Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- A micro-computed tomography evaluation of voids using calcium silicate-based materials in teeth with simulated internal root resorption
- Vildan Tek, Sevinç Aktemur Türker
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(1):e5. Published online November 29, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e5
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
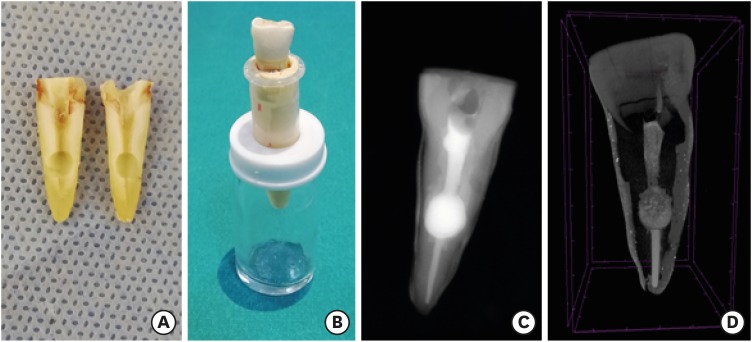
ePub Objectives The obturation quality of MTA, Biodentine, Total Fill BC root canal sealer (RCS), and warm gutta-percha (WGP) in teeth with simulated internal root resorption (IRR) was evaluated by using micro-computed tomography.
Materials and Methods Standardized IRR cavities were created using 40 extracted maxillary central incisor teeth and randomly assigned into 4 groups (
n = 10). IRR cavities were filled with MTA, Biodentine, Total Fill BC RCS (bulk-fill form) and WGP + Total Fill BC RCS. Percentage of voids between resorptive cavity walls and obturation material (external void), and inside the filling materials (internal voids) were measured.Results Total Fill BC sealer in the bulk-fill form presented significantly highest values of external and internal void percentages (
p < 0.05). Biodentine showed a significantly lowest external void percentage (p < 0.05). WGP + Total Fill BC RCS presented significantly lower values of internal void percentages than all groups (p < 0.05), except Biodentine (p > 0.05).Conclusion None of the filling materials were created void-free obturation in resorption cavities. Biodentine may favor its application in teeth with IRR over Angelus MTA and bulk-fill form of Total Fill BC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Removal of AH Plus Bioceramic Sealer from Artificial Internal Resorption Cavities Using Different Irrigation Activation Systems
Mine Büker, Meltem Sümbüllü, Emine Şimşek, Fadime Sena Sezer
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2025; 28(3): 383. CrossRef - Functional and Bioactive Performance of Premixed Bioceramic Sealers with Warm Obturation: A Scoping Review
Patryk Wiśniewski, Stanisław Krokosz, Małgorzata Pietruska, Anna Zalewska
Gels.2025; 11(11): 932. CrossRef - Evaluation of the effectiveness of different supplemental cleaning techniques in the retreatment of roots with small simulated internal resorption cavities: an in vitro comparative study
Sine Güngör Us, Özgür Uzun, Nazlı Merve Güngör
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Different Techniques and Materials for Filling in 3-dimensional Printed Teeth Replicas with Perforating Internal Resorption by Means of Micro–Computed Tomography
Angelo J.S. Torres-Carrillo, Helena C. Assis, Rodrigo E. Salazar-Gamarra, Leonardo Moreira Teodosio, Alice C. Silva-Sousa, Jardel F. Mazzi-Chaves, Priscila B. Ferreira-Soares, Manoel D. Sousa-Neto, Fabiane C. Lopes-Olhê
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(2): 205. CrossRef - Three-Dimensional Measurement of Obturation Quality of Bioceramic Materials in Filling Artificial Internal Root Resorption Cavities Using Different Obturation Techniques: An In Vitro Comparative Study
Ammar M. Sharki, Ahmed H. Ali
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(7): 997. CrossRef - Evaluation of calcium hydroxide root canal filling materials by cone beam computed tomography and three-dimensional modeling
Asel Usdat Ozturk, Ekin Dogan, Venus Seyedoskuyi, Berk Senguler, Asli Topaloglu-Ak
Folia Medica.2024; 66(2): 250. CrossRef - Clinical applications of calcium silicate‐based materials: a narrative review
S Küçükkaya Eren
Australian Dental Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study root canal fillings
Gustavo De‐Deus, Erick Miranda Souza, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Marco Simões‐Carvalho, Daniele Moreira Cavalcante, Marco Aurélio Versiani
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S2): 384. CrossRef - An Updated Review on Properties and Indications of Calcium Silicate‐Based Cements in Endodontic Therapy
Fateme Eskandari, Alireza Razavian, Rozhina Hamidi, Khadije Yousefi, Susan Borzou, Zohaib Khurshid
International Journal of Dentistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy Of Calcium Silicate-Based Sealers In Root Canal Treatment: A Systematic Review
Hattan Mohammed Omar Baismail, Mohammed Ghazi Moiser Albalawi, Alaa Mofareh Thoilek Alanazi, Muhannad Atallah Saleem Alatawi, Badr Soliman Alhussain
Annals of Dental Specialty.2021; 9(1): 87. CrossRef
- Removal of AH Plus Bioceramic Sealer from Artificial Internal Resorption Cavities Using Different Irrigation Activation Systems
- 2,330 View
- 26 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Influence of size and insertion depth of irrigation needle on debris extrusion and sealer penetration
- Emel Uzunoglu-Özyürek, Hakan Karaaslan, Sevinç Aktemur Türker, Bahar Özçelik
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(1):e2. Published online December 22, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e2
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
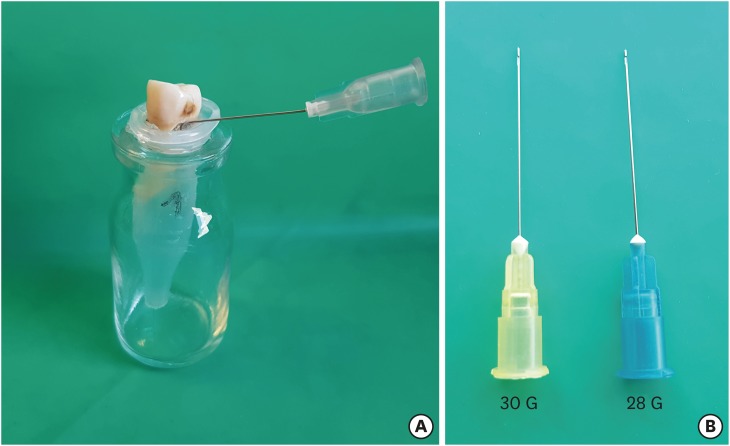
ePub Objectives To determine the effect of size and insertion depth of irrigation needle on the amount of apical extruded debris and the amount of penetration depth of sealer using a confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM).
Materials and Methods Twenty maxillary premolars were assigned to 2 groups (
n = 10), according to the size of needle tip, 28 G or 30 G. Buccal roots of samples were irrigated with respective needle type inserted 1 mm short of the working length (WL), while palatal roots were irrigated with respective needle type inserted 3 mm short of the WL. Prepared teeth were removed from the pre-weighed Eppendorf tubes. Canals were filled with F3 gutta-percha cone and rhodamine B dye-labeled AH 26 sealer. Teeth were transversally sectioned at 1 and 3 mm levels from the apex and observed under a CLSM. Eppendorf tubes were incubated to evaporate the irrigant and were weighed again. The difference between pre- and post-weights was calculated, and statistical evaluation was performed.Results Inserting needles closer to the apex and using needles with wider diameters were associated with significantly more debris extrusion (
p < 0.05). The position of needles and level of sections had statistically significant effects on sealer penetration depth (p < 0.05 for both).Conclusions Following preparation, inserting narrower needles compatible with the final apical diameter of the prepared root canal at 3 mm short of WL during final irrigation might prevent debris extrusion and improve sealer penetration in the apical third.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of laser-induced pulpal anesthesia of single-rooted teeth with irreversible pulpitis treated by single-visit root canal therapy - A randomized clinical trial
Geeta Asthana, Dhwani Morakhia, Ravina Parmar, Rajashree Tamuli
Endodontology.2025; 37(3): 244. CrossRef - Efficacy of different irrigation needles used in endodontics: an in silico and an in vitro investigation
Maulee Sheth, Ankit Arora, Sonali Kapoor, Balraj Shukla
Biomaterial Investigations in Dentistry.2025; 12: 264. CrossRef - Preliminary insights: exploring irrigation practices during endodontic treatment among general dental practitioners in Malaysia
Kai Qi Chiew, Xin Ni Lim, Shekhar Bhatia, Naveen Chhabra
British Dental Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficiency of diode laser in control of post-endodontic pain: a randomized controlled trial
Hend H. Ismail, Maram Obeid, Ehab Hassanien
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(6): 2797. CrossRef - Endodontic management of an aberrant germinated composite odontome: A case report
Ankit Arora, Kavina Desai, Sonali Kapoor, Seema Gajera
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(3): 684. CrossRef - Potentials of 3D-Modeling in the Preclinical Stage of Root Needle Research
Aleksandr V. Kuligin, Larisa N. Kazakova, Oksana S. Tereshchuk, Vadim V. Bokov
I.P. Pavlov Russian Medical Biological Herald.2022; 30(1): 95. CrossRef - Effect of root canal geometry and needle type on apical extrusion of irrigant: an ex vivo study
Büşra SERÇE FİKİRLİ, Bülent ALTUNKAYNAK, Güven KAYAOĞLU
Acta Odontologica Turcica.2022; 39(3): 58. CrossRef - An in vitro radiological evaluation of irrigant penetration in the root canals using three different irrigation systems: Waterpik WP-100 device, passive irrigation, and manual dynamic irrigation systems
Suragani Hemalatha, Archana Srinivasan, A Srirekha, Lekha Santhosh, C Champa, Ashwija Shetty
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2022; 25(4): 403. CrossRef - Preparation Ability of ProTaper Next and XP-endo Shaper Instruments in Isthmus-containing Root Canal System
Mustafa Sarıkahya, Tayfun Alaçam
Conservative Dentistry and Endodontic Journal.2021; 5(2): 28. CrossRef - Penetration depth of irrigants into root dentine after sonic, ultrasonic and photoacoustic activation
K. M. Galler, V. Grubmüller, R. Schlichting, M. Widbiller, A. Eidt, C. Schuller, M. Wölflick, K.‐A. Hiller, W. Buchalla
International Endodontic Journal.2019; 52(8): 1210. CrossRef
- Effect of laser-induced pulpal anesthesia of single-rooted teeth with irreversible pulpitis treated by single-visit root canal therapy - A randomized clinical trial
- 1,594 View
- 18 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Influence of a glide path on the dentinal crack formation of ProTaper Next system
- Sevinç Aktemur Türker, Emel Uzunoğlu
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(4):286-289. Published online September 2, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.4.286
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim was to evaluate dentinal crack formation after root canal preparation with ProTaper Next system (PTN) with and without a glide path.
Materials and Methods Forty-five mesial roots of mandibular first molars were selected. Fifteen teeth were left unprepared and served as controls. The experimental groups consist of mesiobuccal and mesiolingual root canals of remaining 30 teeth, which were divided into 2 groups (
n = 15): Group PG/PTN, glide path was created with ProGlider (PG) and then canals were shaped with PTN system; Group PTN, glide path was not prepared and canals were shaped with PTN system only. All roots were sectioned perpendicular to the long axis at 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 8 mm from the apex, and the sections were observed under a stereomicroscope. The presence/absence of cracks was recorded. Data were analyzed with chi-square tests with Yates correction.Results There were no significant differences in crack formation between the PTN with and without glide path preparation. The incidence of cracks observed in PG/PTN and PTN groups was 17.8% and 28.9%, respectively.
Conclusions The creation of a glide path with ProGlider before ProTaper Next rotary system did not influence dentinal crack formation in root canals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative Evaluation of the Shaping Ability of the Recent, Fifth-generation ProTaper Next and Revo-S NiTi Rotary Endodontic Files Using Three-dimensional Imaging: An Imaging-based Study
Prajna Pattanaik, Akilan Balasubramanian, P. Veeralakshmi, Gautam Singh, Vandana Sadananda, Hina Ahmed, J. Suresh Babu, C. Swarnalatha, Abhishek Singh Nayyar
Journal of Microscopy and Ultrastructure.2025; 13(4): 177. CrossRef - Glide Path in Endodontics: A Literature Review of Current Knowledge
Vlad Mircea Lup, Giulia Malvicini, Carlo Gaeta, Simone Grandini, Gabriela Ciavoi
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(8): 257. CrossRef - Microscopic Assessment of Dentinal Defects Induced by ProTaper Universal, ProTaper Gold, and Hyflex Electric Discharge Machining Rotary File Systems – An in vitro Study
Takhellambam Premlata Devi, Amandeep Kaur, Shamurailatpam Priyadarshini, B. S. Deepak, Sumita Banerjee, Ng Sanjeeta
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2021; 12(3): 230. CrossRef - Influence of Negotiation, Glide Path, and Preflaring Procedures on Root Canal Shaping—Terminology, Basic Concepts, and a Systematic Review
Gianluca Plotino, Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Frederic Bukiet, Nicola M. Grande, Sajesh K. Veettil, Gustavo De-Deus, Hany Mohamed Aly Ahmed
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(6): 707. CrossRef
- Comparative Evaluation of the Shaping Ability of the Recent, Fifth-generation ProTaper Next and Revo-S NiTi Rotary Endodontic Files Using Three-dimensional Imaging: An Imaging-based Study
- 1,398 View
- 5 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Effects of dentin moisture on the push-out bond strength of a fiber post luted with different self-adhesive resin cements
- Sevinç Aktemur Türker, Emel Uzunoğlu, Zeliha Yılmaz
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(4):234-240. Published online November 12, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.4.234
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the effects of intraradicular moisture on the pushout bond strength of a fibre post luted with several self-adhesive resin cements.
Materials and Methods Endodontically treated root canals were treated with one of three luting cements: (1) RelyX U100, (2) Clearfil SA, and (3) G-Cem. Roots were then divided into four subgroups according to the moisture condition tested: (I) dry: excess water removed with paper points followed by dehydration with 95% ethanol, (II) normal moisture: canals blot-dried with paper points until appearing dry, (III) moist: canals dried by low vacuum using a Luer adapter, and (IV) wet: canals remained totally flooded. Two 1-mm-thick slices were obtained from each root sample and bond strength was measured using a push-out test setup. The data were analysed using a two-way analysis of variance and the Bonferroni
post hoc test withp = 0.05.Results Statistical analysis demonstrated that moisture levels had a significant effect on the bond strength of luting cements (
p < 0.05), with the exception of G-Cem. RelyX U100 displayed the highest bond strength under moist conditions (III). Clearfil SA had the highest bond strength under normal moisture conditions (II). Statistical ranking of bond strength values was as follows: RelyX U100 > Clearfil SA > G-Cem.Conclusions The degree of residual moisture significantly affected the adhesion of luting cements to radicular dentine.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Push-Out Bond Strength of Different Luting Cements Following Post Space Irrigation with 2% Chitosan: An In Vitro Study
Shimaa Rifaat, Ahmed Rahoma, Hind Muneer Alharbi, Sawsan Jamal Kazim, Shrouq Ali Aljuaid, Basmah Omar Alakloby, Faraz A. Farooqi, Noha Taymour
Prosthesis.2025; 7(1): 18. CrossRef - Dentin bond strength of resin luting agents under a simulated intra-oral environment
Takashi Washino, Hanemi Tsuruta, Masaomi Ikeda, Michael F. Burrow, Toru Nikaido
Asian Pacific Journal of Dentistry.2024; 24(2): 13. CrossRef - Effects of a relined fiberglass post with conventional and self-adhesive resin cement
Wilton Lima dos Santos Junior, Marina Rodrigues Santi, Rodrigo Barros Esteves Lins, Luís Roberto Marcondes Martins
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of dentin moisture on the adhesive properties of luting fiber posts using adhesive strategies
Renata Terumi JITUMORI, Rafaela Caroline RODRIGUES, Alessandra REIS, João Carlos GOMES, Giovana Mongruel GOMES
Brazilian Oral Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of different intraradicular chemical pretreatments on the bond strength of adhesive interface between dentine and fiber post cements: A systematic review and network meta‐analysis
Ana Luiza Barbosa Jurema, Ayla Macyelle de Oliveira Correia, Manuela da Silva Spinola, Eduardo Bresciani, Taciana Marco Ferraz Caneppele
European Journal of Oral Sciences.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - SELF ADEZİV REZİN SİMANLAR / SELF ADHESIVE RESIN CEMENTS
Kübra AMAÇ, Engin ESENTÜRK, Bilge TURHAN BAL
Atatürk Üniversitesi Diş Hekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi.2022; : 1. CrossRef - Postspace pretreatment with 17% ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid, 7% maleic acid, and 1% phytic acid on bond strength of fiber posts luted with a self-adhesive resin cement
PriyaC Yadav, Ramya Raghu, Ashish Shetty, Subhashini Rajasekhara
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2021; 24(6): 558. CrossRef - Development and characterization of biological bovine dentin posts
Alice Gonçalves Penelas, Eduardo Moreira da Silva, Laiza Tatiana Poskus, Amanda Cypriano Alves, Isis Ingrid Nogueira Simões, Viviane Hass, José Guilherme Antunes Guimarães
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2019; 92: 197. CrossRef - Evaluation of the influence of time and concentration of sodium hypochlorite on the bond strength of glass fibre post
Beau Knight, Robert M. Love, Roy George
Australian Endodontic Journal.2018; 44(3): 267. CrossRef - Test methods for bond strength of glass fiber posts to dentin: A review
F. C. Dos Santos, M. D. Banea, H. L. Carlo, S. De Barros
The Journal of Adhesion.2017; 93(1-2): 159. CrossRef - Is the bonding of self-adhesive cement sensitive to root region and curing mode?
Thaynara Faelly BOING, Giovana Mongruel GOMES, João Carlos GOMES, Alessandra REIS, Osnara Maria Mongruel GOMES
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2017; 25(1): 2. CrossRef - A Twofold Comparison between Dual Cure Resin Modified Cement and Glass Ionomer Cement for Orthodontic Band Cementation
Hanaa El Attar, Omnia Elhiny, Ghada Salem, Ahmed Abdelrahman, Mazen Attia
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.2016; 4(4): 695. CrossRef - Shear bond strengths of various self-adhesive resin cements between bovine dentin and 4 types of adherends
Ah-Jin Kim, Da-Ryeong Park, Seunghan Oh, Ji-Myung Bae
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2015; 42(4): 365. CrossRef
- Push-Out Bond Strength of Different Luting Cements Following Post Space Irrigation with 2% Chitosan: An In Vitro Study
- 1,595 View
- 4 Download
- 13 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


