Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Physicochemical characterization of two bulk fill composites at different depths
- Guillermo Grazioli, Carlos Enrique Cuevas-Suárez, Leina Nakanishi, Alejandro Francia, Rafael Ratto de Moraes
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(3):e39. Published online July 5, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e39
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
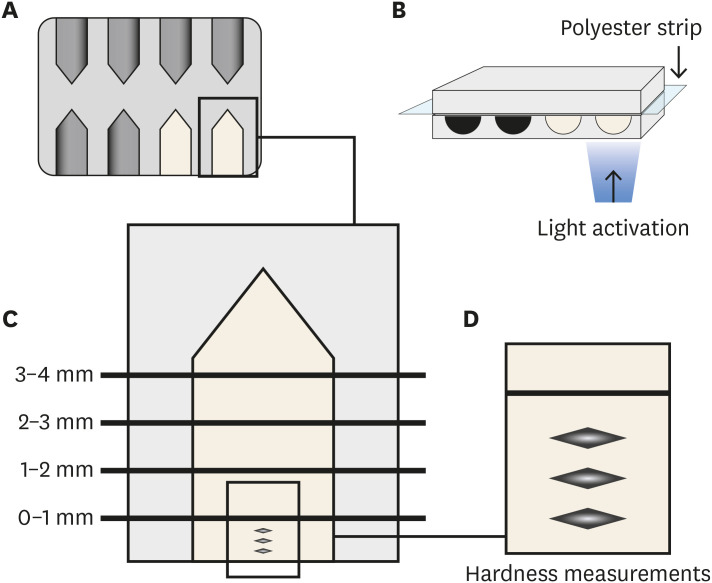
ePub Objectives This study analyzed the physical-chemical behavior of 2 bulk fill resin composites (BFCs; Filtek Bulk Fill [FBF], and Tetric-N-Ceram Bulk Fill [TBF]) used in 2- and 4-mm increments and compared them with a conventional resin composite (Filtek Z250).
Materials and Methods Flexural strength and elastic modulus were evaluated by using a 3-point bending test. Knoop hardness was measured at depth areas 0–1, 1–2, 2–3, and 3–4 mm. The translucency parameter was measured using an optical spectrophotometer. Real-time polymerization kinetics was analyzed using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy.
Results Flexural strength was similar among the materials, while TBF showed lower elastic modulus (Z250: 6.6 ± 1.3, FBF: 6.4 ± 0.9, TBF: 4.3 ± 1.3). The hardness of Z250 was similar only between 0–1 mm and 1–2 mm. Both BFCs had similar hardness until 2–3 mm, and showed significant decreases at 3–4 mm (FBF: 33.45 ± 1.95 at 0–1 mm to 23.19 ± 4.32 at 3–4 mm, TBF: 23.17 ± 2.51 at 0–1 mm to 15.11 ± 1.94 at 3–4 mm). The BFCs showed higher translucency than Z250. The polymerization kinetics of all the materials were similar at 2-mm increments. At 4-mm, only TBF had a similar degree of conversion compared with 2 mm.
Conclusions The BFCs tested had similar performance compared to the conventional composite when used in up to 2-mm increments. When the increment was thicker, the BFCs were properly polymerized only up to 3 mm.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Microhardness According to Surface, Distance and Time of Photopolymerization of a Bulk-Fill Resin: In Vitro Study
María José Loayza-Gallegos, Gino Hernan Vidalón-Romo, Julissa Amparo Dulanto-Vargas
Odovtos - International Journal of Dental Sciences.2026; 1(1): 384. CrossRef - Comparative In Vitro Analysis of Mechanical Properties in Three High-Viscosity Bulk-Fill Composite Resins
Carlos I. Santacruz, Jorge I. Fajardo, César A. Paltán, Ana del Carmen Armas-Vega, Eleonor Vélez León
Journal of Composites Science.2025; 9(11): 623. CrossRef - Translucency of bulk‐fill composite materials: A systematic review
Gaetano Paolone, Sofia Baldani, Niccolò De Masi, Mauro Mandurino, Giacomo Collivasone, Nicola Scotti, Enrico Gherlone, Giuseppe Cantatore
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2024; 36(7): 995. CrossRef - Can composite packaging and selective enamel etching affect the clinical behavior of bulk-fill composite resin in posterior restorations? 24-month results of a randomized clinical trial
Marcos de Oliveira BARCELEIRO, Chane TARDEM, Elisa Gomes ALBUQUERQUE, Leticia de Souza LOPES, Stella Soares MARINS, Luiz Augusto POUBEL, Roberta BARCELOS, Romina ÑAUPARI-VILLASANTE, Alessandro Dourado LOGUERCIO, Fernanda Signorelli CALAZANS
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - No-Cap Flowable Bulk-Fill Composite: Physico-Mechanical Assessment
Abdullah Alshehri, Feras Alhalabi, Ali Robaian, Mohammed A. S. Abuelqomsan, Abdulrahman Alshabib, Eman Ismail, Faisal Alzamil, Nawaf Alotaibi, Hamad Algamaiah
Polymers.2023; 15(8): 1847. CrossRef - The Microhardness and Surface Roughness Assessment of Bulk-Fill Resin Composites Treated with and without the Application of an Oxygen-Inhibited Layer and a Polishing System: An In Vitro Study
Ann Carrillo-Marcos, Giuliany Salazar-Correa, Leonor Castro-Ramirez, Marysela Ladera-Castañeda, Carlos López-Gurreonero, Hernán Cachay-Criado, Ana Aliaga-Mariñas, Alberto Cornejo-Pinto, Luis Cervantes-Ganoza, César Félix Cayo-Rojas
Polymers.2022; 14(15): 3053. CrossRef
- Microhardness According to Surface, Distance and Time of Photopolymerization of a Bulk-Fill Resin: In Vitro Study
- 2,216 View
- 20 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Bond strength of self-adhesive resin cements to composite submitted to different surface pretreatments
- Victor Hugo dos Santos, Sandro Griza, Rafael Ratto de Moraes, André Luis Faria-e-Silva
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(1):12-16. Published online January 20, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.1.12
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Extensively destroyed teeth are commonly restored with composite resin before cavity preparation for indirect restorations. The longevity of the restoration can be related to the proper bonding of the resin cement to the composite. This study aimed to evaluate the microshear bond strength of two self-adhesive resin cements to composite resin.
Materials and Methods Composite discs were subject to one of six different surface pretreatments: none (control), 35% phosphoric acid etching for 30 seconds (PA), application of silane (silane), PA + silane, PA + adhesive, or PA + silane + adhesive (
n = 6). A silicone mold containing a cylindrical orifice (1 mm2 diameter) was placed over the composite resin. RelyX Unicem (3M ESPE) or BisCem (Bisco Inc.) self-adhesive resin cement was inserted into the orifices and light-cured. Self-adhesive cement cylinders were submitted to shear loading. Data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA and Tukey's test (p < 0.05).Results Independent of the cement used, the PA + Silane + Adhesive group showed higher microshear bond strength than those of the PA and PA + Silane groups. There was no difference among the other treatments. Unicem presented higher bond strength than BisCem for all experimental conditions.
Conclusions Pretreatments of the composite resin surface might have an effect on the bond strength of self-adhesive resin cements to this substrate.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An Innovative Method of Permanent Retention on Veneered Crowns
Yugandhar Garlapati, Sampath Krishna Veni, Jashva Vamsi Kogila, Polisetty Siva Krishna, K. N. Anand Kumar
Journal of Indian Orthodontic Society.2025; 59(3): 279. CrossRef - Effect of Cement Type on Marginal Microleakage of Zirconia Crowns with or without Cervical Margin Relocation: An In Vitro Study
RI Farah
Operative Dentistry.2025; 50(2): 194. CrossRef - Challenges faced when masking a single discoloured tooth - Part 2: indirect restoration procedures
May Aljanahi, Argwan Alhussin, Haitham Elbishari
British Dental Journal.2025; 239(1): 25. CrossRef - Influence of mechanochemical treatment and oxygen inhibited layer on the adhesion of self-adhesive resin cement to bulk-fill composite resin
Sreya Dutta, Samikhya Priyadarsani Sahu, Anushka Arora, Srikant Natarajan, Abhishek Parolia, Manuel Thomas
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2024; 27(2): 79. CrossRef - Substrate Rigidity Effect on CAD/CAM Restorations at Different Thicknesses
César Rogério Pucci, Ana Paula Valente Pinho Mafetano, Alexandre Luiz Souto Borges, Guilherme Schmitt de Andrade, Amanda Maria de Oliveira Dal Piva, Cornelis J. Kleverlaan, João Paulo Mendes Tribst
European Journal of Dentistry.2023; 17(04): 1020. CrossRef - Microgap Formation between a Dental Resin-Matrix Computer-Aided Design/Computer-Aided Manufacturing Ceramic Restorative and Dentin after Various Surface Treatments and Artificial Aging
Alexandros Galanopoulos, Dimitrios Dionysopoulos, Constantinos Papadopoulos, Petros Mourouzis, Kosmas Tolidis
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(4): 2335. CrossRef - Dental Luting Cements: An Updated Comprehensive Review
Artak Heboyan, Anna Vardanyan, Mohmed Isaqali Karobari, Anand Marya, Tatevik Avagyan, Hamid Tebyaniyan, Mohammed Mustafa, Dinesh Rokaya, Anna Avetisyan
Molecules.2023; 28(4): 1619. CrossRef - Effect of full-step versus simplified resin cement luting strategies on the push-out bond strength of indirect resin composite restorations bonded to dentin
Bianca Cristina Dantas da Silva, Isabelle Helena Gurgel de Carvalho, Taciana Emília Leite Vila-Nova, Gabriela Monteiro de Araújo, Boniek Castillo Dutra Borges, Marília Regalado Galvão Rabelo Caldas, Isauremi Vieira de Assunção, Mutlu Özcan, Rodrigo Othávi
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2023; 37(24): 3552. CrossRef - Effect of various polymerization protocols on the cytotoxicity of conventional and self-adhesive resin-based luting cements
Ece Irem Oguz, Ufuk Hasanreisoglu, Sadullah Uctasli, Mutlu Özcan, Mehmet Kiyan
Clinical Oral Investigations.2020; 24(3): 1161. CrossRef - Repair bond strength of resin composite to three aged CAD/CAM blocks using different repair systems
Pinar Gul, Latife Altınok-Uygun
The Journal of Advanced Prosthodontics.2020; 12(3): 131. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Surface Characteristics of Dental CAD/CAM Materials after Different Surface Treatments
Konstantinos Papadopoulos, Kimon Pahinis, Kyriaki Saltidou, Dimitrios Dionysopoulos, Effrosyni Tsitrou
Materials.2020; 13(4): 981. CrossRef - Adhesive Systems Used in Indirect Restorations Cementation: Review of the Literature
Cristian Abad-Coronel, Belén Naranjo, Pamela Valdiviezo
Dentistry Journal.2019; 7(3): 71. CrossRef - Effects of different etching methods and bonding procedures on shear bond strength of orthodontic metal brackets applied to different CAD/CAM ceramic materials
S. Kutalmış Buyuk, Ahmet Serkan Kucukekenci
The Angle Orthodontist.2018; 88(2): 221. CrossRef - Ceramic repairs with resins: silanization protocols
Teresa Cristina Vasconcelos dos Santos
Journal of Dental Health, Oral Disorders & Therapy.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of different surface treatments on bond strength of novel CAD/CAM restorative materials to resin cement
Meltem Bektaş Kömürcüoğlu, Elçin Sağırkaya, Ayça Tulga
The Journal of Advanced Prosthodontics.2017; 9(6): 439. CrossRef - Adhesive bonding to polymer infiltrated ceramic
Judith SCHWENTER, Fredy SCHMIDLI, Roland WEIGER, Jens FISCHER
Dental Materials Journal.2016; 35(5): 796. CrossRef - Orthodontic bracket bonding to glazed full-contour zirconia
Ji-Young Kwak, Hyo-Kyung Jung, Il-Kyung Choi, Tae-Yub Kwon
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(2): 106. CrossRef - Effect of Silanization on Microtensile Bond Strength of Different Resin Cements to a Lithium Disilicate Glass Ceramic
Cristina Parise Gré, Renan C de Ré Silveira, Shizuma Shibata, Carlo TR Lago, Luiz CC Vieira
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2016; 17(2): 149. CrossRef - Effects of air abrasion with alumina or glass beads on surface characteristics of CAD/CAM composite materials and the bond strength of resin cements
ARAO Nobuaki, YOSHIDA Keiichi, SAWASE Takashi
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2015; 23(6): 629. CrossRef - Resin cement to indirect composite resin bonding: Effect of various surface treatments
Omer Kirmali, Cagatay Barutcugil, Osman Harorli, Alper Kapdan, Kursat Er
Scanning.2015; 37(2): 89. CrossRef - Impact of different adhesives on work of adhesion between CAD/CAM polymers and resin composite cements
Christine Keul, Manuel Müller-Hahl, Marlis Eichberger, Anja Liebermann, Malgorzata Roos, Daniel Edelhoff, Bogna Stawarczyk
Journal of Dentistry.2014; 42(9): 1105. CrossRef - Effect of Plasma Deposition Using Low-Power/Non-thermal Atmospheric Pressure Plasma on Promoting Adhesion of Composite Resin to Enamel
Geum-Jun Han, Jae-Hoon Kim, Sung-No Chung, Bae-Hyeock Chun, Chang-Keun Kim, Byeong-Hoon Cho
Plasma Chemistry and Plasma Processing.2014; 34(4): 933. CrossRef - Bonding efficacy of a self-adhesive resin cement to enamel and dentin
Linhu Wang, Haixing Xu, Songyang Li, Bin Shi, Rong Li, Mingfu Ye, Jing Yang
Journal of Wuhan University of Technology-Mater. Sci. Ed..2014; 29(6): 1307. CrossRef
- An Innovative Method of Permanent Retention on Veneered Crowns
- 1,787 View
- 8 Download
- 23 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


