Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
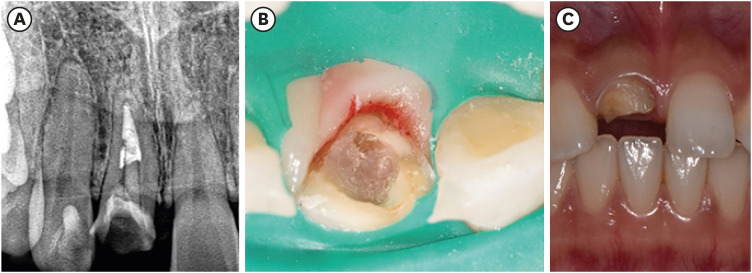
- Fiber-reinforced composite post removal using guided endodontics: a case report
- Changgi Cho, Hyo Jin Jo, Jung-Hong Ha
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(4):e50. Published online September 23, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e50
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Although several techniques have been proposed to remove fiber-reinforced composite (FRC) post, no safe and efficient technique has been established. Recently, a guided endodontics technique has been introduced in cases of pulp canal obliteration. This study describes 2 cases of FRC post removal from maxillary anterior teeth using this guided endodontics technique with a dental operating microscope. Optically scanned data set from plaster cast model was superimposed with the data set of cone-beam computed tomography. By implant planning software, the path of a guide drill was selected. Based on them, a customized stent was fabricated and utilized to remove the FRC post. Employing guided endodontics, the FRC post was removed quickly and safely with minimizing the loss of the remaining tooth structure. The guided endodontics was a useful option for FRC post removal.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparing the Effectiveness of a Robotic and Dynamic Navigation System in Fiber Post removal: An In Vitro Study
Duo Zhou, Fulu Xu, Jiayun Dai, Xingyang Wang, Yifan Ping, Juan Wang
Journal of Endodontics.2026; 52(2): 261. CrossRef - Application of 3D-printed resin guides for the removal of molar fiber posts
Yumin Wu, Lumei Huang, Bing Ge, Yuhang Zhang, Juan Zhang, Haifeng Xie, Ye Zhu, Chen Chen
Journal of Dentistry.2025; 153: 105462. CrossRef - Guided Removal of Long and Short Fiber Posts Using Endodontic Static Guides: A Case Report
Sahar Shafagh, Mamak Adel, Atiyeh Sabzpai
Clinical Case Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Guided versus non-guided fiber post removal: A systematic review and meta-analysis of the accuracy, efficiency, and dentin preservation of static navigation techniques in the removal of fiber posts
Mohamad Elabdalla, Farshad Khosraviani, Shahryar Irannejadrankouhi, Niloofar Ghadimi, Turgut Yağmur Yalçın, Shaheen Wathiq Tawfeeq Al Hajaj, Mahmood Dashti
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2025; 134(3): 630.e1. CrossRef - Top 100 Most-cited Scientific Articles in Guided Endodontic 2018–2024: A Bibliometric Analysis
Gustavo Adrián Morales Valladares, Raquel Esmeralda Guillén Guillén, Martha Elena Gallegos Intriago, Mary Yussely Burgos Barreiro, Claudia Jhelissa Campos Vélez, Andrés Alexander Castillo Chacón, Silvana Beatriz Terán Ayala
The Open Dentistry Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Nonsurgical Management of a Tooth With Intracanal Fiber Post and Periapical Lesion Using Guided Endodontic Technique
Mamak Adel, Zohreh Asgari
Clinical Case Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of Guided Endodontics on the Success of Endodontic Treatment: An Umbrella Review of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
Aakansha Puri, Dax Abraham, Alpa Gupta
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Endodontia guiada por tomografia computadorizada de feixe cônico
Maysa Gaudereto Laurindo, Celso Neiva Campos, Anamaria Pessoa Pereira Leite, Paola Cantamissa Rodrigues Ferreira
Cadernos UniFOA.2024; 19(54): 1. CrossRef - Removal of fiber posts using conventional versus guided endodontics: a comparative study of dentin loss and complications
R. Krug, F. Schwarz, C. Dullin, W. Leontiev, T. Connert, G. Krastl, F. Haupt
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Accuracy and Efficiency of the Surgical-Guide-Assisted Fiber Post Removal Technique for Anterior Teeth: An Ex Vivo Study
Ryota Ito, Satoshi Watanabe, Kazuhisa Satake, Ryuma Saito, Takashi Okiji
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(10): 333. CrossRef - Endodontic management of severely calcified mandibular anterior teeth using guided endodontics: A report of a case and a review of the literature
Mina Davaji, Sahar Karimpour
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2024; 14(2): 245. CrossRef - A laboratory study comparing the static navigation technique using a bur with a conventional freehand technique using ultrasonic tips for the removal of fibre posts
Francesc Abella Sans, Zeena Tariq Alatiya, Gonzalo Gómez Val, Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Paul Michael Howell Dummer, Fernando Durán‐Sindreu Terol, Juan Gonzalo Olivieri
International Endodontic Journal.2024; 57(3): 355. CrossRef - A three‐dimensional printed assembled sleeveless guide system for fiber‐post removal
Yang Xue, Lei Zhang, Ye Cao, Yongsheng Zhou, Qiufei Xie, Xiaoxiang Xu
Journal of Prosthodontics.2023; 32(2): 178. CrossRef - Accuracy of a 3D printed sleeveless guide system used for fiber post removal: An in vitro study
Siyi Mo, Yongwei Xu, Lei Zhang, Ye Cao, Yongsheng Zhou, Xiaoxiang Xu
Journal of Dentistry.2023; 128: 104367. CrossRef - Expert consensus on digital guided therapy for endodontic diseases
Xi Wei, Yu Du, Xuedong Zhou, Lin Yue, Qing Yu, Benxiang Hou, Zhi Chen, Jingping Liang, Wenxia Chen, Lihong Qiu, Xiangya Huang, Liuyan Meng, Dingming Huang, Xiaoyan Wang, Yu Tian, Zisheng Tang, Qi Zhang, Leiying Miao, Jin Zhao, Deqin Yang, Jian Yang, Junqi
International Journal of Oral Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Knowledge, attitude, practice and perception survey on post and core restorations
Aruna Kumari Veronica, Shamini Sai, Anand V Susila
Endodontology.2023; 35(3): 228. CrossRef
- Comparing the Effectiveness of a Robotic and Dynamic Navigation System in Fiber Post removal: An In Vitro Study
- 4,411 View
- 91 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref

-
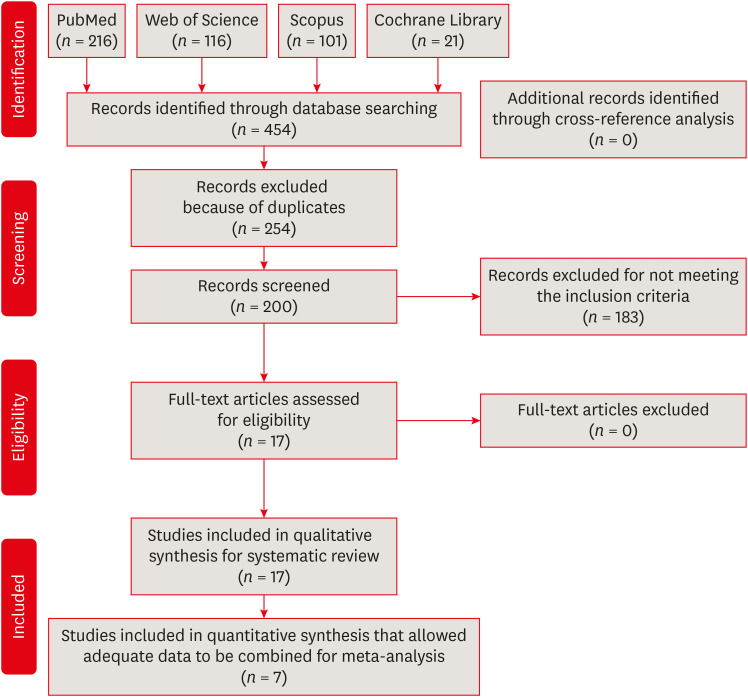
Influence of reciprocating and rotary instrumentation on microbial reduction: a systematic review and meta-analysis of
in vitro studies - Selen Küçükkaya Eren, Emel Uzunoğlu-Özyürek, Sevilay Karahan
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(2):e19. Published online March 10, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e19
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to conduct a systematic review and meta-analysis of
in vitro studies regarding the effectiveness of reciprocating and rotary instrumentation on microbial reduction in root canals.Materials and Methods PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, the Cochrane Library, and the gray literature were searched through December 2019. Studies comparing the influence of reciprocating and rotary instrumentation on the removal of microorganisms from root canals that quantified the antimicrobial effect were included. Data extraction was completed using a systematic form for data collection. The risk of bias of the studies was evaluated. Standardized mean differences (SMDs) and confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated using a random effects meta-analysis.
Results Seventeen
in vitro studies were included in this systematic review, of which 7 provided adequate data for inclusion in the meta-analysis. Both reciprocating and rotary systems were similarly effective in reducing the microbial load in infected root canals (SMD [95% CI], 0.0481 [−0.271, 0.367]). Three studies showed a low risk of bias, whereas most of the studies (82%) presented a medium risk.Conclusions Although both techniques decrease the microbial content (with reductions of 23.32%–88.47% and 23.33%–89.86% for reciprocating and rotary instrumentation, respectively)
, they are not able to provide complete disinfection of root canals.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mapping risk of bias criteria in systematic reviews of in vitro endodontic studies: an umbrella review
Rafaella Rodrigues da Gama, Lucas Peixoto de Araújo, Evandro Piva, Leandro Perello Duro, Adriana Fernandes da Silva, Wellington Luiz de Oliveira da Rosa
Evidence-Based Dentistry.2025; 26(4): 179. CrossRef - Fifteen years of engine‐driven nickel–titanium reciprocating instruments, what do we know so far? An umbrella review
Felipe Immich, Lucas Peixoto de Araújo, Rafaella Rodrigues da Gama, Wellington Luiz de Oliveira da Rosa, Evandro Piva, Giampiero Rossi‐Fedele
Australian Endodontic Journal.2024; 50(2): 409. CrossRef - Does minimally invasive canal preparation provide higher fracture resistance of endodontically treated teeth? A systematic review ofin vitrostudies
Sıla Nur Usta, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Seda Falakaloğlu, Mustafa Gündoğar
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of Combined Ultrasonic Tip and Mechanized Instrumentation on the Reduction of the Percentage of Non-Instrumented Surfaces in Oval/Flat Root Canals: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Marcella Dewes Cassal, Pedro Cardoso Soares, Marcelo dos Santos
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of Different Access Cavity Designs and Ni–Ti Files on the Elimination of Enterococcus faecalis from the Root Canal System: An In Vitro Study
Gizem Andac, Atakan Kalender, Buket Baddal, Fatma Basmaci
Applied Sciences.2022; 12(4): 2049. CrossRef - Shaping Properties and Outcomes of Nickel-Titanium Reciprocation Systems in Primary Teeth: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of In Vitro Studies
SelvaKumar Haridoss, Bhavyaa R, Kavitha Swaminathan, Aruna P
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Root Canal Sealers and Obturation Techniques on Vertical Root Fracture Resistance. An In Vitro Experiment
Mazen F. Alkahtany, Khalid H. Almadi, Fahad A. Alahmad, Abdullah M. Alshehri, Abdulrahman A. AlSwayyed, Omar M. AlZahran, Ali AlHadan, Abdulaziz S. Almustafa, Fahim Vohra, Tariq Abduljabbar
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(17): 8022. CrossRef
- Mapping risk of bias criteria in systematic reviews of in vitro endodontic studies: an umbrella review
- 2,454 View
- 35 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref

-
Removal efficacy and cytotoxicity of a calcium hydroxide paste using
N -2-methyl-pyrrolidone as a vehicle - Myung-Jin Lim, Hyun-Jin Jang, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kwang-Won Lee, Kyung-San Min
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(4):290-300. Published online October 20, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.4.290
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study investigated the removal efficacy and cytotoxicity of a newly developed calcium hydroxide paste (cleaniCal, Maruchi) using
N -2-methyl-pyrrolidone (NMP) as a vehicle in comparison with ApexCal (Ivoclar Vivadent) and Calcipex II (Nishika), which use different vehicles such as polyethylene glycol and propylene glycol, respectively.Materials and Methods Thirty maxillary premolars with oval-shaped canals were divided into 3 groups and the teeth were filled with one of the pastes. After removal of the paste, micro-computed tomographic (μ-CT) imaging was obtained to assess the volume of residual paste in the root canal of each tooth. The teeth were then split longitudinally and the area of the paste-coated surface was evaluated by stereomicroscopy. The cytotoxicity of each product was assessed using an agar overlay assay. The effect of each vehicle on cell viability was evaluated using the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. The data were analyzed using one-way analysis of variance and Tukey's tests to detect any significance (
p < 0.05).Results In the μ-CT and stereomicroscopic analysis, cleaniCal exhibited less remnants of medicament than ApexCal and Calcipex. cleaniCal showed a higher cytotoxicity than the other pastes in the agar overlay assay. Furthermore, NMP exhibited lower cell viability compared to the other vehicles.
Conclusions cleaniCal showed better removal efficacy compared to the other products. However, clinicians should be aware of the higher cytotoxicity of the NMP-based material and consider its possible adverse effects on periradicular tissue when it is overfilled.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Removal of Calcium Hydroxide Paste Leaked Into the Maxillary Sinus
Dohee Kim, Young Kim, Jeong Joon Han
Ear, Nose & Throat Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Synergistic effects of reduced graphene oxide on the antibacterial activity of calcium hydroxide-based intracanal medicaments containing different vehicles
Mi-Ah Kim, Min-Kyeong Kim, Eun-Sook Kang, Kyung-San Min
Journal of Oral Science.2025; 67(1): 35. CrossRef - Lipoteichoic Acid from Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus GG as a Novel Intracanal Medicament Targeting Enterococcus faecalis Biofilm Formation
Ji-Young Yoon, Somin Park, Dongwook Lee, Ok-Jin Park, WooCheol Lee, Seung Hyun Han
Journal of Microbiology.2024; 62(10): 897. CrossRef - Rheological properties and handling characteristics of four injectable calcium hydroxide pastes
Min-Jung KIM, In-Bog LEE
Dental Materials Journal.2024; 43(6): 796. CrossRef - Role of vehicles on antimicrobial efficacy of calcium hydroxide
Dikshya Purohit, Shronika, Pradyumna Misra, Gaurav Jain, Preeti Shukla
Asian Journal of Oral Health and Allied Sciences.2023; 13: 9. CrossRef - Conservative Management of Molar Incisor Hypomineralization Using Biomimetic Material in a 9-Year-Old Boy
Sahili Mungekar-Markandey, Ashwin Jawdekar
Journal of Dental Research and Review.2022; 9(4): 320. CrossRef - Sonic irrigation for removal of calcium hydroxide in the apical root canal: A micro-CT and light-coupled tracking analysis
Wonjoon Moon, Shin Hye Chung, Juhea Chang, Zhaoqiang Zhang
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(6): e0268791. CrossRef - Effect of N-2-methyl-pyrrolidone on Enterococcus faecalis biofilms
Mi-Ah KIM, Prasanna NEELAKANTAN, Kyung-San MIN
Dental Materials Journal.2022; 41(5): 774. CrossRef - Characterization, Antimicrobial Effects, and Cytocompatibility of a Root Canal Sealer Produced by Pozzolan Reaction between Calcium Hydroxide and Silica
Mi-Ah Kim, Vinicius Rosa, Prasanna Neelakantan, Yun-Chan Hwang, Kyung-San Min
Materials.2021; 14(11): 2863. CrossRef - Synthesis, structure, and theoretical studies of a calcium complex of a unique dianion derived from 1-methylpyrrolidin-2-one
Ray J. Butcher, Andrew P. Purdy, Paul A. Brown, Daniel Gunlycke
Acta Crystallographica Section E Crystallographic Communications.2021; 77(1): 70. CrossRef - Effect of a calcium hydroxide-based intracanal medicament containing N-2-methyl pyrrolidone as a vehicle against Enterococcus faecalis biofilm
Taegun KIM, Mi-Ah KIM, Yun-Chan HWANG, Vinicius ROSA, Massimo DEL FABBRO, Kyung-San MIN
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Removal of Calcium Hydroxide Paste Leaked Into the Maxillary Sinus
- 2,226 View
- 11 Download
- 11 Crossref

- Effect of ultrasonic tip designs on intraradicular post removal
- Anny Carine Barros Aguiar, Daniely Amorim de Meireles, André Augusto Franco Marques, Emílio Carlos Sponchiado Júnior, Angela Delfina Bitencourt Garrido, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(4):265-269. Published online July 17, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.4.265
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives To evaluate the effect of different ultrasonic tip designs on intraradicular post removal.
Materials and Methods The crowns of forty human canine teeth were removed, and after biomechanical preparation and filling, the roots were embedded in acrylic resin blocks. The post spaces were made, and root canal molding was performed with self-cured acrylic resin. After casting (Cu-Al), the posts were cemented with zinc phosphate cement. The specimens were randomly separated into 4 groups (
n = 10), as follows: G1 - no ultrasonic vibration (control); G2 - ultrasonic vibration using an elongated cylindrical-shaped and active rounded tip; G3 - ultrasonic vibration with a flattened convex and linear active tip; G4 - ultrasonic vibration with active semicircular tapered tip. Ultrasonic vibration was applied for 15 seconds on each post surface and tensile test was performed in a Universal Testing Machine (Instron 4444 - 1 mm/min).Results G4 presented the highest mean values, however, with no statistically significant difference in comparison to G3 (
P > 0.05). G2 presented the lowest mean values with statistically significant difference to G3 and G4 (P < 0.05).Conclusions Ultrasonic vibration with elongated cylindrical-shaped and active rounded tip was most effective in reducing force required for intraradicular post removal.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of ultrasonic vibration protocols for cast post removal on the incidence of root dentin defects
Giulliano C. Serpa, Orlando A. Guedes, Neurinelma S. S. Freitas, Julio A. Silva, Carlos Estrela, Daniel A. Decurcio
Journal of Oral Science.2023; 65(3): 190. CrossRef - Activación ultrasónica durante la preparación bio químico mecánica del tratamiento endodóntico no quirúrgico. Revisión de la literatura
Gisselle Cantanzaro, Nelsin Villaroel, Diana Dorta
ODOUS Científica .2022; 22(2): 135. CrossRef - Endodontic Retreatment Using Dynamic Navigation: A Case Report
Jonathan Bardales-Alcocer, Marco Ramírez-Salomón, Elma Vega-Lizama, María López-Villanueva, Gabriel Alvarado-Cárdenas, Kenneth S. Serota, Jorgeraul Ramírez-Wong
Journal of Endodontics.2021; 47(6): 1007. CrossRef - Assessment of a Cavity to Optimize Ultrasonic Efficiency to Remove Intraradicular Posts
Izabela Araujo Aguiar Graça, Emílio Carlos Sponchiado Júnior, André Augusto Franco Marques, Leandro de Moura Martins, Ângela Delfina Bittencourt Garrido
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(8): 1350. CrossRef - REMOVAL ALLOY CAST ROOT INLAY BY LOWPOWER ULTRASONIC AND STANDARD TIP
L. D. Vejsgejm, T. N. Gomenjuk
Journal of Volgograd State Medical University.2017; 14(4): 37. CrossRef - Questioning the spot light on Hi-tech endodontics
Jojo Kottoor, Denzil Albuquerque
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(1): 80. CrossRef
- The effect of ultrasonic vibration protocols for cast post removal on the incidence of root dentin defects
- 1,647 View
- 15 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Effect of two different calcium hydroxide paste removal techniques on apical leakage: an electrochemical study
- Chan-Je Park, Kyung-A Jeon, Ho-Beom Kwon
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(3):186-191. Published online May 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.3.186
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study evaluated the effect of two different calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2) paste removal techniques on the apical leakage of canals obturated with gutta percha cones and sealer after removing a Ca(OH)2 dressing using an electrochemical method.
Seventy extracted single-rooted teeth were instrumented on with Profile rotary files under NaOCl irrigation. Fifty-eight canals were filled with calcium hydroxide paste, which was then removed using one of the following two techniques. In group A, calcium hydroxide was removed using only NaOCl irrigation, and in group B, the canals were re-prepared with a Profile rotary files-one size larger than the previous instrument and were irrigated with NaOCl. In both groups, the root surfaces were coated twice with nail varnish from CEJ to an area 4 mm away from the apex after canal obturation. Apical leakage was measured using an electrochemical method for 24 days.
All the specimens showed leakage that increased markedly in the first three days. There was no significant difference between the two groups (p > 0.05). The effect of two calcium hydroxide paste removal techniques on the apical leakage was not different during a short period.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Comparison of the irrigation systems in calcium hydroxide removal
Jae-Seung Eun, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(6): 508. CrossRef
- A Comparison of the irrigation systems in calcium hydroxide removal
- 1,405 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The efficacy of chemo-mechanical removal of dentin carious lesion
- Soon-Bin Lim, Kyung-Kyu Choi, Sang-Jin Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(3):149-157. Published online May 31, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.3.149
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Mechanical removals in decayed teeth have been performed using drill and sharp hand instruments. These methods have some disadvantages such as pain, local anesthesia and overextended cavities. Therefore chemo-mechanical excavation of dentin carious lesions has been introduced. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the efficacy of traditional mechanical methods using burs and chemo-mechanical methods (Carisolv) of caries dentin.
Mechanical caries removal was carried with low speed round bur. Chemo-mechanical caries excavation was performed with Carisolv (Medi-team), using the Carisolv hand instruments. The mean time to remove caries with two different methods was evaluated and the data analyzed with SPSS software (ver 11.5) by t-test (p < 0.05). For histomorphometry of caries removal were also carried with mechanical or chemo-mechanical (Carisolv) methods from 20 extracted caries permanent molars. Complete caries removal was verified with a #23 sharp explorers, Caries Detector (Kuraray Co. Japan), and standard apical radiography.
1. Chemo-mechanical method was taken more times than mechanical method (1.5 fold) (p < 0.05).
2. Excavation for caries took more time for molar lesion than premolar lesion, and the least time was taken to remove the caries in incisor lesion (p < 0.05).
3. There were no significant differences to remove the caries between the maxilla and mandible (p > 0.05).
4. The remaining carious dentin was detected after the chemo-mechanical removal of the carious dentin, and no smear layer were seen after the mechanical and chemo-mechanical removal of the carious dentin.
- 839 View
- 2 Download

- THE EFFECT OF GUTTA-PERCHA REMOVAL USING NICKEL-TITANIUM ROTARY INSTRUMENTS
- Jeong-Hun Jeon, Jeong-Beom Min, Ho-Keel Hwang
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(3):212-218. Published online January 14, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.3.212
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub ABSTRACT The purpose of this study was to quantify the amount of remaining gutta-percha/sealer on the walls of root canals when three types of nickel-titanium rotary instruments(Profile, ProTaper and K3) and a hand instrument(Hedstrom file) used to remove these materials.
The results of this study were as follows:
In the total time for gutta-percha removal, Profile group was the fastest and followed by K3, Protaper, Hedstrom file group.
In case of the evaluation of the volume of remained gutta-percha from radiograph, K3 group got the highest score and followed by Protaper, Hedstrom file, Profile group in the apical 1/3.
In case of the evaluation of the volume of gutta-percha remained from stereomicroscope, K3 group got the highest score and followed by Protaper, Hedstrom file, Profile group in the apical 1/3.
These results showed that instrumentation using nickel-titanium rotary instrument groups was faster than that using hand instrument group. The effect of gutta-percha removal using Profile group was better than that using Protaper and K3 group in the nickel-titanium rotary instrument groups.
- 966 View
- 0 Download


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


