Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Bibliometric analysis of the GentleWave system: trends, collaborations, and research gaps
- Raimundo Sales de Oliveira Neto, Thais de Moraes Souza, João Vitor Oliveira de Amorim, Thaine Oliveira Lima, Guilherme Ferreira da Silva, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, Murilo Priori Alcalde, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(2):e17. Published online May 12, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e17
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
The study aimed to conduct a bibliometric analysis of the GentleWave system (Sonendo, Inc.).
Methods
An electronic search was conducted in June 2024 using the Web of Science Collection database. Two reviewers independently screened publications, extracting data on authorship, publication details, study design, and citation metrics. Statistical analyses were performed in R to assess variable correlations, while the VOSviewer (Visualization of Similarities Viewer) software was used to map author and keyword networks.
Results
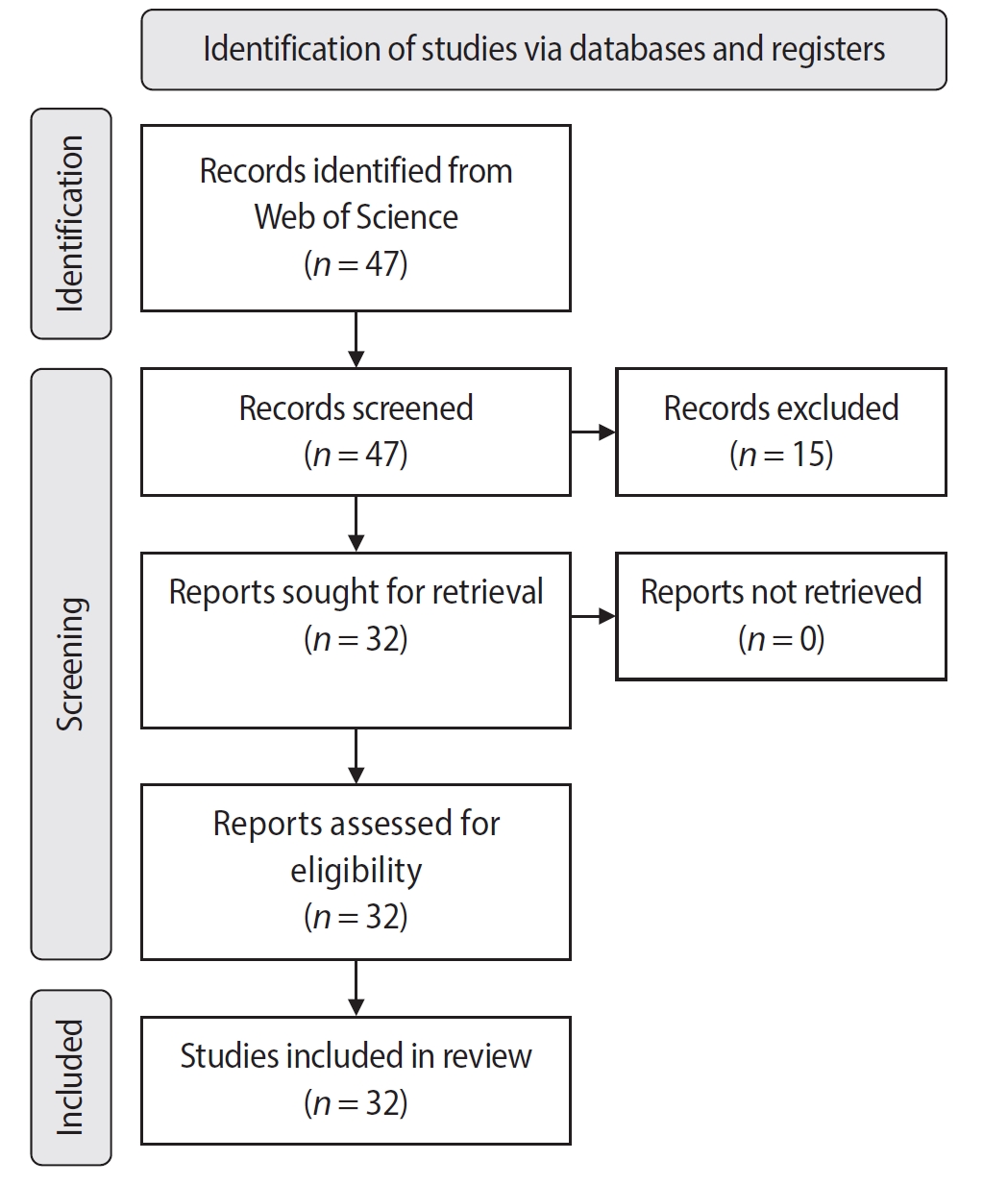
The search yielded 47 records, with 32 studies included. Publications spanned 2014 to 2024. The Journal of Endodontics published the highest number of studies (n = 15), and the International Endodontic Journal had the highest impact factor (5.4). The University of British Columbia and Sonendo, Inc. were the most frequent affiliations. Among the 32 articles, 28 were in vitro studies, primarily focusing on microbiology (n = 9). A total of 95 authors were identified, with Haapasalo and Shen being the most cited (n = 229). The articles accumulated 495 citations, demonstrating a strong positive correlation between the number of studies and citation counts (r = 0.98).
Conclusions
The analysis highlights a predominance of in vitro studies. Geographic concentration in the United States and Canada limits diversity, while the strong correlation between study numbers and citations suggests that increased publication volume enhances visibility. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Three-year Outcomes of Conventional Versus Minimally Invasive Endodontic Treatment Protocols: A Retrospective Study
Kiavash Hossini, He Liu, Ya Shen, Jolanta Aleksejuniene, Fahda Algahtani, Ahmed Hieawy
Journal of Endodontics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Three-year Outcomes of Conventional Versus Minimally Invasive Endodontic Treatment Protocols: A Retrospective Study
- 3,506 View
- 87 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Effect of irrigation protocols on smear layer removal, bond strength and nanoleakage of fiber posts using a self-adhesive resin cement
- Rodrigo Stadler Alessi, Renata Terumi Jitumori, Bruna Fortes Bittencourt, Giovana Mongruel Gomes, João Carlos Gomes
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(3):e28. Published online July 27, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e28
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
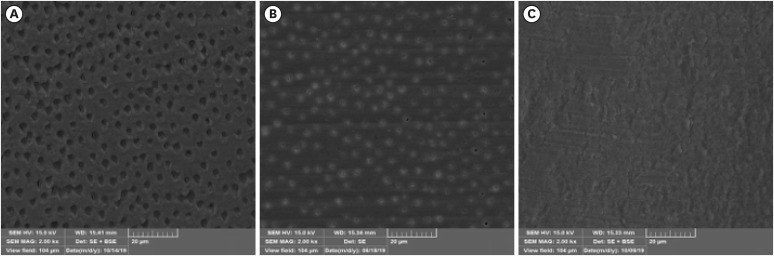
ePub Objectives This study aimed to investigate the effect of the application method of 2% chlorhexidine (CHX) and its influence on the adhesion of fiberglass posts cemented with a self-adhesive resin cement.
Materials and Methods Sixty human mandibular premolars were endodontically treated and divided into 5 groups (
n = 12), according to the canal irrigant and its application method: 2 groups with conventional syringe irrigation (CSI)—2.5% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) (control) and 2% CHX— and 3 groups with 2% CHX irrigation/activation—by passive ultrasonic irrigation (PUI), Easy Clean file, and XP-Endo Finisher file. Two roots per group were evaluated for smear layer (SL) removal by scanning electron microscopy. For other roots, fiber posts were luted using a self-adhesive resin cement. The roots were sectioned into 6 slices for push-out bond strength (BS) (7/group) and nanoleakage (NL) (3/group). Data from SL removal were submitted to Kruskal-Wallis and Student-Newman-Keuls tests (α = 0.05). Data from BS and NL were evaluated by 2-way analysis of variance and Tukey’s test (α = 0.05).Results For SL removal and BS, the CHX irrigation/activation promoted better values than CSI with CHX (
p < 0.05), but it was not significantly different from CSI with NaOCl (p > 0.05). For NL, the lowest values were obtained by the chlorhexidine irrigation/activation groups (p < 0.05).Conclusions Active 2% CHX irrigation can be used to improve the post space cleaning and adhesion before fiber post cementation with self-adhesive resin cements.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of radiotherapy dose and endodontic irrigants on universal resin cement bonding to root dentin: mechanical and interfacial analyses
Lívia Ribeiro, Luíz Carlos de Lima Dias-Júnior, Paulo Henrique dos Santos, Mariana Comparotto Minamisako, Paulo Marcelo Rodrigues, Vicente Ribeiro Netto, Bruno Alexandre Pacheco de Castro Henriques, Renata Gondo Machado, Cleonice da Silveira Teixeira, Luc
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2026; 146: 104252. CrossRef - Laser‐Activated Irrigation via Photon‐Induced Photoacoustic Streaming and Shock Wave Enhanced Emission on Smear Layer Removal Efficacy, Pushout Bond Strength, and Sealer Adaptation: A SEM Assessment
Basil Almutairi, Fahad Alkhudhairy
Microscopy Research and Technique.2025; 88(6): 1806. CrossRef - The impact of passive ultrasonic irrigation on the bond strength of two different self-etch adhesives to human pulp chamber dentine: a laboratory investigation
Mohammed Turky, Jukka Matinlinna, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska, Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Paul M. H. Dummer, Ahmad Abdel Hamid Elheeny, Nermin Alsayed Mahmoud
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of nanoparticles incorporation titanium dioxide and zirconium oxide within self-adhesive resin cement on the push-out bond strength of the fiber post to the radicular dentin: An in vitro study
Sawsan Hameed Al-Jubori, Maha Anwer AL-Murad
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2025; 15(2): 162. CrossRef - The Effects of Different Post Space Conditioning Procedures and Different Endodontic Sealers on the Push-Out Bond Strengths of Fiber Posts
Leyla Ayranci, Ahmet Serkan Küçükekenci, Fatih Sarı, Ahmet Çetinkaya
Clinical and Experimental Health Sciences.2025; 15(3): 620. CrossRef - Evaluation of Microleakage Using Different Luting Cements in Kedo Zirconia Crowns: An In Vitro Assessment
Guru Vishnu, Ganesh Jeevanandan
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Effects of radiotherapy dose and endodontic irrigants on universal resin cement bonding to root dentin: mechanical and interfacial analyses
- 3,463 View
- 69 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- The use of auxiliary devices during irrigation to increase the cleaning ability of a chelating agent
- Marina Carvalho Prado, Fernanda Leal, Renata Antoun Simão, Heloisa Gusman, Maíra do Prado
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(2):105-110. Published online February 3, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.2.105
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study investigated the cleaning ability of ultrasonically activated irrigation (UAI) and a novel activation system with reciprocating motion (EC, EasyClean, Easy Equipamentos Odontológicos) when used with a relatively new chelating agent (QMix, Dentsply). In addition, the effect of QMix solution when used for a shorter (1 minute) and a longer application time (3 minutes) was investigated.
Materials and Methods Fifty permanent human teeth were prepared with K3 rotary system and 6% sodium hypochlorite. Samples were randomly assigned to five groups (
n = 10) according to the final irrigation protocol: G1, negative control (distilled water); G2, positive control (QMix 1 minute); G3, QMix 1 minute/UAI; G4, QMix 1 minute/EC; G5, QMix 3 minutes. Subsequently the teeth were prepared and three photomicrographs were obtained in each root third of root walls, by scanning electron microscopy. Two blinded and pre-calibrated examiners evaluated the images using a four-category scoring system. Data were statistically analyzed using Kruskal-Wallis and Dunn tests (p < 0.05).Results There were differences among groups (
p < 0.05). UAI showed better cleaning ability than EC (p < 0.05). There were improvements when QMix was used with auxiliary devices in comparison with conventional irrigation (p < 0.05). Conventional irrigation for 3 minutes presented significantly better results than its use for 1 minute (p < 0.05).Conclusions QMix should be used for 1 minute when it is used with UAI, since this final irrigation protocol showed the best performance and also allowed clinical optimization of this procedure.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative Evaluation of Different Methods of Activation of Chelating Solution for Smear Layer Removal in the Apical Portion of the Root Canal Using a Scanning Electron Microscopy: An In Vitro Study
Mrunal B Alhat, Sudha B Mattigatti, Rushikesh R Mahaparale, Kapil D Wahane, Apoorva Jadhav
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Impact of Laser-Activated and Conventional Irrigation Techniques on Sealer Penetration into Dentinal Tubules
Dilara Koruk, Fatma Basmacı, Dilan Kırmızı, Umut Aksoy
Photobiomodulation, Photomedicine, and Laser Surgery.2022; 40(8): 565. CrossRef - Utilização dos atuais métodos de agitação de soluções endodônticas no canal radicular
Lívia Rodrigues Schneider, Larissa Giovanella
Revista Científica Multidisciplinar Núcleo do Conhecimento.2022; : 135. CrossRef - Smear layer removal by passive ultrasonic irrigation and 2 new mechanical methods for activation of the chelating solution
Ricardo Machado, Isadora da Silva, Daniel Comparin, Bianca Araujo Marques de Mattos, Luiz Rômulo Alberton, Ulisses Xavier da Silva Neto
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Proteomic analysis of human dental pulp in different clinical diagnosis
Poliana Amanda Oliveira Silva, Stella Maris de Freitas Lima, Mirna de Souza Freire, André Melro Murad, Octávio Luiz Franco, Taia Maria Berto Rezende
Clinical Oral Investigations.2021; 25(5): 3285. CrossRef - Effect of QMix irrigant in removal of smear layer in root canal system: a systematic review of in vitro studies
Margaret Soo Yee Chia, Abhishek Parolia, Benjamin Syek Hur Lim, Jayakumar Jayaraman, Isabel Cristina Celerino de Moraes Porto
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of 17% EDTA and QMiX ultrasonic activation on smear layer removal and sealer penetration: ex vivo study
Felipe de Souza Matos, Fabrício Rutz da Silva, Luiz Renato Paranhos, Camilla Christian Gomes Moura, Eduardo Bresciani, Marcia Carneiro Valera
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Micro-CT evaluation of different final irrigation protocols on the removal of hard-tissue debris from isthmus-containing mesial root of mandibular molars
Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Carla Rodrigues Carvalho, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Marina Carvalho Prado, Ricardo Tadeu Lopes, Gustavo De-Deus, Edson Jorge Lima Moreira
Clinical Oral Investigations.2019; 23(2): 681. CrossRef
- Comparative Evaluation of Different Methods of Activation of Chelating Solution for Smear Layer Removal in the Apical Portion of the Root Canal Using a Scanning Electron Microscopy: An In Vitro Study
- 1,394 View
- 7 Download
- 8 Crossref

-
Antibacterial effect of urushiol on
E. faecalis as a root canal irrigant - Sang-Wan Kim, Dong-Hoon Shin
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(1):54-59. Published online January 25, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.1.54

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to compare the antibacterial activity of urushiol against
Enterococcus faecalis (E. faecalis ) to that of NaOCl.Materials and Methods The canals of thirty two single rooted human teeth were instrumented with Ni-Ti files (ProTaper Next X1, X2, X3, Dentsply). A pure culture of
E. faecalis ATCC 19433 was prepared in sterile brain heart infusion (BHI) broth. The teeth were submerged in the suspension ofE. faecalis and were incubated at 37℃ for 7 days to allow biofilm formation. The teeth were randomly divided into three experimental groups according to the irrigant used, and a negative control group where no irrigant was used (n = 8). Group 1 used physiologic normal saline, group 2 used 6% NaOCl, and group 3 used 10 wt% urushiol solution. After canal irrigation, each sample was collected by the sequential placement of 2 sterile paper points (ProTaper NEXT paper points, size X3, Dentsply). Ten-fold serial dilutions on each vials, and 100 µL were cultured on a BHI agar plate for 8 hours, and colony forming unit (CFU) analysis was done. The data were statistically analyzed using Kruskal-Wallis and Mann-whitney U tests.Results Saline group exhibited no difference in the CFU counts with control group, while NaOCl and urushiol groups showed significantly less CFU counts than saline and control groups (
p < 0.05).Conclusions The result of this study suggests 10% urushiol and 6% NaOCl solution had powerful antibacterial activity against
E. faecalis when they were used as root canal irrigants.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A critical review on innovative targets for signal disruption in Enterococcus faecalis infection management
Kayeen Vadakkan, Gajanan Sampatrao Ghodake, Chin Wei Lai, Selvaraj Vijayanand, Janarthanam Hemapriya
Microbial Pathogenesis.2025; 207: 107876. CrossRef - Effect of proanthocyanidins application on push-out bond strength of root canal filling after different final irrigation procedures
Funda Fundaoğlu Küçükekenci, Ahmet Serkan Küçükekenci
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Silver-Ion-Coated Rotary Nickel Titanium Files - An In Vitro Study
Jhanvi H. Sadaria, Kondas V. Venkatesh, Dhanasekaran Sihivahanan
Indian Journal of Dental Research.2025; 36(3): 344. CrossRef - Antimicrobial efficacy of natural-based endodontic solutions: a systematic review with a network meta-analysis
Danilo Cassiano FERRAZ, Anahi de Paula MELO, Felipe de Souza MATOS, Luiz Renato PARANHOS, Camilla Christian Gomes MOURA, Cauane BLUMENBERG, Juliane Maria GUERREIRO-TANOMARU, Mário TANOMARU-FILHO
Brazilian Oral Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Irrigants and irrigation activation systems in Endodontics
Brenda P. F. A. Gomes, Emelly Aveiro, Anil Kishen
Brazilian Dental Journal.2023; 34(4): 1. CrossRef - Effectiveness of sodium hypochlorite gel and solutions in endodontics: A systematic review
Sourabh Barbhi, SR Srinidhi, Rajesh Shetty, Poonam Joshi, Vini Mehta, Sanket Aras
Endodontology.2023; 35(4): 290. CrossRef - Antibiofilm activity of phytochemicals against Enterococcus faecalis: A literature review
Islam A. A. Ali, Prasanna Neelakantan
Phytotherapy Research.2022; 36(7): 2824. CrossRef - Chemical compounds Anti-bacterial of Citrus aurantifolia Ethanol Extract to Inhibit the Early Biofilm Formation and Growth of Enterococcus faecalis Root Canal Isolate
Nur Asmah, Dewi Fatma Suniarti, Endang Winiati Bachtiar, Dewi Angraini Margono, Basri A. Gani
Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology.2022; : 2667. CrossRef - Antibacterial efficacy of silver diamine fluoride as a root canal irrigant
Ebtissam M. Al‐Madi, Manar A. Al‐Jamie, Noura M. Al‐Owaid, Amal A. Almohaimede, Albandary M. Al‐Owid
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2019; 5(5): 551. CrossRef
- A critical review on innovative targets for signal disruption in Enterococcus faecalis infection management
- 2,069 View
- 19 Download
- 9 Crossref

-
Antimicrobial and cytotoxic activity of
Ferula gummosa plant essential oil compared to NaOCl and CHX: a preliminaryin vitro study - Abbas Abbaszadegan, Ahmad Gholami, Hosein Mirhadi, Mina Saliminasab, Aboozar Kazemi, Mahmood Reza Moein
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(1):50-57. Published online December 26, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.1.50
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The usage of medicinal plants as natural antimicrobial agents has grown in many fields including dental medicine. The aim of this
in vitro study was three-fold: (i) to determine the chemical compositions of theFerula gummosa essential oil (FGEO), (ii) to compare the antimicrobial efficacy of the oil with sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) and chlorhexidine (CHX), (iii) to assess the toxic behavior of FGEO in different concentrations compared to 5% NaOCl and 0.2% CHX.Materials and Methods Gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS) was used to determine the chemical compositions of the oil. The disk diffusion method and a broth micro-dilution susceptibility assay were exploited to assess the antimicrobial efficacy against
Enterococcus faecalis ,Staphylococcus aureus ,Streptococcus mitis , andCandida albicans . The cytocompatibility of the FGEO was assessed on L929 fibroblasts, and compared to that of NaOCl and CHX.Results Twenty-seven constituents were recognized in FGEO. The major component of the oil was β-pinene (51.83%). All three irrigants significantly inhibited the growth of all examined microorganisms compared to the negative control group. FGEO at 50 µg/mL was effective in lower concentration against
Enterococcus faecalis than 5% NaOCl and 0.2% CHX, and was also more potent than 0.2% CHX againstCandida albicans andStaphylococcus aureus . FGEO was a cytocompatible solution, and had significantly lower toxicity compared to 5% NaOCl and 0.2% CHX.Conclusions FGEO showed a promising biological potency as a root canal disinfectant. More investigations are required on the effectiveness of this oil on intracanal bacterial biofilms.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Isolation, characterization and control of Botrytis spp. pathogenic on strawberry in Iran
Fatemeh Maghsoodi, Parissa Taheri, Saeed Tarighi
Heliyon.2025; 11(2): e42037. CrossRef - Novel chitosan-alginate dressings with UIO-66-NH2 nanoparticles and ferula gummosa extracts for effective wound healing
Fatemeh Mojtahedi, Mohammad Reza Nasiri, Saba Naeimaei Ali, Azadeh Mohammadgholi, Shekoufe Mohebbi, Zahra Shahbazi, Reza Behfar, Saina Namazifard, Hassan Noorbazargan, Fahimeh Baghbani-Arani
Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects.2025; 719: 137004. CrossRef -
Phytochemical analysis and bioactivity assessment of
Ferula longipes
Coss. ex Bonn. &Maury. methanolic extract: insights into antioxidant, and anti-corrosive properties
Abada Faten, Boulkroune Mina, Bicha Sabrina, Atalar Mehmet Nuri, Bensouici Chawki, Akkal Salah
Natural Product Research.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Investigation of bioactivity, biocompatibility, and antibacterial properties of a hydroxyapatite-enhanced nanocomposite for dental applications
Xin Yan, Ali ebrahimi, Reza Mohammadi, Mona Mohajeri Tehrani, Pardis Chaboki, Mohammed Mustafa, Almustafa Alhumadi, I. B. Sapaev, Ahmed Hjazi, Khadije Yousefi, Mojdeh Yousefi
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Phytochemical Profiling of Ferula varia Extract and Its Antibiofilm Activity Against Streptococcus mutans
Marlen K. Smagulov, Yana K. Levaya, Karakoz Zh. Badekova, Svetlana A. Ivasenko, Gayane A. Atazhanova, Vika Gabe, Margarita Yu. Ishmuratova, Tomas Kacergius
Molecules.2025; 30(21): 4178. CrossRef - Chemical compositions and antibacterial activity of essential oil from Ferula lapidosa korovin flowers
Kholida Khasanova, Anarbay Babekov, Komila Eshbakova, Kurbonazar Juraev, Usmonov Kamoliddin, Jaxongir Tursunov, Bokhodir Mamarasulov
Medicinal Plants - International Journal of Phytomedicines and Related Industries.2025; 17(1): 91. CrossRef - Research methods assessing sodium hypochlorite cytotoxicity: A scoping review
Hernán Coaguila-Llerena, Luana Raphael da Silva, Gisele Faria
Heliyon.2024; 10(1): e23060. CrossRef - Comparison the effect of Ferula gummosa and Chlorhexidine on dental cariogenic bacteria
bahareh nazemi salman, ali Yazdi Nejad, fakhri haghi, mahtab Mohammadi Gheydari, samira basir shabestari
journal of research in dental sciences.2024; 21(2): 125. CrossRef - Use of irrigating substances of natural origin in Endodontics
Yoneisy Abraham-Millán, Rosa María Montano-Silva, Yaima Pupo-Martínez
Salud, Ciencia y Tecnología - Serie de Conferencias.2023; 2: 591. CrossRef - Comparison effects of Ferula gummosa essential oil and Beta-pinene Alginate nanoparticles on human melanoma and breast cancer cells proliferation and apoptotic index in short term normobaric hyperoxic model
Mahmoud Osanloo, Somayyeh Pishamad, Ali ghanbariasad, Elham Zarenezhad, Media Alipanah, Hiva Alipanah
BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A promising insight into the inhibition of lipid oxidation, protein degradation and biogenic amine accumulation in postmortem fish: Functional glazing layers of modified bio-polymer
Xiaodan Hui, Yu Wan, Hao Dong, Jian Peng, Weiliang Wu, Xingfen Yang, Qi He
LWT.2023; 177: 114575. CrossRef -
Efficacy of hypochlorous acid as an alternative oral antimicrobial agent on human gingival fibroblasts,
Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans
, and
Candida albicans
biofilms
in vitro
Gözdem Bayraktar, Ayşe Mine Yılmaz Göler, Burak Aksu, Hafize Öztürk Özener
Biofouling.2023; 39(9-10): 980. CrossRef - Molecular Docking and Antibacterial Assessment of Monocyclic β‐Lactams against Broad‐Spectrum and Nosocomial Multidrug‐Resistant Pathogens
Elham Riazimontazer, Roghayeh Heiran, Aliasghar Jarrahpour, Ahmad Gholami, Zahra Hashemi, Aboozar Kazemi
ChemistrySelect.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Antioxidant and antimicrobial characteristics of chitosan and galbanum gum composite coating incorporated with cumin essential oil on the shelf life of chicken fillets
Leila Aghababaei, Maryam Hasani, Peyman Mahasti Shotorbani, Afshin Akhondzadeh Basti, Hassan Hamedi
Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization.2022; 16(3): 1820. CrossRef - Assessing edible composite coating of sodium alginate–galbanum gum impregnated with nettle extract on improving the shelf life of rainbow trout fillet
Maliheh Zarandi, Maryam Hasani, Peyman Mahasti Shotorbani, Afshin Akhondzadeh Basti, Hassan Hamedi
Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization.2022; 16(4): 2556. CrossRef - Antibacterial Activity of Essential Oils against Oral Pathogens
Thaís A. S. Oliveira, Mariana B. Santiago, Valmore H. P. Santos, Eliane O. Silva, Carlos H. G. Martins, Antônio E. M. Crotti
Chemistry & Biodiversity.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolic Profile, Bioactivities, and Variations in the Chemical Constituents of Essential Oils of the Ferula Genus (Apiaceae)
Priyankaraj Sonigra, Mukesh Meena
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Cytotoxicity and Gene Expression Changes of a Novel Homeopathic Antiseptic Oral Rinse in Comparison to Chlorhexidine in Gingival Fibroblasts
Masako Fujioka-Kobayashi, Benoit Schaller, Michael A. Pikos, Anton Sculean, Richard J. Miron
Materials.2020; 13(14): 3190. CrossRef - Current herbal medicine as an alternative treatment in dentistry: In vitro, in vivo and clinical studies
Ehsan Tafazoli Moghadam, Mohsen Yazdanian, Elahe Tahmasebi, Hamid Tebyanian, Reza Ranjbar, Alireza Yazdanian, Alexander Seifalian, Ali Tafazoli
European Journal of Pharmacology.2020; 889: 173665. CrossRef - A review of Ferula species: Biochemical characteristics, pharmaceutical and industrial applications, and suggestions for biotechnologists
Maryam Salehi, Mohammad Reza Naghavi, Moslem Bahmankar
Industrial Crops and Products.2019; 139: 111511. CrossRef - Investigation effects of extracted compounds from shell and cluster of pistachio nut on the inactivation of free radicals
Morteza Mohammadi, Mohammad Ghorbani, Adel Beigbabaei, Samira Yeganehzad, Alireza Sadeghi-Mahoonak
Heliyon.2019; 5(9): e02438. CrossRef - Effect of Irrigation Time of Antiseptic Solutions on Bone Cell Viability and Growth Factor Release
Kosaku Sawada, Ken Nakahara, Maiko Haga-Tsujimura, Masako Fujioka-Kobayashi, Tateyuki Iizuka, Richard J. Miron
Journal of Craniofacial Surgery.2018; 29(2): 376. CrossRef - Mining Ferula gummosa transcriptome to identify miRNAs involved in the regulation and biosynthesis of terpenes
Ahmad Sobhani Najafabadi, Mohammad Reza Naghavi
Gene.2018; 645: 41. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Persea major Kopp (Lauraceae) extract against Enterococcus faecalis: a preliminary in vitro study
Lusiane Volpato, Marilisa Carneiro Leão Gabardo, Denise Piotto Leonardi, Paulo Henrique Tomazinho, Leila Teresinha Maranho, Flares Baratto-Filho
BMC Research Notes.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Epigallocatechin Gallate, an Antibacterial Cross-linking Agent, on Proliferation and Differentiation of Human Dental Pulp Cells Cultured in Collagen Scaffolds
Young-Sun Kwon, Hee-Jin Kim, Yun-Chan Hwang, Vinicius Rosa, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kyung-San Min
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(2): 289. CrossRef - A novel bioactive edible coating based on sodium alginate and galbanum gum incorporated with essential oil of Ziziphora persica: The antioxidant and antimicrobial activity, and application in food model
Hassan Hamedi, Mina Kargozari, Peyman Mahasti Shotorbani, Nima Babolani Mogadam, Maryam Fahimdanesh
Food Hydrocolloids.2017; 72: 35. CrossRef - Antimicrobial and Cytotoxic Activity of Cinnamomum zeylanicum, Calcium Hydroxide, and Triple Antibiotic Paste as Root Canal Dressing Materials
Abbas Abbaszadegan, Sahar Dadolahi, Ahmad Gholami, Mahmoud Reza Moein, Shahram Hamedani, Younes Ghasemi, Paul Vincent Abbott
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2016; 17(2): 105. CrossRef - Natural Therapeutic Options in Endodontics - A Review
Nagendrababu Venkateshbabu, Suresh Anand, Mohan Abarajithan, Sultan O. Sheriff, Pulikkotil S. Jacob, Nath Sonia
The Open Dentistry Journal.2016; 10(1): 214. CrossRef - Ferula gummosa, a Traditional Medicine with Novel Applications
Mohaddese Mahboubi
Journal of Dietary Supplements.2016; 13(6): 700. CrossRef - Effects of Antiseptic Solutions Commonly Used in Dentistry on Bone Viability, Bone Morphology, and Release of Growth Factors
Kosaku Sawada, Masako Fujioka-Kobayashi, Eizaburo Kobayashi, Benoit Schaller, Richard J. Miron
Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.2016; 74(2): 247. CrossRef - Antiseptic solutions modulate the paracrine‐like activity of bone chips: differential impact of chlorhexidine and sodium hypochlorite
Kosaku Sawada, Jordi Caballé‐Serrano, Dieter D. Bosshardt, Benoit Schaller, Richard J. Miron, Daniel Buser, Reinhard Gruber
Journal of Clinical Periodontology.2015; 42(9): 883. CrossRef - Tributyl tetradecyl phosphonium chloride for biofouling control in reverse osmosis processes
Taek-Seung Kim, Hee-Deung Park
Desalination.2015; 372: 39. CrossRef
- Isolation, characterization and control of Botrytis spp. pathogenic on strawberry in Iran
- 2,339 View
- 10 Download
- 32 Crossref

- Accuracy of Root ZX in teeth with simulated root perforation in the presence of gel or liquid type endodontic irrigant
- Hyeong-Soon Shin, Won-Kyung Yang, Mi-Ri Kim, Hyun-Jung Ko, Kyung-Mo Cho, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(3):149-154. Published online August 29, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.3.149
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives To evaluate the accuracy of the Root ZX in teeth with simulated root perforation in the presence of gel or liquid type endodontic irrigants, such as saline, 5.25% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl), 2% chlorhexidine liquid, 2% chlorhexidine gel, and RC-Prep, and also to determine the electrical conductivities of these endodontic irrigants.
Materials and Methods A root perforation was simulated on twenty freshly extracted teeth by means of a small perforation made on the proximal surface of the root at 4 mm from the anatomic apex. Root ZX was used to locate root perforation and measure the electronic working lengths. The results obtained were compared with the actual working length (AWL) and the actual location of perforations (AP), allowing tolerances of 0.5 or 1.0 mm. Measurements within these limits were considered as acceptable. Chi-square test or the Fisher's exact test was used to evaluate significance. Electrical conductivities of each irrigant were also measured with an electrical conductivity tester.
Results The accuracies of the Root ZX in perforated teeth were significantly different between liquid types (saline, NaOCl) and gel types (chlorhexidine gel, RC-Prep). The accuracies of electronic working lengths in perforated teeth were higher in gel types than in liquid types. The accuracy in locating root perforation was higher in liquid types than gel types. 5.25% NaOCl had the highest electrical conductivity, whereas 2% chlorhexidine gel and RC-Prep gel had the lowest electrical conductivities among the five irrigants.
Conclusions Different canal irrigants with different electrical conductivities may affect the accuracy of the Root ZX in perforated teeth.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- In Vivo and In Vitro Accuracy and Precision Evaluations of Mini Electronic Apex Locators
Özlem Kara, Rüstem Kemal Sübay
Australian Endodontic Journal.2025; 51(2): 329. CrossRef - Effect of different kinematics and perforation diameter on integrated electronic apex locator accuracy in detecting root canal perforations
Ecenur Tuzcu, Safa Kurnaz
European Journal of Oral Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of precipitate formation in the root canal on the accuracy of electronic apex locators
Kürşat Er, Simay Koç, Damla Erkal, Dide Tekinarslan, Ömer Kesmez, Feride Demir, Eszther Borbely
Journal of Oral Science.2025; 67(4): 161. CrossRef - Effect of Different Electroconductive Root Canal Irrigations on the Accuracy of Different Apex Locators: An In Vitro Comparative Study
Eman M. Yahya, Ashraf S. Alchalabi, Emad Farhan Alkhalidi
Journal of International Society of Preventive and Community Dentistry.2024; 14(3): 211. CrossRef - The precision of radiographic and electronic working length estimation methods in endodontics: A systematic review of clinical studies
Anithakumari Rangappa, Buvaneshwari Arul, Jayalakshmi Somasundaram, Velmurugan Natanasabapathy
Endodontology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of the accuracy of electronic apex locators and cone-beam computed tomography in detection of root canal perforation and working length during endodontic retreatment
Simay Koç, Hatice Harorlı, Alper Kuştarcı
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Accuracy and Reliability of Three Electronic Apex Locators in Determining the Apical Constriction of Molar Canals: A Micro-CT Evaluation
Reem M. Barakat, Rahaf A. Almohareb, Arwa O. Alharbi, Asma Alhazmi, Reem Alomar
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(17): 5199. CrossRef - Accuracy of the integrated electronic apex locator in locating simulated perforation under various irrigating solutions in an in vitro study
Chintan Joshi, Surabhi Joshi, Urooj Desai, Sweety Thumar, Aashray Patel, Ankita Khunt
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2024; 23: e241118. CrossRef - The Accuracy of Different Apex Locator Systems in Detecting Root Perforations in the Presence of Different Irrigation Solutions
Oğuz Burhan Çetinkaya, Emre Çulha, Uğur Aydın
European Journal of Therapeutics.2023; 30(1): 39. CrossRef - In Vitro Comparison of the Accuracy of Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Scanning and Electronic Apex Locators in Detection of Simulated Root Perforations in Different Localizations
Hatice Harorlı, Simay Koç, Alper Kuştarcı
Journal of Endodontics.2023; 49(12): 1676. CrossRef - Accuracy of different electronic apex locators in determination of minimum Root perforation diameter
Simay Koç, Alper Kuştarcı, Kürşat Er
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(S1): 179. CrossRef - The influence of MTAD and QMix on the accuracy of electronic apex locator in locating simulated perforations
A Dumani, AA Ates, CS Ucan, S Yilmaz, I Unal, O Yoldas
Nigerian Journal of Clinical Practice.2022; 25(3): 281. CrossRef - Synthesis and evaluation of grafted xanthan gum as a drug carrier in developing lornoxicam gel formulations
SandipAshok Murtale, PrakashS Goudanavar, NRaghavendra Naveen, WalaaF Alsanie, Majid Alhomrani, AbdulhakeemS Alamri, SyedMohammed Basheeruddin Asdaq, MdKhalid Anwer, Nagaraja Sreeharsha, MazenAl Gharsan, Santosh Fattepur
Pharmacognosy Magazine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - KOMBİNE İRRİGASYON SOLÜSYONLARININ ELEKTRİKSEL İLETKENLİĞİNİN KARŞILAŞTIRILMASI
Ayşin DUMANİ, Şehnaz YILMAZ, Oğuz YOLDAŞ, Güray KILINÇÇEKER
Atatürk Üniversitesi Diş Hekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi.2022; : 1. CrossRef - Accuracy of electronic apex locator in the presence of different irrigating solutions
Padmanabh Jha, Vineeta Nikhil, Shalya Raj, Rohit Ravinder, Preeti Mishra
Endodontology.2021; 33(4): 232. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Accuracy of Different Apex Locators: Propex IQ, Raypex 6, Root ZX, and Apex ID with CBCT and Periapical Radiograph—In Vitro Study
Okba Mahmoud, Mawada Hassan Awad Abdelmagied, Ahmad Hisham Dandashi, Bakr Nssaief Jasim, Hussam Alddin Tawfik Kayali, Saaid Al Shehadat, Luca Testarelli
International Journal of Dentistry.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Evaluation of Temperature Increase From Joule Heat in Numerical Tooth Model by Applying 500 kHz Current for Apical Periodontitis Treatment—Effect of Applied Voltage and Tooth Conductivity
Hiroo Tarao, Masatake Akutagawa, Takahiro Emoto, Amane Takei, Hiromichi Yumoto, Toshihiko Tominaga, Toshitaka Ikehara, Yosuke Kinouchi
Bioelectromagnetics.2021; 42(3): 224. CrossRef - Confort visual en oficinas, factor temporal en la evaluación de deslumbramiento
J. Yamin, A. Pattini, E. Colombo
Informes de la Construcción.2020; 72(557): e329. CrossRef - The influence of two forms of chlorhexidine on the accuracy of contemporary electronic apex locators
Ewa Marek, Ryta Łagocka, Katarzyna Kot, Krzysztof Woźniak, Mariusz Lipski
BMC Oral Health.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficiency of an integrated apex locator in determining working length in various irrigating solutions: An in vivo study
RakeshReddy Chukka, MalatiDevi Bellam, NarenderReddy Marukala, Sainath Dinapadu, NareshKumar Konda, Jithender Nagilla
Journal of Pharmacy And Bioallied Sciences.2020; 12(5): 410. CrossRef - Accuracy of two electronic apex locators in locating root perforations in curved canals in dry and wet conditions: A comparative in vitro study
MonishaParshotam Khatri, SheetalB Ghivari, Madhu Pujar, Reshma Faras, Pallavi Gopeshetti, Amulya Vanti
Dental Research Journal.2019; 16(6): 407. CrossRef - Consistency of electronic measurements of endodontic working length when using multiple devices from the same manufacturer—an in vitro study
Franziska Haupt, M Hülsmann
Clinical Oral Investigations.2018; 22(9): 3107. CrossRef - The Influence of Various Irrigants on the Accuracy of 2 Electronic Apex Locators in Locating Simulated Root Perforations
Demet Altunbaş, Alper Kuştarcı, Mustafa Toyoğlu
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(3): 439. CrossRef - Accuracy and Repeatability of 3 Apex Locators in Locating Root Canal Perforations: An Ex Vivo Study
Fábio Luiz Cunha D'Assunção, Julio Cézar Nascimento Sousa, Kayo César Amaro Felinto, Thiago Clístines de Medeiros, Diego Tavares Leite, Raissa Bezerra de Lucena, Joab de Oliveira Lima
Journal of Endodontics.2014; 40(8): 1241. CrossRef
- In Vivo and In Vitro Accuracy and Precision Evaluations of Mini Electronic Apex Locators
- 1,410 View
- 7 Download
- 24 Crossref

- Comparison of Antibacterial effect of Listerine® with Various root canal irrigants
- Young Hun Kim, Min-Kyung Kang, Eun-Kyoung Choi, So-Young Yang, Inseok Yang, In-Chol Kang, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(6):500-507. Published online November 30, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.6.500
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study is to compare the antibacterial effect of Listerine® on two microorganisms (
P. gingivalis andE. faecalis ) with various root canal irrigants (NaOCl, CHX, EDTA) and to identify possibility of using Listerine® as a root canal irrigant.Porphyromonas gingivalis ATCC 3327 andEnterococcus faecalis ATCC 29212 were used in this experiment. For the test irrigants, 0.5%, 1%, 2.5%, 5.25% NaOCl, 0.1%, 0.2%, 1%, 2% CHX, 0.5M EDTA (18.6% EDTA) and Listerine® were prepared. Distiled water was used as control. Two methods-1) Comparison of turbidity in broth and 2) Agar diffusion test-were used to determine the extent of antibacterial effect of Listerine® and to compare it with that of NaOCl, CHX, and EDTA. All solutions tested were effective against two bacterial strains compared with control (p<0.001). Any concentration of NaOCl, CHX, and EDTA showed similarly high effectiveness against all bacterial strains. In all experiment, Listerine® showed significantly low antibacterial effect compared with the other root canal irrigants (p<0.05).In conclusion, the results reflect remarkably low antibacterial effect of Listerine® as compared with root canal irrigants in general so it is not suitable for the root canal irrigant.
- 962 View
- 2 Download

-
Evaluation of time-dependent antimicrobial effect of sodium dichloroisocyanurate (NaDCC) on
Enterococcus faecalis in the root canal - Hye-Jeong Kim, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(2):121-129. Published online March 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.2.121
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to assess the antibacterial effect of sodium dichloroisocyanurate (NaDCC), sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl), and chlorhexidine (CHX) on
Enterococcus faecalis and to evaluate and to compare the time-dependant antimicrobial effect of NaDCC with NaOCl and CHX in the root canalin vitro before and after instrumentation.Extracted human single teeth were prepared by serial instrumentation technique. The samples were autoclaved and contaminated for 3 days with
E. faecalis monocultures. The teeth were then divided into 4 groups. Each group was irrigated and inserted with 2% NaOCl, 2% NaDCC, 2% CHX and sterilized saline. After 6, 12, 24, 72h, and 1 week incubation, sterilized paper point was inserted into the root canal. Paper points containing root canal contents were then placed on the agar plate. And then each root canal was prepared with #4 and #5 GG (Gates-Glidden) drill. The debris were collected in the sterilized microtube and the plates were incubated at 37℃ in an increased CO2 atmosphere. After 24h incubation the growth of bacteria around the paper points were measured.NaOCl and NaDCC solution shows similar antimicrobial effect for
E. faecalis at 6, 12, 24, 72h and 1 week. In control group, irrigated with sterilized saline, no antimicrobial effect was observed.The results are in agreement with other investigators, who have shown the bactericidal property and possibility of NaDCC as a root canal irrigation solution. Thus it seems that NaDCC solutions can be clinically applied into the root canal within 1 week after dilution.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pulmonary toxicity of sodium dichloroisocyanurate after intratracheal instillation in sprague-dawley rats
Jean Yoo, Haewon Kim, Yeon-Mi Lim, Byung-Il Yoon, Pilje Kim, Ig-Chun Eom, Ilseob Shim
Human & Experimental Toxicology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Enterococcus faecium and Enterococcus faecalis in endodontic infections: antibiotic resistance profile and susceptibility to photodynamic therapy
Ana Carolina Chipoletti Prado, Patrícia Pimentel De Barros, Jéssica Diane Dos Santos, Luciane Dias De Oliveira, Claudio Antônio Talge Carvalho, Marcia Carneiro Valera, Antonio Olavo Cardoso Jorge, Juliana Campos Junqueira
Lasers in Dental Science.2017; 1(2-4): 91. CrossRef - Evaluation of Antimicrobial Activity and Disease Control Efficacy of Sodium Dichloroisocyanurate (NaDCC) Against Major Strawberry Diseases
Da-Ran Kim, Gun-Hye Gang, Hyun-Ji Cho, Hae-Suk Yoon, Youn-Sig Kwak
The Korean Journal of Pesticide Science.2015; 19(1): 47. CrossRef - Effect of Gamma Irradiation and Its Convergent Treatments on Lily Leaf Blight Pathogen, Botrytis elliptica, and the Disease Development
Ji-Hoon Kim, Sung-Chul Yun
Research in Plant Disease.2014; 20(2): 71. CrossRef - Microorganism penetration in dentinal tubules of instrumented and retreated root canal walls.In vitroSEM study
Saad Al-Nazhan, Alaa Al-Sulaiman, Fellwa Al-Rasheed, Fatimah Alnajjar, Bander Al-Abdulwahab, Abdulhakeem Al-Badah
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(4): 258. CrossRef - Analysis of para-chloroaniline after chemical interaction between alexidine and sodium hypochlorite using mass spectrometry: A preliminary study
Hyeon-Sik Kim, Seung-Hyun Han, Soram Oh, Sang-Min Lim, Yu Gu, Kee-Yeon Kum
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(4): 295. CrossRef - The comparison of different canal irrigation methods to prevent reaction precipitate between sodium hypochlorite and chlorhexidine
Moon-Sun Choi, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(2): 80. CrossRef - Comparison of Antibacterial effect of Listerine® with Various root canal irrigants
Young Hun Kim, Min-Kyung Kang, Eun-Kyoung Choi, So-Young Yang, Inseok Yang, In-Chol Kang, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(6): 500. CrossRef - Evaluation ofEnterococcus faecalisremoval efficacy of the EndoVac® and EndoActivator® intracanal irrigation methods
Seung-Gon Song, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(5): 390. CrossRef - The effect of MTAD as a final root canal irrigants on the coronal bacterial leakage of obturated root canals
Tae Woo Kim, Seok Woo Chang, Dong Sung Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2008; 33(4): 397. CrossRef
- Pulmonary toxicity of sodium dichloroisocyanurate after intratracheal instillation in sprague-dawley rats
- 2,004 View
- 13 Download
- 10 Crossref

- The effect of MTAD on the apical leakage of obturated root canals: an electrochemical study
- Dong-Sung Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(2):119-124. Published online March 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.2.119
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of newly developed endodontic root canal cleanser (MTAD) on the apical leakage of obturated root canal using an electrochemical method.
Canals of 60 extracted single-rooted human teeth were prepared by using a crown-down technique with rotary nickel-titanium files. In Group 1 (positive control group) and 2 (negative control group), 5.25% NaOCl was used as a canal irrigant and no canal wall treatment was done. In group 3, only 5.25% NaOCl were used as canal irrigant, canal wall treatment and final rinse. In group 4, specimens were irrigated with 5.25% NaOCl, treated with 5
ml of 17% EDTA for 5 minutes and final rinsed with 5.25% NaOCl. Specimens of group 5 were irrigated with 1.3% NaOCl and treated with 5 ml of MTAD for 5 minutes. All root canals are dried with paper points and obtuated with gutta-percha and AH plus as a sealer using a continuous wave of condensation technique except in the group 1. The electrical resistance between the standard and experimental electrodes in canals was measured over a period of 10 days. Rising of apical leakage with time was observed for all the groups. Group 4 and 5 showed lower apical leakage than group 3 but differences between the group 3, 4 and 5 were no statistical significance at any measurement time.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of soft chelating irrigation on the sealing ability of GP/AH Plus root fillings
Yi-Suk Yu, Tae-Gun Kim, Kwang-Won Lee, Mi-Kyung Yu
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(6): 484. CrossRef
- Effect of soft chelating irrigation on the sealing ability of GP/AH Plus root fillings
- 1,201 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Evaluation of Sodium Dichloroisocyanurate as a root canal irrigation solution; Cl- concentration, pH, Cytotoxicity and Antimicrobial effect in vitro
- Woo-Cheol Lee, Bong-Sun Kang, Cheol-Ho Kim, Ho-Hyun Son
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2003;28(5):425-430. Published online September 30, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.5.425
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the clinical applications of the Sodium Dichloroisocyanurate effervescent tablet as a routine root canal irrigant by performing several in vitro tests such as Cl- content, cytotoxicity, antimicrobial effect as well as its pH level compared to the equivalent concentration of sodium hypochlorite solution.
Sodium Dichloroisocyanurate demonstrated lower level of Cl- concentation than each dilution of sodium hypochlorite solution. Both solution has increased level of Cl- as the concentration of each solution increased. There was no significant change of Cl- concentration in sodium hypochlorite as time goes by. However, Cl- concentration in Sodium Dichloroisocyanurate was increased.
The antimicrobial effects of both solutions were increased when their concentrations were increased. One day after dilution, antimicrobial effect of Sodium Dichloroisocyanurate was slightly higher than sodium hypochlorite, however, there was no difference in 1 week dilution solution. One month dilution solution of sodium hypochlorite still retain its activity, but antimicrobial effect of Sodium Dichloroisocyanurate was drastically decreased 1 month after dilution.
The cytotoxicity of Sodium Dichloroisocyanurate was rather higher than same concentration of sodium hypochlorite solution until 1 week after dilution. Then in 1 month, cytotoxicity of Sodium Dichloroisocyanurate was decreased than that of 1 week dilution solution, especially 4% Sodium Dichloroisocyanurate solution has almost no toxicity. However, 1% and 2% sodium hypochlorite solution has unchanged moderate degree of cytotoxicity after the dilution. Furthermore, 4% sodium hypochlorite solution showed high level of toxicity.
The pH level of Sodium Dichloroisocyanurate showed that the solution was weak acid (pH5). On the other hand, sodium hypochlorite was revealed as a strong alkaline solution (pH12). There was no change in pH following the dilution of each solution.
As results, Sodium Dichloroisocyanurate solution fully satisfy the basic requirements as a root canal irrigation solution. However, we strongly recommend to use this solution clinically in low concentration and try to apply into the root canal within 1 week after dilution.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of pH, free available chlorine and tissue dissolution property of solid dosage chlorine releasing agents for root canal irrigation based on contact time – An in vitro study
S. Aishwarya, Debolina Bishayi, Vinod Rakesh Jathanna, Manuel S. Thomas, Srikant Natarajan, Suchitra Shenoy, Aradhana Marathe
Endodontology.2025; 37(2): 217. CrossRef - Evaluation of time-dependent antimicrobial effect of sodium dichloroisocyanurate (NaDCC) onEnterococcus faecalisin the root canal
Hye-Jeong Kim, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2007; 32(2): 121. CrossRef
- Evaluation of pH, free available chlorine and tissue dissolution property of solid dosage chlorine releasing agents for root canal irrigation based on contact time – An in vitro study
- 1,285 View
- 9 Download
- 2 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


