Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Restor Dent Endod > Volume 34(4); 2009 > Article
- Original Article Difference in bond strength according to filling techniques and cavity walls in box-type occlusal composite resin restoration
- Eun-Joo Ko, Dong-Hoon Shin
-
2009;34(4):-355.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.4.350
Published online: July 31, 2009
Department of Conservative Dentistry, College of Dentistry, Dankook University, Korea.
- Corresponding author: Dong-Hoon Shin. Department of Conservative Dentistry, College of Dentistry, Dankook University, San 7-1, Shinbu-dong, Cheonan, 330-716, Korea. Tel: 82-41-550-1965, Fax: 82-41-550-1963, donyshin@dankook.ac.kr
• Received: December 15, 2008 • Revised: June 2, 2009 • Accepted: June 5, 2009
Copyright © 2009 The Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry
- 1,009 Views
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref
Abstract
-
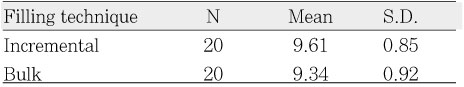
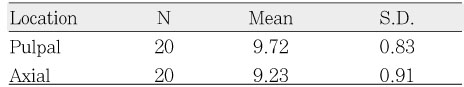
Bond strength depends on characteristics of bonding surface and restorative technique. The majority of studies dealing with dentin bond strength were carried out on flat bonding surface, therefore, difference of bond strength between axial wall and pulpal wall is not clear yet. This study evaluated bonding difference between cavity walls in class I composite resin restoration with different filling techniques.Twenty extracted caries-free human third molars were used. Cavities were prepared in 6 × 4 × 3 mm box-type and divided into four groups according to filling technique and bonding surface: Group I; bulk filling - pulpal wall, Group II; bulk filling - axial wall, Group III; incremental filling - pulpal wall, Group IV; incremental filling - axial wall.Cavities were filled with Filtek Z250®(3M/ESPE., USA) and Clearfill SE bond®(Kuraray, Japan). After 24 hour-storage in 37℃ water, the resin bonded teeth were sectioned bucco-lingualy at the center of cavity.Specimens were vertically sectioned into 1.0 × 1.0 mm thick serial sticks perpendicular to the bond surface using a low-speed diamond saw (Accutom 50, Struers, Copenhagen, Denmark) under water cooling. The trimmed specimens were then attached to the testing device and in turn, was placed in a universal testing machine (EZ test, Shimadzu Co., Kyoto, Japan) for micro-tensile testing at a cross-head speed of 1 mm/min. The results obtained were statistically analyzed using 2-way ANOVA and t-test at a significance level of 95%.The results were as follows:1. There was no significant difference between bulk filling and incremental filling.2. There was no significant difference between pulpal wall and axial wall, either.Within the limit of this study, it was concluded that microtensile bond strength was not affected by the filling technique and the site of cavity walls.
- 1. Suzuki T, Finger WJ. Dentin adhesives: Site of dentin vs bonding of composite resins. Dent Mater. 1988;4: 379-383.ArticlePubMed
- 2. Tagami J, Tao L, Pashley DH. Correlation among dentin depth, permeability, and bond strength of adhesive resins. Dent Mater. 1990;6: 45-50.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Pereira PN, Okuda M, Sano H, Yoshikawa T, Burrow MF, Tagami J. Effect of intrinsic wetness and regional difference on dentin bond strength. Dent Mater. 1999;15: 46-53.ArticlePubMed
- 4. Nakajima M, Shono T, Zheng L, Tagami J, Pashley DH. Effect of moist vs dry bonding to normal vs cariesaffected dentin with Scotchbond Multi-Purpose Plus. J Dent Res. 1999;78: 1298-1303.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 5. Feilzer AJ, de Gee AJ, Davidson CL. Setting stress in composite resin in relation to configuration of the restoration. J Dent Res. 1987;66: 1636-1639.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 6. Ogata M, Okuda M, Nakajima M, Pereira PNR, Sono H, Tagami J. Influence of the direction of tubules on bond strength to dentin. Oper Dent. 2001;26: 27-35.PubMed
- 7. Pashley DH, Sano H, Ciucchi B, Yoshiyama M, Carvalho RM. Adhesion testing of dentin bonding agents: a review. Dent Mater. 1995;11: 117-125.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Sattabanasuk V, Vachiramon V, Qian F, Armstrong SR. Resin-dentin bond strength as related to different surface preparation methods. J Dent. 2007;35: 467-475.ArticlePubMed
- 9. Phrukkanon S, Burrow MF, Tyas MJ. The effect of dentine location and tubule orientation on the bond strengths between resin and dentine. J Dent. 1999;27: 265-274.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Nikolaenko SA, Lohbauer U, Roggendorf M, Petschelt A, Dasch W, Frankenberger R. Influence of c-factor and layering technique on microtensile bond strength to dentin. Dent Mater. 2004;20: 579-585.ArticlePubMed
- 11. Buonocore MG. A simple method of increasing the adhesion of acrylic filling materials to enamel surfaces. J Dent Res. 1955;34(6):849-853.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 12. Prévost AP, Fuller JL, Peterson LC. Composite and intermediate resin tag formation in acid-etched enamel: A scanning electron microscopy evaluation. J Prosthet Dent. 1984;52: 204-207.ArticlePubMed
- 13. Gwinnett AJ. Smear layer: Morphological considerations. Oper Dent Suppl. 1984;3: 2-12.PubMed
- 14. Kanca J 3rd. Resin bonding to wet substrate 1. Bonding to dentin. Quintessence Int. 1992;23: 39-41.PubMed
- 15. Pashley DH, Carvalho RM, Sano H, Nakajima M, Yoshiyama M, Shono Y, Fernandes CA, Tay F. The microtensile bond test. A review. J Adhes Dent. 1999;1: 299-309.PubMed
- 16. Matsumoto H, Gres JE, Marker VA, Okabe T, Ferracane JL, Harvey GA. Depth of cure of visible light-cured resin: clinical simulation. J Prosthet Dent. 1986;55: 574-578.ArticlePubMed
- 17. He Z, Shimada Y, Tagami J. The effects of cavity size and incremental technique on micro-tensile bond strength of resin composite in class I cavities. Dent Mater. 2007;23: 533-538.ArticlePubMed
- 18. Loguercio AD, Reis A, Ballester RY. Polymerization shrinkage: effects of constraint and filling technique in composite restoration. Dent Mater. 2004;20: 236-243.PubMed
- 19. Tjan AH, Bergh BH, Linder C. Effect of various incremental techniques on the marginal adaptation of class II composite resin restoration. J Prosthet Dent. 1992;67: 62-66.PubMed
- 20. Sano H, Shono H, Sonoda H, Takatsu T, Ciucchi B, Carvalho R, Pashley DH. Relationship between surface area for adhesion and tensile bond strength-Evaluation of a micro-tensile bond test. Dent Mater. 1994;10: 236-240.ArticlePubMed
- 21. Ogata M, Nakajima M, Sano H, Tagami J. Effect of dentin primer application on regional bond strength to cervical wedge-shaped cavity walls. Oper Dent. 1999;24: 81-88.PubMed
- 22. Yoshiyama M, Matauo T, Ebisu S, Pashley D. Regional bond strengths of self-etching/self-priming adhesive systems. J Dent. 1998;26: 609-616.ArticlePubMed
- 23. Watanabe LG, Marshall GW, Marshal J. Dentin shear strength: effects of tubule orientation and intraoral location. Dent Mater. 1996;12: 109-115.PubMed
- 24. Kim Y, Park J, Lee C, Song Y, Seo DK, Roh BD. The influence of cavity configuration on the microtensile bond strength between composite resin and dentin. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2008;33: 472-479.Article
- 25. Koo BJ, Shin DH. The effect of c-factor and volume on microleakage of composite resin restorations with enamel margins. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2006;31: 452-459.
- 26. Cho YG, Yoo SH. Comparative enamel bond strength between light-and dual-cured composites bonded by self-etching adhesives. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2007;32: 1-8.Article
- 27. Jung MR, Choi GW, Park SH, Park SJ. The bonding durability of total etching adhesives on dentin. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2007;32: 365-375.Article
- 28. Park JS, Kim JS, Kim MS, Son HH, Kwon HC, Cho BH. Aging effect on the microtensile bond strength of self-etching adhesives. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2006;31: 415-425.Article
REFERENCES
Tables & Figures
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- The effect of the strength and wetting characteristics of Bis-GMA/TEGDMA-based adhesives on the bond strength to dentin
Eun-Sook Park, Chang-Keun Kim, Ji-Hyun Bae, Byeong-Hoon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(2): 139. CrossRef
Difference in bond strength according to filling techniques and cavity walls in box-type occlusal composite resin restoration
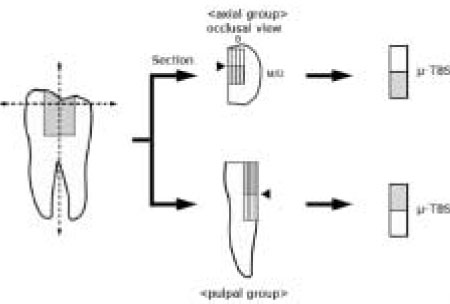
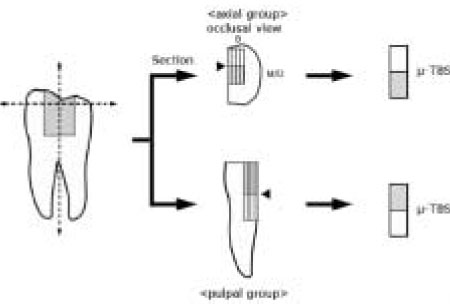
Figure 1
Specimen preparation.
µ-TBS : microtensile bond strength test
B : Buccal, M : Mesial, D : Distal
Figure 1
Difference in bond strength according to filling techniques and cavity walls in box-type occlusal composite resin restoration
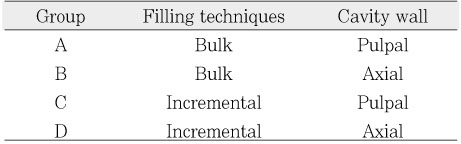
Groups divided by filling technique and cavity wall
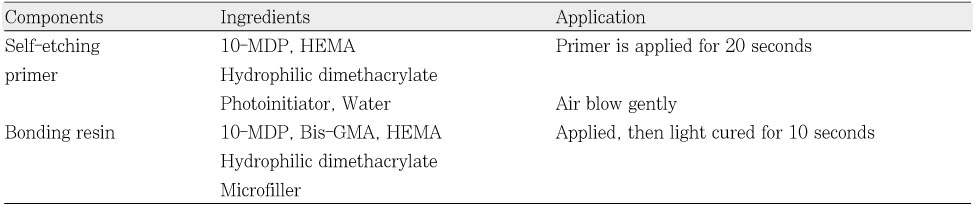
Composition and application protocol of Clearfil SE bond®
Two-way ANOVA result between factors of filling technique and cavity wall
Microtensile bond strength according to resin filling techniques (MPa)
Microtensile bond strength according to cavity walls (MPa)
Table 1
Groups divided by filling technique and cavity wall
Table 2
Composition and application protocol of Clearfil SE bond®
Table 3
Two-way ANOVA result between factors of filling technique and cavity wall
Table 4
Microtensile bond strength according to resin filling techniques (MPa)
Table 5
Microtensile bond strength according to cavity walls (MPa)

 KACD
KACD

 ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite

