Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Restor Dent Endod > Volume 29(5); 2004 > Article
-
Original Article
Antibiotic susceptibility in mutans streptococci and
Streptococcus anginosus isolated from dental plaque - Joong-Ki Kook1,3, Sang-Soo Lim2,3, So Young Yoo1,3, Ho-Keel Hwang2,3
-
2004;29(5):-469.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.5.462
Published online: September 30, 2004
1Department of Oral Biochemistry, College of Dentistry, Chosun University, Korea.
2Department of Conservative Dentistry, College of Dentistry, Chosun University, Korea.
3Oral Biology Research Institute, College of Dentistry, Chosun University, Korea.
- Corresponding author: Ho-Keel Hwang. Department of Conservative Dentistry, and Oral Biology Research Institute, College of Dentistry, Chosun University 375 Seo-suk Dong, Dong-Gu, Gwang-ju, Korea, 501-749. Tel: 82-62-220-3846, Fax: 82-62-232-9064, rootcanal@hanmail.net
Copyright © 2004 Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry
- 1,784 Views
- 11 Download
Abstract
- The aim of this study was to investigate the susceptibility of mutans streptococci (S. mutans and S. sobrinus) and Streptococcus anginosus, for seven antibiotics, penicillin G, amoxicillin, ciprofloxacin, cefuroxime, erythromycin, bacitracin, and vancomycin. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of seven antibiotics against 3 species (type strains) of mutans streptococci and S. anginosus, 10 strains (wild type) of S. mutans, 7 strains (wild type) of S. sobrinus, and 11 strains (wild type) of S. anginosus, were measured by broth dilution method. All of the type strains of mutans streptococci and S. anginosus had the same susceptibility for penicillin G, amoxicillin, cefuroxime and bacitracin. Type strain of S. anginosus was sensitive in ciprofloxacin, but those of mutans streptococci were not. All of the clinical isolates of mutans streptococci and S. anginosus had the same susceptibility for the seven antibiotics. Our data reveal that mutans streptococci and S. anginosus have similar antibiotic-resistant character. In addition, these results may offer the basic data to verify the antibiotic-resistant mechanism of mutans streptococci and S. anginosus.
- 1. Ruoff KL, Whiley RA, Beighton D. In: Murray ER, Baron EJ, Pfaller MA, Tenover FC, Yolken RH, editors. Streptococcus. Manual of CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY. 1999;7th Ed. Washington: ASM press; 283-296.
- 2. Whiley RA, Beighton D. Current classification of the oral streptococci. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1998;13: 195-216.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Igarashi T, Ichikawa K, Yamamoto A, Goto N. Identification of mutans streptococcal species by the PCR products of the dex genes. J Microbiol Methods. 2001;46: 99-105.ArticlePubMed
- 4. Gold OG, Jordan HV, van Houte J. A selective medium for the isolation of Streptococcus mutans. Arch Oral Biol. 1973;18: 1357-1364.PubMed
- 5. Little WA, Korts DC, Thomson LA, Bowen WH. Comparative recovery of Streptococcus mutans on ten isolation media. J Clin Microbiol. 1977;5(6):578-583.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 6. Tanzer JM, Borjesson AC, Laskowski L, Kurasz AB, Testa M. Glucose-sucrose-potassium tellurite-bacitracin agar, an alternative to mitis salivarius-bacitracin agar for enumeration of Streptococcus mutans. J Clin Microbiol. 1984;20(4):653-659.PubMedPMC
- 7. Kim PS, Hwang HK, Kim HS, Lim SA, Kang HY, Yoo SY, Kook JK. Identification of non-mutans btreptococci growing on Mitis-Salivarius Bacitracin agar medium. J Dent Res. 2003;82(Special issue B):B-351.
- 8. Shklair IL, Keene HJ. A biochemical scheme for the separation of the five varieties of Streptococcus mutans. Arch Oral Biol. 1974;19: 1079-1081.ArticlePubMed
- 9. Shklair IL, Keene HJ. In: Stiles HM, Loesche WJ, O'Brien TC, editors. Biochemical characterization and distribution of Streptococcus mutans in three diverse populations. Microbial aspects of dental caries. 1976;Washington, D.C.: Information Retrieval Inc; 201-210.
- 10. Murray PR, Jorgensen JH. Quantitative susceptibility test methods in major united states medical center. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981;20(1):66-70.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 11. Jorgensen JH, Turnidge JD, Washington A. In: Murray ER, Baron EJ, Pfaller MA, Tenover FC, Yolken RH, editors. Antibacterial susceptibility tests: dilution and disk diffusion methods. Manual of CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY. 1999;7th Ed. Washington: ASM press; 1526-1543.
- 12. Băncescu G, Skaug N, Dumitriu S, Băncescu A. Antimicrobial susceptibility of some streptococci strains of anginosus group isolated from oral and maxillofacial infections. Roum Arch Microbiol Immunol. 1999;58(1):57-63.PubMed
- 13. Horii T, Arakawa Y, Ohta M, Ichiyama S, Wacharotayankun R, Kato N. Plasmid-mediated AmpC-type beta-lactamase isolated from Klebsiella pneumoniae confers resistance to broad-spectrum beta-lactams, including moxalactam. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993;37(5):984-990.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 14. Cloeckaert A, Baucheron S, Flaujac G, Schwarz S, Kehrenberg C, Martel JL, Chaslus-Dancla E. Plasmid-mediated florfenicol resistance encoded by the floR gene in Escherichia coli isolated from cattle. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2000;44(10):2858-2860.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 15. Simjee S, White DG, McDermott PF, Wagner DD, Zervos MJ, Donabedian SM, English LL, Hayes JR, Walker RD. Characterization of Tn1546 in vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium isolated from canine urinary tract infections: evidence of gene exchange between human and animal enterococci. J Clin Microbiol. 2002;40(12):4659-4665.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 16. Bauernfeind A, Wagner S, Jungwirth R, Schneider I, Meyer D. A novel class C beta-lactamase(FOX-2) in Escherichia coli conferring resistance to cephamycins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1997;41(9):2041-2046.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 17. Nelson EC, Elisha BG. Molecular basis of AmpC hyperproduction in clinical isolates of Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1999;43(4):957-959.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 18. Bonnet R, Chanal C, Ageron E, Sirot D, De Champs C, Grimont P, Sirot J. Inducible AmpC beta-lactamase of a new member Enterobacteriaceae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002;46(10):3316-3319.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 19. Petrosino JF, Pendleton AR, Weiner JH, Rosenberg SM. Chromosomal system for studying AmpC-mediated beta-lactam resistance mutation in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002;46(5):1535-1539.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 20. Noguchi N, Emura A, Matsuyama H, O'Hara K, Sasatsu M, Kono M. Nucleotide sequence and characterization of erythromycin resistance determinant that encodes macrolide 2'-phosphotransferase I in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1995;39(10):2359-2363.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 21. van Boxtel RA, van de Klundert JA. Expression of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa gentamicin resistance gene aacC3 in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1998;42(12):3173-3178.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 22. Gotoh N, Tsujimoto H, Poole K, Yamagishi J, Nishino T. The outer membrane protein OprM of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is encoded by oprK of the mexA-mexB-oprK multidrug resistance operon. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1995;39(11):2567-2569.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 23. Mitchell BA, Brown MH, Skurray RA. QacA multidrug efflux pump from Staphylococcus aureus: comparative analysis of resistance to diamidines, biguanidines, and guanylhydrazones. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1998;42(2):475-477.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 24. Kaatz GW, Seo SM, O'Brien L, Wahiduzzaman M, Foster TJ. Evidence for the existence of a multidrug efflux transporter distinct from NorA in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2000;44(5):1404-1406.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 25. Siqueira JF, Rocas IN, Moraes SR, Santos KR. Direct amplification of rRNA gene sequences for identification of selected oral pathogens in root canal infections. Int Endod J. 2002;35(4):345-351.ArticlePubMed
- 26. Tateda M, Shiga K, Saijo S, Sone M, Hori T, Yokoyama J, Matsuura K, Takasaka T, Miyagi T. Streptococcus anginosus in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: implication in carcinogenesis. Int J Mol Med. 2000;6(6):699-703.ArticlePubMed
- 27. Shiga K, Tateda M, Saijo S, Hori T, Sato I, Tateno H, Matsuura K, Takasaka T, Miyagi T. Presence of Streptococcus infection in extra-oropharyngeal head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and its implication in carcinogenesis. Oncol Rep. 2001;8(2):245-248.ArticlePubMed
- 28. Kim MS, Kim SG, Chung HM, Kim SG, Kook JK, Kim MK, Kim HS, Yoo SY. Molecular identification of bacteria from osteomyelitis of the jaws. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2003;29(1):48-55.
REFERENCES
Tables & Figures
REFERENCES
Citations

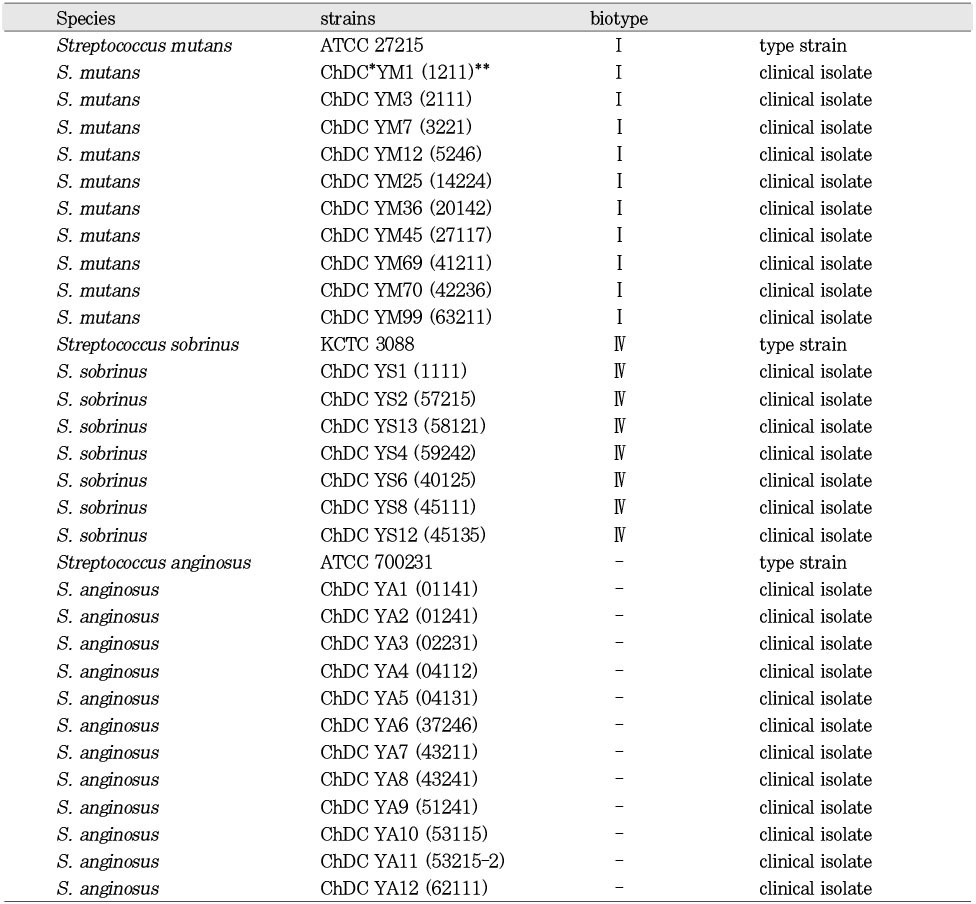
Bacteria strains used in this study
*Department of Oral Biochemistry, College of Dentistry, Chosun University
( )**Older-name
*Aerobically at 37℃ for 48 h.
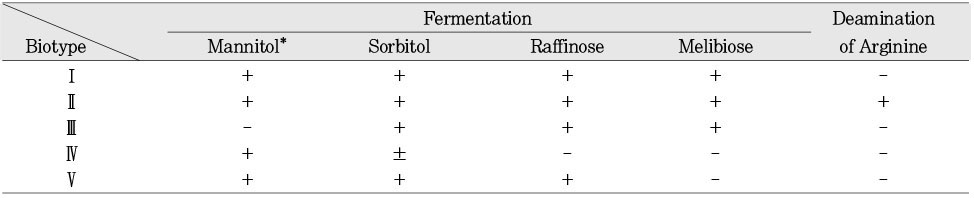
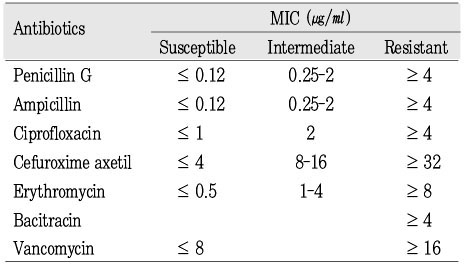
Interpretive standards for dilution susceptibility testing11)
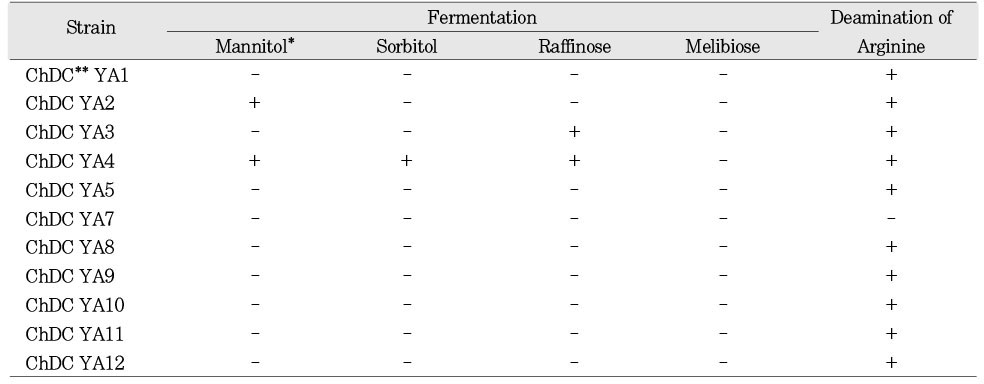
Biochemical test of S. anginosus isolated on MSB agar
*Aerobically at 37℃ for 48 h.
**Department of Oral Biochemistry, College of Dentistry, Chosun University
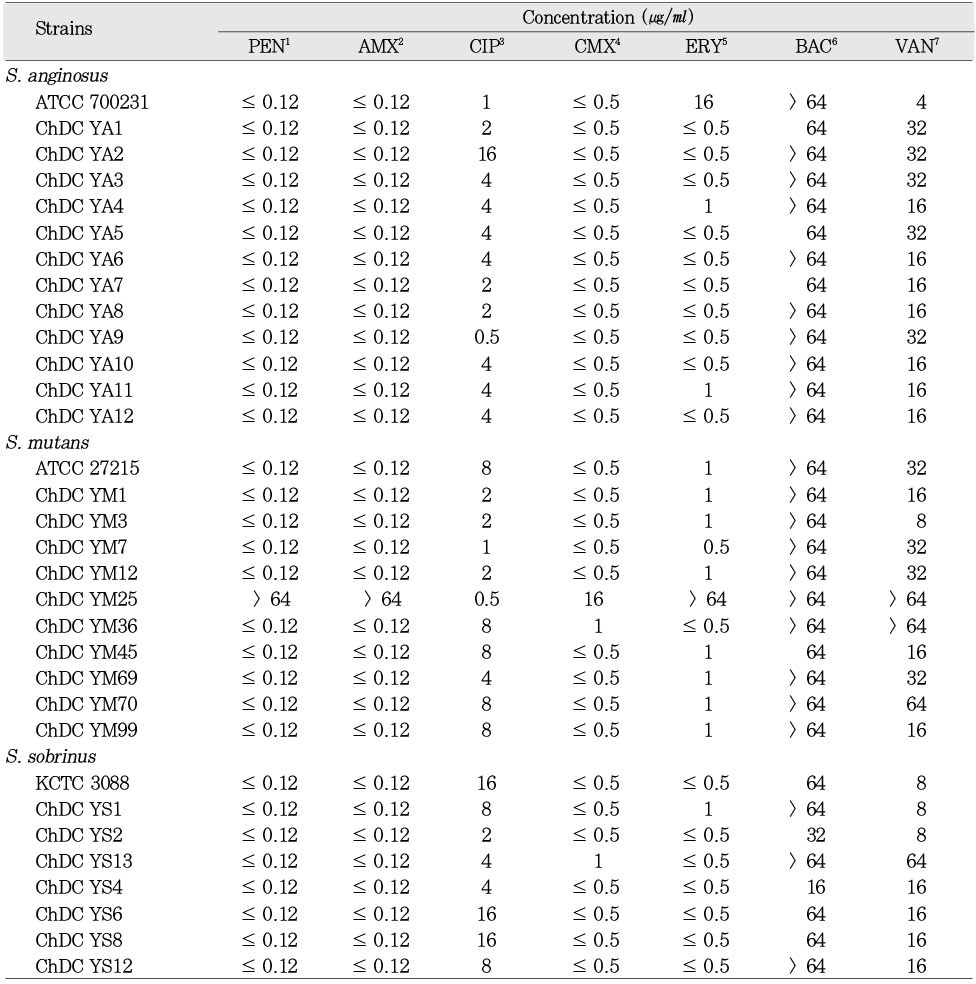
Minimum inhibitory concentration of antibiotics against mutans streptococci and S. anginosus
1Penicillin G, 2Amoxicillin, 3Ciprofloxacin, 4Cefuroxime, 5Erythromycin, 6Bacitracin, 7Vancomycin
*Department of Oral Biochemistry, College of Dentistry, Chosun University ( )**Older-name
*Aerobically at 37℃ for 48 h.
*Aerobically at 37℃ for 48 h. **Department of Oral Biochemistry, College of Dentistry, Chosun University
1Penicillin G, 2Amoxicillin, 3Ciprofloxacin, 4Cefuroxime, 5Erythromycin, 6Bacitracin, 7Vancomycin

 KACD
KACD
 ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite

