Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Comparison of remineralization in caries-affected dentin using calcium silicate, glass ionomer cement, and resin-modified glass ionomer cement: an in vitro study
- Kwanchanok Youcharoen, Onwara Akkaratham, Papichaya Intajak, Pipop Saikaew, Sirichan Chiaraputt
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(4):e37. Published online November 14, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e37
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study evaluated the ability of calcium silicate cement (CSC) as a remineralizing agent compared with conventional glass ionomer cement (GIC) and resin-modified GIC (RMGIC) to remineralize artificial caries-affected dentin.
Methods
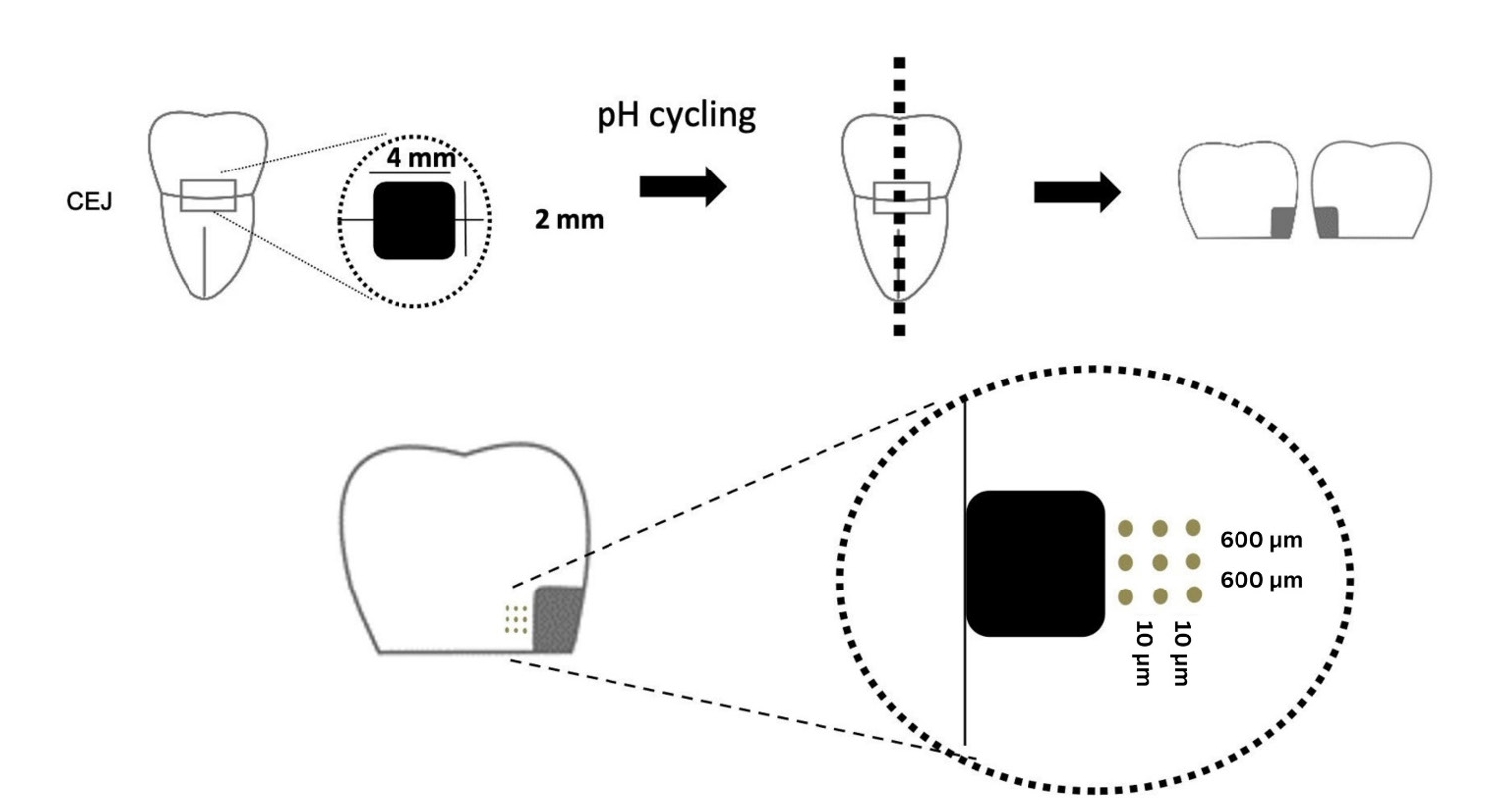
Twenty-five class V cavities were prepared on extracted human third molars. Twenty teeth underwent artificial caries induction. The remaining five teeth with sound dentin serve as the positive control. The twenty demineralized teeth were subdivided into four groups (n = 5): carious dentin without restoration (negative control [NC]), carious dentin restored with CSC (Biodentine, Septodont), carious dentin restored with GI (Fuji IX, GC Corporation), and carious dentin restored with RMGIC (Fuji II LC, GC Corporation). Following restoration, the specimens were stored in artificial saliva for 7 days. The elastic modulus was evaluated by a nanoindentation test. The mineral composition was analyzed by scanning electron microscopy-energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM-EDX), and the mineral composition at the dentin-material interface.
Results
CSC had a higher modulus of elasticity compared to GI, RMGI, and NC groups (p < 0.05). Higher calcium and phosphorus content was observed under CSC restorations, as indicated by SEM-EDX examination, which may lead to better remineralization.
Conclusions
Compared to GI and RMGI, CSC showed the best remineralization and mechanical reinforcement in caries-affected dentin, indicating CSC for use in minimally invasive restorative dentistry.
- 1,805 View
- 213 Download

- Effects of calcium silicate cements on neuronal conductivity
- Derya Deniz-Sungur, Mehmet Ali Onur, Esin Akbay, Gamze Tan, Fügen Daglı-Comert, Taner Cem Sayın
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(2):e18. Published online March 7, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e18
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated alterations in neuronal conductivity related to calcium silicate cements (CSCs) by investigating compound action potentials (cAPs) in rat sciatic nerves.
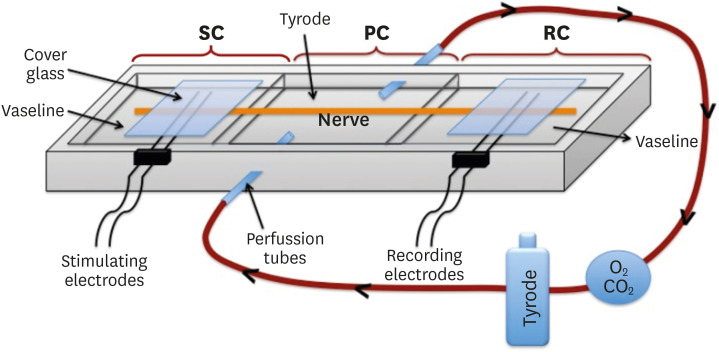
Materials and Methods Sciatic nerves were placed in a Tyrode bath and cAPs were recorded before, during, and after the application of test materials for 60-minute control, application, and recovery measurements, respectively. Freshly prepared ProRoot MTA, MTA Angelus, Biodentine, Endosequence RRM-Putty, BioAggregate, and RetroMTA were directly applied onto the nerves. Biopac LabPro version 3.7 was used to record and analyze cAPs. The data were statistically analyzed.
Results None of the CSCs totally blocked cAPs. RetroMTA, Biodentine, and MTA Angelus caused no significant alteration in cAPs (
p > 0.05). Significantly lower cAPs were observed in recovery measurements for BioAggregate than in the control condition (p < 0.05). ProRoot MTA significantly but transiently reduced cAPs in the application period compared to the control period (p < 0.05). Endosequence RRM-Putty significantly reduced cAPs.Conclusions Various CSCs may alter cAPs to some extent, but none of the CSCs irreversibly blocked them. The usage of fast-setting CSCs during apexification or regeneration of immature teeth seems safer than slow-setting CSCs due to their more favorable neuronal effects.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Endodontic Sealers and Innovations to Enhance Their Properties: A Current Review
Anna Błaszczyk-Pośpiech, Natalia Struzik, Maria Szymonowicz, Przemysław Sareło, Maria Wiśniewska-Wrona, Kamila Wiśniewska, Maciej Dobrzyński, Magdalena Wawrzyńska
Materials.2025; 18(18): 4259. CrossRef
- Endodontic Sealers and Innovations to Enhance Their Properties: A Current Review
- 1,593 View
- 21 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Comparative analysis of bond strength to root dentin and compression of bioceramic cements used in regenerative endodontic procedures
- Maykely Naara Morais Rodrigues, Kely Firmino Bruno, Ana Helena Gonçalves de Alencar, Julyana Dumas Santos Silva, Patrícia Correia de Siqueira, Daniel de Almeida Decurcio, Carlos Estrela
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(4):e59. Published online November 9, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e59
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study compared the Biodentine, MTA Repair HP, and Bio-C Repair bioceramics in terms of bond strength to dentin, failure mode, and compression.
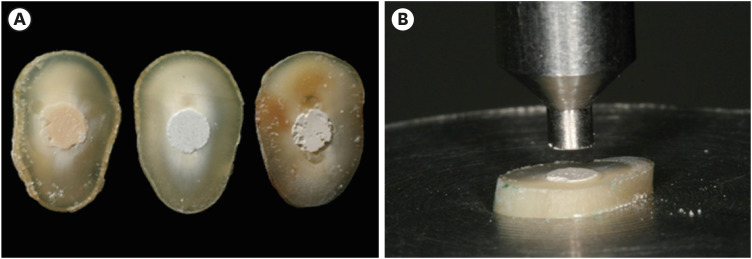
Materials and Methods Fifty-four slices obtained from the cervical third of 18 single-rooted human mandibular premolars were randomly distributed (
n = 18). After insertion of the bioceramic materials, the push-out test was performed. The failure mode was analyzed using stereomicroscopy. Another set of cylindrically-shaped bioceramic samples (n = 10) was prepared for compressive strength testing. The normality of data distribution was analyzed using the Shapiro-Wilk test. The Kruskal-Wallis and Friedman tests were used for the push-out test data, while compressive strength was analyzed with analysis of variance and the Tukey test, considering a significance level of 0.05.Results Biodentine presented a higher median bond strength value (14.79 MPa) than MTA Repair HP (8.84 MPa) and Bio-C Repair (3.48 MPa), with a significant difference only between Biodentine and Bio-C Repair. In the Biodentine group, the most frequent failure mode was mixed (61%), while in the MTA Repair HP and Bio-C Repair groups, it was adhesive (94% and 72%, respectively). Biodentine showed greater resistance to compression (29.59 ± 8.47 MPa) than MTA Repair HP (18.68 ± 7.40 MPa) and Bio-C Repair (19.96 ± 3.96 MPa) (
p < 0.05).Conclusions Biodentine showed greater compressive strength than MTA Repair HP and Bio-C Repair, and greater bond strength than Bio-C Repair. The most frequent failure mode of Biodentine was mixed, while that of MTA Repair HP and Bio-C Repair was adhesive.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of marginal adaptation and bond strength of apical root canal plugs using different bioceramic cements
Michel Sena Fernandes Faria Lima, Alberto Nogueira da Gama Antunes, Kênia Maria Pereira Soares de Toubes, Fábio Fernandes Borém Bruzinga, Camila de Sousa Caneschi, Luís Fernando dos Santos Alves Morgan, Frank Ferreira Silveira
BMC Oral Health.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of Release of Calcium Ions from Apical Plugs of Different Bioceramic Sealers in Regenerative Endodontics for Immature Permanent Teeth
Alok Dubey, Nischitha Naik, Bhavana Sujanamulk, Mushir Mulla, Munaz Mulla, Alkananda Sahoo, Mohamed T Salama, Murali Patla S Bhat
World Journal of Dentistry.2026; 17(1): 69. CrossRef - Obturation quality analysis of furcation perforations repaired with different magnifications and biomaterials
Mustafa Mert Tulgar, Yağmur Kılıç, Merve Işık Aydın, Ali Keleş
BMC Oral Health.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparación de la resistencia compresiva entre el Agregado Trióxido Mineral y BiodentineTM en perforaciones de furca de molares inferiores permanentes
Jheymy Gerardo Huatuco-Granda, John Paul Torres-Navarro, Rosa Josefina Roncal-Espinoza
Revista Facultad de Odontología.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of different calcium-silicate based materials on fracture resistance of immature permanent teeth with replacement root resorption and osteoclastogenesis
Gabriela Leite de Souza, Gabrielle Alves Nunes Freitas, Maria Tereza Hordones Ribeiro, Nelly Xiomara Alvarado Lemus, Carlos José Soares, Camilla Christian Gomes Moura
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation the Marginal Adaptation for the Bio C Repair and Other Root end Filling Material by Using Scanning Electron Microscope (A Comparative In Vitro Study)
Fatimah HAMADHİ, Zainab M.
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2023; 26(3): 261. CrossRef - Dentin Bond Strength of Calcium Silicate-Based Materials: A Systematic Review of In Vitro Studies
Natalia Radulica, José Luis Sanz, Adrián Lozano
Applied Sciences.2023; 14(1): 104. CrossRef - Evaluation Of The Push-out Bond Strength Of The Bio-C Repair And Compare It With The Mineral Trioxide Aggregate And Amalgam When Used As Root-end Filling Material
Fatimah R. Hammadi, Zainab M Abdul-Ameer
Dental Hypotheses.2023; 14(2): 62. CrossRef - Effect of different root canal irrigants on push-out bond strength of two novel root-end filling materials
Nada Omar, Rasha M. Abdelraouf, Tamer M. Hamdy
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of irrigation systems on the bond strength of calcium-silicate-based cement used as pulp barrier in regenerative endodontic treatment
Cihan Hascizmeci, Burak Buldur
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2023; 37(23): 3393. CrossRef
- Evaluation of marginal adaptation and bond strength of apical root canal plugs using different bioceramic cements
- 3,296 View
- 73 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref

- Conservative approach of a symptomatic carious immature permanent tooth using a tricalcium silicate cement (Biodentine): a case report
- Cyril Villat, Brigitte Grosgogeat, Dominique Seux, Pierre Farge
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(4):258-262. Published online November 12, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.4.258
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The restorative management of deep carious lesions and the preservation of pulp vitality of immature teeth present real challenges for dental practitioners. New tricalcium silicate cements are of interest in the treatment of such cases. This case describes the immediate management and the follow-up of an extensive carious lesion on an immature second right mandibular premolar. Following anesthesia and rubber dam isolation, the carious lesion was removed and a partial pulpotomy was performed. After obtaining hemostasis, the exposed pulp was covered with a tricalcium silicate cement (Biodentine, Septodont) and a glass ionomer cement (Fuji IX extra, GC Corp.) restoration was placed over the tricalcium silicate cement. A review appointment was arranged after seven days, where the tooth was asymptomatic with the patient reporting no pain during the intervening period. At both 3 and 6 mon follow up, it was noted that the tooth was vital, with normal responses to thermal tests. Radiographic examination of the tooth indicated dentin-bridge formation in the pulp chamber and the continuous root formation. This case report demonstrates a fast tissue response both at the pulpal and root dentin level. The use of tricalcium silicate cement should be considered as a conservative intervention in the treatment of symptomatic immature teeth.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bioceramic Pulpotomy and Direct Pulp
Capping on Complicated Fractures
Reattachment of Young Mature
Permanent Teeth: Case Series
A. Lavanya
The Traumaxilla.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical and radiographic outcomes of pulpotomy materials in permanent teeth: a systematic review of calcium hydroxide, MTA, biodentine, and iRoot BP plus
Anggi Putri Riandani, Arief Cahyanto, Rana Abdelbaset Lotfy Diab, Ratih Widyasari, Atia Nurul Sidiqa, Hendra Dian Adhita Dharsono, Myrna Nurlatifah Zakaria
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - How Does Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid Irrigation Affect Biodentine? A Multimethod Ex Vivo Study
Katarzyna Dąbrowska, Aleksandra Palatyńska-Ulatowska, Leszek Klimek
Materials.2024; 17(6): 1230. CrossRef - Evaluation of Biodentine Tricalcium Silicate-Based Cement after Chlorhexidine Irrigation
Katarzyna Dąbrowska, Aleksandra Palatyńska-Ulatowska, Leszek Klimek
Applied Sciences.2024; 14(19): 8702. CrossRef - Evaluation of the chemical, physical, and biological properties of a newly developed bioceramic cement derived from cockle shells: an in vitro study
Monthip Wannakajeepiboon, Chankhrit Sathorn, Chatvadee Kornsuthisopon, Busayarat Santiwong, Thanakorn Wasanapiarnpong, Pairoj Linsuwanont
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Protección pulpar directa y posterior apexogénesis. Informe de un caso clínico / Direct pulp capping followed by apexogenesis. A clinical case report
Osvaldo Zmener, Ana C. Boetto
Revista de la Asociación Odontológica Argentina.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of Irrigation with Citric Acid on Biodentine Tricalcium Silicate-Based Cement: SEM-EDS In Vitro Study
Katarzyna Dąbrowska, Aleksandra Palatyńska-Ulatowska, Leszek Klimek
Materials.2022; 15(10): 3467. CrossRef - The Immunomodulatory and Regenerative Effect of Biodentine™ on Human THP‐1 Cells and Dental Pulp Stem Cells: In Vitro Study
Duaa Abuarqoub, Nazneen Aslam, Rand Zaza, Hanan Jafar, Suzan Zalloum, Renata Atoom, Walhan Alshaer, Mairvat Al-Mrahleh, Abdalla Awidi, Bruna Sinjari
BioMed Research International.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Biodentine: Material of choice for apexification
Himanshu Aeran, Mahema Sharma, Avantika Tuli
International Journal of Oral Health Dentistry.2021; 7(1): 54. CrossRef - Minimal Intervention in Dentistry: A Literature Review on Biodentine as a Bioactive Pulp Capping Material
Naji Ziad Arandi, Mohammad Thabet, Mona Abbassy
BioMed Research International.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Biodentine Pulpotomies on Permanent Traumatized Teeth with Complicated Crown Fractures
Léa Haikal, Beatriz Ferraz dos Santos, Duy-Dat Vu, Marina Braniste, Basma Dabbagh
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(9): 1204. CrossRef - Influence of sodium hypochlorite and ultrasounds on surface features and chemical composition of Biodentine tricalcium silicate-based material
Aleksandra PALATYŃSKA-ULATOWSKA, Katarzyna BUŁA, Leszek KLIMEK
Dental Materials Journal.2020; 39(4): 587. CrossRef - Effects of two fast-setting pulp-capping materials on cell viability and osteogenic differentiation in human dental pulp stem cells: An in vitro study
Yan Sun, Jun Liu, Tao Luo, Ya Shen, Ling Zou
Archives of Oral Biology.2019; 100: 100. CrossRef - Healing Capacity of Autologous Bone Marrow–derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Partially Pulpotomized Dogs' Teeth
Mona H. El-Zekrid, Salah H. Mahmoud, Fawzy A. Ali, Mohamed E. Helal, Mohammed E. Grawish
Journal of Endodontics.2019; 45(3): 287. CrossRef - Large Periapical or Cystic Lesions in Association with Roots Having Open Apices Managed Nonsurgically Using 1-step Apexification Based on Platelet-rich Fibrin Matrix and Biodentine Apical Barrier: A Case Series
Sarang Sharma, Vivek Sharma, Deepak Passi, Dhirendra Srivastava, Shibani Grover, Shubha Ranjan Dutta
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(1): 179. CrossRef - Microleakage and Shear Bond Strength of Biodentine at Different Setting Time
Yong Ho Song, Nanyoung Lee, Sangho Lee, Myeongkwan Jih
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2018; 45(3): 344. CrossRef - Biodentine™ material characteristics and clinical applications: a 3 year literature review and update
S. Rajasekharan, L. C. Martens, R. G. E. C. Cauwels, R. P. Anthonappa
European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry.2018; 19(1): 1. CrossRef - Case Report: Immediate pain relief after partial pulpotomy of cariously exposed young permanent molar using mineral trioxide aggregate and root maturation, with two years follow-up
Passant Nagi, Nevine Waly, Adel Elbardissy, Mohammed Khalifa
F1000Research.2018; 7: 1616. CrossRef - Factors affecting the outcomes of direct pulp capping using Biodentine
Mariusz Lipski, Alicja Nowicka, Katarzyna Kot, Lidia Postek-Stefańska, Iwona Wysoczańska-Jankowicz, Lech Borkowski, Paweł Andersz, Anna Jarząbek, Katarzyna Grocholewicz, Ewa Sobolewska, Krzysztof Woźniak, Agnieszka Droździk
Clinical Oral Investigations.2018; 22(5): 2021. CrossRef - Mineral trioxide aggregate and other bioactive endodontic cements: an updated overview – part I: vital pulp therapy
M. Parirokh, M. Torabinejad, P. M. H. Dummer
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(2): 177. CrossRef - Effect of iRoot Fast Set root repair material on the proliferation, migration and differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells in vitro
Yan Sun, Tao Luo, Ya Shen, Markus Haapasalo, Ling Zou, Jun Liu, Gianpaolo Papaccio
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(10): e0186848. CrossRef - Dislodgement resistance of calcium silicate‐based materials from root canals with varying thickness of dentine
Ö. İ. Ulusoy, Y. N. Paltun, N. Güven, B. Çelik
International Endodontic Journal.2016; 49(12): 1188. CrossRef - Expression of Mineralization Markers during Pulp Response to Biodentine and Mineral Trioxide Aggregate
Mariana O. Daltoé, Francisco Wanderley G. Paula-Silva, Lúcia H. Faccioli, Patrícia M. Gatón-Hernández, Andiara De Rossi, Léa Assed Bezerra Silva
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(4): 596. CrossRef - Biodentine Reduces Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha–induced TRPA1 Expression in Odontoblastlike Cells
Ikhlas A. El Karim, Maelíosa T.C. McCrudden, Mary K. McGahon, Tim M. Curtis, Charlotte Jeanneau, Thomas Giraud, Chris R. Irwin, Gerard J. Linden, Fionnuala T. Lundy, Imad About
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(4): 589. CrossRef - Coronal Pulpotomy Technique Analysis as an Alternative to Pulpectomy for Preserving the Tooth Vitality, in the Context of Tissue Regeneration: A Correlated Clinical Study across 4 Adult Permanent Molars
Raji Viola Solomon, Umrana Faizuddin, Parupalli Karunakar, Grandhala Deepthi Sarvani, Sevvana Sree Soumya, Jiiang H. Jeng
Case Reports in Dentistry.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - A Review on Biodentine, a Contemporary Dentine Replacement and Repair Material
Özlem Malkondu, Meriç Karapinar Kazandağ, Ender Kazazoğlu
BioMed Research International.2014; 2014: 1. CrossRef - The use of platelet rich plasma in the treatment of immature tooth with periapical lesion: a case report
Günseli Güven Polat, Ceren Yıldırım, Özlem Martı Akgün, Ceyhan Altun, Didem Dinçer, Cansel Köse Özkan
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(3): 230. CrossRef - Biodentine-a novel dentinal substitute for single visit apexification
Gurudutt Nayak, Mohammad Faiz Hasan
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(2): 120. CrossRef
- Bioceramic Pulpotomy and Direct Pulp
Capping on Complicated Fractures
Reattachment of Young Mature
Permanent Teeth: Case Series
- 2,101 View
- 5 Download
- 28 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


