Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Stress distribution of restorations in external cervical root resorption under occlusal and traumatic loads: a finite element analysis
- Padmapriya Ramanujam, Paul Kevin Abishek Karthikeyan, Vignesh Srinivasan, Selvakarthikeyan Ulaganathan, Velmurugan Natanasabapathy, Nandini Suresh
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(2):e21. Published online May 21, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e21
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
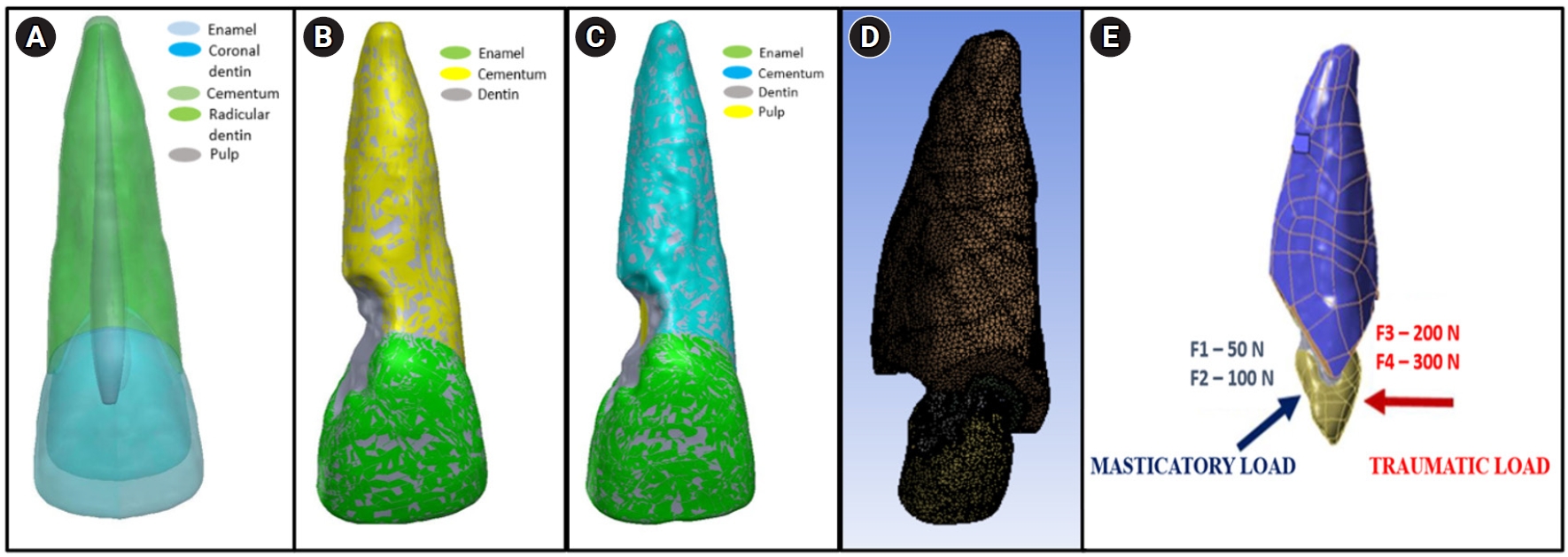
This study analyzed the stress distribution in a maxillary central incisor with external cervical resorptive defect restored with different restorative materials under normal masticatory and traumatic loading conditions using finite element analysis.
Methods
Cone-beam computed tomography of an extracted intact incisor and created resorptive models (Patel’s 3D classification-2Bd and 2Bp) in the maxillary central incisor was performed for finite element models. The 2Bd models were restored either with glass ionomer cement (GIC)/Biodentine (Septodont) or a combination of both with composite resin. 2Bp models were restored externally with a combination technique and internally with root canal treatment. The other model was external restoration with GIC and internal with fiber post. Two masticatory loads were applied at 45˚ to the palatal aspect, and two traumatic loads were applied at 90˚ to the buccal aspect. Maximum von Mises stresses were calculated, and stress distribution patterns were studied.
Results
In 2Bd models, all restorative strategies decreased stress considerably, similar to the control model under all loads. In 2Bp models, the dentin component showed maximum stress at the deepest portion of the resorptive defect, which transfers into the adjacent pulp space. In 2Bp defects, a multilayered restoration externally and root canal treatment internally provides better stress distribution compared to the placement of a fiber post.
Conclusions
Increase in load, proportionally increased von Mises stress, despite the direction or angulation of the load. Multilayered restoration is preferred for 2Bd defects, and using an internal approach of root canal treatment is suggested to restore 2Bp defects.
- 2,083 View
- 136 Download

- Does photobiomodulation on the root surface decrease the occurrence of root resorption in reimplanted teeth? A systematic review of animal studies
- Theodoro Weissheimer, Karolina Frick Bischoff, Carolina Horn Troian Michel, Bruna Barcelos Só, Manoela Domingues Martins, Matheus Albino Souza, Ricardo Abreu da Rosa, Marcus Vinícius Reis Só
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(3):e24. Published online June 12, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e24
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
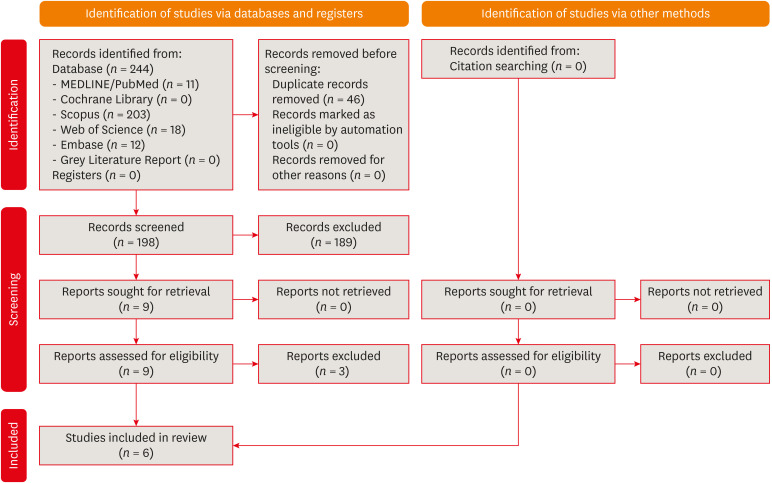
ePub This review aimed to answer the following question “Does photobiomodulation treatment of the root surface decrease the occurrence of root resorption in reimplanted teeth?” Electronic searches were performed in the MEDLINE/PubMed, Cochrane Library, Scopus, Web of Science, Embase, and Grey Literature Report databases. Risk of bias was evaluated using SYRCLE Risk of Bias tool. The Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluations (GRADE) tool was used to assess the certainty of evidence. In total, 6 studies were included. Five studies reported a reduced occurrence of root resorption in teeth that received photobiomodulation treatment of the root surface prior to replantation. Only 1 study reported contradictory results. The photobiomodulation parameters varied widely among studies. GRADE assessment showed a low certainty of evidence. It can be inferred that photobiomodulation treatment of the root surface prior to replantation of teeth can reduce the occurrence of root resorption. Nonetheless, further clinical studies are needed.
Trial Registration PROSPERO Identifier: CRD42022349891
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Feasibility and Outcomes of Cell-based Regenerative Endodontic Therapy in Postautogenous Transplantation of a Mature Tooth: A Case Report
Noriaki Yoshihashi
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(1): 85. CrossRef - Evidence Mapping and Quality Assessment of Systematic Reviews in Dental Traumatology: A 54 Months Update
Nitesh Tewari, Pavithra Devi, Hemlata Nehta, Ekta Wadhwani, Rigzen Tamchos, Georgios Tsilingaridis, Vijay Prakash Mathur, Morankar Rahul
Dental Traumatology.2025; 41(6): 727. CrossRef - Photobiomodulation Literature Watch September 2023
James D. Carroll
Photobiomodulation, Photomedicine, and Laser Surgery.2024; 42(7): 498. CrossRef
- Feasibility and Outcomes of Cell-based Regenerative Endodontic Therapy in Postautogenous Transplantation of a Mature Tooth: A Case Report
- 2,880 View
- 44 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Effects of different calcium-silicate based materials on fracture resistance of immature permanent teeth with replacement root resorption and osteoclastogenesis
- Gabriela Leite de Souza, Gabrielle Alves Nunes Freitas, Maria Tereza Hordones Ribeiro, Nelly Xiomara Alvarado Lemus, Carlos José Soares, Camilla Christian Gomes Moura
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(2):e21. Published online May 5, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e21
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the effects of Biodentine (BD), Bio-C Repair (BCR), and mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) plug on the fracture resistance of simulated immature teeth with replacement root resorption (RRR) and
in vitro -induced osteoclastogenesis.Materials and Methods Sixty bovine incisors simulating immature teeth and RRR were divided into 5 groups: BD and BCR groups, with samples completely filled with the respective materials; MTA group, which utilized a 3-mm apical MTA plug; RRR group, which received no root canal filling; and normal periodontal ligament (PL) group, which had no RRR and no root canal filling. All the teeth underwent cycling loading, and compression strength testing was performed using a universal testing machine. RAW 264.7 macrophages were treated with 1:16 extracts of BD, BCR, and MTA containing receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B ligand (RANKL) for 5 days. RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation was assessed by staining with tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase. The fracture load and osteoclast number were analyzed using 1-way ANOVA and Tukey’s test (α = 0.05).
Results No significant difference in fracture resistance was observed among the groups (
p > 0.05). All materials similarly inhibited osteoclastogenesis (p > 0.05), except for BCR, which led to a lower percentage of osteoclasts than did MTA (p < 0.0001).Conclusions The treatment options for non-vital immature teeth with RRR did not strengthen the teeth and promoted a similar resistance to fractures in all cases. BD, MTA, and BCR showed inhibitory effects on osteoclast differentiation, with BCR yielding improved results compared to the other materials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- In vitro comparison of fracture strength of maxillary incisors with the simulated external root resorption cavities repaired with BioMTA or Biodentine
Tufan Ozasir, Birgul Ozasir, Nagihan Aribal, Derin Bugu Yuzer, Baris Kandemir, Kamran Gulsahi
Journal of Dental Sciences.2025; 20(3): 1532. CrossRef - Comparative Analysis of Gene Expression in Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells Exposed to Biodentine and Bio-C Repair: Implications for Cementogenesis—An In Vitro Study
Mahmoud M. Bakr, Mahmoud Al Ankily, Mohammed Meer, Mohamed Shamel
Oral.2025; 5(1): 19. CrossRef - Efficacy of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate Versus Biodentine as a Direct Pulp Capping Material in Carious Human Mature Permanent Teeth: A Systematic Review
Rashmi Misra, Nikita Toprani, Sumita Bhagwat, Aashaka Vaishnav, Aastha Dureja, Omkar Bhosale
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Restoration Strategy and Cavity Location on the Fracture Resistance of Teeth with External Cervical Resorption
Saadet Elpe, Öznur Sarıyılmaz
Journal of Endodontics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Different Techniques and Materials for Filling in 3-dimensional Printed Teeth Replicas with Perforating Internal Resorption by Means of Micro–Computed Tomography
Angelo J.S. Torres-Carrillo, Helena C. Assis, Rodrigo E. Salazar-Gamarra, Leonardo Moreira Teodosio, Alice C. Silva-Sousa, Jardel F. Mazzi-Chaves, Priscila B. Ferreira-Soares, Manoel D. Sousa-Neto, Fabiane C. Lopes-Olhê
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(2): 205. CrossRef
- In vitro comparison of fracture strength of maxillary incisors with the simulated external root resorption cavities repaired with BioMTA or Biodentine
- 2,758 View
- 68 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- The prevalence and characteristics of external cervical resorption based on cone-beam computed tomographic imaging: a cross-sectional study
- Matheus Diniz Ferreira, Matheus Barros-Costa, Felipe Ferreira Costa, Deborah Queiroz Freitas
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(4):e39. Published online October 11, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e39
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
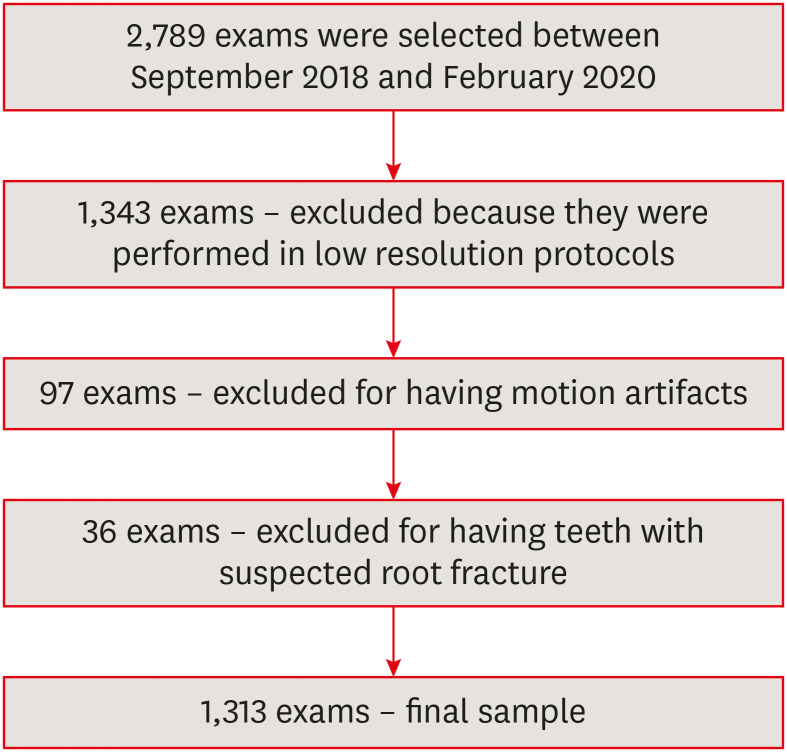
ePub Objectives This study investigated the prevalence and characteristics of external cervical resorption (ECR) regarding sex, age, tooth, stages of progression, and portal of entry, using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) scans.
Materials and Methods CBCT scans of 1,313 patients from a Brazilian subpopulation comprising 883 female and 430 male patients (mean age, 55.2 years), acquired using a PreXion 3D CBCT unit, were evaluated. All permanent teeth included in the scans were evaluated for the presence of ECR according to the 3-dimensional classification and the portal of entry. The association between the presence of ECR and the factors studied was assessed using the χ2 test. Intra-observer agreement was analyzed with the kappa test (
α = 0.05).Results In total, 6,240 teeth were analyzed, of which 84 (1.35%) were affected by ECR. A significant association was found between the presence of ECR and sex, with a higher prevalence in male patients (
p = 0.002). The most frequently affected teeth were the mandibular and maxillary central incisors. The most common height was the mid-third of the root. For the portal of entry, 44% of cases were on the proximal surfaces, 40.5% on the lingual/palatal surface and 15.5% on the buccal surface. Intra-observer agreement was excellent.Conclusions The prevalence of ECR was 1.35%, with a higher prevalence in male patients and a wide age distribution. The mandibular and maxillary central incisors were the most commonly affected teeth, and cases of ECR most frequently showed a height into the mid-third of the root and proximal entry.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- External Cervical Resorption Treatment: A Single‐Center Retrospective Cohort Study of Cases Treated Over a 20‐Year Period
Terrell F. Pannkuk
Dental Traumatology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Prise en charge des lésions cervicales
C. Mocquot, L. Detzen, I. Fontanille, B. Orlik, F. Decup
EMC - Médecine buccale.2025; 18(3): 1. CrossRef - Features of external root resorption as predictors of disease progression: A CBCT cross-sectional study
Tânia Maria Soares Reis, Daniella Ribeiro Ferrari, Rafael Binato Junqueira, Priscila Dias Peyneau, Eduardo Murad Villoria, Maria Augusta Visconti, Francielle Silvestre Verner
Odontology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence and Characterization of External Cervical Resorption Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography
Isadora Carneiro Pereira Machado, Marilia Oliveira Morais, Adriana Lustosa Pereira Bicalho, Patricia Helena Pereira Ferrari, Juliano Martins Bueno, José Luiz Cintra Junqueira, Mariana Quirino Silveira Soares
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(2): 164. CrossRef - Influence of tube current and metal artifact reduction on the diagnosis of external cervical resorption in teeth adjacent to a dental implant in CBCT: an ex-vivo study
Thamiles Gonzalez-Passos, Matheus Barros-Costa, Matheus L Oliveira, Deborah Queiroz Freitas
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Maxillary anterior teeth with extensive root resorption treated with multidisciplinary approach: A case report
Thais Machado de Carvalho Coutinho, Carollyne Souza Campello, Juliana Pires Abdelnur, Vivian Ronquete, Carlos Henrique Sardenberg Pereira, Marilia F Marceliano-Alves
International Journal of Case Reports and Images.2023; 14(1): 8. CrossRef - Clinical and radiographic features of external cervical resorption – An observational study
Shanon Patel, Francesc Abella, Kreena Patel, Paul Lambrechts, Nassr Al‐Nuaimi
International Endodontic Journal.2023; 56(12): 1475. CrossRef
- External Cervical Resorption Treatment: A Single‐Center Retrospective Cohort Study of Cases Treated Over a 20‐Year Period
- 3,733 View
- 55 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref

- A micro-computed tomography evaluation of voids using calcium silicate-based materials in teeth with simulated internal root resorption
- Vildan Tek, Sevinç Aktemur Türker
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(1):e5. Published online November 29, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e5
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
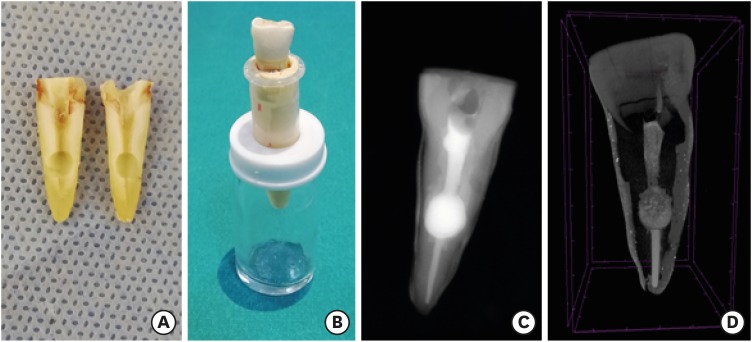
ePub Objectives The obturation quality of MTA, Biodentine, Total Fill BC root canal sealer (RCS), and warm gutta-percha (WGP) in teeth with simulated internal root resorption (IRR) was evaluated by using micro-computed tomography.
Materials and Methods Standardized IRR cavities were created using 40 extracted maxillary central incisor teeth and randomly assigned into 4 groups (
n = 10). IRR cavities were filled with MTA, Biodentine, Total Fill BC RCS (bulk-fill form) and WGP + Total Fill BC RCS. Percentage of voids between resorptive cavity walls and obturation material (external void), and inside the filling materials (internal voids) were measured.Results Total Fill BC sealer in the bulk-fill form presented significantly highest values of external and internal void percentages (
p < 0.05). Biodentine showed a significantly lowest external void percentage (p < 0.05). WGP + Total Fill BC RCS presented significantly lower values of internal void percentages than all groups (p < 0.05), except Biodentine (p > 0.05).Conclusion None of the filling materials were created void-free obturation in resorption cavities. Biodentine may favor its application in teeth with IRR over Angelus MTA and bulk-fill form of Total Fill BC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Removal of AH Plus Bioceramic Sealer from Artificial Internal Resorption Cavities Using Different Irrigation Activation Systems
Mine Büker, Meltem Sümbüllü, Emine Şimşek, Fadime Sena Sezer
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2025; 28(3): 383. CrossRef - Functional and Bioactive Performance of Premixed Bioceramic Sealers with Warm Obturation: A Scoping Review
Patryk Wiśniewski, Stanisław Krokosz, Małgorzata Pietruska, Anna Zalewska
Gels.2025; 11(11): 932. CrossRef - Evaluation of the effectiveness of different supplemental cleaning techniques in the retreatment of roots with small simulated internal resorption cavities: an in vitro comparative study
Sine Güngör Us, Özgür Uzun, Nazlı Merve Güngör
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Different Techniques and Materials for Filling in 3-dimensional Printed Teeth Replicas with Perforating Internal Resorption by Means of Micro–Computed Tomography
Angelo J.S. Torres-Carrillo, Helena C. Assis, Rodrigo E. Salazar-Gamarra, Leonardo Moreira Teodosio, Alice C. Silva-Sousa, Jardel F. Mazzi-Chaves, Priscila B. Ferreira-Soares, Manoel D. Sousa-Neto, Fabiane C. Lopes-Olhê
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(2): 205. CrossRef - Three-Dimensional Measurement of Obturation Quality of Bioceramic Materials in Filling Artificial Internal Root Resorption Cavities Using Different Obturation Techniques: An In Vitro Comparative Study
Ammar M. Sharki, Ahmed H. Ali
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(7): 997. CrossRef - Evaluation of calcium hydroxide root canal filling materials by cone beam computed tomography and three-dimensional modeling
Asel Usdat Ozturk, Ekin Dogan, Venus Seyedoskuyi, Berk Senguler, Asli Topaloglu-Ak
Folia Medica.2024; 66(2): 250. CrossRef - Clinical applications of calcium silicate‐based materials: a narrative review
S Küçükkaya Eren
Australian Dental Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study root canal fillings
Gustavo De‐Deus, Erick Miranda Souza, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Marco Simões‐Carvalho, Daniele Moreira Cavalcante, Marco Aurélio Versiani
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S2): 384. CrossRef - An Updated Review on Properties and Indications of Calcium Silicate‐Based Cements in Endodontic Therapy
Fateme Eskandari, Alireza Razavian, Rozhina Hamidi, Khadije Yousefi, Susan Borzou, Zohaib Khurshid
International Journal of Dentistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy Of Calcium Silicate-Based Sealers In Root Canal Treatment: A Systematic Review
Hattan Mohammed Omar Baismail, Mohammed Ghazi Moiser Albalawi, Alaa Mofareh Thoilek Alanazi, Muhannad Atallah Saleem Alatawi, Badr Soliman Alhussain
Annals of Dental Specialty.2021; 9(1): 87. CrossRef
- Removal of AH Plus Bioceramic Sealer from Artificial Internal Resorption Cavities Using Different Irrigation Activation Systems
- 2,509 View
- 34 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Effect of calcium hydroxide on inflammatory root resorption and ankylosis in replanted teeth compared with other intracanal materials: a review
- Maryam Zare Jahromi, Mahmood Reza Kalantar Motamedi
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(3):e32. Published online August 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e32
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Calcium hydroxide (CH) is the gold-standard intracanal dressing for teeth subjected to traumatic avulsion. A common complication after the replantation of avulsed teeth is root resorption (RR). The current review was conducted to compare the effect of CH with that of other intracanal medications and filling materials on inflammatory RR and replacement RR (ankylosis) in replanted teeth. The PubMed and Scopus databases were searched through June 2018 using specific keywords related to the title of the present article. The materials that were compared to CH were in 2 categories: 1) mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) and endodontic sealers as permanent filling materials for single-visit treatment, and 2) Ledermix, bisphosphonates, acetazolamide, indomethacin, gallium nitrate, and enamel matrix-derived protein (Emdogain) as intracanal medicaments for multiple-visit management of avulsed teeth prior to the final obturation. MTA can be used as a single-visit root filling material; however, there are limited data on its efficacy due to a lack of clinical trials. Ledermix and acetazolamide were comparable to CH in reducing RR. Emdogain seems to be an interesting material, but the data supporting its use as an intracanal medication remain very limited. The conclusions drawn in this study were limited by the insufficiency of clinical trials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Endodontic Intracanal Medicaments and Agents
Anu Priya Guruswamy Pandian, Depti Bellani, Ritya Mary Jibu, Varsha Agnihotri
Dental Clinics of North America.2026; 70(1): 45. CrossRef - Efficacy of Simvastatin in Inhibiting Bone Resorption and Promoting Healing in Delayed Tooth Avulsion: A Case Series
Rajesh Kumar, Supraja N Atluri, Alekhya Achanta, Chittaranjan Bogishetty, Tejaswini R Chunduri, Tejaswini PSS, Ramakrishna Ravi
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Interdisziplinäre Lösung nach dentalem Trauma mit Avulsion und Wurzelresorption
Eva Maier, Julia Lubauer, Kerstin M. Galler
Oralprophylaxe & Kinderzahnmedizin.2025; 47(3): 161. CrossRef - Bioactive potential of Bio-C Temp demonstrated by systemic mineralization markers and immunoexpression of bone proteins in the rat connective tissue
Camila Soares Lopes, Mateus Machado Delfino, Mário Tanomaru-Filho, Estela Sasso-Cerri, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Paulo Sérgio Cerri
Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The use of mineral trioxide aggregate for treatment of children with complications of dental trauma
L.Yu. Kharkova, M.V. Korolenkova
Stomatology.2024; 103(4): 59. CrossRef - Instant Re-Implantation of Avulsed Teeth
Smita Paul, Sambarta Das, Nirmal Debbarma, Barun Dasgupta, Bidyut Seal, Ayesha Satapathy
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2024; 16(Suppl 4): S3461. CrossRef - Interpretation by literature review of the use of calcium hydroxide as an intra-ductal medication
María Belén Muñoz Padilla, Verónica Alicia Vega Martínez, Camila Alejandra Villafuerte Moya
Salud, Ciencia y Tecnología.2024; 4: 924. CrossRef - Evaluation of the physicochemical properties of intracanal medications used in traumatized teeth
Patricia Almeida da Silva de Macedo, Walbert de Andrade Vieira, Paulo Henrique Gabriel, Karla de Faria Vasconcelos, Francisco Haiter Neto, Ana Carolina Correia Laurindo de Cerqueira Neto, Brenda Paula Figueiredo de Almeida Gomes, Marcos Roberto dos Santo
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2024; 23: e242997. CrossRef - Treatment of Teeth with Root Resorptions: A Case Report and Systematic Review
Damla Erkal, Abdullah Başoğlu, Damla Kırıcı, Nezahat Arzu Kayar, Simay Koç, Kürşat Er
Galician Medical Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Successful outcome of permanent maxillary incisor reimplanted after 30 hours of extra‐oral time—a case report with 5‐year follow‐up
Ibadat Preet Kaur, Ashok Kumar, Mukul Kumar, Kanistika Jha
Clinical Case Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Replantation of an Avulsed Tooth: A Case Report
Nishad Kadulkar, Rubi Kataki, Adrija Deka, Salouno Thonai
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Avulsion of Permanent Mandibular Incisors: A Report of Two Cases with Pertinent Literature
Ibadat Preet Kaur, Jitendra Sharan, Pallawi Sinha, Ashok Kumar, Anand Marya, Leandro Napier de Souza
Case Reports in Dentistry.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - The Impact of Autologous Platelet Concentrates on the Periapical Tissues and Root Development of Replanted Teeth: A Systematic Review
Zohaib Khurshid, Faris Yahya I. Asiri, Shariq Najeeb, Jithendra Ratnayake
Materials.2022; 15(8): 2776. CrossRef
- Endodontic Intracanal Medicaments and Agents
- 4,035 View
- 85 Download
- 13 Crossref

- Effects of the cathepsin K inhibitor with mineral trioxide aggregate cements on osteoclastic activity
- Hee-Sun Kim, Soojung Kim, Hyunjung Ko, Minju Song, Miri Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(2):e17. Published online April 23, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e17
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
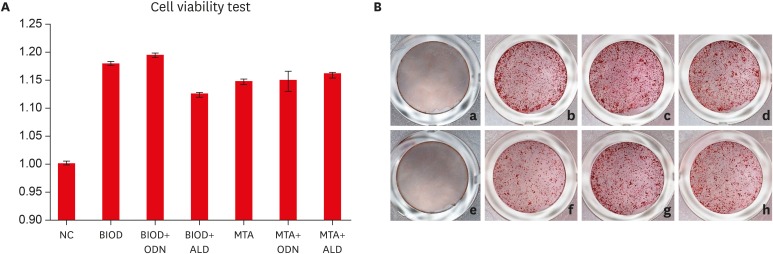
ePub Objectives Root resorption is an unexpected complication after replantation procedures. Combining anti-osteoclastic medicaments with retrograde root filling materials may avert this resorptive activity. The purpose of this study was to assess effects of a cathepsin K inhibitor with calcium silicate-based cements on osteoclastic activity.
Methods MC3T3-E1 cells were cultured for biocompatibility analyses. RAW 264.7 cells were cultured in the presence of the receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B and lipopolysaccharide, followed by treatment with Biodentine (BIOD) or ProRoot MTA with or without medicaments (Odanacatib [ODN], a cathepsin inhibitor and alendronate, a bisphosphonate). After drug treatment, the cell counting kit-8 assay and Alizarin red staining were performed to evaluate biocompatibility in MC3T3-E1 cells. Reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction, tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) staining and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays were performed in RAW 264.7 cells to determine the expression levels of inflammatory cytokines, interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2). Data were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance and Tukey's
post hoc test (p < 0.05).Results Biocompatibility results showed that there were no significant differences among any of the groups. RAW 264.7 cells treated with BIOD and ODN showed the lowest levels of TNF-α and PGE2. Treatments with BIOD + ODN were more potent suppressors of inflammatory cytokine expression (
p < 0.05).Conclusion The cathepsin K inhibitor with calcium silicate-based cement inhibits osteoclastic activity. This may have clinical application in preventing inflammatory root resorption in replanted teeth.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Root-filling materials for endodontic surgery: biological and clinical aspects
Andreas Koutroulis, Vasileios Kapralos, Dag Ørstavik, Pia Titterud Sunde
Biomaterial Investigations in Dentistry.2024; 11: 115. CrossRef - Effect of intra‐alveolar delivery of Frondoside A on inflammatory response of delayed tooth replantation
Lan Herr, Ju Ri Ye, Sang Wook Kang, Sang Tae Ro, Yong Kwon Chae, Ko Eun Lee, Mi Sun Kim, Myeong Kwan Jih, Chunui Lee, Sung Chul Choi, Ok Hyung Nam
Dental Traumatology.2024; 40(2): 178. CrossRef - Bone-targeting PLGA derived lipid drug delivery system ameliorates bone loss in osteoporotic ovariectomized rats
Youyun Zeng, Yiding Shen, Shuyi Wu, Lei Cai, Zhen Wang, Kexin Cai, Jiating Shen, Kendrick Hii Ru Yie, Hualin Zhang, Lihua Xu, Jinsong Liu
Materials & Design.2022; 221: 110967. CrossRef
- Root-filling materials for endodontic surgery: biological and clinical aspects
- 1,558 View
- 8 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Surgical management of a failed internal root resorption treatment: a histological and clinical report
- Saeed Asgary, Mohammad Jafar Eghbal, Leili Mehrdad, Sanam Kheirieh, Ali Nosrat
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(2):137-142. Published online March 21, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.2.137
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This article presents the successful surgical management of a failed mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) orthograde obturation of a tooth with a history of impact trauma and perforated internal root resorption. A symptomatic maxillary lateral incisor with a history of perforation due to internal root resorption and nonsurgical repair using MTA was referred. Unintentional overfill of the defect with MTA had occurred 4 yr before the initial visit. The excess MTA had since disappeared, and a radiolucent lesion adjacent to the perforation site was evident radiographically. Surgical endodontic retreatment was performed using calcium enriched mixture (CEM) cement as a repair material. Histological examination of the lesion revealed granulation tissue with chronic inflammation, and small fragments of MTA encapsulated within fibroconnective tissue. At the one and two year follow up exams, all signs and symptoms of disease had resolved and the tooth was functional. Complete radiographic healing of the lesion was observed two years after the initial visit. This case report illustrates how the selection of an appropriate approach to treatment of a perforation can affect the long term prognosis of a tooth. In addition, extrusion of MTA into a periradicular lesion should be avoided.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Managing Internal Inflammatory Root Resorption and Perforation of a Mandibular Primary Molar: A Case Report With 15 Months Follow‐Up
Mana Mowji, Motahareh Khosrojerdi
Clinical Case Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Endodontic management of internal replacement resorption of two maxillary central incisors with the aid of cone-beam computed tomography as the diagnostic tool: a case report and review of literature
Fatemeh Eskandari, Safoora Sahebi, Negar Ghorbani Jahandizi, Hossein Mofidi
Journal of Medical Case Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Removal of AH Plus Bioceramic Sealer from Artificial Internal Resorption Cavities Using Different Irrigation Activation Systems
Mine Büker, Meltem Sümbüllü, Emine Şimşek, Fadime Sena Sezer
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2025; 28(3): 383. CrossRef - Evaluation of the effectiveness of different supplemental cleaning techniques in the retreatment of roots with small simulated internal resorption cavities: an in vitro comparative study
Sine Güngör Us, Özgür Uzun, Nazlı Merve Güngör
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comprehensive review of composition, properties, clinical applications, and future perspectives of calcium-enriched mixture (CEM) cement: a systematic analysis
Saeed Asgary, Mahtab Aram, Mahta Fazlyab
BioMedical Engineering OnLine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The various forms of tooth resorption
Jordan Samuel Blum
Australian Endodontic Journal.2024; 50(2): 191. CrossRef - Bioceramics in Endodontics: Updates and Future Perspectives
Xu Dong, Xin Xu
Bioengineering.2023; 10(3): 354. CrossRef - Imaging techniques and various treatment modalities used in the management of internal root resorption: A systematic review
R. S Digholkar, S D Aggarwal, P S Kurtarkar, P. B Dhatavkar, V L Neil, D N Agarwal
Endodontology.2023; 35(2): 85. CrossRef - Treatment of Teeth with Root Resorptions: A Case Report and Systematic Review
Damla Erkal, Abdullah Başoğlu, Damla Kırıcı, Nezahat Arzu Kayar, Simay Koç, Kürşat Er
Galician Medical Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of calcium silicate cements on neuronal conductivity
Derya Deniz-Sungur, Mehmet Ali Onur, Esin Akbay, Gamze Tan, Fügen Daglı-Comert, Taner Cem Sayın
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Mineral trioxide aggregate and other bioactive endodontic cements: an updated overview – part II: other clinical applications and complications
M. Torabinejad, M. Parirokh, P. M. H. Dummer
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(3): 284. CrossRef - Periodontal healing following non-surgical repair of an old perforation with pocket formation and oral communication
Saeed Asgary, Prashant Verma, Ali Nosrat
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Conservative Management of Class 4 Invasive Cervical Root Resorption Using Calcium-enriched Mixture Cement
Saeed Asgary, Ali Nosrat
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(8): 1291. CrossRef - Importance of CBCT in the management plan of upper canine with internal resorption
Roberto Fornara, Dario Re Cecconi
Giornale Italiano di Endodonzia.2015; 29(2): 70. CrossRef
- Managing Internal Inflammatory Root Resorption and Perforation of a Mandibular Primary Molar: A Case Report With 15 Months Follow‐Up
- 2,217 View
- 14 Download
- 14 Crossref

- Enamel matrix derivative for replanted teeth in animal models: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Sahng G. Kim, Steven I. Ryu
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(4):194-203. Published online November 12, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.4.194
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives To investigate the effect of enamel matrix derivative (EMD) on periodontal healing of replanted teeth in animal models.
Materials and Methods The authors searched MEDLINE, PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, Web of Knowledge and Scopus for articles published up to Oct 2012. Animal studies in which EMD was applied in transplanted or replanted teeth with adequate controls and histological data were considered. Normal periodontal healing or root resorption determined by histology after EMD was applied in replanted teeth with adequate controls was used as outcome measures. The following search strategy was used: ('Emdogain' OR 'enamel matrix proteins' OR 'enamel matrix derivative') AND ('avulsion' OR 'transplantion' OR 'autotransplantation' OR 'replantation').
Results Six animal studies were included in the final review. There was great heterogeneity in study design among included studies. Two studies with similar study designs were identified and analyzed by a meta-analysis. The pooled estimates showed a significantly higher normal healing and surface resorption and significantly less inflammatory and replacement resorption in EMD-treated groups compared with non-EMD-treated groups.
Conclusions With the limitations of this systematic review, the use of EMD led to greater normal periodontal healing and surface root resorption and less inflammatory and replacement root resorption in the presence of periodontal ligaments. However, no definite conclusion could be drawn with regard to the effect of EMD on periodontal healing and root resorption when no periodontal ligaments exist.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Intentional Replantation of Failed Root Canal Treated Tooth
Pritesh Kisanlal Agrawal, Narayan G. Jibhkate, Saurabh A. Redij
Journal of Interdisciplinary Dentistry.2024; 14(2): 128. CrossRef - Enamel matrix derivative in the treatment of tooth replantation: from a biological basis to clinical application
Yao Lin, Liangping Chen, Yuling Xu, Mingwei Xu, Qinghua Liu, Junbing He
Annals of Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Fibrillin protein, a candidate for creating a suitable scaffold in PDL regeneration while avoiding ankylosis
Kyoko Oka
genesis.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Can delayed grafting of frozen teeth achieve periodontal ligament healing?
Yue Chen, Liang Chen, Min Zhou, Shouyin Yi, Juan Ran, Yuansi Long, Jing Luo, Kun Tian
Medical Hypotheses.2022; 167: 110945. CrossRef - Permanent tooth avulsion in children and adults: Therapeutic options for longer survival
Simona Stojanović, Miloš Tijanić, Kristina Burić, Nina Burić, Milan Spasić, Kosta Todorović, Branislava Stojković, Marija Jovanović, Milica Petrović, Dušan Mitić
Acta stomatologica Naissi.2021; 37(83): 2213. CrossRef - Evidence mapping and quality assessment of systematic reviews in dental traumatology
Nitesh Tewari, Vijay Prakash Mathur, Amandeep Kaur, Divesh Sardana, Morankar Rahul, Rigzen Tamchos, Priyanshi Ritwik, Shubhi Goel, Julie Schiavo
Dental Traumatology.2021; 37(1): 17. CrossRef - Application of Enamel Matrix Derivative (Emdogain) in Endodontic Therapy: A Comprehensive Literature Review
Howard H. Wang, Nima D. Sarmast, Elham Shadmehr, Nikola Angelov, Shahrokh Shabahang, Mahmoud Torabinejad
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(7): 1066. CrossRef - Periodontal wound healing following reciprocal autologous root transplantation in class III furcation defects
Naoshi Takeuchi, Yoshinori Shirakata, Yukiya Shinohara, Kotaro Sena, Kazuyuki Noguchi
Journal of Periodontal & Implant Science.2017; 47(6): 352. CrossRef - Effects of Fibrillin Application on Periodontal Ligament Regeneration in Mouse Model of Tooth Replantation
Shougo Tamura, Kyoko Oka, Satoshi Itaya, Michiko Kira-Tatsuoka, Masako Toda, Arisa Higa, Masao Ozaki
Journal of Hard Tissue Biology.2016; 25(3): 295. CrossRef - Autotransplantation: a viable treatment option for adolescent patients with significantly compromised teeth
D Ong, Y Itskovich, G Dance
Australian Dental Journal.2016; 61(4): 396. CrossRef - Influence of enamel matrix derivative on healing of root surfaces after bonding treatment and intentional replantation of vertically fractured roots
Tsutomu Sugaya, Mahito Tomita, Youji Motoki, Hirofumi Miyaji, Masamitsu Kawamami
Dental Traumatology.2016; 32(5): 397. CrossRef - The effect of cathepsin K inhibitor on osteoclastic activity compared to alendronate and enamel matrix protein
Wonkyung Yang, Hyunjung Ko, Heesun Kim, Miri Kim
Dental Traumatology.2015; 31(3): 202. CrossRef - The effects of bone morphogenetic protein-2 and enamel matrix derivative on the bioactivity of mineral trioxide aggregate in MC3T3-E1cells
Youngdan Jeong, Wonkyung Yang, Hyunjung Ko, Miri Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(3): 187. CrossRef - What is the Best Root Surface Treatment for Avulsed Teeth?
Elif B Tuna , Duygu Yaman , Seiko Yamamato
The Open Dentistry Journal.2014; 8(1): 175. CrossRef
- Intentional Replantation of Failed Root Canal Treated Tooth
- 1,699 View
- 4 Download
- 14 Crossref

- Invasive cervical resorption: treatment challenges
- Yookyung Kim, Chan-Young Lee, Euiseong Kim, Byoung-Duck Roh
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(4):228-231. Published online November 21, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.4.228
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Invasive cervical resorption is a relatively uncommon form of external root resorption. It is characterized by invasion of cervical region of the root by fibrovascular tissue derived from the periodontal ligament. This case presents an invasive cervical resorption occurring in maxillary lateral incisor, following damage in cervical cementum from avulsion and intracoronal bleaching procedure. Flap reflection, debridement and restoration with glass ionomer cement were performed in an attempt to repair the defect. But after 2 mon, more resorption extended apically. Considering root stability and recurrence potential, we decided to extract the tooth. Invasive cervical resorption in advanced stages may present great challenges for clinicians. Therefore, prevention and early detection must be stressed when dealing with patients presenting history of potential predisposing factors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Features of external root resorption as predictors of disease progression: A CBCT cross-sectional study
Tânia Maria Soares Reis, Daniella Ribeiro Ferrari, Rafael Binato Junqueira, Priscila Dias Peyneau, Eduardo Murad Villoria, Maria Augusta Visconti, Francielle Silvestre Verner
Odontology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Outcome of Decoronation in Severe Cases of External Cervical Root Resorption in Young Patients
Dina Moss, Eyal Nuni, Hagay Slutzky, Daniel Moreinos, Iris Slutzky-Goldberg
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Surgical repair of external cervical resorption - Prognosis and prognostic factors
Po-Yuan Jeng, Shu-Hui Chang, Chen-Ying Wang, Li-Deh Lin, Jiiang-Huei Jeng, Yi-Ling Tsai
Journal of Dental Sciences.2024; 19(1): 377. CrossRef - The Disease Process, Diagnosis and Treatment of Invasive Cervical Resorption: A Review
Olivia Rotondi, PhiAnh Waldon, Sahng G. Kim
Dentistry Journal.2020; 8(3): 64. CrossRef - Combined endodontic and periodontal management of a class 3 invasive cervical resorption in a mandibular first molar
Takayoshi Nagahara, Katsuhiro Takeda, Yusuke Aida, Tomoyuki Iwata, Ryoichi Yagi, Hidemi Kurihara, Hideki Shiba
Clinical Case Reports.2018; 6(10): 2005. CrossRef - External cervical resorption: a three‐dimensional classification
S. Patel, F. Foschi, F. Mannocci, K. Patel
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(2): 206. CrossRef - Invasive cervical resorption and the oro-facial cleft patient: a review and case series
A. O'Mahony, C. McNamara, A. Ireland, J. Sandy, J. Puryer
British Dental Journal.2017; 222(9): 677. CrossRef - Characteristics and treatment of invasive cervical resorption in vital teeth. A narrative review and a report of two cases
P. Tsaousoglou, E. Markou, N. Efthimiades, I. Vouros
British Dental Journal.2017; 222(6): 423. CrossRef - Fifteen-year Clinical Follow-up of Restoration of Extensive Cervical Resorption in a Maxillary Central Incisor
EG Reston, RPR Bueno, LQ Closs, J Zettermann
Operative Dentistry.2017; 42(2): E55. CrossRef - The Assessment and Management of External Cervical Resorption with Periapical Radiographs and Cone-beam Computed Tomography: A Clinical Study
Kreena Patel, Francesco Mannocci, Shanon Patel
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(10): 1435. CrossRef - Management of invasive cervical resorption in a maxillary central incisor
SSenthil Kumar, NS Mohan Kumar, JV Karunakaran, S Nagendran
Journal of Pharmacy And Bioallied Sciences.2015; 7(6): 712. CrossRef
- Features of external root resorption as predictors of disease progression: A CBCT cross-sectional study
- 2,319 View
- 14 Download
- 11 Crossref

- The verification of the MTT assay on the viability of periodontal ligamental cells in rat molars through the histologic examination
- Hyun-Ki Kim, Eui-Seoung Kim, In-Bok Choi, Jin Kim, Seung-Jong Lee
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2003;28(5):385-391. Published online September 30, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.5.385
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study is to examine the viability of PDL cells in rat molars by using MTT assay and to verify the MTT assay through the histologic observation. Thirty of Sprague-Dawley white female rats of 4-weeks old with a body weight of about 100 grams were used. Groupings are as follows:
Immediate Group : Positive control group(n=10)-after extraction immediately.
Dried Group : Negative control group(n=10)-after drying for an hour under warm dry.
ViaSpan® Group : 1hour ViaSpan® group(n=10)-after storing in ViaSpan® at 4℃ for 1hour.
Ten teeth of each group were treated as same as above and replanted to the original socket of experimental animals. After two weeks of replantation, all the experimental animals were sacrificed. And after fixation, extracted maxillary jaw was dimineralized. After it was embedded in paraffin, serial section by 5µm was carried out and for construction of specimen, hematoxylin-eosin dye was used.
The mean MTT measurement of immediate group(positive control) is 2.81 and the mean measurement of dried group(negative control) is 0.98 which is significant differnt(P<0.05). The mean measurement of ViaSpan® group is 2.65 and there is significant difference between dried group and ViaSpan® group(P<0.05). However, there is no difference between immediate group and ViaSpan® group. The average resorption points of immediate group is 3.03 points. In the dried group, average 6.44 points resorption and 2.68 points showed resorption in the ViaSpan® group. Unlike with MTT assay, there was no significant difference between the immediate group and ViaSpan® group.
The usage of MTT assay as a viable cell marker may give us a better indication of the maintenance of periodontal ligament cell vitality.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Concentration of propolis as a storage medium for avulsed teeth: a systematic review
Chaya Chhabra, Kumar Gaurav Chhabra, Seemadevi Thangeswaran, Shraddha Shere
Frontiers in Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Trichosanthis Radix Extract on Collagen Production
Mi-Young Yun, Hye-Won Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Cosmetology.2024; 30(2): 408. CrossRef - Evaluation of periodontal ligament cell viability in rat teeth according to various extra-oral dry storage times using MTT assay
In-Soo Jeon, Eui-Seong Kim, Jin Kim, Seung-Jong Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2006; 31(5): 398. CrossRef
- Concentration of propolis as a storage medium for avulsed teeth: a systematic review
- 1,041 View
- 2 Download
- 3 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


