Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Restor Dent Endod > Volume 47(3); 2022 > Article
- Research Article Effect of intracanal cryotherapy on postoperative pain after endodontic treatment: systematic review with meta-analysis
-
Fernanda Garcias Hespanhol1
 , Ludmila Silva Guimarães1
, Ludmila Silva Guimarães1 , Lívia Azeredo Alves Antunes1,2
, Lívia Azeredo Alves Antunes1,2 , Leonardo Santos Antunes1,2
, Leonardo Santos Antunes1,2
-
Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(3):e30.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e30
Published online: July 4, 2022
1Postgraduate Program, School of Dentistry, Fluminense Federal University, Niterói, RJ, Brazil.
2Specific Formation Department, School of Dentistry of Nova Friburgo, Fluminense Federal University, Niterói, RJ, Brazil.
- Correspondence to Leonardo Santos Antunes, DDS, MSc, PhD. Professor, Department of Specific Formation, School of Dentistry, Fluminense Federal University, Rua Doutor Silvio Henrique Braune, 22 Centro, Nova Friburgo, Rio de Janeiro 28625-650, Brazil. leonardoantunes@id.uff.br
Copyright © 2022. The Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Abstract
-
Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of final irrigation with cold saline solution after endodontic treatment compared with saline solution at room temperature against postoperative pain following endodontic treatment.
-
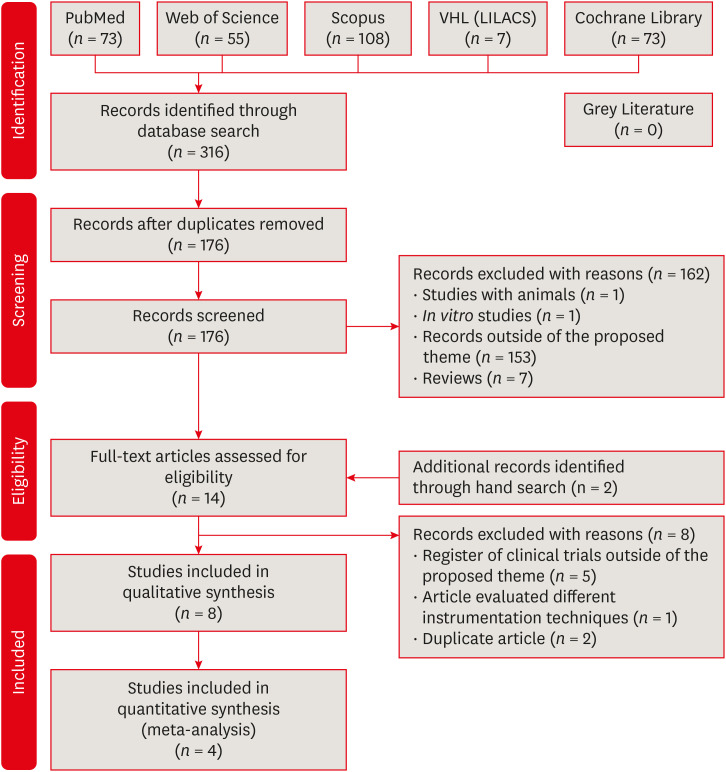
Materials and Methods A broad search was performed in the PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, Cochrane Library, Virtual Health Library (LILACS), and Grey Literature databases. Two independent reviewers performed data extraction, risk of bias using the Cochrane methodology, and certainty of evidence using the Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluations (GRADE) approach.
-
Results Eight studies were included in qualitative synthesis. Intracanal cryotherapy favored the reduction of postoperative pain in the systematic review. Four studies were included in meta-analyses. The meta-analysis showed that intracanal cryotherapy reduced postoperative pain in teeth with symptomatic apical periodontitis (SAP) at 24 hours. There was no association between intracanal cryotherapy and control (room temperature) groups in teeth with normal periapical tissue with respect to postoperative pain at 24 hours and 48 hours.
-
Conclusions Intracanal cryotherapy was effective in reducing postoperative pain after endodontic treatment in teeth with SAP.
INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Electronic database used and search strategy
RESULTS
Characteristics of the included studies: endodontic treatment
| Author/year | Study design | Case/Control | Gender (Case/Control) | Types of teeth | Diagnostic pulp | Instrumentation | Irrigation | Foraminal enlargement | No. of sessions | Cryotherapy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al-Nahlawi et al. 2016 [24] | Randomized clinical trial with blind assessment technique | Group I (control): 25 | MD | Single-rooted teeth | Vital teeth with irreversible pulpitis | Rotatory (ProTaper Universal) | NaOCl 5.25% | No | 1 | 20 mL of 2°C to 4°C cold saline for 5 min using Endovac at WL |
| Group II (room temperature saline): 25 | ||||||||||
| Group III (cold saline): 25 | ||||||||||
| Keskin et al. 2017 [25] | MD | Control group (room temperature): 85 | Female: (45/57) | Incisor, Premolar, Molar | Asymptomatic irreversible pulpitis or symptomatic irreversible pulpitis with either normal apical tissues or symptomatic apical periodontitis | Rotatory (Protaper Next) | NaOCl 5.25% | No | 1 | 2.5°C cold saline for 5 min using a 31 G Navi-Tip needle 2 mm short of the WL |
| Cryotherapy group: 85 | Male: (40/28) | |||||||||
| Vera et al. 2018 [28] | Randomized multicenter clinical trial | Control group (room temperature): 105 | Female: (60/57) | Uniradicular teeth | Necrotic pulp and symptomatic apical periodontitis | Rotatory (Kerr Endo) | NaOCl 5.25% | No | 2 | 20 mL of 2.5°C cold saline for 5 min using Endovac to the WL |
| Cryotherapy group: 105 | Male: (33/36) | |||||||||
| Bazaid and Kenawi 2018 [29] | Randomized control trial | Control group (room temperature): 16 | MD | MD | Irreversible pulpitis with either normal apical tissues or apical periodontitis. | Manual (Hand files to size 25) | NaOCl | No | 1 | 2.5°C cold saline for 2 min using side vented needle |
| Cryotherapy group: 20 | ||||||||||
| Gundogdu and Arslan 2018 [26] | Randomized prospective clinical trial | Control group (room temperature): 21 | Female: 9 | Maxillary or mandibular molar teeth | Vital teeth with symptomatic apical periodontitis. | Reciprocating (Reciproc) | NaOCl 2.5% | No | 1 | Intracanal Cryotherapy Group: 20 mL of 2.5°C cold saline for 5 min |
| Male: 12 | Intraoral Cryotherapy Group: small ice packs on the vestibular surface of the tooth for 30 min | |||||||||
| Intracanal cryotherapy group: 22 | Female: 10 | Extraoral Cryotherapy Group: ice packs on the cheek surface for 30 min | ||||||||
| Male: 12 | ||||||||||
| Intraoral cryotherapy group: 21 | Female: 9 | |||||||||
| Male: 12 | ||||||||||
| Extraoral cryotherapy group: 20 | Female: 10 | |||||||||
| Male: 10 | ||||||||||
| Jain et al. 2018 [27] | In vivo study | Control group (room temperature): 30 | MD | Mandibular first molar | Symptomatic irreversible pulpitis with normal periodicals tissue, asymptomatic or symptomatic apical periodontitis. | Manual (Step back technique) | NaOCl 2.5% | No | 2 | 5 mL of 2.5°C cold saline with side vented |
| Cryotherapy group: 30 | ||||||||||
| Vieyra and Guardado, 2018 [30] | Randomized clinical trial | Control group (room temperature): 80 | Female: 43 | Maxillary and mandibular molar, premolar, anterior teeth | Vital teeth with irreversible pulpitis | Reciprocating (Reciproc) | NaOCl 5.25% | No | 1 | Group A: 5 mL of 6°C EDTA 17% + 10 mL of 6°C cold saline dispensed to the WL using Endovac for 1 min |
| Male: 37 | Group B: 5 mL of 2.5°C EDTA 17% + 10 mL of 2.5°C cold saline dispensed to the WL using Endovac for 1 min | |||||||||
| Group A (6°C): 80 | Female: 43 | |||||||||
| Male: 37 | ||||||||||
| Group B (2.5°C): 80 | Female: 43 | |||||||||
| Male: 37 | ||||||||||
| Alharthi et al. 2019 [31] | Randomized controlled trial | Group I (Cryotherapy): 35 | MD | Single-rooted teeth | Vital and non-vital teeth | Rotatory (ProTaper Universal) | NaOCl 5.25% | No | 1 | 10 mL of 1.5–2.5°C cold saline delivered to the WL by using a two |
| Group II (Room temperature): 35 | 96 side–vented needle over a period of 5 min | |||||||||
| Group III (Control): 35 |
Analysis tools of post-operative pain
| Author/year | Assessment | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Period | Measurement | Postoperative medications | Results | |
| Al- Nahlawi et al., 2016 [24] | VAS | 6 hr, 12 hr, 24 hr, 48 hr, 7 days | 0–100 | Ibuprofen 400 mg | VAS pain values after 6, 12, 24, and 48 hr in cold saline irrigation group were lower than those of both saline irrigation at room temperature and control groups. |
| Keskin et al., 2017 [25] | VAS | 24 hr, 48 hr | 0: no pain | MD | Patients in the cryotherapy group reported significantly lower VAS scores compared with patients in the control group (p < 0.05) at 24 hr follow-ups. |
| 1–3: mild pain | |||||
| 4–6: moderate pain | |||||
| 7–9: severe pain | |||||
| 10: the worst pain experienced | |||||
| Vera et al., 2018 [28] | VAS | 6 hr, 24 hr, 72 hr | Mild pain | Ibuprofen 600 mg | Patients in the cryotherapy group suffered significantly less pain after 6, 24, and 72 hr and needed fewer analgesics postoperatively (p < 0.05). |
| Moderate pain | |||||
| Intense pain | |||||
| Bazaid and Kenawi, 2018 [29] | VAS | 24 hr, 48 hr | MD | MD | Intracanal cryotherapy is effective in reducing postoperative pain in patients with irreversible pulpitis with apical periodontitis. But it does not affect patients with irreversible pulpitis without apical periodontitis. |
| Gundogdu and Arslan, 2018 [26] | VAS | 24 hr, 72 hr, 5 days, 7 days | MD | Ibuprofen 400 mg | When compared with control group, all the cryotherapy groups exhibited lower postoperative pain levels on the first, third, fifth, and seventh days and lower levels of pain on percussion on the seventh day (p < 0.05). |
| Jain et al., 2018 [27] | VAS | 6 hr, 24 hr, 48 hr | 0–10 | MD | There was no significant difference between cryotherapy and normal saline groups in irreversible pulpitis with normal periapical tissue. |
| In irreversible pulpitis with asymptomatic apical periodontitis, at 6 hr, normal saline group were significantly higher pain than cryotherapy group. | |||||
| In irreversible pulpitis with symptomatic apical periodontitis, at 6, 24, and 48 hr, normal saline group were significantly higher pain than cryotherapy group. | |||||
| Therefore, intracanal cryotherapy is effective in reducing post-operative pain in patient with irreversible pulpitis with apical periodontitis. | |||||
| Vieyra and Guardado, 2018 [30] | VAS | 24 hr, 48 hr, 72 hr | 0–0.5 cm: no pain | MD | No statistically relevant modification (p > 0.05) between control group and group A were encountered concerning level or period of pain. There was no statistically relevant difference (p > 0.05) among Group A and control group compared with Group B. Group B showed less pain than the rest of the groups in relation to the existence of pain at any of the three time points measured. |
| 0.6–4.0 cm: mild pain | |||||
| 0.45–7.4 cm: moderate pain | |||||
| 7.5–10 cm: severe pain | |||||
| Alharthi et al., 2019 [31] | VAS | 6 hr, 24 hr, 48 hr | 0: no pain | MD | Group I had the lowest post-endodontic pain (6 , 24 and 48 hr). Nevertheless, there was no significant difference between Group I and Group II. The highest post-endodontic pain (6, 24 and 48 hr) was in Group III. |
| 1–3: mild pain | |||||
| 4–6: moderate pain | |||||
| 7–9: severe pain | |||||
| 10: the worst pain | |||||
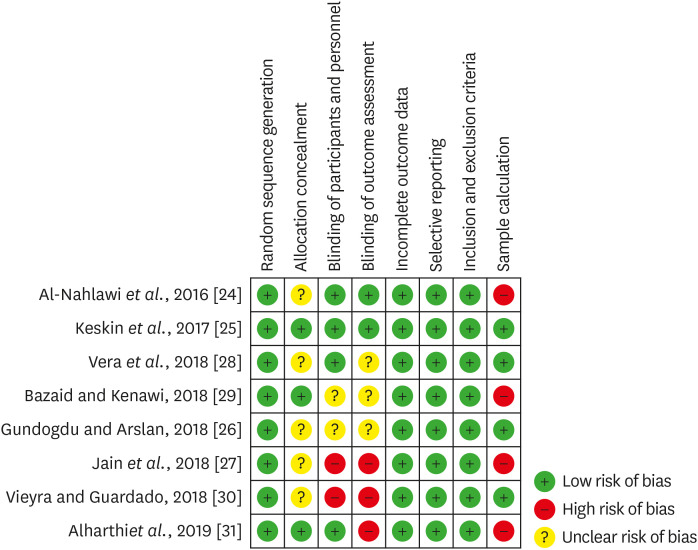
Quality assessment of the selected studies (The Cochrane Collaboration tool for assessing risk of bias).
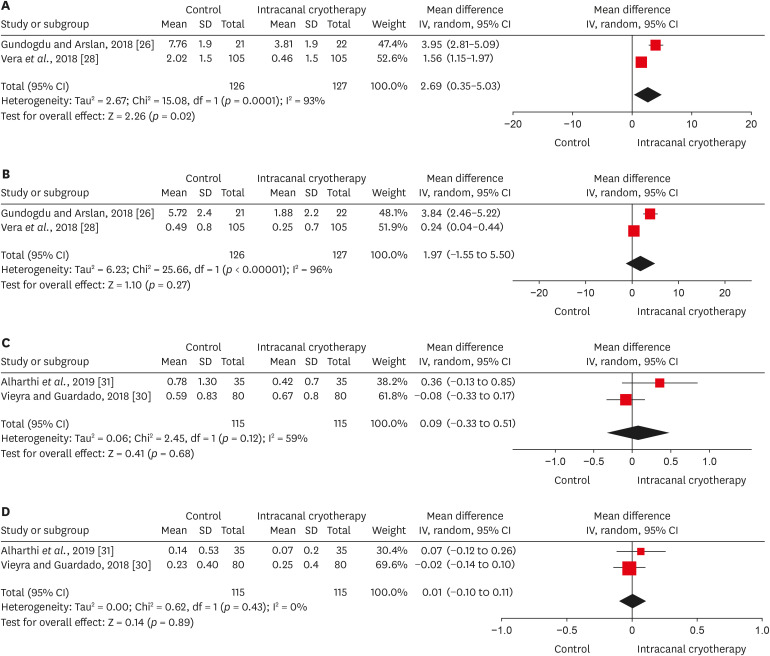
Forest plots of postoperative pain between intracanal cryotherapy group and control group (saline solution at room temperature). (A) Symptomatic apical periodontitis at 24 hours. (B) Symptomatic apical periodontitis at 72 hours. (C) Normal periapical tissue at 24 hours. (D) Normal periapical tissue at 48 hours.
Evidence profile in relation to symptomatic periapical tissue
Evidence profile in relation to normal periapical tissue
DISCUSSION
CONCLUSIONS
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
-
Funding: The work was supported by individual scholarships FAPERJ – Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro (#E-26/010.100995/2018; #E-26/202.805/2019; #E-26/010.002195/2019), and CNPQ – Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico.
-
Conflict of Interest: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
-
Author Contributions:
Conceptualization: Hespanhol FG, Guimarães LS, Antunes LAA, Antunes LS.
Data curation: Hespanhol FG, Guimarães LS, Antunes LAA, Antunes LS.
Formal analysis: Hespanhol FG, Guimarães LS, Antunes LAA.
Funding acquisition: Antunes LAA, Antunes LS.
Investigation: Hespanhol FG, Guimarães LS, Antunes LAA, Antunes LS.
Methodology: Hespanhol FG, Guimarães LS, Antunes LAA, Antunes LS.
Project administration: Antunes LAA, Antunes LS.
Resources: Hespanhol FG, Guimarães LS, Antunes LAA, Antunes LS.
Software: Hespanhol FG, Guimarães LS,.
Supervision: Antunes LAA, Antunes LS.
Validation: Hespanhol FG, Guimarães LS, Antunes LAA, Antunes LS.
Visualization: Hespanhol FG, Guimarães LS, Antunes LAA, Antunes LS.
Writing - original draft: Hespanhol FG, Guimarães LS, Antunes LAA, Antunes LS.
Writing - review & editing: Hespanhol FG, Guimarães LS, Antunes LAA, Antunes LS.
- 1. Rosenberg PA. Clinical strategies for managing endodontic pain. Endod Topics 2002;3:78-92.Article
- 2. Sathorn C, Parashos P, Messer H. The prevalence of postoperative pain and flare-up in single- and multiple-visit endodontic treatment: a systematic review. Int Endod J 2008;41:91-99.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Ferraz CC, Gomes NV, Gomes BP, Zaia AA, Teixeira FB, Souza-Filho FJ. Apical extrusion of debris and irrigants using two hand and three engine-driven instrumentation techniques. Int Endod J 2001;34:354-358.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 4. Bürklein S, Schäfer E. Apically extruded debris with reciprocating single-file and full-sequence rotary instrumentation systems. J Endod 2012;38:850-852.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Tanalp J, Güngör T. Apical extrusion of debris: a literature review of an inherent occurrence during root canal treatment. Int Endod J 2014;47:211-221.ArticlePubMed
- 6. Peuhkuri K, Nevala R, Vapaatalo H, Moilanen E, Korpela R. Ibuprofen augments gastrointestinal symptoms in lactose maldigesters during a lactose tolerance test. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 1999;13:1227-1233.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 7. Püspök A, Kiener HP, Oberhuber G. Clinical, endoscopic, and histologic spectrum of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced lesions in the colon. Dis Colon Rectum 2000;43:685-691.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Etienney I, Beaugerie L, Viboud C, Flahault A. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs as a risk factor for acute diarrhoea: a case crossover study. Gut 2003;52:260-263.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 9. Khan AZ, George K, DeFriend DJ. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced colonic stenosis: an unusual cause of a right-sided colonic mass: report of a case. Dis Colon Rectum 2003;46:403-405.PubMed
- 10. Belitsky RB, Odam SJ, Hubley-Kozey C. Evaluation of the effectiveness of wet ice, dry ice, and cryogenic packs in reducing skin temperature. Phys Ther 1987;67:1080-1084.PubMed
- 11. Modabber A, Rana M, Ghassemi A, Gerressen M, Gellrich NC, Hölzle F, Rana M. Three-dimensional evaluation of postoperative swelling in treatment of zygomatic bone fractures using two different cooling therapy methods: a randomized, observer-blind, prospective study. Trials 2013;14:238.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 12. Doğanay Yıldız E, Arslan H. Effect of low-level laser therapy on postoperative pain in molars with symptomatic apical periodontitis: a randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial. J Endod 2018;44:1610-1615.ArticlePubMed
- 13. Coelho MS, Vilas-Boas L, Tawil PZ. The effects of photodynamic therapy on postoperative pain in teeth with necrotic pulps. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther 2019;27:396-401.ArticlePubMed
- 14. Fayyad DM, Abdelsalam N, Hashem N. Cryotherapy: a new paradigm of treatment in endodontics. J Endod 2020;46:936-942.ArticlePubMed
- 15. Swenson C, Swärd L, Karlsson J. Cryotherapy in sports medicine. Scand J Med Sci Sports 1996;6:193-200.ArticlePubMed
- 16. Watkins AA, Johnson TV, Shrewsberry AB, Nourparvar P, Madni T, Watkins CJ, Feingold PL, Kooby DA, Maithel SK, Staley CA, Master VA. Ice packs reduce postoperative midline incision pain and narcotic use: a randomized controlled trial. J Am Coll Surg 2014;219:511-517.ArticlePubMed
- 17. McDowell JH, McFarland EG, Nalli BJ. Use of cryotherapy for orthopaedic patients. Orthop Nurs 1994;13:21-30.Article
- 18. Kwekkeboom KL. Pain management strategies used by patients with breast and gynecologic cancer with postoperative pain. Cancer Nurs 2001;24:378-386.ArticlePubMed
- 19. Koç M, Tez M, Yoldaş O, Dizen H, Göçmen E. Cooling for the reduction of postoperative pain: prospective randomized study. Hernia 2006;10:184-186.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 20. Bleakley C, McDonough S, MacAuley D. The use of ice in the treatment of acute soft-tissue injury: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Am J Sports Med 2004;32:251-261.PubMed
- 21. Forsgren H, Heimdahl A, Johansson B, Krekmanov L. Effect of application of cold dressings on the postoperative course in oral surgery. Int J Oral Surg 1985;14:223-228.ArticlePubMed
- 22. Laureano Filho JR, de Oliveira e Silva ED, Batista CI, Gouveia FM. The influence of cryotherapy on reduction of swelling, pain and trismus after third-molar extraction: a preliminary study. J Am Dent Assoc 2005;136:774-778.PubMed
- 23. Hubbard TJ, Denegar CR. Does cryotherapy improve outcomes with soft tissue injury? J Athl Train 2004;39:278-279.PubMedPMC
- 24. Al-Nahlawi T, Hatab TA, Alrazak MA, Al-Abdullah A. Effect of intracanal cryotherapy and negative irrigation technique on postendodontic pain. J Contemp Dent Pract 2016;17:990-996.ArticlePubMed
- 25. Keskin C, Özdemir Ö, Uzun İ, Güler B. Effect of intracanal cryotherapy on pain after single-visit root canal treatment. Aust Endod J 2017;43:83-88.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 26. Gundogdu EC, Arslan H. Effects of various cryotherapy applications on postoperative pain in molar teeth with symptomatic apical periodontitis: a preliminary randomized prospective clinical trial. J Endod 2018;44:349-354.ArticlePubMed
- 27. Jain A, Davis D, Bahuguna R, Agrawal A, Singh S, Ramachandran R, Varguese A. Role of cryotherapy in reducing postoperative pain in patients with irreversible pulpitis: an in-vivo study. Int J Dent Med Sci Res 2018;2:43-49.
- 28. Vera J, Ochoa J, Romero M, Vazquez-Carcaño M, Ramos-Gregorio CO, Aguilar RR, Cruz A, Sleiman P, Arias A. Intracanal cryotherapy reduces postoperative pain in teeth with symptomatic apical periodontitis: a randomized multicenter clinical trial. J Endod 2018;44:4-8.ArticlePubMed
- 29. Bazaid DS, Kenawi LM. The effect of intracanal cryotherapy in reducing postoperative pain in patients with irreversible pulpitis: a randomized control trial. Int J Health Sci Res 2018;8:83-88.
- 30. Vieyra JP, Guardado JA. Reduction of post-endodontic pain after one-visit root canal treatment using three cryotherapy protocols with different temperature. Ann Materials Sci Eng 2018;3:1033.
- 31. Alharthi AA, Aljoudi MH, Almaliki MN, Almalki MA, Sunbul MA. Effect of intra-canal cryotherapy on post-endodontic pain in single-visit RCT: a randomized controlled trial. Saudi Dent J 2019;31:330-335.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 32. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med 2009;151:264-269.ArticlePubMed
- 33. Higgins JP, Altman DG, Gøtzsche PC, Jüni P, Moher D, Oxman AD, Savovic J, Schulz KF, Weeks L, Sterne JA; Cochrane Statistical Methods Group. Cochrane Bias Methods Group. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2011;343:d5928.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 34. Deeks JJ, Higgins JP. Chapter 10: Analysing data and undertaking meta-analyses. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons; 2019. p. 243-296.
- 35. Ammari MM, Soviero VM, da Silva Fidalgo TK, Lenzi M, Ferreira DM, Mattos CT, de Souza IP, Maia LC. Is non-cavitated proximal lesion sealing an effective method for caries control in primary and permanent teeth? A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Dent 2014;42:1217-1227.ArticlePubMed
- 36. Borges Silva EA, Guimarães LS, Küchler EC, Antunes LA, Antunes LS. Evaluation of effect of foraminal enlargement of necrotic teeth on postoperative symptoms: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Endod 2017;43:1969-1977.ArticlePubMed
- 37. Moher D, Hopewell S, Schulz KF, Montori V, Gøtzsche PC, Devereaux PJ, Elbourne D, Egger M, Altman DG. CONSORT 2010 explanation and elaboration: updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials. BMJ 2010;340:c869.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 38. Varela P, Souza E, de Deus G, Duran-Sindreu F, Mercadé M. Effectiveness of complementary irrigation routines in debriding pulp tissue from root canals instrumented with a single reciprocating file. Int Endod J 2019;52:475-483.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 39. Zehnder M. Root canal irrigants. J Endod 2006;32:389-398.ArticlePubMed
- 40. Zehnder M, Kosicki D, Luder H, Sener B, Waltimo T. Tissue-dissolving capacity and antibacterial effect of buffered and unbuffered hypochlorite solutions. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2002;94:756-762.ArticlePubMed
- 41. Gernhardt CR, Eppendorf K, Kozlowski A, Brandt M. Toxicity of concentrated sodium hypochlorite used as an endodontic irrigant. Int Endod J 2004;37:272-280.ArticlePubMed
- 42. de Sermeño RF, da Silva LA, Herrera H, Herrera H, Silva RA, Leonardo MR. Tissue damage after sodium hypochlorite extrusion during root canal treatment. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2009;108:e46-e49.Article
- 43. Silva EJ, Menaged K, Ajuz N, Monteiro MR, Coutinho-Filho TS. Postoperative pain after foraminal enlargement in anterior teeth with necrosis and apical periodontitis: a prospective and randomized clinical trial. J Endod 2013;39:173-176.ArticlePubMed
- 44. Haefeli M, Elfering A. Pain assessment. Eur Spine J 2006;15(Suppl 1):S17-S24.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 45. Nair PN. Apical periodontitis: a dynamic encounter between root canal infection and host response. Periodontol 2000 1997;13:121-148.ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
Tables & Figures
REFERENCES
Citations

- Postoperative Pain After Endodontic Treatment in HIV‐Positive Patients Under HAART: A Prospective Observational Cohort Study
Marcos Felipe Iparraguirre Nuñovero, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Luciana Reis Azevedo Alanis, Bruno Cavalini Cavenago, Ulisses Xavier da Silva Neto, Everdan Carneiro
International Endodontic Journal.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of low-temperature intracanal sodium hypochlorite on root surface temperature reduction and organic tissue dissolution: an in vitro study
Marcos Felipe Iparraguirre Nuñovero, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Ulisses Xavier da Silva Neto, Vânia Portela Ditzel Westphalen, Pedro Cesar Gomes Titato, Bruno Cavalini Cavenago, Everdan Carneiro
Scientific Reports.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of intracanal cryotherapy on postoperative pain in symptomatic apical periodontitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials
Nishtha K. Patel, Prerak Doshi, Shaily R. Dalal, Pooja R. Kesharani, Shilpa S. Shah, Mohil H. Kale
Endodontology.2025; 37(2): 101. CrossRef - Evaluation of Post‐Endodontic Pain Reduction Using Intracanal Cryotherapy in Symptomatic Apical Periodontitis
Anam Fayyaz Bashir, Ussamah Waheed Jatala, Muhammad Amber Fareed, Sheryar Sheryar, Saadia Ahmad Chattha, Saima Razaq Khan, Shahzad Ahmad, Shazia Iqbal, Muhammad Sohail Zafar, Shahzad Ali
Australian Endodontic Journal.2025; 51(3): 677. CrossRef - Comparing cryotherapy and ketorolac tromethamine against room-temperature saline irrigation using interleukin-8 levels and post-operative pain within single-visit endodontic treatment of symptomatic irreversible pulpitis superimposed by apical periodontit
Yousra Khaled Ezzat, Alaa Diab, Olfat Shaker, Sarah Abouelenien
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Determining Efficacy of Intracanal Cryotherapy on Post Endodontic Pain in Irreversible Pulpitis
Anam Fayyaz Bashir, Ussamah Waheed Jatala, Moeen ud din Ahmad, Muhammad Talha Khan, Saima Razzaq Khan, Aisha Arshad Butt
Pakistan Journal of Health Sciences.2024; : 68. CrossRef - The effect of intracanal cryotherapy with and without foraminal enlargement on pain prevention after endodontic treatment: a randomized clinical trial
Marcos Felipe Iparraguirre Nuñovero, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, André Vinícius Kaled Segato, Ulisses Xavier da Silva Neto, Vania Portela Ditzel Westphalen, Everdan Carneiro
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of cryotherapy duration on experimentally induced connective tissue inflammationin vivo
Jorge Vera, Mayra Alejandra Castro-Nuñez, María Fernanda Troncoso-Cibrian, Ana Gabriela Carrillo-Varguez, Edgar Ramiro Méndez Sánchez, Viviana Sarmiento, Lourdes Lanzagorta-Rebollo, Prasanna Neelakantan, Monica Romero, Ana Arias
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of knowledge and awareness of pediatric oral health among school teachers of Hazaribag before and after oral health education.
Vipin Ahuja, Annapurna Ahuja, Nilima Thosar
F1000Research.2023; 12: 1292. CrossRef
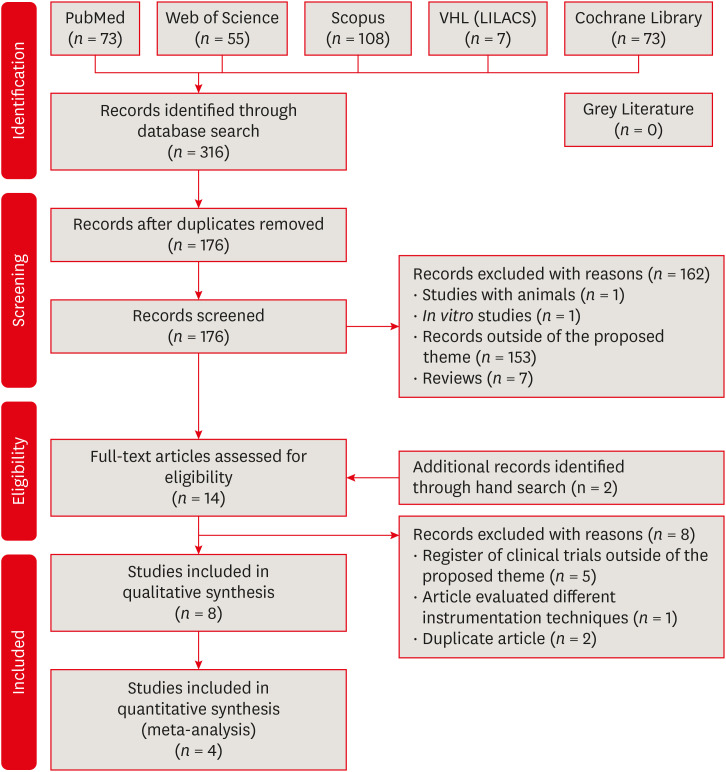
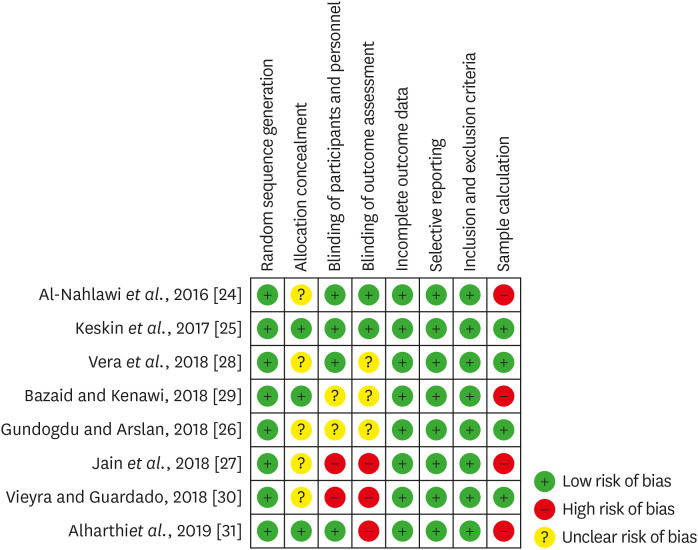
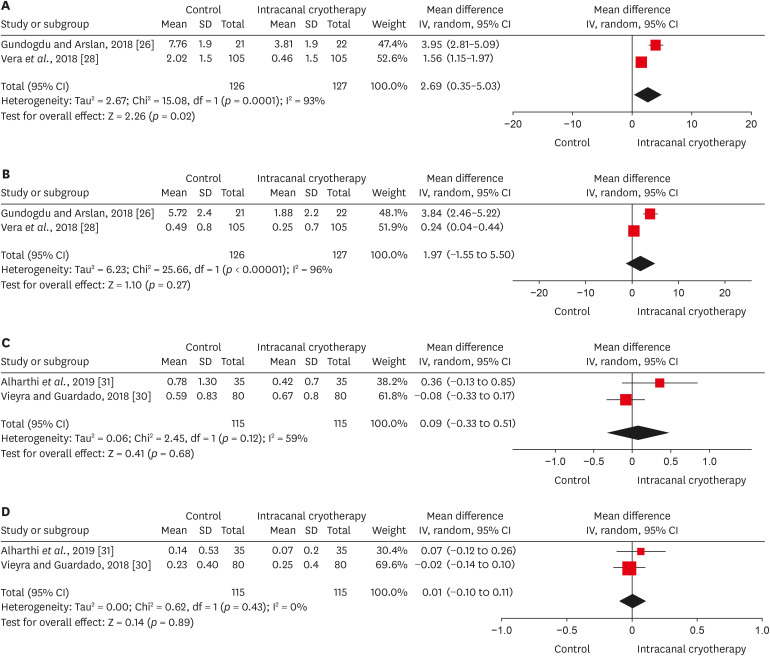
Figure 1
Figure 2
Figure 3
Electronic database used and search strategy
| Database | Search strategy |
|---|---|
| PubMed | #1(root canal preparation[MeSH Terms]) OR root canal therapy[MeSH Terms]) OR root canal obturation[MeSH Terms]) OR periapical periodontitis[MeSH Terms]) OR dental pulp necrosis[MeSH Terms]) OR root canal preparation[Title/Abstract]) OR root canal therapy[Title/Abstract]) OR root canal obturation[Title/Abstract]) OR periapical periodontitis[Title/Abstract]) OR dental pulp necrosis[Title/Abstract]) OR root canal treatment[Title/Abstract]) OR endodontic treatment[Title/Abstract]) OR endodontic obturation[Title/Abstract]) OR root canal instrumentation[Title/Abstract]) OR apical periodontitis[Title/Abstract] |
| #2(pain[MeSH Terms]) OR postoperative pain[MeSH Terms]) OR hyperemia[MeSH Terms]) OR edema[MeSH Terms]) OR hyperesthesia[MeSH Terms]) OR pain[Title/Abstract]) OR postoperative pain[Title/Abstract]) OR hyperemia[Title/Abstract]) OR edema[Title/Abstract]) OR hyperesthesia[Title/Abstract]) OR postendodontic pain[Title/Abstract]) OR touch pain[Title/Abstract] | |
| #3(cryotherapy[MeSH Terms]) OR cryotherapy[Title/Abstract]) OR cold therapy[Title/Abstract]) OR cold[Title/Abstract] | |
| #1 and #2 and #3 | |
| Scopus | #1(TITLE-ABS-KEY (root AND canal AND preparation) OR TITLE-ABS KEY (root AND canal AND therapy) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (root AND canal AND obturation) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (periapical AND periodontitis) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (dental AND pulp AND necrosis) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (root AND canal AND treatment) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (endodontic AND treatment) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (endodontic AND obturation) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (root AND canal AND instrumentation) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (apical AND periodontitis)) |
| #2(TITLE-ABS-KEY (postendodontic AND pain) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (pain) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (postoperative AND pain) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (touch AND pain) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (hyperemia) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (edema) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (hyperesthesia)) | |
| #3TITLE-ABS-KEY (cryotherapy) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (cold AND therapy) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (cold)) | |
| #1 and #2 and #3 | |
| Web of Science |
#1TOPIC: (root canal preparation) |
|
#2TOPIC: (postendodontic pain) | |
|
#3TOPIC: (cryotherapy) | |
| #1 and #2 and #3 | |
| Cochrane Library | ‘root canal therapy OR root canal preparation OR root canal obturation OR periapical periodontitis OR dental pulp necrosis OR endodontic obturation OR apical periodontitis)) AND (tw:(pain OR postoperative pain OR hyperemia OR edema OR hyperesthesia)) AND (tw:(cryotherapy OR cold therapy OR cold in Title, Abstract, Keywords in Trials’ |
| VHL (LILACS) | (tw:(root canal therapy OR root canal preparation OR root canal obturation OR periapical periodontitis OR dental pulp necrosis OR endodontic obturation OR apical periodontitis)) AND (tw:(pain OR postoperative pain OR hyperemia OR edema OR hyperesthesia)) AND (tw:(cryotherapy OR cold therapy OR cold)) |
| Grey Literature | (root canal preparation OR endodontic treatment) AND (postoperative pain) AND (cryotherapy) |
Characteristics of the included studies: endodontic treatment
| Author/year | Study design | Case/Control | Gender (Case/Control) | Types of teeth | Diagnostic pulp | Instrumentation | Irrigation | Foraminal enlargement | No. of sessions | Cryotherapy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al-Nahlawi | Randomized clinical trial with blind assessment technique | Group I (control): 25 | MD | Single-rooted teeth | Vital teeth with irreversible pulpitis | Rotatory (ProTaper Universal) | NaOCl 5.25% | No | 1 | 20 mL of 2°C to 4°C cold saline for 5 min using Endovac at WL |
| Group II (room temperature saline): 25 | ||||||||||
| Group III (cold saline): 25 | ||||||||||
| Keskin | MD | Control group (room temperature): 85 | Female: (45/57) | Incisor, Premolar, Molar | Asymptomatic irreversible pulpitis or symptomatic irreversible pulpitis with either normal apical tissues or symptomatic apical periodontitis | Rotatory (Protaper Next) | NaOCl 5.25% | No | 1 | 2.5°C cold saline for 5 min using a 31 G Navi-Tip needle 2 mm short of the WL |
| Cryotherapy group: 85 | Male: (40/28) | |||||||||
| Vera | Randomized multicenter clinical trial | Control group (room temperature): 105 | Female: (60/57) | Uniradicular teeth | Necrotic pulp and symptomatic apical periodontitis | Rotatory (Kerr Endo) | NaOCl 5.25% | No | 2 | 20 mL of 2.5°C cold saline for 5 min using Endovac to the WL |
| Cryotherapy group: 105 | Male: (33/36) | |||||||||
| Bazaid and Kenawi 2018 [ | Randomized control trial | Control group (room temperature): 16 | MD | MD | Irreversible pulpitis with either normal apical tissues or apical periodontitis. | Manual (Hand files to size 25) | NaOCl | No | 1 | 2.5°C cold saline for 2 min using side vented needle |
| Cryotherapy group: 20 | ||||||||||
| Gundogdu and Arslan 2018 [ | Randomized prospective clinical trial | Control group (room temperature): 21 | Female: 9 | Maxillary or mandibular molar teeth | Vital teeth with symptomatic apical periodontitis. | Reciprocating (Reciproc) | NaOCl 2.5% | No | 1 | Intracanal Cryotherapy Group: 20 mL of 2.5°C cold saline for 5 min |
| Male: 12 | Intraoral Cryotherapy Group: small ice packs on the vestibular surface of the tooth for 30 min | |||||||||
| Intracanal cryotherapy group: 22 | Female: 10 | Extraoral Cryotherapy Group: ice packs on the cheek surface for 30 min | ||||||||
| Male: 12 | ||||||||||
| Intraoral cryotherapy group: 21 | Female: 9 | |||||||||
| Male: 12 | ||||||||||
| Extraoral cryotherapy group: 20 | Female: 10 | |||||||||
| Male: 10 | ||||||||||
| Jain | In vivo study | Control group (room temperature): 30 | MD | Mandibular first molar | Symptomatic irreversible pulpitis with normal periodicals tissue, asymptomatic or symptomatic apical periodontitis. | Manual (Step back technique) | NaOCl 2.5% | No | 2 | 5 mL of 2.5°C cold saline with side vented |
| Cryotherapy group: 30 | ||||||||||
| Vieyra and Guardado, 2018 [ | Randomized clinical trial | Control group (room temperature): 80 | Female: 43 | Maxillary and mandibular molar, premolar, anterior teeth | Vital teeth with irreversible pulpitis | Reciprocating (Reciproc) | NaOCl 5.25% | No | 1 | Group A: 5 mL of 6°C EDTA 17% + 10 mL of 6°C cold saline dispensed to the WL using Endovac for 1 min |
| Male: 37 | Group B: 5 mL of 2.5°C EDTA 17% + 10 mL of 2.5°C cold saline dispensed to the WL using Endovac for 1 min | |||||||||
| Group A (6°C): 80 | Female: 43 | |||||||||
| Male: 37 | ||||||||||
| Group B (2.5°C): 80 | Female: 43 | |||||||||
| Male: 37 | ||||||||||
| Alharthi | Randomized controlled trial | Group I (Cryotherapy): 35 | MD | Single-rooted teeth | Vital and non-vital teeth | Rotatory (ProTaper Universal) | NaOCl 5.25% | No | 1 | 10 mL of 1.5–2.5°C cold saline delivered to the WL by using a two |
| Group II (Room temperature): 35 | 96 side–vented needle over a period of 5 min | |||||||||
| Group III (Control): 35 |
MD, missing data; NaOCl, sodium hypochlorite; WL, working length.
Analysis tools of post-operative pain
| Author/year | Assessment | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Period | Measurement | Postoperative medications | Results | |
| Al- Nahlawi | VAS | 6 hr, 12 hr, 24 hr, 48 hr, 7 days | 0–100 | Ibuprofen 400 mg | VAS pain values after 6, 12, 24, and 48 hr in cold saline irrigation group were lower than those of both saline irrigation at room temperature and control groups. |
| Keskin | VAS | 24 hr, 48 hr | 0: no pain | MD | Patients in the cryotherapy group reported significantly lower VAS scores compared with patients in the control group ( |
| 1–3: mild pain | |||||
| 4–6: moderate pain | |||||
| 7–9: severe pain | |||||
| 10: the worst pain experienced | |||||
| Vera | VAS | 6 hr, 24 hr, 72 hr | Mild pain | Ibuprofen 600 mg | Patients in the cryotherapy group suffered significantly less pain after 6, 24, and 72 hr and needed fewer analgesics postoperatively ( |
| Moderate pain | |||||
| Intense pain | |||||
| Bazaid and Kenawi, 2018 [ | VAS | 24 hr, 48 hr | MD | MD | Intracanal cryotherapy is effective in reducing postoperative pain in patients with irreversible pulpitis with apical periodontitis. But it does not affect patients with irreversible pulpitis without apical periodontitis. |
| Gundogdu and Arslan, 2018 [ | VAS | 24 hr, 72 hr, 5 days, 7 days | MD | Ibuprofen 400 mg | When compared with control group, all the cryotherapy groups exhibited lower postoperative pain levels on the first, third, fifth, and seventh days and lower levels of pain on percussion on the seventh day ( |
| Jain | VAS | 6 hr, 24 hr, 48 hr | 0–10 | MD | There was no significant difference between cryotherapy and normal saline groups in irreversible pulpitis with normal periapical tissue. |
| In irreversible pulpitis with asymptomatic apical periodontitis, at 6 hr, normal saline group were significantly higher pain than cryotherapy group. | |||||
| In irreversible pulpitis with symptomatic apical periodontitis, at 6, 24, and 48 hr, normal saline group were significantly higher pain than cryotherapy group. | |||||
| Therefore, intracanal cryotherapy is effective in reducing post-operative pain in patient with irreversible pulpitis with apical periodontitis. | |||||
| Vieyra and Guardado, 2018 [ | VAS | 24 hr, 48 hr, 72 hr | 0–0.5 cm: no pain | MD | No statistically relevant modification ( |
| 0.6–4.0 cm: mild pain | |||||
| 0.45–7.4 cm: moderate pain | |||||
| 7.5–10 cm: severe pain | |||||
| Alharthi | VAS | 6 hr, 24 hr, 48 hr | 0: no pain | MD | Group I had the lowest post-endodontic pain (6 , 24 and 48 hr). Nevertheless, there was no significant difference between Group I and Group II. The highest post-endodontic pain (6, 24 and 48 hr) was in Group III. |
| 1–3: mild pain | |||||
| 4–6: moderate pain | |||||
| 7–9: severe pain | |||||
| 10: the worst pain | |||||
MD, missing data; VAS, visual analogue scale.
Evidence profile in relation to symptomatic periapical tissue
| Certainty assessment | No. of patients | Effect | Certainty | Importance | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of studies | Study design | Risk of bias | Inconsistency | Indirectness | Imprecision | Other considerations | Intracanal cryotherapy | Control | Relative (95% CI) | Absolute (95% CI) | |||
| Symptomatic periapical tissue (24 hr) | |||||||||||||
| 2 | Randomized trials | Serious* | Very serious† | Not serious | Serious‡ | Publication bias strongly suspected‡ | 127 | 126 | - | MD 2.69 higher (0.35 higher to 5.03 higher) | ⊕○○○ | IMPORTANT | |
| VERY LOW | |||||||||||||
| Symptomatic periapical tissue (72 hr) | |||||||||||||
| 2 | Randomized trials | Serious* | Very serious† | Not serious | Serious‡ | Publication bias strongly suspected‡ | 127 | 126 | - | MD 1.97 higher (1.55 lower to 5.5 higher) | ⊕○○○ | IMPORTANT | |
| VERY LOW | |||||||||||||
CI, confidence interval; MD, mean difference.
*Unclear of important domains by Cochrane Collaboration tool for assessing risk of bias: Allocation concealment, Blinding of participants, personnel, and outcome assessment; †Considerable heterogeneity across studies and there is no overlap of confidence intervals; ‡Small sample.
Evidence profile in relation to normal periapical tissue
| Certainty assessment | No. of patients | Effect | Certainty | Importance | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of studies | Study design | Risk of bias | Inconsistency | Indirectness | Imprecision | Other considerations | Intracanal cryotherapy | Control | Relative (95% CI) | Absolute (95% CI) | |||
| Normal periapical tissue (24 hr) | |||||||||||||
| 2 | Randomized trials | Serious* | Serious† | Not serious | Serious‡ | Publication bias strongly suspected‡ | 115 | 115 | - | MD 0.09 higher (0.33 lower to 0.51 higher) | ⊕○○○ | IMPORTANT | |
| VERY LOW | |||||||||||||
| Normal periapical tissue (48 hr) | |||||||||||||
| 2 | Randomized trials | Serious* | Not serious | Not serious | Serious‡ | Publication bias strongly suspected‡ | 115 | 115 | - | MD 0.01 higher (0.1 lower to 0.11 higher) | ⊕○○○ | IMPORTANT | |
| VERY LOW | |||||||||||||
CI, confidence interval; MD, mean difference.
*Lack of important domains by Cochrane Collaboration tool for assessing risk of bias: Allocation concealment, Blinding of participants, personnel, and outcome assessment, and Sample calculation; †Moderate heterogeneity across studies and there is little overlap of confidence intervals; ‡Small sample.
MD, missing data; NaOCl, sodium hypochlorite; WL, working length.
MD, missing data; VAS, visual analogue scale.
CI, confidence interval; MD, mean difference.
*Unclear of important domains by Cochrane Collaboration tool for assessing risk of bias: Allocation concealment, Blinding of participants, personnel, and outcome assessment; †Considerable heterogeneity across studies and there is no overlap of confidence intervals; ‡Small sample.
CI, confidence interval; MD, mean difference.
*Lack of important domains by Cochrane Collaboration tool for assessing risk of bias: Allocation concealment, Blinding of participants, personnel, and outcome assessment, and Sample calculation; †Moderate heterogeneity across studies and there is little overlap of confidence intervals; ‡Small sample.

 KACD
KACD
 ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite

