Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Effects of the endodontic access cavity on apical debris extrusion during root canal preparation using different single-file systems
- Pelin Tüfenkçi, Koray Yılmaz, Mehmet Adigüzel
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(3):e33. Published online June 4, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e33
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
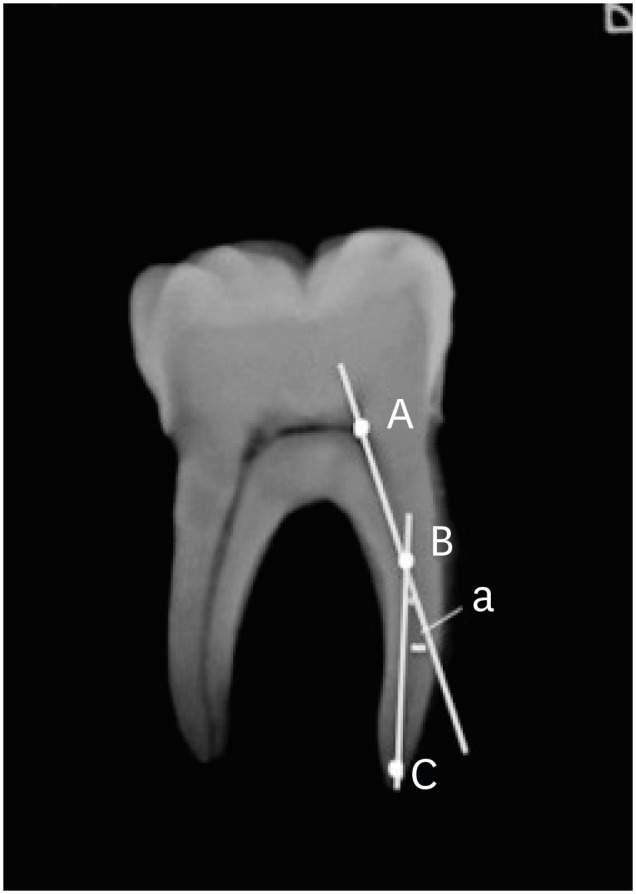
ePub Objectives This study was conducted to evaluate the effects of traditional and contracted endodontic cavity (TEC and CEC) preparation with the use of Reciproc Blue (RPC B) and One Curve (OC) single-file systems on the amount of apical debris extrusion in mandibular first molar root canals.
Materials and Methods Eighty extracted mandibular first molar teeth were randomly assigned to 4 groups (
n = 20) according to the endodontic access cavity shape and the single file system used for root canal preparation (reciprocating motion with the RCP B and rotary motion with the OC): TEC-RPC B, TEC-OC, CEC-RPC B, and CEC-OC. The apically extruded debris during preparation was collected in Eppendorf tubes. The amount of extruded debris was quantified by subtracting the weight of the empty tubes from the weight of the Eppendorf tubes containing the debris. Data were analyzed using 1-way analysis of variance with the Tukeypost hoc test. The level of significance was set atp < 0.05.Results The CEC-RPC B group showed more apical debris extrusion than the TEC-OC and CEC-OC groups (
p < 0.05). There were no statistically significant differences in the amount of apical debris extrusion among the TEC-OC, CEC-OC, and TEC-RPC B groups.Conclusions RPC B caused more apical debris extrusion in the CEC groups than did the OC single-file system. Therefore, it is suggested that the RPC B file should be used carefully in teeth with a CEC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative Evaluation of Periapical Expulsion Using Manual, Rotary, and Reciprocating Instrumentation With EndoVac Irrigation: An In Vitro Study
Sachin Metkari, Sanpreet S Sachdev, Pravin Patil, Manoj Ramugade, Kishor D Sapkale, Kulvinder S Banga, Dinesh Rao
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Debris Extrusion and Preparation Time by Traverse, R‐Motion Glider C, and Other Glide Path Systems in Severely Curved Canals
Taher Al Omari, Layla Hassouneh, Khawlah Albashaireh, Alaa Dkmak, Rami Albanna, Ali Al-Mohammed, Ahmed Jamleh, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
International Journal of Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Minimal İnvaziv Giriş Kavitelerinin Alt Kesici Dişlerdeki Apikal Ekstrüzyona Etkisi
İrem Haskarabağ, Cangül Keskin
Türk Diş Hekimliği Araştırma Dergisi.2025; 4(2): 75. CrossRef - Evaluation of apically extruded debris from root canal filling removal of the mesiobuccal canal of maxillary molars using XP shaper and protaper with two different irrigation
Sanaz Mirsattari, Maryam Zare Jahromi, Masoud Khabiri
Dental Research Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Impact of Minimum Invasive Access Cavity Design on the Quality of Instrumentation of Root Canals of Maxillary Molars Using Cone-Beam Computed Tomography: An in Vitro Study
Fahad H Baabdullah, Samia M Elsherief , Rayan A Hawsawi, Hetaf S Redwan
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of Bacterial Load and Post-Endodontic Pain after One-Visit Root Canal Treatment Using Two Types of Endodontic Access Openings: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial
Ahmed M. Al-Ani, Ahmed H. Ali, Garrit Koller
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(4): 88. CrossRef - The effect of different kinematics on apical debris extrusion with a single-file system
Taher M. N. Al Omari, Giusy Rita Maria La Rosa, Rami Haitham Issa Albanna, Abedelmalek Tabnjh, Flavia Papale, Eugenio Pedullà
Odontology.2023; 111(4): 910. CrossRef - The effects of laser and ultrasonic irrigation activation methods on smear and debris removal in traditional and conservative endodontic access cavities
Hüseyin Gündüz, Esin Özlek
Lasers in Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of access cavity design, sodium hypochlorite formulation and XP‐endo Shaper usage on apical debris extrusion – A laboratory investigation
Jerry Jose, Aishuwariya Thamilselvan, Kavalipurapu Venkata Teja, Giampiero Rossi–Fedele
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(1): 6. CrossRef - Apically extruded debris, canal transportation, and shaping ability of nickel-titanium instruments on contracted endodontic cavities in molar teeth
Qinqin Zhang, Jingyi Gu, Jiadi Shen, Ming Ma, Ying Lv, Xin Wei
Journal of Oral Science.2023; 65(4): 203. CrossRef - Impact of contracted endodontic cavities on instrumentation efficacy—A systematic review
Manan Shroff, Karkala Venkappa Kishan, Nimisha Shah, Purnima Saklecha
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(1): 202. CrossRef - Present status and future directions – Minimal endodontic access cavities
Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Gustavo De‐Deus, Erick Miranda Souza, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Daniele Moreira Cavalcante, Marco Simões‐Carvalho, Marco Aurélio Versiani
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S3): 531. CrossRef - Effect of guided conservative endodontic access and different file kinematics on debris extrusion in mesial root of the mandibular molars: An in vitro study
Sathish Sundar, Aswathi Varghese, KrithikaJ Datta, Velmurugan Natanasabapathy
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2022; 25(5): 547. CrossRef - A critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study apical extrusion of debris and irrigants
Jale Tanalp
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S1): 153. CrossRef - Current strategies for conservative endodontic access cavity preparation techniques—systematic review, meta-analysis, and decision-making protocol
Benoit Ballester, Thomas Giraud, Hany Mohamed Aly Ahmed, Mohamed Shady Nabhan, Frédéric Bukiet, Maud Guivarc’h
Clinical Oral Investigations.2021; 25(11): 6027. CrossRef - Extrusion of debris with and without intentional foraminal enlargement – A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Ricardo Machado, Gislayne Vigarani, Tainara Macoppi, Ajinkya Pawar, Stella Maria Glaci Reinke, Ana Cristina Kovalik Gonçalves
Australian Endodontic Journal.2021; 47(3): 741. CrossRef - Apical debris extrusion of single-file systems in curved canals
Ecehan Hazar, Olcay Özdemir, Mustafa Murat Koçak, Baran Can Sağlam, Sibel Koçak
Endodontology.2021; 33(3): 128. CrossRef - Quantitative Evaluation of Apically Extruded Debris in Root Canals prepared by Single-file Reciprocating and Single File Rotary Instrumentation Systems: A Comparative In vitro Study
Sonal Sinha, Konark Singh, Anju Singh, Swati Priya, Avanindra Kumar, Sahil Kawle
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2021; 13(Suppl 2): S1398. CrossRef - THE INFLUENCE OF DIFFERENT PECKING DEPTH ON AMOUNT OF APICALLY EXTRUDED DEBRIS DURING ROOT CANAL PREPARATION
Fatih ÇAKICI, Busra UYSAL, Elif Bahar CAKİCİ, Adem GUNAYDIN
Atatürk Üniversitesi Diş Hekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi.2021; : 1. CrossRef
- Comparative Evaluation of Periapical Expulsion Using Manual, Rotary, and Reciprocating Instrumentation With EndoVac Irrigation: An In Vitro Study
- 2,632 View
- 25 Download
- 19 Crossref

- Comparison of postoperative pain intensity after using reciprocating and continuous rotary glide path systems: a randomized clinical trial
- Mehmet Adıgüzel, Koray Yılmaz, Pelin Tüfenkçi
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(1):e9. Published online February 12, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e9
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
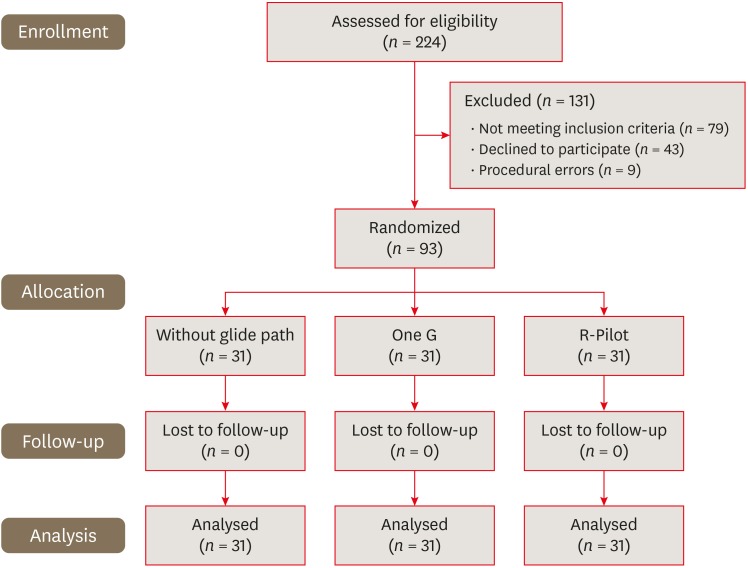
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to compare postoperative pain intensity after root canal treatment with One G (OG) vs. R-Pilot (RP) files used for glide path preparation.
Materials and Methods Ninety-three single-canaled mandibular premolar teeth with asymptomatic non-vital pulp were randomly assigned into 3 groups (
n = 31): OG, RP, or without glide path (WGP). After creating the glide path, the root canals were prepared using sequential Mtwo rotary files to size 30/0.05. One endodontic specialist carried out single-visit endodontic treatment. The patients were asked to rate the severity of postoperative pain on a visual analogue scale at 24, 48, and 72 hours after the visit. They were also asked to record their intake of prescribed analgesics taken. The data were analyzed using the χ2, Friedman, Kruskal-Wallis, and Mann-WhitneyU tests.Results In all 3 groups, postoperative pain decreased significantly at each time interval (
p < 0.05). At 24 hours, the OG group had less postoperative pain than the WGP group (p < 0.05). However, no significant difference was found between the RP group and the others. No statistically significant difference was found among the WGP, OG, and RP groups in postoperative pain intensity at 48 or 72 hours or in analgesic tablet intake at the 3 assessed time intervals.Conclusions The OG group had less postoperative pain than the WGP group in the first 24 hours. The OG and RP systems were similar regarding postoperative pain intensity and analgesic intake.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of glide path preparation on postoperative pain using TruNatomy and Reciproc Blue in single-visit root canal therapy: A randomized clinical trial
Fatima Siddiqui, Sajid Ali, Huma Iftekhar, Rajendra Kumar Tewari, Ashok Kumar, Sharique Alam
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(12): 1222. CrossRef - Postoperative pain in patients following endodontic treatment by XP-endo Shaper files: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Henal Nilesh Dedhia, Vibha R. Hegde, Maitri B. Bhayani, Sanitra R. Hegde
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(11): 1168. CrossRef - Postoperative Pain Following Single Visit Root Canal Treatment With Reciproc Blue And Hyflex EDM Instrumentation; A Prospective Randomized Clinical Trial
Nimet Gençoğlu, Anıl Özgün Karatekin, Mustafa Gündoğar
Meandros Medical And Dental Journal.2024; 25(1): 78. CrossRef - Glide Path in Endodontics: A Literature Review of Current Knowledge
Vlad Mircea Lup, Giulia Malvicini, Carlo Gaeta, Simone Grandini, Gabriela Ciavoi
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(8): 257. CrossRef - Post-Operative Pain in Reciprocating Versus Rotary Kinematics Post-Endodontic Treatment: A Systematic Review
Youssef Algarni
Archives of Pharmacy Practice.2024; 15(2): 53. CrossRef - Evaluation of Pain Following the Use of Different Single-file Glide Path Systems: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Zeliha Danaci, Kübra Yeşildal Yeter
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(2): 120. CrossRef - Incidence of postoperative pain after using single continuous, single reciprocating, and full sequence continuous rotary file system: a prospective randomized clinical trial
Umesh Kumar, Pragnesh Parmar, Ruchi Vashisht, Namita Tandon, Charan Kamal Kaur
Journal of Dental Anesthesia and Pain Medicine.2023; 23(2): 91. CrossRef - Impact of kinematics on the efficiency and safety of an engine-driven file for glide path preparation in MB2 canals of maxillary molars
Larissa B. B. Araújo, Pedro H. S. Calefi, Murilo P. Alcalde, Giulio Gavini, Rodrigo R. Vivan, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 27(3): 1153. CrossRef - Evaluation of Postoperative Pain after Pulpectomy using Different File Systems in Primary Teeth
Lakshimi Lakshmanan, Sujatha Somasundaram, Ganesh Jeevanandan, EMG Subramanian
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2021; 12(1): 3. CrossRef - Evaluation of type of kinematics on glide path procedures and torsional fatigue resistance after preparation of moderately curved canals
Murilo Priori Alcalde, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Pedro Henrique Souza Calefi, Victor de Moraes Cruz, Bruno Carvalho de Vasconcelos, Marcus Vinícius Reis Só, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan
Brazilian Oral Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of glide path kinematics during endodontic treatment on the occurrence and intensity of intraoperative and postoperative pain: a systematic review of randomized clinical trials
Thaís Christina Cunha, Felipe de Souza Matos, Luiz Renato Paranhos, Ítalo de Macedo Bernardino, Camilla Christian Gomes Moura
BMC Oral Health.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Effect of glide path preparation on postoperative pain using TruNatomy and Reciproc Blue in single-visit root canal therapy: A randomized clinical trial
- 3,197 View
- 23 Download
- 11 Crossref

- The effect of root canal preparation on the surface roughness of WaveOne and WaveOne Gold files: atomic force microscopy study
- Taha Özyürek, Koray Yılmaz, Gülşah Uslu, Gianluca Plotino
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(1):e10. Published online February 2, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e10
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
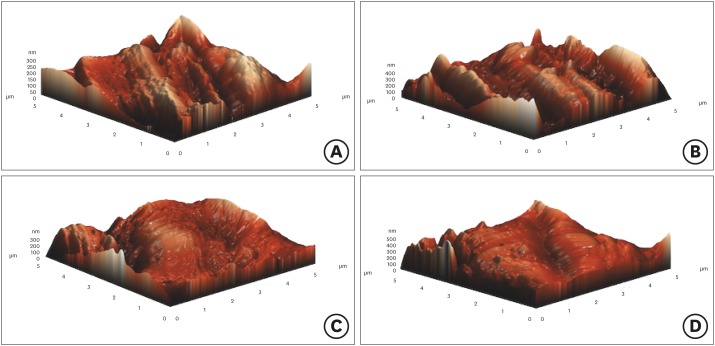
ePub Objectives To examine the surface topography of intact WaveOne (WO; Dentsply Sirona Endodontics) and WaveOne Gold (WOG; Dentsply Sirona Endodontics) nickel-titanium rotary files and to evaluate the presence of alterations to the surface topography after root canal preparations of severely curved root canals in molar teeth.
Materials and Methods Forty-eight severely curved canals of extracted molar teeth were divided into 2 groups (
n = 24/each group). In group 1, the canals were prepared using WO and in group 2, the canals were prepared using WOG files. After the preparation of 3 root canals, instruments were subjected to atomic force microscopy analysis. Average roughness and root mean square values were chosen to investigate the surface features of endodontic files. The data was analyzed using one-way analysis of variance andpost hoc Tamhane's tests at 5% significant level.Results The surface roughness values of WO and WOG files significantly changed after use in root canals (
p < 0.05). The used WOG files exhibited higher surface roughness change when compared with the used WO files (p < 0.05).Conclusions Using WO and WOG Primary files in 3 root canals affected the surface topography of the files. After being used in root canals, the WOG files showed a higher level of surface porosity value than the WO files.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative Analysis of Surface Roughness and Plastic Deformation of Reciprocating Instruments after Clinical Use
Ángel Herrera, Magdalena Azabal, Jesús R. Jimenez-Octavio, Juan C. del Real-Romero, Sara López de Armentia, Juan M. Asensio-Gil, Ana Arias
Materials.2024; 17(16): 3978. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Surface Roughness of Different Rotary Nickel-Titanium (NiTi) Files After Autoclaving: An Atomic Force Microscopic Study
Angela Alex, Ranjith Kumar Sivarajan, Vijay Venkatesh
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of endodontic irrigants on surface roughness of various nickel-titanium rotary endodontic instruments
Tamer M. Hamdy, Yasmine Mohsen Alkabani, Amira Galal Ismail, Manar M. Galal
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Metallurgical Tests in Endodontics: A Narrative Review
Alessio Zanza, Marco Seracchiani, Rodolfo Reda, Gabriele Miccoli, Luca Testarelli, Dario Di Nardo
Bioengineering.2022; 9(1): 30. CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue Resistance and Surface Roughness of Rotary NiTi Instruments after Simulated Clinical Use in Curved Root Canals – An Atomic Force Microscopy Study
Raksha Bhat, Arjun Kini, Preethesh Shetty, Payalben Kansara, Bapanaiah Penugonda
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - In Vitro Study of Irrigation solution of Chitosan Nanoparticles to Inhibit the Adhesion and Biofilm Formation of Enterococcus faecalis in the Root Canal
Imelda Darmawi, Trimurni Abidin, Harry Agusnar, Basri A. Gani
Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology.2022; : 2691. CrossRef - Alteration in surface roughness of reciprocating endodontic instruments
Khoa Van Pham
F1000Research.2021; 10: 875. CrossRef - Surface profile of different heat-treated nickel-titanium files before and after root canal preparation
Iandara de Lima Scardini, Denise Maria Zezell, Juliana Lisboa Couto Marques, Laila Gonzales Freire, Marcelo dos Santos
Brazilian Dental Journal.2021; 32(6): 8. CrossRef - Impact of Endodontic Instrumentation on Surface Roughness of Various Nickel-Titanium Rotary Files
Muhammad Sohail Zafar
European Journal of Dentistry.2021; 15(02): 273. CrossRef - A new method for assessment of nickel-titanium endodontic instrument surface roughness using field emission scanning electronic microscope
Khoa Van Pham, Canh Quang Vo
BMC Oral Health.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Surface Alterations Induced on Endodontic Instruments by Sterilization Processes, Analyzed with Atomic Force Microscopy: A Systematic Review
Mario Dioguardi, Vito Crincoli, Luigi Laino, Mario Alovisi, Enrica Laneve, Diego Sovereto, Bruna Raddato, Khrystyna Zhurakivska, Filiberto Mastrangelo, Domenico Ciavarella, Lucio Lo Russo, Lorenzo Lo Muzio
Applied Sciences.2019; 9(22): 4948. CrossRef - Atomic force microscopy and energy dispersive X‐ray spectrophotometry analysis of reciprocating and continuous rotary nickel‐titanium instruments following root canal retreatment
Bulem Üreyen Kaya, Cevat Emre Erik, Gülsen Kiraz
Microscopy Research and Technique.2019; 82(7): 1157. CrossRef - Influence of heat treatment on torsional resistance and surface roughness of nickel‐titanium instruments
E. J. N. L. Silva, J. F. N. Giraldes, C. O. de Lima, V. T. L. Vieira, C. N. Elias, H. S. Antunes
International Endodontic Journal.2019; 52(11): 1645. CrossRef
- Comparative Analysis of Surface Roughness and Plastic Deformation of Reciprocating Instruments after Clinical Use
- 1,739 View
- 12 Download
- 13 Crossref

- Incidence of apical crack formation and propagation during removal of root canal filling materials with different engine driven nickel-titanium instruments
- Taha Özyürek, Vildan Tek, Koray Yılmaz, Gülşah Uslu
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(4):332-341. Published online November 4, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.4.332
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives To determine the incidence of crack formation and propagation in apical root dentin after retreatment procedures performed using ProTaper Universal Retreatment (PTR), Mtwo-R, ProTaper Next (PTN), and Twisted File Adaptive (TFA) systems.
Materials and Methods The study consisted of 120 extracted mandibular premolars. One millimeter from the apex of each tooth was ground perpendicular to the long axis of the tooth, and the apical surface was polished. Twenty teeth served as the negative control group. One hundred teeth were prepared, obturated, and then divided into 5 retreatment groups. The retreatment procedures were performed using the following files: PTR, Mtwo-R, PTN, TFA, and hand files. After filling material removal, apical enlargement was done using apical size 0.50 mm ProTaper Universal (PTU), Mtwo, PTN, TFA, and hand files. Digital images of the apical root surfaces were recorded before preparation, after preparation, after obturation, after filling removal, and after apical enlargement using a stereomicroscope. The images were then inspected for the presence of new apical cracks and crack propagation. Data were analyzed with χ2 tests using SPSS 21.0 software.
Results New cracks and crack propagation occurred in all the experimental groups during the retreatment process. Nickel-titanium rotary file systems caused significantly more apical crack formation and propagation than the hand files. The PTU system caused significantly more apical cracks than the other groups after the apical enlargement stage.
Conclusions This study showed that retreatment procedures and apical enlargement after the use of retreatment files can cause crack formation and propagation in apical dentin.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Microcracks induced by XP-endo retreatment system in root canals filled with bioceramic sealer: A micro-computed tomographic analysis
Sarah M. Alkahtany
The Saudi Dental Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A comparative evaluation of different retreatment methods on apical root microcracks initiation and propagation: An in vitro study
Shweta Lodha, Zinnie Nanda
Endodontology.2025; 37(2): 175. CrossRef - Efficacy of Endodontic Files in Root Canal Retreatment: A Systematic Review of In Vitro Studies
Anna Soler-Doria, José Luis Sanz, Marcello Maddalone, Leopoldo Forner
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2025; 16(8): 293. CrossRef - Efficacy of Various Heat-treated Retreatment File Systems on Dentin Removal and Crack Analysis: An in vitro Study
Swathi Suresh, Pradeep Solete, Delphine Priscilla Antony, Kavalipurapu Venkata Teja, Adimulapu Hima Sandeep, Sruthi Sairaman, Marco Cicciù, Giuseppe Minervini
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A comparative evaluation of the dentinal microcracks formed and propagated during the removal of gutta-percha using hand and three rotary retreatment file systems: A micro-computed tomography study
Srivastava Sanjeev, Rita Gupta, Dubey Sandeep, Tewari Tanu, Shukla Namita, Singh Arohan
Endodontology.2023; 35(2): 155. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of incidence of dentinal defects after root canal preparation using hand, rotary, and reciprocating files: An ex vivo study
Debanjan Das, Sudipto Barai, Rohit Kumar, Sourav Bhattacharyya, AsimB Maity, Pushpa Shankarappa
Journal of International Oral Health.2022; 14(1): 78. CrossRef - Critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study removal of root filling materials
Mahdi A. Ajina, Pratik K. Shah, Bun San Chong
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S1): 119. CrossRef - Evaluation of Dentinal Crack Propagation, Amount of Gutta Percha Remaining and Time Required During Removal of Gutta Percha Using Two Different Rotary Instruments and Hand Instruments - An In vitro Study
S Tejaswi, A Singh, S Manglekar, UK Ambikathanaya, S Shetty
Nigerian Journal of Clinical Practice.2022; 25(4): 524. CrossRef - The Influence of Root Canal Preparation with ProTaper Next, WaveOne Gold, and Twisted Files on Dentine Crack Formation
Wojciech Eliasz, Beata Czarnecka, Anna Surdacka
Machines.2021; 9(12): 332. CrossRef - The potential effect of instrumentation with different nickel titanium rotary systems on dentinal crack formation—An in vitro study
Márk Fráter, András Jakab, Gábor Braunitzer, Zsolt Tóth, Katalin Nagy, Andrej M. Kielbassa
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(9): e0238790. CrossRef - Micro–computed Tomographic Assessment of the Residual Filling Volume, Apical Transportation, and Crack Formation after Retreatment with Reciproc and Reciproc Blue Systems in Curved Root Canals
Damla Kırıcı, Sezer Demirbuga, Ertuğrul Karataş
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(2): 238. CrossRef - Force and vibration generated in apical direction by three endodontic files of different kinematics during simulated canal preparation: An in vitro analytical study
Ankit Nayak, PK Kankar, Prashant K Jain, Niharika Jain
Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part H: Journal of Engineering in Medicine.2019; 233(8): 839. CrossRef - Effect of Aging on Dentinal Crack Formation after Treatment and Retreatment Procedures: a Micro-CT Study
Lilian Rachel de Lima Aboud, Bernardo Camargo dos Santos, Ricardo Tadeu Lopes, Leonardo Aboud Costa Viana, Miriam Fátima Zaccaro Scelza
Brazilian Dental Journal.2018; 29(6): 530. CrossRef
- Microcracks induced by XP-endo retreatment system in root canals filled with bioceramic sealer: A micro-computed tomographic analysis
- 1,861 View
- 12 Download
- 13 Crossref

- The effects of autoclave sterilization on the cyclic fatigue resistance of ProTaper Universal, ProTaper Next, and ProTaper Gold nickel-titanium instruments
- Taha Özyürek, Koray Yılmaz, Gülşah Uslu
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(4):301-308. Published online November 2, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.4.301
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives It was aimed to compare the cyclic fatigue resistances of ProTaper Universal (PTU), ProTaper Next (PTN), and ProTaper Gold (PTG) and the effects of sterilization by autoclave on the cyclic fatigue life of nickel-titanium (NiTi) instruments.
Materials and Methods Eighty PTU, 80 PTN, and 80 PTG were included to the present study. Files were tested in a simulated canal. Each brand of the NiTi files were divided into 4 subgroups: group 1, as received condition; group 2, pre-sterilized instruments exposed to 10 times sterilization by autoclave; group 3, instruments tested were sterilized after being exposed to 25%, 50%, and 75% of the mean cycles to failure, then cycled fatigue test was performed; group 4, instruments exposed to the same experiment with group 3 without sterilization. The number of cycles to failure (NCF) was calculated. The data was statistically analyzed by using one-way analysis of variance and
post hoc Tukey tests.Results PTG showed significantly higher NCF than PTU and PTN in group 1 (
p < 0.05). Sterilization significantly increased the NCF of PTN and PTG (p < 0.05) in group 2. PTN in group 3 had significantly higher cyclic fatigue resistance than PTN group 4 (p < 0.05). Also, significantly higher NCF was observed for PTG in group 2 than in groups 3 and 4 (p < 0.05).Conclusions PTG instrument made of new gold alloy was more resistant to fatigue failure than PTN and PTU. Autoclaving increased the cyclic fatigue resistances of PTN and PTG.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of Autoclaving on the Mechanical Performance and Metallurgical Behavior of ProTaper Ultimate, BlueShaper, and ZenFlex Nickel–Titanium Systems
Fatima Bardan, Mohamed El-Kishawi, Ensanya Ali Abou Neel, Saaid Al Shehadat, Rashid El Abed, Ahmed Jamleh
Journal of Endodontics.2026; 52(2): 292. CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue Evaluation of Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instruments Using an Electrical Resistance-based Method
Congyu Yang, Yi Min, Wei Fan
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(10): 1471. CrossRef - The influence of autoclave sterilization on the cyclic fatigue of M-wire rotary endodontic instruments
Nenad Stosic, Jelena Popovic, Antonije Stankovic, Aleksandar Mitic, Marija Nikolic, Kosta Todorovic
Vojnosanitetski pregled.2024; 81(10): 642. CrossRef - Evaluatation of two nickle-titanium systems’ (Neolix and X Pro Gold) resistance to fracture after immersion in sodium hypochlorite.
Solmaz Araghi, Abbas Delvarani, Faeze dehghan, Parisa Kaghazloo
journal of research in dental sciences.2024; 21(1): 17. CrossRef - Comparing the EdgeFile X3, GenEndo, HeroGold, and ProTaper Gold Rotary Instruments Regarding the Effect of Different Concentrations and Temperature of NaOCl on Cyclic Fatigue Resistance
Garima Tyagi, Parul Shakarwal, Prakash Kumar, Annu Kumari, Aditya Singh, Pallavi Kusum
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2023; 24(9): 715. CrossRef - Cyclic fatigue resistance of EdgeTaper Platinum, Protaper Gold, and TruNatomy Prime rotary files before and after autoclave sterilization
Rahaf A. Almohareb, Reem M. Barakat, Fahda N. Algahtani, Manal F. Alkadi
PeerJ.2023; 11: e14656. CrossRef - Comparison of the fracture resistance of the teeth prepared with ProTaper Universal, ProTaper Next, and ProTaper Gold rotary files
Amin Salem Milani, Shabnam Ganjpour, Fatemeh Dehghani, Saeed Rahimi, Pouya Sabanik
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2022; 8(6): 1421. CrossRef - Impacts of NaOCl and Irritrol irrigation solutions with/without autoclave sterilisation on the cyclic fatigue resistance of different nickel‐titanium files
Fatma Kermeoglu, Mohamad Abduljalil
Australian Endodontic Journal.2022; 48(3): 392. CrossRef - Fracture Resistance of Heat-Treated Nickel-Titanium Rotary Files After Usage and Autoclave Sterilization: An In Vitro Study
Rashid El Abed, Aisha Alshehhi, Yoo Jung Kang, Dana Al Raeesi, Amar H. Khamis, Mohamed Jamal, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2022; 48(11): 1428. CrossRef - Nitinol Type Alloys General Characteristics and Applications in Endodontics
Leszek A. Dobrzański, Lech B. Dobrzański, Anna D. Dobrzańska-Danikiewicz, Joanna Dobrzańska
Processes.2022; 10(1): 101. CrossRef - The Impact of Multiple Autoclave Cycles on the Surface Roughness of Thermally Treated Nickel-Titanium Endodontic Files
Raidan Ba-Hattab, Rahaf A. Almohareb, Rana Alkhalaf, Shikhah Binnjefan, Meral Sulayem, Reem M. Barakat, Ismail Demir
Advances in Materials Science and Engineering.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Effect of autoclave sterilisation and heat activated sodium hypochlorite irrigation on the performance of nickel-titanium rotary files against cyclic fatigue
Zuha Ayad Jaber, Sattar Jabbar Abdul-Zahra Al-Hmedat, Sarmad Adel Hameed, Suhad Jabbar Hamed Al-Nasrawi, Abtesam Imhemed Aljdaimi, Julfikar Haider
Advances in Materials and Processing Technologies.2022; 8(1): 1071. CrossRef - Effect of different axial speed patterns on cyclic fatigue resistance of rotary nickel-titanium instruments
Myint Thu, Arata Ebihara, Keiichiro Maki, Miki Nishijo, Shunsuke Kimura, Taro Nakatsukasa, Moe Sandar Kyaw, Takashi Okiji
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue Resistance and Shaping Ability of Heat-Treated Nickel-Titanium Instruments after Repeated Use
SG Kamali, D Turkaydin
Nigerian Journal of Clinical Practice.2021; 24(2): 247. CrossRef - Effects of repeated sterilization cycles on the surface alterations of ProTaper Next, TF Adaptive, HyFlex CM, and 2Shape instruments
Olcay Özdemir, Sibel Koçak, Mustafa Murat Koçak, Baran Can Sağlam
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2021; 15(2): 76. CrossRef - Cleaning of endodontic files with and without enzymatic detergent by means of the manual method versus the ultrasonic method
César F Cayo-Rojas, Estefany Brito-Ávila, Ana S Aliaga-Mariñas, Karen K Hernández-Caba, Emylain D Saenz-Cazorla, Marysela I Ladera-Castañeda, Luis A Cervantes-Ganoza
Journal of International Society of Preventive and Community Dentistry.2021; 11(3): 307. CrossRef - Effect of number of uses and sterilization on the instrumented area and resistance of reciprocating instruments
Victor de Ornelas Peraça, Samantha Rodrigues Xavier, Fabio de Almeida Gomes, Luciane Geanini Pena dos Santos, Erick Miranda Souza, Fernanda Geraldo Pappen
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of sterilization procedures on the physical and mechanical properties of rotating endodontic instruments: a systematic review and network meta-analysis
Mario Dioguardi, Claudia Arena, Diego Sovereto, Riccardo Aiuto, Luigi Laino, Gaetano Illuzzi, Enrica Laneve, Bruna Raddato, Vito Carlo Alberto Caponio, Antonio Dioguardi, Khrystyna Zhurakivska, Giuseppe Troiano, Lorenzo Lo Muzio
Frontiers in Bioscience-Landmark.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - EFFECTS OF SODIUM HYPOCHLORIDE ON CYCLIC FATIGUE RESISTANCE OF BIORACE ROTARY INSTRUMENT WITH DIFFERENT TIP SIZES
Ayfer ATAV ATEŞ, Burçin ARICAN
Atatürk Üniversitesi Diş Hekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi.2021; : 1. CrossRef - The Influence of NiTi Alloy on the Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Endodontic Files
Celia Ruiz-Sánchez, Vicente Faus-Llácer, Ignacio Faus-Matoses, Álvaro Zubizarreta-Macho, Salvatore Sauro, Vicente Faus-Matoses
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(11): 3755. CrossRef - Novel Electronic Device to Quantify the Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Endodontic Reciprocating Files after Using and Sterilization
Álvaro Zubizarreta-Macho, Óscar Alonso-Ezpeleta, Alberto Albaladejo Martínez, Vicente Faus Matoses, Javier Caviedes Brucheli, Rubén Agustín-Panadero, Jesús Mena Álvarez, Fernando Vizmanos Martínez-Berganza
Applied Sciences.2020; 10(14): 4962. CrossRef - Influence of autoclave sterilization procedures on the cyclic fatigue resistance of heat-treated nickel-titanium instruments: a systematic review
Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Mayara Zanon, Fernanda Hecksher, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Rafaela Andrade de Vasconcelos, Tatiana Kelly da Silva Fidalgo
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Management of Instrument Sterilization Workflow in Endodontics: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Mario Dioguardi, Diego Sovereto, Gaetano Illuzzi, Enrica Laneve, Bruna Raddato, Claudia Arena, Vito Carlo Alberto Caponio, Giorgia Apollonia Caloro, Khrystyna Zhurakivska, Giuseppe Troiano, Lorenzo Lo Muzio
International Journal of Dentistry.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Effect of autoclave sterilization on cyclic fatigue and torsional fracture resistance of NiTi rotary instruments
Wooyoung Kim, Soram Oh, Gil-Joo Ryu, Tae-Hwan Kim, Sung-Jae Kim, Dong-Hyung Kim, Bin-Na Lee, Kee-Yeon Kum, Seok Woo Chang, Ji-Hyun Jang
Odontology.2020; 108(2): 194. CrossRef - Effects of Sodium Hypochlorite Concentration and Temperature on the Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Heat-treated Nickel-titanium Rotary Instruments
Hussam Alfawaz, Abdullah Alqedairi, Hala Alsharekh, Eman Almuzaini, Shahd Alzahrani, Ahmed Jamleh
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(10): 1563. CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Heat-treated Nickel-titanium Instruments after Immersion in Sodium Hypochlorite and/or Sterilization
Eugenio Pedullà, Angela Benites, Giusy M. La Rosa, Gianluca Plotino, Nicola M. Grande, Ernesto Rapisarda, Luigi Generali
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(4): 648. CrossRef
- Impact of Autoclaving on the Mechanical Performance and Metallurgical Behavior of ProTaper Ultimate, BlueShaper, and ZenFlex Nickel–Titanium Systems
- 1,782 View
- 26 Download
- 26 Crossref

-
In vitro comparison of the cyclic fatigue resistance of HyFlex EDM, One G, and ProGlider nickel titanium glide path instruments in single and double curvature canals - Koray Yılmaz, Gülşah Uslu, Taha Özyürek
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(4):282-289. Published online October 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.4.282
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives It was aimed to compare the cyclic fatigue resistances of ProGlider (PG), One G (OG), and HyFlex EDM (HEDM) nickel titanium glide path files in single- and double-curved artificial canals.
Materials and Methods 40 PG (16/0.02), 40 OG (14/0.03), and 40 HEDM (10/0.05) single-file glide path files were used in the present study. Sixty files were subjected to cyclic fatigue test by using double-curved canals and 60 files by using single-curved canal (
n = 20). The number of cycles to fracture (NCF) was calculated and the length of the fractured fragment (FL) was determined by a digital micro-caliper. Twelve pieces of fractured files were examined with scanning electron microscope to determine fracture types of the files (n = 2). The NCF and the FL data were analyzed using one-way analysis of variance andpost hoc Tukey test using SPSS 21 software (p < 0.05).Results In all of the groups, NCF values were significantly lower in double-curved canals when compared to single-curved canals (
p < 0.05). For both of single- and double-curved canals, NCF values of HEDM group in apical and coronal curvatures were found to be significantly higher than NCF values of PG and OG groups (p < 0.05). In both of single- and double-curved canals, NCF value of PG group was found significantly higher than OG group (p < 0.05).Conclusions Within the limitations of this study, HEDM glide path files were found to have the highest cyclic fatigue resistance in both of single- and double-curved canals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of canal curvature on cyclic fatigue resistance of rotary instruments using different irrigation materials (in vitro study)
Mohammed Hamoudi Alsunboli, Sally Saad Ali Ihsan, Duha Qais Sabah
F1000Research.2024; 12: 449. CrossRef - Glide Path in Endodontics: A Literature Review of Current Knowledge
Vlad Mircea Lup, Giulia Malvicini, Carlo Gaeta, Simone Grandini, Gabriela Ciavoi
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(8): 257. CrossRef - Static and Dynamic Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instruments in a Double-Curved Stainless Steel Artificial Canal
Hoang-Lan-Anh Le, Thuan-Loc Tran, Thu-Thuy Nguyen, Tran-Lan-Khue Pham, Van-Khoa Pham
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(4): 2687. CrossRef - The effect of canal curvature on cyclic fatigue resistance of rotary instruments using different irrigation materials (in vitro study)
Mohammed Hamoudi Alsunboli, Sally Saad Ali Ihsan, Duha Qais Sabah
F1000Research.2023; 12: 449. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of torsional and cyclic fatigue resistance of ProGlider, WaveOne Gold Glider, and TruNatomy Glider in simulated curved canal
Pedro de Souza Dias, Augusto Shoji Kato, Carlos Eduardo da Silveira Bueno, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Pedro Henrique Souza Calefi, Rina Andréa Pelegrine
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Investigation of the efficacy of different Ni-Ti systems on acrylic blocks for correcting ledge formation
Osman Ünlü, Hüseyin Gürkan Güneç, Faruk Haznedaroğlu
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of postoperative pain in single visit endodontics using heat-treated nickel − titanium file systems – A randomized clinical trial
Priyanka Unnikrishnan, Lalitagauri Mandke, Leena Padhye
Endodontology.2023; 35(2): 94. CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Glide Path Rotary Files: A Systematic Review of in Vitro Studies
Israa Ashkar, José Luis Sanz, Leopoldo Forner
Materials.2022; 15(19): 6662. CrossRef - Endodontic Management of Dilacerated Maxillary First Molar with Tactile Controlled Activation Technique – A Case Report
Vijay Yadav, Rega Kumar, Ruchika Roongta Nawal, Sangeeta Talwar
Journal of Pierre Fauchard Academy (India Section).2022; : 67. CrossRef - Combination of a new ultrasonic tip with rotary systems for the preparation of flattened root canals
Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Jáder Camilo Pinto, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue of TruNatomy Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instrument in Single and Double Curvature Canals: A Comparative Study
Sarah A Rashid, Hikmet A AI-Gharrawi
World Journal of Dentistry.2021; 12(1): 28. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of a new system for root canal filling using calcium silicate-based root canal sealers
Mario Tanomaru-Filho, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Jader Camilo Pinto, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of torque, force generation and canal shaping ability between manual and nickel-titanium glide path instruments in rotary and optimum glide path motion
Pyae Hein Htun, Arata Ebihara, Keiichiro Maki, Shunsuke Kimura, Miki Nishijo, Daisuke Tokita, Takashi Okiji
Odontology.2020; 108(2): 188. CrossRef - Torsional fatigue strength of reciprocating and rotary pathfinding instruments manufactured from different NiTi alloys
Rodrigo Ricci VIVAN, Murilo Priori ALCALDE, George CANDEIRO, Giulio GAVINI, Celso Luis CALDEIRA, Marco Antonio Hungaro DUARTE
Brazilian Oral Research.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of postoperative pain intensity after using reciprocating and continuous rotary glide path systems: a randomized clinical trial
Mehmet Adıgüzel, Koray Yılmaz, Pelin Tüfenkçi
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Cyclic fatigue resistance of the WaveOne Gold Glider, ProGlider, and the One G glide path instruments in double-curvature canals
Damla Kırıcı, Alper Kuştarcı
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Intraoperative Pain During Glide Path Creation with the Use of a Rotary or Reciprocating System
Pelin TUFENKCİ, Mehmet ADIGUZEL, Koray YILMAZ
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2019; 22(1): 66. CrossRef
- The effect of canal curvature on cyclic fatigue resistance of rotary instruments using different irrigation materials (in vitro study)
- 1,540 View
- 9 Download
- 17 Crossref

- Cyclic fatigue life of Tango-Endo, WaveOne GOLD, and Reciproc NiTi instruments
- Koray Yılmaz, Taha Özyürek
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(2):134-139. Published online April 11, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.2.134
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives To compare the fatigue life of Tango-Endo, WaveOne GOLD, and Reciproc NiTi instruments under static model via artificial canals with different angles of curvature.
Materials and Methods Reciproc R25, WaveOne GOLD Primary, and Tango-Endo instruments were included in this study (
n = 20). All the instruments were rotated in artificial canals which were made of stainless steel with an inner diameter of 1.5 mm, 45°, 60°, and 90° angles of curvatures and a radius of curvature of 5 mm until fracture occurred, and the time to fracture was recorded in seconds using a digital chronometer. The data were analyzed using Kruskal-Wallis andpost-hoc Dunn tests were used for the statistical analysis of data in SPSS 21.0 software.Results Tango-Endo files were found to have significantly higher values than WaveOne GOLD and Reciproc files in terms of fatigue life (
p < 0.05). However, there was no statistically significant difference between fatigue life of Reciproc and WaveOne GOLD files (p > 0.05). It was determined that increasing the angle of curvature of the stainless canals caused significant decreases in fatigue life of all of three files (p < 0.05).Conclusions Within the limitations of the present study, the cyclic fatigue life of Tango-Endo in canals having different angles of curvature was statistically higher than Reciproc and WaveOne GOLD.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Apically extruded debris of different file systems used with various kinematic movements during retreatment: An in vitro study
Tuğba Koşar, Davut Çelik, Tamer Taşdemir
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(S1): 33. CrossRef - Nickel-titanium files in endodontics: Development, improvement and modifications of nickel-titanium alloy
Slavoljub Zivkovic, Milica Jovanovic-Medojevic, Jelena Neskovic, Marijana Popovic-Bajic
Vojnosanitetski pregled.2023; 80(3): 262. CrossRef - FATIGUE FAILURE OF NICKEL-TITANIUM INSTRUMENTS IN ENDODONTICS AND ITS INFLUENCING FACTORS
A Jusku, T Dodeková, J Staněk, B Özel, P Jirásek, V Polanská, Ľ Harvan
Česká stomatologie a praktické zubní lékařství.2022; 122(2): 51. CrossRef - Reciproc Endodontic File Surface Defects After Single Use
Mohammed Howait
Journal of International Society of Preventive and Community Dentistry.2021; 11(1): 98. CrossRef - A comparative evaluation of cyclic fatigue resistance of Reciproc Blue, WaveOne Gold and 2Shape nickel–titanium rotary files in different artificial canals
Ankita Grace Lall, Suparna Ganguly Saha, Vijay Alageshan, Parmeet Banga
Endodontology.2021; 33(1): 1. CrossRef - Cutting efficiency of heat‐treated nickel–titanium single‐file systems at different incidence angles
Eugenio Pedullà, Pietro La Paglia, Giusy Rita Maria La Rosa, Anna Maria Gueli, Stefania Pasquale, David E. Jaramillo, Leopoldo Forner, Fabio Lo Savio, Guido La Rosa, Ernesto Rapisarda
Australian Endodontic Journal.2021; 47(1): 20. CrossRef - Influence of the type of reciprocating motion on the cyclic fatigue resistance of reciprocating files in a dynamic model
Álvaro Zubizarreta-Macho, Alberto Albaladejo Martínez, Carlos Falcão Costa, Norberto Quispe-López, Ruben Agustín-Panadero, Jesús Mena-Álvarez
BMC Oral Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Cutting efficiency of conventional and heat‐treated nickel–titanium rotary or reciprocating glide path instruments
E. Pedullà, G. Leanza, G. R. M. La Rosa, A. M. Gueli, S. Pasquale, G. Plotino, E. Rapisarda
International Endodontic Journal.2020; 53(3): 376. CrossRef - Influence of static and dynamic cyclic fatigue tests on the lifespan of four reciprocating systems at different temperatures
A. Keleş, A. Eymirli, O. Uyanık, E. Nagas
International Endodontic Journal.2019; 52(6): 880. CrossRef - Comparison of Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of 5 Heat-treated Nickel-titanium Reciprocating Systems in Canals with Single and Double Curvatures
Mohammad I. Al-Obaida, Khalid Merdad, Mohammed S. Alanazi, Hesham Altwaijry, Mohammad AlFaraj, Ali A. Alkhamis, Ebtissam M. Al-Madi
Journal of Endodontics.2019; 45(10): 1237. CrossRef - Assessment of mechanical properties of WaveOne Gold Primary reciprocating instruments
Tong FANGLI, Keiichiro MAKI, Shunsuke KIMURA, Miki NISHIJO, Daisuke TOKITA, Arata EBIHARA, Takashi OKIJI
Dental Materials Journal.2019; 38(3): 490. CrossRef - Comparison between Single-file Rotary Systems: Part 2—The Effect of Length of the Instrument Subjected to Cyclic Loading on Cyclic Fatigue Resistance
Adham A. Azim, Mohamed Tarrosh, Katharina A. Azim, Lucila Piasecki
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(12): 1837. CrossRef - Comparison of cyclic fatigue resistance of XP-endo Shaper, HyFlex CM, FlexMaster and Race instruments
Mehmet Adiguzel, Ipek Isken, Ismail Ilker Pamukcu
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2018; 12(3): 208. CrossRef
- Apically extruded debris of different file systems used with various kinematic movements during retreatment: An in vitro study
- 1,718 View
- 10 Download
- 13 Crossref

- Effect of adaptive motion on cyclic fatigue resistance of a nickel titanium instrument designed for retreatment
- Taha Özyürek, Koray Yılmaz, Gülşah Uslu
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(1):34-38. Published online December 19, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.1.34

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to evaluate the cyclic fatigue resistance of the ProTaper Universal D1 file (Dentsply Maillefer) under continuous and adaptive motion.
Materials and Methods Forty ProTaper Universal D1 files were included in this study. The cyclic fatigue tests were performed using a dynamic cyclic fatigue testing device, which had an artificial stainless steel canal with a 60° angle of curvature and a 5 mm radius of curvature. The files were randomly divided into two groups (Group 1, Rotary motion; Group 2, Adaptive motion). The time to failure of the files were recorded in seconds. The number of cycles to failure (NCF) was calculated for each group. The data were statistically analyzed using Student's
t -test. The statistical significant level was set atp < 0.05.Results The cyclic fatigue resistance of the adaptive motion group was significantly higher than the rotary motion group (
p < 0.05).Conclusion Within the limitations of the present study, the ‘Adaptive motion’ significantly increased the resistance of the ProTaper Universal D1 file to cyclic facture.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of Different Separated File Retrieval Strategies on the Biomechanical Behavior of a Mandibular Molar: A Finite Element Analysis Study
Anas Sira, Nawar Naguib Nawar, Shehabeldin Mohamed Saber, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(1): 64. CrossRef - Surface Alterations of Ni‐Ti Files After Retreatment of Root Canals Filled With Different Sealers: AFM and SEM Study
Duygu Aksoy, Sibel Koçak, Mustafa Murat Koçak, Baran Can Sağlam
Microscopy Research and Technique.2025; 88(10): 2704. CrossRef - Evaluatation of two nickle-titanium systems’ (Neolix and X Pro Gold) resistance to fracture after immersion in sodium hypochlorite.
Solmaz Araghi, Abbas Delvarani, Faeze dehghan, Parisa Kaghazloo
journal of research in dental sciences.2024; 21(1): 17. CrossRef - Assessment the impact of operator experience on cyclic fatigue resistance in reciprocating and rotary NiTi files: a comparative study between dental students and pediatric dentistry specialists
Hande Özyürek, Mesut Elbay, Taha Özyürek
Frontiers in Materials.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of gutta-percha removal from the dentinal tubules using different instrumentation techniques with or without solvent: An In vitro study
MukeshKumar Hasija, Babita Meena, Deepti Wadhwa, KulvinderKaur Wadhwani, Virender Yadav
Journal of the International Clinical Dental Research Organization.2020; 12(1): 27. CrossRef - Influences of Continuous Rotation and TF adaptive Motion on the Resistance of Different Retreatment File Systems to Deformation and Fracture: An In Vitro study
Divya Meena, Ramyadharshini LNU, V Nivedha, Anand Sherwood
Journal of Operative Dentistry & Endodontics.2018; 3(2): 71. CrossRef - Comparison of cyclic fatigue life of nickel-titanium files: an examination using high-speed camera
Taha Özyürek, Neslihan Büşra Keskin, Fatma Furuncuoğlu, Uğur İnan
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2017; 42(3): 224. CrossRef
- The Effect of Different Separated File Retrieval Strategies on the Biomechanical Behavior of a Mandibular Molar: A Finite Element Analysis Study
- 1,595 View
- 6 Download
- 7 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


