Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Fifty-year follow-up of dens invaginatus treated by nonsurgical and surgical endodontic treatments: a case report
- Qais Arow, Eyal Rosen, Galit Sela, Shlomo Elbahary, Igor Tsesis
- Restor Dent Endod 2026;51(1):e1. Published online December 18, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2026.51.e1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
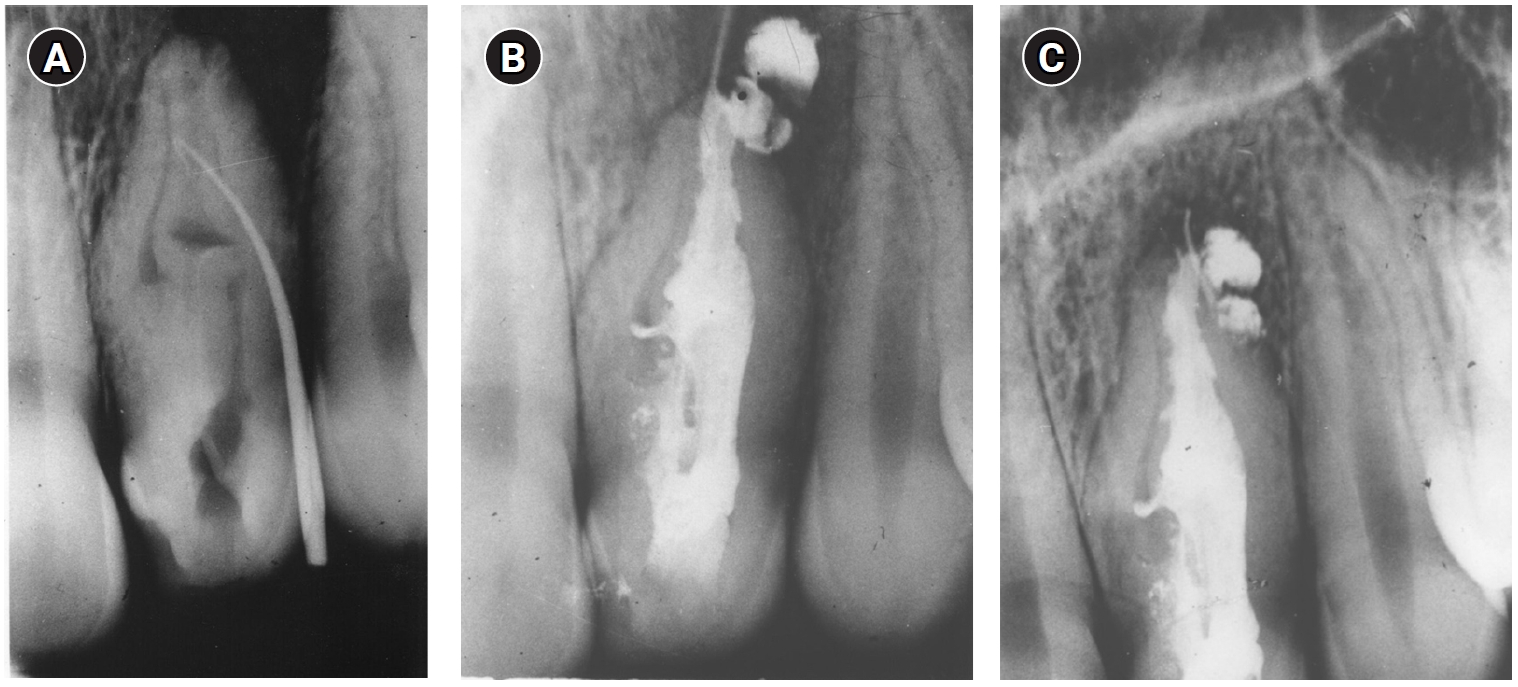
ePub - This case report presents a lateral maxillary incisor with dens invaginatus (DI) type IIIb that was treated both nonsurgically and surgically over 50 years. Treatment of teeth with DI can be challenging. Suggested options may include nonsurgical root canal treatment, endodontic surgery, or extraction. In this case report, a 13-year-old patient with a lateral maxillary incisor with DI type IIIb was treated by nonsurgical root canal treatment, modern endodontic surgery, and reoperation over the course of 50 years. There was complete healing at the last follow-up, 11 years after the reoperation. Correct diagnosis and proper treatment using modern endodontic techniques can enable teeth with DI to survive throughout the life span of the patient.
- 730 View
- 60 Download

- Success rates comparison of endodontic microsurgery and single implants with comprehensive and explicit criteria: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Min Jung Ko, Ju Hyun Park, Na Rae Lee, Joon-Ho Yoon, Young-Taek Kim, Sin-Yeon Cho
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(1):e8. Published online February 19, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e8
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
While the success criteria of endodontic microsurgery (EMS) have been consistently defined and widely accepted, the success criteria of dental implants are outdated and focus only on the implant fixture and surrounding bone. This study aimed to evaluate the outcomes of EMS and single implants (SIs) with explicit criteria.
Methods
We searched for articles published from January 2010 to February 2022 and discussed them and consulted with a clinical advisory committee composed of four dental specialists and one epidemiologist during article selection and data extraction.
Results
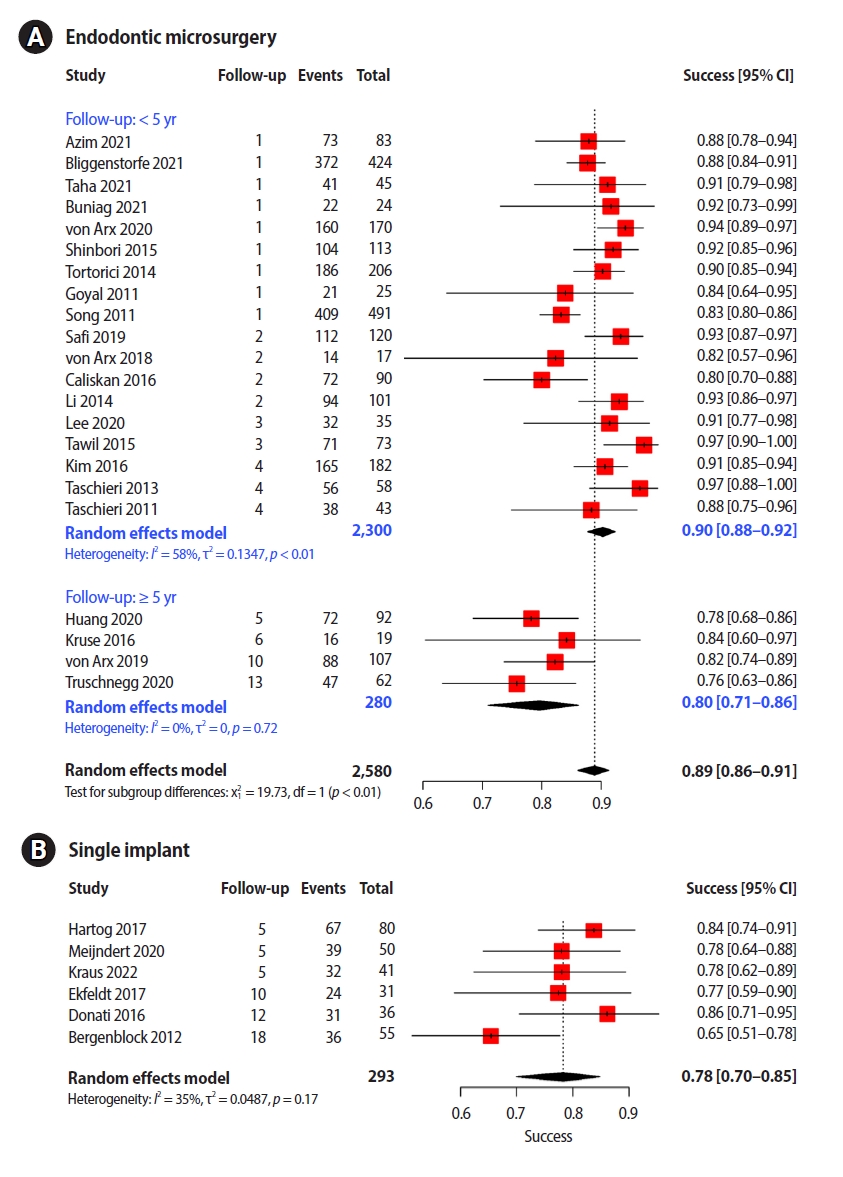
Twenty-two EMS studies and six SI studies were included in the meta-analysis. Teeth treated using EMS had a pooled success rate of 89% (90% at <5-year follow-up and 80% at ≥5-year follow-up) and the pooled success rate of SI was 78%.
Conclusions
The success rates of the two procedures with similar follow-up periods were comparable. Subgroup analysis found no other variable that significantly influenced study heterogeneity. Considering the treatment sequence and the similar success rates, it would be advantageous to consider EMS, rather than implants, first in a situation where both procedures are applicable. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Surgical Management of a Separated Instrument and Radicular Cyst: A Nine-Month Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) Follow-up
Dipti Chauhan, Hemant Yadav, Anshu Minocha, Vishal Sharma
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Cost-effectiveness of Endodontic Retreatment vs Implants: A 5-year Retrospective Analysis in India
Pramod Kumar, Himanshu Sharma
Journal of Clinical Insights and Research in Dentistry.2025; 1(3): 121. CrossRef
- Surgical Management of a Separated Instrument and Radicular Cyst: A Nine-Month Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) Follow-up
- 8,744 View
- 165 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Endodontic micro-resurgery and guided tissue regeneration of a periapical cyst associated to recurrent root perforation: a case report
- Fernando Córdova-Malca, Hernán Coaguila-Llerena, Lucía Garré-Arnillas, Jorge Rayo-Iparraguirre, Gisele Faria
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(4):e35. Published online September 3, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e35
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
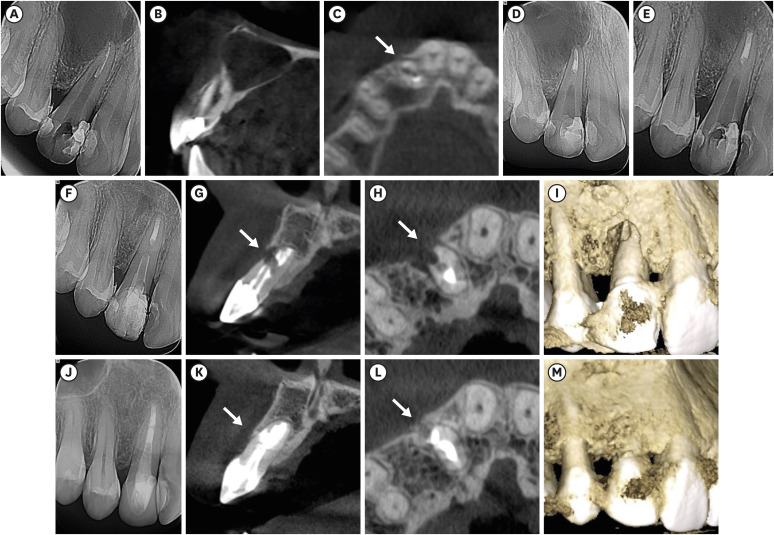
ePub Although the success rates of microsurgery and micro-resurgery are very high, the influence of a recurrent perforation combined with radicular cyst remains unclear. A 21-year-old white female patient had a history of root perforation in a previously treated right maxillary lateral incisor. Analysis using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) revealed an extensive and well-defined periapical radiolucency, involving the buccal and palatal bone plate. The perforation was sealed with bioceramic material (Biodentine) in the pre-surgical phase. In the surgical phase, guided tissue regeneration (GTR) was performed by combining xenograft (lyophilized bovine bone) and autologous platelet-rich fibrin applied to the bone defect. The root-end preparation was done using an ultrasonic tip. The retrograde filling was performed using a bioceramic material (Biodentine). Histopathological analysis confirmed a radicular cyst. The patient returned to her referring practitioner to continue the restorative procedures. CBCT analysis after 1-year recall revealed another perforation in the same place as the first intervention, ultimately treated by micro-resurgery using the same protocol with GTR, and a bioceramic material (MTA Angelus). The 2-year recall showed healing and bone neoformation. In conclusion, endodontic micro-resurgery with GTR showed long-term favorable results when a radicular cyst and a recurrent perforation compromised the success.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Outcome of endodontic micro-resurgery: A systematic review
Faisal Alnassar, Riyadh Alroomy, Qamar Hashem, Abdullah Alqedairi, Nabeel Almotairy
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2025; 15(2): 112. CrossRef - Platelet-Rich Plasma and Platelet-Rich Fibrin in Endodontics: A Scoping Review
Simão Rebimbas Guerreiro, Carlos Miguel Marto, Anabela Paula, Joana Rita de Azevedo Pereira, Eunice Carrilho, Manuel Marques-Ferreira, Siri Vicente Paulo
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(12): 5479. CrossRef - Non-surgical Approach to a Maxillary Cyst-Like Lesion: Orthograde Endodontic Treatment With Neodymium-Doped Yttrium Aluminum Garnet (Nd:YAG) Decontamination of the Canal System
Beatrice Spaggiari, Paolo Vescovi, Silvia Pizzi, Roberta Iaria, Ilaria Giovannacci
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Persistent Periradicular Lesion Associated With Concurrent Root Fracture and Odontogenic Keratocyst: A Case Report
Mehdi Vatanpour, Fatemeh Rezaei
Clinical Case Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Management of Apico-marginal Defects With Endodontic Microsurgery and Guided Tissue Regeneration: A Report of Thirteen Cases
Abayomi O. Baruwa, Jorge N.R. Martins, Mariana D. Pires, Beatriz Pereira, Pedro May Cruz, António Ginjeira
Journal of Endodontics.2023; 49(9): 1207. CrossRef
- Outcome of endodontic micro-resurgery: A systematic review
- 3,063 View
- 55 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

-
A new minimally invasive guided endodontic microsurgery by cone beam computed tomography and 3-dimensional printing technology

- Jong-Eun Kim, June-Sung Shim, Yooseok Shin
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(3):e29. Published online July 25, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e29
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
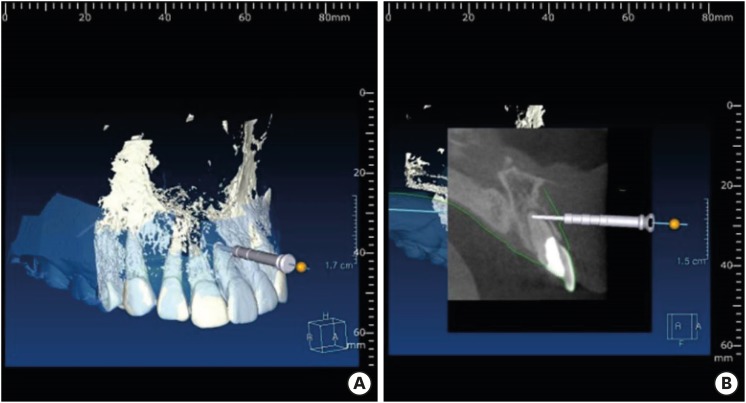
ePub Endodontic microsurgery is defined as the treatment performed on the root apices of an infected tooth, which was unresolved with conventional root canal therapy. Recently, the advanced technology in 3-dimensional model reconstruction based on computed tomography such as cone beam computed tomography has opened a new avenue in application of personalized, accurate diagnosis and has been increasingly used in the field of dentistry. Nevertheless, direct intra-oral localization of root apex based on the 3-dimensional information is extremely difficult and significant amount of bone removal is inevitable when freehand surgical procedure was employed. Moreover, gingival flap and alveolar bone fenestration are usually required, which leads to prolonged time of surgery, thereby increasing the chance of trauma as well as the risk of infection. The purpose of this case report is to present endodontic microsurgery using the guide template that can accurately target the position of apex for the treatment of an anterior tooth with calcified canal which was untreatable with conventional root canal therapy and unable to track the position of the apex due to the absence of fistula.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A narrative review of papilla preservation techniques in clinical dentistry
Yinghua Fu, Zhixin Zhang, Xiaoping Tang, Jiangling Su
Medicine.2025; 104(3): e41033. CrossRef - Segmentation algorithms of dental CT images: A comprehensive review from classical to deep learning trend
Dianhao Wu, Jingang Jiang, Jinke Wang, Zhuming Bi, Guang Yu
Expert Systems with Applications.2025; 275: 126853. CrossRef - Endodontic Microsurgery of Mandibular Molars with an Autonomous Robotic System
Haiying Zhang, Zi Yang, Mangnan Liu, Yaoxin Wang, Mei Fu, Benxiang Hou, Chen Zhang
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(12): 1830. CrossRef - Removal of Extraradicular Separated Instrument by Targeted Endodontic Microsurgery Using the 3D‐Printed Guide and Trephine: A Case Report
Lin Yang, Liang Chen
Clinical Case Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Augmented Reality-Assisted Micro-Invasive Apicectomy with Markerless Visual–Inertial Odometry: An In Vivo Pilot Study
Marco Farronato, Davide Farronato, Federico Michelini, Giulio Rasperini
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(23): 12588. CrossRef - 3D finite element analysis of stress distribution on the shape of resected root-end or with/without bone graft of a maxillary premolar during endodontic microsurgery
Aein Mon, Mi-El Kim, Kee-Yeon Kum, Ho-Beom Kwon
Journal of Dental Sciences.2024; 19(2): 837. CrossRef - TREATMENT OF YATROGENIC POST-TRAUMATIC NEUROPATHY ASSOCIATED WITH
ENDODONTIC THERAPY USING 3D TECHNOLOGIES
Karen Sevterteryan, Vladislav Tarasenok, Lyudmila Tatintsyan
BULLETIN OF STOMATOLOGY AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY.2024; : 73. CrossRef - Advancements in guided surgical endodontics: A scoping review of case report and case series and research implications
Giusy Rita Maria La Rosa, Matteo Peditto, Andrea Venticinque, Antonia Marcianò, Alberto Bianchi, Eugenio Pedullà
Australian Endodontic Journal.2024; 50(2): 397. CrossRef - Comparison of a Novel Static Computer-aided Surgical and Freehand Techniques for Osteotomy and Root-end Resection
Kyle Westbrook, Corey Rollor, Sara A. Aldahmash, Guadalupe G. Fay, Elias Rivera, Jeffery B. Price, Ina Griffin, Patricia A. Tordik, Frederico C. Martinho
Journal of Endodontics.2023; 49(5): 528. CrossRef - Comparison of the Three-Dimensional Accuracy of Guided Apicoectomy Performed with a Drill or a Trephine: An In Vitro Study
Ramóna Kiscsatári, Eszter Nagy, Máté Szabó, Gábor Braunitzer, József Piffkó, Márk Fráter, Márk Ádám Antal
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(17): 9642. CrossRef - Review of “Outcome of Endodontic Surgery: A Meta- Analysis of the Literature—Part 1: Comparison
of Traditional Root-End Surgery and Endodontic Microsurgery” by Setzer and Colleagues in J Endod 36(11):1757-1765, 2010
Oleksandr Nozhenko
Journal of Endodontic Microsurgery.2023; 2: 41. CrossRef - The Impact of the Preferred Reporting Items for Case Reports in Endodontics (PRICE) 2020 Guidelines on the Reporting of Endodontic Case Reports
Sofian Youssef, Phillip Tomson, Amir Reza Akbari, Natalie Archer, Fayjel Shah, Jasmeet Heran, Sunmeet Kandhari, Sandeep Pai, Shivakar Mehrotra, Joanna M Batt
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - New-designed 3D printed surgical guide promotes the accuracy of endodontic microsurgery: a study of 14 upper anterior teeth
Dan Zhao, Weige Xie, Tianguo Li, Anqi Wang, Li Wu, Wen Kang, Lu Wang, Shiliang Guo, Xuna Tang, Sijing Xie
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - An Exploratory In Vitro Microcomputed Tomographic Investigation of the Efficacy of Semicircular Apicoectomy Performed with Trephine Bur
Eszter Nagy, Brigitta Vőneki, Lívia Vásárhelyi, Imre Szenti, Márk Fráter, Ákos Kukovecz, Márk Ádám Antal
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(16): 9431. CrossRef - The Time Has Come: Journal of Endodontic Microsurgery: A First Peer-Reviewed Open Access Publication Focused on Microsurgery in Endodontics
Ievgen Fesenko
Journal of Endodontic Microsurgery.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Prefabricated Grid-guided Endodontic Microsurgery: A Pilot Study
Cruz Nishanthine, Manali Ramakrishnan Srinivasan, Ravi Devi, Kadhar Begam Farjana, Dasarathan Duraivel
Journal of Operative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022; 6(2): 58. CrossRef - Guided osteotomy
Saini Rashmi, Saini V Kr
Tanta Dental Journal.2022; 19(3): 172. CrossRef - Accuracy of digitally planned, guided apicoectomy with a conventional trephine and a custom-made endodontic trephine: An in vitro comparative study
Eszter Nagy, Gábor Braunitzer, Dániel Gerhard Gryschka, Ibrahim Barrak, Mark Adam Antal
Journal of Stomatology, Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.2022; 123(4): 388. CrossRef - Stress Distribution on Trephine-Resected Root-end in Targeted Endodontic Microsurgery: A Finite Element Analysis
Yeon-Jee Yoo, Hiran Perinpanayagam, Miel Kim, Qiang Zhu, Seung-Ho Baek, Ho-Beom Kwon, Kee-Yeon Kum
Journal of Endodontics.2022; 48(12): 1517. CrossRef - An Update on Endodontic Microsurgery of Mandibular Molars: A Focused Review
Sun Mi Jang, Euiseong Kim, Kyung-San Min
Medicina.2021; 57(3): 270. CrossRef - When to consider the use of CBCT in endodontic treatment planning in adults
Nisha Patel, Andrew Gemmell, David Edwards
Dental Update.2021; 48(11): 932. CrossRef
- A narrative review of papilla preservation techniques in clinical dentistry
- 2,442 View
- 31 Download
- 21 Crossref

- Effects of four novel root-end filling materials on the viability of periodontal ligament fibroblasts
- Makbule Bilge Akbulut, Pembegul Uyar Arpaci, Ayce Unverdi Eldeniz
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(3):e24. Published online May 25, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e24
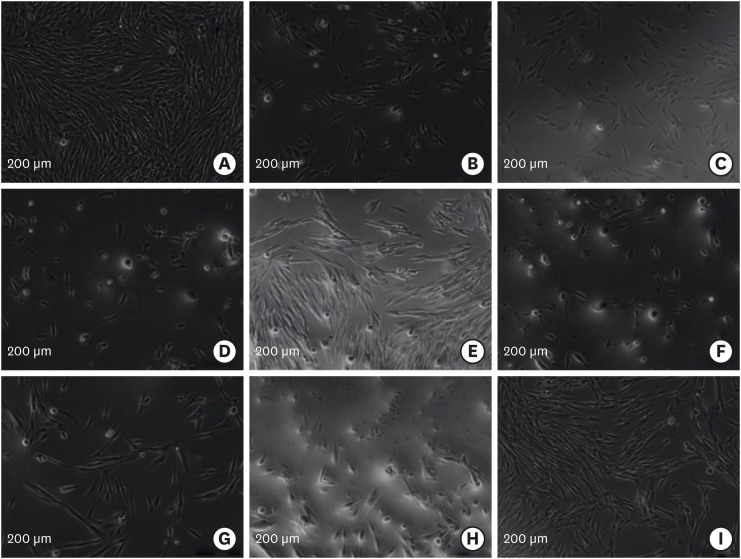
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this
in vitro study was to evaluate the biocompatibility of newly proposed root-end filling materials, Biodentine, Micro-Mega mineral trioxide aggregate (MM-MTA), polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) bone cement, and Smart Dentin Replacement (SDR), in comparison with contemporary root-end filling materials, intermediate restorative material (IRM), Dyract compomer, ProRoot MTA (PMTA), and Vitrebond, using human periodontal ligament (hPDL) fibroblasts.Materials and Methods Ten discs from each material were fabricated in sterile Teflon molds and 24-hour eluates were obtained from each root-end filling material in cell culture media after 1- or 3-day setting. hPDL fibroblasts were plated at a density of 5 × 103/well, and were incubated for 24 hours with 1:1, 1:2, 1:4, and 1:8 dilutions of eluates. Cell viability was evaluated by XTT assay. Data was statistically analysed. Apoptotic/necrotic activity of PDL cells exposed to material eluates was established by flow cytometry.
Results The Vitrebond and IRM were significantly more cytotoxic than the other root-end filling materials (
p < 0.05). Those cells exposed to the Biodentine and Dyract compomer eluates showed the highest survival rates (p < 0.05), while the PMTA, MM-MTA, SDR, and PMMA groups exhibited similar cell viabilities. Three-day samples were more cytotoxic than 1-day samples (p < 0.05). Eluates from the cements at 1:1 dilution were significantly more cytotoxic (p < 0.05). Vitrebond induced cell necrosis as indicated by flow cytometry.Conclusions This
in vitro study demonstrated that Biodentine and Compomer were more biocompatible than the other root-end filling materials. Vitrebond eluate caused necrotic cell death.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Three Retrograde Filling Materials on Production of Inflammatory Cytokines and Resorbing Mediators
Samaneh Arab, Marjan Bahraminasab, Masoumeh Motamedi, Jamshid Hadjati, Alaviye Vahid
Journal of Microbiota.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Apoptotic effects of biodentine, calcium-enriched mixture (CEM) cement, ferric sulfate, and mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) on human mesenchymal stem cells isolated from the human pulp of exfoliated deciduous teeth
Bahareh NAZEMI SALMAN, Mahshid MOHEBBI RAD, Ehsan SABURI
Minerva Dental and Oral Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of Mechanical/Chemical Properties and Cytotoxicity of Resin-Modified Glass Ionomer Cements Containing Sr/F-Bioactive Glass Nanoparticles and Methacrylate Functionalized Polyacids
Wisitsin Potiprapanpong, Parichart Naruphontjirakul, Chutikarn Khamsuk, Somruethai Channasanon, Arnit Toneluck, Siriporn Tanodekaew, Naruporn Monmaturapoj, Anne M. Young, Piyaphong Panpisut
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(12): 10231. CrossRef - Comparative biological properties of resin-free and resin-based calcium silicate-based endodontic repair materials on human periodontal ligament stem cells
Shehabeldin M. Saber, Shaimaa M. Gomaa, Mohamed M. Elashiry, Ahmed El-Banna, Edgar Schäfer
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(11): 6757. CrossRef - Comparison of root end sealing ability of three retrograde filling materials in teeth with root apices resected at 900 using dye penetration method under fluorescent microscope
Dr. Payal Chaudhari, Manoj Chandak, Dr. Aditya Patel
F1000Research.2023; 12: 1049. CrossRef - The Effects of Tricalcium-Silicate-Nanoparticle-Containing Cement: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies
Naho Ezawa, Yoshihiko Akashi, Kei Nakajima, Katsutoshi Kokubun, Masahiro Furusawa, Kenichi Matsuzaka
Materials.2023; 16(12): 4451. CrossRef - Evaluation of the cytotoxic effects of a new Harvard MTA compared to MTA Flow and ProRoot MTA on human gingival fibroblasts
Abdel-Rahman Youssef, Samia Elsherief
The Saudi Dental Journal.2021; 33(7): 679. CrossRef - Cytotoxicity and Bioactivity of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate and Bioactive Endodontic Type Cements: A Systematic Review
Uma Dixit, Rucha Shivajirao Bhise Patil, Rupanshi Parekh
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2021; 14(1): 30. CrossRef - MTT versus other cell viability assays to evaluate the biocompatibility of root canal filling materials: a systematic review
A. V. B. Pintor, L. D. Queiroz, R. Barcelos, L. S. G. Primo, L. C. Maia, G. G. Alves
International Endodontic Journal.2020; 53(10): 1348. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of the flow and filling ability of endodontic materials using different test models
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Gisselle Moraima Chavez-Andrade, Jader Camilo Pinto, Fábio Luiz Camargo Villela Berbert, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Long-term Follow-up for Apical Microsurgery of Teeth with Core and Post Restorations
Astrid Truschnegg, Petra Rugani, Barbara Kirnbauer, Lumnije Kqiku, Norbert Jakse, Robert Kirmeier
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(2): 178. CrossRef - Comparison of Cytotoxic Effects of Calcium Silicate-based Materials on Human Pulp Fibroblasts
Mehmet Adıgüzel, Fuat Ahmetoğlu, Ayçe Ünverdi Eldeniz, Mehmet Gökhan Tekin, Bülent Göğebakan
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2019; 13(4): 241. CrossRef
- Effects of Three Retrograde Filling Materials on Production of Inflammatory Cytokines and Resorbing Mediators
- 1,842 View
- 5 Download
- 12 Crossref

- Proximity of the mandibular molar root apex from the buccal bone surface: a cone-beam computed tomographic study
- Dokyung Kim, Jung-Hong Ha, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young-Kyung Kim, Sung Kyo Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(3):182-188. Published online July 14, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.3.182
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to evaluate the proximity of the mandibular molar apex to the buccal bone surface in order to provide anatomic information for apical surgery.
Materials and Methods Cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) images of 127 mandibular first molars and 153 mandibular second molars were analyzed from 160 patients' records. The distance was measured from the buccal bone surface to the root apex and the apical 3.0 mm on the cross-sectional view of CBCT.
Results The second molar apex and apical 3 mm were located significantly deeper relative to the buccal bone surface compared with the first molar (
p < 0.01). For the mandibular second molars, the distance from the buccal bone surface to the root apex was significantly shorter in patients over 70 years of age (p < 0.05). Furthermore, this distance was significantly shorter when the first molar was missing compared to nonmissing cases (p < 0.05). For the mandibular first molars, the distance to the distal root apex of one distal-rooted tooth was significantly greater than the distance to the disto-buccal root apex (p < 0.01). In mandibular second molar, the distance to the apex of C-shaped roots was significantly greater than the distance to the mesial root apex of non-C-shaped roots (p < 0.01).Conclusions For apical surgery in mandibular molars, the distance from the buccal bone surface to the apex and apical 3 mm is significantly affected by the location, patient age, an adjacent missing anterior tooth, and root configuration.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Expert consensus on intentional tooth replantation
Zhengmei Lin, Dingming Huang, Shuheng Huang, Zhi Chen, Qing Yu, Benxiang Hou, Lihong Qiu, Wenxia Chen, Jiyao Li, Xiaoyan Wang, Zhengwei Huang, Jinhua Yu, Jin Zhao, Yihuai Pan, Shuang Pan, Deqin Yang, Weidong Niu, Qi Zhang, Shuli Deng, Jingzhi Ma, Xiuping
International Journal of Oral Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Outcome of intentional replantation of endodontically treated teeth with periapical pathosis: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Faizan Javed, Kamil Zafar, Farhan R. Khan
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(S1): 494. CrossRef - Proximity of maxillary molar apexes to the cortical bone surface and the maxillary sinus
Han Shin Lee, Dokyung Kim, Sung Kyo Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Alveolar bone thickness overlying healthy maxillary and mandibular teeth: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Marziyeh Shafizadeh, Azita Tehranchi, Armin Shirvani, Saeed Reza Motamedian
International Orthodontics.2021; 19(3): 389. CrossRef - Relationship between the anatomic structures and mandibular posterior teeth for endodontic surgery in a Turkish population: a cone-beam computed tomographic analysis
Zeliha Uğur Aydın, Duygu Göller Bulut
Clinical Oral Investigations.2019; 23(9): 3637. CrossRef
- Expert consensus on intentional tooth replantation
- 2,223 View
- 5 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Apicoectomy of maxillary anterior teeth through a piezoelectric bony-window osteotomy: two case reports introducing a new technique to preserve cortical bone
- Viola Hirsch, Meetu R. Kohli, Syngcuk Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(4):310-315. Published online July 5, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.4.310
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Two case reports describing a new technique of creating a repositionable piezoelectric bony window osteotomy during apicoectomy in order to preserve bone and act as an autologous graft for the surgical site are described. Endodontic microsurgery of anterior teeth with an intact cortical plate and large periapical lesion generally involves removal of a significant amount of healthy bone in order to enucleate the diseased tissue and manage root ends. In the reported cases, apicoectomy was performed on the lateral incisors of two patients. A piezoelectric device was used to create and elevate a bony window at the surgical site, instead of drilling and destroying bone while making an osteotomy with conventional burs. Routine microsurgical procedures - lesion enucleation, root-end resection, and filling - were carried out through this window preparation. The bony window was repositioned to the original site and the soft tissue sutured. The cases were re-evaluated clinically and radiographically after a period of 12 - 24 months. At follow-up, radiographic healing was observed. No additional grafting material was needed despite the extent of the lesions. The indication for this procedure is when teeth present with an intact or near-intact buccal cortical plate and a large apical lesion to preserve the bone and use it as an autologous graft.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Virtual surgical planning with dual-stage guide using internal irrigation for cortical plate access and apicectomy
Hadeel M. Abdelhamid, Andrew B. Cameron, Roy George
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2026; 16(1): 121. CrossRef - Accuracy of 3‐dimensional surgical guide for endodontic microsurgery with a new design concept: A cadaver study
Se‐Won Ha, Stephanie M. Choi, Sunil Kim, Minju Song, Kyung‐Seok Hu, Euiseong Kim
International Endodontic Journal.2025; 58(2): 295. CrossRef - Expert consensus on apical microsurgery
Hanguo Wang, Xin Xu, Zhuan Bian, Jingping Liang, Zhi Chen, Benxiang Hou, Lihong Qiu, Wenxia Chen, Xi Wei, Kaijin Hu, Qintao Wang, Zuhua Wang, Jiyao Li, Dingming Huang, Xiaoyan Wang, Zhengwei Huang, Liuyan Meng, Chen Zhang, Fangfang Xie, Di Yang, Jinhua Yu
International Journal of Oral Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Apicoectomy: A review of clinical concepts and techniques
Vivek Thakur, Rahul Kaul
Journal of Oral Research and Review.2025; 17(1): 77. CrossRef - Management of Periapical Lesion and Discoloration with Periapical Microsurgery Followed up by Internal-External Bleaching and Direct Composite Restoration: One-Year Clinical Evaluation
Opik Hidayat, Suhardjo Sitam, Irmaleny Irmaleny, Setyo Harnowo, Wawan Suridwan
Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dentistry.2025; Volume 17: 217. CrossRef - Guided endodontics in the application of personalized mini-invasive treatment in clinical cases: a literature review
Shuangshuang Ren, Wanping Wang, Mingyue Cheng, Wenyue Tang, Yue Zhao, Leiying Miao
The Saudi Dental Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A novel three-dimensional printed guide for handling three strategic steps of surgical endodontics
Ankit Arora, Kavina Desai, Sonali Kapoor, Seema Gajera, Vatsal Joshi
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2025; 15(3): 297. CrossRef - Periapical microsurgical endodontic treatment of the maxillary second premolar: a clinical case
K. A. Ordashiev, S. M. Kurbanova, P. A. Gamzatova, A. K. Dalgatova, K. Z. Agaragimov, S. M. Kadyrbekova, D. R. Kazavatov, R. S. Adzhamatov, K. M. Kaziev, F. M. Murtazalieva
Endodontics Today.2025; 23(4): 692. CrossRef - Dynamically guided transantral piezoelectric endodontic microsurgery: A case report with technical considerations
Paula Andrea Villa‐Machado, Felipe Augusto Restrepo‐Restrepo, Sergio Iván Tobón‐Arroyave
International Endodontic Journal.2024; 57(4): 490. CrossRef - Piezoelectric Endodontic Microsurgery with Modified Cortical Window Technique: A Case Report
Rafael Fernández-Grisales, Wilder Rojas, Carolina Berruecos-Orozco
Journal of Endodontic Microsurgery.2023; 2: 34. CrossRef - The bone lid technique in lateral sinus lift: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Lucia Schiavon, Alessandro Perini, Giulia Brunello, Giada Ferrante, Massimo Del Fabbro, Daniele Botticelli, Fouad Khoury, Stefano Sivolella
International Journal of Implant Dentistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Present status and future directions: Surgical endodontics
Frank C. Setzer, Samuel I. Kratchman
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S4): 1020. CrossRef - Is apicectomy with retrograde filling still relevant in contemporary dental practice? A 25‐year retrospective review
Charles Ezechukwu Anyanechi
Oral Surgery.2022; 15(4): 537. CrossRef - Targeted Endodontic Microsurgery
Smitha Reddy, Sravya Gadhiraju, Akram Quraishi, Shekhar Kamishetty
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2022; 13(3): 280. CrossRef - Endodontic Microsurgery of Mandibular Second Molars Using the Bony Lid Approach: A Case Series
Cheng Bi, Mengting Zhou, Yu Zhang, Pei Zheng
Journal of Endodontics.2022; 48(12): 1533. CrossRef - Bone Window Technique in Endodontic Microsurgery – Report of Two Cases
Spyros Floratos, Vasileios Molonis, Apostolos Tsolakis, Stylianos Kykalos, Konstantinos Kontzoglou
Journal of Endodontic Microsurgery.2022; 2: 24. CrossRef - Effect of the Piezoelectric Device on Intraoperative Hemorrhage Control and Quality of Life after Endodontic Microsurgery: A Randomized Clinical Study
Jaya Bharathi, Shweta Mittal, Sanjay Tewari, Shikha Tewari, Jigyasa Duhan, Pankaj Sangwan, Vinay Kumar
Journal of Endodontics.2021; 47(7): 1052. CrossRef - Three-dimensional printing: A revealing pathway to an unpredictable maze
MeetkumarS Dedania, NimishaC Shah, Ankit Arora, Nidhi Pisal
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2020; 23(5): 533. CrossRef - The Application of “Bone Window” Technique in Endodontic Microsurgery
Su-Min Lee, Ya-Hsin Yu, Yu Wang, Euiseong Kim, Syngcuk Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(6): 872. CrossRef - Evaluation of surface integrity of root end cavities prepared using conventional and piezoelectric devices: A scanning electron microscopy study
MithraN Hegde, ManjiriNagesh Honap, Sreenath Narayanan
Indian Journal of Dental Research.2019; 30(5): 772. CrossRef - Targeted Endodontic Microsurgery: Computed Tomography–based Guided Stent Approach with Platelet-rich Fibrin Graft: A Report of 2 Cases
Witold Popowicz, Aleksandra Palatyńska-Ulatowska, Meetu Ralli Kohli
Journal of Endodontics.2019; 45(12): 1535. CrossRef - The bone lid technique in oral surgery: a case series study
S. Sivolella, G. Brunello, F. Fistarol, E. Stellini, C. Bacci
International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.2017; 46(11): 1490. CrossRef
- Virtual surgical planning with dual-stage guide using internal irrigation for cortical plate access and apicectomy
- 2,754 View
- 44 Download
- 22 Crossref

- Patients' perception and satisfaction with apicoectomy
- Euiseong Kim, Seung-Jong Lee, Jeong-Won Park, Su-Jung Shin
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(2):114-118. Published online March 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.2.114
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study was aimed to examine the patients' perception and satisfaction with the results of endodontic microsurgery which was apicoectomy with retrofilling.
Materials and Methods A questionnaire was given to 109 patients, who were recalled after a minimum of 3 months upon endodontic microsurgery in the Department of Conservative Dentistry, Yonsei University. A contingency table and correlation analysis were used to determine if there were any correlations between age/gender and the patients' responses (
p = 0.05).Results Approximately 60% of respondents answered they had never heard of surgical endodontic procedures. 63.3% of respondents chose the surgical option because they wanted to keep their natural teeth. If the patient required the same procedure on another tooth later, 100 out of 109 respondents answered they would choose microsurgery instead of extraction. Most patients (82.57%) appeared to be satisfied with the surgical procedure.
Conclusions Endodontic microsurgery consisting of apicoectomy and retrofilling seems to appeal to majority of patients as a satisfactory and valuable treatment choice.
- 1,243 View
- 12 Download


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


