M. El‐Far
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(7): 1026. CrossRef - Effectiveness of a reciprocating single file, single cone endodontic treatment approach: a randomized controlled pragmatic clinical trial
Fabricio Eneas Diniz de Figueiredo, Laila F. Lima, Ludmila S. Oliveira, Maria A. Ribeiro, Marcos B. Correa, Manoel Brito-Junior, André L. Faria-e-Silva
Clinical Oral Investigations.2020; 24(7): 2247. CrossRef - Influence of glide path kinematics during endodontic treatment on the occurrence and intensity of intraoperative and postoperative pain: a systematic review of randomized clinical trials
Thaís Christina Cunha, Felipe de Souza Matos, Luiz Renato Paranhos, Ítalo de Macedo Bernardino, Camilla Christian Gomes Moura
BMC Oral Health.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of postoperative pain intensity following the use of three different instrumentation techniques: A randomized clinical trial
Mehmet Adiguzel, Pelin Tufenkci, ismail Ilker Pamukcu
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2019; 13(2): 133. CrossRef - Reciprocating kinematics leads to lower incidences of postoperative pain than rotary kinematics after endodontic treatment: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trial
ChristineMen Martins, VictorEduardo De Souza Batista, AmandaCaselato Andolfatto Souza, AnaCristina Andrada, GrazielaGarrido Mori, JoaoEduardo Gomes Filho
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2019; 22(4): 320. CrossRef - Intraoperative Pain During Glide Path Creation with the Use of a Rotary or Reciprocating System
Pelin TUFENKCİ, Mehmet ADIGUZEL, Koray YILMAZ
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2019; 22(1): 66. CrossRef
-
1,745
View
-
14
Download
-
9
Crossref
-
Comparison of canal transportation in simulated curved canals prepared with ProTaper Universal and ProTaper Gold systems
-
Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Brenda Leite Muniz, Frederico Pires, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Aline Almeida Neves, Erick Miranda Souza, Gustavo De-Deus
-
Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(1):1-5. Published online February 4, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.1.1
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
The purpose of this study was to assess the ability of ProTaper Gold (PTG, Dentsply Maillefer) in maintaining the original profile of root canal anatomy. For that, ProTaper Universal (PTU, Dentsply Maillefer) was used as reference techniques for comparison. Materials and MethodsTwenty simulated curved canals manufactured in clear resin blocks were randomly assigned to 2 groups (n = 10) according to the system used for canal instrumentation: PTU and PTG groups, upto F2 files (25/0.08). Color stereomicroscopic images from each block were taken exactly at the same position before and after instrumentation. All image processing and data analysis were performed with an open source program (FIJI). Evaluation of canal transportation was obtained for two independent canal regions: straight and curved levels. Student's t test was used with a cut-off for significance set at α = 5%. ResultsInstrumentation systems significantly influenced canal transportation (p < 0.0001). A significant interaction between instrumentation system and root canal level (p < 0.0001) was found. PTU and PTG systems produced similar canal transportation at the straight part, while PTG system resulted in lower canal transportation than PTU system at the curved part. Canal transportation was higher at the curved canal portion (p < 0.0001). ConclusionsPTG system produced overall less canal transportation in the curved portion when compared to PTU system.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Shaping, and disinfecting abilities of ProTaper Universal, ProTaper Gold, and Twisted Files: A correlative microcomputed tomographic and bacteriologic analysis
Malavika Sivakumar, Ruchika Roongta Nawal, Sangeeta Talwar, CP Baveja, Rega Kumar, Sudha Yadav, S Santosh Kumar
Endodontology.2023; 35(1): 54. CrossRef - Advancing Nitinol: From heat treatment to surface functionalization for nickel–titanium (NiTi) instruments in endodontics
Wai-Sze Chan, Karan Gulati, Ove A. Peters
Bioactive Materials.2023; 22: 91. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Root Canal Centering Ability of Two Heat-treated Single-shaping NiTi Rotary Instruments in Simulated Curved Canals: An In Vitro Study
Preethi Varadan, Chakravarthy Arumugam, Athira Shaji, R R Mathan
World Journal of Dentistry.2023; 14(6): 535. CrossRef - An Appraisal on Newer Endodontic File Systems: A Narrative Review
Shalini Singh, Kailash Attur, Anjali Oak, Mohammed Mustafa, Kamal Kumar Bagda, Nishtha Kathiria
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2023; 23(9): 944. CrossRef - Shaping ability of modern Nickel–Titanium rotary systems on the preparation of printed mandibular molars
Seda Falakaloglu, Emmanuel Silva, Burcu Topal, Emre İriboz, Mustafa Gündoğar
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2022; 25(5): 498. CrossRef - An Investigation of the Accuracy and Reproducibility of 3D Printed Transparent Endodontic Blocks
Martin Smutný, Martin Kopeček, Aleš Bezrouk
Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove, Czech Republic).2022; 65(2): 59. CrossRef - Nitinol Type Alloys General Characteristics and Applications in Endodontics
Leszek A. Dobrzański, Lech B. Dobrzański, Anna D. Dobrzańska-Danikiewicz, Joanna Dobrzańska
Processes.2022; 10(1): 101. CrossRef - Impact of Endodontic Kinematics on Stress Distribution During Root Canal Treatment: Analysis of Photoelastic Stress
Shelyn Akari Yamakami, Julia Adornes Gallas, Igor Bassi Ferreira Petean, Aline Evangelista Souza-Gabriel, Manoel Sousa-Neto, Ana Paula Macedo, Regina Guenka Palma-Dibb
Journal of Endodontics.2022; 48(2): 255. CrossRef - Shaping ability of ProTaper Gold and WaveOne Gold nickel-titanium rotary instruments in simulated S-shaped root canals
Lu Shi, Junling Zhou, Jie Wan, Yunfei Yang
Journal of Dental Sciences.2022; 17(1): 430. CrossRef - A Comparative Study of Two Martensitic Alloy Systems in Endodontic Files Carried out by Unskilled Hands
Juan Algar, Alejandra Loring-Castillo, Ruth Pérez-Alfayate, Carmen Martín Carreras-Presas, Ana Suárez
Applied Sciences.2022; 12(12): 6289. CrossRef - Quantitative evaluation of apically extruded debris using TRUShape, TruNatomy, and WaveOne Gold in curved canals
Nehal Nabil Roshdy, Reham Hassan
BDJ Open.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Canal Transportation, Separation Rate, and Preparation Time between One Shape and Neoniti (Neolix): An In Vitro CBCT Study
Maryam Kuzekanani, Faranak Sadeghi, Nima Hatami, Maryam Rad, Mansoureh Darijani, Laurence James Walsh, Sivakumar Nuvvula
International Journal of Dentistry.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Shaping ability of ProTaper Gold, One Curve, and Self-Adjusting File systems in severely curved canals: A cone-beam computed tomography study
MeenuG Singla, Hemanshi Kumar, Ritika Satija
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2021; 24(3): 271. CrossRef - Cone-beam computed tomographic analysis of apical transportation and centering ratio of ProTaper and XP-endo Shaper NiTi rotary systems in curved canals: an in vitro study
Hamed Karkehabadi, Zeinab Siahvashi, Abbas Shokri, Nasrin Haji Hasani
BMC Oral Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Mechanical Tests, Metallurgical Characterization, and Shaping Ability of Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instruments: A Multimethod Research
Emmanuel J.N.L. Silva, Jorge N.R. Martins, Carolina O. Lima, Victor T.L. Vieira, Francisco M. Braz Fernandes, Gustavo De-Deus, Marco A. Versiani
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(10): 1485. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of a new system for root canal filling using calcium silicate-based root canal sealers
Mario Tanomaru-Filho, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Jader Camilo Pinto, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of vibration characteristics of file systems for root canal shaping according to file length
Seong-Jun Park, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho, Hyo-Jin Ji, Eun-Hye Lee, Jin-Woo Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - New thermomechanically treated NiTi alloys – a review
J. Zupanc, N. Vahdat‐Pajouh, E. Schäfer
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(10): 1088. CrossRef - Shaping ability of four root canal instrumentation systems in simulated 3D-printed root canal models
David Christofzik, Andreas Bartols, Mahmoud Khaled Faheem, Doreen Schroeter, Birte Groessner-Schreiber, Christof E. Doerfer, Cyril Charles
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(8): e0201129. CrossRef - OPEN-SOURCE SOFTWARE IN DENTISTRY: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
Małgorzata Chruściel-Nogalska, Tomasz Smektała, Marcin Tutak, Katarzyna Sporniak-Tutak, Raphael Olszewski
International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care.2017; 33(4): 487. CrossRef - Mechanical Properties of Various Heat-treated Nickel-titanium Rotary Instruments
Hye-Jin Goo, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Eugenio Pedullà, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(11): 1872. CrossRef - A comparison of the shaping ability of three nickel-titanium rotary instruments: a micro-computed tomography study via a contrast radiopaque technique in vitro
Zhao Wei, Zhi Cui, Ping Yan, Han Jiang
BMC Oral Health.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Root Canal Transportation and Centering Ability of Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instruments in Mandibular Premolars Assessed Using Cone-Beam Computed Tomography
Iussif Mamede-Neto, Alvaro Henrique Borges, Orlando Aguirre Guedes, Durvalino de Oliveira, Fábio Luis Miranda Pedro, Carlos Estrela
The Open Dentistry Journal.2017; 11(1): 71. CrossRef - Blue Thermomechanical Treatment Optimizes Fatigue Resistance and Flexibility of the Reciproc Files
Gustavo De-Deus, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Victor Talarico Leal Vieira, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Carlos Nelson Elias, Gianluca Plotino, Nicola Maria Grande
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(3): 462. CrossRef
-
1,459
View
-
6
Download
-
24
Crossref
|