Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Color stability and solubility of Biodentine and NeoPutty in contact with different irrigation solutions
- Sıla Nur Usta, Cangül Keskin
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(3):e25. Published online June 19, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e25

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
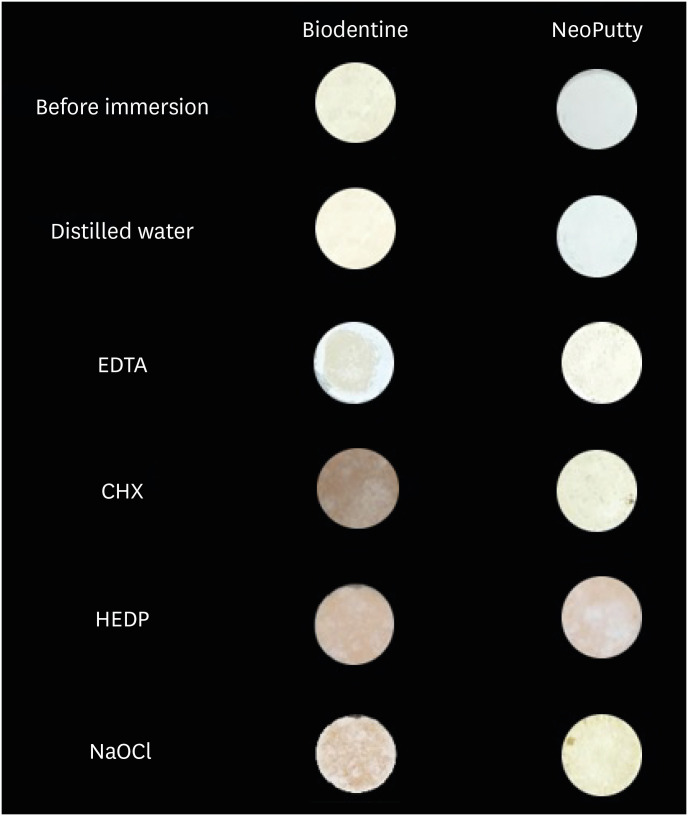
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the color stability and solubility of Biodentine and NeoPutty in contact with different irrigation solutions.
Materials and Methods Biodentine and NeoPutty were set in cylindrical molds with 7 mm diameter and 1.5 mm high and immersed in distilled water, 17% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), 2% chlorhexidine (CHX), 9% 1-hydroxyethylidene 1,1-diphosphonate (HEDP), and 5% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) solutions for 24 hours. The color change was measured with a spectrophotometer. The solubility values were calculated as the mass loss was expressed as a percentage of the original mass using an analytical balance with 10−4 g accuracy. Data were analyzed with Kruskal-Wallis followed by Mann-Whitney
U tests, and 2-way analysis of variance test followed by Bonferroni corrections for pairwise comparisons for solubility and color stability with a 5% significance threshold, respectively.Results Biodentine exhibited higher color changes compared to the NeoPutty contact with all solutions except distilled water (
p < 0.05). Both hydraulic cements (HCs) showed higher discoloration values immersion in CHX followed by NaOCl. No statistically significant difference was found between Biodentine and NeoPutty regardless of irrigation solution in terms of solubility (p > 0.05). Solubility values were lower in the distilled water group compared to EDTA and CHX (p < 0.05).Conclusions Tested HCs showed solubility and color changes at various rates. NeoPutty could be an appropriate material in aesthetic areas. The usage of HEDP as an irrigant solution can be considered suitable for various endodontic treatments due to its relatively lower solubility and discoloration values.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sealing ability of Biodentine, zirconia reinforced glass ionomer cement and Mineral Trioxide Aggregate as furcation perforation repair materials: an in vitro analysis
Sumita Panwar, Yajuvender Singh Hada
Biomaterial Investigations in Dentistry.2026; 13: 21. CrossRef
- Sealing ability of Biodentine, zirconia reinforced glass ionomer cement and Mineral Trioxide Aggregate as furcation perforation repair materials: an in vitro analysis
- 2,812 View
- 154 Download
- 1 Crossref

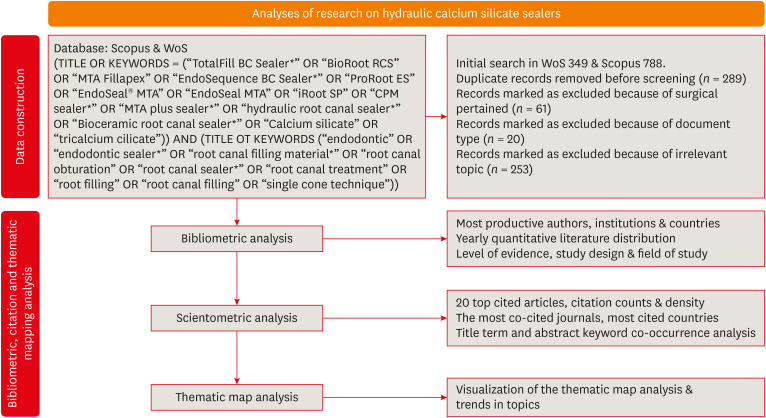
- A scientometric, bibliometric, and thematic map analysis of hydraulic calcium silicate root canal sealers
- Anastasios Katakidis, Konstantinos Kodonas, Anastasia Fardi, Christos Gogos
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(4):e41. Published online November 13, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e41
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This scientometric and bibliometric analysis explored scientific publications related to hydraulic calcium silicate-based (HCSB) sealers used in endodontology, aiming to describe basic bibliometric indicators and analyze current research trends.
Materials and Methods A comprehensive search was conducted in Web of Science and Scopus using specific HCSB sealer and general endodontic-related terms. Basic research parameters were collected, including publication year, authorship, countries, institutions, journals, level of evidence, study design and topic of interest, title terms, author keywords, citation counts, and density.
Results In total, 498 articles published in 136 journals were retrieved for the period 2008–2023. Brazil was the leading country, and the universities of Bologna in Italy and Sao Paolo in Brazil were represented equally as leading institutions. The most frequently occurring keywords were “calcium silicate,” “root canal sealer MTA-Fillapex,” and “biocompatibility,” while title terms such as “calcium,” “sealers,” “root,” “canal,” “silicate based,” and “endodontic” occurred most often. According to the thematic map analysis, “solubility” appeared as a basic theme of concentrated research interest, and “single-cone technique” was identified as an emerging, inadequately developed theme. The co-occurrence analysis revealed 4 major clusters centered on sealers’ biological and physicochemical properties, obturation techniques, retreatability, and adhesion.
Conclusions This analysis presents bibliographic features and outlines changing trends in HCSB sealer research. The research output is dominated by basic science articles scrutinizing the biological and specific physicochemical properties of commonly used HCSB sealers. Future research needs to be guided by studies with a high level of evidence that utilize innovative, sophisticated technologies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Top-cited articles on vital pulp therapy for irreversible pulpitis in permanent teeth: a bibliometric analysis
İkbal Sena Çelebi Keskin, Ferda Karabay
Odontology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Agri-Food Sector: Contemporary Trends, Possible Gaps, and Prospective Directions
José Roberto Herrera Cantorani, Meire Ramalho de Oliveira, Luiz Alberto Pilatti, Thales Botelho de Sousa
Metrics.2025; 2(1): 3. CrossRef - Scientific mapping of experimental research on solar cookers: Global trends, evolution, and future directions
Flavio Odoi-Yorke, Bismark Baah, Richard Opoku
Solar Energy Advances.2025; 5: 100093. CrossRef - Bibliometric analysis of the GentleWave system: trends, collaborations, and research gaps
Raimundo Sales de Oliveira Neto, Thais de Moraes Souza, João Vitor Oliveira de Amorim, Thaine Oliveira Lima, Guilherme Ferreira da Silva, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, Murilo Priori Alcalde, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2025; 50(2): e17. CrossRef - Top 100 Most Cited Articles on Antibiotics in Endodontics: A Bibliometric Analysis
Hajar Albanyan, Mohammed Asseery, Haitham Alahmari, Ikram Ul Haq, Ali Alaqla
Journal of Endodontics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A Scientometric Review of Practical Applications in Quantum Natural Language Processing (QNLP): Trends, Gaps, and Research Opportunities
Victor R. Silva, Fábio R. Barbosa, Jasson C. Silva, Francisco J. Santos, Ricardo A. L. Rabelo, Joel J. P. C. Rodrigues
IEEE Access.2025; 13: 210169. CrossRef - A bibliometric analysis of global research trend and progress on Dy doped materials
Sangeeta Kadyan, Manju Nain, Ashima Makhija, Poonam Punia, Anil Ohlan, Sajjan Dahiya, R. Punia, A.S. Maan
Journal of Alloys and Compounds Communications.2024; 3: 100006. CrossRef - Comparative bioactivity and immunomodulatory potential of the new Bioroot Flow and AH Plus Bioceramic sealer: An in vitro study on hPDLSCs
José Luis Sanz, Sergio López-García, David García-Bernal, Francisco Javier Rodríguez-Lozano, Leopoldo Forner, Adrián Lozano, Laura Murcia
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Analyzing collaboration and impact: A bibliometric review of four highly published authors’ research profiles on collaborative maps
Willy Chou, Julie Chi Chow
Medicine.2024; 103(28): e38686. CrossRef
- Top-cited articles on vital pulp therapy for irreversible pulpitis in permanent teeth: a bibliometric analysis
- 2,922 View
- 46 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref

- Calcium silicate-based root canal sealers: a literature review
- Miyoung Lim, Chanyong Jung, Dong-Hoon Shin, Yong-bum Cho, Minju Song
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(3):e35. Published online June 9, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e35
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Epoxy resin-based sealers are currently widely used, and several studies have considered AH Plus to be the gold-standard sealer. However, it still has limitations, including possible mutagenicity, cytotoxicity, inflammatory response, and hydrophobicity. Drawing upon the advantages of mineral trioxide aggregate, calcium silicate-based sealers were introduced with high levels of biocompatibility and hydrophilicity. Because of the hydrophilic environment in root canals, water resorption and solubility of root canal sealers are important factors contributing to their stability. Sealers displaying lower microleakage and stronger push-out bond strength are also needed to endure the dynamic tooth environment. Although the physical properties of calcium silicate-based sealers meet International Organization for Standardization recommendations, and they have consistently reported to be biocompatible, they have not overcome conventional resin-based sealers in actual practice. Therefore, further studies aiming to improve the physical properties of calcium silicate-based sealers are needed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Does the Use of a Bioceramic Sealer Reduce Postoperative Pain Compared With an Epoxy Resin‐Based Sealer After Primary Root Canal Treatment and Retreatment?—An Umbrella Review
Lokhasudhan Govindaraju, Rajeswari Kalaiselvam, Mathan Rajan Rajendran, Aleksandar Jakovljevic, Jelena Jacimovic, Henry F. Duncan, Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu
International Endodontic Journal.2026; 59(3): 341. CrossRef - Evidence synthesis of postoperative pain with bioceramic vs. epoxy resin sealers: umbrella review of randomized trials within existing systematic reviews
Mrunali Dahikar, Ashish Mandwe, Kulvinder Singh Banga, Alexander Maniangat Luke, Suraj Arora, Unmesh Khanvilkar, Ajinkya M. Pawar
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of interactions between sealers and irrigants on the physicochemical and surface characteristics of endodontic sealers
Hye-In Kim, Yeon-Ju You, Yemi Kim, Jin-Woo Kim, Young-Eun Jang
Clinical Oral Investigations.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Physical and mechanical properties of a strontium silicate-based sealer
Shannon Wong, Xiaofei Zhu, Tun-Yi Hsu, Sami Chogle, Russell A. Giordano, Yuwei Fan
Odontology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of Release of Calcium Ions from Apical Plugs of Different Bioceramic Sealers in Regenerative Endodontics for Immature Permanent Teeth
Alok Dubey, Nischitha Naik, Bhavana Sujanamulk, Mushir Mulla, Munaz Mulla, Alkananda Sahoo, Mohamed T Salama, Murali Patla S Bhat
World Journal of Dentistry.2026; 17(1): 69. CrossRef - Push-out bond strength of bioceramic-based sealers following different irrigation activation techniques
Fatma Begüm Peker, Hümeyra Çapkın, Ahsen Narbay
Journal of Applied Biomaterials & Functional Materials.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Different Tapered Gutta-Percha Points on Push-Out Bond Strength of Two Root Canal Sealers
Warattama Suksaphar, Pakit Tungsawat, Ninnita Wongwatanasanti, Siripat Lertnantapanya, Prattana Yodmanothum
European Journal of General Dentistry.2025; 14(03): 285. CrossRef - Effect of Electrical Heat Carrier Temperature on Bacterial Leakage of Endodontically Treated Teeth Using a Bioceramic Sealer
Mir Ahmad Nabavi, Mahmood Reza Kalantar Motamedi, Pedram Fattahi, Saber Khazaei
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Nanoparticles modified bioceramic sealers on solubility, antimicrobial efficacy, pushout bond strength and marginal adaptation at apical-third of canal dentin
Basil Almutairi, Fahad Alkhudhairy
PeerJ.2025; 13: e18840. CrossRef - Assessing the antimicrobial properties of bioceramic sealers enhanced with herbal extracts against E. faecalis
KS Sachin, K Shibani Shetty, KB Jeyalakshmi, S Harishma, S Harshini
Folia Medica.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Estudio comparativo de la solubilidad de dos selladores endodónticos biocerámicos y un sellador a base de resinas
//Comparative study of the solubility of two bioceramic endodontic sealers and one epoxi-resin based sealer
Alejandro Leonhardt, Nicolás Paduli, Osvaldo Zmener, Miguel Chantiri
Revista de la Asociación Odontológica Argentina.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Enhancing root canal sealing: Exploring the sealing potential of epoxy and calcium silicate-based sealers with chitosan nanoparticle enhancement
S. Harishma, Srilekha Jayakumar, K Shibani Shetty, Barkavi Panchatcharam, Jwaalaa Rajkumar, S. Harshini
Endodontology.2025; 37(3): 306. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Genotoxicity and Cytotoxicity of Bioceramic Endodontic Sealers in HepG2 and V79 Cell Lines: An In Vitro Study Using the Comet and Micronucleus Assays
Antonija Tadin, Marija Badrov, Danijela Juric Kacunic, Nada Galic, Matea Macan, Ivan Kovacic, Davor Zeljezic
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2025; 16(5): 169. CrossRef - In Vitro Apatite-Forming Ability of Different Root Canal Sealers (A Comparative Study)
Raghad A Al-Askary, Wiaam M. O. Al-Ashou, Sawsan H. Al-Jubori
Journal of International Society of Preventive and Community Dentistry.2025; 15(2): 173. CrossRef - Microstructural and elemental characterization of novel bioactive glass bioceramic sealer using Fourier transform infrared and X-ray diffraction analysis
Poulomi Guha, Pradeep Solete, Delphine Antony, Nishitha Arun, Mohmed Isaqali Karobari, Surendar Ramamoorthi
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(5): 412. CrossRef - Microstructural and Elemental Characterization of Calcium Silicate-Based Sealers
Mateusz Radwanski, Ireneusz Piwonski, Tomasz Szmechtyk, Salvatore Sauro, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska
Nanomaterials.2025; 15(10): 756. CrossRef - Apical negative pressure-enhanced sealer infiltration for obturating long oval-shaped root canals with the single-cone technique
Yaxu Feng, Brian E. Bergeron, Shijin Zhang, Danyang Sun, Kole Fisher, Franklin R. Tay, Bing Fan
Journal of Dentistry.2025; 160: 105909. CrossRef - Effects of different apical preparation sizes and root canal sealers on the fracture resistance of roots aged for 12 months in endodontically retreated mandibular premolars
Dilek Hancerliogullari, Sevda Durust Baris, Ali Turkyilmaz, Ali Erdemir
British Dental Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of different endodontic treatment protocols on tooth survival: A retrospective cohort study with multistate analysis and group balancing
Ahmed Elmaasarawi, Mohamed Mekhemar, Andreas Bartols
International Endodontic Journal.2025; 58(10): 1529. CrossRef - Evaluation of 2,6-xylidine precipitate on sealer penetration of calcium silicate-based sealer and resin-based sealer: An in vitro study
M. B. Kalpana, Divya Shetty, Rajaram Naik
Endodontology.2025; 37(2): 183. CrossRef - Translational Advances in Regenerative Dentistry: Functional Biomaterials and Emerging Technologies
Seher Yaylacı, Hacer Eberliköse, Hakan Ceylan
Current Oral Health Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Marginal adaptation of heat and non-heat compatible bioceramic sealers in warm obturation: an in vitro SEM study
Thanomsuk Jearanaiphaisarn, Thanida Leelayuttakarn, Panisara Amatamahuthana, Pinmanus Chenpairojsakul, Keskanya Subbalekha, Pavena Chivatxaranukul
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of irrigating solutions on the hydration of calcium silicate-based dental biomaterials: An in vitro study
Pradeep M. Divya, Amit Jena, Saumyakanta Mohanty, Govind Shashirekha, Rashmi Rekha Mallick, Priyanka Sarangi
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(8): 758. CrossRef - Multispecies Biofilms Treated With Endodontic Sealers or Calcium Hydroxide: Antimicrobial Activity and Changes in Community Composition
Steven K. Uttech, Ronald Ordinola‐Zapata, W. Craig Noblett, Maria Martell, Bruno Lima, Christopher Staley
International Endodontic Journal.2025; 58(11): 1764. CrossRef - A comparative analysis of adhesion abilities between AH Plus® Bioceramic, Ceraseal® and AH Plus® on root canal dentine surfaces
Ike Dwi Maharti, Indira Larasputri, Nendar Herdianto, Anggraini Margono, Riesma Tasomara, Romilda Rosseti
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(9): 881. CrossRef - Clinical and radiographic success of single-cone bioceramic obturation versus traditional techniques: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Firas Elmsmari, Yousef Elsayed, Abdelrahman Aboubakr, Mahdi Kaafarani, Osama Nour, Ajinkya M. Pawar
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2025; 15(6): 1422. CrossRef - The Effect of Irrigation Solutions on the Setting Time, Solubility, and pH of Three Types of Premixed Bioceramic‐Based Root Canal Sealers
Kitichai Singharat, Ninnita Wongwatanasanti, Warattama Suksaphar, Pakit Tungsawat, Zhengrui Li
International Journal of Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Endodontie – State of the Art von A bis Z
Will Qian, Andreas Bartols
Zahnmedizin up2date.2025; 19(04): 281. CrossRef - Assessing Volume of Two Sealers’ Remnants after Reinstrumentation Using 3D Imaging Technology: An In Vitro Comparative Study
Khalel Mutaz Dawod, Raghad Abdulrazzaq Al-Hashimi
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2025; 26(8): 743. CrossRef - Functional and Bioactive Performance of Premixed Bioceramic Sealers with Warm Obturation: A Scoping Review
Patryk Wiśniewski, Stanisław Krokosz, Małgorzata Pietruska, Anna Zalewska
Gels.2025; 11(11): 932. CrossRef - Correlation of Bond Strength and Dentinal Tubule Penetration Evaluation of Four Different Endodontic Sealers: AH Plus, MTA Fillapex, Endoseal MTA, and Endoseal TCS (Maruchi): An In Vitro Study
Arezoo Mirzaei Sadeghloo, Seyedali Seyedmajidi, Akam Saeidi, Elham Mahmoudi, Murilo Baena Lopes
International Journal of Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Osteogenic Potential of Various Premixed Hydraulic Calcium Silicate-Based Sealers on Human Bone Marrow Stem Cells
Na-Hyun You, Donghee Lee, Yemi Kim, Sieun Nam, Sin-Young Kim
Materials.2025; 18(23): 5326. CrossRef - Polydopamine‐Functionalized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles as a Root Canal Sealer: Characterization, Biological, and Physicochemical Properties
Arul Nayagi Raj, Aditya Shetty, Lakshmi Nidhi Rao, Giuseppe Ciccarella
Bioinorganic Chemistry and Applications.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Management of rarely seen internal tunnelling root resorption associated with a maxillary permanent incisor
Kirsty A. Carney, Thibault N. E. Colloc, Julie K. Kilgariff
British Dental Journal.2024; 236(12): 955. CrossRef - Top tips for treatment planning: tooth-by-tooth prognosis - Part 3: endodontic prognosis
Prashanti Eachempati, Andrew Harris, Guy Lambourn, Tony Francis, Ewen McColl
British Dental Journal.2024; 237(9): 686. CrossRef - Retreatability of calcium silicate-based sealers based on micro-computed tomographic evaluation − A systematic review
Sundus Mohammed Bukhary
The Saudi Dental Journal.2024; 36(10): 1278. CrossRef - Evaluation of Setting Time, Flowability, Film Thickness, and Radiopacity of Experimental Monocalcium Silicate‐Based Root Canal Sealers
Sukanya Juntha, Pakit Tungsawat, Ninnita Wongwatanasanti, Warattama Suksaphar, Siripat Lertnantapanya, Carlos M. Ardila
International Journal of Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Root Canal Treatment and Demand for Continuing Education among Thai Dental Practitioners
Ninnita Wongwatanasanti, Pakit Tungsawat, Warattama Suksaphar, Siripat Lertnantapanya, Prattana Yodmanotham
The Open Dentistry Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical outcome of non-surgical root canal treatment using different sealers and techniques of obturation in 237 patients: A retrospective study
Mateusz Radwanski, Krystyna Pietrzycka, Tan Fırat Eyüboğlu, Mutlu Özcan, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Endodontic sealers after exposure to chlorhexidine digluconate: An assessment of physicochemical properties
Vasileios Kapralos, Josette Camilleri, Andreas Koutroulis, Håkon Valen, Dag Ørstavik, Pia Titterud Sunde
Dental Materials.2024; 40(3): 420. CrossRef - Assessment the bioactivity of zinc oxid eugenol sealer after the addition of different concentrations of nano hydroxyapatite-tyrosine amino acid
Rasha M. Al-Shamaa, Raghad A. Al-Askary
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2024; 23: e243733. CrossRef - Interfacial adaptation of newly prepared nano-tricalcium silicate-58s bioactive glass-based endodontic sealer
Nawal A. Al-Sabawi, Sawsan Hameed Al-Jubori
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2024; 18(2): 115. CrossRef - Marginal adaptation of customized gutta percha cone with calcium silicate based sealer versus MTA and biodentine apical plugs in simulated immature permanent teeth (an in vitro study)
Mary M. Mina, Sybel M. Moussa, Mahmoud R. Aboelseoud
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Solubility of Endoseal and AH26 Root Canal Sealers
Nooshin Fakhari, Ali Reza Mirjani, Abbas Bagheri, Jalil Modaresi
Journal of Research in Dental and Maxillofacial Sciences.2024; 9(1): 1. CrossRef - Novel bioactive nanospheres show effective antibacterial effect against multiple endodontic pathogens
Jin Liu, Haoze Wu, Jun Qiu, Sirui Yang, Doudou Xiang, Xinhua Zhang, Jinxin Kuang, Min Xiao, Qing Yu, Xiaogang Cheng
Heliyon.2024; 10(7): e28266. CrossRef - Evaluation of canal patency and cleanliness following retreatment of bioceramic sealer‐obturated root canals using three different irrigant activation protocols
Daiasharailang Lyngdoh, Sharique Alam, Huma Iftekhar, Surendra Kumar Mishra
Australian Endodontic Journal.2024; 50(3): 475. CrossRef - Antibiofilm Efficacy of Calcium Silicate-Based Endodontic Sealers
Matilde Ruiz-Linares, Vsevolod Fedoseev, Carmen Solana, Cecilia Muñoz-Sandoval, Carmen María Ferrer-Luque
Materials.2024; 17(16): 3937. CrossRef - Enhancing the Biological Properties of Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Calcium Silicate Cements: An In Vitro Study
Minji Choi, Jiyoung Kwon, Ji-Hyun Jang, Duck-Su Kim, Hyun-Jung Kim
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2024; 15(11): 337. CrossRef - Cytotoxicity and cell migration evaluation of a strontium silicate-based root canal sealer on stem cells from rat apical papilla: an in vitro study
Guanglei Zhou, Yu Zhao, Liangjing Cai, Liwei Liu, Xu Li, Lu Sun, Jiayin Deng
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - An In Vitro Comparative Analysis of Physico–Mechanical Properties of Commercial and Experimental Bioactive Endodontic Sealers
Abdulmajeed Kashaf, Faisal Alonaizan, Khalid S. Almulhim, Dana Almohazey, Deemah Abdullah Alotaibi, Sultan Akhtar, Ashwin C. Shetty, Abdul Samad Khan
Bioengineering.2024; 11(11): 1079. CrossRef - Chemical, Antibacterial, and Cytotoxic Properties of Four Different Endodontic Sealer Leachates Over Time
Jo-Hsun Chen, Veksina Raman, Sarah A. Kuehne, Josette Camilleri, Josefine Hirschfeld
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(11): 1612. CrossRef - Comparative Analysis of Fracture Resistance of Endodontic Sealer Types and Filling Methods
Yun Song, Kee-Deog Kim, Bock-Young Jung, Wonse Park, Nan-Sim Pang
Materials.2024; 18(1): 40. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Removal of Bioceramic Sealers Using Rotary Retreatment Files Supplemented with Passive Ultrasonic Activation: An In Vitro Study
Anuradha B Patil, Amrut Bambawale, Pooja R Barghare, Sumanthini V Margasahayam, Divya Naik, Jayeeta S Verma
World Journal of Dentistry.2024; 15(4): 292. CrossRef - Nonsurgical Endodontic Management of Nonperforating Internal Root Resorption in a Maxillary Central Incisor: A Case Report with a 4-Year Follow-Up
Paras M. Gehlot, Divya S. Rajkumar, Annapoorna B. Mariswamy, Upendra Natha N. Reddy, Chaitanya Chappidi
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2024; 16(Suppl 3): S3005. CrossRef - Evaluating the Sealing Performance of Endodontic Sealers: Insights Into Achieving Complete Sealing
Ajay Chhabra, Ramya K P., Saravana Prathap, Priyanka Yadav, Himani Mehra, Sona J Parvathy
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of vehicles on the physical properties and biocompatibility of premixed calcium silicate cements
Gitae SON, Gyeung Mi SEON, Sang Hoon CHOI, Hyeong-Cheol YANG
Dental Materials Journal.2024; 43(2): 276. CrossRef - Comparative cytotoxicity study of putty- and powder-type calcium silicate cements
Sora Park, Dohyun Cho, Ji Hyeon Yoon, Yeonjoo Kang, Quang Canh Vo, Gitae Son, Hongjoo Park, Hyeong-Cheol Yang
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2024; 51(4): 259. CrossRef - Physical-chemical properties and acellular bioactivity of newly prepared nano-tricalcium silicate-58s bioactive glass-based endodontic sealer
Nawal A. Al-Sabawi, Sawsan Hameed Al-Jubori
Journal of Oral Biosciences.2023; 65(4): 305. CrossRef - Dentinal Tubule Penetrability and Bond Strength of Two Novel Calcium Silicate-Based Root Canal Sealers
Karissa Shieh, Jack Yang, Elsa Heng Zhu, Ove Andreas Peters, Sepanta Hosseinpour
Materials.2023; 16(9): 3309. CrossRef - Cytotoxicity and Mineralization Activity of Calcium Silicate-Based Root Canal Sealers Compared to Conventional Resin-Based Sealer in Human Gingival Fibroblast Cells
Mohammad Shokrzadeh, Farzaneh Sadat Motafeghi, Anahita Lotfizadeh, Mohammad Ghorbani, Azam Haddadi Kohsar, Cesar Rogério Pucci
International Journal of Dentistry.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Effect of three different photosensitizers in photodynamic therapy on bond strength of a calcium silicate‐based sealer to radicular dentin
Cihan Küden, Seda Nur Karakaş
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(S1): 265. CrossRef - Effect of endodontic sealer on postoperative pain: a network meta-analysis
Cynthia Maria Chaves Monteiro, Ana Cristina Rodrigues Martins, Alessandra Reis, Juliana Larocca de Geus
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Antimicrobial Activity of Five Calcium Silicate Based Root Canal Sealers against a Multispecies Engineered Biofilm: An In Vitro Study
Carla Zogheib, Issam Khalil, Wajih Hage, Dolla Karam Sarkis, Mireille Kallasy, Germain Sfeir, May Mallah, Roula El Hachem
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2023; 24(9): 707. CrossRef - Calcium silicate sealers in endodontics
Archana Chavan, Nidambur Ballal
Acta stomatologica Naissi.2023; 39(87): 2624. CrossRef - Assessing the Sealing Performance and Clinical Outcomes of Endodontic Treatment in Patients with Chronic Apical Periodontitis Using Epoxy Resin and Calcium Salicylate Seals
Razvan Mihai Horhat, Bogdan Andrei Bumbu, Laura Orel, Oana Velea-Barta, Laura Cirligeriu, Gratiana Nicoleta Chicin, Marius Pricop, Mircea Rivis, Stefania Dinu, Delia Ioana Horhat, Felix Bratosin, Roxana Manuela Fericean, Rodica Anamaria Negrean, Luminita
Medicina.2023; 59(6): 1137. CrossRef -
In Vitro Cytotoxicity and Mineralization Potential of an Endodontic Bioceramic Material
Soumya Sheela, Mohannad Nassar, Fatma M. AlGhalban, Mehmet O. Gorduysus
European Journal of Dentistry.2023; 17(02): 548. CrossRef - Dislodgment Resistance, Adhesive Pattern, and Dentinal Tubule Penetration of a Novel Experimental Algin Biopolymer-Incorporated Bioceramic-Based Root Canal Sealer
Galvin Sim Siang Lin, Norhayati Luddin, Huwaina Abd Ghani, Josephine Chang Hui Lai, Tahir Yusuf Noorani
Polymers.2023; 15(5): 1317. CrossRef - Impact of Final Irrigation Protocol on the Push-Out Bond Strength of Two Types of Endodontic Sealers
Germain Sfeir, Frédéric Bukiet, Wajih Hage, Roula El Hachem, Carla Zogheib
Materials.2023; 16(5): 1761. CrossRef - Clinical Approaches to the Three-Dimensional Endodontic Obturation Protocol for Teeth with Periapical Bone Lesions
Angela Gusiyska, Elena Dyulgerova
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(17): 9755. CrossRef - Evaluating the bioactivity of endodontic sealers with respect to their thermo-nanomechanical properties
Andreea Marica, Luminita Fritea, Florin Banica, Iosif Hulka, Gerlinde Rusu, Cosmin Sinescu, Traian Octavian Costea, Simona Cavalu
Materials Science-Poland.2023; 41(3): 126. CrossRef - Advances and challenges in regenerative dentistry: A systematic review of calcium phosphate and silicate-based materials on human dental pulp stem cells
B. Christie, N. Musri, N. Djustiana, V. Takarini, N. Tuygunov, M.N. Zakaria, A. Cahyanto
Materials Today Bio.2023; 23: 100815. CrossRef - Radiographic Evaluation of Periapical Healing Rates Between Bio-Ceramic Sealer and AH+ Sealer: A Retrospective Study
Dalia Nayil Alharith, Iman T. Mansi, YoumnaElsaid Abdulmotalib, HebaFuad Amous, TagreedSuliman Aljulban, Haifa Mohammed Al Aiban, Sali Mohamad Haffar
Annals of Dental Specialty.2023; 11(2): 124. CrossRef - Obturation canalaire
N. Linas, M.-L. Munoz-Sanchez, N. Decerle, P.-Y. Cousson
EMC - Médecine buccale.2023; 16(5): 1. CrossRef - Biodentine Inhibits the Initial Microbial Adhesion of Oral Microbiota In Vivo
Ali Al-Ahmad, Michael Haendel, Markus Altenburger, Lamprini Karygianni, Elmar Hellwig, Karl Wrbas, Kirstin Vach, Christian Tennert
Antibiotics.2022; 12(1): 4. CrossRef - Pilot Evaluation of Sealer-Based Root Canal Obturation Using Epoxy-Resin-Based and Calcium-Silicate-Based Sealers: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Minju Song, Min-Gyu Park, Sang-Won Kwak, Ruben H. Kim, Jung-Hong Ha, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Materials.2022; 15(15): 5146. CrossRef - The antibacterial activity of mineral trioxide aggregate containing calcium fluoride
Miyoung Lim, Seunghoon Yoo
Journal of Dental Sciences.2022; 17(2): 836. CrossRef - Physicochemical and Mechanical Properties of Premixed Calcium Silicate and Resin Sealers
Naji Kharouf, Salvatore Sauro, Ammar Eid, Jihed Zghal, Hamdi Jmal, Anta Seck, Valentina Macaluso, Frédéric Addiego, Francesco Inchingolo, Christine Affolter-Zbaraszczuk, Florent Meyer, Youssef Haikel, Davide Mancino
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2022; 14(1): 9. CrossRef - Comparison of Fracture Resistance between Single-cone and Warm Vertical Compaction Technique Using Bio-C Sealer® in Mandibular Incisors: An In Vitro Study
Raphael Lichaa, George Deeb, Rami Mhanna, Carla Zogheib
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2022; 23(2): 143. CrossRef - In vitro physicochemical characterization of five root canal sealers and their influence on an ex vivo oral multi‐species biofilm community
Flavia M. Saavedra, Lauter E. Pelepenko, William S. Boyle, Anqi Zhang, Christopher Staley, Mark C. Herzberg, Marina A. Marciano, Bruno P. Lima
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(7): 772. CrossRef - Premixed Calcium Silicate-Based Root Canal Sealer Reinforced with Bioactive Glass Nanoparticles to Improve Biological Properties
Min-Kyung Jung, So-Chung Park, Yu-Jin Kim, Jong-Tae Park, Jonathan C. Knowles, Jeong-Hui Park, Khandmaa Dashnyam, Soo-Kyung Jun, Hae-Hyoung Lee, Jung-Hwan Lee
Pharmaceutics.2022; 14(9): 1903. CrossRef - A critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study root canal fillings
Gustavo De‐Deus, Erick Miranda Souza, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Marco Simões‐Carvalho, Daniele Moreira Cavalcante, Marco Aurélio Versiani
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S2): 384. CrossRef - Bioactivity Potential of Bioceramic-Based Root Canal Sealers: A Scoping Review
Mauro Schmitz Estivalet, Lucas Peixoto de Araújo, Felipe Immich, Adriana Fernandes da Silva, Nadia de Souza Ferreira, Wellington Luiz de Oliveira da Rosa, Evandro Piva
Life.2022; 12(11): 1853. CrossRef - The influence of humidity on bond strength of AH Plus, BioRoot RCS, and Nanoseal-S sealers
Sunanda Laxman Gaddalay, Damini Vilas Patil, Ramchandra Kabir
Endodontology.2022; 34(3): 202. CrossRef - The Effect of Bioceramic HiFlow and EndoSequence Bioceramic Sealers on Increasing the Fracture Resistance of Endodontically Treated Teeth: An In Vitro Study
Mohamad Khir Abdulsamad Alskaf, Hassan Achour, Hasan Alzoubi
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Unravelling the effects of ibuprofen-acetaminophen infused copper-bioglass towards the creation of root canal sealant
Chitra S, Riju Chandran, Ramya R, Durgalakshmi D, Balakumar S
Biomedical Materials.2022; 17(3): 035001. CrossRef - A Micro-CT Analysis of Initial and Long-Term Pores Volume and Porosity of Bioactive Endodontic Sealers
Mateusz Radwanski, Michal Leski, Adam K. Puszkarz, Jerzy Sokolowski, Louis Hardan, Rim Bourgi, Salvatore Sauro, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska
Biomedicines.2022; 10(10): 2403. CrossRef - A comprehensive in vitro comparison of the biological and physicochemical properties of bioactive root canal sealers
Sabina Noreen Wuersching, Christian Diegritz, Reinhard Hickel, Karin Christine Huth, Maximilian Kollmuss
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 26(10): 6209. CrossRef - Stability and solubility test of endodontic materials
Ivan Matovic, Jelena Vucetic
Stomatoloski glasnik Srbije.2022; 69(4): 169. CrossRef - Antimicrobial effectiveness of root canal sealers againstEnterococcus faecalis
Paola Castillo-Villagomez, Elizabeth Madla-Cruz, Fanny Lopez-Martinez, Idalia Rodriguez-Delgado, Jorge Jaime Flores-Treviño, Guadalupe Ismael Malagon-Santiago, Myriam Angelica de La Garza-Ramos
Biomaterial Investigations in Dentistry.2022; 9(1): 47. CrossRef - Tricalcium silicate cement sealers
Anita Aminoshariae, Carolyn Primus, James C. Kulild
The Journal of the American Dental Association.2022; 153(8): 750. CrossRef - Influence of variations in the environmental pH on the solubility and water sorption of a calcium silicate‐based root canal sealer
E. J. N. L. Silva, C. M. Ferreira, K. P. Pinto, A. F. A. Barbosa, M. V. Colaço, L. M. Sassone
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(8): 1394. CrossRef - Calcium Silicate-Based Root Canal Sealers: A Narrative Review and Clinical Perspectives
Germain Sfeir, Carla Zogheib, Shanon Patel, Thomas Giraud, Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Frédéric Bukiet
Materials.2021; 14(14): 3965. CrossRef - Development of A Nano-Apatite Based Composite Sealer for Endodontic Root Canal Filling
Angelica Bertacci, Daniele Moro, Gianfranco Ulian, Giovanni Valdrè
Journal of Composites Science.2021; 5(1): 30. CrossRef - Bone repair in defects filled with AH Plus sealer and different concentrations of MTA: a study in rat tibiae
Jessica Emanuella Rocha Paz, Priscila Oliveira Costa, Albert Alexandre Costa Souza, Ingrid Macedo de Oliveira, Lucas Fernandes Falcão, Carlos Alberto Monteiro Falcão, Maria Ângela Area Leão Ferraz, Lucielma Salmito Soares Pinto
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Characterization, Antimicrobial Effects, and Cytocompatibility of a Root Canal Sealer Produced by Pozzolan Reaction between Calcium Hydroxide and Silica
Mi-Ah Kim, Vinicius Rosa, Prasanna Neelakantan, Yun-Chan Hwang, Kyung-San Min
Materials.2021; 14(11): 2863. CrossRef - Synthesis and Characterization of Novel Calcium-Silicate Nanobioceramics with Magnesium: Effect of Heat Treatment on Biological, Physical and Chemical Properties
Konstantina Kazeli, Ioannis Tsamesidis, Anna Theocharidou, Lamprini Malletzidou, Jonathan Rhoades, Georgia K. Pouroutzidou, Eleni Likotrafiti, Konstantinos Chrissafis, Theodoros Lialiaris, Lambrini Papadopoulou, Eleana Kontonasaki, Evgenia Lymperaki
Ceramics.2021; 4(4): 628. CrossRef - Calcium Silicate Cements vs. Epoxy Resin Based Cements: Narrative Review
Mario Dioguardi, Cristian Quarta, Diego Sovereto, Giuseppe Troiano, Khrystyna Zhurakivska, Maria Bizzoca, Lorenzo Lo Muzio, Lucio Lo Russo
Oral.2021; 1(1): 23. CrossRef - In Vitro Microleakage Evaluation of Bioceramic and Zinc-Eugenol Sealers with Two Obturation Techniques
Francesco De Angelis, Camillo D’Arcangelo, Matteo Buonvivere, Rachele Argentino, Mirco Vadini
Coatings.2021; 11(6): 727. CrossRef - Efficacy Of Calcium Silicate-Based Sealers In Root Canal Treatment: A Systematic Review
Hattan Mohammed Omar Baismail, Mohammed Ghazi Moiser Albalawi, Alaa Mofareh Thoilek Alanazi, Muhannad Atallah Saleem Alatawi, Badr Soliman Alhussain
Annals of Dental Specialty.2021; 9(1): 87. CrossRef - Apical Sealing Ability of Two Calcium Silicate-Based Sealers Using a Radioactive Isotope Method: An In Vitro Apexification Model
Inês Raquel Pereira, Catarina Carvalho, Siri Paulo, José Pedro Martinho, Ana Sofia Coelho, Anabela Baptista Paula, Carlos Miguel Marto, Eunice Carrilho, Maria Filomena Botelho, Ana Margarida Abrantes, Manuel Marques Ferreira
Materials.2021; 14(21): 6456. CrossRef
- Does the Use of a Bioceramic Sealer Reduce Postoperative Pain Compared With an Epoxy Resin‐Based Sealer After Primary Root Canal Treatment and Retreatment?—An Umbrella Review
- 13,692 View
- 249 Download
- 100 Crossref

- Influence of 10-MDP concentration on the adhesion and physical properties of self-adhesive resin cements
- Kazuhiko Shibuya, Naoko Ohara, Serina Ono, Kumiko Matsuzaki, Masahiro Yoshiyama
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(4):e45. Published online November 12, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e45
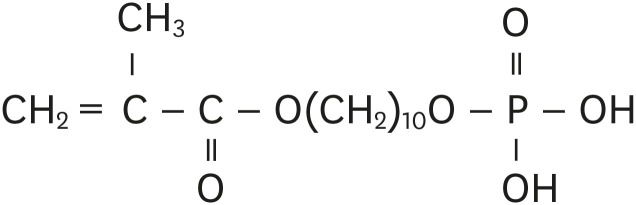
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Self-adhesive resin cements contain functional monomers that enable them to adhere to the tooth structure without a separate adhesive or etchant. One of the most stable functional monomers used for chemical bonding to calcium in hydroxyapatite is 10-methacryloyloxydecyl dihydrogen phosphate (10-MDP). The aim of this study was to evaluate the influence of the10-MDP concentration on the bond strength and physical properties of self-adhesive resin cements.
Materials and Methods We used experimental resin cements containing 3 different concentrations of 10-MDP: 3.3 wt% (RC1), 6.6 wt% (RC2), or 9.9 wt% (RC3). The micro-tensile bond strength of each resin cement to dentin and a hybrid resin block (Estenia C&B, Kuraray Noritake Dental) was measured, and the fractured surface morphology was analyzed. Further, the flexural strength of the resin cements was measured using the three-point bending test. The water sorption and solubility of the cements following 30 days of immersion in water were measured.
Results The bond strength of RC2 was significantly higher than that of RC1. There was no significant difference between the bond strength of RC2 and that of RC3. The water sorption of RC3 was higher than that of any other cement. There were no significant differences in the three-point bending strength or water solubility among all three types of cements.
Conclusions Within the limitations of this study, it is suggested that 6.6 wt% 10-MDP showed superior properties than 3.3 wt% or 9.9 wt% 10-MDP in self-adhesive resin cement.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bonding effectiveness of 10-MDP containing resin composite cements: a systematic review with meta-analysis
Sofia Bignotto de Carvalho, Lívia Maiumi Uehara, João Marcos Carvalho-Silva, Andréa Cândido dos Reis
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2026; 146: 104260. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Color Stability in Bioactive and Conventional Resin Cements Under Thermal Stress Conditions
Alaa Turkistani, Hanin E. Yeslam
Biomimetics.2025; 10(7): 432. CrossRef - Influence of temperature and curing modes on polymerization of self-adhesive resin cements
Hae-In Kim, Jin-Woo Kim, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2025; 52(3): 143. CrossRef - Clinical Performance and Retention of Partial Implant Restorations Cemented with Fuji Plus® and DentoTemp™: A Retrospective Clinical Study with Mechanical Validation
Sergiu-Manuel Antonie, Laura-Cristina Rusu, Ioan-Achim Borsanu, Remus Christian Bratu, Emanuel-Adrian Bratu
Medicina.2025; 61(12): 2183. CrossRef - A thorough assessment of 10-MDP primers in modern dental adhesive systems
Ahmed A Abduljawad, Harraa SM Salih, Omar F Tawfiq
Journal of Baghdad College of Dentistry.2024; 36(3): 79. CrossRef - Material properties and finite element analysis of adhesive cements used for zirconia crowns on dental implants
Megha Satpathy, Hai Pham, Shreya Shah
Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering.2024; : 1. CrossRef - Clinical reliability of self-adhesive luting resins compared to other adhesive procedures: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Mohammed Ahmed Alghauli, Ahmed Yaseen Alqutaibi, Sebastian Wille, Matthias Kern
Journal of Dentistry.2023; 129: 104394. CrossRef - Influence of autoclave sterilization on bond strength between zirconia frameworks and Ti-base abutments using different resin cements
Reinhold Lang, Karl-Anton Hiller, Lena Kienböck, Katrin Friedl, Karl-Heinz Friedl
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2022; 127(4): 617.e1. CrossRef - Varying 10-methacryloyloxydecyl dihydrogen phosphate (10-MDP) level improves polymerisation kinetics and flexural strength in self-adhesive, remineralising composites
António H.S. Delgado, Nazanin Owji, Paul Ashley, Anne M. Young
Dental Materials.2021; 37(9): 1366. CrossRef - Investigating a Commercial Functional Adhesive with 12-MDPB and Reactive Filler to Strengthen the Adhesive Interface in Eroded Dentin
Madalena Belmar da Costa, António HS Delgado, Tomás Amorim Afonso, Luís Proença, Ana Sofia Ramos, Ana Mano Azul
Polymers.2021; 13(20): 3562. CrossRef
- Bonding effectiveness of 10-MDP containing resin composite cements: a systematic review with meta-analysis
- 2,801 View
- 17 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Discoloration of various CAD/CAM blocks after immersion in coffee
- Sasipin Lauvahutanon, Maho Shiozawa, Hidekazu Takahashi, Naohiko Iwasaki, Meiko Oki, Werner J. Finger, Mansuang Arksornnukit
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(1):9-18. Published online December 8, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.1.9

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated color differences (Δ
E s) and translucency parameter changes (ΔTP s) of various computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM) blocks after immersion in coffee.Materials and Methods Eight CAD/CAM blocks and four restorative composite resins were evaluated. The CIE
L *a *b * values of 2.0 mm thick disk-shaped specimens were measured using the spectrophotometer on white and black backgrounds (n = 6). The ΔE s and ΔTP s of one day, one week, and one month immersion in coffee or water were calculated. The values of each material were analyzed by two-way ANOVA and Tukey's multiple comparisons (α = 0.05). The ΔE s after prophylaxis paste polishing of 1 month coffee immersion specimens, water sorption and solubility were also evaluated.Results After one month in coffee, Δ
E s of CAD/CAM composite resin blocks and restorative composites ranged from 1.6 to 3.7 and from 2.1 to 7.9, respectively, and ΔTP s decreased. The ANOVA of ΔE s and ΔTP s revealed significant differences in two main factors, immersion periods and media, and their interaction except for ΔE s of TEL (Telio CAD, Ivoclar Vivadent). The ΔE s significantly decreased after prophylaxis polishing except GRA (Gradia Block, GC). There was no significant correlation between ΔE s and water sorption or solubility in water.Conclusions The Δ
E s of CAD/CAM blocks after immersion in coffee varied among products and were comparable to those of restorative composite resins. The discoloration of CAD/CAM composite resin blocks could be effectively removed with prophylaxis paste polishing, while that of some restorative composites could not be removed.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Color Stability and Surface Roughness of CAD/CAM Hybrid Ceramics and Resin Composites After Simulated Toothbrushing in Coffee: An In Vitro Study
Mustafa Hayati Atala
Applied Sciences.2026; 16(3): 1576. CrossRef - Effect of polishing and bleaching on color, whiteness, and translucency of CAD/CAM monolithic materials
Ranulfo Castillo Peña, Alejandro Cardenas Ramos, José Maurício dos Santos Nunes Reis, Lívia Nordi Dovigo, Jean‐Pierre Guy Olivier Salomon, María del Mar Pérez, Renata Garcia Fonseca
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2025; 37(2): 440. CrossRef - Translucency and color stability of advanced lithium disilicate ceramic material: An in vitro study
Bader M. Alazemi, Mohammad R. Rayyan
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(1): 33. CrossRef - The impact of bleaching using 15% carbamide peroxide on surface properties of CAD-CAM composite structures
Rasha A. Alamoush, Jiawei Yang, Abdulaziz Alhotan, Julfikar Haider, Burak Yilmaz, Alaaeldin Elraggal
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Efficacy of 3 Bleaching Methods on Stained Polymer-Based CAD/CAM Materials
Rua Babaier, Julfikar Haider, Rasha A. Alamoush, Nick Silikas
International Dental Journal.2025; 75(2): 1327. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of colour stability of conventional, 3d printed and cad cam fabricated provisional restorations- An in-vitro study
Om Shiva Prashanth Vislawath, Anulekha CK, Mahesh Pulagam, Sree Devi Kondareddy, Sai Krishna Seelam, Syeda Afeefa Tahseen
IP Annals of Prosthodontics and Restorative Dentistry.2025; 11(1): 40. CrossRef - Influence of different finishing and polishing protocols of composite CAD CAM blocks on surface roughness and biological response of gingival mesenchymal stem cells
Mohamed F. Haridy, Mohamed Shamel, Raghda A. Khalil, Ahmed Refaat Mohamed, Hoda Fouda, Hend S. Ahmed
Odontology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Water Sorption of Three Provisional Crown and Bridge Materials: An In Vitro Study
Gholamreza Esfahanizadeh, Farzan Younesi, Mohammadreza Hosseini kordkheili, Hosein Akbari
Journal of Research in Dental and Maxillofacial Sciences.2025; 10(3): 210. CrossRef - Influence of Post-Curing in Nitrogen-Saturated Condition on the Degree of Conversion and Color Stability of 3D-Printed Resin Crowns
Bohyun Lim, Dohyun Kim, Je Seon Song, Sunil Kim, Hoon Kim, Yooseok Shin
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(3): 68. CrossRef - Assessment of color stability and translucency of various CAD/CAM ceramics of different compositions and Thicknesses: An in vitro study
Passent Ellakany, Nourhan M. Aly, Shahad T. Alameer, Turki Alshehri, Shaimaa M. Fouda
The Saudi Dental Journal.2024; 36(7): 1019. CrossRef - Water absorption in artificial composites: Curse or blessing?
Thomas Niem, Antje Hübner, Bernd Wöstmann
Dental Materials.2024; 40(8): 1097. CrossRef - Determination of the Color Change of Various Esthetic Monolithic Monochromatic Computer-Aided Design/Computer-Aided Manufacturing Materials
Katarina Bauer, Andreja Carek, Ljerka Slokar Benić, Tomislav Badel
Materials.2024; 17(13): 3160. CrossRef - Effect of coffee staining and simulated oral hygiene methods on the color and translucency of a nanoceramic resin
Luiz Felipe Schneider, Bruna Mueller, Rubens Nisie Tango, Claudia Angela Maziero Volpato
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2024; 36(7): 1020. CrossRef - Clinical Applications and Mechanical Properties of CAD-CAM Materials in Restorative and Prosthetic Dentistry: A Systematic Review
Imena Rexhepi, Manlio Santilli, Gianmaria D’Addazio, Giuseppe Tafuri, Eugenio Manciocchi, Sergio Caputi, Bruna Sinjari
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2023; 14(8): 431. CrossRef - Effect of aging on color, gloss and surface roughness of CAD/CAM composite materials
Ioannis Papathanasiou, Spiros Zinelis, George Papavasiliou, Phophi Kamposiora
Journal of Dentistry.2023; 130: 104423. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Effect of an Energy Drink And 35% Hydrogen Peroxide on Discoloration and Microhardness of Current Restorative Materials
Recep KARA
Selcuk Dental Journal.2023; 10(3): 526. CrossRef - The impact of the diode laser 940 nm photoactivated bleaching on color change of different composite resin restorations
Amal Alaa Mawlood, Niaz H. Hamasaeed
Journal of Advanced Pharmaceutical Technology & Research.2023; 14(2): 155. CrossRef - Discoloration of fiber-reinforced composite resin disc for computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing after immersion in coffee and curry solutions
Maho SHIOZAWA, Yumi TSUCHIDA, Tetsuya SUZUKI, Hidekazu TAKAHASHI
Dental Materials Journal.2023; 42(1): 64. CrossRef - In vitro comparison of the color degradation of two computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing provisional materials: A 12-month simulation
SuzannaMaria Sayegh, Maha Daou, Georges Najjar, Elie Zebouni
The Journal of Indian Prosthodontic Society.2023; 23(1): 38. CrossRef - Effect of Simulated Annual At-home Bleaching on Susceptibility to Staining, Translucency, and Whiteness Variations of Computer-aided Design and Computer-aided Manufacturing Monolithic Materials
AC Ramos, RC Peña, LN Dovigo, MM Pérez, RG Fonseca
Operative Dentistry.2023; 48(4): 404. CrossRef - EFFECT OF DIFFERENT TEAS ON SURFACE ROUGHNESS OF CONVENTIONAL AND BULK-FILL COMPOSITE RESINS
Esra ÖZYURT, Ayşegül KURT
Atatürk Üniversitesi Diş Hekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi.2022; : 1. CrossRef - Effect of thickness on color appearance of multilayer CAD/CAM composite resin blocks
Roubing Ha, Yumi Tsuchida, Maho Shiozawa, Hidekazu Takahashi
Odontology.2022; 110(4): 664. CrossRef - Color changes of dental zirconia immersed in food and beverage containing water-soluble/lipid-soluble pigments
Hiro MATSUMOTO, Takatsugu YAMAMOTO, Tohru HAYAKAWA
Dental Materials Journal.2022; 41(6): 824. CrossRef - Long‐term hydrolytic stability of CAD/CAM composite blocks
Rasha A. Alamoush, Nesreen A. Salim, Nick Silikas, Julian D. Satterthwaite
European Journal of Oral Sciences.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Color stability of a resin nanoceramic after surface treatments, adhesive cementation, and thermal aging
Joseane Silva, Madalena Lucia Pinheiro Dias Engler, Rodrigo Baumgardt Barbosa Lima, Maria Jesús Suarez, Jean-Pierre Guy Oliver Salomon, Claudia Angela Maziero Volpato
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2022; 127(3): 498.e1. CrossRef - Color Stability and Staining Susceptibility of Direct Resin-Based Composites after Light-Activated In-Office Bleaching
Pei-Wen Peng, Chiung-Fang Huang, Ching-Ying Hsu, Ann Chen, Ho-Him Ng, Man-Si Cheng, Shiang Tsay, Jia-Yi Lai, Tzu-Sen Yang, Wei-Fang Lee
Polymers.2021; 13(17): 2941. CrossRef - Evaluation of the colour and translucency parameter of conventional and Computer-aided design and computer-aided manufacturing (CAD-CAM) feldspathic porcelains after staining and laser-assisted bleaching
Foujan Chitsaz, Safoura Ghodsi, SolalehAmirpour Harehdasht, Bahar Goodarzi, Somayeh Zeighami
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2021; 24(6): 628. CrossRef - Investigation the effects of whitening toothpastes on color change of resin‐based CAD/CAM blocks
Numan Aydın, Serpil Karaoglanoglu, Elif Aybala Oktay
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2021; 33(6): 884. CrossRef - Effect of different beverages on color stability and surface properties of composite resin materials
Esra Özyurt, Ayşegül Kurt
Color Research & Application.2021; 46(6): 1382. CrossRef - One-year clinical performance of lithium disilicate versus resin composite CAD/CAM onlays
Joana Souza, Mª Victoria Fuentes, Eugenia Baena, Laura Ceballos
Odontology.2021; 109(1): 259. CrossRef - MEKANİK VE PAT İLE PARLATMA İŞLEMLERİNİN CAD/CAM HİBRİT BLOKLARIN RENK STABİLİTESİNE ETKİSİ
Gaye SAĞLAM, Şükriye Ec GEDUK
Atatürk Üniversitesi Diş Hekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi.2021; : 1. CrossRef - Mechanical degradation of contemporary CAD/CAM resin composite materials after water ageing
Michael Wendler, Anja Stenger, Julian Ripper, Eva Priewich, Renan Belli, Ulrich Lohbauer
Dental Materials.2021; 37(7): 1156. CrossRef - Evaluation of Stain Susceptibility of Different CAD/CAM Blocks After Immersion in Coffee
Soner ŞİŞMANOĞLU, Aliye Tuğçe GÜRCAN
Düzce Üniversitesi Sağlık Bilimleri Enstitüsü Dergisi.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Color stability and surface roughness of resin based direct and indirect restorative materials
Bilge ERSÖZ, Serpil Karaoğlanoğlu, Elif Aybala Oktay, Numan Aydın
European Annals of Dental Sciences.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Color Stability and Translucency of Polymer-Infiltrated Ceramic-Network Materials—A Systematic Review of the Literature
Nawaf Labban
Journal of Biomaterials and Tissue Engineering.2021; 11(10): 1865. CrossRef - Influence of accelerated ageing on the physical properties of CAD/CAM restorative materials
Thomas Niem, Nivin Youssef, Bernd Wöstmann
Clinical Oral Investigations.2020; 24(7): 2415. CrossRef - Evaluation of the repair capacities and color stabilities of a resin nanoceramic and hybrid CAD/CAM blocks
Hasibe Sevilay Bahadır, Yusuf Bayraktar
The Journal of Advanced Prosthodontics.2020; 12(3): 140. CrossRef - Color Stability of Dental Reinforced CAD/CAM Hybrid Composite Blocks Compared to Regular Blocks
Yeong-Ah Kang, Han-Ah Lee, Joseph Chang, Wonjoon Moon, Shin Hye Chung, Bum-Soon Lim
Materials.2020; 13(21): 4722. CrossRef - Long‐term stainability of interim prosthetic materials in acidic/staining solutions
Sandro B. Bitencourt, Roberta Y. Kanda, Caroline de Freitas Jorge, Valentim A. R. Barão, Cortino Sukotjo, Alvin G. Wee, Marcelo C. Goiato, Aldiéris A. Pesqueira
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2020; 32(1): 73. CrossRef - Materials in digital dentistry—A review
Taiseer A. Sulaiman
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2020; 32(2): 171. CrossRef - Residual monomer elution from different conventional and CAD/CAM dental polymers during artificial aging
Madalena Lucia Pinheiro Dias Engler, Jan-Frederik Güth, Christine Keul, Kurt Erdelt, Daniel Edelhoff, Anja Liebermann
Clinical Oral Investigations.2020; 24(1): 277. CrossRef - Energy dissipation capacities of CAD-CAM restorative materials: A comparative evaluation of resilience and toughness
Thomas Niem, Nivin Youssef, Bernd Wöstmann
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2019; 121(1): 101. CrossRef - Translucency, hardness and strength parameters of PMMA resin containing graphene-like material for CAD/CAM restorations
Shruti Vidhawan Agarwalla, Ritika Malhotra, Vinicius Rosa
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2019; 100: 103388. CrossRef - Impact of storage media and temperature on color stability of tooth-colored CAD/CAM materials for final restorations
Anja Liebermann, Dirk Vehling, Marlis Eichberger, Bogna Stawarczyk
Journal of Applied Biomaterials & Functional Materials.2019;[Epub] CrossRef
- Color Stability and Surface Roughness of CAD/CAM Hybrid Ceramics and Resin Composites After Simulated Toothbrushing in Coffee: An In Vitro Study
- 2,212 View
- 10 Download
- 44 Crossref

- The effect of the strength and wetting characteristics of Bis-GMA/TEGDMA-based adhesives on the bond strength to dentin
- Eun-Sook Park, Chang-Keun Kim, Ji-Hyun Bae, Byeong-Hoon Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(2):139-148. Published online March 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.2.139
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study investigated the effect of the strength and wetting characteristics of adhesives on the bond strength to dentin. The experimental adhesives containing various ratios of hydrophobic, low-viscosity Bis-M-GMA, with Bis-GMA and TEGDMA, were made and evaluated on the mechanical properties and bond strength to dentin.
Materials and Methods Five experimental adhesives formulated with various Bis-GMA/Bis-M-GMA/TEGDMA ratios were evaluated on their viscosity, degree of conversion (DC), flexural strength (FS), and microtensile bond strength (MTBS). The bonded interfaces were evaluated with SEM and the solubility parameter was calculated to understand the wetting characteristics of the adhesives.
Results Although there were no significant differences in the DC between the experimental adhesives at 48 hr after curing (
p > 0.05), the experimental adhesives that did not contain Bis-GMA exhibited a lower FS than did those containing Bis-GMA (p < 0.05). The experimental adhesives that had very little to no TEGDMA showed significantly lower MTBS than did those containing a higher content of TEGDMA (p < 0.05). The formers exhibited gaps at the interface between the adhesive layer and the hybrid layer. The solubility parameter of TEGDMA approximated those of the components of the primed dentin, rather than Bis-GMA and Bis-M-GMA.Conclusions To achieve a good dentin bond, a strong base monomer, such as Bis-GMA, cannot be completely replaced by Bis-M-GMA for maintaining mechanical strength. For compatible copolymerization between the adhesive and the primed dentin as well as dense cross-linking of the adhesive layer, at least 30% fraction of TEGDMA is also needed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Equivalence study of the resin-dentine interface of internal tunnel restorations when using an enamel infiltrant resin with ethanol-wet dentine bonding
Andrej M. Kielbassa, Sabrina Summer, Wilhelm Frank, Edward Lynch, Julia-Susanne Batzer
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Physical properties and cytotoxicity of antimicrobial dental resin adhesives containing dimethacrylate oligomers of Ciprofloxacin and Metronidazole
Yasaman Delaviz, Timothy W. Liu, Ashley R. Deonarain, Yoav Finer, Babak Shokati, J. Paul Santerre
Dental Materials.2019; 35(2): 229. CrossRef
- Equivalence study of the resin-dentine interface of internal tunnel restorations when using an enamel infiltrant resin with ethanol-wet dentine bonding
- 2,164 View
- 7 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Physical and chemical properties of experimental mixture of mineral trioxide aggregate and glass ionomer cement
- Yu-Na Jeong, So-Young Yang, Bum-Jun Park, Yeong-Joon Park, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(5):344-352. Published online September 30, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.5.344
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to determine the setting time, compressive strength, solubility, and pH of mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) mixed with glass ionomer cement (GIC) and to compare these properties with those of MTA, GIC, IRM, and SuperEBA.
Materials and Methods Setting time, compressive strength, and solubility were determined according to the ISO 9917 or 6876 method. The pH of the test materials was determined using a pH meter with specified electrode for solid specimen.
Results The setting time of MTA mixed with GIC was significantly shorter than that of MTA. Compressive strength of MTA mixed with GIC was significantly lower than that of other materials at all time points for 7 days. Solubility of 1 : 1 and 2 : 1 specimen from MTA mixed with GIC was significantly higher than that of other materials. Solubility of 1 : 2 specimen was similar to that of MTA. The pH of MTA mixed with GIC was 2-4 immediately after mixing and increased to 5-7 after 1 day.
Conclusions The setting time of MTA mixed with GIC was improved compared with MTA. However, other properties such as compressive strength and pH proved to be inferior to those of MTA. To be clinically feasible, further investigation is necessary to find the proper mixing ratio in order to improve the drawbacks of MTA without impairing the pre-existing advantages and to assess the biocompatibility.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of particle size reduction on the physicochemical and mechanical properties of conventional glass ionomer cement
Nozimjon Tuygunov, Farangis Abdurahimova, Sevara Rizaeva, Zohaib Khurshid, Arief Cahyanto, Myrna Nurlatifah Zakaria, Bakhtinur Khudanov
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Setting Time, Compressive Strength, Solubility, and pH of Four Kinds of MTA
Jing-Ling Che, Jae-Hwan Kim, Seon-Mi Kim, Nam-ki Choi, Hyun-Joo Moon, Moon-Jin Hwang, Ho-Jun Song, Yeong-Joon Park
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2016; 43(1): 61. CrossRef - Do conventional glass ionomer cements release more fluoride than resin-modified glass ionomer cements?
Maria Fernanda Costa Cabral, Roberto Luiz de Menezes Martinho, Manoel Valcácio Guedes-Neto, Maria Augusta Bessa Rebelo, Danielson Guedes Pontes, Flávia Cohen-Carneiro
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(3): 209. CrossRef - Synthesis and Properties of a New Dental Material Based on Nano‐Structured Highly Active Calcium Silicates and Calcium Carbonates
Vukoman Jokanović, Božana Čolović, Miodrag Mitrić, Dejan Marković, Bojana Ćetenović
International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology.2014; 11(1): 57. CrossRef - Evaluation of the effect of blood contamination on the compressive strength of MTA modified with hydration accelerators
Kaveh Oloomi, Eshaghali Saberi, Hadi Mokhtari, Hamid Reza Mokhtari Zonouzi, Ali Nosrat, Mohammad Hossein Nekoofar, Paul Michael Howell Dummer
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(3): 128. CrossRef - Endodontic management of a maxillary lateral incisor with dens invaginatus and external root irregularity using cone-beam computed tomography
Young-Jun Lim, Sook-Hyun Nam, Sung-Ho Jung, Dong-Ryul Shin, Su-Jung Shin, Kyung-San Min
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(1): 50. CrossRef
- Effect of particle size reduction on the physicochemical and mechanical properties of conventional glass ionomer cement
- 1,583 View
- 3 Download
- 6 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


