Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Evaluation of the effects of different file systems and apical functions of integrated endodontic motors on debris extrusion: an ex vivo experimental study
- Sıla Nur Usta, Antonio Magan-Fernandez, Cumhur Aydın
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(2):e14. Published online April 14, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e14
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
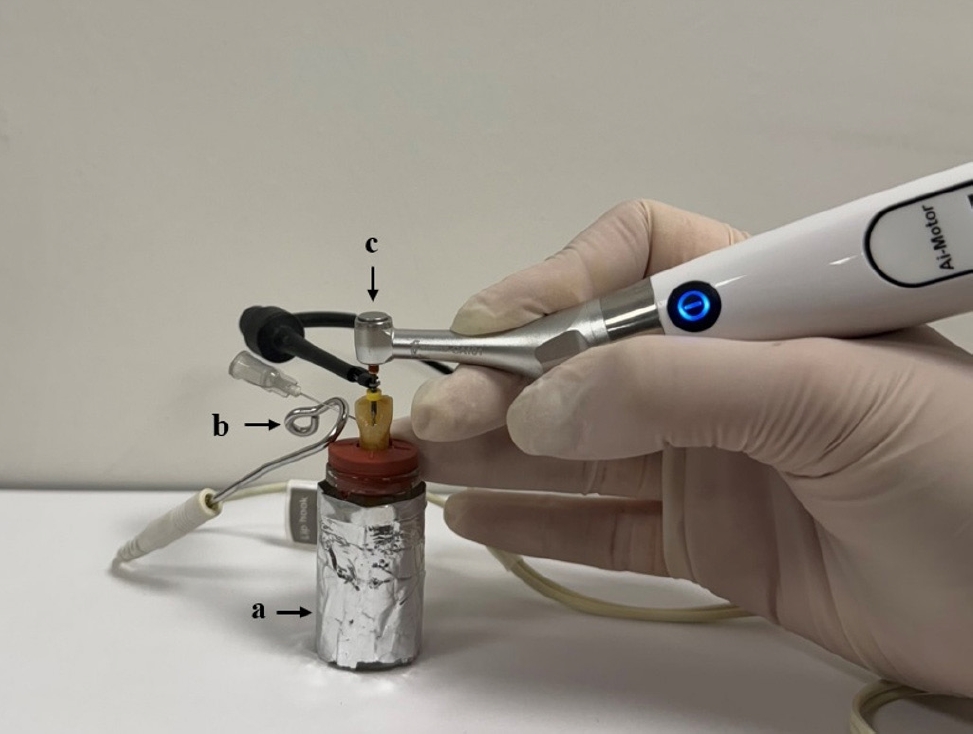
This study aimed to evaluate the effects of two different file systems operated with three apical functions of an endodontic motor integrated with an electronic apex locator on debris extrusion.
Methods
Sixty single-rooted teeth were prepared and divided into two main groups and three subgroups based on the file system (OneShape [Micro-Mega SA] and WaveOne [Dentsply Maillefer]) and apical function of the endodontic motor used (auto apical stop [AAS], auto apical reverse [AAR], and auto apical slowdown [ASD]). The teeth were mounted in pre-weighed glass tubes filled with 0.9% sodium chloride to complete the circuit with the apex locator. Files were advanced until the respective apical function (stop, reverse, or slowdown) was activated. The extruded debris was collected, dried, and weighed by subtracting pre-weighed values from post-weighed values. Preparation time was also recorded. Statistical analyses were performed to compare the groups.
Results
OneShape was associated with significantly less debris extrusion compared to WaveOne, regardless of the apical function (p < 0.05). The ASD function resulted in the least debris extrusion compared to AAS and AAR (p < 0.05). Preparation time was significantly longer in the ASD function (p < 0.05), while no differences were observed between the file systems (p > 0.05).
Conclusions
The OneShape file system and the ASD function produced the least amount of apical debris. While the ASD function requires more preparation time, its potential to minimize debris extrusion suggests it may reduce postoperative symptoms. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Inflammatory Mediator Levels and Postoperative Pain Following Root Canal Shaping with Different Apical Actions: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Mustafa Mert Tulgar, Yağmur Kılıç, Oğuz Karalar, Huriye Erbak Yılmaz, Emrah Karataşlıoğlu
Journal of Endodontics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Inflammatory Mediator Levels and Postoperative Pain Following Root Canal Shaping with Different Apical Actions: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- 4,126 View
- 216 Download
- 1 Crossref

-
Effectiveness and safety of rotary and reciprocating kinematics for retreatment of curved root canals: a systematic review of
in vitro studies - Lucas Pinho Simões, Alexandre Henrique dos Reis-Prado, Carlos Roberto Emerenciano Bueno, Ana Cecília Diniz Viana, Marco Antônio Húngaro Duarte, Luciano Tavares Angelo Cintra, Cleidiel Aparecido Araújo Lemos, Francine Benetti
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(2):e22. Published online April 6, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e22
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
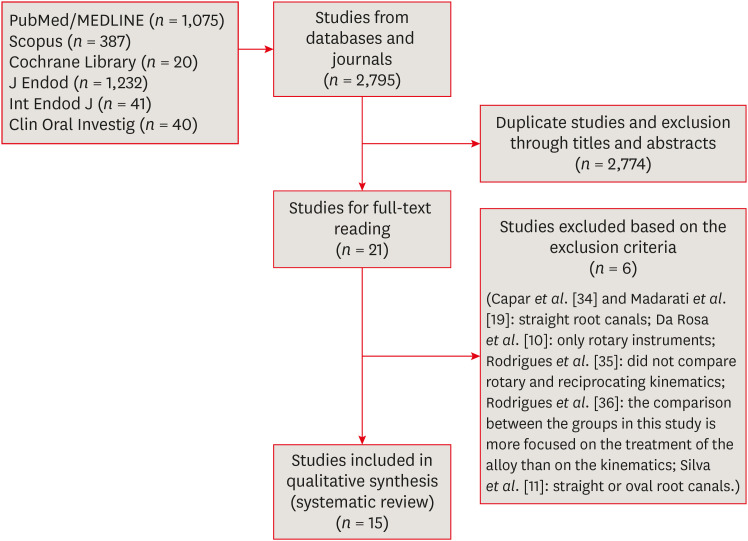
ePub Objectives This systematic review (register-osf.io/wg7ba) compared the efficacy and safety of rotary and reciprocating kinematics in the removal of filling material from curved root canals.
Materials and Methods Only
in vitro studies evaluating both kinematics during retreatment were included. A systematic search (PubMed/MEDLINE, Scopus, and other databases, until January 2021), data extraction, and risk of bias analysis (Joanna Briggs Institute checklist) were performed. Efficacy in filling removal was the primary outcome.Results The search resulted in 2,795 studies, of which 15 were included. Efficacy was measured in terms of the remaining filling material and the time required for this. Nine studies evaluated filling material removal, of which 7 found no significant differences between rotary and reciprocating kinematics. Regarding the time for filling removal, 5 studies showed no difference between both kinematics, 2 studies showed faster results with rotary systems, and other 2 showed the opposite. No significant differences were found in apical transportation, centering ability, instrument failure, dentin removed and extruded debris. A low risk of bias was observed.
Conclusions This review suggests that the choice of rotary or reciprocating kinematics does not influence the efficacy of filling removal from curved root canals. Further studies are needed to compare the kinematics safety in curved root canals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- EVALUATION OF MICROLEAKAGE AFTER ENDODONTIC FILLING IN TEETH WITH APICAL WIDENING: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
Isabella da Costa Ferreira, Gabriela da Costa Ferreira, Isabella Figueiredo de Assis Macedo, Gustavo Oliveira Campos, Isabella Faria da Cunha Peixoto, Ana Cecília Diniz Viana, Rodrigo Rodrigues Amaral, Warley Luciano Fonseca Tavares
ARACÊ .2025; 7(10): e8792. CrossRef - Fifteen years of engine‐driven nickel–titanium reciprocating instruments, what do we know so far? An umbrella review
Felipe Immich, Lucas Peixoto de Araújo, Rafaella Rodrigues da Gama, Wellington Luiz de Oliveira da Rosa, Evandro Piva, Giampiero Rossi‐Fedele
Australian Endodontic Journal.2024; 50(2): 409. CrossRef - Efficacy of Various Heat-treated Retreatment File Systems on the Apical Deformity and Canal Centering Ability in a Single-rooted Teeth using Nano CT
Swathi S, Pradeep Solete, Ganesh Jeevanandan, Delphine Priscilla Antony S, Kavalipurapu Venkata Teja, Dona Sanju
The Open Dentistry Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Micro-CT evaluation of the removal of root fillings using rotary and reciprocating systems supplemented by XP-Endo Finisher, the Self-Adjusting File, or Er,Cr:YSGG laser
Gülsen Kiraz, Bulem Üreyen Kaya, Mert Ocak, Muhammet Bora Uzuner, Hakan Hamdi Çelik
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of sodium hypochlorite on cyclic fatigue resistance of nickel–titanium instruments: A systematic review and meta-analysis of in vitro studies
Alexandre Henrique dos Reis-Prado, Lucas Guimarães Abreu, Lara Cancella de Arantes, Kiani dos Santos de Paula, Sabrina de Castro Oliveira, Juliana Goto, Ana Cecília Diniz Viana, Francine Benetti
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(11): 6291. CrossRef - Retreatment of XP-endo Shaper and R-Endo files in curved root canals
Hayam Y. Hassan, Fahd M. Hadhoud, Ayman Mandorah
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Advancing Endodontics through Kinematics
Shilpa Bhandi, Dario Di Nardo, Francesco Pagnoni, Rosemary Abbagnale
World Journal of Dentistry.2023; 14(6): 479. CrossRef
- EVALUATION OF MICROLEAKAGE AFTER ENDODONTIC FILLING IN TEETH WITH APICAL WIDENING: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
- 3,162 View
- 58 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref

- Comparison of the cyclic fatigue resistance of One Curve, F6 Skytaper, Protaper Next, and Hyflex CM endodontic files
- Charlotte Gouédard, Laurent Pino, Reza Arbab-Chirani, Shabnam Arbab-Chirani, Valérie Chevalier
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(2):e16. Published online March 4, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e16
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study compared the cyclic fatigue resistance of One Curve (C wire) and F6 Skytaper (conventional austenite nickel-titanium [NiTi]), and 2 instruments with thermo-mechanically treated NiTi: Protaper Next X2 (M wire) and Hyflex CM (CM wire).
Materials and Methods Ten new instruments of each group (size: 0.25 mm, 6% taper in the 3 mm tip region) were tested using a rotary bending machine with a 60° curvature angle and a 5 mm curvature radius, at room temperature. The number of cycles until fracture was recorded. The length of the fractured instruments was measured. The fracture surface of each fragment was examined with a scanning electron microscope (SEM). The data were analyzed using one-way analysis of variance and the
post hoc Tukey test. The significance level was set at 0.05.Results At 60°, One Curve, F6 Skytaper and Hyflex CM had significantly longer fatigue lives than Protaper Next X2 (
p < 0.05). No statistically significant differences were found in the cyclic fatigue lives of One Curve, F6 Skytaper, and Hyflex CM (p > 0.05). SEM images of the fracture surfaces of the different instruments showed typical features of fatigue failure.Conclusions Within the conditions of this study, at 60° and with a 5 mm curvature radius, the cyclic fatigue life of One Curve was not significantly different from those of F6 Skytaper and Hyflex CM. The cyclic fatigue lives of these 3 instruments were statistically significantly longer than that of Protaper Next.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of cyclic fatigue in three pediatric endodontic rotary file systems in root canals of primary molars: A finite element analysis (FEA)
Monika sri S.S., K.C. Vignesh, K. Vivek, Kavitha Swaminathan, Selvakumar Haridoss
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2025; 15(2): 310. CrossRef - Stress analysis of different experimental finite element models of rotary endodontic instruments
Manar M. Galal, Amira Galal Ismail, Nada Omar
Bulletin of the National Research Centre.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Understanding Cyclic Fatigue in Three Nickel–Titanium Pediatric Files: An In Vitro Study for Enhanced Patient Care
Alwaleed Abushanan, Rajashekhara Bhari Sharanesha, Fahd Aljarbou, Hadi Alamri, Mohammed Hamad Almasud, Abdulfatah AlAzmah, Sara Alghamdi, Mubashir Baig Mirza
Medicina.2025; 61(5): 830. CrossRef - Analyzing Surface Morphology Changes Induced by Cyclic Fatigue in Three Different Nickel–Titanium Rotary Files Using Scanning Electron Microscopy Analysis
Chintan Joshi, Mahima P Jain, Sweety M Thumar, Jay H Dave, Applu R Bhatt, Juhi I Dholani
World Journal of Dentistry.2024; 15(7): 579. CrossRef - Nickel ion release and surface analyses on instrument fragments fractured beyond the apex: a laboratory investigation
Sıdıka Mine Toker, Ekim Onur Orhan, Arzu Beklen
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Evaluation of cyclic fatigue in three pediatric endodontic rotary file systems in root canals of primary molars: A finite element analysis (FEA)
- 3,232 View
- 43 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- Influence of glide path size and operating kinetics on time to reach working length and fracture resistance of Twisted File adaptive and Endostar E3 nickel-titanium file systems
- Tamilkumaran Ramyadharshini, Inbaraj Anand Sherwood, V Shanmugham Vigneshwar, Prakasam Ernest Prince, Murugadoss Vaanjay
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(2):e22. Published online March 5, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e22
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
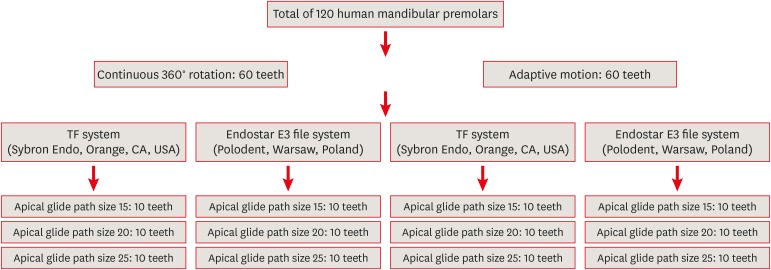
ePub Objectives This study investigated the influence of glide path size and operating kinetics on the time to reach the working length and the fracture resistance of Twisted File (TF) and Endostar E3 files.
Materials and Methods A total of 120 mandibular single-rooted premolars were selected. Two methods of kinetic motion (TF adaptive and continuous rotary motion) and file systems (TF and Endostar E3) were employed. The files were used in root canals prepared to apical glide path sizes of 15, 20, and 25. The time taken to reach the working length and the number of canals used before the instrument deformed or fractured were noted. Fractured instruments were examined with scanning electron microscopy.
Results The TF system took significantly more time to reach the working length than the Endostar E3 system. Both systems required significantly more time to reach the working length at the size 15 glide path than at sizes 20 and 25. A greater number of TFs than Endostar E3 files exhibited deformation, and a higher incidence of instrument deformation was observed in adaptive than in continuous rotary motion; more deformation was also observed with the size 15 glide path. One TF was fractured while undergoing adaptive motion.
Conclusions No significant difference was observed between continuous rotary and adaptive motion. The TF system and adaptive motion were associated with a higher incidence of deformation and fracture. Apical glide path sizes of 20 and 25 required significantly less time to reach the working length than size 15.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of the Adaptive Torque Control Motion on the Ability of Neolix EDMax to Reach Working Length When Used as a Single Shaping File—An In Vitro Study
Vlad Mircea Lup, Carlo Gaeta, Ashkan Tavakkoli, Andreas Louloudiadis, Simone Grandini, Gabriela Ciavoi
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(6): 262. CrossRef - Glide Path in Endodontics: A Literature Review of Current Knowledge
Vlad Mircea Lup, Giulia Malvicini, Carlo Gaeta, Simone Grandini, Gabriela Ciavoi
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(8): 257. CrossRef - Assessment of Different File Systems for Working Time Based on Glide Path, Operating Kinetics, and the Fracture Resistance
Ruchika Gupta, Divya Batra, Debkant Jena, Nandita Bansal, Alka Arora, Divya Gaurav Dudulwar
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2021; 22(1): 69. CrossRef
- Influence of the Adaptive Torque Control Motion on the Ability of Neolix EDMax to Reach Working Length When Used as a Single Shaping File—An In Vitro Study
- 1,708 View
- 13 Download
- 3 Crossref

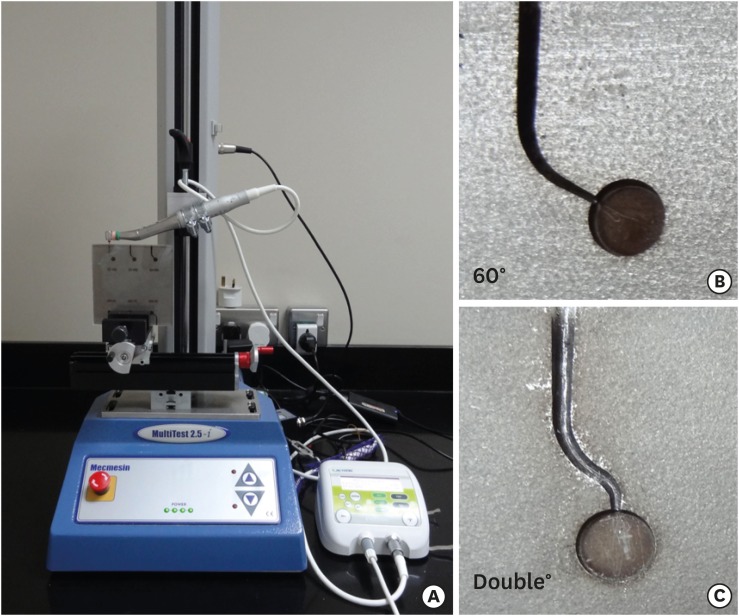
- Cyclic fatigue, bending resistance, and surface roughness of ProTaper Gold and EdgeEvolve files in canals with single- and double-curvature
- Wafaa A. Khalil, Zuhair S. Natto
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(2):e19. Published online April 26, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e19
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to evaluate the cyclic fatigue, bending resistance, and surface roughness of EdgeEvolve (EdgeEndo) and ProTaper Gold (Dentsply Tulsa Dental Specialties) nickel-titanium (NiTi) rotary files.
Materials and Methods The instruments (
n = 15/each) were tested for cyclic fatigue in single- (60° curvature, 5-mm radius) and double-curved (coronal curvature 60°, 5-mm radius, and apical curvature of 30° and 2-mm radius) artificial canals. The number of cycles to fracture was calculated. The bending resistance of both files were tested using a universal testing machine where the files were bent until reach 45°. Scanning electron microscopy and x-ray energy-dispersive spectrometric analysis were used for imaging the fractured segments, while the atomic force microscope was used to quantify the surface roughness average (Ra).Results EdgeEvolve files exhibited higher cyclic fatigue resistance than ProTaper Gold files in single- and double-curved canals (
p < 0.05) and both files were more resistant to cyclic fatigue in single-curved canals than double-curved canals (p < 0.05). EdgeEvolve files exhibited significantly more flexibility than did ProTaper Gold files (p < 0.05). Both files had approximately similar Ni and Ti contents (p > 0.05). EdgeEvolve files showed significantly lower Ra values than ProTaper Gold files (p < 0.05).Conclusions Within the limitation of this study, EdgeEvolve files exhibited significantly higher cyclic fatigue resistance than ProTaper Gold files in both single- and double-curved canals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of Design, Cyclic Fatigue Resistance, and Metallurgical Properties of Original, Replica‐Like, and Counterfeit Nickel‐Titanium Files
Mert Unal, Elif Bahar Cakici
Microscopy Research and Technique.2026; 89(1): 87. CrossRef - An in vitro comparison of alterations in surface topographies of three different rotary files after root canal preparation with different irrigating solutions: Atomic force microscopic study
PremSai Parepalli, TB. V G. Raju, PKrishna Prasad, GowtamDev Dondapati, VenkataSrija Kintada, Alekhya Mediboyina
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2023; 26(3): 299. CrossRef - Assessment of surface topographic changes of nickel–titanium rotary endodontic file at repeated usage: An in vitro study
E. Viswas, VSS Krishna, E. Sridevi, A. J. Sai Sankar, K. Siva Sankar, B. Nagesh
Endodontology.2023; 35(2): 149. CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue Resistance and Surface Roughness of Rotary NiTi Instruments after Simulated Clinical Use in Curved Root Canals – An Atomic Force Microscopy Study
Raksha Bhat, Arjun Kini, Preethesh Shetty, Payalben Kansara, Bapanaiah Penugonda
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Metallurgical Tests in Endodontics: A Narrative Review
Alessio Zanza, Marco Seracchiani, Rodolfo Reda, Gabriele Miccoli, Luca Testarelli, Dario Di Nardo
Bioengineering.2022; 9(1): 30. CrossRef - Influence of nickel-titanium rotary systems with varying cross-sectional, pitch, and rotational speed on deflection and cyclic fatigue: a finite element analysis study
Wignyo Hadriyanto, Lukita Wardani, Christina Nugrohowati, Ananto Alhasyimi, Rachmat Sriwijaya, Margareta Rinastiti, Widowati Siswomihardjo, Gunadi, T. Yamada, A.A.C. Pramana, Y. Ophinni, A. Gusnanto, W.A. Kusuma, J. Yunus, Afiahayati, R. Dharmastiti, T.
BIO Web of Conferences.2021; 41: 05005. CrossRef - Can the Separated Instrument be Removed From the Root Canal System out by Magnetism? A Hypothesis
Mohammad Daryaeian, Sanjay Miglani, AbdolMahmood Davarpanah, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Mohsen Ramazani
Dental Hypotheses.2019; 10(4): 108. CrossRef - Resistance to cyclic fatigue of reciprocating instruments determined at body temperature and phase transformation analysis
Raymond Scott, Ana Arias, José C. Macorra, Sanjay Govindjee, Ove A. Peters
Australian Endodontic Journal.2019; 45(3): 400. CrossRef
- Comparison of Design, Cyclic Fatigue Resistance, and Metallurgical Properties of Original, Replica‐Like, and Counterfeit Nickel‐Titanium Files
- 1,404 View
- 8 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Cyclic fatigue resistance, torsional resistance, and metallurgical characteristics of M3 Rotary and M3 Pro Gold NiTi files
- Eugenio Pedullà, Fabio Lo Savio, Giusy Rita Maria La Rosa, Gabriele Miccoli, Elena Bruno, Silvia Rapisarda, Seok Woo Chang, Ernesto Rapisarda, Guido La Rosa, Gianluca Gambarini, Luca Testarelli
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(2):e25. Published online April 23, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e25
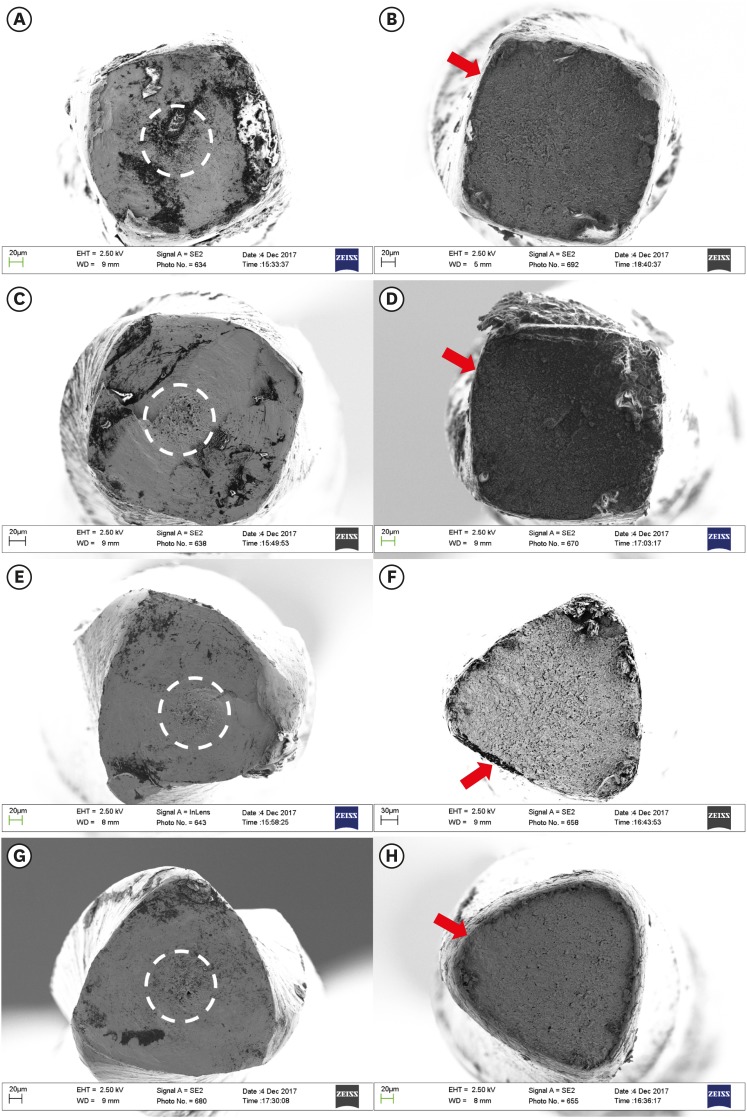
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives To evaluate the mechanical properties and metallurgical characteristics of the M3 Rotary and M3 Pro Gold files (United Dental).
Materials and Methods One hundred and sixty new M3 Rotary and M3 Pro Gold files (sizes 20/0.04 and 25/0.04) were used. Torque and angle of rotation at failure (
n = 20) were measured according to ISO 3630-1. Cyclic fatigue resistance was tested by measuring the number of cycles to failure in an artificial stainless steel canal (60° angle of curvature and a 5-mm radius). The metallurgical characteristics were investigated by differential scanning calorimetry. Data were analyzed using analysis of variance and the Student-Newman-Keuls test.Results Comparing the same size of the 2 different instruments, cyclic fatigue resistance was significantly higher in the M3 Pro Gold files than in the M3 Rotary files (
p < 0.001). No significant difference was observed between the files in the maximum torque load, while a significantly higher angular rotation to fracture was observed for M3 Pro Gold (p < 0.05). In the DSC analysis, the M3 Pro Gold files showed one prominent peak on the heating curve and 2 prominent peaks on the cooling curve. In contrast, the M3 Rotary files showed 1 small peak on the heating curve and 1 small peak on the cooling curve.Conclusions The M3 Pro Gold files showed greater flexibility and angular rotation than the M3 Rotary files, without decrement of their torque resistance. The superior flexibility of M3 Pro Gold files can be attributed to their martensite phase.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative Evaluation of Dentinal Microcrack Using M3 ProGold, Mtwo Rotary File and Hand File in Root Canal Therapy: An In-Vitro Study
Reyhaneh Shoorgashti, Marzie Jafari, Mohadeseh Alimohammadi, Niloofar Ebrahimi
Middle East Journal of Rehabilitation and Health Studies.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Differences in Niti and Glide Path Rotary System: Preparation of Canal Centering and Transportation in Double-curved Root Canals
Calvin Reinnaldi, Wiena Widyastuti, Taufiq Ariwibowo, Sri Ratna Laksmiastuti
The Open Dentistry Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - In Vitro Cleaning Efficacy of Neolix and M3 Immatural Rotary Files in Comparison with Hand Files in Primary Molar Root Canals
Shabnam Maleki, Effat Khodadadi, Seyedali Seyedmajidi, Elham Mahmoudi
Journal of Research in Dental and Maxillofacial Sciences.2025; 10(2): 88. CrossRef - Comparison of Debris Extrusion and Instrumentation Time Among ProTaper Next, Neoniti, and M3‐Pro Gold Rotary Systems: An In Vitro Study
Robab Farhang, Bita Alizadeh, Saeedeh Galledar, Sara Noorolouny, Rashin Alyali, Bahareh Pouya, Ahmad Nouroloyouni, Elango Natarajan
Advances in Materials Science and Engineering.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Continuous Rotation and Optimal Torque Reverse Kinematics on the Cyclic Fatigue Strength of Endodontic NiTi Clockwise Cutting Rotary Instruments
Jorge N. R. Martins, Emmanuel J. N. L. Silva, Duarte Marques, Marco A. Versiani
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(10): 317. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of the Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of WaveOne Gold in Reciprocation, ProGlider in Rotary Motion, and Manual Files in a Reciprocating Handpiece Within Simulated Curved Canals: An In Vitro Study
Shivangi M Pujara, Hardik B Shah, Leena H Jobanputra
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The extended finite element method in endodontics: A scoping review and future directions for cyclic fatigue testing of nickel–titanium instruments
Philip Yuan‐Ho Chien, Laurence James Walsh, Ove Andreas Peters
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluatation of two nickle-titanium systems’ (Neolix and X Pro Gold) resistance to fracture after immersion in sodium hypochlorite.
Solmaz Araghi, Abbas Delvarani, Faeze dehghan, Parisa Kaghazloo
journal of research in dental sciences.2024; 21(1): 17. CrossRef - Characterization of the file‐specific heat‐treated ProTaper Ultimate rotary system
Jorge N. R. Martins, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Duarte Marques, Natasha Ajuz, Mário Rito Pereira, Rui Pereira da Costa, Francisco Manuel Braz Fernandes, Marco Aurélio Versiani
International Endodontic Journal.2023; 56(4): 530. CrossRef - Influence of different heat treatments and temperatures on the cyclic fatigue resistance of endodontic instruments with the same design
Walid Nehme, Alfred Naaman, Franck Diemer, Maria Laura Leotta, Giusy Rita Maria La Rosa, Eugenio Pedullà
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 27(4): 1793. CrossRef - Analysis of cyclic fatigue resistance of ProTaper Universal and ProTaper Next rotary instruments
Nenad Stosic, Jelena Popovic, Marija Andjelkovic-Apostolovic, Aleksandar Mitic, Radomir Barac, Marija Nikolic, Marko Igic
Stomatoloski glasnik Srbije.2022; 69(3): 109. CrossRef - What Meaningful Information Are the Instruments Mechanical Testing Giving Us? A Comprehensive Review
Jorge N.R. Martins, Rui F. Martins, Francisco Manuel Braz Fernandes, Emmanuel J.N.L. Silva
Journal of Endodontics.2022; 48(8): 985. CrossRef - Metallurgical Tests in Endodontics: A Narrative Review
Alessio Zanza, Marco Seracchiani, Rodolfo Reda, Gabriele Miccoli, Luca Testarelli, Dario Di Nardo
Bioengineering.2022; 9(1): 30. CrossRef - A Comparative Study of Four different Contemporary NiTi Rotary Endodontic Files by Metallurgical and Mechanical Analysis with Energy-dispersive X-ray Spectrophotometry with FE-SEM and Cyclic Fatigue Resistance Evaluation
Akash Azad, Shraddha Chokshi
Journal of Research and Advancement in Dentistry.2022; 14(1): 21. CrossRef - Impact of Peracetic Acid on the Dynamic Cyclic Fatigue of Heat-Treated Nickel-Titanium Rotary Endodontic Instrument
Suhad Jabbar Hamed Al-Nasrawi, Zuha Ayad Jaber, Nibrass Talib Al-Quraine, Abtesam Imhemed Aljdaimi, Sattar Jabbar Abdul-Zahra Al-Hmedat, Saleh Zidan, Julfikar Haider, Luca Testarelli
International Journal of Dentistry.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Influence of shaft length on torsional behavior of endodontic nickel–titanium instruments
Gianluca Gambarini, Marco Seracchiani, Alessio Zanza, Gabriele Miccoli, Andrea Del Giudice, Luca Testarelli
Odontology.2021; 109(3): 568. CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Nickel-titanium Rotary Instruments according to the Angle of File Access and Radius of Root Canal
Eugenio Pedullà, Giusy Rita Maria La Rosa, Chiara Virgillito, Ernesto Rapisarda, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Luigi Generali
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(3): 431. CrossRef - Torsional Resistance of Two New Heat Treated Nickel Titanium Rotary Instruments: An in Vitro Evaluation
Gianluca Gambarini, Gabriele Miccoli, Dario Di Nardo, Andrea Del Giudice, Alessandro Mazzoni, Marco Seracchiani, Luca Testarelli
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of heat treatment on torsional resistance and surface roughness of nickel‐titanium instruments
E. J. N. L. Silva, J. F. N. Giraldes, C. O. de Lima, V. T. L. Vieira, C. N. Elias, H. S. Antunes
International Endodontic Journal.2019; 52(11): 1645. CrossRef
- Comparative Evaluation of Dentinal Microcrack Using M3 ProGold, Mtwo Rotary File and Hand File in Root Canal Therapy: An In-Vitro Study
- 1,772 View
- 19 Download
- 19 Crossref

-
Comparison of apical extrusion of intracanal bacteria by various glide-path establishing systems: an
in vitro study - Alberto Dagna, Rashid El Abed, Sameeha Hussain, Ibrahim H Abu-Tahun, Livia Visai, Federico Bertoglio, Floriana Bosco, Riccardo Beltrami, Claudio Poggio, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(4):316-323. Published online October 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.4.316
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study compared the amount of apically extruded bacteria during the glide-path preparation by using multi-file and single-file glide-path establishing nickel-titanium (NiTi) rotary systems.
Materials and Methods Sixty mandibular first molar teeth were used to prepare the test apparatus. They were decoronated, blocked into glass vials, sterilized in ethylene oxide gas, infected with a pure culture of
Enterococcus faecalis, randomly assigned to 5 experimental groups, and then prepared using manual stainless-steel files (group KF) and glide-path establishing NiTi rotary files (group PF with PathFiles, group GF with G-Files, group PG with ProGlider, and group OG with One G). At the end of canal preparation, 0.01 mL NaCl solution was taken from the experimental vials. The suspension was plated on brain heart infusion agar and colonies of bacteria were counted, and the results were given as number of colony-forming units (CFU).Results The manual instrumentation technique tested in group KF extruded the highest number of bacteria compared to the other 4 groups (
p < 0.05). The 4 groups using rotary glide-path establishing instruments extruded similar amounts of bacteria.Conclusions All glide-path establishment instrument systems tested caused a measurable apical extrusion of bacteria. The manual glide-path preparation showed the highest number of bacteria extruded compared to the other NiTi glide-path establishing instruments.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Apical Extrusion of Bacteria during Canal Preparation: A Systematic Review of Laboratory Studies
Thamyres M. Monteiro, Warley O. Silva, Jeferson O. Marques, Ana Carolina S.P. Guerra, Flávio R.F. Alves
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(7): 866. CrossRef - Glide Path in Endodontics: A Literature Review of Current Knowledge
Vlad Mircea Lup, Giulia Malvicini, Carlo Gaeta, Simone Grandini, Gabriela Ciavoi
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(8): 257. CrossRef - Evaluation of apically extruded debris using protaper universal, protaper next, one curve, Xp shaper, and edge file: An in vitro study
Murtada Qadir Muhaibes, Shatha Abdulkareem Alwakeel
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2024; 14(1): 31. CrossRef - Effect of Multiple Glide Path Files on Apical Debris Extrusion in Severely Curved Mesial Roots of Mandibular Molars: An In Vitro Study
Niranjan Desai, Ashish S Bhadane, Nishant K Vyavahare, Dipali Y Shah, Akash S Kale, Simran K Chaudhari
Journal of Operative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024; 8(1): 1. CrossRef - Evaluation of Pain Following the Use of Different Single-file Glide Path Systems: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Zeliha Danaci, Kübra Yeşildal Yeter
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(2): 120. CrossRef - Impact of Different Glidepath Techniques on the Overall Performance of WaveOne Gold in an Artificial S-Shape Canal
Vlad Mircea Lup, Olivia Andreea Marcu, Carlo Gaeta, Gabriela Ciavoi
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(6): 182. CrossRef - Influence of different irrigant activation methods on apical debris extrusion and bacterial elimination from infected root canals
KSadia Ada, Shibani Shetty, KB Jayalakshmi, PrasannaLatha Nadig, PG Manje Gowda, ArulK Selvan
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2023; 26(1): 31. CrossRef - A Comparative Evaluation of the Apically Extruded Debris from Root Canals Prepared by R-Motion NiTi File System
Farah B. Al-Saffar, Hikmet A. Al-Gharrawi, Luca Testarelli
International Journal of Dentistry.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Effect of glide path files with different metallurgy on intracanal bacterial extrusion by HyFlex electrical discharge machining file
Priyanka Soni, Pragya Kumar, Sonali Taneja, Anshi Jain
Endodontology.2022; 34(3): 168. CrossRef - Impact of kinematics on the efficiency and safety of an engine-driven file for glide path preparation in MB2 canals of maxillary molars
Larissa B. B. Araújo, Pedro H. S. Calefi, Murilo P. Alcalde, Giulio Gavini, Rodrigo R. Vivan, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 27(3): 1153. CrossRef - Critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study removal of root filling materials
Mahdi A. Ajina, Pratik K. Shah, Bun San Chong
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S1): 119. CrossRef - A Comparative Evaluation of Apically Extruded Debris using Three Rotary and One Reciprocating Instrumentation Ni-Ti Systems
Maha Adnan Habeeb
Journal of Orofacial Sciences.2022; 14(2): 93. CrossRef - A critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study apical extrusion of debris and irrigants
Jale Tanalp
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S1): 153. CrossRef - Evaluation of type of kinematics on glide path procedures and torsional fatigue resistance after preparation of moderately curved canals
Murilo Priori Alcalde, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Pedro Henrique Souza Calefi, Victor de Moraes Cruz, Bruno Carvalho de Vasconcelos, Marcus Vinícius Reis Só, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan
Brazilian Oral Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of a glide path creation necessity at the initial stages of endodontic treatment
Z. S. Khabadze, Yu. A. Generalova
Endodontics Today.2021; 19(1): 39. CrossRef - Influence of glide path kinematics during endodontic treatment on the occurrence and intensity of intraoperative and postoperative pain: a systematic review of randomized clinical trials
Thaís Christina Cunha, Felipe de Souza Matos, Luiz Renato Paranhos, Ítalo de Macedo Bernardino, Camilla Christian Gomes Moura
BMC Oral Health.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Apically extruded debris produced during glide path preparation using R‐Pilot, WaveOne Gold Glider and ProGlider in curved root canals
Cangül Keskin, Özlem Sivas Yilmaz, Uğur Inan
Australian Endodontic Journal.2020; 46(3): 439. CrossRef - Influence of Negotiation, Glide Path, and Preflaring Procedures on Root Canal Shaping—Terminology, Basic Concepts, and a Systematic Review
Gianluca Plotino, Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Frederic Bukiet, Nicola M. Grande, Sajesh K. Veettil, Gustavo De-Deus, Hany Mohamed Aly Ahmed
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(6): 707. CrossRef - Mechanical Properties of Various Glide Path Preparation Nickel-titanium Rotary Instruments
Joo-Yeong Lee, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Ibrahim H. Abu-Tahun, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2019; 45(2): 199. CrossRef - Effective Establishment of Glide-Path to Reduce Torsional Stress during Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instrumentation
Ibrahim H. Abu-Tahun, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Asgeir Sigurdsson, Mehmet Baybora Kayahan, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Materials.2019; 12(3): 493. CrossRef - Postoperative pain after glide path preparation using manual, reciprocating and continuous rotary instruments: a randomized clinical trial
C. Keskin, Ö. Sivas Yilmaz, U. Inan, Ö. Özdemir
International Endodontic Journal.2019; 52(5): 579. CrossRef - Intraoperative Pain During Glide Path Creation with the Use of a Rotary or Reciprocating System
Pelin TUFENKCİ, Mehmet ADIGUZEL, Koray YILMAZ
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2019; 22(1): 66. CrossRef - Effects of Different Glide Path Files on Apical Debris Extrusion in Curved Root Canals
Betul Gunes, Kubra Yesildal Yeter
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(7): 1191. CrossRef
- Apical Extrusion of Bacteria during Canal Preparation: A Systematic Review of Laboratory Studies
- 1,488 View
- 11 Download
- 23 Crossref

- Preference of undergraduate students after first experience on nickel-titanium endodontic instruments
- Sang Won Kwak, Gary Shun-Pan Cheung, Jung-Hong Ha, Sung Kyo Kim, Hyojin Lee, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(3):176-181. Published online June 23, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.3.176
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to compare two nickel-titanium systems (rotary
vs . reciprocating) for their acceptance by undergraduate students who experienced nickel-titanium (NiTi) instruments for the first time.Materials and Methods Eighty-one sophomore dental students were first taught on manual root canal preparation with stainless-steel files. After that, they were instructed on the use of ProTaper Universal system (PTU, Dentsply Maillefer), then the WaveOne (WO, Dentsply Maillefer). They practiced with each system on 2 extracted molars, before using those files to shape the buccal or mesial canals of additional first molars. A questionnaire was completed after using each file system, seeking students' perception about 'Ease of use', 'Flexibility', 'Cutting-efficiency', 'Screwing-effect', 'Feeling-safety', and 'Instrumentation-time' of the NiTi files, relative to stainless-steel instrumentation, on a 5-point Likert-type scale. They were also requested to indicate their preference between the two systems. Data was compared between groups using
t -test, and with Chi-square test for correlation of each perception value with the preferred choice (p = 0.05).Results Among the 81 students, 55 indicated their preferred file system as WO and 22 as PTU. All scores were greater than 4 (better) for both systems, compared with stainless-steel files, except for 'Screwing-effect' for PTU. The scores for WO in the categories of 'Flexibility', 'Screwing-effect', and 'Feeling-safety' were significantly higher scores than those of PTU. A significant association between the 'Screwing-effect' and students' preference for WO was observed.
Conclusions Novice operators preferred nickel-titanium instruments to stainless-steel, and majority of them opted for reciprocating file instead of continuous rotating system.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors influencing the agreement between teachers and students in the assessment of preclinical endodontics using a rubric
B. Baracco, N. Escribano, D. Da Silva, V. Belliard, L. Ceballos, V. Fuentes
BMC Medical Education.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Technical Quality and Students' Perception of Endodontic Preclinical Training Using Natural or LikeReal Artificial Teeth
Gabriela Biagioni, Fernanda Comodo, Marcelo Santos Coelho
European Journal of Dental Education.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Endodontic Procedural Errors and Associated Factors among Undergraduate Dental Students: A Cross-sectional Study
Vivek Padmanabhan, Md Sofiqul Islam, Mohamed A Elsayed, Duaa R Saleh, Amal M Alnahdi
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2024; 24(12): 998. CrossRef - Clinicians’ perspectives, inducements, preferences, and clinical experiences regarding the use of electronic apex locator and apex locator integrated engine-driven instrumentation: a cross-sectional study
Sena Kaşıkçı, Sena Kolunsağ Özbek, Ebru Şirinoğlu, Olcay Özdemir
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation and Comparison of Manual and Mechanical Endodontic Instrumentation Completed by Undergraduate Dental Students on Endodontic Blocks
António Ginjeira, Abayomi O. Baruwa, Karla Baumotte
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(11): 363. CrossRef - The first experiences of preclinical dentistry students with rotary instruments: A pilot study
Işıl Kaya Büyükbayram, Gizem Çolakoğlu, Sana Mahroos Al-Shammari, Katia Stoicefidis
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2024; 14(2): 205. CrossRef - Comparative Efficacy of Manual vs. Rotary/Reciprocating NiTi Instrumentation by Novice Dental Students on Simulated Root Canals
Ethan Smith, Olivia Davis
International Journal of Dental Research and Allied Sciences.2024; 4(2): 82. CrossRef - First Experience of an Undergraduate Dental Student with a Reciprocating System in Simulated Root Canals—A Pilot Study
Ana Rita Arede, Inês Ferreira, Ana Cristina Braga, Irene Pina-Vaz
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(8): 4848. CrossRef - Effect on undergraduate student self-confidence in using 3D printed primary molars for root canal treatment simulation training
C. Delfosse, T. Marquillier, S. Ndoye, P.-Y. Cousson, M. Hennequin, C. Catteau
European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry.2023; 24(1): 105. CrossRef - Influence of operator expertise on glide path and root canal preparation of curved root canals with rotary and reciprocating motions
Ana Belén Dablanca‐Blanco, Ana Arias, María José Ginzo‐Villamayor, María Consuelo Pérez, Pablo Castelo‐Baz, Benjamín Martín‐Biedma
Australian Endodontic Journal.2022; 48(1): 37. CrossRef - Quality of root canal treatment performed by undergraduate students using nickel‐titanium reciprocating versus hand instruments
Seniha Miçooğulları Kurt, Gözde Kandemir Demirci, Burcu Serefoglu, Mehmet Emin Kaval, Pelin Güneri, Mehmet Kemal Çalışkan
Journal of Dental Education.2022; 86(12): 1662. CrossRef - Radiographic assessment of endodontic mishaps in an undergraduate student clinic: a 2-year retrospective study
Manal Matoug-Elwerfelli, Ahmed Abdou, Wejdan Almutairi, Malak Alhuthayli, Shaikhah Aloyaynaa, Rahaf Almohareb
PeerJ.2022; 10: e13858. CrossRef - Ex vivo shaping ability of reciprocating instruments operated by new users: Reciproc versus WaveOne
Mary S. H. Lam, Jeffrey W. W. Chang, Gary S. P. Cheung
Clinical Oral Investigations.2021; 25(5): 2791. CrossRef - Body temperature fatigue behaviour of reciprocating and rotary glide path instruments in sodium hypochlorite solutions alone or combined with etidronate
Dario Perez‐Villalba, José C. Macorra, Juan J. Perez‐Higueras, Ove A. Peters, Ana Arias
Australian Endodontic Journal.2021; 47(3): 450. CrossRef - Undergraduate Students’ Acceptance of a Reciprocating One-File System for Endodontic Treatment
Benjamin Mahmoodi, Adriano Azaripour, Kawe Sagheb, Keyvan Sagheb, Brita Willershausen, Jens Weusmann
European Journal of Dentistry.2020; 14(03): 393. CrossRef - Fracture of endodontic instruments - Part 1: Literature review on factors that influence instrument breakage
Maheshan Pillay, Martin Vorster, Peet J Van der Vyver
South African Dental Journal.2020; 75(10): 553. CrossRef - A comparative study of root canal shaping using protaper universal and protaper next rotary files in preclinical dental education
Gül Çelik, Feyza Özdemir Kısacık, Emir Faruk Yılmaz, Arife Mersinlioğlu, İhsan Furkan Ertuğrul, Hikmet Orhan
PeerJ.2019; 7: e7419. CrossRef - Undergraduate dentistry students’ perception of difficulties regarding endodontic treatment
Lorrane G. Tavares, Stella M. F. Lima, Miriane G. Lima, Marcos P. Arruda, Thiago C. Menegazzi, Taia M. B. Rezende
Australian Endodontic Journal.2019; 45(1): 98. CrossRef - First Experience of Rotary Nickel Titanium Root Canal Instrumentation Performed by Undergraduate Students and General Dentists
marwa sharaan, Noreen Kamel, Dimitrios Tziafas
Journal of Dentistry and Oral Care.2017; 3(2): 1. CrossRef
- Factors influencing the agreement between teachers and students in the assessment of preclinical endodontics using a rubric
- 1,445 View
- 8 Download
- 19 Crossref

- Effect of repetitive pecking at working length for glide path preparation using G-file
- Jung-Hong Ha, Hyo-Jin Jeon, Rashid El Abed, Seok-Woo Chang, Sung-Kyo Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(2):123-127. Published online January 7, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.2.123
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Glide path preparation is recommended to reduce torsional failure of nickel-titanium (NiTi) rotary instruments and to prevent root canal transportation. This study evaluated whether the repetitive insertions of G-files to the working length maintain the apical size as well as provide sufficient lumen as a glide path for subsequent instrumentation.
Materials and Methods The G-file system (Micro-Mega) composed of G1 and G2 files for glide path preparation was used with the J-shaped, simulated resin canals. After inserting a G1 file twice, a G2 file was inserted to the working length 1, 4, 7, or 10 times for four each experimental group, respectively (
n = 10). Then the canals were cleaned by copious irrigation, and lubricated with a separating gel medium. Canal replicas were made using silicone impression material, and the diameter of the replicas was measured at working length (D0) and 1 mm level (D1) under a scanning electron microscope. Data was analysed by one-way ANOVA andpost-hoc tests (p = 0.05).Results The diameter at D0 level did not show any significant difference between the 1, 2, 4, and 10 times of repetitive pecking insertions of G2 files at working length. However, 10 times of pecking motion with G2 file resulted in significantly larger canal diameter at D1 (
p < 0.05).Conclusions Under the limitations of this study, the repetitive insertion of a G2 file up to 10 times at working length created an adequate lumen for subsequent apical shaping with other rotary files bigger than International Organization for Standardization (ISO) size 20, without apical transportation at D0 level.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Glide Path – An Ineluctable Route for Successful Endodontic Mechanics: A Literature Review
Mahima Bharat Mehta, Anupam Sharma, Aniket Jadhav, Aishwarya Handa, Abhijit Bajirao Jadhav, Ashwini A. Narayanan
Journal of the International Clinical Dental Research Organization.2024; 16(2): 101. CrossRef - Effect of repetitive up-and-down movements on torque/force generation, surface defects and shaping ability of nickel-titanium rotary instruments: an ex vivo study
Moe Sandar Kyaw, Arata Ebihara, Yoshiko Iino, Myint Thu, Keiichiro Maki, Shunsuke Kimura, Pyae Hein Htun, Takashi Okiji
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of the Number of Pecking Motions at Working Length on the Shaping Ability of Single-file Systems in Long Oval-shaped Curved Canals
Lixiao Wang, Ruitian Lin, Hui Chen, Zihan Li, Franklin R. Tay, Lisha Gu
Journal of Endodontics.2022; 48(4): 548. CrossRef - Influence of pecking frequency at working length on the volume of apically extruded debris: A micro-computed tomography analysis
Li-Xiao Wang, Hui Chen, Rui-Tian Lin, Li-Sha Gu
Journal of Dental Sciences.2022; 17(3): 1274. CrossRef - Comparison of the effects from coronal pre‐flaring and glide‐path preparation on torque generation during root canal shaping procedure
Sang Won Kwak, Jung‐Hong Ha, Ya Shen, Markus Haapasalo, Hyeon‐Cheol Kim
Australian Endodontic Journal.2022; 48(1): 131. CrossRef - Effective Establishment of Glide-Path to Reduce Torsional Stress during Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instrumentation
Ibrahim H. Abu-Tahun, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Asgeir Sigurdsson, Mehmet Baybora Kayahan, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Materials.2019; 12(3): 493. CrossRef - Stress Generation during Pecking Motion of Rotary Nickel-titanium Instruments with Different Pecking Depth
Jung-Hong Ha, Sang Won Kwak, Asgeir Sigurdsson, Seok Woo Chang, Sung Kyo Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(10): 1688. CrossRef - Debris extrusion by glide-path establishing endodontic instruments with different geometries
Jung-Hong Ha, Sung Kyo Kim, Sang Won Kwak, Rashid El Abed, Yong Chul Bae, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Dental Sciences.2016; 11(2): 136. CrossRef - Effects of Pitch Length and Heat Treatment on the Mechanical Properties of the Glide Path Preparation Instruments
Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Chan-Joo Lee, Rashid El Abed, Ibrahim H. Abu-Tahun, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(5): 788. CrossRef
- Glide Path – An Ineluctable Route for Successful Endodontic Mechanics: A Literature Review
- 1,338 View
- 7 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Buckling resistance, bending stiffness, and torsional resistance of various instruments for canal exploration and glide path preparation
- Sang-Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, WooCheol Lee, Sung-Kyo Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(4):270-275. Published online July 16, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.4.270
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study compared the mechanical properties of various instruments for canal exploration and glide-path preparations.
Materials and Methods The buckling resistance, bending stiffness, ultimate torsional strength, and fracture angle under torsional load were compared for C+ file (CP, Dentsply Maillefer), M access K-file (MA, Dentsply Maillefer), Mani K-file (MN, Mani), and NiTiFlex K-file (NT, Dentsply Maillefer). The files of ISO size #15 and a shaft length of 25 mm were selected. For measuring buckling resistance (
n = 10), the files were loaded in the axial direction of the shaft, and the maximum load was measured during the files' deflection. The files (n = 10) were fixed at 3-mm from the tip and then bent 45° with respect to their long axis, while the bending force was recorded by a load cell. For measuring the torsional properties, the files (n = 10) were also fixed at 3-mm, and clockwise rotations (2-rpm) were applied to the files in a straight state. The torsional load and the distortion angle were recorded until the files succumbed to the torque.Results The CP was shown to require the highest load to buckle and bend the files, and the NT showed the least. While MA and MN showed similar buckling resistances, MN showed higher bending stiffness than MA. The NT had the lowest bending stiffness and ultimate torsional strength (
p < 0.05).Conclusions The tested instruments showed different mechanical properties depending on the evaluated parameters. CP and NT files were revealed to be the stiffest and the most flexible instruments, respectively.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Buckling resistance of various pathfinding endodontic instruments: An in vitro study
Ujjwal Das, Rajesh Kumar Das, Kallol Kumar Saha, Lugu Buru Murmu, Srimanta Banerjee, Rishila Nag
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(4): 384. CrossRef - Comparison of torsional, bending, and buckling resistances of different nickel-titanium glide path files
Feyyaz Çeliker, İrem Çetinkaya
Matéria (Rio de Janeiro).2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Analysis of Endodontic 0.15 Stainless-Steel K-Files: Exploring Design, Composition, and Mechanical Performance
Abayomi Omokeji Baruwa, Filipa Chasqueira, Sofia Arantes-Oliveira, João Caramês, Duarte Marques, Jaime Portugal, Jorge N. R. Martins
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(2): 29. CrossRef - Comparative Analysis of Endodontic ISO Size 06, 08, and 10 Stainless Steel K-Files Used for Glide Path Procedures
Abayomi Omokeji Baruwa, Filipa Chasqueira, Sofia Arantes-Oliveira, João Caramês, Duarte Marques, Jaime Portugal, Jorge N. R. Martins
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(4): 98. CrossRef - Glide Path in Endodontics: A Literature Review of Current Knowledge
Vlad Mircea Lup, Giulia Malvicini, Carlo Gaeta, Simone Grandini, Gabriela Ciavoi
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(8): 257. CrossRef - Shaping Ability and Buckling Resistance of TruNatomy, WaveOne gold, and XP-Endo Shaper Single-File Systems
Neveen Ali Shaheen, Nahla Gamal Eldin Elhelbawy
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2022; 13(3): 261. CrossRef - A comparison of different hand and rotary endodontic glide path files for buckling resistance
Ruchika Gupta, Pramod Mohite, Suvarna Patil, Nandita Bansal
Endodontology.2021; 33(2): 102. CrossRef - Buckling Resistance of Various Nickel-Titanium Glide Path Preparation Instruments in Dynamic or Static Mode
Jung-Hong Ha, Sang Won Kwak, Antheunis Versluis, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(8): 1125. CrossRef - Influence of heat treatment on color and flexibility of nickel-titanium endodontic instruments
Bernardo Corrêa de ALMEIDA, Carlos Nelson ELIAS
RGO - Revista Gaúcha de Odontologia.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Negotiation, Glide Path, and Preflaring Procedures on Root Canal Shaping—Terminology, Basic Concepts, and a Systematic Review
Gianluca Plotino, Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Frederic Bukiet, Nicola M. Grande, Sajesh K. Veettil, Gustavo De-Deus, Hany Mohamed Aly Ahmed
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(6): 707. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of buckling resistance of Proglider and One-G file: An in vitro study
Priyanka Himmatrao Patil, Meenal Nitin Gulve, Swapnil Janardan Kolhe
Endodontology.2018; 30(1): 21. CrossRef - Mechanical Properties of Various Heat-treated Nickel-titanium Rotary Instruments
Hye-Jin Goo, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Eugenio Pedullà, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(11): 1872. CrossRef - Debris extrusion by glide-path establishing endodontic instruments with different geometries
Jung-Hong Ha, Sung Kyo Kim, Sang Won Kwak, Rashid El Abed, Yong Chul Bae, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Dental Sciences.2016; 11(2): 136. CrossRef
- Buckling resistance of various pathfinding endodontic instruments: An in vitro study
- 2,333 View
- 44 Download
- 13 Crossref

- A comparison of dimensional standard of several nickel-titanium rotary files
- Ki-Won Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho, Se-Hee Park, Ki-Yeol Choi, Bekir Karabucak, Jin-Woo Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(1):7-11. Published online January 20, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.1.7
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to compare the dimensional standard of several nickel-titanium (Ni-Ti) rotary files and verify the size conformity.
Materials and Methods ProFile (Dentsply Maillefer), RaCe (FKG Dentaire), and TF file (SybronEndo) #25 with a 0.04 and 0.06 taper were investigated, with 10 in each group for a total of 60 files. Digital images of Ni-Ti files were captured under light microscope (SZX16, Olympus) at 32×. Taper and diameter at D1 to D16 of each files were calculated digitally with AnalySIS TS Materials (OLYMPUS Soft Imaging Solutions). Differences in taper, the diameter of each level (D1 to D16) at 1 mm interval from (ANSI/ADA) specification No. 101 were statistically analyzed using one-way ANOVA and Scheffe's
post-hoc test at 95% confidence level.Results TF was the only group not conform to the nominal taper in both tapers (
p < 0.05). All groups except 0.06 taper ProFile showed significant difference from the nominal diameter (p < 0.05).Conclusions Actual size of Ni-Ti file, especially TF, was different from the manufacturer's statements.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Ex Vivo Evaluation of the Fit of Matched Gutta Percha Points in Human Root Canals Prepared With the Corresponding Nickel‐Titanium Files
Samuel Deng, Paul V. Abbott
Australian Endodontic Journal.2025; 51(3): 684. CrossRef - Diameter and Taper Variability of Single-file Instrumentation Systems and Their Corresponding Gutta-percha Cones
Franziska Haupt, Miriam Seidel, Marta Rizk, Hans-Georg Sydow, Annette Wiegand, Tina Rödig
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(9): 1436. CrossRef
- Ex Vivo Evaluation of the Fit of Matched Gutta Percha Points in Human Root Canals Prepared With the Corresponding Nickel‐Titanium Files
- 1,379 View
- 11 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Cyclic fatigue resistance tests of Nickel-Titanium rotary files using simulated canal and weight loading conditions
- Ok-In Cho, Antheunis Versluis, Gary SP Cheung, Jung-Hong Ha, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(1):31-35. Published online February 26, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.1.31
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study compared the cyclic fatigue resistance of nickel-titanium (NiTi) files obtained in a conventional test using a simulated canal with a newly developed method that allows the application of constant fatigue load conditions.
Materials and Methods ProFile and K3 files of #25/.06, #30/.06, and #40/.04 were selected. Two types of testing devices were built to test their fatigue performance. The first (conventional) device prescribed curvature inside a simulated canal (C-test), the second new device exerted a constant load (L-test) whilst allowing any resulting curvature. Ten new instruments of each size and brand were tested with each device. The files were rotated until fracture and the number of cycles to failure (NCF) was determined. The NCF were subjected to one-way ANOVA and Duncan's
post-hoc test for each method. Spearman's rank correlation coefficient was computed to examine any association between methods.Results Spearman's rank correlation coefficient (ρ = -0.905) showed a significant negative correlation between methods. Groups with significant difference after the L-test divided into 4 clusters, whilst the C-test gave just 2 clusters. From the L-test, considering the negative correlation of NCF, K3 gave a significantly lower fatigue resistance than ProFile as in the C-test. K3 #30/.06 showed a lower fatigue resistance than K3 #25/.06, which was not found by the C-test. Variation in fatigue test methodology resulted in different cyclic fatigue resistance rankings for various NiTi files.
Conclusions The new methodology standardized the load during fatigue testing, allowing determination fatigue behavior under constant load conditions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of autoclave sterilization on the cyclic fatigue resistance of EdgeFile X7, 2Shape, and F-one nickel–titanium endodontic instruments
ArkanH Al-Amidi, HikmetAbdul-Rahim Al-Gharrawi
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2023; 26(1): 26. CrossRef - Investigation of cyclic fatigue of rotary endodontic instruments
Z. S. Khabadze, F. R. Ismailov
Endodontics Today.2022; 20(1): 28. CrossRef - Torsional Resistance of Heat-Treated Nickel-Titanium Instruments under Different Temperature Conditions
Hyo Jin Jo, Sang Won Kwak, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Sung Kyo Kim, Jung-Hong Ha
Materials.2021; 14(18): 5295. CrossRef - Effect of surface treatment on the mechanical properties of nickel-titanium files with a similar cross-section
Sang Won Kwak, Joo Yeong Lee, Hye-Jin Goo, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2017; 42(3): 216. CrossRef - Effect from Rotational Speed on Torsional Resistance of the Nickel-titanium Instruments
Jung-Hong Ha, Sang Won Kwak, Sung Kyo Kim, Asgeir Sigurdsson, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(3): 443. CrossRef - Mechanical Properties of Various Heat-treated Nickel-titanium Rotary Instruments
Hye-Jin Goo, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Eugenio Pedullà, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(11): 1872. CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue Resistance and Force Generated by OneShape Instruments during Curved Canal Preparation
Zhuyu Wang, Wen Zhang, Xiaolei Zhang, Luigi F. Rodella
PLOS ONE.2016; 11(8): e0160815. CrossRef - Conditioning of root canal anatomy on static and dynamics of nickel-titanium rotary instruments
Italo Di Giuseppe, Davide Di Giuseppe, Vito Antonio Malagnino, Enrico Paolo Silla, Francesco Somma
Giornale Italiano di Endodonzia.2015; 29(2): 58. CrossRef - Effect from surface treatment of nickel‐titanium rotary files on the fracture resistance
Bo Hoon Kim, Jung‐Hong Ha, Woo Cheol Lee, Sang‐Won Kwak, Hyeon‐Cheol Kim
Scanning.2015; 37(1): 82. CrossRef - Effect of alloy type on the life‐time of torsion‐preloaded nickel‐titanium endodontic instruments
Jung‐Hong Ha, Sung Kyo Kim, Gary Shun‐Pan Cheung, Seong Hwa Jeong, Yong Chul Bae, Hyeon‐Cheol Kim
Scanning.2015; 37(3): 172. CrossRef - ‘Screw‐in’ tendency of rotary nickel–titanium files due to design geometry
J. H. Ha, G. S. P. Cheung, A. Versluis, C. J. Lee, S. W. Kwak, H. C. Kim
International Endodontic Journal.2015; 48(7): 666. CrossRef - Elastic Limits in Torsion of Reciprocating Nickel-Titanium Instruments
Jung-Hong Ha, Seo-Ryeong Kim, Antheunis Versluis, Gary Shun-Pan Cheung, Jin-Woon Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(5): 715. CrossRef - Buckling resistance, bending stiffness, and torsional resistance of various instruments for canal exploration and glide path preparation
Sang-Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, WooCheol Lee, Sung-Kyo Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(4): 270. CrossRef - Safety of the Factory Preset Rotation Angle of Reciprocating Instruments
Jin-Woon Kim, Jung-Hong Ha, Gary Shun-Pan Cheung, Antheunis Versluis, Sang-Won Kwak, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2014; 40(10): 1671. CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Rotary NiTi Instruments after Simulated Clinical Use in Curved Root Canals
Oscar Faciola Pessoa, Juliana Melo da Silva, Giulio Gavini
Brazilian Dental Journal.2013; 24(2): 117. CrossRef - Methods and models to study nickel–titanium instruments
Ya Shen, Gary S.P. Cheung
Endodontic Topics.2013; 29(1): 18. CrossRef - An overview of the mechanical properties of nickel–titanium endodontic instruments
Huimin Zhou, Bin Peng, Yu‐Feng Zheng
Endodontic Topics.2013; 29(1): 42. CrossRef
- Effect of autoclave sterilization on the cyclic fatigue resistance of EdgeFile X7, 2Shape, and F-one nickel–titanium endodontic instruments
- 1,444 View
- 5 Download
- 17 Crossref

- A survey of experience-based preference of Nickel-Titanium rotary files and incidence of fracture among general dentists
- WooCheol Lee, Minju Song, Euiseong Kim, Hyojin Lee, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(4):201-206. Published online November 21, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.4.201
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose was to investigate the preference and usage technique of NiTi rotary instruments and to retrieve data on the frequency of re-use and the estimated incidence of file separation in the clinical practice among general dentists.
Materials and Methods A survey was disseminated via e-mail and on-site to 673 general dentists. The correlation between the operator's experience or preferred technique and frequency of re-use or incidence of file fracture was assessed.
Results A total of 348 dentists (51.7%) responded. The most frequently used NiTi instruments was ProFile (39.8%) followed by ProTaper. The most preferred preparation technique was crown-down (44.6%). 54.3% of the respondents re-used NiTi files more than 10 times. There was a significant correlation between experience with NiTi files and the number of reuses (
p = 0.0025). 54.6% of the respondents estimated experiencing file separation less than 5 times per year. The frequency of separation was significantly correlated with the instrumentation technique (p = 0.0003).Conclusions A large number of general dentists in Korea prefer to re-use NiTi rotary files. As their experience with NiTi files increased, the number of re-uses increased, while the frequency of breakage decreased. Operators who adopt the hybrid technique showed less tendency of separation even with the increased number of re-use.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Migration of a Separated Endodontic File Into the Mandibular Canal: An 8-Year Follow-up Case Report
Chiaki Akiba Katz, Misaki Fujimoto, Hidetaka Kuroda, Koichiro Muromachi
Journal of Endodontics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Adoption of rotary instrumentation among general practitioners in Qassim region, Saudi Arabia: A cross-sectional survey
Badi B. Alotaibi
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2024; 14(2): 181. CrossRef - Undergraduate Endodontic Training and Its Relation to Contemporary Practice: Multicenter Cross-Sectional Study in Saudi Arabia
Fahda N. Algahtani, Reem M. Barakat, Lujain M. Alqarni, Alanoud F. Alqabbani, Manal F. Alkadi, Rahaf A. Almohareb, André Luiz Ferreira Costa
International Journal of Clinical Practice.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Fracture Incidence of Kedo-S Square Pediatric Rotary Files: A Prospective Clinical Study
Lakshimi Lakshmanan, Ganesh Jeevanandan, Prabhadevi C Maganur, Satish Vishwanathaiah
European Journal of Dentistry.2022; 16(03): 594. CrossRef - Prevention and management of fractured instruments in endodontic treatment
Wei-Rong Tang
World Journal of Surgical Procedures.2015; 5(1): 82. CrossRef - Influence of operator's experience level on lifespan of the WaveOne Primary file in extracted teeth
Abdulrahman Mohammed Saleh, Saeid Tavanafar, Pouyan Vakili-Gilani, Noor Jamal Al Sammerraie, Faahim Rashid
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 222. CrossRef
- Migration of a Separated Endodontic File Into the Mandibular Canal: An 8-Year Follow-up Case Report
- 1,876 View
- 9 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Mechanical and geometric features of endodontic instruments and its clinical effect
- Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(1):1-11. Published online January 14, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Abstract Introduction: The aim of this paper is to discuss the mechanical and geometric features of Nickel-titanium (NiTi) rotary files and its clinical effects. NiTi rotary files have been introduced to the markets with their own geometries and claims that they have better ability for the root canal shaping than their competitors. The contents of this paper include the (possible) interrelationship between the geometries of NiTi file (eg. tip, taper, helical angle, etc) and clinical performance of the files as follows;
- Fracture modes of NiTi rotary files
- Non-cutting guiding tip and glide path
- Taper and clinical effects
- Cross-sectional area and clinical effects
- Heat treatments and surface characteristics
- Screw-in effect and preservation of root dentin integrity
- Designs for reducing screw-in effect
Conclusions: Based on the reviewed contents, clinicians may have an advice to use various brands of NiTi rotary instruments regarding their advantages which would fit for clinical situation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cyclic fatigue resistance tests of Nickel-Titanium rotary files using simulated canal and weight loading conditions
Ok-In Cho, Antheunis Versluis, Gary SP Cheung, Jung-Hong Ha, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(1): 31. CrossRef
- Cyclic fatigue resistance tests of Nickel-Titanium rotary files using simulated canal and weight loading conditions
- 2,654 View
- 69 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Influence of taper on the screw-in effect of nickel-titanium rotary files in simulated resin root canal
- Hye-Jin Sung, Jung-Hong Ha, Sung-Kyo Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(5):380-386. Published online September 30, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.5.380
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The introduction of nickel-titanium alloy endodontic instruments has greatly simplified shaping the root canal systems. However, these new instruments have several unexpected disadvantages. One of these is tendency to screw into the canal. In this study, the influence of taper on the screw-in effect of the Ni-Ti rotary instrument were evaluated.
Materials and Methods A total of 20 simulated root canals with an S-shaped curvature in clear resin blocks were divided into two groups. ProFile .02, .04, .06 (Dentsply-Maillefer) and GT rotary files .08, .10, .12 (Dentsply) were used in Profile group, and K3 .04, .06, .08, .10, and .12 (SybronEndo, Glendora) were used in K3 group. Files were used with a single pecking motion at a constant speed of 300 rpm. A special device was made to measure the force of screw-in effect. A dynamometer of the device recorded the screw-in force during simulated canal preparation and the recorded data was stored in computer with designed software. The data were subjected to one-way ANOVA and Tukey's multiple range test for post-hoc test.
p value of less than 0.05 was regarded significant.Results The more tapered instruments generated more screw-in forces in Profile group (
p < 0.05). In K3 group, 0.08, 0.10. and 0.12 tapered instruments showed more screw-in force than 0.04 tapered one, and 0.08 and 0.12 tapered instruments showed more screw-in force than 0.06 tapered one (p < 0.05).Conclusions The more tapered instruments seems to produce more screw-in force. To avoid this screw-in force during instrumentation, more attention may be needed when using more tapered instruments.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Radial Lands and Alternating Cutting Edges Contribute to Reduced Screw-in and Torque in Curved Root Canals - An In Vitro Study
Greta Heimberg, Sebastian Bürklein, Edgar Schäfer, Thomas Gerhard Wolf, David Donnermeyer
Journal of Endodontics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of Torque and Force Induced by Rotary Nickel-Titanium Instruments during Root Canal Preparation: A Systematic Review
Myint Thu, Arata Ebihara, Sherif Adel, Takashi Okiji
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(7): 3079. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of mechanical properties of differently tapered nickeltitanium endodontic rotary instruments
Yohei FUKUMORI, Miki NISHIJYO, Daisuke TOKITA, Kana MIYARA, Arata EBIHARA, Takashi OKIJI
Dental Materials Journal.2018; 37(4): 667. CrossRef - Influence of glide path on the screw-in effect and torque of nickel-titanium rotary files in simulated resin root canals
Jung-Hong Ha, Sang-Shin Park
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(4): 215. CrossRef - Mechanical and geometric features of endodontic instruments and its clinical effect
Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(1): 1. CrossRef
- Radial Lands and Alternating Cutting Edges Contribute to Reduced Screw-in and Torque in Curved Root Canals - An In Vitro Study
- 2,145 View
- 21 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Influence of root canal curvature on the screw-in effect of nickel-titanium rotary files in simulated resin root canal
- Ji-Young Son, Jung-Hong Ha, Young-Kyung Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(5):374-379. Published online September 30, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.5.374
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Nickel-titanium (Ni-Ti) rotary instruments have some unexpected disadvantages including the tendency to screw-in to the canal. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the influence of root canal curvatures on the screw-in effect of Ni-Ti rotary files.
Materials and Methods A total of 80 simulated root canals in clear resin blocks were used in the study. Canals with curvature of 0, 10, 20 and 30 degrees were instrumented with ProTaper instruments SX, S1, S2 and a ProFile of #25/0.06 to 1.0-2.0 mm beyond the initial point of root curvature. The screw-in force was measured with a specially designed device while canal was instrumented with a ProFile of #30/0.06 at a constant speed of 300 rpm. The data were subjected to one-way ANOVA and Scheffe multiple range test for post-hoc test.
Results Larger degree of canal curvature generated significantly lesser screw-in forces in all groups (
p < 0.001).Conclusions More attention needs to be paid when using rotary instruments in canals with less curvature than canals with more curvatures to prevent or reduce any accidental overinstrumentation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of different kinematics on stationary and dynamic torsional behavior of JIZAI nickel-titanium rotary instruments: An in vitro study
Myint Thu, Arata Ebihara, Moe Sandar Kyaw, Satoshi Omori, Keiichiro Maki, Shunsuke Kimura, Hayate Unno, Takashi Okiji
Journal of Dental Sciences.2023; 18(3): 1170. CrossRef - Analysis of Torque and Force Induced by Rotary Nickel-Titanium Instruments during Root Canal Preparation: A Systematic Review
Myint Thu, Arata Ebihara, Sherif Adel, Takashi Okiji
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(7): 3079. CrossRef - Mechanical and geometric features of endodontic instruments and its clinical effect
Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(1): 1. CrossRef
- Influence of different kinematics on stationary and dynamic torsional behavior of JIZAI nickel-titanium rotary instruments: An in vitro study
- 1,225 View
- 4 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Comparison of screw-in effect for several nickel-titanium rotary instruments in simulated resin root canal
- Jung-Hong Ha, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young-Kyung Kim, Sung-Kyo Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(4):267-272. Published online July 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.4.267
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Screw-in effect is one of the unintended phenomena that occurs during the root canal preparation with nickel-titanium rotary files. The aim of this study was to compare the screw-in effect among various nickel-titanium rotary file systems.
Six different nickel-titanium rotary instruments (ISO 20/.06 taper) were used: K3™ (SybronEndo, Glendora, CA, USA), Mtwo (VDW GmbH, München, Germany), NRT with safe-tip and with active tip (Mani Inc., Shioya-gun, Japan), ProFile® (Dentsply-Maillefer, Ballaigues, Switzerland) and ProTaper® (Dentsply-Maillefer, Ballaigues, Switzerland). For ProTaper®, S2 was selected because it has size 20. Root canal instrumentations were done in sixty simulated single-curved resin root canals with a rotational speed of 300 rpm and single pecking motion. A special device was designed to measure the force of screw-in effect. A dynamometer of the device recorded the screw-in force during simulated canal preparation and the recorded data was stored in a computer with designed software (LCV-USE-VS, Lorenz Messtechnik GmbH, Alfdorf, Germany). The data were subjected to one-way ANOVA and Tukey's multiple range test for post-hoc test. P value of less than 0.05 was regarded significant.
ProTaper® produced significantly more screw-in effects than any other instruments in the study (p < 0.001). K3™ produced significantly more screw-in effects than Mtwo, and ProFile® (p < 0.001). There was no significant difference among Mtwo, NRT, and ProFile® (p > 0.05), and between NRT with active tip and NRT with safe one neither (p > 0.05).
From the result of the present study, it was concluded, therefore, that there seems significant differences of screw-in effect among the tested nickel-titanium rotary instruments. The radial lands and rake angle of nickel-titanium rotary instrument might be the cause of the difference.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of Radial Lands on the Reduction of Torque/Force Generation of a Heat-Treated Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instrument
Taro Nakatsukasa, Arata Ebihara, Moe Sandar Kyaw, Satoshi Omori, Hayate Unno, Shunsuke Kimura, Keiichiro Maki, Takashi Okiji
Applied Sciences.2022; 12(5): 2620. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of mechanical properties and shaping performance of heat-treated nickel titanium rotary instruments used in the single-length technique
Taro NAKATSUKASA, Arata EBIHARA, Shunsuke KIMURA, Keiichiro MAKI, Miki NISHIJO, Daisuke TOKITA, Takashi OKIJI
Dental Materials Journal.2021; 40(3): 743. CrossRef - Analysis of Torque and Force Induced by Rotary Nickel-Titanium Instruments during Root Canal Preparation: A Systematic Review
Myint Thu, Arata Ebihara, Sherif Adel, Takashi Okiji
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(7): 3079. CrossRef - Influence of rotational speed on torque/force generation and shaping ability during root canal instrumentation of extracted teeth with continuous rotation and optimum torque reverse motion
M. S. Kyaw, A. Ebihara, Y. Kasuga, K. Maki, S. Kimura, P. H. Htun, T. Nakatsukasa, T. Okiji
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(9): 1614. CrossRef - Influence of glide path on the screw-in effect and torque of nickel-titanium rotary files in simulated resin root canals
Jung-Hong Ha, Sang-Shin Park
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(4): 215. CrossRef - Influence of root canal curvature on the screw-in effect of nickel-titanium rotary files in simulated resin root canal
Ji-Young Son, Jung-Hong Ha, Young-Kyung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(5): 374. CrossRef - Influence of taper on the screw-in effect of nickel-titanium rotary files in simulated resin root canal
Hye-Jin Sung, Jung-Hong Ha, Sung-Kyo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(5): 380. CrossRef
- Impact of Radial Lands on the Reduction of Torque/Force Generation of a Heat-Treated Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instrument
- 1,699 View
- 6 Download
- 7 Crossref

- A comparison of the shaping ability of four rotary nickel-titanium files in simulated root canals
- Bo-Hye Kim, Kyoung-Kyu Choi, Sang-Hyuk Park, Gi-Woon Choi
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(2):88-95. Published online March 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.2.088
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare the root canal shaping ability of 4 rotary NiTi instruments in simulated root canals.
For the preparation of thirty two curved root canals, Mtwo instruments using "single length"technique, and Profile, ProTaper Universal, and K3 using crown-down technique (N = 8) were used. All canal samples were prepared by reaching an apical canal size of #30. Pre- and post-instrumentation digital images were recorded and an assessment of canal shape was determined using a computer image analysis program SigmaScan Pro (Systat Software Inc., San Jose, CA, USA). The changes of the dimension of inner walls of canals, (2) the changes of the dimension of outer walls of canals, and (3) the centering ratio were measured at 7 measuring points, and then data were statistically analyzed using one-way ANOVA and Duncan's test. The results were as below;
The root canal shaping ability of Profile was significantly faster than that of other rotary NiTi instruments (p < 0.05).
The deformation and fracture of all instruments used for this study were not experienced.
In the degree of changes of the dimension of inner walls of canals, Profile demonstrated the lowest changes of the dimension of inner walls of canals except at the measuring points of the 1 and 2 mm (p < 0.05). However, the ProTaper Universal showed the highest changes of the dimension of inner walls of canals at all measuring points (p < 0.05).
In the degree of changes of the dimension of outer walls of canals, Mtwo demonstrated the lowest changse of the dimension of outer walls of canals except at the measuring point of the 1 mm (p < 0.05). However, Profile exhibited the highest changes of the dimension of outer walls of canals at the measuring points of 3 and 4 mm and ProTaper Universal and K3 showed the largest changes of the dimension of outer walls of canals at the measuring points of 1, 2, 6, and 7 mm (p < 0.05).
In degree of centering ratio, Profile demonstrated the least centering ratio comparing with the centering ratio shown by other NiTi instruments at the measuring points of 1, 4, 5, and 6 mm.
Results suggest that in the coronal part of canal preparation, active cutting files such as ProTaper Universal may efficiently flare the canal orifice and form a better taper, and in the apical part of the canal, files which have a better centering ability such as Profile may maintain the original canal curvature and reduce the shaping time.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A comparison of dimensional standard of several nickel-titanium rotary files
Ki-Won Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho, Se-Hee Park, Ki-Yeol Choi, Bekir Karabucak, Jin-Woo Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(1): 7. CrossRef
- A comparison of dimensional standard of several nickel-titanium rotary files
- 1,060 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Stress distribution of three NiTi rotary files under bending and torsional conditions using 3-dimensional finite element analysis
- Tae-Oh Kim, Chan-Joo Lee, Byung-Min Kim, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(4):323-331. Published online July 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.4.323
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Flexibility and fracture properties determine the performance of NiTi rotary instruments. The purpose of this study was to evaluate how geometrical differences between three NiTi instruments affect the deformation and stress distributions under bending and torsional conditions using finite element analysis.
Three NiTi files (ProFile .06 / #30, F3 of ProTaper and ProTaper Universal) were scanned using a Micro-CT. The obtained structural geometries were meshed with linear, eight-noded hexahedral elements. The mechanical behavior (deformation and von Mises equivalent stress) of the three endodontic instruments were analyzed under four bending and rotational conditions using ABAQUS finite element analysis software. The nonlinear mechanical behavior of the NiTi was taken into account.
The U-shaped cross sectional geometry of ProFile showed the highest flexibility of the three file models. The ProTaper, which has a convex triangular cross-section, was the most stiff file model. For the same deflection, the ProTaper required more force to reach the same deflection as the other models, and needed more torque than other models for the same amount of rotation. The highest von Mises stress value was found at the groove area in the cross-section of the ProTaper Universal.
Under torsion, all files showed highest stresses at their groove area. The ProFile showed highest von Mises stress value under the same torsional moment while the ProTaper Universal showed the highest value under same rotational angle.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of internal stress on cyclic fatigue failure in .06 taper ProFile
Hye-Rim Jung, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho, Se-Hee Park
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(2): 79. CrossRef
- Effect of internal stress on cyclic fatigue failure in .06 taper ProFile
- 1,309 View
- 7 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Change of working length in curved canals by various instrumentation techniques
- Jeong-Im Jo, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young Kyung Kim, Sung Kyo Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(1):30-35. Published online January 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.1.030
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub To evaluate the change of working length with various instrumentation techniques in curved canals, working length and canal curvature were determined before and after canal instrumentation in buccal or mesial canals of extracted human molars. Stainless steel K-files (MANI®, Matsutani Seisakusho Co. Takanezawa, Japan), nickel-titanium K-files (Naviflex NT™, Brassler, Savannah, USA), ProFile®, and ProTaper™ (Dentsply-Maillefer, Ballaigues, Switzerland) were used to prepare the canals with crown-down technique. In two hand instrumentation groups, coronal flaring was made with Gates Glidden burs. Apical canals were instrumented until apical diameter had attained a size of 30. Positional relation between the tooth apex and the #10 K-file tip was examined by using AutoCAD 2000 (Autodesk Corp., San Rafael. CA, USA) under a stereomicroscope before and after coronal flaring, and after apical instrumentation. Degree of canal curvature was also measured with Schneider's method in radiographs. Data of working length and canal curvature changes were statistically analyzed with one-way ANOVA and Tukey's studentized range test.
Working length and canal curvature were decreased significantly in each step in all instrumentation groups. Coronal flaring using Gates Glidden burs in hand instrument groups and whole canal instrumentation using stainless steel hand K-files caused significantly more working length change than in ProFile instrumentation group (p < 0.05).
The result of this study demonstrates that all of the above kinds of instrumentation in curved canals cause reduction of working length and canal curvature at each instrumentation steps, and hand instrumentation causes more working length change than ProFile.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of the Accuracy of an Endomotor-Integrated Apex Locator Versus a Standalone Electronic Apex Locator in Teeth with Simulated Apical Root Resorption: An In Vitro Study
Yunus Emre Çakmak, Damla Erkal, Hatice Harorlı, Simay Koç
European Journal of Therapeutics.2025; 31(3): 173. CrossRef - Does Root Canal Shaping Effect the Accuracy of Electronic Apex Locators in Curved and Straight Root Canals?
Dide Tekinarslan, Damla Erkal, Esen Ercan, Simay Koc, Kürşat Er
Clinical and Experimental Health Sciences.2024; 14(3): 727. CrossRef - Comparative Study of Four Endodontic File Systems to Assess Changes in Working Length during Root Canal Instrumentation and the Effect of Canal Curvature on Working Length Change
Michelle Tien, Hermawan Tjoa, Maggie Zhou, Paul V. Abbott
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(1): 110. CrossRef - Study of endodontic working length of Korean posterior teeth
Jeong-Yeob Kim, Sang-Hoon Lee, Gwang-Hee Lee, Sang-Hyuk Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(6): 429. CrossRef
- Evaluation of the Accuracy of an Endomotor-Integrated Apex Locator Versus a Standalone Electronic Apex Locator in Teeth with Simulated Apical Root Resorption: An In Vitro Study
- 1,871 View
- 10 Download
- 4 Crossref

- A comparative study of the canal configuration after shaping by protaper rotary and hand files in resin simulated canals
- In-Seok Yang, In-Chol Kang, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(5):393-401. Published online September 30, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.5.393
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare the canal configuration after shaping by ProTaper rotary files and ProTaper hand files in resin simulated canals.
Forty resin simulated canals with a curvature of J-shape and S-shape were divided into four groups by 10 blocks each. Simulated root canals in resin block were prepared by ProTaper rotary files and ProTaper hand files using a crown-down pressureless technique. All simulated canals were prepared up to size #25 file at end-point of preparation. Pre- and post-instrumentation images were recorded with color scanner. Assessment of canal shape was completed with an image analysis program. Measurements were made at 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7 mm from the apex. At each level, outer canal width, inner canal width, total canal width, and amount of transportation from original axis were recorded. Instrumentation time was recorded. The data were analyzed statistically using independent
t -test.The result was that ProTaper hand files cause significantly less canal transportation from original axis of canal body and maintain original canal configuration better than ProTaper rotary files, however ProTaper hand files take more shaping time.
- 724 View
- 3 Download

- Shaping ability of four rotary nickel-titanium instruments to prepare root canal at danger zone
- Seok-Dong Choi, Myoung-Uk Jin, Ki-Ok Kim, Sung-Kyo Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(5):446-453. Published online September 30, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.5.446
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The aim of this study was to evaluate the shaping abilities of four different rotary nickel-titanium instruments with anticurvature motion to prepare root canal at danger zone by measuring the change of dentin thickness in order to have techniques of safe preparation of canals with nickel-titanium files.
Mesiobuccal and mesiolingual canals of forty mesial roots of extracted human lower molars were instrumented using the crown-down technique with ProFile, GT™ Rotary file, Quantec file and ProTaper™. In each root, one canal was prepared with a straight up-and-down motion and the other canal was with an anticurvature motion. Canals were instrumented until apical foramens were up to size of 30 by one operator. The muffle system was used to evaluate the root canal preparation. After superimposing the pre- and post-instrumentation canal, change in root dentin thickness was measured at the inner and outer sides of the canal at 1, 3, and 5 mm levels from the furcation. Data were analyzed using two-way ANOVA.
Root dentin thickness at danger zone was significantly thinner than that at safe zone at all levels (
p < 0.05).There was no significant difference in the change of root dentin thickness between the straight up-and-down and the anticurvature motions at both danger and safe zones in all groups (
p > 0.05).ProTaper removed significantly more dentin than other files especially at furcal 3 mm level of danger and safe zones (
p < 0.05)Therefore, it was concluded that anticurvature motion with nickel-titanium rotary instruments does not seem to be effective in danger zone of lower molars.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Conservation of dentin thickness in the root canals orifice following two preparation techniques
Ranjdar Talabani, Shawbo Ahmad, Arass Noori
Sulaimani Dental Journal.2014; 1(2): 6. CrossRef - Change of working length in curved canals by various instrumentation techniques
Jeong-Im Jo, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young Kyung Kim, Sung Kyo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2006; 31(1): 30. CrossRef - Effect of anticurvature filing method on preparation of the curved root canal using ProFile
Hyun-Ji Song, Juhea Chang, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2005; 30(4): 327. CrossRef
- Conservation of dentin thickness in the root canals orifice following two preparation techniques
- 1,342 View
- 1 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Evaluation of canal preparation with Ni-Ti rotary files by micro computed tomography
- Jeong-Ho Lee, Mi-Ja Kim, Chang-In Seok, Woo-Cheol Lee, Seung-Ho Baek
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(4):378-385. Published online July 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.4.378
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare the effects of preparation with GT files and profiles .04 in shaping of root canals and reconstruct the three-dimensional root canal system using micro computed tomography.
40 canals of the extracted human mandibular molars were used, and randomly distributed into two experimental groups. In group 1, canals were prepared by GT files. In group 2, Profiles .04. were used. Apical preparation size was #30.
For each tooth pre and post operative cross-sectional images were obtained by the micro CT at 50 micron intervals. Pre and post operative cross-sectional images of 1, 2, 3, 5, and 8mm from the apex were compared. For each section, canal area and centering ratio were determined. For each tooth pre- and post-operative root canal volume from the furcation to the apex of the roots was calculated by three-dimensional image software. Following results were obtained:
1. At 8mm from the apex, area of dentin removed by GT rotary file was significantly larger than that by Profile .04. And at the other levels there was not a significant difference.
2. There was a trend for GT rotary file to remain more centered in the canals than Profile .04 at all levels. But at 3mm level, there was a statistically significant difference.
3. In root canal volume increments after instrumentation, there was no significant difference between two groups.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of apical canal shapes produced sequentially during instrumentation with stainless steel hand and Ni-Ti rotary instruments using Micro-computed tomography
Woo-Jin Lee, Jeong-Ho Lee, Kyung-A Chun, Min-Seock Seo, Yeon-Jee Yoo, Seung-Ho Baek
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(3): 231. CrossRef - Comparative study on morphology of cross-section and cyclic fatigue test with different rotary NiTi files and handling methods
Jae-Gwan Kim, Kee-Yeon Kum, Eui-Seong Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2006; 31(2): 96. CrossRef
- Evaluation of apical canal shapes produced sequentially during instrumentation with stainless steel hand and Ni-Ti rotary instruments using Micro-computed tomography
- 1,282 View
- 2 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Effect of surface defects and cross-sectional configuration on the fatigue fracture of NiTi rotary files under cyclic loading
- Yu-Mi Shin, Eui-Sung Kim, Kwang-Man Kim, Kee-Yeon Kum
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(3):267-272. Published online May 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.3.267
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this in vitro study was to evaluate the effect of surface defects and cross-sectional configuration of NiTi rotary files on the fatigue life under cyclic loading. Three NiTi rotary files (K3™, ProFile®, and HERO 642®) with #30/.04 taper were evaluated. Each rotary file was divided into 2 subgroups: control (no surface defects) and experimental group (artificial surface defects). A total of six groups of each 10 were tested. The NiTi rotary files were rotated at 300rpm using the apparatus which simulated curved canal (40 degree of curvature) until they fracture. The number of cycles to fracture was calculated and the fractured surfaces were observed with a scanning electron microscope. The data were analyzed statistically. The results showed that experimental groups with surface defects had lower number of cycles to fracture than control group but there was only a statistical significance between control and experimental group in the K3™ (p<0.05). There was no strong correlation between the cross-sectional configuration area and fracture resistance under experimental conditions. Several of fractured files demonstrated characteristic patterns of brittle fracture consistent with the propagation of pre-existing cracks.
This data indicate that surface defects of NiTi rotary files may significantly decrease fatigue life and it may be one possible factor for early fracture of NiTi rotary files in clinical practice.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Torsional behavior and microstructure characterization of additively manufactured NiTi shape memory alloy tubes
Keyvan Safaei, Mohammadreza Nematollahi, Parisa Bayati, Hediyeh Dabbaghi, Othmane Benafan, Mohammad Elahinia
Engineering Structures.2021; 226: 111383. CrossRef - Effect of internal stress on cyclic fatigue failure in K3
Jun-Young Kim, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho, Se-Hee Park
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(2): 74. CrossRef - An evaluation of rotational stability in endodontic electronic motors
Se-Hee Park, Hyun-Woo Seo, Chan-Ui Hong
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(4): 246. CrossRef - Effect of cross-sectional area of 6 nickel-titanium rotary instruments on the fatigue fracture under cyclic flexural stress: A fractographic analysis
Soo-Youn Hwang, So-Ram Oh, Yoon Lee, Sang-Min Lim, Kee-Yeon Kum
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(5): 424. CrossRef - The Effect of Surface Defects on the Cyclic Fatigue Fracture of HEROShaper Ni-Ti rotary files in a Dynamic Model: A Fractographic Analysis
Jung-Kyu Lee, Eui-Sung Kim, Myoung-Whai Kang, Kee-Yeon Kum
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2007; 32(2): 130. CrossRef - Comparative study on morphology of cross-section and cyclic fatigue test with different rotary NiTi files and handling methods
Jae-Gwan Kim, Kee-Yeon Kum, Eui-Seong Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2006; 31(2): 96. CrossRef
- Torsional behavior and microstructure characterization of additively manufactured NiTi shape memory alloy tubes
- 1,098 View
- 2 Download
- 6 Crossref

- SHAPING ABILITY OF NICKEL-TITANIUMROTARY FILES
- Wan-Ky Park, Hee-Joo Lee, Bock Hur
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(1):44-50. Published online January 14, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.1.044
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub ABSTRACT This study compared the shaping ability of nickel-titanium rotary files with different rake angle and radial land.
The nickel-titanium files used in this study were Profile(Dentsply, Maillefer, Ballaigues, Switzerland), Hero 642(Micromega, Besancon, France), and K3(SybronEndo, Glendora, Ca, USA) file. Resin blocks substituted for root canals. 36 resin blocks were divided into 3 groups with 12 canals each. The time for canal preparation was recorded. The images of pre- and postoperative resin canal were scanned and those were superimposed. Amounts of canal deviation, total canal widths, inner canal widths, and outer canal widths were measured at apical 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7mm levels.
The amount of canal deviation was the smallest in Profile group, and the time for canal preparation was the shortest in Hero 642 group. K3 group resulted in competent characteristics in both measurements. Positive rake angle seemed to result in fast shaping of root canal and radial land guide the instrument in center of the canals and around curvatures. Radial land also tended to reduce the sense of screwing into the root canal.
The proper selection of the nickel-titanium file based on the knowledge about file design is needed for the safer, simpler and faster root canal therapy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of screw-in effect for several nickel-titanium rotary instruments in simulated resin root canal
Jung-Hong Ha, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young-Kyung Kim, Sung-Kyo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(4): 267. CrossRef - Influence of root canal curvature on the screw-in effect of nickel-titanium rotary files in simulated resin root canal
Ji-Young Son, Jung-Hong Ha, Young-Kyung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(5): 374. CrossRef - Comparison of shaping ability using various Nickel-Titanium rotary files and hybrid technique
Jung-Won Kim, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2007; 32(6): 530. CrossRef - Comparison of shaping ability of rotary Ni-Ti file systems used by undergraduates
Mun-Seong Kang, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Bock Hur, Jeong-Kil Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2006; 31(1): 1. CrossRef - Comparative study on morphology of cross-section and cyclic fatigue test with different rotary NiTi files and handling methods
Jae-Gwan Kim, Kee-Yeon Kum, Eui-Seong Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2006; 31(2): 96. CrossRef - Comparison of shaping ability between various hybrid instrumentation methods with ProTaper
Eun-Sook Hong, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2006; 31(1): 11. CrossRef
- Comparison of screw-in effect for several nickel-titanium rotary instruments in simulated resin root canal
- 958 View
- 5 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Effect of various canal preparation techniques using rotary nickel-titanium files on the maintenance of canal curvature
- Cheol-Hwan Lee, Kyung-Mo Cho, Chan-Ui Hong
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2003;28(1):41-49. Published online January 31, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.1.041
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub There are increasing usage of Nickel-Titanium rotary files in modern clinical endodontic treatment because it is effective and faster than hand filing due to reduced step.
This study was conducted to evaluate the effect of canal preparations using 3 different rotary Nickel-Titanium files that has different cross sectional shape and taper on the maintenance of canal curvature. Simulated resin block were instrumented with Profile(Dentsply, USA), GT rotary files(Dentsply, USA), Hero 642(Micro-Mega, France), and Pro-Taper(Dentsply, USA).
The image of Pre-instrumentation and Post-instrumentation were acquired using digital camera and overspreaded in the computer. Then the total differences of canal diameter, deviation at the outer portion of curvature, deviation at the inner portion of curvature, movement of center of the canal and the centering ratio at the pre-determined level from the apex were measured.
Results were statistically analyzed by means of ANOVA, followed by Scheffe test at a significance level of 0.05.
The results were as follows;
1. Deviation at the outer portion of curvature, deviation at the inner portion of curvature were showed largest in Pro-Taper, so also did in the total differences of canal diameter(p<0.05).
2. All the groups showed movements of center. Profile combined with GT rotary files and Hero 642 has no difference but Pro-Taper showed the most deviation(p<0.05).
3. At the 1, 2, 3mm level from the apex movements of center directed toward the outer portion of curvature, but in 4, 5 mm level directed toward the inner portion of curvature(p<0.05).
As a results of this study, it could be concluded that combined use of other Nickel-Titanium rotary files is strongly recommended when use Pro-Taper file because it could be remove too much canal structure and also made more deviation of canal curvature than others.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Stress distribution of three NiTi rotary files under bending and torsional conditions using a mathematic analysis
T. O. Kim, G. S. P. Cheung, J. M. Lee, B. M. Kim, B. Hur, H. C. Kim
International Endodontic Journal.2009; 42(1): 14. CrossRef - Comparison of shaping ability using various Nickel-Titanium rotary files and hybrid technique
Jung-Won Kim, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2007; 32(6): 530. CrossRef - A study of insertion depth of buchanan plugger after shaping using NI-TI rotary files in simulated resin root canals
Youn-Sik Park, Dong-Jun Kim, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2006; 31(2): 125. CrossRef - Step by step analysis of root canal instrumentation with ProTaper®
Mi-Hee Kim, Bock Huh, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Jeong-Kil Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2006; 31(1): 50. CrossRef - Effect of anticurvature filing method on preparation of the curved root canal using ProFile
Hyun-Ji Song, Juhea Chang, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2005; 30(4): 327. CrossRef - A comparison of shaping ability of the three ProTaper® instrumentation techniques in simulated canals
So-Youn Kim, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2005; 30(1): 58. CrossRef
- Stress distribution of three NiTi rotary files under bending and torsional conditions using a mathematic analysis
- 968 View
- 2 Download
- 6 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


