Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Cone-beam computed tomography analysis of maxillary premolar canal anatomy: Ahmed’s versus Vertucci’s classifications in a Jordanian cohort
- Raidan Ba-Hattab, Muna M. Shaweesh, Nessrin A. Taha, Elham S. Abu Alhaija
- Restor Dent Endod 2026;51(1):e11. Published online February 26, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2026.51.e11
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
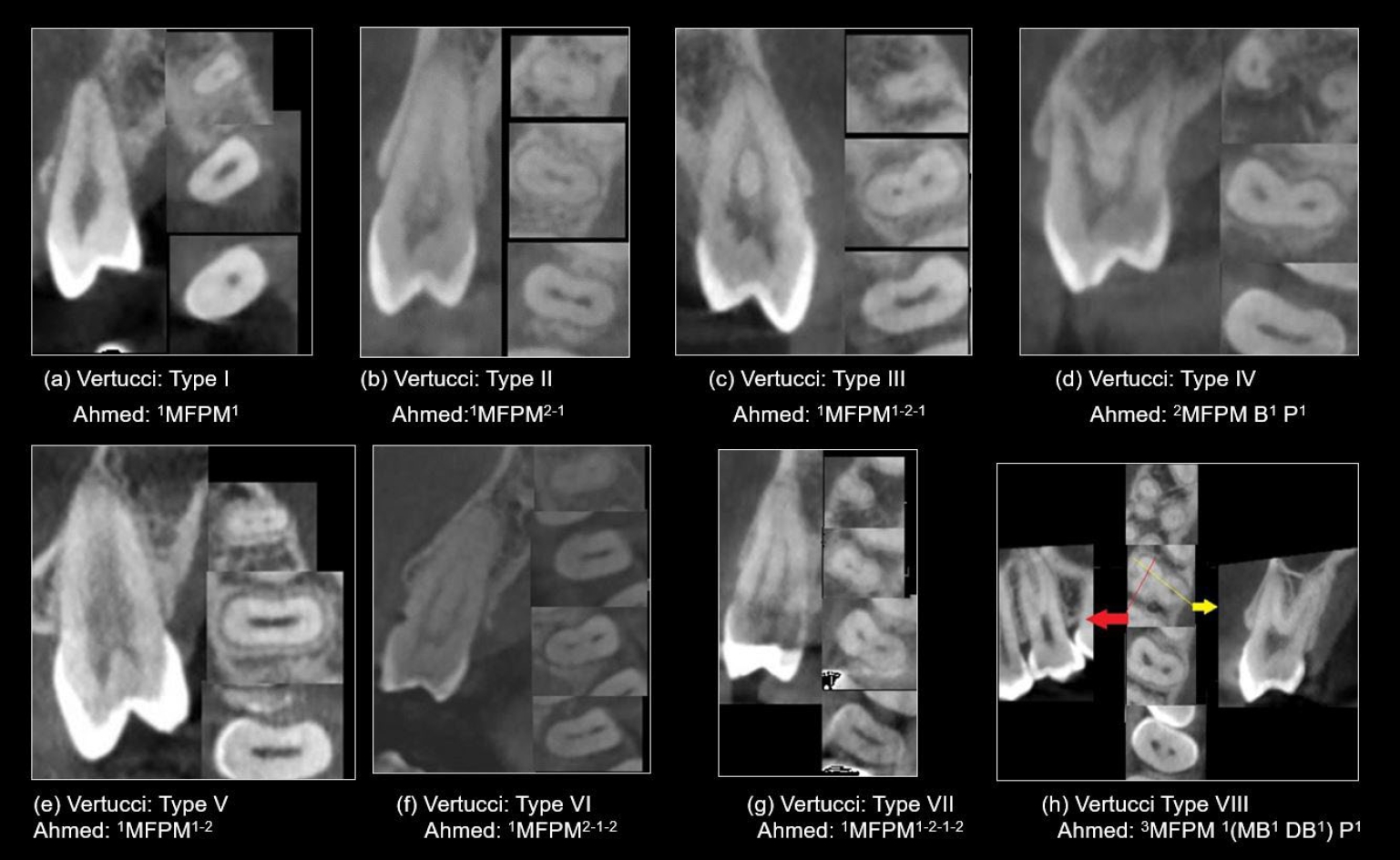
This study analyzed the root and canal configurations of maxillary premolars in a Jordanian subpopulation using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) and classified them based on Vertucci’s and Ahmed’s systems.
Methods
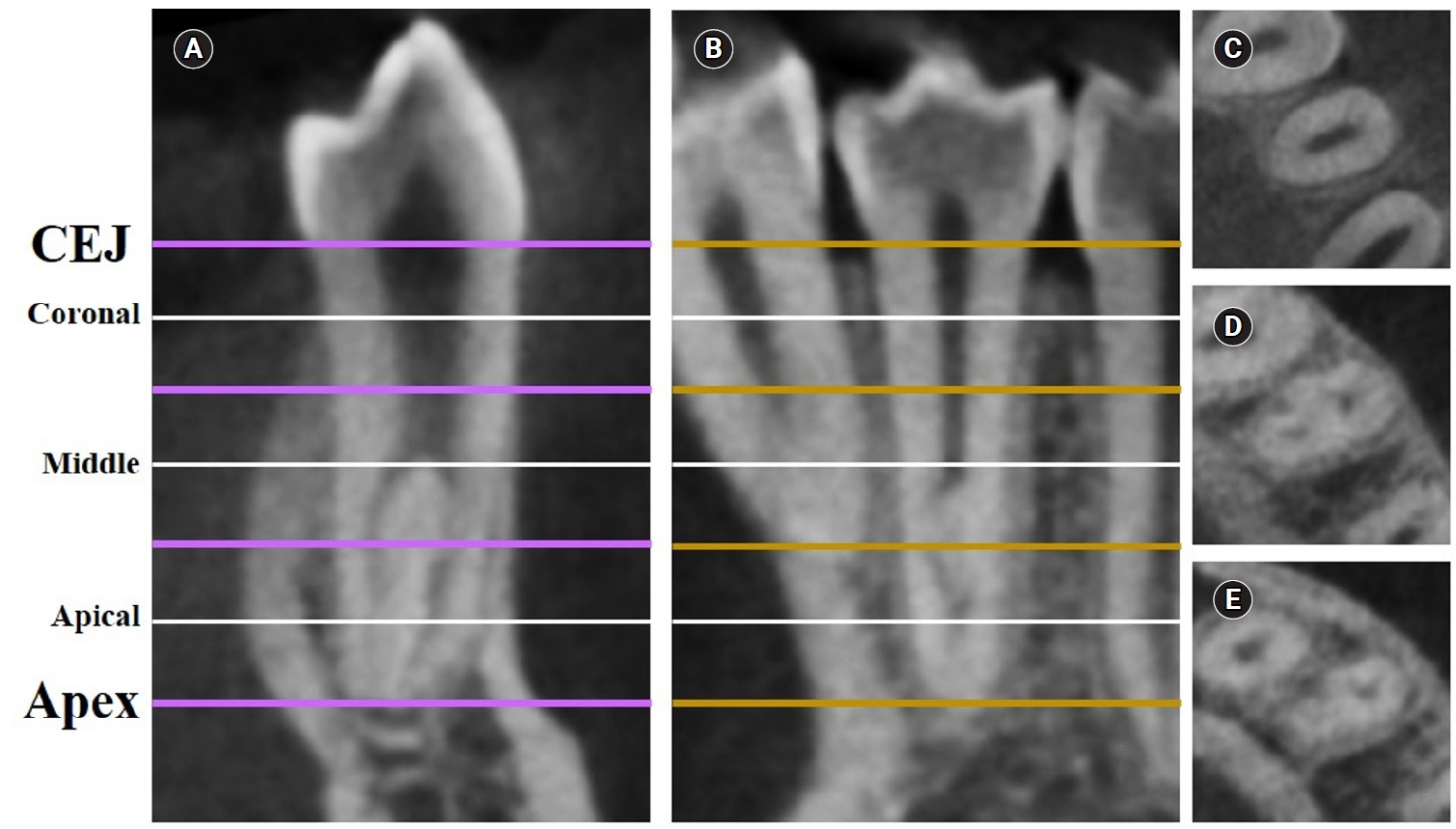
Two hundred CBCT scans of 800 maxillary premolars were retrospectively assessed for root morphology, canal configurations, and root canal divergence and merging. Data was statistically analyzed.
Results
The study included 70 males and 130 females. Most right and left maxillary first premolars (RFPM, LFPM) had two roots (59.0% and 58.5%), with a significant association between sex and root number for RFPM and LFPM (p < 0.05). In contrast, the right and left maxillary second premolars (RSPM, LSPM) mostly had a single root (87.5% and 88.5%), with no association with sex. Vertucci’s classification showed type IV as the predominant configuration in first premolars (RFPM, 65.0% and LFPM, 67.0%) and type I in second premolars (RSPM, 44.0% and LSPM, 49.0%). A significant sex association was found only with RSPM. Ahmed’s classification revealed that maxillary premolar with two separated roots and two separated canals (2MP B1 P1) was mostly found in first premolars (RFPM, 58.0% and LFPM, 56.0%), and maxillary premolar with one root and one canal (1MP1) in second premolars (RSPM, 44.0% and LSPM, 49.0%), with a significant sex association for RSPM and LSPM (p < 0.05). Age had no impact, and symmetry was observed between the right and left sides. Three-rooted premolars were identified in four cases. Almost all of Vertucci’s types and numerous codes from Ahmed’s classification were documented.
Conclusions
CBCT revealed diverse anatomical variations in the Jordanian subpopulation, with Ahmed’s classification providing more detailed canal configurations than Vertucci’s, uncovering previously overlooked variations.
- 166 View
- 16 Download

- Dentin thickness of C-shaped root canal walls in mandibular premolars based on cone-beam computed tomography: a retrospective cross-sectional study
- Elif Aslan, Ali Canberk Ulusoy, Bilge Hakan Sen, B. Guniz Baksi, Erinc Onem, Ali Mert
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(2):e18. Published online May 15, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e18
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study aimed to measure the dentin thickness of C-shaped canals in mandibular first and second premolars at coronal, middle, and apical root levels using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT).
Methods
Dentin thicknesses of buccal, lingual, mesial, and distal root walls of 41 C-shaped premolars were measured at three different root levels on axial CBCT slices. The measurements were made at the midpoint of each third, along with 1 mm below and above the midpoint. C-shape configurations of the premolar root canals were also recorded. Analysis of variance, Kruskal-Wallis, and the independent samples t-tests were used for the comparisons (p = 0.05).
Results
The thickest walls for both premolars were buccal and lingual walls at all three root levels (p < 0.05). The thinnest walls for the first premolar teeth were mesial and distal walls of the lingual canal, while it was the mesial end of the buccal and lingual canals for the second premolars (p < 0.05). Dentin wall thicknesses at the mesial end of buccal and lingual canals of C1-shaped first premolars were thinner than C2-shaped first premolars at the apical level (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
Danger zones for C-shaped mandibular first and second premolars are predominantly mesial walls facing the radicular groove and distal wall of the lingual canal. CBCT imaging during endodontic treatment is recommended to avoid complications. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Anatomical complexity in mandibular second molars: prevalence of C-shaped canals, radicular grooves, taurodontism, and radices molarum in Saudi population
Ahmed A. Madfa, Abdullah F. Alshammari, Eyad Almagadawyi, Ebtsam A. Aledaili, Afaf Al-Haddad
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Anatomical complexity in mandibular second molars: prevalence of C-shaped canals, radicular grooves, taurodontism, and radices molarum in Saudi population
- 3,559 View
- 135 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Shape and anatomical relationship of the mental foramen to the mandibular premolars in an Indian sub-population: a retrospective CBCT analysis
- Komal Sheth, Kulvinder Singh Banga, Ajinkya M. Pawar, James L. Gutmann, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(1):e1. Published online December 13, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
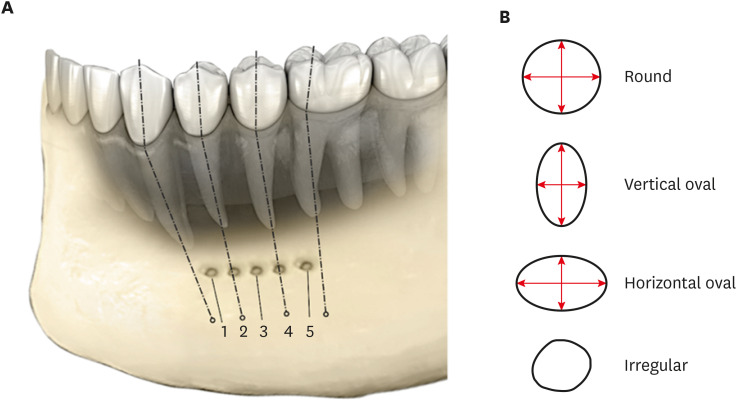
ePub Objectives This study assessed the shape and anatomical relationship of the mental foramen (MF) to mandibular posterior teeth in an Indian sub-population.
Materials and Methods In total, 475 existing cone-beam computed tomography records exhibiting 950 MFs and including the bilateral presence of mandibular premolars and first molars were assessed. Images were evaluated 3-dimensionally to ascertain the position, shape, and anatomical proximity of MFs to mandibular teeth. The position and shape of MFs were measured and calculated. The Pythagorean theorem was used to calculate the distance between the root apex of the mandibular teeth and the MF.
Results MFs exhibited a predominantly round shape (left: 67% and right: 65%) followed by oval (left: 30% and right: 31%) in both males and females and in different age groups. The root apices of mandibular second premolars (left: 71% and right: 62%) were closest to the MF, followed by distal to the first premolars and mesial to the second premolars. The mean vertical distance between the MF and the nearest tooth apex calculated on sagittal sections was 2.20 mm on the right side and 2.32 mm on the left side; no significant difference was found according to sex or age. The distance between the apices of the teeth and the MF was ≥ 4 mm (left; 4.09 ± 1.27 mm and right; 4.01 ± 1.15 mm).
Conclusions These findings highlight the need for clinicians to be aware of the location of the MF in treatment planning and while performing non-surgical and surgical endodontic procedures.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Anatomical and radiographic assessment of variations of the mental foramen and their impact on success of local anaesthesia administration
Isratul Jannat, M. Ummay Salma, Nipu Rani Chowdhury, Kulsum Nahar, Dilruba Binte Mostafa, Khandokar Emanuzzaman Emon, Shahela Sarmin
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences.2026; 14(3): 823. CrossRef - Optimising Treatment Strategies: Labial versus Labio-inferior Plating Using Three-dimensional Miniplates for Mandibular Symphysis and Parasymphysis Fractures
Akash P Muralidharan, Kalyani Bhate, K Mithun Nilgiri, Sumithra S Nair, Lakshmi Shetty, Rose Johnson
Advances in Human Biology.2025; 15(2): 242. CrossRef - Morphometric analysis of mental foramen in retained cadaveric specimens of mandibles of Sri Lankan population
Dadallage Tharanga De Silva, Usliyanage Clifford Priyantha Perera
Anatomical Science International.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A Cross-Sectional CBCT Study of Anterior Loop, Accessory Mental Foramen, and Lingual Foramina in Patients’ Mandibles: Implications for Safer Implant Planning
Abbas Shokri, Mohammad Mahdi Maleki, Leili Tapak
Journal of Maxillofacial and Oral Surgery.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Radiographic Recognition of Mental Nerve for Secured Dental Implant Placement by Cone-Beam Computed Tomography in Mosul City Population
Asmaa B. Al-Saffar, Mekdad H. Alrigbo, Rawaa Y. Al-Rawee
Journal of Craniofacial Surgery.2024; 35(7): 2049. CrossRef - Accuracy of Implant Size Prediction Based on Edentulous Ridge Dimension on Cone-beam Computed Tomography - A Retrospective Study
Hunter R. Jolicoeur, Gerard A. Camargo, Tamara G. Stephenson, Wenjian Zhang
Annals of Maxillofacial Surgery.2024; 14(2): 187. CrossRef - Mental Foramenin Panoramik Radyografi ve Konik Işınlı Bilgisayarlı Tomografi Görüntüleri Üzerinde Morfolojik Analizi
Ezgi UZUN, Burak Kerem APAYDIN, Ayşen TİL
Selcuk Dental Journal.2023; 10(3): 540. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Possible Relationship between the Curvature and
Horizontal Course of the Inferior Alveolar Canal
Cansu G. Koca, M. Fatih Çiçek, Sanaz Sadry, Ozan Yenidünya, Fatma Akkoca Kaplan, Aras Erdil
Current Medical Imaging Formerly Current Medical Imaging Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Anatomical and radiographic assessment of variations of the mental foramen and their impact on success of local anaesthesia administration
- 2,997 View
- 50 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref

- Endodontic treatment of a C-shaped mandibular second premolar with four root canals and three apical foramina: a case report
- Thikamphaa Bertrand, Sahng Gyoon Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(1):68-73. Published online January 19, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.1.68

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This case report describes a unique C-shaped mandibular second premolar with four canals and three apical foramina and its endodontic management with the aid of cone-beam computer tomography (CBCT). C-shaped root canal morphology with four canals was identified under a dental operating microscope. A CBCT scan was taken to evaluate the aberrant root canal anatomy and devise a better instrumentation strategy based on the anatomy. All canals were instrumented to have a 0.05 taper using 1.0 mm step-back filing with appropriate apical sizes determined from the CBCT scan images and filled using a warm vertical compaction technique. A C-shaped mandibular second premolar with multiple canals is an anatomically rare case for clinicians, yet its endodontic treatment may require a careful instrumentation strategy due to the difficulty in disinfecting the canals in the thin root area without compromising the root structure.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Unique root anatomy of mandibular second premolars: clinical strategies for effective disinfection and preservation of dentine structure in root canal treatment—a case report
Ji Wook Jeong, Erika Silguero Gonzalez, Scott R. Makins, Timothy Kirkpatrick
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - PRICE 2020 guidelines for reporting case reports in Endodontics: explanation and elaboration
V. Nagendrababu, B. S. Chong, P. McCabe, P. K. Shah, E. Priya, J. Jayaraman, S. J. Pulikkotil, P. M. H. Dummer
International Endodontic Journal.2020; 53(7): 922. CrossRef - A cone-beam computed tomography study of C-shaped root canal systems in mandibular second premolars in a Taiwan Chinese subpopulation
Yi-Chin Chen, Chia-Lun Tsai, Yi-Chen Chen, Gin Chen, Shue-Fen Yang
Journal of the Formosan Medical Association.2018; 117(12): 1086. CrossRef - Anatomic Comparison of Contralateral Premolars
Gaute Floer Johnsen, Sazan Dara, Sameenah Asjad, Pia Titterud Sunde, Håvard Jostein Haugen
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(6): 956. CrossRef - Endodontic Management of Dilacerated Maxillary Central Incisor fused to a Supernumerary Tooth using Cone Beam Computed Tomography: An Unusual Clinical Presentation
Thilla S Vinothkumar, Deivanayagam Kandaswamy, Ganesh Arathi, Sathishkumar Ramkumar, Gnanasekaran Felsypremila
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2017; 18(6): 522. CrossRef
- Unique root anatomy of mandibular second premolars: clinical strategies for effective disinfection and preservation of dentine structure in root canal treatment—a case report
- 2,753 View
- 15 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Use of cone-beam computed tomography and three-dimensional modeling for assessment of anomalous pulp canal configuration: a case report
- Alper Sinanoglu, Dilek Helvacioglu-Yigit, Ibrahim Mutlu
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(2):161-165. Published online December 4, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.2.161
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Three-dimensional (3D) reconstruction of cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) scans appears to be a valuable method for assessing pulp canal configuration. The aim of this report is to describe endodontic treatment of a mandibular second premolar with aberrant pulp canal morphology detected by CBCT and confirmed by 3D modeling. An accessory canal was suspected during endodontic treatment of the mandibular left second premolar in a 21 year old woman with a chief complaint of pulsating pain. Axial cross-sectional CBCT scans revealed that the pulp canal divided into mesiobuccal, lingual, and buccal canals in the middle third and ended as four separate foramina. 3D modeling confirmed the anomalous configuration of the fused root with a deep lingual groove. Endodontic treatment of the tooth was completed in two appointments. The root canals were obturated using lateral compaction of gutta-percha and root canal sealer. The tooth remained asymptomatic and did not develop periapical pathology until 12 months postoperatively. CBCT and 3D modeling enable preoperative evaluation of aberrant root canal systems and facilitate endodontic treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploring Technological Progress in Three-Dimensional Imaging for Root Canal Treatments: A Systematic Review
Kanwalpreet Kaur, Ravinder S. Saini, Sunil Kumar Vaddamanu, Shashit Shetty Bavabeedu, Vishwanath Gurumurthy, Shan Sainudeen, Vinod Babu Mathew, Shafait Ullah Khateeb, Aida Mokhlesi, Seyed Ali Mosaddad, Artak Heboyan
International Dental Journal.2025; 75(2): 1097. CrossRef - Root Canal Treatment of Oehlers Type III Dens Invaginatus in Maxillary Lateral Incisor and Remote Sinus Tract Using Dental Surgical Microscope and Cone-Beam Computed Tomography
Rie Fujii, Tomohiro Asai, Masashi Yamada, Ryo Sako, Yoshiki Tamiya, Masahiro Furusawa
The Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College.2023; 64(2): 67. CrossRef - CBCT and Micro-CT analysis of the mandibular first premolars with C-shaped canal system in a Chinese population author
Yimeng Zhang, Xunben Weng, Yu Fu, Xuekai Qi, Yihuai Pan, Yu Zhao
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Exploring Technological Progress in Three-Dimensional Imaging for Root Canal Treatments: A Systematic Review
- 1,433 View
- 9 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Study of endodontic working length of Korean posterior teeth
- Jeong-Yeob Kim, Sang-Hoon Lee, Gwang-Hee Lee, Sang-Hyuk Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(6):429-435. Published online November 30, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.6.429
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to investigate average working lengths of Korean posterior teeth and evaluate validity of endodontic file length.
Materials and Methods The endodontic working length of the posterior teeth of 670 Korean patients were measured than each mean value and standard deviation were investigated than the frequency deviation and standard deviation per each length were calculated.
Results Among the canals of premolar, 66.5% of canal length was marked under 20 mm by endodontic working length and 95.4% could be measured under 22 mm and Among the canals of molars, 95.5% of canal length was marked under 20 mm endodontic working length.
Conclusions With the result of measurement of endodontic working length of premolars of Korean, it suggested that 23 mm endodontic file is more proper than the 21 mm and 25 mm file on the market.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Rare Case of Nonsyndromic Generalized Radiculomegaly with a Literature Review
Mohammad Al-Obaida, Kevin Seymour
Case Reports in Dentistry.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Fluoride Release and Recharge Properties of Several Fluoride-Containing Restorative Materials
Dongyun Lee, Jongsoo Kim, Miran Han, Jisun Shin
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2020; 47(2): 196. CrossRef - Comparison of Microhardness and Compressive Strength of Alkasite and Conventional Restorative Materials
Kunho Lee, Jongsoo Kim, Jisun Shin, Miran Han
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2020; 47(3): 320. CrossRef - Fluoride Release of Giomer and Compomer Through the Dental Adhesive Layer
Minseon Hwang, Howon Park, Juhyun Lee, Hyunwoo Seo
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2017; 44(2): 180. CrossRef
- A Rare Case of Nonsyndromic Generalized Radiculomegaly with a Literature Review
- 6,196 View
- 37 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Root canal treatment of a mandibular second premolar with three separate root canals
- Seok-Ryun Lee, Seol-Hee Shin, Sung-Ok Hong, Chang-Kyu Song, Hoon-Sang Chang, Kyung-San Min
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(4):302-305. Published online July 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.4.302
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Mandibular premolars show a wide variety of root canal anatomy. Especially, the occurrence of three canals with three separate foramina in mandibular second premolars is very rare. This case report describes the root canal treatment of an unusual morphological configuration of the root canal system and supplements previous reports of the existence of such configuration in mandibular second premolar.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effective management of mandibular second premolar with root anomalies
Ashwaq Faia Asiri
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2023; 13(1): 28. CrossRef
- Effective management of mandibular second premolar with root anomalies
- 1,942 View
- 10 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Stress distribution of endodontically treated maxillary second premolars restored with different methods: Three-dimensional finite element analysis
- Dong-Yeol Lim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Bock Hur, Kwang-Hoon Kim, Kwon Son, Jeong-Kil Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(1):69-79. Published online January 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.1.069
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the influence of elastic modulus of restorative materials and the number of interfaces of post and core systems on the stress distribution of three differently restored endodontically treated maxillary second premolars using 3D FE analysis. Model 1, 2 was restored with a stainless steel or glass fiber post and direct composite resin. A PFG or a sintered alumina crown was considered. Model 3 was restored by EndoCrown. An oblique 500 N was applied on the buccal (Load A) and palatal (Load B) cusp. The von Mises stresses in the coronal and root structure of each model were analyzed using ANSYS. The elastic modulus of the definitive restorations rather than the type of post and core system was the primary factor that influenced the stress distribution of endodontically treated maxillary premolars. The stress concentration at the coronal structure could be lowered through the use of definitive restoration of high elastic modulus. The stress concentration at the root structure could be lowered through the use of definitive restoration of low elastic modulus.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- How loss of tooth structure impacts the biomechanical behavior of a single-rooted maxillary premolar: FEA
Roaa Abdelwahab Abdelfattah, Nawar Naguib Nawar, Engy M. Kataia, Shehabeldin Mohamed Saber
Odontology.2024; 112(1): 279. CrossRef - Effect of Proximal Caries-driven Access on the Biomechanical Behavior of Endodontically Treated Maxillary Premolars
Nawar Naguib Nawar, Roaa Abdelwahab Abdelfattah, Mohamed Kataia, Shehabeldin Mohamed Saber, Engy Medhat Kataia, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2023; 49(10): 1337. CrossRef - Survival and success of endocrowns: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Raghad A. Al-Dabbagh
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2021; 125(3): 415.e1. CrossRef - Influence of Cavity Design on Stress Distribution in Second Premolar Tooth Using Finite Element Analysis
Z. Parlar, E.U. Gökçek, K. Yildirim, A. Kahyaoglu
Acta Physica Polonica A.2017; 132(3-II): 949. CrossRef - Influence of post types and sizes on fracture resistance in the immature tooth model
Jong-Hyun Kim, Sung-Ho Park, Jeong-Won Park, Il-Young Jung
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(4): 257. CrossRef
- How loss of tooth structure impacts the biomechanical behavior of a single-rooted maxillary premolar: FEA
- 1,761 View
- 8 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Effects of occlusal load on the cervical stress distribution: A three-dimensional finite element study
- Hyeong-Mo Lee, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Sung-Gwan Woo, Kwang-Hoon Kim, Kwon Son, Jeong-Kil Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(6):427-436. Published online November 30, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.6.427
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The objective of this study was to investigate the effects of various occlusal loads on the stress distribution of the buccal cervical region of a normal maxillary second premolar, using a three dimensional finite element analysis (3D FEA).
After 3D FE modeling of maxillary second premolar, a static load of 500N of three load cases was applied. Stress analysis was performed using ANSYS (Swanson Analysis Systems, Inc., Houston, USA). The maximum principal stresses and minimum principal stresses were sampled at thirteen nodal points in the buccal cervical enamel for each four horizontal planes, 1.0 mm above CEJ, 0.5 mm above CEJ, CEJ, 0.5 mm under CEJ.
The results were as follows
1. The peak stress was seen at the cervical enamel surface of the mesiobuccal line angle area, asymmetrically.
2. The values of compressive stresses were within the range of the failure stress of enamel. But the values of tensile stresses exceeded the range of the failure stress of enamel.
3. The tensile stresses from the perpendicular load at the buccal incline of palatal cusp may be shown to be the primary etiological factors of the NCCLs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Biomechanical and Occlusal Factors Influencing the Longevity of Single-Unit Restorations: A Comprehensive Review
Wedad S Alaida, Safa A Gadi, Rokia E Al-Ghannam, Moayad F Alamri, Feras I Mirdad, Ruba M Argaibeh, Bushra A Alqahtani, Abdulrahman M Alqahtani, Abdulelah A Al Jaban, Turki M Alkuraydimi, Abdulrahman S Alamari
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of restoration type on the stress distribution of endodontically treated maxillary premolars; Three-dimensional finite element study
Heun-Sook Jung, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Bock Hur, Kwang-Hoon Kim, Kwon Son, Jeong-Kil Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(1): 8. CrossRef - Stress distribution of endodontically treated maxillary second premolars restored with different methods: Three-dimensional finite element analysis
Dong-Yeol Lim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Bock Hur, Kwang-Hoon Kim, Kwon Son, Jeong-Kil Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(1): 69. CrossRef
- Biomechanical and Occlusal Factors Influencing the Longevity of Single-Unit Restorations: A Comprehensive Review
- 1,770 View
- 4 Download
- 3 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


