Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- The effectiveness of the supplementary use of the XP-endo Finisher on bacteria content reduction: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Ludmila Smith de Jesus Oliveira, Rafaella Mariana Fontes de Bragança, Rafael Sarkis-Onofre, André Luis Faria-e-Silva
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(3):e37. Published online June 18, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e37
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
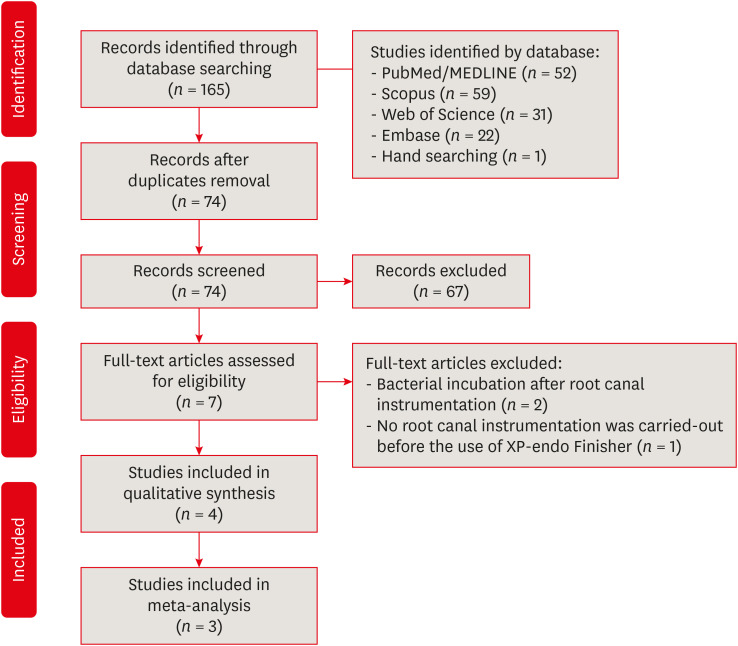
ePub Objectives This systematic review evaluated the efficacy of the supplementary use of the XP-endo Finisher on bacteria content reduction in the root canal system.
Materials and Methods In-vitro studies evaluating the use of the XP-endo Finisher on bacteria content were searched in four databases in July 2020. Two authors independently screened the studies for eligibility. Data were extracted, and risk of bias was assessed. Data were meta-analyzed by using random-effects model to compare the effect of the supplementary use (experimental) or not (control) of the XP-endo Finisher on bacteria counting reduction, and results from different endodontic protocols were combined. Four studies met the inclusion criteria while 1 study was excluded from the meta-analysis due to its high risk of bias and outlier data. The 3 studies that made it to the meta-analysis had an unclear risk of bias for at least one criterion.Results No heterogeneity was observed among the results of the studies included in the meta-analysis. The study excluded from the meta-analysis assessing the bacteria counting deep in the dentin demonstrated further bacteria reduction upon the use of the XP-endo Finisher.
Conclusions This systematic review found no evidence supporting the supplementary use of the XP-endo Finisher on further bacteria counting the reduction in the root canal.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mapping risk of bias criteria in systematic reviews of in vitro endodontic studies: an umbrella review
Rafaella Rodrigues da Gama, Lucas Peixoto de Araújo, Evandro Piva, Leandro Perello Duro, Adriana Fernandes da Silva, Wellington Luiz de Oliveira da Rosa
Evidence-Based Dentistry.2025; 26(4): 179. CrossRef - Characteristics and Effectiveness of XP‐Endo Files and Systems: A Narrative Review
Sarah M. Alkahtany, Rana Alfadhel, Aseel AlOmair, Sarah Bin Durayhim, Kee Y. Kum
International Journal of Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact XP-endo finisher on the 1-year follow-up success of posterior root canal treatments: a randomized clinical trial
Ludmila Smith de Jesus Oliveira, Fabricio Eneas Diniz de Figueiredo, Janaina Araújo Dantas, Maria Amália Gonzaga Ribeiro, Carlos Estrela, Manoel Damião Sousa-Neto, André Luis Faria-e-Silva
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(12): 7595. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of the effectiveness of modern irrigants activation techniques in the process of mechanical root canal system treatment (Literature review)
Anatoliy Potapchuk, Vasyl Almashi, Arsenii Horzov, Victor Buleza
InterConf.2023; (34(159)): 200. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of the effectiveness of modern irrigants activation techniques in the protocol of chemomechanical root canal system treatment (literature review)
A. Potapchuk, V. Almashi, Y. Rak, Y. Melnyk, V. Buleza, A. Horzov
SUCHASNA STOMATOLOHIYA.2023; 114(3): 4. CrossRef - Methodological quality assessment criteria for the evaluation of laboratory‐based studies included in systematic reviews within the specialty of Endodontology: A development protocol
Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Paul V. Abbott, Christos Boutsioukis, Henry F. Duncan, Clovis M. Faggion, Anil Kishen, Peter E. Murray, Shaju Jacob Pulikkotil, Paul M. H. Dummer
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(4): 326. CrossRef
- Mapping risk of bias criteria in systematic reviews of in vitro endodontic studies: an umbrella review
- 2,633 View
- 15 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- A novel antimicrobial-containing nanocellulose scaffold for regenerative endodontics
- Victoria Kichler, Lucas Soares Teixeira, Maick Meneguzzo Prado, Guilherme Colla, Daniela Peressoni Vieira Schuldt, Beatriz Serrato Coelho, Luismar Marques Porto, Josiane de Almeida
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(2):e20. Published online March 16, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e20
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to evaluate bacterial nanocellulose (BNC) membranes incorporated with antimicrobial agents regarding cytotoxicity in fibroblasts of the periodontal ligament (PDLF), antimicrobial activity, and inhibition of multispecies biofilm formation.
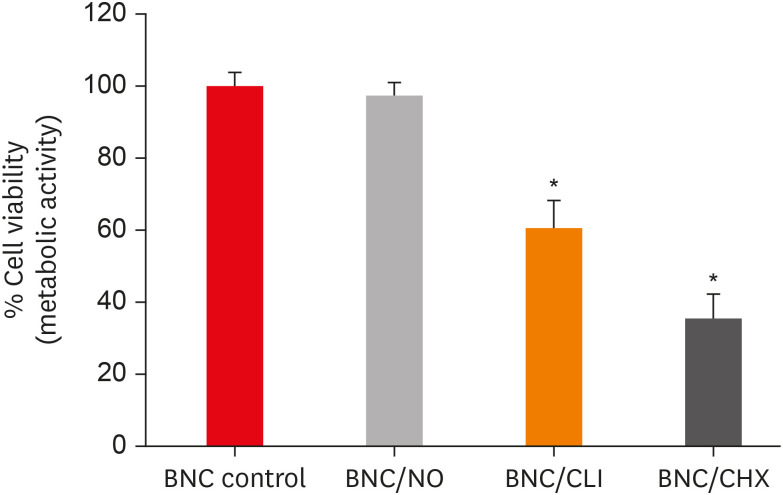
Materials and Methods The tested BNC membranes were BNC + 1% clindamycin (BNC/CLI); BNC + 0.12% chlorhexidine (BNC/CHX); BNC + nitric oxide (BNC/NO); and conventional BNC (BNC; control). After PDLF culture, the BNC membranes were positioned in the wells and maintained for 24 hours. Cell viability was then evaluated using the MTS calorimetric test. Antimicrobial activity against
Enterococcus faecalis ,Actinomyces naeslundii , andStreptococcus sanguinis (S. sanguinis ) was evaluated using the agar diffusion test. To assess the antibiofilm activity, BNC membranes were exposed for 24 hours to the mixed culture. After sonicating the BNC membranes to remove the remaining biofilm and plating the suspension on agar, the number of colony-forming units (CFU)/mL was determined. Data were analyzed by 1-way analysis of variance and the Tukey, Kruskal-Wallis, and Dunn tests (α = 5%).Results PDLF metabolic activity after contact with BNC/CHX, BNC/CLI, and BNC/NO was 35%, 61% and 97%, respectively, compared to BNC. BNC/NO showed biocompatibility similar to that of BNC (
p = 0.78). BNC/CLI showed the largest inhibition halos, and was superior to the other BNC membranes againstS. sanguinis (p < 0.05). The experimental BNC membranes inhibited biofilm formation, with about a 3-fold log CFU reduction compared to BNC (p < 0.05).Conclusions BNC/NO showed excellent biocompatibility and inhibited multispecies biofilm formation, similarly to BNC/CLI and BNC/CHX.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Topic: Perspectives on Success and Failure of Endodontic Treatments
Ilma Robo, Manola Kelmendi, Eva Habazaj, Kleves Elezi, Rialda Xhizdari, Nevila Alliu
SN Comprehensive Clinical Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Data about application of chlorhexidine as a periodontal irrigant –
Systematic Review.
Ilma Robo, Manola Kelmendi , Eva Habazaj , Kristi Sulanjaku , Nevila Alliu
Acta Stomatologica Marisiensis Journal.2025; 8(1): 6. CrossRef - Aqueous‐Phase Surface Amidation of TEMPO‐CNF Films for Improved Adsorption of Organic Pollutants in Water
Domenico Santandrea, Cécile Sillard, Valentina Beghetto, Julien Bras
ChemPlusChem.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Materials design of gas-releasing nanoplatforms: strategies for precision delivery in oral healthcare
Haodong Zhong, Weiming Tan, Jian Zhang, Xiongwei Huang, Haizhan Chen, Jiyuan Zou, Yuxin Ye, Tao Wang, Xuechao Yang, Jiang Li, Li Yang, Lvhua Guo, Tao Luo
Materials & Design.2025; 258: 114704. CrossRef - Pushing the limits of bacterial cellulose for biomedicine: a review
Cristina Campano, Virginia Rivero-Buceta, Ana M. Hernandez-Arriaga, Maria T. Manoli, M. Auxiliadora Prieto
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.2025; 323: 146701. CrossRef - Antibiofilm activity of three-dimensional bacterial nanocellulose scaffolds containing antimicrobial agents
Fernanda Keil Kressin, Isabela Aparecida Stahelin, Gilmar da Rosa Souza Jr, Karina Cesca, Ricardo Ruiz Mazzon, Rayssa Sabino-Silva, Taynara Santos Goulart, Cleonice da Silveira Teixeira, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia, Josiane de Almeida
Brazilian Dental Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Prospective and applications of bacterial nanocellulose in dentistry
Yasmin Alimardani, Esmaeel Mirzakhani, Fereshteh Ansari, Hadi Pourjafar, Nadia Sadeghi
Cellulose.2024; 31(13): 7819. CrossRef - Bacterial nanocelluloses as sustainable biomaterials for advanced wound healing and dressings
Atefeh Zarepour, Bahar Gok, Yasemin Budama-Kilinc, Arezoo Khosravi, Siavash Iravani, Ali Zarrabi
Journal of Materials Chemistry B.2024; 12(48): 12489. CrossRef - Sulfated endospermic nanocellulose crystals prevent the transmission of SARS-CoV-2 and HIV-1
Enrique Javier Carvajal-Barriga, Wendy Fitzgerald, Emilios K. Dimitriadis, Leonid Margolis, R. Douglas Fields
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A Novel Approach for the Fabrication of 3D-Printed Dental Membrane Scaffolds including Antimicrobial Pomegranate Extract
Hatice Karabulut, Songul Ulag, Basak Dalbayrak, Elif Arisan, Turgut Taskin, Mehmet Guncu, Burak Aksu, Alireza Valanezhad, Oguzhan Gunduz
Pharmaceutics.2023; 15(3): 737. CrossRef - Current advances of nanocellulose application in biomedical field
M.Y. Leong, Y.L. Kong, M.Y. Harun, C.Y. Looi, W.F. Wong
Carbohydrate Research.2023; 532: 108899. CrossRef - Bacterial cellulose as a potential biopolymer in biomedical applications: a state-of-the-art review
Prachi Shrivastav, Sheersha Pramanik, Gayatri Vaidya, Mohamed A. Abdelgawad, Mohammed M. Ghoneim, Ajeet Singh, Bassam M. Abualsoud, Larissa Souza Amaral, Mohammed A. S. Abourehab
Journal of Materials Chemistry B.2022; 10(17): 3199. CrossRef - Nanocelluloses as new generation materials: natural resources, structure-related properties, engineering nanostructures, and technical challenges
Ahmed Barhoum, Vibhore K. Rastogi, Bhupender K. Mahur, Amit Rastogi, Fatehy M. Abdel-Haleem, Pieter Samyn
Materials Today Chemistry.2022; 26: 101247. CrossRef - The current natural/chemical materials and innovative technologies in periodontal diseases therapy and regeneration: A narrative review
Peyman Esmaeili Fard Barzegar, Reza Ranjbar, Mohsen Yazdanian, Elahe Tahmasebi, Mostafa Alam, Kamyar Abbasi, Hamid Tebyaniyan, Keyvan Esmaeili Fard Barzegar
Materials Today Communications.2022; 32: 104099. CrossRef
- Topic: Perspectives on Success and Failure of Endodontic Treatments
- 2,284 View
- 34 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 14 Crossref

-
Inhibition of nicotine-induced
Streptococcus mutans biofilm formation by salts solutions intended for mouthrinses - Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad, Mary Anne S. Melo, Richard L. Gregory
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(1):e4. Published online January 16, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e4
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
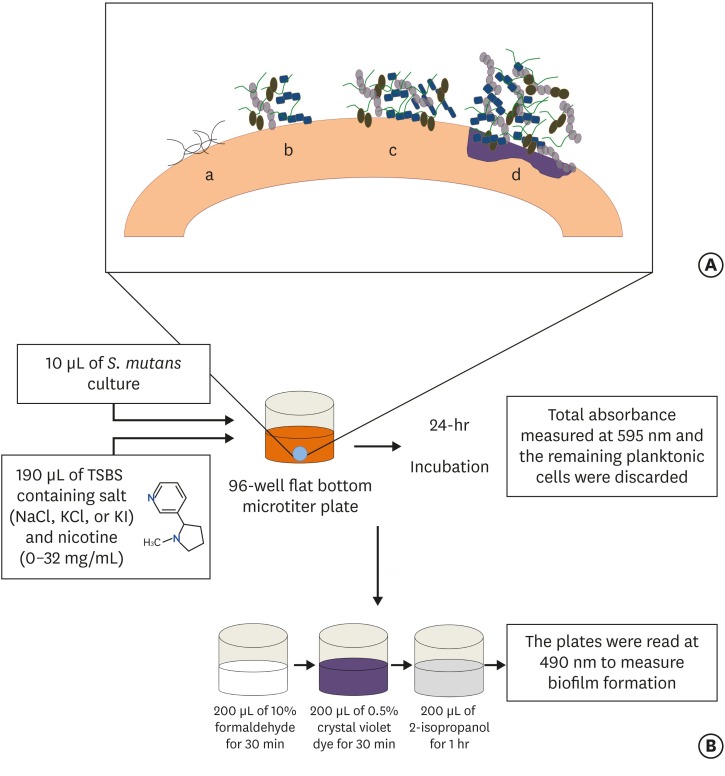
ePub Objectives Biofilm formation is critical to dental caries initiation and development. The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of nicotine exposure on
Streptococcus mutans (S. mutans ) biofilm formation concomitantly with the inhibitory effects of sodium chloride (NaCl), potassium chloride (KCl) and potassium iodide (KI) salts. This study examined bacterial growth with varying concentrations of NaCl, KCl, and KI salts and nicotine levels consistent with primary levels of nicotine exposure.Materials and Methods A preliminary screening experiment was performed to investigate the appropriate concentrations of NaCl, KCl, and KI to use with nicotine. With the data, a
S. mutans biofilm growth assay was conducted using nicotine (0–32 mg/mL) in Tryptic Soy broth supplemented with 1% sucrose with and without 0.45 M of NaCl, 0.23 M of KCl, and 0.113 M of KI. The biofilm was stained with crystal violet dye and the absorbance measured to determine biofilm formation.Results The presence of 0.45 M of NaCl, 0.23 M of KCl, and 0.113 M of KI significantly inhibited (
p < 0.05) nicotine-inducedS. mutans biofilm formation by 52%, 79.7%, and 64.1%, respectively.Conclusions The results provide additional evidence regarding the biofilm-enhancing effects of nicotine and demonstrate the inhibitory influence of these salts in reducing the nicotine-induced biofilm formation. A short-term exposure to these salts may inhibit
S. mutans biofilm formation.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Biofilm forming and swarming activities of Bacillus cereus modulated by multiclass compounds
Abdul Rafay Rafiq, Mohsin Tariq, Syeda Tahseen Zahra, Temoor Ahmed
The Microbe.2026; 10: 100644. CrossRef - The Influence of Nicotine on Collagen Binding in Streptococcus mutans Serotype C Strains: An In Vitro Study
Naif N Abogazalah, Richard L Gregory, Mohammed M Al Moaleem
World Journal of Dentistry.2026; 16(11): 967. CrossRef - The Inhibition of Streptococcus mutans Biofilms following Exposure to Different Chocolate Ingredients
Hadi A. Almoabid, Leen Saleh Almutairi, Abdul Samad Khan, Mohammed A. Aljaffary, Rasha AlSheikh, Khalid S. Almulhim, Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad
European Journal of Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The impact of Caralluma munbyana extracts on Streptococcus mutans biofilm formation
Turki Alshehri, Israa Alkhalifah, Areeb Alotaibi, Alaa F. Alsulaiman, Abdullah Al Madani, Basil Almutairi, Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Tobacco‐enhanced biofilm formation by Porphyromonas gingivalis and other oral microbes
Jinlian Tan, Gwyneth J. Lamont, David A. Scott
Molecular Oral Microbiology.2024; 39(5): 270. CrossRef - Nicotine is a potent extracellular polysaccharide inducer in Fusobacterium nucleatum biofilms
Adaias Oliveira Matos, Valentim Adelino Ricardo Barão, Richard Lee Gregory
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of eucalyptus oil on Streptococcus mutans and Enterococcus faecalis growth
Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad, Rasha N. AlSheikh
BDJ Open.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Microorganisms: crucial players of smokeless tobacco for several health attributes
Akanksha Vishwakarma, Digvijay Verma
Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology.2021; 105(16-17): 6123. CrossRef - Microbiology of the American Smokeless Tobacco
A. J. Rivera, R. E. Tyx
Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology.2021; 105(12): 4843. CrossRef - The Impact of Photosensitizer Selection on Bactericidal Efficacy Of PDT against Cariogenic Biofilms: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Maurício Ítalo Silva Teófilo, Teresa Maria Amorim Zaranza de Carvalho Russi, Paulo Goberlanio de Barros Silva, Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad, Mary Anne S. Melo, Juliana P.M.L. Rolim
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2021; 33: 102046. CrossRef - Antibacterial Activities of Methanol and Aqueous Extracts of Salvadora persica against Streptococcus mutans Biofilms: An In Vitro Study
Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad, Lamia Mokeem, Mary Anne S. Melo, Richard L. Gregory
Dentistry Journal.2021; 9(12): 143. CrossRef - The burden of root caries: Updated perspectives and advances on management strategies
Mohammed S. AlQranei, Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad, Mary A.S. Melo
Gerodontology.2021; 38(2): 136. CrossRef - Emerging Contact-Killing Antibacterial Strategies for Developing Anti-Biofilm Dental Polymeric Restorative Materials
Heba Mitwalli, Rashed Alsahafi, Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad, Michael D. Weir, Hockin H. K. Xu, Mary Anne S. Melo
Bioengineering.2020; 7(3): 83. CrossRef - In-Vitro Model of Scardovia wiggsiae Biofilm Formation and Effect of Nicotine
Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad, Hadeel M. Ayoub, Richard L. Gregory
Brazilian Dental Journal.2020; 31(5): 471. CrossRef - Antibacterial efficacy and remineralization capacity of glycyrrhizic acid added casein phosphopeptide‐amorphous calcium phosphate
Feride Sahin, Fatih Oznurhan
Microscopy Research and Technique.2020; 83(7): 744. CrossRef - Concentration dependence of quaternary ammonium monomer on the design of high-performance bioactive composite for root caries restorations
Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad, Maria S. Ibrahim, Michael D. Weir, Hockin H.K. Xu, Mary Anne S. Melo
Dental Materials.2020; 36(8): e266. CrossRef
- Biofilm forming and swarming activities of Bacillus cereus modulated by multiclass compounds
- 1,819 View
- 14 Download
- 16 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


