Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Restor Dent Endod > Volume 39(3); 2014 > Article
- Open Lecture on Statistics Statistical notes for clinical researchers: Nonparametric statistical methods: 1. Nonparametric methods for comparing two groups
- Hae-Young Kim
-
2014;39(3):-239.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.3.235
Published online: May 20, 2014
Department of Dental Laboratory Science and Engineering, College of Health Science & Department of Public Health Science, Graduate School, Korea University, Seoul, Korea.
- Correspondence to Hae-Young Kim, DDS, PhD. Associate Professor, Department of Dental Laboratory Science & Engineering, Korea University College of Health Science, San 1 Jeongneung 3-dong, Seongbuk-gu, Seoul, Korea 136-703. TEL, +82-2-940-2845; FAX, +82-2-909-3502, kimhaey@korea.ac.kr
©Copyights 2014. The Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 2,664 Views
- 56 Download
- 31 Crossref
Nonparametric statistical methods
1) Applying nonparametric methods on data satisfying assumptions of parametric methods may result in less power. However loss of power may be little or none for analysis of data which cannot satisfy the assumptions.
2) Tied values can be problematic and appropriate adjustment may be required.
3) Limited flexibility in generalizing to more complex analytic methods compared to parametric methods.
Nonparametric methods for comparing two groups
a) Number of all possible cases when 4 observations were selected from the set with 8 observations: 8! / (4! * 4!) = 70
-
b) Number of cases with larger difference of rank sum from A group to B group = 4 cases
Rank combinations of A group with (5, 6, 7, 8), (4, 6, 7, 8), (3, 6, 7, 8), and (4, 5, 7, 8).
-
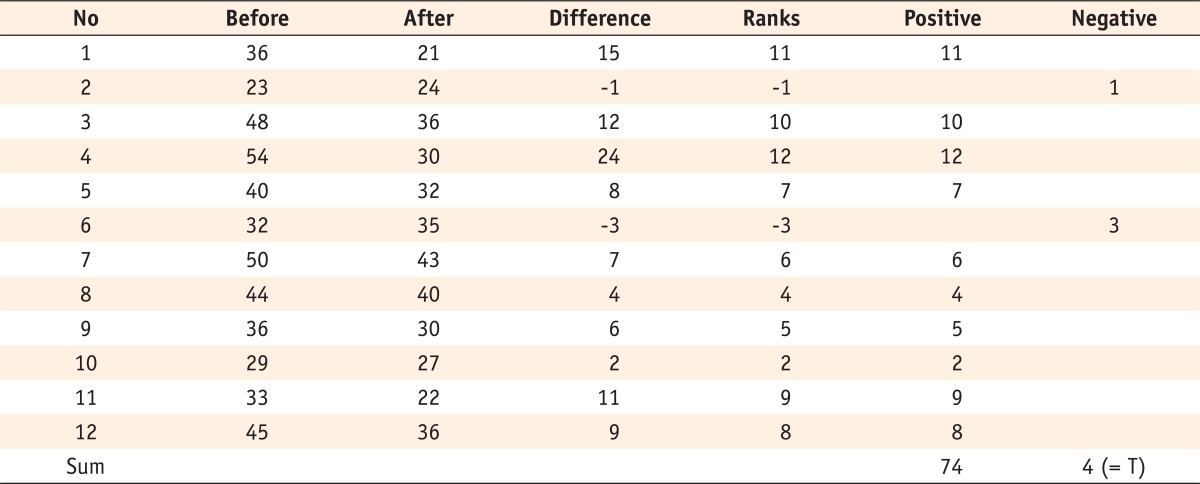
a) Small sample size (N < 20): find the p value for T value and sample size n in the table for the Wilcoxon signedrank test.
For this example, p value = 0.0017 for T = 4 when sample size = 12. -
b) Larger ample size (N > 20): use z distribution approximation.
Statistical decision: reject null hypothesis if |z| > 1.96 at the significance level α = 0.05. If the sample size was larger than 20, the asymptotic p value 0.006 (below e) could be used.
Tables & Figures
REFERENCES
Citations

- Racial Trauma and Black Mothers’ Mental Health: Does Cognitive Flexibility Buffer the Effects of Racialized Stress?
Gabriela S. Revi, Lori A. Francis
Journal of Racial and Ethnic Health Disparities.2026; 13(1): 660. CrossRef - Comparing patient and healthcare professional preferences for patient-centered integrated care in China: a best-worst scaling study
Yue Yin, Wenqing Gao, Xiujuan Cui, Minlin Li, Zijin Fang, Yixin Du, Wenxi Tang
BMC Health Services Research.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Unveiling the Digital Phenotype of Physical Activity Behavior in Community-Dwelling Older Adults Using Machine Learning
Anas Abdulghani, Kim Daniels, Bruno Bonnechère
Bioengineering.2026; 13(2): 205. CrossRef - Evaluation of a Cohort-Based Healthy Aging With HIV Wellness Pilot Intervention: “People Aging and Thriving With HIV” in Colorado
Erin Burk-Leaver, Christopher Zivalich, Justine Sunshine, Christopher A. Lowry, Kristine M. Erlandson
Journal of the Association of Nurses in AIDS Care.2025; 36(2): 167. CrossRef - The Use of Gamification in English Learning for Sustainable Development Goals (Sdgs): a Case Study in a Junior High School English Club
Fitria Aftinia, Ahmad Munir, Him'mawan Adi Nugroho
Journal of Lifestyle and SDGs Review.2025; 5(3): e04941. CrossRef - Informing equitable access to care: a cross-sectional study of travel burden to primary and rheumatology care for people with rheumatoid arthritis
Xiaoxiao Liu, Alka B Patel, Judy E Seidel, Dianne P. Mosher, John Hagens, Deborah A Marshall
International Journal for Equity in Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of Teaching Medical Students about Obesity in South Asians
Sumay Dasgupta, Enam Haque
MedEdPublish.2025; 15: 13. CrossRef - Student Perceptions of Live Versus Recorded Presentations
Natalie Hallemans, Charles Copeland
STEM Journal.2025; 26(2): 28. CrossRef - The Femoral Head Edema Zone: A Novel Classification Scheme to Better Predict Osteonecrosis Progression
Deniz C. Ince, Vivek P. Shah, Kenichi Kikuchi, Kyle P. O’Connor, Elizabeth L. Yanik, John C. Clohisy, Cecilia Pascual-Garrido
The Journal of Arthroplasty.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Enhancing reliability of self-report ergonomic assessment for manufacturing operations: exhaustive variability evaluation with targeted control measures
Charu Tripathi, Manish Arora, Amaresh Chakrabarti
International Journal of Occupational Safety and Ergonomics.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Comparative Single Vesicle Analysis of Aqueous Humor Extracellular Vesicles before and after Radiation in Uveal Melanoma Eyes
Shreya Sirivolu, Chen-Ching Peng, Paolo Neviani, Benjamin Y. Xu, Jesse L. Berry, Liya Xu
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(11): 6035. CrossRef - Automated Assesment of Eye-hand Coordination Skill using a Vertical Tracing Task on a Gaze-sensitive Human Computer Interaction Platform for children with Autism
Dharma Rane, Madhu Singh, Uttama Lahiri
Proceedings of the ACM on Human-Computer Interaction.2024; 8(ETRA): 1. CrossRef - Modified Jade Wind-Barrier Formula (MJWB) for Preventing Common Cold in Elderly with Qi-deficiency Constitution: A Controlled Trial
Yiu Lin Wong, Jialing Zhang, Linda LD Zhong, David Moher, Zhaoxiang Bian
OBM Integrative and Complementary Medicine.2024; 09(01): 1. CrossRef - Fundamentals of Nonparametric Statistical Tests for Dental Clinical Research
Arturo Garrocho-Rangel, Saray Aranda-Romo, Rita Martínez-Martínez, Verónica Zavala-Alonso, Juan Carlos Flores-Arriaga, Amaury Pozos-Guillén
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(10): 314. CrossRef - The Feasibility of Whole-Body Vibration Training as an Approach to Improve Health in Autistic Adults
Amy Allnutt, Sara Pappa, Michael Nordvall
Disabilities.2024; 4(3): 429. CrossRef - Piloting “From the Inside Out” — a toolkit addressing tuberculosis-related self-stigma
Stephen H.-F. Macdonald, Nadine Ferris France, Ian Hodgson, Fadhil Ali, Christa Dewi, Iman Abdurrakhman, Yeremia Mozart Runtu, Alva Juan, Jhon Sugiharto, Elaine Byrne, Ronan M. Conroy
BMC Global and Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Right ventricular stroke work index from echocardiography in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension—the role in short-term follow-up assessment
Raluca Jumatate, Anna Werther-Evaldsson, Annika Ingvarsson, Göran Rådegran, Carl Cronstedt Meurling, Ellen Ostenfeld
European Heart Journal - Imaging Methods and Practice.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Virtual Reality Based Gaze-Sensitive Aiming Task Platform: Role of Attention Allocation in Task Performance for Individuals With Autism and Typically Developing Individuals
Dharma Rane, Prachi Sharma, Madhu Singh, Uttama Lahiri
IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering.2023; 31: 1492. CrossRef - Comparison of post-operative outcomes of large direct inguinal hernia repairs based on operative approach (open vs. laparoscopic vs. robotic) using the ACHQC (Abdominal Core Health Quality Collaborative) database
Dimitrios N. Varvoglis, Manuel Sanchez-Casalongue, Molly A. Olson, Noah DeAngelo, Ian Garbarine, Jeffrey Lipman, Timothy M. Farrell, David Wayne Overby, Arielle Perez, Randal Zhou
Surgical Endoscopy.2023; 37(4): 2923. CrossRef - Simulation-based Reconstructed Diffusion unveils the effect of aging on protein diffusion in Escherichia coli
Luca Mantovanelli, Dmitrii S. Linnik, Michiel Punter, Hildeberto Jardón Kojakhmetov, Wojciech M. Śmigiel, Bert Poolman, Stefan Klumpp
PLOS Computational Biology.2023; 19(9): e1011093. CrossRef - Distinctive visual tasks for characterizing mild cognitive impairment and dementia using oculomotor behavior
Dharma Rane, Deba Prasad Dash, Alakananda Dutt, Anirban Dutta, Abhijit Das, Uttama Lahiri
Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - An exploratory cross-sectional study of the effects of ongoing relationships with accompanying patients on cancer care experience, self-efficacy, and psychological distress
Marie-Pascale Pomey, Monica Iliescu Nelea, Louise Normandin, Cécile Vialaron, Karine Bouchard, Marie-Andrée Côté, Maria Alejandra Rodriguez Duarte, Djahanchah Philip Ghadiri, Israël Fortin, Danielle Charpentier, Mélanie Lavoie-Tremblay, Nicolas Fernandez,
BMC Cancer.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Towards Human-Robot Collaborative Surgery: Trajectory and Strategy Learning in Bimanual Peg Transfer
Zhaoyang Jacopo Hu, Ziwei Wang, Yanpei Huang, Aran Sena, Ferdinando Rodriguez y Baena, Etienne Burdet
IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters.2023; 8(8): 4553. CrossRef - Investigating mechanosensitive channels activation in concert with the mechanical properties of red blood cells
Nicoletta Braidotti, Catalin Dacian Ciubotaru, Davide Rizzo, Lorenzo Bergamo, Annalisa Bernareggi, Dan Cojoc
Discover Mechanical Engineering.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Bitter Taste Perception and Dental Biofilm Cariogenicity in Orthodontics
Nithivoot Luengthamchat, Sittichai Koontongkaew, Kusumawadee Utispan
International Dental Journal.2022; 72(6): 805. CrossRef - A Smart Mobile App to Simplify Medical Documents and Improve Health Literacy: System Design and Feasibility Validation
Rasha Hendawi, Shadi Alian, Juan Li
JMIR Formative Research.2022; 6(4): e35069. CrossRef - Probing the polyphenolic flavonoid, morin as a highly efficacious inhibitor against amyloid(A4V) mutant SOD1 in fatal amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
E. Srinivasan, G. Chandrasekhar, R. Rajasekaran
Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics.2022; 727: 109318. CrossRef - Nurse's difficulty and their educational needs regarding pediatric cancer care in Japan
Mayu Yoshitsugu, Ikuko Sobue
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Common Pitfalls in Analysis of Tissue Scores
David K. Meyerholz, Nathan L. Tintle, Amanda P. Beck
Veterinary Pathology.2019; 56(1): 39. CrossRef - Effects of breathing motion on PET acquisitions
Yoshiki Owaki, Tadaki Nakahara, Takeshi Shimizu, Anne M. Smith, Wing K. Luk, Kazumasa Inoue, Masahiro Fukushi, Kiyotaka Nakajima
Nuclear Medicine Communications.2018; 39(7): 665. CrossRef - Decreased waterborne pathogenic bacteria in an urban aquifer related to intense shallow geothermal exploitation
Alejandro García-Gil, Samanta Gasco-Cavero, Eduardo Garrido, Miguel Mejías, Jannis Epting, Mercedes Navarro-Elipe, Carmen Alejandre, Elena Sevilla-Alcaine
Science of The Total Environment.2018; 633: 765. CrossRef
Parametric methods and nonparametric methods for comparing two or more groups
Procedures from 1st step to 3rd step of the Wilcoxon signed-rank test

 KACD
KACD


 ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite

